The Prognostic Role of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Immune Microenvironment Signatures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
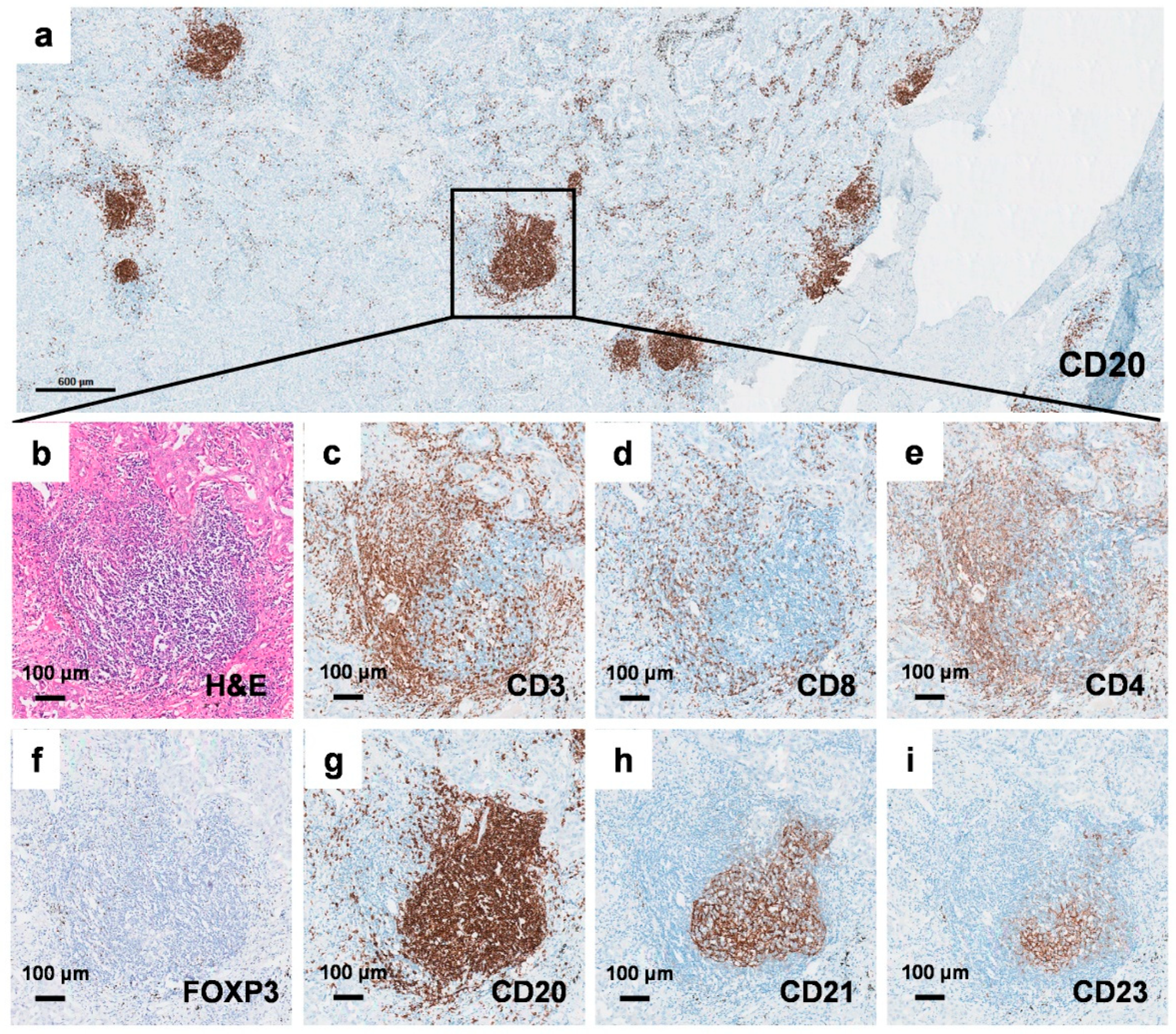
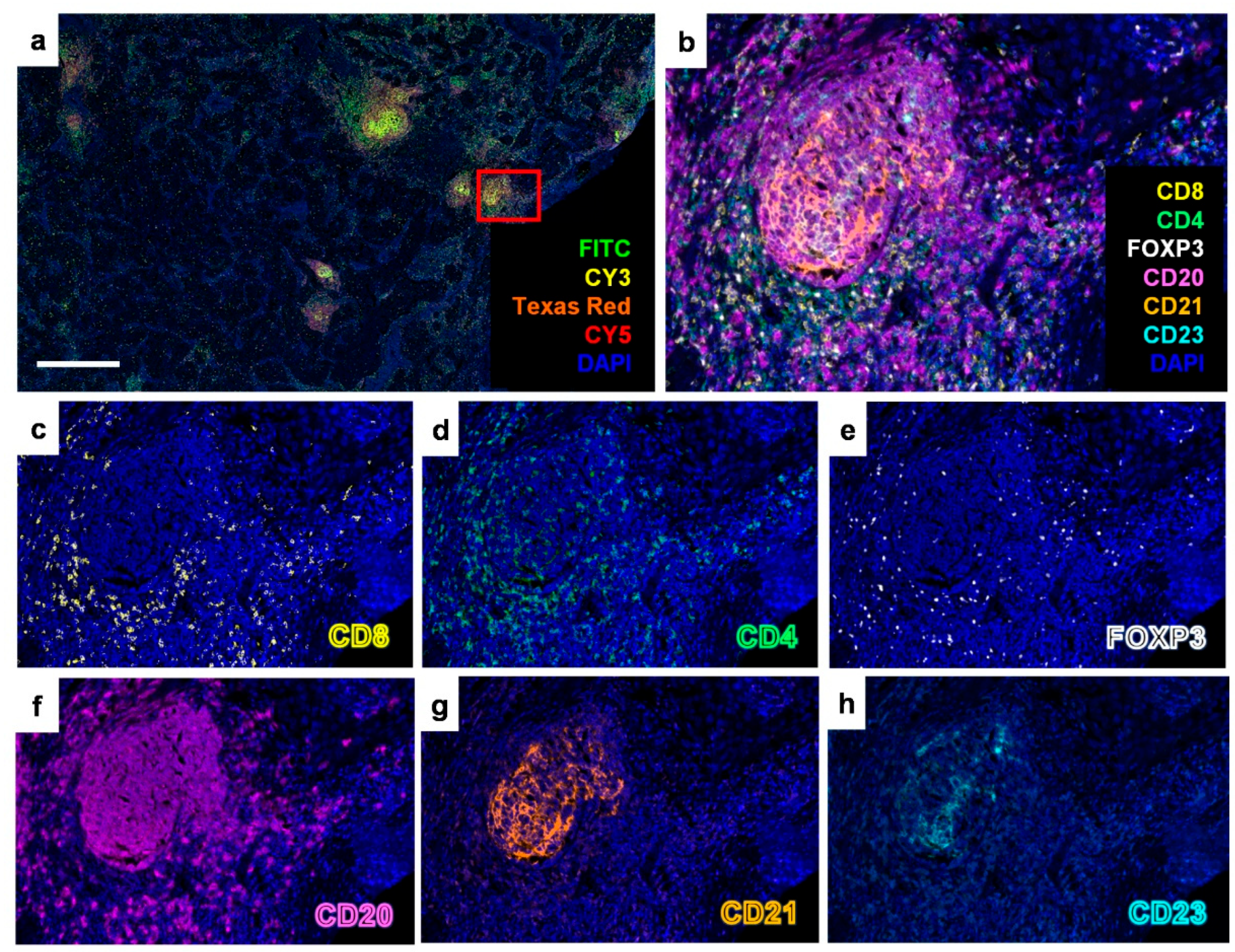
2.1. Identification of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
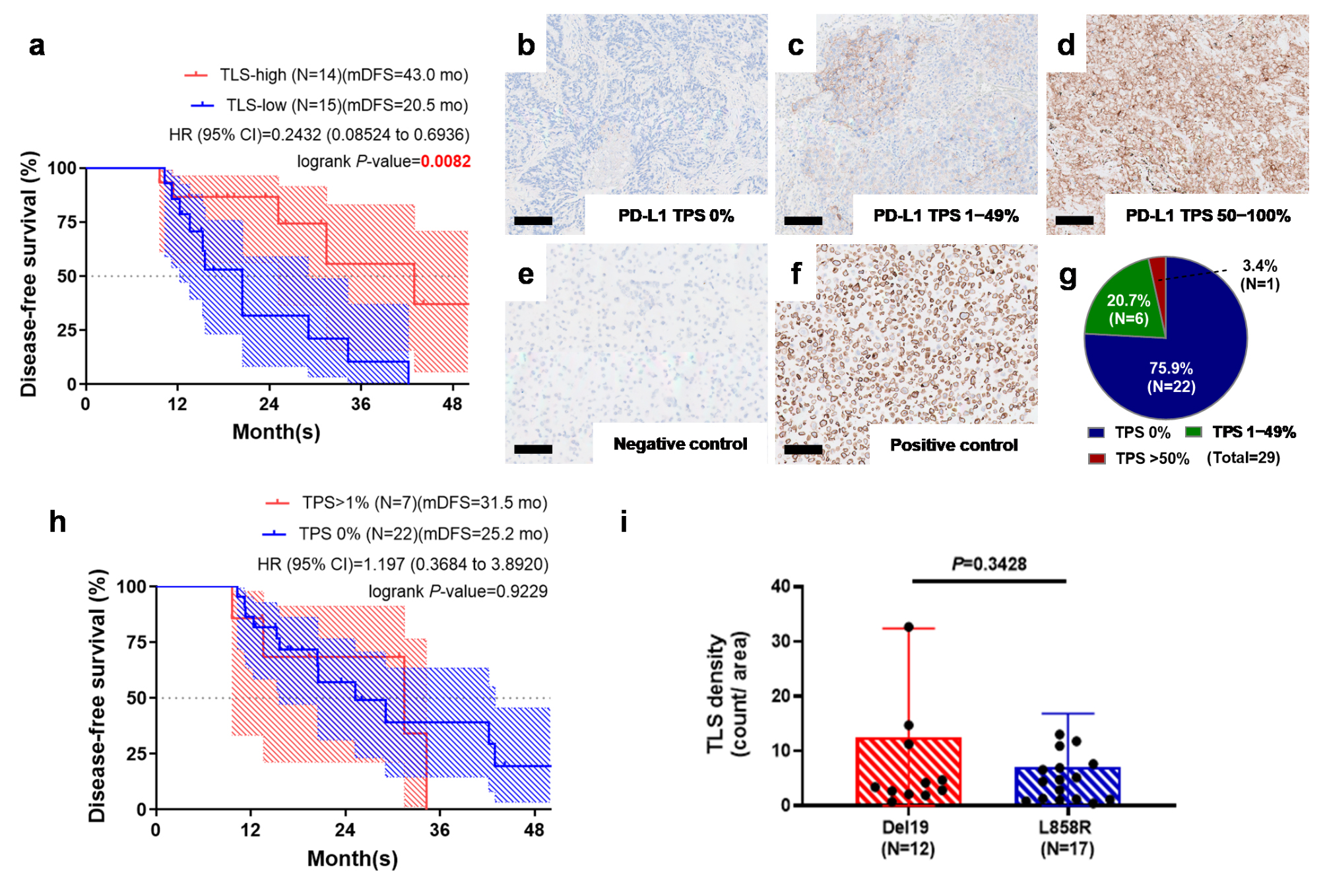
2.2. Tertiary Lymphoid Structure Rather than PD-L1 TPS Serves as a Favorable Prognostic Factor in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma
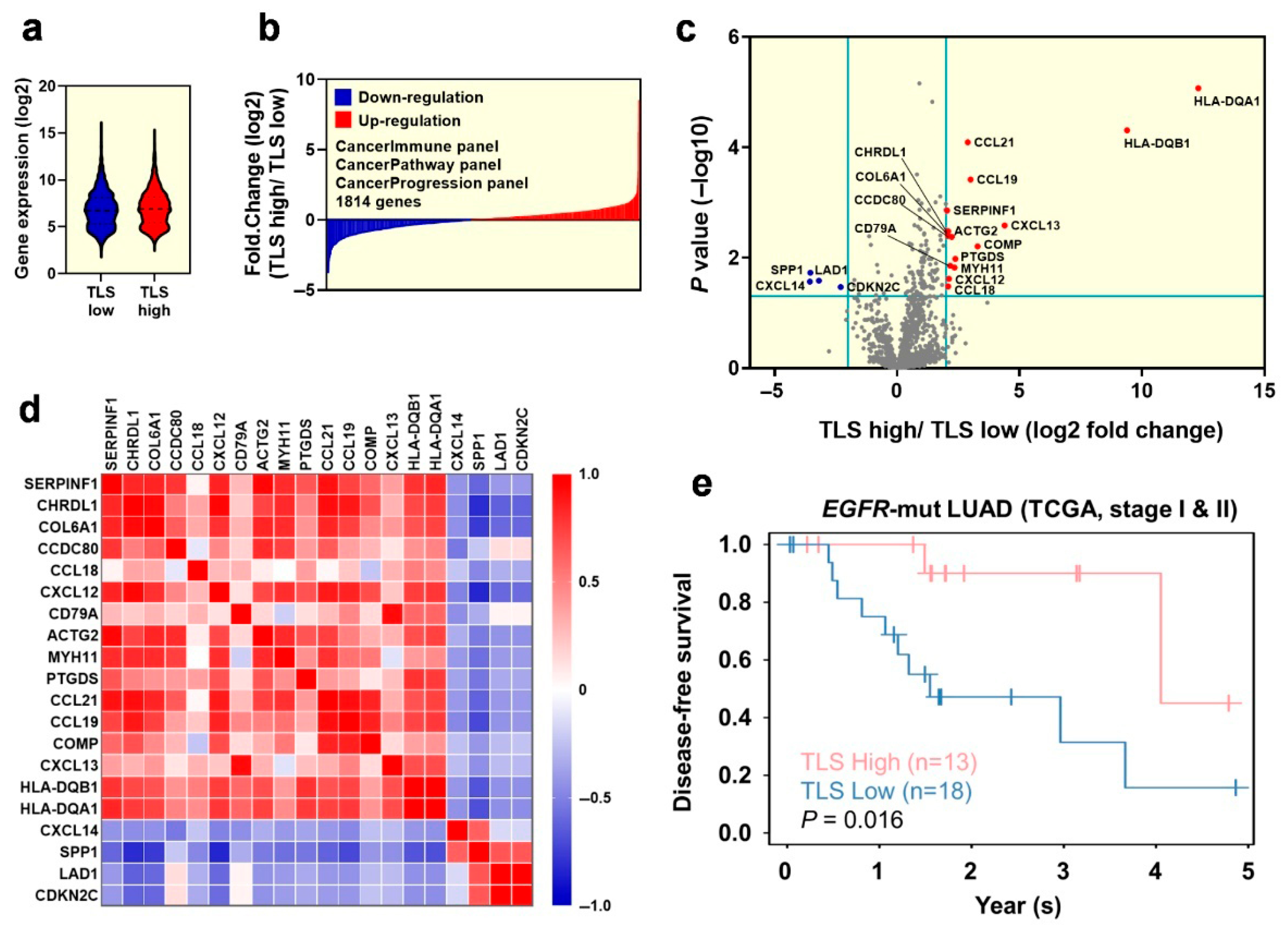
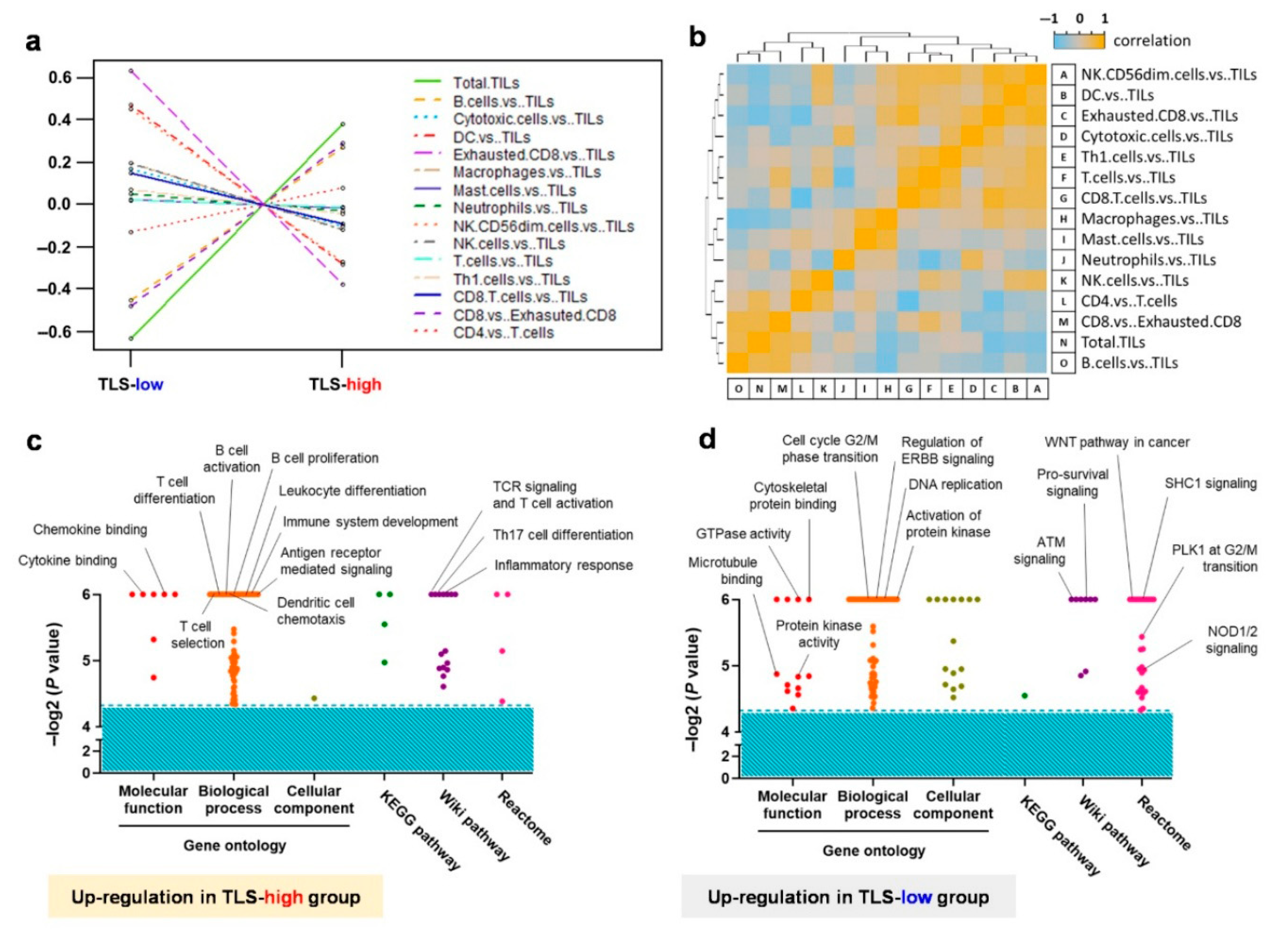
2.3. Exploration of the Differentiated Genes for the Tumor Microenvironment in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma Patinets with TLS Expression
2.4. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Crucial Immune Cell Type and Molecular Functions Within the Tumor Microenvironment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
4.3. Multiplex Fluorescent IHC Staining and Analysis
4.4. PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) Measurement
4.5. NanoString Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
4.7. Patient Enrollment and Outcome Measurements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Antibody | Species | Reference | Clone | Source | Antigen Retrieval | Concentration Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 | Rabbit | ab16669 | SP7 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:150 |
| CD8 | Rabbit | ab178089 | SP239 | Abcam | pH9 | 1:100 |
| CD4 | Rabbit | ab213215 | SP35 | Abcam | pH9 | 1:50 |
