Global Hypomethylation as Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Biomarker in Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Methylation-Sensitive Restriction Enzyme Droplet Digital PCR (MSRE-ddPCR)
2.4. Statistics
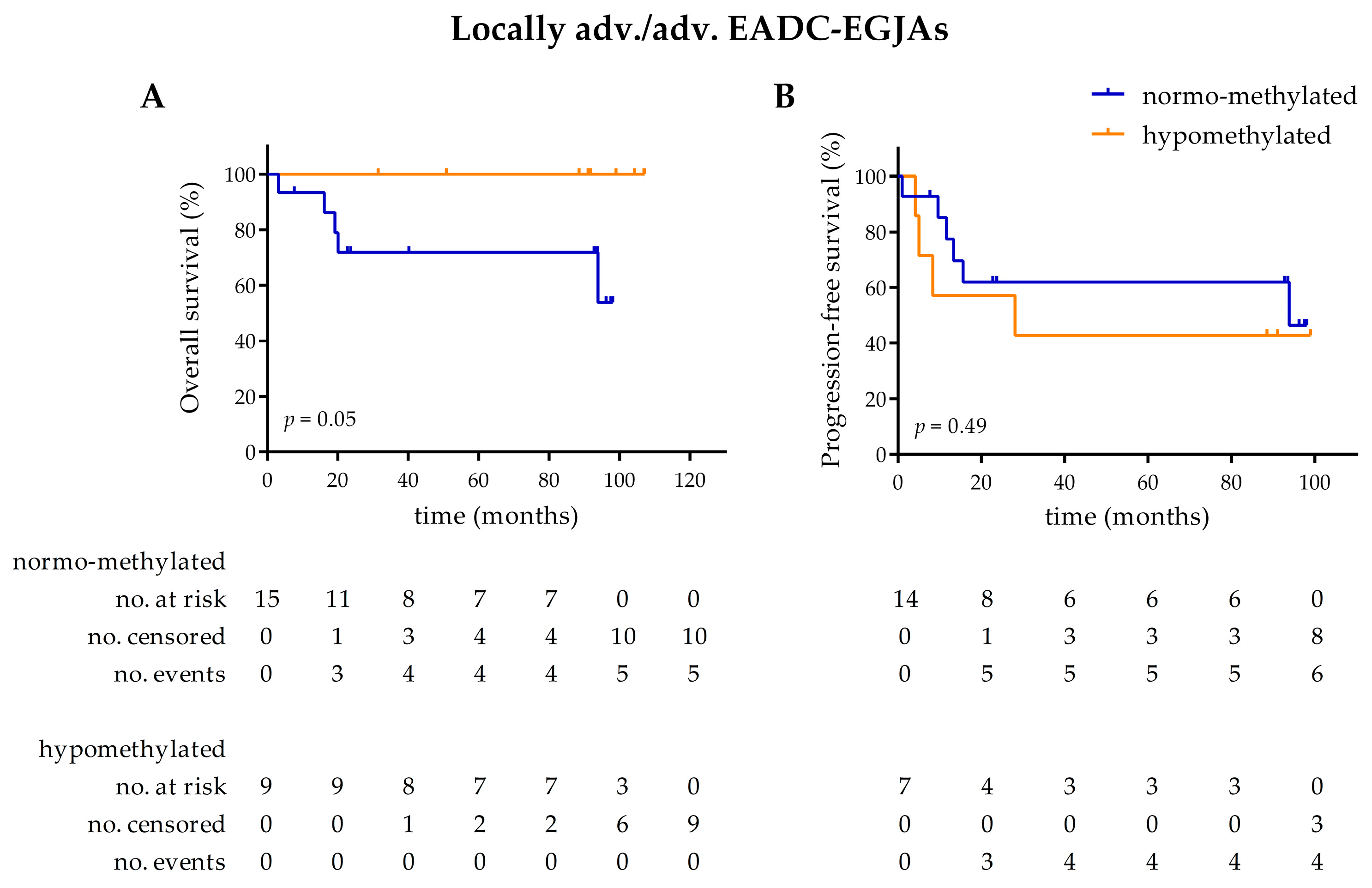
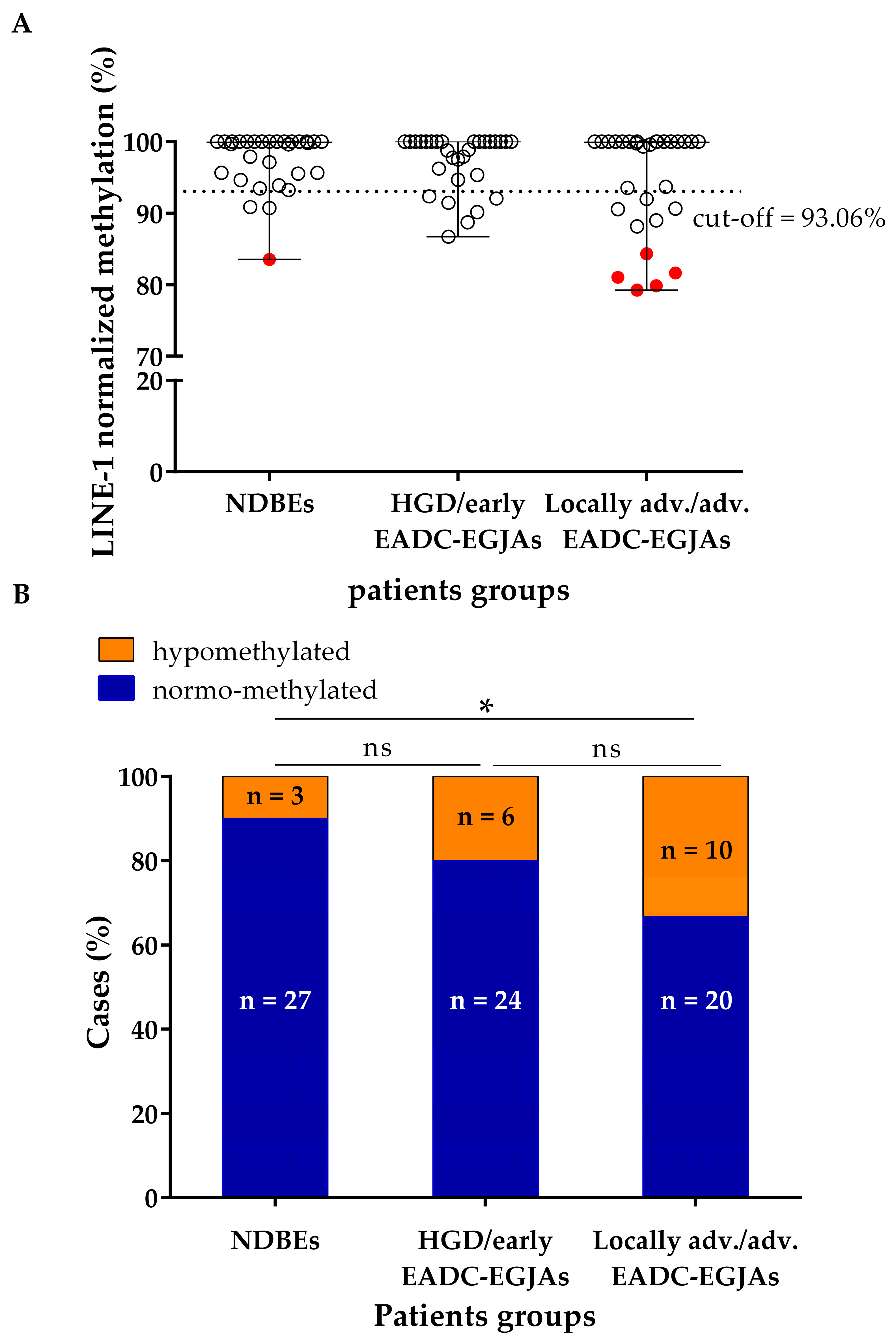
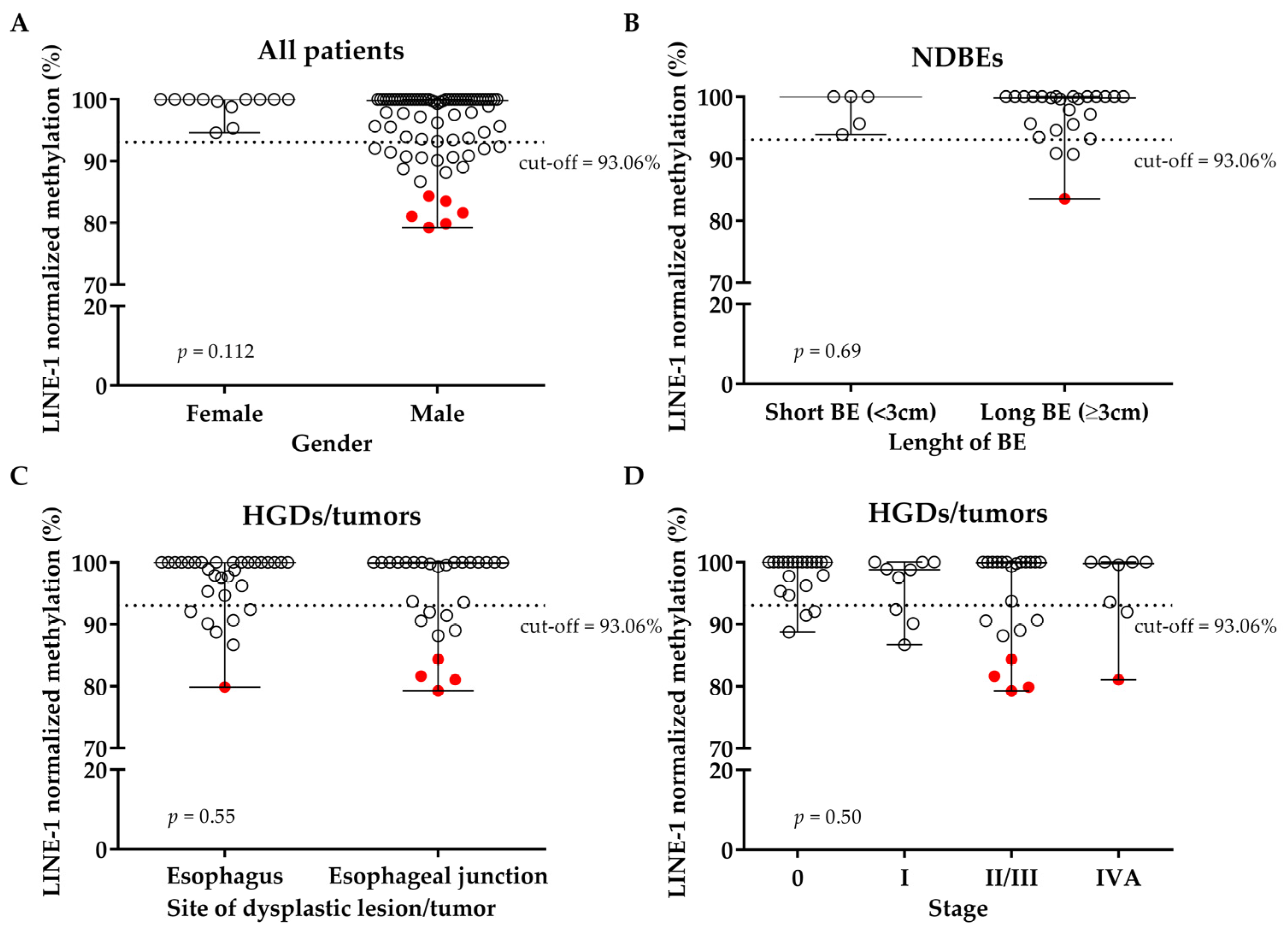
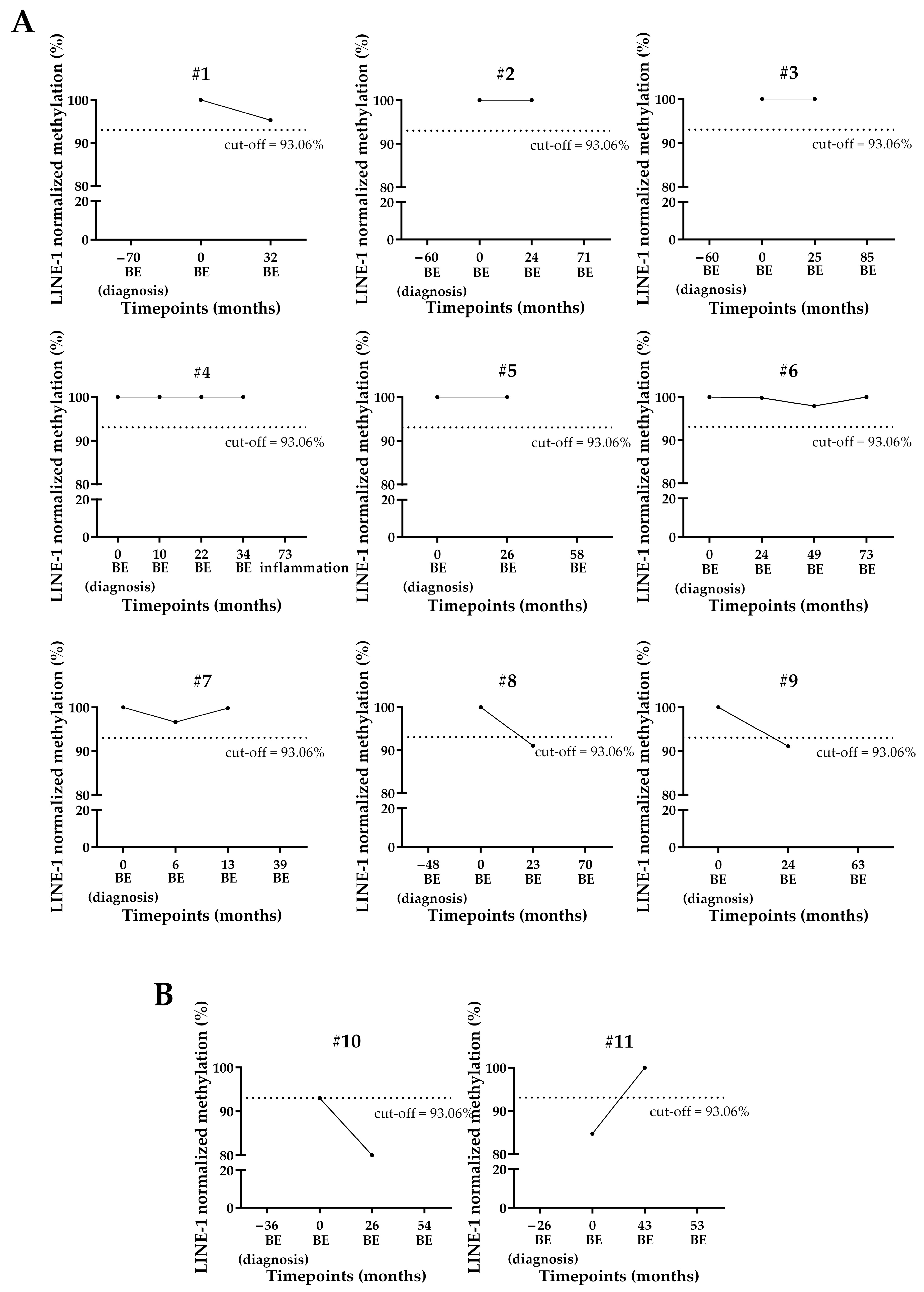
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients
3.2. LINE-1 Normalized Methylation Analysis in Cell-Free DNA at Baseline
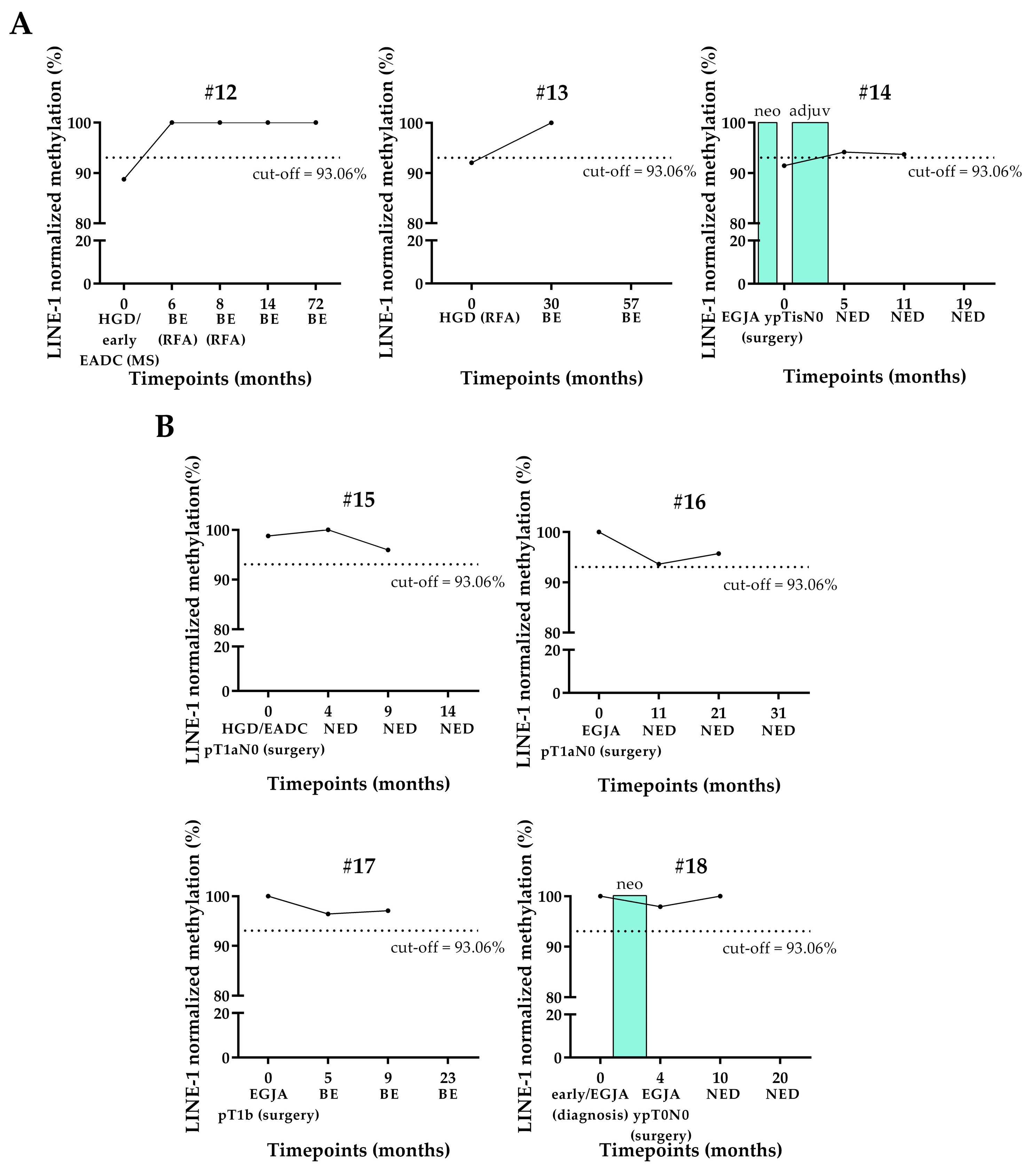
3.3. LINE-1 Normalized Methylation Analysis in Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) of Longitudinal Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| BE | Barrett’s esophagus |
| cfDNA | cell-free DNA |
| ddPCR | droplet digital PCR |
| EADC | esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| EC | esophageal cancer |
| EGJA | esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma |
| ESCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
| gDNA | germline DNA |
| GERD | gastro-esophageal reflux disease |
| HGD | high-grade dysplasia |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LGD | low-grade dysplasia |
| LINE-1 | long-interspersed nuclear element-1 |
| MRD | Minimal residual disease |
| MS | mucosectomy |
| MSRE-ddPCR | Methylation-Sensitive Restriction Enzyme and droplet digital PCR |
| NDBE | non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus |
| NED | no evidence of disease |
| OS | overall survival |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| RFA | radiofrequency ablation |
| SD | stable disease |
Appendix A
References
- Morgan, E.; Soerjomataram, I.; Rumgay, H.; Coleman, H.G.; Thrift, A.P.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Ferlay, J.; Arnold, M. The Global Landscape of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Incidence and Mortality in 2020 and Projections to 2040: New Estimates From GLOBOCAN 2020. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 649–658.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Q.; Ma, Y.-L.; Qin, Q.; Wang, P.-H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, P.-F.; Cui, Y. Epidemiology of Esophageal Cancer in 2020 and Projections to 2030 and 2040. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, T.W.; Gress, D.M.; Patil, D.T.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Kelsen, D.P.; Blackstone, E.H. Cancer of the Esophagus and Esophagogastric Junction—Major Changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer Eighth Edition Cancer Staging Manual. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty, M.G.; Freedman, N.D.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Abnet, C.C. A Prospective Cohort Study of Obesity and Risk of Oesophageal and Gastric Adenocarcinoma in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Gut 2012, 61, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Blankenstein, M.; Looman, C.W.N.; Hop, W.C.J.; Bytzer, P. The Incidence of Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus: Barrett’s Esophagus Makes a Difference. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.B.; Kamangar, F.; Whiteman, D.C.; Freedman, N.D.; Gammon, M.D.; Bernstein, L.; Brown, L.M.; Risch, H.A.; Ye, W.; Sharp, L.; et al. Cigarette Smoking and Adenocarcinomas of the Esophagus and Esophagogastric Junction: A Pooled Analysis From the International BEACON Consortium. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, E.C.; Verheij, M.; Allum, W.; Cunningham, D.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D. Gastric Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, v38–v49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; van Hagen, P.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy plus Surgery versus Surgery Alone for Oesophageal or Junctional Cancer (CROSS): Long-Term Results of a Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.S.; Guo, M.D.; Herskovic, A.; Macdonald, J.S.; Martenson, J.A., Jr.; Al-Sarraf, M.; Byhardt, R.; Russell, A.H.; Beitler, J.J.; Spencer, S.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy of Locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer. JAMA 1999, 281, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.J.; Lomboy, C.T.; Pera, M.; Carpenter, H.A. Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagogastric Junction and Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Falk, G.W.; Iyer, P.G.; Souza, R.F.; Yadlapati, R.H.; Sauer, B.G.; Wani, S. Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus: An Updated ACG Guideline. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 559–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Vantanasiri, K.; Mohan, B.P.; Goyal, R.; Garg, N.; Gerberi, D.; Kisiel, J.B.; Singh, S.; Iyer, P.G. Prevalence of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma With and Without Gastroesophageal Reflux: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1381–1394.