Video-Assisted Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: First Clinical Experience and Outcomes in an Eastern European Medical Center
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
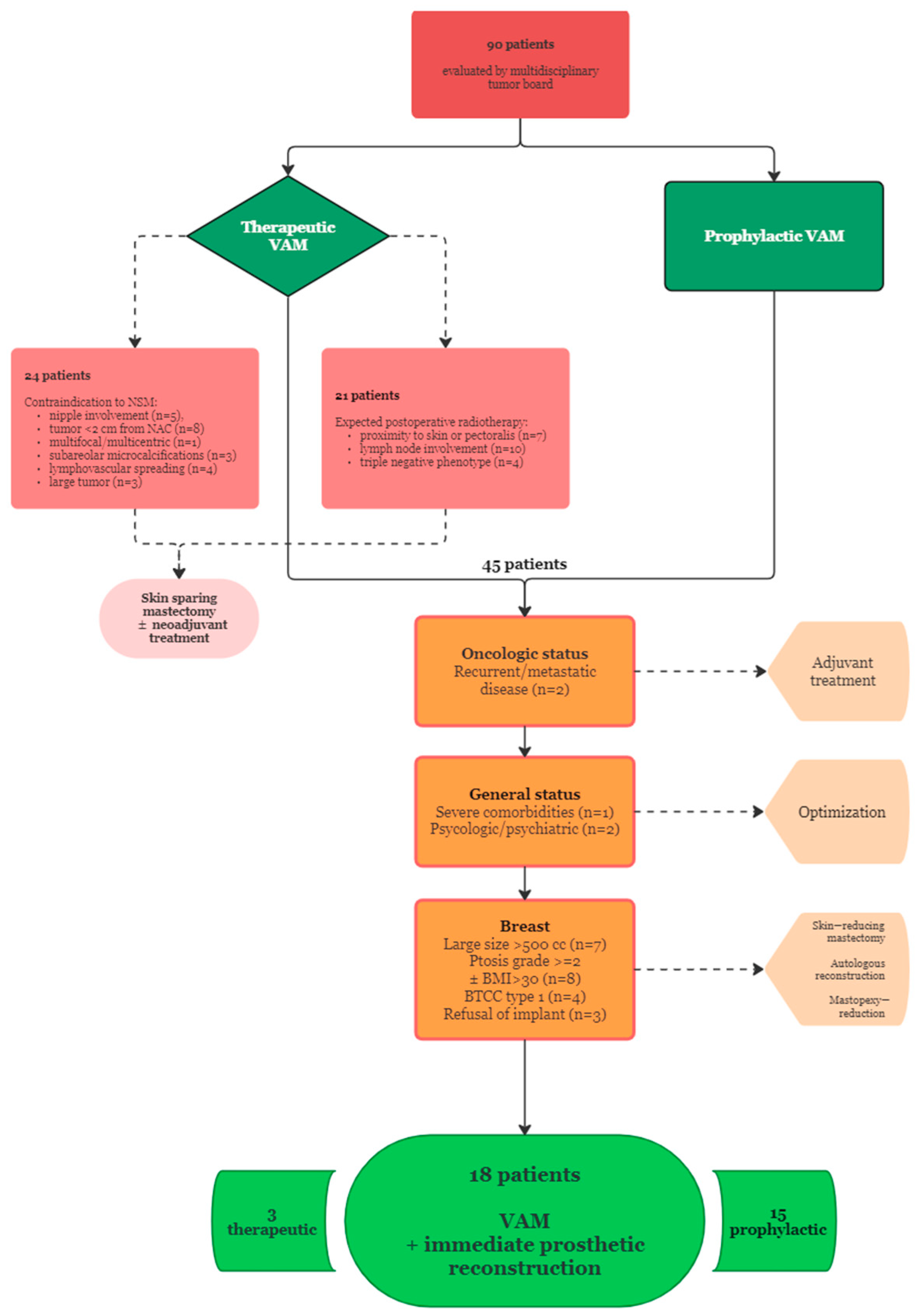
2. Materials and Methods
- Therapeutic VAM (TM): breast cancer patients with histologically confirmed diagnosis prepared to undergo oncologic resection and the following tumor characteristics: T2 or below, stage I or II, absence of NAC, skin or pectoralis major invasion according to preoperative imaging and clinical examination, more than 2 cm distance from tumor to NAC, absence of lymphovascular spread, immunohistochemistry phenotype other than triple negative;
- Risk-reducing VAM (RRM): breast cancer patients with contralateral mastectomy ± reconstruction with no evidence of locoregional or distant recurrence willing to undergo removal of the remaining breast for the following reasons: the presence of BRCA1/2 mutations, familial history of breast or gynecological cancer, young age at initial diagnosis.