| FOXP3 | Mouse | ab20034 | 236A/E7 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:200 |
| CD20 | Mouse | ab9475 | L26 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:100 |
| CD21 | Rabbit | ab75985 | EP3093 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:300 |
| CD23 | Rabbit | ab16702 | SP23 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:100 |
| PanCK | Mouse | ab7753 | C-11 | Abcam | pH6 | 1:200 |
References
- Fridman, W.H.; Meylan, M.; Petitprez, F.; Sun, C.M.; Italiano, A.; Sautes-Fridman, C. B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures as determinants of tumour immune contexture and clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Thommen, D.S. Tertiary lymphoid structures in cancer. Science 2022, 375, eabf9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautes-Fridman, C.; Verneau, J.; Sun, C.M.; Moreira, M.; Chen, T.W.; Meylan, M.; Petitprez, F.; Fridman, W.H. Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and B cells: Clinical impact and therapeutic modulation in cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 48, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmink, B.A.; Reddy, S.M.; Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Basar, R.; Thakur, R.; Yizhak, K.; Sade-Feldman, M.; Blando, J.; Han, G.; et al. B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response. Nature 2020, 577, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitprez, F.; de Reynies, A.; Keung, E.Z.; Chen, T.W.; Sun, C.M.; Calderaro, J.; Jeng, Y.M.; Hsiao, L.P.; Lacroix, L.; Bougouin, A.; et