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poehlmann, A.; Kuester, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Guenther, T.; Roessner, A. Inflammation and Barrett’s Carcinogenesis. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2012, 208, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, T.K.; Krishnan, K.; Samala, N.; Singh, J.; Cluley, J.; Perla, S.; Howden, C.W. The Incidence of Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma in Non-Dysplastic Barrett’s Oesophagus: A Meta-Analysis. Gut 2012, 61, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, A.; Puli, S.; El-Serag, H.B.; Bansal, A.; Wani, S.; Sharma, P. Incidence of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus and High-Grade Dysplasia: A Meta-Analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contino, G.; Vaughan, T.L.; Whiteman, D.; Fitzgerald, R.C. The Evolving Genomic Landscape of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 657–673.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachler, M.D.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Peng, S.; McKenna, A.; Agoston, A.T.; Odze, R.D.; Davison, J.M.; Nason, K.S.; Loda, M.; Leshchiner, I.; et al. Paired Exome Analysis of Barrett’s Esophagus and Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, G.; Braunschweig, R.; Pasquier, N.; Bosman, F.T.; Benhattar, J. Methylation of APC, TIMP3, and TERT: A New Predictive Marker to Distinguish Barrett’s Oesophagus Patients at Risk for Malignant Transformation. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, M. DNA Methylation in Cancer: Too Much, but Also Too Little. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5400–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-J.; Xue, H.-Y.; Qi, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, S.-J. LINE-1 in Cancer: Multifaceted Functions and Potential Clinical Implications. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.S. A Simple Method for Estimating Global DNA Methylation Using Bisulfite PCR of Repetitive DNA Elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, T.A.; Zhong, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.; Kernstine, K.H.; Wang, Z.; Riggs, A.D.; Pfeifer, G.P. High-Resolution Mapping of DNA Hypermethylation and Hypomethylation in Lung Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daskalos, A.; Nikolaidis, G.; Xinarianos, G.; Savvari, P.; Cassidy, A.; Zakopoulou, R.; Kotsinas, A.; Gorgoulis, V.; Field, J.K.; Liloglou, T. Hypomethylation of Retrotransposable Elements Correlates with Genomic Instability