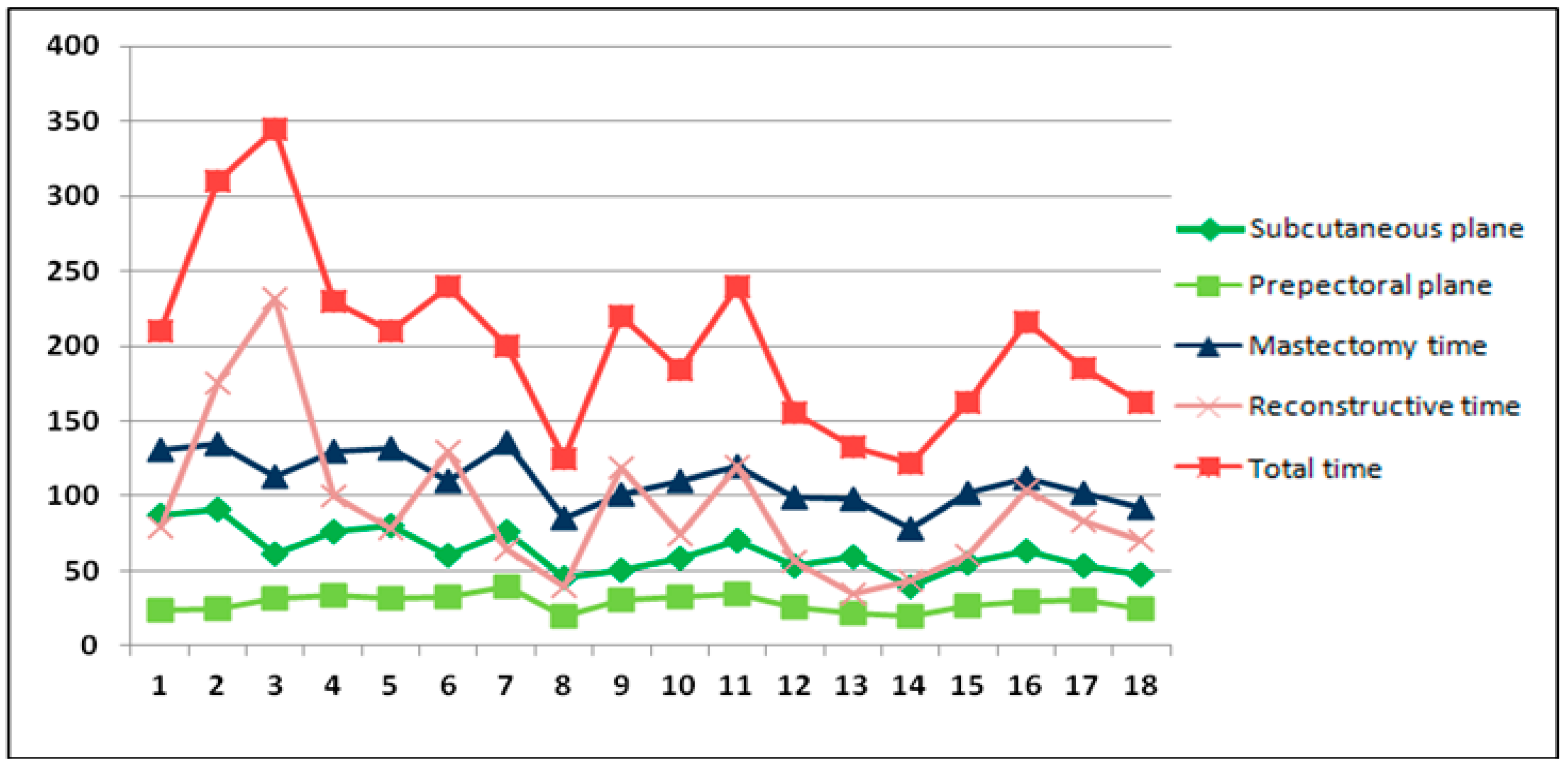
- Superficial plane dissection time;
- Prepectoral plane dissection time;
- Total mastectomy time: from skin incision to mastectomy specimen removal and hemostasis, including the previous two times;
- Reconstructive time: from breast pocket measurement to skin closure;
- Total operative time: from incision to skin closure.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Selection
- Contraindications to NSM: nipple involvement (n = 5), tumor location within 2 cm from NAC (n = 8), multifocal/multicentric lesions (n = 1), subareolar microcalcifications (n = 3), lymphovascular spreading (n = 4), large tumor (n = 3);
- Proximity of the tumor to the skin surface or pectoralis muscle (n = 7), axillary lymph node involvement (n = 10), triple negative phenotype (n = 4);
- Recurrent or metastatic breast cancer (n = 2);
- Large breast size requiring implant volumes over 500 cc (n = 7);
- Ptosis grade >= 2 according to Regnault’s classification ± BMI > 30, requiring skin flap reduction (n = 8);
- Poor breast coverage (type 1) according to the BTCC classification, as measured by digital mammography (n = 4);
- Severe comorbid conditions (n = 1);
- Significant psychological or psychiatric conditions (n = 2);
- Autologous breast reconstruction option (n = 3).