al. B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma. Nature 2020, 577, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrita, R.; Lauss, M.; Sanna, A.; Donia, M.; Skaarup Larsen, M.; Mitra, S.; Johansson, I.; Phung, B.; Harbst, K.; Vallon-Christersson, J.; et al. Tertiary lymphoid structures improve immunotherapy and survival in melanoma. Nature 2020, 577, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; He, Y.T.; Dong, S.; Wei, X.W.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, W.D.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, F.; Shang, X.M.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis revealed a suppressive tumor immune microenvironment in EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Jiang, T.; Liu, X.; Mao, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC: Dusk or Dawn? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1267–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Hirsh, V.; Cadranel, J.; Chen, Y.M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.W.; Zhou, C.; Su, W.C.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): A phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rami-Porta, R.; Call, S.; Dooms, C.; Obiols, C.; Sanchez, M.; Travis, W.D.; Vollmer, I. Lung cancer staging: A concise update. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1800190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, N. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tsang, J.Y.S.; Hlaing, T.; Hu, J.; Ni, Y.B.; Chan, S.K.; Cheung, S.Y.; Tse, G.M. Distinct Tertiary Lymphoid Structure Associations and Their Prognostic Relevance in HER2 Positive and Negative Breast Cancers. Oncologist 2017, 22, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeddu, C.; Donisi, C.; Liscia, N.; Lai, E.; Scartozzi, M.; Maccio, A. EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Resistance to Immunotherapy: Role of the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Gao, J.; Ma, X.; Song, J.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Bao, X.; et al. The radiological characteristics, tertiary lymphoid structures, and survival status associated with EGFR mutation in patients with subsolid nodules like stage I-II LUAD. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Chen, K.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Hsu, C.L.; Liu, Y.N.; Su, K.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Wu, C.T.; et al. Association of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression with Fusion Variants and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma Receiving Crizotinib. Oncologist 2020, 25, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuminello, S.; Veluswamy, R.; Lieberman-Cribbin, W.; Gnjatic, S.; Petralia, F.; Wang, P.; Flores, R.; Taioli, E. Prognostic value of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment of early-stage lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 7142–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Ho, C.C.; Chen, K.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Hsu, C.L.; Su, K.