in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Kawakami, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Minamoto, T. Long Interspersed Nuclear Element 1 Hypomethylation Is a Marker of Poor Prognosis in Stage IA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2418–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunami, E.; de Maat, M.; Vu, A.; Turner, R.R.; Hoon, D.S.B. LINE-1 Hypomethylation During Primary Colon Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, S.; Nosho, K.; Kirkner, G.J.; Kawasaki, T.; Chan, A.T.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Fuchs, C.S. A Cohort Study of Tumoral LINE-1 Hypomethylation and Prognosis in Colon Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mima, K.; Nowak, J.A.; Qian, Z.R.; Cao, Y.; Song, M.; Masugi, Y.; Shi, Y.; da Silva, A.; Gu, M.; Li, W.; et al. Tumor LINE-1 Methylation Level and Colorectal Cancer Location in Relation to Patient Survival. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55098–55109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Seo, A.N.; Jung, H.Y.; Gwak, J.M.; Jung, N.; Cho, N.-Y.; Kang, G.H. Alu and LINE-1 Hypomethylation Is Associated with HER2 Enriched Subtype of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoesel, A.Q.; Van De Velde, C.J.H.; Kuppen, P.J.K.; Liefers, G.J.; Putter, H.; Sato, Y.; Elashoff, D.A.; Turner, R.R.; Shamonki, J.M.; De Kruijf, E.M.; et al. Hypomethylation of LINE-1 in Primary Tumor Has Poor Prognosis in Young Breast Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.A.; Elo, J.P.; Florl, A.R.; Pennanen, S.; Santourlidis, S.; Engers, R.; Buchardt, M.; Seifert, H.H.; Visakorpi, T. Genomewide DNA Hypomethylation Is Associated with Alterations on Chromosome 8 in Prostate Carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 35, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegnasubramanian, S.; Haffner, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Gurel, B.; Cornish, T.C.; Wu, Z.; Irizarry, R.A.; Morgan, J.; Hicks, J.; DeWeese, T.L.; et al. DNA Hypomethylation Arises Later in Prostate Cancer Progression than CpG Island Hypermethylation and Contributes to Metastatic Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8954–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Baba, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Chikamoto, A.; Kosumi, K.; Hayashi, H.; Nitta, H.; Hashimoto, D.; Beppu, T.; Baba, H. LINE-1 Methylation Level and Patient Prognosis in a Database of 208 Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Utsunomiya, T.; Ikemoto, T.; Yamada, S.; Morine, Y.; Imura, S.; Arakawa, Y.; Takasu, C.; Ishikawa, D.; Imoto, I.; et