3.2. Demographic and Oncologic Characteristics
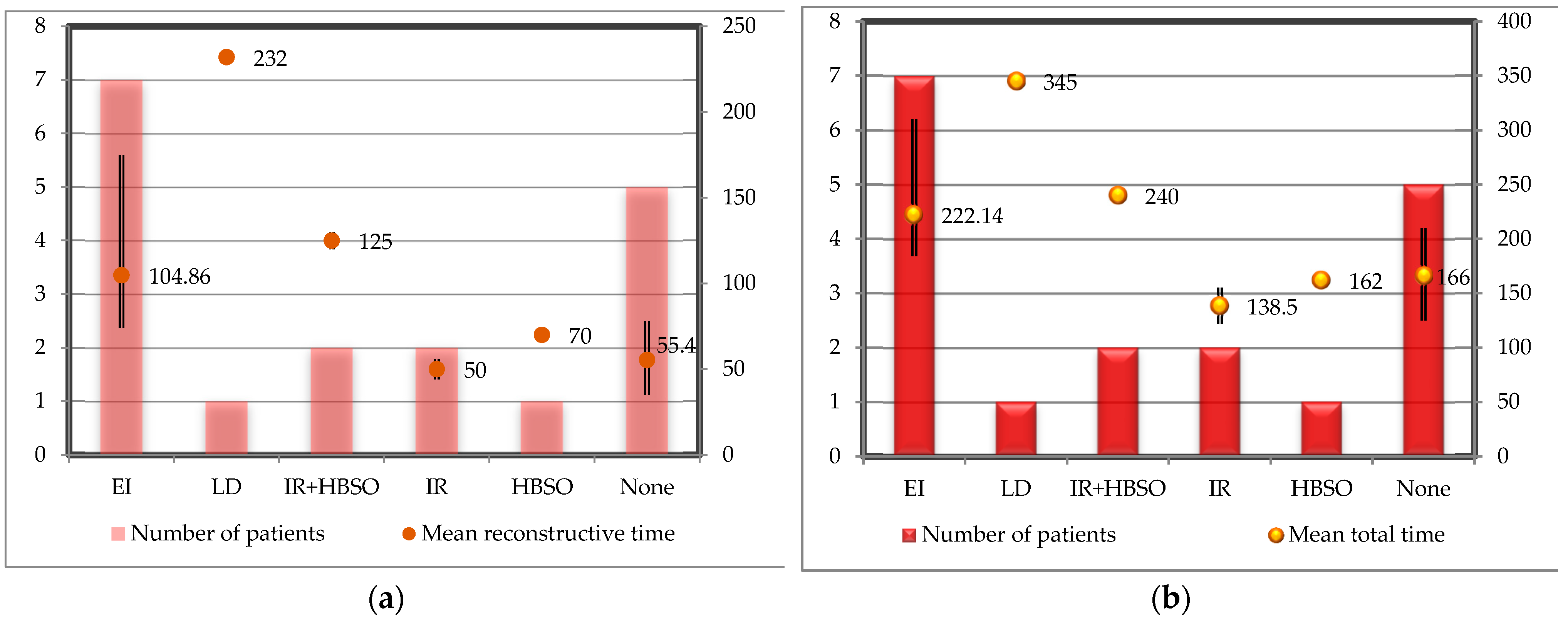
3.3. Surgery
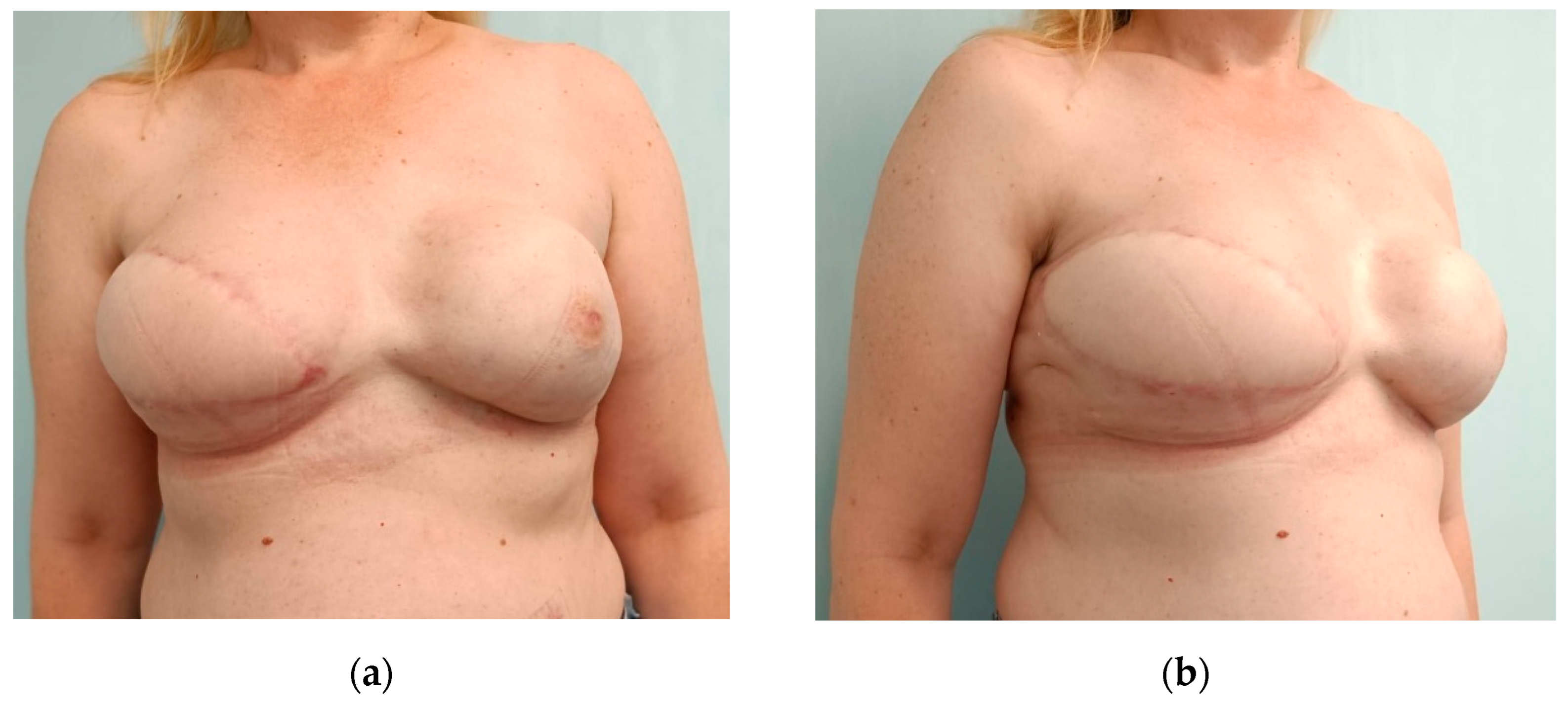
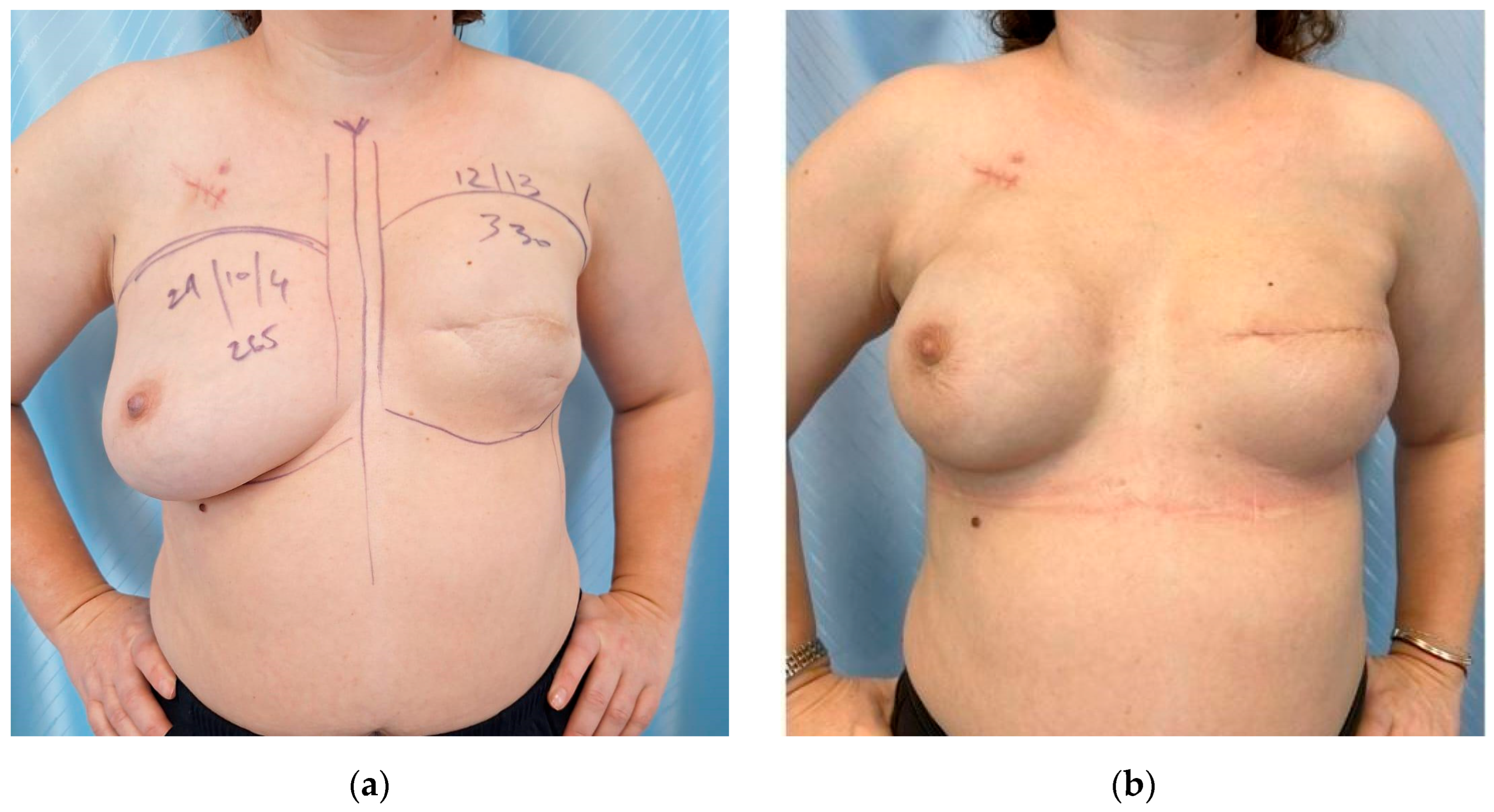
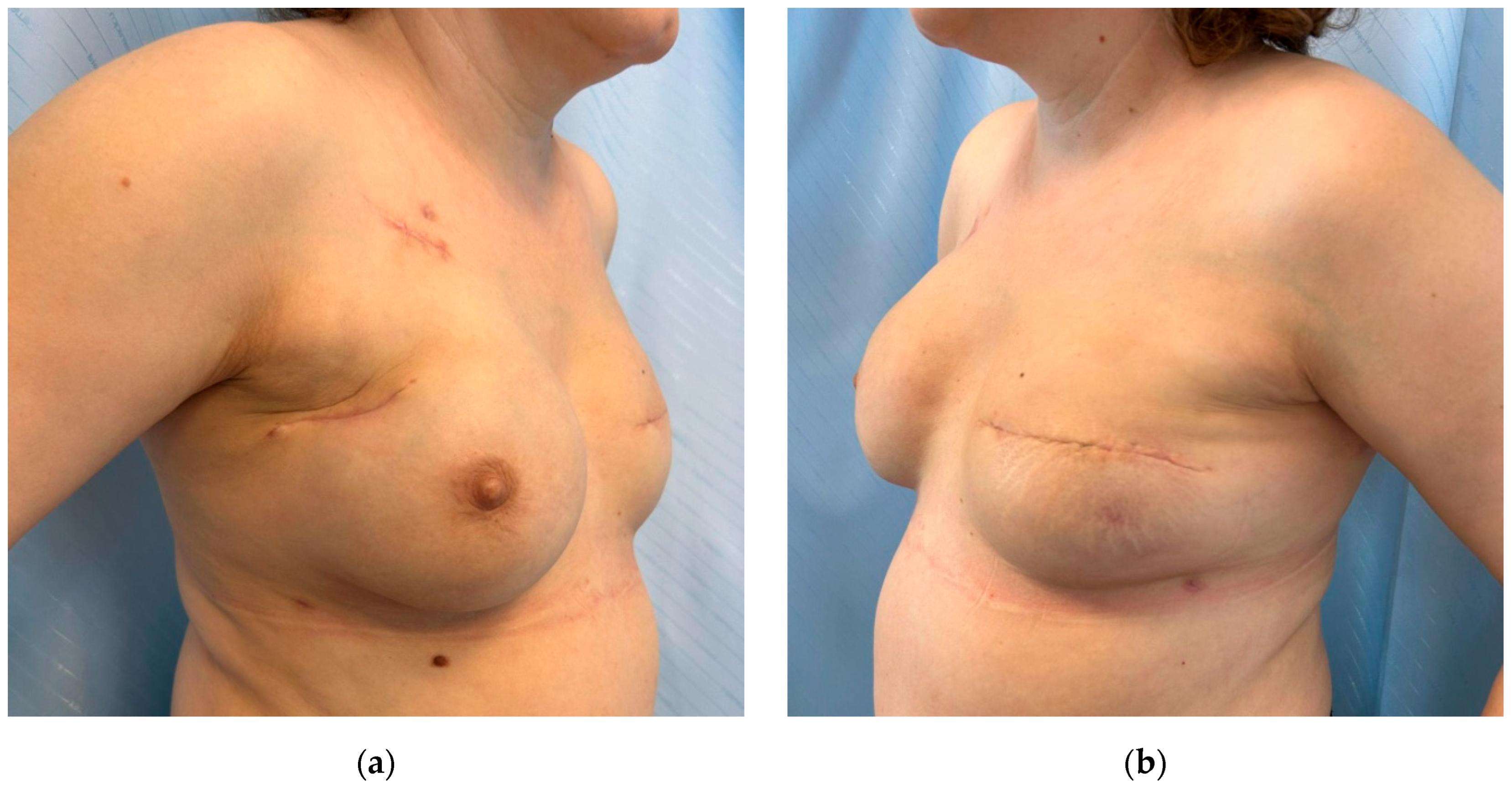
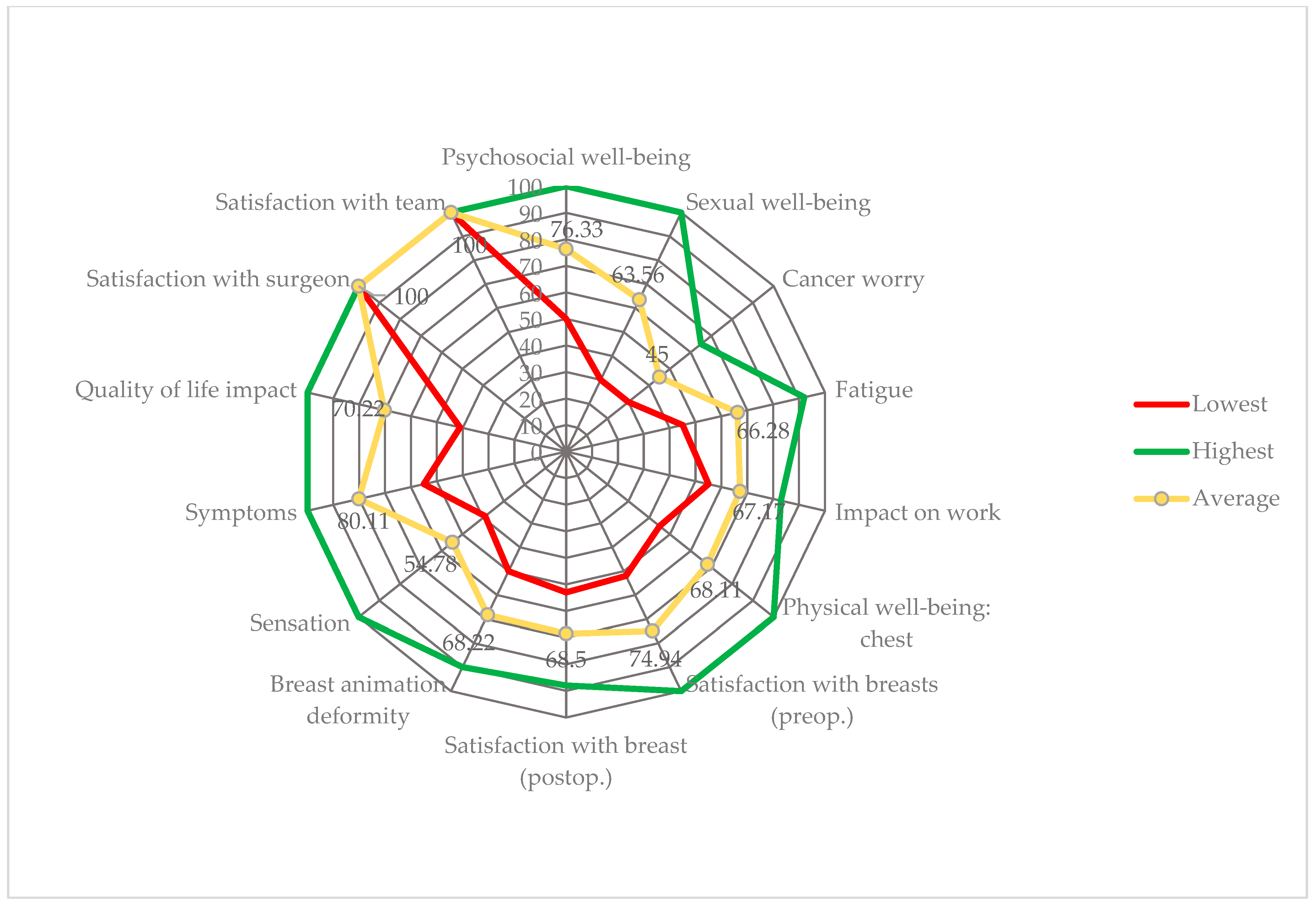
3.4. Postoperative Aspects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAC | nipple-areolar complex |
| BCS | breast conserving surgery |
| NSM | nipple-sparing mastectomy |
| BTCC | breast tissue coverage classification |
| VAM | video-assisted mastectomy |
| RRM | risk-reducing video-assisted mastectomy |
| TM | therapeutic video-assisted mastectomy |
| VAS | visual assessment scale |
| BMI | body mass index |
| EI | expander-to-implant exchange |
| HBSO | hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy |
| IR | implant reconstruction (without contralateral procedure) |
| LD | latissimus dorsi flap and implant reconstruction |
| USD | United States dollars |
References
- Stevens, L.A.; McGrath, M.H.; Druss, R.G.; Kister, S.J.; Gump, F.E.; Forde, K.A. The psychological impact of immediate breast reconstruction for women with early breast cancer. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1984, 73, 619–628. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, N.; Downes, M.H.; Ibelli, T.; Amakiri, U.O.; Li, T.; Tebha, S.S.; Balija, T.M.; Schnur, J.B.; Montgomery, G.H.; Henderson, P.W. The psychological impacts of post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: A systematic review. Ann. Breast Surg. 2024, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandberg, Y.; Sandelin, K.; Erikson, S.; Jurell, G.; Liljegren, A.; Lindblom, A.; Lindén, A.; von Wachenfeldt, A.; Wickman, M.; Arver, B. Psychological reactions, quality of life, and body image after bilateral prophylactic mastectomy in women at high risk for breast cancer: A prospective 1-year follow-up study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toesca, A.; Peradze, N.; Galimberti, V.; Manconi, A.; Intra, M.; Gentilini, O.; Sances, D.; Negri, D.; Veronesi, G.; Rietjens, M.; et al. Robotic nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction with implant: First report of surgical technique. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, e28–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satteson, E.S.; Brown, B.J.; Nahabedian, M.Y. Nipple-areolar complex reconstruction and patient satisfaction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gland Surg. 2017, 6, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiah, E.; Laikhter, E.; Comer, C.D.; Manstein, S.M.; Bustos, V.P.; Bain, P.A.; Lee, B.T.; Lin, S.J. Neurotization in innervated breast reconstruction: A systematic review of techniques and outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 2890–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, L.Y.; El Tal, A.K.; Stiff, M.A.; Fakhouri, T.M. Scar prevention and remodeling: A review of the medical, surgical, topical and light treatment approaches. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukenmez, M.; Ozden, B.C.; Agcaoglu, O.; Kecer, M.; Ozmen, V.; Muslumanoglu, M.; Igci, A. Videoendoscopic single-port nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2014, 24, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, L.D.; Sundin, J.; Bakshandeh, N. Endoscopy mastectomy and breast reconstruction: Endoscopic breast surgery. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 1995, 19, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, D. Is it time for breast cancer surgeons to embrace endoscopic-assisted mastectomy? ANZ J. Surg. 2008, 78, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.S.; Ying, S.Y.; Chan, A.C. Endoscopic-assisted subcutaneous mastectomy and axillary dissection with immediate mammary prosthesis reconstruction for early breast cancer. Surg. Endosc. Other Interv. Tech. 2002, 16, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Ishida, M.; Inoue, H.; Kinoshita, J.; Hashizume, M.; Suginachi, K. Early results of an endoscope-assisted subcutaneous mastectomy and reconstruction for breast cancer. Sugery 2002, 131 (Suppl. S1), S324–S329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Chang, Y.W.; Son, G.S.; Lee, H.Y. Preliminary