Repurposing GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Perspective on Epigenetic Strategies to Combat Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Aged Liver
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
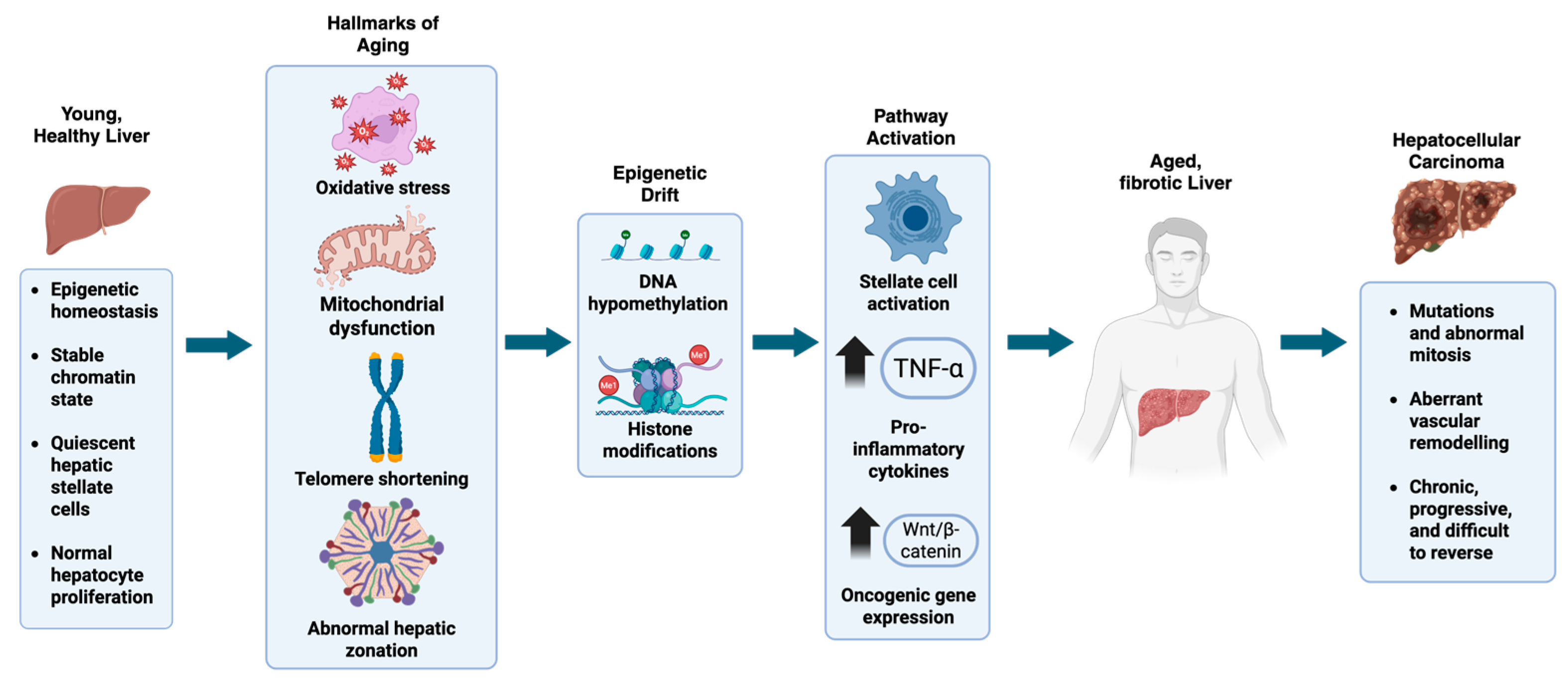
2. Epigenetic Dysregulation in the Aging Liver
3. Mechanisms of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1 RAs)
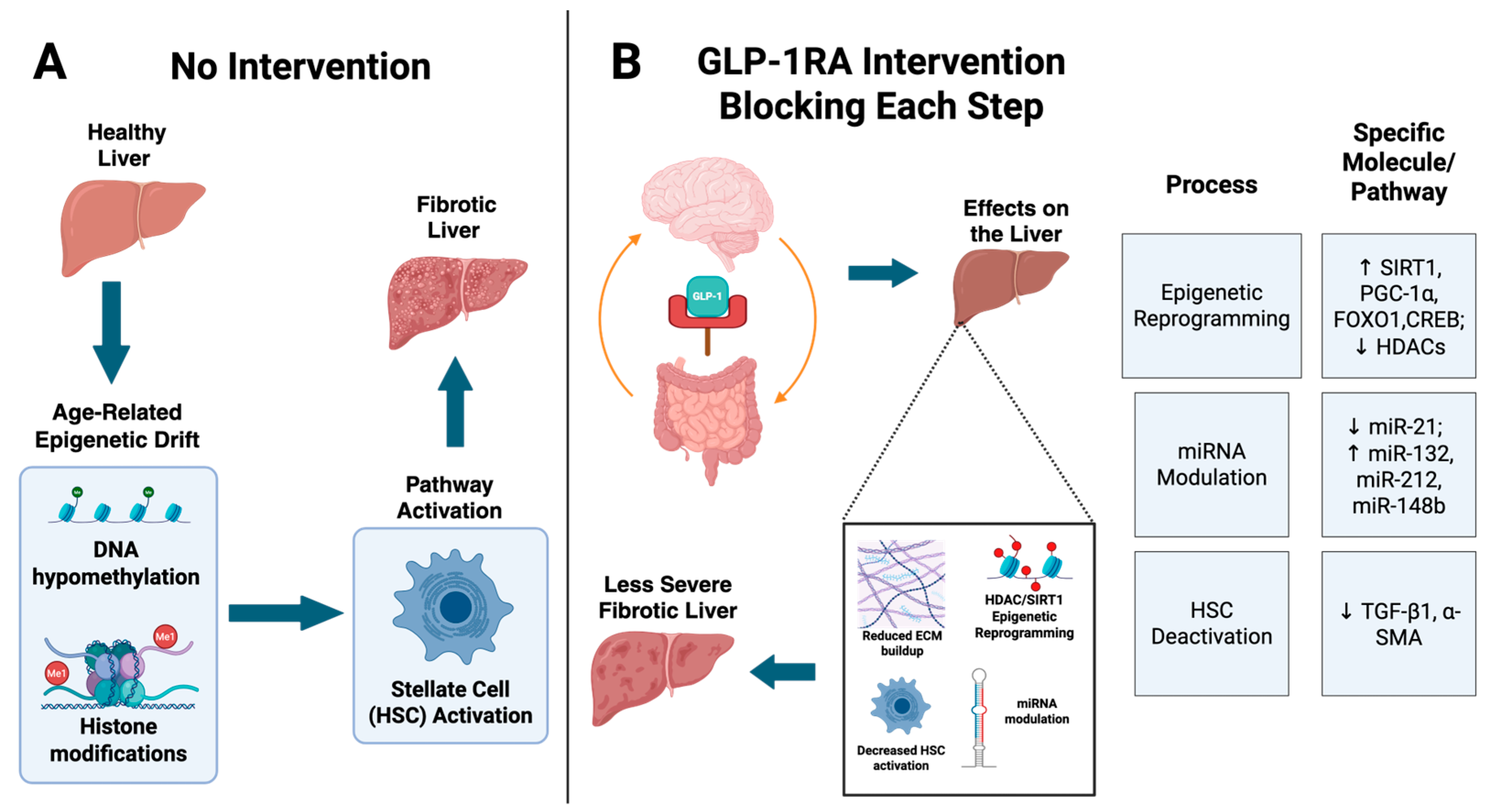
4. GLP-1RAs and Epigenetic Reprogramming in the Liver
Long Non-Coding RNAs Dysregulated in Liver Disease and Their Modulation by GLP-1RAs
5. GLP-1RAs in Fibrosis and HCC Prevention
6. Potential Clinical Implications and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Key Statistics About Liver Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/liver-cancer/about/what-is-key-statistics.html (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Lee, H.A. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly and adolescent/young adult populations. J. Liver Cancer 2025, 25, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Su, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, S.; He, W.; Zhang, Y.; An, X.; He, M. Emerging role of aging in the progression of NAFLD to HCC. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 84, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Ali, Q.; Zhang, T.; T-Nguyen, D.H.; Hanna, S.; Sethiadi, J.; Hissong, E.; E Schwartz, R. Aging disrupts hepatocyte zonation homeostasis in mice and humans. Hepatology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radonjić, T.; Dukić, M.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Popović, M.; Nikolić, N.; Klašnja, S.; Divac, A.; et al. Aging of Liver in Its Different Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanfeliu-Redondo, D.; Gibert-Ramos, A.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Cell senescence in liver diseases: Pathological mechanism and theranostic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Yen, T.-H.; Hsieh, S.-Y. Outcomes of Geriatric Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4332–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Kimura, T.; Kita, R.; Osaki, Y. Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Elderly Patients: A Literature Review. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.-P. Aging and epigenetic drift: A vicious cycle. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baechle, J.J.; Chen, N.; Makhijani, P.; Winer, S.; Furman, D.; Winer, D.A. Chronic inflammation and the hallmarks of aging. Mol. Metab. 2023, 74, 101755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Jeon, A.-J.; Chen, K.; Lee, C.J.M.; Wu, L.; Chong, S.-L.; Anene-Nzelu, C.G.; Foo, R.S.-Y.; Chow, P.K.-H. The epigenetic basis of hepatocellular carcinoma–mechanisms and potential directions for biomarkers and therapeutics. Br. J. Cancer 2025, 132, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Roblero, H.O.; Saavedra-Salazar, L.F.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Arceo-Orozco, S.; Caloca-Camarena, F.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; García-Bañuelos, J.; Frias-Gonzalez, C.; Almeida-López, M.; Martínez-López, E.; et al. Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma. Cells 2024, 13, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wan, J.-Y.; Yuan, C.-S. Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2024, 384, e076410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J. The promise of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) for the treatment of obesity: A look at phase 2 and 3 pipelines. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2025, 34, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermeier, F.; Fisman, E.Z. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and cardiometabolic protection: Historical development and future challenges. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintaridth, P.; Mutirangura, A. Distinctive patterns of age-dependent hypomethylation in interspersed repetitive sequences. Physiol. Genom. 2010, 41, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Gao, X. Repetitive DNA sequence detection and its role in the human genome. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Palma, C.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Faulk, C.D.; Dong, X. Epigenetics, DNA damage, and aging. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Taniguchi, H. Improving the repopulation capacity of elderly human hepatocytes by decoding aging-associated hepatocyte plasticity. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Nagasaka, T.; Nishimura, T.; Ikai, I.; Boland, R.C.; Goel, A. Aberrant methylation of multiple tumor suppressor genes in aging liver, chronic hepatitis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.M.; Eissa, N.; Doghish, A.S.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Abdelmaksoud, N.M.; Mohammed, O.A.; Mageed, S.S.A.; Darwish, S.F. Decoding the secrets of longevity: Unraveling nutraceutical and miRNA-Mediated aging pathways and therapeutic strategies. Front. Aging 2024, 5, 1373741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, S.; Iwama, H.; Kato, K.; Nomura, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoneyama, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Tani, J.; Morishita, A.; Himoto, T.; et al. Profile of microRNAs associated with aging in rat liver. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.E.; Kun, B.; Sabula, I.M.C.; Golomb-Mello, G.; Zablah, A.C.; Kreiling, J.A. The mir-465 family is upregulated with age and attenuates growth hormone signaling in mouse liver. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, M.; Bloomston, P.M. Hepatic Stellate Cells and microRNAs in Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, N.J.; Kang, S.W.; Lockwood, G.P.; Le Couteur, D.G.; Cogger, V.C. Hallmarks of Aging in the Liver. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L. Navigating the complex role of senescence in liver disease. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 137, 3061–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, L.; Alexandersson, I.; Baboota, R.K.; Kroon, T.; Oscarsson, J.; Smith, U.; Boucher, J. Cellular senescence in hepatocytes contributes to metabolic disturbances in NASH. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 957616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, C.; Heller, R.S.; Kirk, R.K.; Ørskov, C.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kaastrup, P.; Hvelplund, A.; Bardram, L.; Calatayud, D.; Knudsen, L.B. GLP-1 Receptor Localization in Monkey and Human Tissue: Novel Distribution Revealed With Extensively Validated Monoclonal Antibody. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, B.P.; Heller, R.S.; Habener, J.F. Tissue distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid encoding the rat glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 2968–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, A.; Liu, Z.; Wong, H.Z.H.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and cancer risk: Advancing precision medicine through mechanistic understanding and clinical evidence. Biomark. Res. 2025, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, M.; Vlaicu, S.I.; Ciumărnean, L.; Milaciu, M.V.; Mărginean, C.; Florea, M.; Vesa, Ș.C.; Popa, M. Chronic Inflammation—A Link between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Dysfunctional Adipose Tissue. Medicina 2022, 58, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S.H. Anti-inflammatory role of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and its clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 15, 20420188231222367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieser, V.; Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H. Inflammation, Cytokines and Insulin Resistance: A Clinical Perspective. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2013, 61, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsiad, E.A.; El Aal, H.A.A.; Salem, H.A.; El-Yamany, M.F.; Rabie, M.A. Liraglutide Attenuates Atorvastatin-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Restoring GLP-1R Expression and Activating Nrf2 and Autophagy Pathways in Wistar Rats. Toxics 2025, 13, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-L.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, Y.-P.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-D. Activation of GLP-1 Receptor Enhances Neuronal Base Excision Repair via PI3K-AKT-Induced Expression of Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1. Theranostics 2016, 6, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Vong, J.S.L.; Zhao, L.; Huang, J.; Yan, L.Y.C.; Ip, B.; Wing, Y.K.; Lai, H.-M.; Mok, V.C.T.; et al. Systemic GLP-1R agonist treatment reverses mouse glial and neurovascular cell transcriptomic aging signatures in a genome-wide manner. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Jin, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Ding, W.; Xie, W.; Kong, H. GLP-1R activation attenuates the progression of pulmonary fibrosis via disrupting NLRP3 inflammasome/PFKFB3-driven glycolysis interaction and histone lactylation. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.E.; Drucker, D.J. Pharmacology, Physiology, and Mechanisms of Incretin Hormone Action. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechederra, M.; Recalde, M.; Gárate-Rascón, M.; Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Ávila, M.A.; Berasain, C. Epigenetic Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Durán, R.; Romero-Gómez, M. Epigenetic mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging field. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, Z.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, K.; Weng, J. SIRT1 Mediates the Effect of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Exenatide on Ameliorating Hepatic Steatosis. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Huang, R.; Xiang, M. SIRT1: Harnessing multiple pathways to hinder NAFLD. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Weng, J. Hepatic functions of GLP-1 and its based drugs: Current disputes and perspectives. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2016, 311, E620–E627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, D.; Angeli, F.S.; Vakilipour, A.; Carlson, O.D.; Tomas, E.; Egan, J.M.; Habener, J.F.; Shannon, R.P. GLP-1(32–36)amide, a novel pentapeptide cleavage product of GLP-1, modulates whole body glucose metabolism in dogs. Peptides 2014, 59, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, D.J.; Irwin, A.; Gardner, C.J.; Daousi, C.; Purewal, T.; Furlong, N.; Goenka, N.; Thomas, E.L.; Adams, V.L.; Pushpakom, S.P.; et al. Improved Glycaemia Correlates with Liver Fat Reduction in Obese, Type 2 Diabetes, Patients Given Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, M.P.; Lisco, G.; Depalo, N.; Rizzi, F.; Volpe, S.; Arrè, V.; Carrieri, L.; Notarnicola, M.; De Nunzio, V.; Curri, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide Modulates Extracellular Matrix Production of LX-2 Cells via Exosomes and Improves Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Gaunt, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Barton, D.; Hull, D.; Parker, R.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Guo, K.; Abouda, G.; A Aldersley, M.; et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.Y.; Oh, I.J.; Choi, D.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, I.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.H.; et al. A GLP-1/GLP-2 receptor dual agonist to treat NASH: Targeting the gut-liver axis and microbiome. Hepatology 2021, 75, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Berger, N.A.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R. Association of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence and Hepatic Decompensation in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kang, X.; Meng, X.; Huang, L.; Du, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liao, C. MALAT1-mediated EZH2 Recruitment to the GFER Promoter Region Curbs Normal Hepatocyte Proliferation in Acute Liver Injury. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Mao, X.; Xu, K. Long Non-coding RNA MALAT1: A Key Player in Liver Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 734643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, S.; Ye, F.; Shen, Y.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wei, L.; Jin, Y.; Fu, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Interacts with p53 Protein and Regulates Partial p53 Target Genes in Hepatoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, K.O.; Tanase, C.E.; Maghami, S.; Fisher, L.E.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. Inflammatory Network of Liver Fibrosis and How It Can Be Targeted Therapeutically. Immuno 2023, 3, 375–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.K. Hepatic Stellate Cells and Liver Fibrosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Q.; Deng, X.-W.; Xu, G.-Q.; Lin, J.; Lu, H.-Z.; Chen, J. Mechanical homeostasis imbalance in hepatic stellate cells activation and hepatic fibrosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbuzenko, D.V. Mechanisms of Epigenetic Regulation in the Fibrogenic Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gene Expr. 2024, 23, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouihan, H.; Will, S.; Guionaud, S.; Boland, M.L.; Oldham, S.; Ravn, P.; Celeste, A.; Trevaskis, J.L. Superior reductions in hepatic steatosis and fibrosis with co-administration of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist and obeticholic acid in mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorli, C.; Harashima, S.