al. Hypomethylation of Long Interspersed Nuclear Element-1 (LINE-1) Is Associated with Poor Prognosis via Activation of c-MET in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.D.; Qu, J.H.; Chang, X.J.; Lu, Y.Y.; Bai, W.L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.X.; An, L.J.; Wang, C.P.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Hypomethylation of Long Interspersed Nuclear Element-1 Promoter Is Associated with Poor Outcomes for Curative Resected Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattamadilok, J.; Huapai, N.; Rattanatanyong, P.; Vasurattana, A.; Triratanachat, S.; Tresukosol, D.; Mutirangura, A. LINE-1 Hypomethylation Level as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2008, 18, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ling, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, M.-Z.; Liu, Y.-P.; Zhang, C.-S. Elevated Expression of MDR1 Associated with Line-1 Hypomethylation in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14392–14400. [Google Scholar]
- Iwagami, S.; Baba, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Shigaki, H.; Miyake, K.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Sakamaki, K.; Ohashi, Y.; Baba, H. LINE-1 Hypomethylation Is Associated With a Poor Prognosis Among Patients With Curatively Resected Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2013, 257, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrin, E.; Curtarello, M.; Dallan, M.; Alfieri, R.; Realdon, S.; Fassan, M.; Saggioro, D. Detection of LINE-1 Hypomethylation in CfDNA of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secrier, M.; Li, X.; De Silva, N.; Eldridge, M.D.; Contino, G.; Bornschein, J.; Macrae, S.; Grehan, N.; O’Donovan, M.; Miremadi, A.; et al. Mutational Signatures in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Define Etiologically Distinct Subgroups with Therapeutic Relevance. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet-O’Hare, T.T.; Rodić, N.; Sharma, R.; Darbari, I.; Abril, G.; Choi, J.A.; Young Ahn, J.; Cheng, Y.; Anders, R.A.; Burns, K.H.; et al. LINE-1 Expression and Retrotransposition in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4894–E4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, A.L.; Weaver, J.M.J.; Eldridge, M.D.; Tavaré, S.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Edwards, P.A.W. Mobile Element Insertions Are Frequent in Oesophageal Adenocarcinomas and Can Mislead Paired-End Sequencing Analysis. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.W.T.; Contino, G.; Killcoyne, S.; Devonshire, G.; Hsu, R.; Abbas, S.; Su, J.; Redmond, A.M.; Weaver, J.M.J.; Eldridge, M.D.; et al. Rearrangement Processes and Structural Variations Show Evidence of Selection in Oesophageal Adenocarcinomas. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitkumthorn, N.; Mutirangura, A. Long Interspersed Nuclear Element-1 Hypomethylation in Cancer: Biology and Clinical Applications. Clin. Epigenet. 2011, 2, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Batran, S.-E.; Homann, N.; Pauligk, C.; Goetze, T.O.; Meiler, J.; Kasper, S.; Kopp, H.-G.; Mayer, F.; Haag, G.M.; Luley, K.; et al. Perioperative Chemotherapy with Fluorouracil plus Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin, and Docetaxel versus Fluorouracil or Capecitabine plus Cisplatin and Epirubicin for Locally Advanced, Resectable Gastric or Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): A Ra. Lancet 2019, 393, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Park, B.H. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Marker for Disease Relapse in Early-Stage Breast Cancer-Bad Blood. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1479–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic CtDNA Analysis Depicts Early-Stage Lung Cancer Evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Cohen, J.D.; Kinde, I.; Ptak, J.; Popoli, M.; Schaefer, J.; Silliman, N.; Dobbyn, L.; Tie, J.; et al. Prognostic Potential of Circulating Tumor DNA Measurement in Postoperative Surveillance of Nonmetastatic Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrin, E.; Mazza, M.; Piano, M.A.; Alfieri, R.; Montagner, I.M.; Magni, G.; Scaini, M.C.; Vassallo, L.; Rosato, A.; Pilati, P.; et al. Putative Clinical Potential of ERBB2 Amplification Assessment by DdPCR in FFPE-DNA and CfDNA of Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Bundo, M.; Nakachi, Y.; Ueda, J.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Oshiumi, H.; et al. LINE-1 Hypomethylation, Increased Retrotransposition and Tumor-Specific Insertion in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupcinskas, J.; Steponaitiene, R.; Langner, C.; Smailyte, G.; Skieceviciene, J.; Kupcinskas, L.; Malfertheiner, P.; Link, A. LINE-1 Hypomethylation Is Not a Common Event in Preneoplastic Stages of Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.M.; Shin, S.H.; Kwon, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kook, M.C.; Kim, Y.W.; Cho, N.Y.; Kim, N.