experience and learning curve of endoscopic nipple-areolar-complex sparing total mastectomy: A single-center retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0311764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, T.; Narui, K.; Muto, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Maegawa, J. Endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate multistage fat grafting for total breast reconstruction: A new combination for minimal scar breast cancer surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 816e–818e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.W.; Lin, S.L.; Chen, S.T.; Kuok, K.M.; Chen, S.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, D.R.; Kuo, S.J. Hybrid technique for nipple-sparing mastectomy: Technique, preliminary results, and patient-reported cosmetic outcome from preliminary 50 procedures. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.G.; Chen, X.C.; Zhong, L. A prospective study comparing endoscopic subcutaneous mastectomy plus immediate reconstruction with implants and breast conserving surgery for breast cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 2945–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfati, B.; Struk, S.; Leymarie, N.; Honart, J.F.; Alkhashnam, H.; Tran de Fremicourt, K.; Conversano, A.; Rimareix, F.; Simon, M.; Michiels, S.; et al. Robotic prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate prosthetic breast reconstruction: A prospective study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2579–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Fukuma, E.; Higa, K.; Ozaki, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Abe, S.; Kurihara, T.; Tozaki, M. Early results of an endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 3406–3413. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.U.; Cha, C.; Pozzi, G.; Kang, Y.J.; Gregorc, V.; Sapino, A.; Gazzetta, G.; Marrazzo, E.; Toesca, A. Robot-assisted nipple sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction: An initial experience. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15669. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wan, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Meng, R.; Sun, X.; Xiao, C. Trans-axillary single port insufflation technique-assisted endoscopic surgery for breast diseases: Clinic experience, cosmetic outcome and oncologic result. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1157545. [Google Scholar]
- Sae-Lim, C.; Lai, H.W.; Lin, S.L.; Huang, H.I.; Chen, S.T.; Chen, D.R. Is minimal-accessed (endoscopic- or robotic-assisted) nipple-sparing mastectomy contraindicated for large breasts? Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 50, 108030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.W.; Lai, H.W. Endoscopic-assisted surgery in the management of breast cancer: 20 years review of trend, techniques and outcomes. Breast 2019, 46, 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, Y.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wen, N.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, Q.; Du, Z. Video-assisted transaxillary nipple-sparing mastectomy and immediate implant-based breast reconstruction: A novel and promising method. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2022, 46, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathat, G.; Herlin, C.; Bonnel, C.; Captier, G.; Duraes, M. Endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate prepectoral implant-based reconstruction: A case report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathat, G.; Chaumette, M.; Fontaine, V.; Rebel, L.; Pissarra, J.; Duflos, C.; Duraes, M. Endoscopic prophylactic nipple-sparing mastectomy: First French survey of 10 patients. J. Gynecol. Obstet. Hum. Reprod. 2025, 54, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, L.C.; Blanchet, N.P. Animation deformity in postmastectomy implant-based reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2017, 5, e1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Pan, C.