-I.; Tsoukas, G.M.; Unger, J.; Karsbøl, J.D.; Hansen, T.; Bain, S.C. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide monotherapy versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multinational, multicentre phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysham, C.; Bergenstal, R.; Malloy, J.; Yan, P.; Walsh, B.; Malone, J.; Taylor, K. DURATION-2: Efficacy and safety of switching from maximum daily sitagliptin or pioglitazone to once-weekly exenatide. Diabet. Med. 2011, 28, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolz, A.; Wolter, S.; Wehmeyer, M.H.; Piecha, F.; Horvatits, T.; Wiesch, J.S.Z.; Lohse, A.W.; Mann, O.; Kluwe, J. Performance of non-invasive fibrosis scores in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with and without morbid obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Kowdley, K.V.; Chalasani, N.; LaVine, J.E.; Ratziu, V.; McCullough, A. Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| GLP-1RA | Mechanism of Action | Effects on Liver (Aged/HCC) | Model/Study Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liraglutide | GLP-1 receptor agonist (daily) | Histological resolution of NASH and metabolic improvement; potential epigenetic modulation via SIRT1 | Diet-induced NASH models; human clinical trial | [48] |
| Reduces pro-fibrotic histone lactylation | Pulmonary fibrosis model (lung fibroblasts) | [38] | ||
| Semaglutide | GLP-1 receptor agonist (weekly) | Exosomes suppress SMAD2 phosphorylation in HSCs; ↓ ECM gene expression and fibrosis markers–improving liver fibrosis in MASLD | Human ex vivo + LX-2 hepatic stellate cells | [47] |
| Tirzepatide | Long-acting dual agonist of GLP-1 and GLP-2 receptors | Stronger metabolic improvements; ↓ steatosis, inflammation, and hepatic fat accumulation | Preclinical NASH models; clinical trials in HCC | [49,50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanna, S.; Sethiadi, J.; Ali, Q.; Sinha, S. Repurposing GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Perspective on Epigenetic Strategies to Combat Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Aged Liver. Cancers 2025, 17, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162600
Hanna S, Sethiadi J, Ali Q, Sinha S. Repurposing GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Perspective on Epigenetic Strategies to Combat Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Aged Liver. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162600
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanna, Silvia, Jason Sethiadi, Qazi Ali, and Saloni Sinha. 2025. "Repurposing GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Perspective on Epigenetic Strategies to Combat Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Aged Liver" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162600
APA StyleHanna, S., Sethiadi, J., Ali, Q., & Sinha, S. (2025). Repurposing GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Perspective on Epigenetic Strategies to Combat Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Aged Liver. Cancers, 17(16), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162600