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, D.; et al. ALU and LINE-1 Hypomethylations in Multistep Gastric Carcinogenesis and Their Prognostic Implications. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.R.; Chung, W.C.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, K.M.; Paik, C.N.; Jung, S.H.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Han, S.W. Differential LINE-1 Hypomethylation of Gastric Low-Grade Dysplasia from High Grade Dysplasia and Intramucosal Cancer. Gut Liver 2011, 5, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigaki, H.; Baba, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Murata, A.; Iwagami, S.; Miyake, K.; Ishimoto, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Baba, H. LINE-1 Hypomethylation in Gastric Cancer, Detected by Bisulfite Pyrosequencing, Is Associated with Poor Prognosis. Gastric Cancer 2013, 16, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Kananazawa, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kakinuma, D.; Matsuno, K.; Ando, F.; Kuriyama, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yoshida, H. Methylation Status and Long-Fragment Cell-Free DNA Are Prognostic Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigalotti, L.; Fratta, E.; Bidoli, E.; Covre, A.; Parisi, G.; Colizzi, F.; Coral, S.; Massarut, S.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Maio, M. Methylation Levels of the “Long Interspersed Nucleotide Element-1” Repetitive Sequences Predict Survival of Melanoma Patients. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J.; Attard, G.; Bidard, F.C.; Curigliano, G.; De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Diehn, M.; Italiano, A.; Lindberg, J.; Merker, J.D.; Montagut, C.; et al. ESMO Recommendations on the Use of Circulating Tumour DNA Assays for Patients with Cancer: A Report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Muralidhar, R.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.-C. Epigenetic Modifications of CfDNA in Liquid Biopsy for the Cancer Care Continuum. Biomed. J. 2025, 48, 100718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, X.; Ma, Y.; Der, R.; Demeester, T.; Bernstein, L.; Chandrasoma, P.T. Body Mass Index Is Associated with Barrett Esophagus and Cardiac Mucosal Metaplasia. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2006, 51, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patients | NDBE | HGD/Early EADC-EGJA | Locally adv./ adv. EADC-EGJA |
|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | |