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Wu, C.T.; Hsu, C.C.; et al. Association between programmed death-ligand 1 expression, immune microenvironments, and clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 124, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; He, Q.; Cai, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, H.; Li, F.; Zhong, R.; Lu, Y.; Peng, H.; Wu, X.; et al. Intratumoral tertiary lymphoid structure (TLS) maturation is influenced by draining lymph nodes of lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, S.; Wen, S.; He, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H. Density of tertiary lymphoid structures and their correlation with prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1423775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, M.; Song, Q. The impact of tertiary lymphoid structures on tumor prognosis and the immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollack, B.P.; Sapkota, B.; Cartee, T.V. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition augments the expression of MHC class I and II genes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4400–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Lin, X.; Xie, M.; Yao, J.; Song, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, W.; et al. Mature tertiary lymphoid structures: Important contributors to anti-tumor immune efficacy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1413067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.S.; Fan, Y.; de Marinis, F.; Iwama, E.; Inoue, T.; Rodriguez-Cid, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.T.; et al. Phase III KEYNOTE-789 Study of Pemetrexed and Platinum With or Without Pembrolizumab for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant, EGFR-Mutant, Metastatic Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Park, K.; Ohe, Y.; Girard, N.; Kim, H.R.; Wu, Y.L.; Gainor, J.; Lee, S.H.; Chiu, C.H.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Chemotherapy in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Disease Progression on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Final Results of CheckMate 722. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Borghaei, H.; Patnaik, A.; Yang, J.C.; Powell, S.F.; Gentzler, R.D.; Martins, R.G.; Stevenson, J.P.; Altan, M.; et al. Long-Term Overall Survival From KEYNOTE-021 Cohort G: Pemetrexed and Carboplatin With or Without Pembrolizumab as First-Line Therapy for Advanced Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Low TLS Density (<4 Counts/cm2) | High TLS Density (>4 Counts/cm2) | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | (%) | n | (%) | |||
| Stage AJCC | I | 12 | 80.0% | 12 | 85.7% | 0.684 |
| II | 3 | 20.0% | 2 | 14.3% | ||
| EGFR mutation | Del19 | 5 | 33.3% | 7 | 50.0% | 0.362 |
| L858R | 10 | 66.7% | 7 | 50.0% | ||
| PDL1 TPS | <1% | 13 | 86.7% | 9 | 64.3% | 0.307 |
| 1–49% | 2 | 13.3% | 4 | 28.6% | ||
| ≥50% | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 7.1% | ||
| Smoking | No | 12 | 80.0% | 13 | 92.9% | 0.316 |
| Yes | 3 | 20.0% | 1 | 7.1% | ||
| Characteristic | HR (95% CI) | p Value | Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage (I vs. II) | 0.989 (0.279 to 3.526) | 0.989 | ||
| EGFR mutation (Del19 vs. L858R) | 1.569 (0.556 to 4.427) | 0.395 | ||
| Smoking history (No vs. Yes) | 0.199 (0.047 to 0.846) | 0.029 | 0.203 (0.038 to 1.076) | 0.061 |
| TLS (high vs. low density) | 0.235 (0.074 to 0.746) | 0.014 | 0.235 (0.071 to 0.774) | 0.016 |
| PDL1 TPS (0% vs. ≥1%) | 0.823 (0.256 to 2.647) | 0.744 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, W.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Yang, J.C.-H. The Prognostic Role of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Immune Microenvironment Signatures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142379
Hsu W-H, Hsu C-C, Hsieh M-S, Yang JC-H. The Prognostic Role of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Immune Microenvironment Signatures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(14):2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142379
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Wei-Hsun, Chia-Chi Hsu, Min-Shu Hsieh, and James Chih-Hsin Yang. 2025. "The Prognostic Role of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Immune Microenvironment Signatures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 14: 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142379
APA StyleHsu, W.-H., Hsu, C.-C., Hsieh, M.-S., & Yang, J. C.-H. (2025). The Prognostic Role of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures and Immune Microenvironment Signatures in Early-Stage EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(14), 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142379






