AI-HOPE-TP53: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent for Pathway-Centric Analysis of TP53-Driven Molecular Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
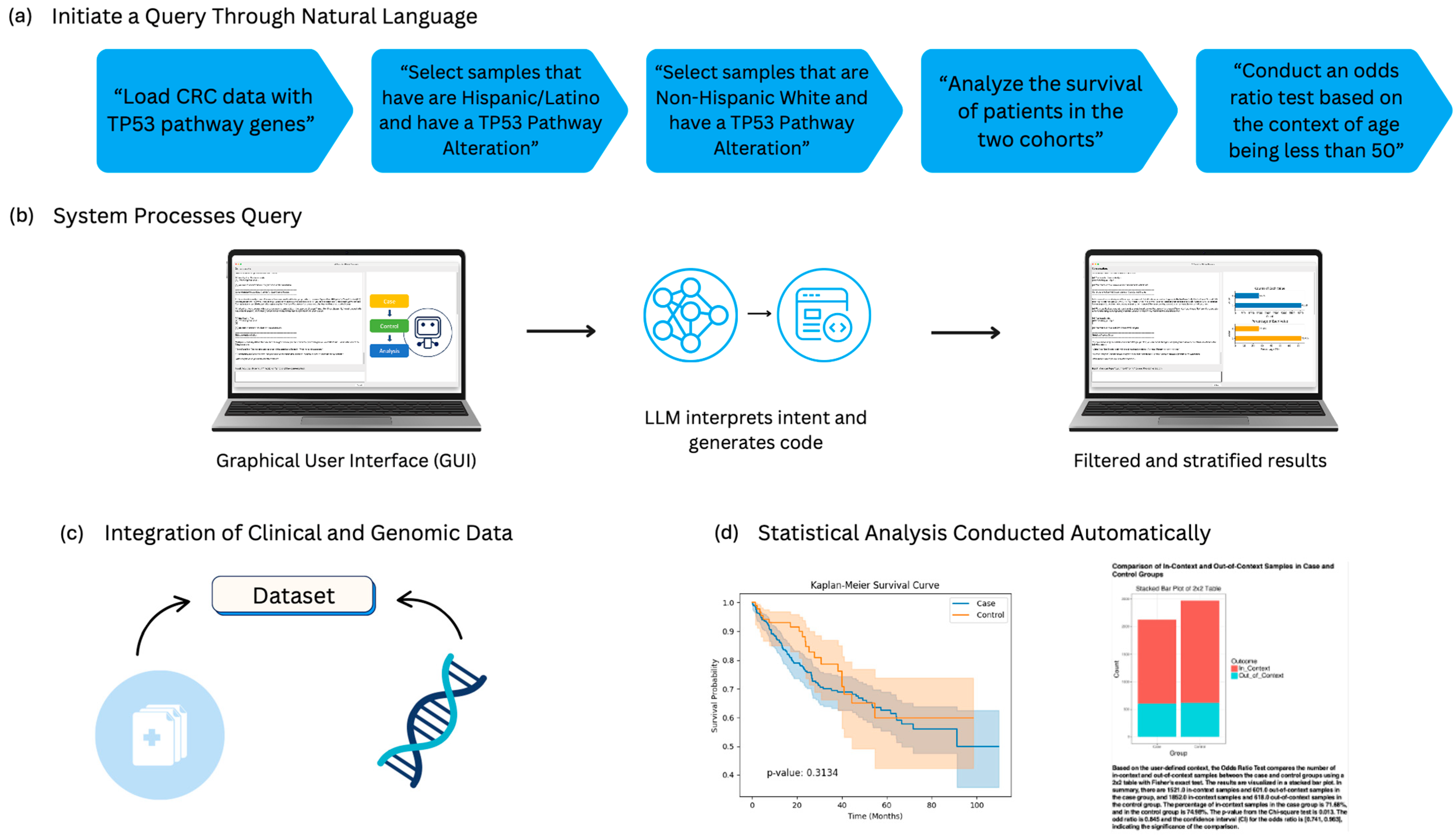
2.1. Architecture and Operational Framework of AI-HOPE-TP53
2.2. Data Integration and Curation
2.3. Query Interpretation and Dynamic Cohort Construction
2.4. Statistical Framework and Analytical Capabilities
2.5. Model Validation and Reproducibility
2.6. Benchmarking and Usability Testing
2.7. Visualization and Export Features
2.8. Accessibility and Support
3. Results
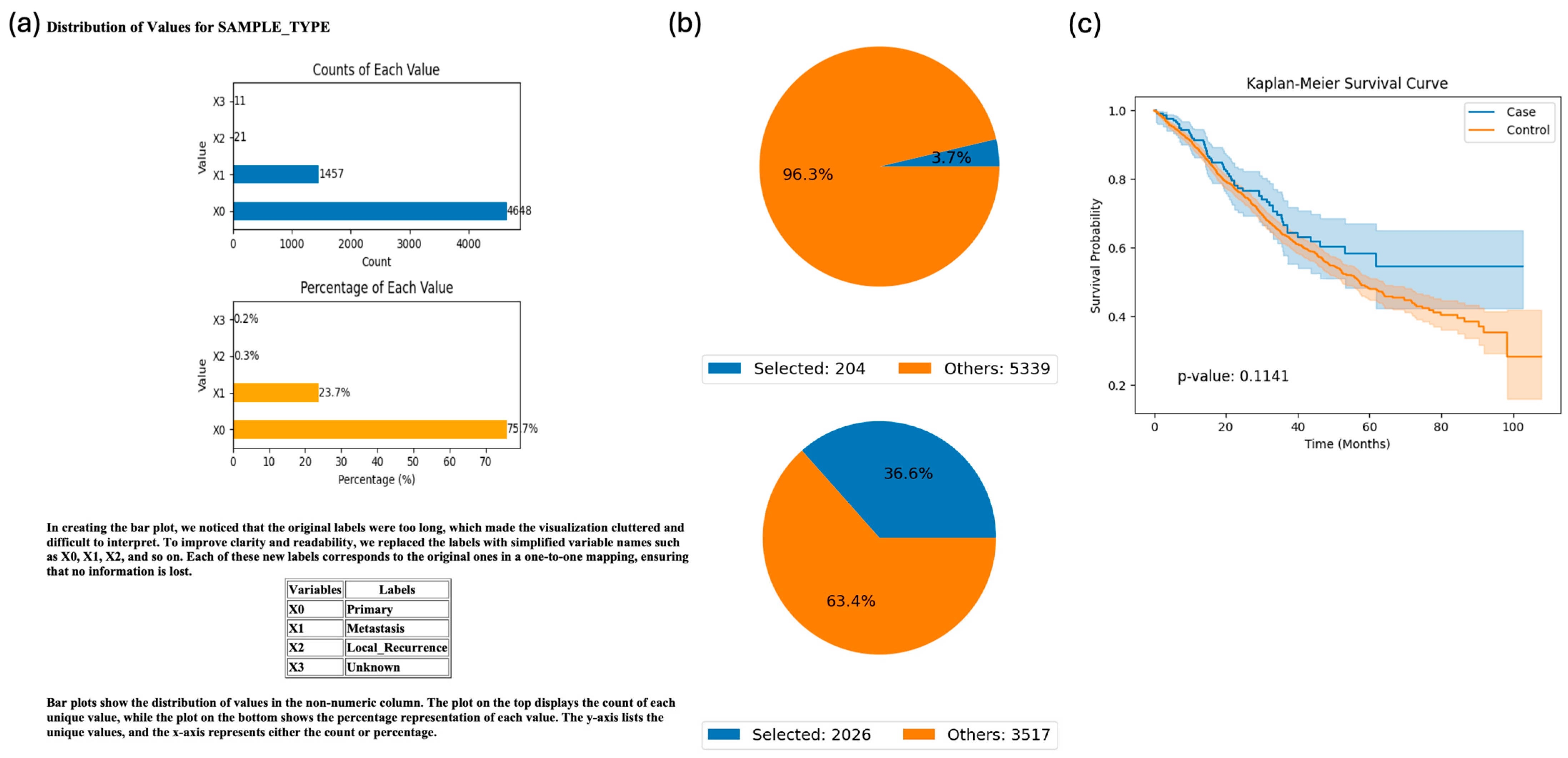
3.1. Application of AI-HOPE-TP53 for Pathway-Centric, Population-Stratified Analysis in Colorectal Cancer
3.2. Validation of Ethnicity-Stratified TP53 Pathway Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer
3.3. Exploratory Analysis: Ethnicity-Specific Survival in TP53-Mutant Colorectal Cancer
3.4. Exploratory Analysis: Tumor Subsite Differences in ATM-Mutant Colorectal Cancer
3.5. Exploratory Analysis: Age-Stratified Survival in TP53-Mutated CRC Treated with FOLFOX
3.6. Exploratory Analysis: Stage-Specific Survival in CHEK1-Mutated Colorectal Cancer
3.7. Exploratory Analysis: Gender-Based Differences in Survival and Treatment Representation in TP53-Altered CRC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, C.; Waldrup, B.; Manjarrez, S.; Carranza, F.G.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. Detecting PI3K and TP53 Pathway Disruptions in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Hispanic/Latino Patients. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigtländer, S.; Hakimhashemi, A.; Grundmann, N.; Meyer, M.; Müller-Nordhorn, J. Comparison of trends in early-onset colorectal cancer in North America and Europe. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, B. Family History a Risk for Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Nurs. 2021, 121, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, L.C.; Mota, J.M.; Braghiroli, M.I.; Hoff, P.M. The Rising Incidence of Younger Patients With Colorectal Cancer: Questions About Screening, Biology, and Treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.G.; Karlitz, J.J.; Yen, T.; Lieu, C.H.; Boland, C.R. The rising tide of early-onset colorectal cancer: A comprehensive review of epidemiology, clinical features, biology, risk factors, prevention, and early detection. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.Y.; Richardson, B.C. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monge, C.; Waldrup, B.; Carranza, F.G.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. WNT and TGF-Beta Pathway Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Among Hispanic/Latino Populations. Cancers 2024, 16, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Robles, A.; Bashashati, M.; Contreras, A.; Chávez, L.O.; Cerro-Rondón, A.D.; Cu, C.; McAlice, M.; Deoker, A. Colorectal Cancer in Hispanics Living Near the U.S.-Mexico Border. Rev. Invest. Clin. 2019, 71, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.D.; Torrejon, N.; Wei, W.; Tullio, K.; Nair, K.G.; Liska, D.; Krishnamurthi, S.S.; Khorana, A.A. Racial disparities negatively impact outcomes in early-onset colorectal cancer independent of socioeconomic status. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 7542–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahnen, D.J.; Wade, S.W.; Jones, W.F.; Sifri, R.; Mendoza Silveiras, J.; Greenamyer, J.; Guiffre, S.; Axilbund, J.; Spiegel, A.; You, Y.N. The increasing incidence of young-onset colorectal cancer: A call to action. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alshenaifi, J.Y.; Vetere, G.; Maddalena, G.; Yousef, M.; White, M.G.; Shen, J.P.; Vilar, E.; Parseghian, C.; Dasari, A.; Morris, V.K.; et al. Mutational and co-mutational landscape of early onset colorectal cancer. Biomarkers 2025, 30, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Antelo, M.; Balaguer, F.; Shia, J.; Shen, Y.; Hur, K.; Moreira, L.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Bujanda, L.; Giraldez, M.D.; Takahashi, M.; et al. A High Degree of LINE-1 Hypomethylation Is a Unique Feature of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. Understanding the complexity of p53 in a new era of tumor suppression. Cancer Cell. 2024, 42, 946–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Guo, M.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y. Targeting p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Shi, C.; Lei, Z.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Unraveling the Role of TP53 in Colorectal Cancer Therapy: From Wild-Type Regulation to Mutant. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2024, 29, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabapathy, K.; Lane, D.P. Therapeutic targeting of p53: All mutants are equal, but some mutants are more equal than others. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Cai, J.; Zhong, H. TP53 signal pathway confers potential therapy target in acute myeloid leukemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 110, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Geng, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, W.; Mo, Y.Q.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Song, G.B.; Sheng, J.P.; Xu, B. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer: Pathogenesis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schaafsma, E.; Takacs, E.M.; Kaur, S.; Cheng, C.; Kurokawa, M. Predicting clinical outcomes of cancer patients with a p53 deficiency gene signature. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. P53 and prognosis: New insights and further complexity. Cell 2005, 120, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponio, V.C.A.; Troiano, G.; Adipietro, I.; Zhurakivska, K.; Arena, C.; Mangieri, D.; Mascitti, M.; Cirillo, N.; Lo Muzio, L. Computational analysis of TP53 mutational landscape unveils key prognostic signatures and distinct pathobiological pathways in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shahbandi, A.; Nguyen, H.D.; Jackson, J.G. TP53 Mutations and Outcomes in Breast Cancer: Reading beyond the Headlines. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goto, T.; Marusawa, H.; Chiba, T. Landscape of genetic aberrations detected in human colorectal cancers. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyrk, T.C.; Lynch, H.T. Microsatellite instability: Impact on cancer progression in proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404, Erratum in Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 960.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dorfner, F.J.; Dada, A.; Busch, F.; Makowski, M.R.; Han, T.; Truhn, D.; Kleesiek, J.; Sushil, M.; Adams, L.C.; Bressem, K.K. Evaluating the effectiveness of biomedical fine-tuning for large language models on clinical tasks. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2025, 32, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Aali, A.; Van Veen, D.; Arefeen, Y.I.; Hom, J.; Bluethgen, C.; Reis, E.P.; Gatidis, S.; Clifford, N.; Daws, J.; Tehrani, A.S.; et al. A dataset and benchmark for hospital course summarization with adapted large language models. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2025, 32, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shankar, S.V.; Dhingra, L.S.; Aminorroaya, A.; Adejumo, P.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Xu, H.; Brandt, C.; Oikonomou, E.K.; Pedroso, A.F.; Khera, R. Automated Transformation of Unstructured Cardiovascular Diagnostic Reports into Structured Datasets Using Sequentially Deployed Large Language Models. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baris, S.D.; Baris, K. Assessment of various artificial intelligence applications in responding to technical questions in endodontic surgery. BMC Oral Health 2025, 25, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Han, K. Machine learning prediction model with shap interpretation for chronic bronchitis risk assessment based on heavy metal exposure: A nationally representative study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed Ahamed Kabeer, B.; Subba, B.; Rinchai, D.; Toufiq, M.; Khan, T.; Yurieva, M.; Chaussabel, D. From gene modules to gene markers: An integrated AI-human approach selects CD38 to represent plasma cell-associated transcriptional signatures. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1510431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, E.W.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. AI-HOPE: An AI-driven conversational agent for enhanced clinical and genomic data integration in precision medicine research. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.W.; Waldrup, B.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. AI-HOPE-TGFbeta: A Conversational AI Agent for Integrative Clinical and Genomic Analysis of TGF-β Pathway Alterations in Colorectal Cancer to Advance Precision Medicine. AI 2025, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.W.; Waldrup, B.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. From Mutation to Prognosis: AI-HOPE-PI3K Enables Artificial Intelligence Agent-Driven Integration of PI3K Pathway Data in Colorectal Cancer Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.W.; Waldrup, B.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. Decoding the JAK-STAT Axis in Colorectal Cancer with AI-HOPE-JAK-STAT: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Approach to Clinical–Genomic Integration. Cancers 2025, 17, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.W.; Waldrup, B.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. Conversational AI agent for precision oncology: AI-HOPE-WNT integrates clinical and genomic data to investigate WNT pathway dysregulation in colorectal cancer. Front. Artif. Intell. 2025, 8, 1624797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xia, Y.; Lou, X.; Huang, K.; Wu, L.; Gao, C. Decoding breast cancer imaging trends: The role of AI and radiomics through bibliometric insights. Breast Cancer Res. 2025, 27, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Lee, S.S.; Wen, Z.H.; Lo, Y.H. The changing scenario of drug discovery using AI to deep learning: Recent advancement, success stories, collaborations, and challenges. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids. 2024, 35, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, M.K.; Raza, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Hussain, I.; Khan, M.F.; Xie, Z.; Shah, S.S.A.; Tareen, A.K.; Bashir, Z.; Khan, K. The recent advances in the approach of artificial intelligence (AI) towards drug discovery. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1408740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szymczak, P.; Zarzecki, W.; Wang, J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Coelho, L.P.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Szczurek, E. AI-Driven Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery: Mining and Generation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2025, 58, 1831–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ullah, I.; Yang, L.; Yin, F.T.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.J. Multi-Omics Approaches in Colorectal Cancer Screening and Diagnosis, Recent Updates and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, X.; Ma, Y.; Bai, Y.; Huang, T.; Lv, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.; Lian, W.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Identification and validation of immunotherapy for four novel clusters of colorectal cancer based on the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 984480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, K.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Qi, Z.; Hou, S.; Wang, W. The Usability and Experience of Artificial Intelligence-Based Conversational Agents in Health Education for Cancer Patients: A Scoping Review. J Clin Nurs. 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artsi, Y.; Sorin, V.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Klang, E. Advancing Clinical Practice: The Potential of Multimodal Technology in Modern Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Idrissi, Y.A.; Rajabi, M.R.; Beumer, J.H.; Monga, S.P.; Saeed, A. Exploring the Impact of the β-Catenin Mutations in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An In-Depth Review. Cancer Control. 2024, 31, 10732748241293680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yaeger, R.; Corcoran, R.B. Targeting Alterations in the RAF-MEK Pathway. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elhanani, O.; Ben-Uri, R.; Keren, L. Spatial profiling technologies illuminate the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2023, 41, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, E.-W.; Waldrup, B.; Velazquez-Villarreal, E. AI-HOPE-TP53: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent for Pathway-Centric Analysis of TP53-Driven Molecular Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172865
Yang E-W, Waldrup B, Velazquez-Villarreal E. AI-HOPE-TP53: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent for Pathway-Centric Analysis of TP53-Driven Molecular Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(17):2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172865
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ei-Wen, Brigette Waldrup, and Enrique Velazquez-Villarreal. 2025. "AI-HOPE-TP53: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent for Pathway-Centric Analysis of TP53-Driven Molecular Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 17: 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172865
APA StyleYang, E.-W., Waldrup, B., & Velazquez-Villarreal, E. (2025). AI-HOPE-TP53: A Conversational Artificial Intelligence Agent for Pathway-Centric Analysis of TP53-Driven Molecular Alterations in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 17(17), 2865. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172865