| 30 (33.3%) | 30 (33.3%) | 30 (33.3%) | |
| Age | |||
| Median (min; max) | 54.5 (21; 75) | 68 (36; 86) | 66 (41; 87) |
| IQR | 14.2 | 10.2 | 18 |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 25 (83.3%) | 27 (90%) | 26 (86.7%) |
| Female | 5 (16.7%) | 3 (10%) | 4 (13.3%) |
| Length of BE lesion | |||
| Short (<3 cm) | 5 (16.67%) | / | / |
| Long (≥3 cm) | 25 (83.33%) | / | / |
| Tumor site of lesion/ tumor | |||
| Esophagus | 30 (100%) | 26 (86.67%) | 6 (20%) |
| Esophageal junction | 0 (0%) | 4 (13.33%) | 24 (80%) |
| cStage | |||
| 0 | / | 21 (70%) | 0 (0%) |
| I | / | 9 (30%) | 0 (0%) |
| III | / | 0 (0%) | 22 (73.3%) |
| IVA | / | 0 (0%) | 3 (10%) |
| IVB | / | 0 (0%) | 2 (6.7%) |
| Unknown | / | 0 (0%) | 3 (10%) |
| pStage | |||
| 0 | / | 2 (18.18%) * | 0 (0%) |
| I | / | 9 (81.82%) * | 3 (10%) |
| II-IIIB | / | 0 (0%) | 16 (53.3%) |
| IVA | / | 0 (0%) | 5 (16.7%) |
| Unknown (no surgery) | / | 0 (0%) | 6 (20%) |
| Neoadjuvant treatment | |||
| Yes | / | 2 (6.67%) | 29 (96.7%) |
| No | / | 28 (93.33%) | 1 (3.3%) |
| Adjuvant treatment | |||
| Yes | / | / | 12 (40%) |
| No | / | / | 18 (60%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boldrin, E.; Piano, M.A.; Volpato, A.; Alfieri, R.; Franco, M.; Morbin, T.; Masier, A.; Realdon, S.; Mattara, G.; Magni, G.; et al. Global Hypomethylation as Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Biomarker in Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162668
Boldrin E, Piano MA, Volpato A, Alfieri R, Franco M, Morbin T, Masier A, Realdon S, Mattara G, Magni G, et al. Global Hypomethylation as Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Biomarker in Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162668
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoldrin, Elisa, Maria Assunta Piano, Alice Volpato, Rita Alfieri, Monica Franco, Tiziana Morbin, Annalisa Masier, Stefano Realdon, Genny Mattara, Giovanna Magni, and et al. 2025. "Global Hypomethylation as Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Biomarker in Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162668
APA StyleBoldrin, E., Piano, M. A., Volpato, A., Alfieri, R., Franco, M., Morbin, T., Masier, A., Realdon, S., Mattara, G., Magni, G., Rosato, A., Pilati, P., Fantin, A., & Curtarello, M. (2025). Global Hypomethylation as Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) Biomarker in Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(16), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162668







