Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figure 6A as published. The gene label “WDR54” was incorrectly used instead of “WBP5”.
The correct figure is provided below:
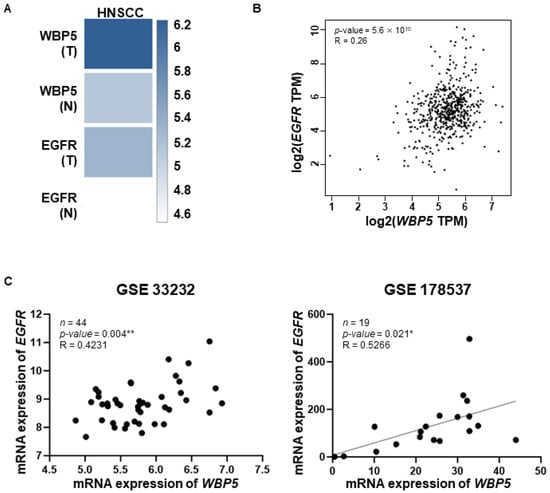
Figure 6.
Correlation of WBP5 and EGFR expression across different cancer types and datasets. (A) Heatmaps of WBP5 and EGFR expression across HNSCC, with darker blue indicating higher expression levels. (B) Scatter plot showing the correlation between WBP5 and EGFR expression (log2 TPM) across samples, with a positive correlation (R = 0.26, p = 5.6 × 1010). (C) Scatter plots showing the correlation between WBP5 and EGFR expression in specific datasets (GSE33232 and GSE178537). Both datasets demonstrate a positive correlation between WBP5 and EGFR expression, with GSE33232 (R = 0.4231, p = 0.004) and GSE178537 (R = 0.5266, p = 0.021) (* p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01).
Text Correction
There was an error in the original publication [1]. The protein name was incorrectly written as “WW domain C-binding protein 5 (WBP5)”, instead of “WW domain protein 5 (WBP5)” in the Introduction, paragraph 2.
The correct text is provided below:
“WW domain protein 5 (WBP5), alternatively referred to as Transcriptional Elongation Factor A-like 9 (TCEAL9), engages with diverse signaling pathways and associated with WW domains [3]”.
A correction has been made to Materials and Methods, 4.8. Cell Culturing and Viability Assessment, where “WDR54-knockdown FaDu cells” was incorrectly written instead of “WBP5-knockdown FaDu cells”.
The correct text is provided below:
“Assays were conducted using WBP5-knockdown FaDu cells. For the cell viability experiments, 3 × 103 cells/well were seeded into 96-well plates, while 1 × 103 cells/well were plated for proliferation analysis.”
The authors apologize for any inconvenience caused and state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Jeong, E.-j.; Kim, E.; Jung, K.-Y.; Baek, S.-K.; Kim, Y.S. WBP5 Expression Influences Prognosis and Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).