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S. Postoperative outcomes of minimally invasive versus conventional nipple-sparing mastectomy with prosthesis breast reconstruction in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Robot. Surg. 2024, 18, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.M.; Al Youha, S.; Joukhadar, N.; Konder, R.; Stecco, C.; Wheelock, M.E. Anatomy of the breast fascial system: A systematic review of the literature. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhong, X.; Yang, Q.; Wei, L.; Li, D.; Li, H. Endoscopic bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomy via a single axillary incision with immediate pre-pectoral implant-based breast reconstruction. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 207, e65392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarello, M.; Pagliara, D.; Barone Adesi, L.; Visconti, G.; Wild, J.B.; Matey, P. Direct to implant breast reconstruction with prepectoralmicropolyurethane foam-coated implant: Analysis of patient satisfaction. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, e454–e461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancati, A.; Angrigiani, C.; Hammond, D.; Nava, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Rostagno, R.; Gercovich, G. Preoperative digital mammography imaging in conservative mastectomy and immediate reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2016, 5, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, C.S. Increasing role of oncoplastic surgery for breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Avino, A.; Gheoca-Mutu, D.E.; Răducu, L.; Nedelea, S.A.; Jecan, C.R.; Lascar, I. Patient-reported quality of life 3 months after breast reconstruction. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2021, 116, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gheoca, D.E.; Avino, A.; Răducu, L.; Marina, C.N.; Ștefan, M.C.; Tomescu, L.F.; Tulin, A.D.; Jecan, C.R. 6 years of breast reconstruction in one center—An objective analysis. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2021, 116 (Suppl. S2), 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, K.; Shimizu, K. Endoscopic video-assisted breast surgery: Procedures and short-term results. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2006, 73, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Hong, S.; Xu, S. A challenging surgical technique: Single-port endoscopic-assisted radical mastectomy in retrograde way and immediate reconstruction using prosthesis implantation. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.W.; Chen, S.T.; Chen, D.R.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, T.W.; Kuo, S.J.; Kuo, Y.L.; Hung, C.S. Current trends in and indications for endoscopy-assisted breast surgery for breast cancer: Results from a six-year study conducted by the taiwan endoscopic breast surgery cooperative group. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.; Klok, J.A.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.R.; Levene, M.B.; Svensson, G. Analyses of cosmetic results following primary radiation therapy for stages I and II carcinoma of the breast. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1979, 5, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, S.; Tamaki, Y.; Yano, K.; Okishiro, N.; Yanagisawa, T.; Imasato, M.; Shimazu, K.; Kim, S.J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Tanji, Y.; et al. Cosmetic outcome and patient satisfaction after skin-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer with immediate reconstruction of the breast. Surgery 2008, 143, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Hashizume, M.; Sugimachi, K.; Kataoka, A.; Ohno, S.; Kuwano, H.; Maehara, Y. Early experience of endoscopic extirpation of benign breast tumors via an extra-mammary incision. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 176, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Kompatscher, P. Endoscopic capsulotomy of capsular contracture after breast augmentation: A very challenging therapeutic approach. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 90, 1125–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz, L.; Moody, A.M.; Tappy, E.E.; Blankenship, S.A.; Hecht, E.M. Overall survival, disease-free survival, local recurrence, and nipple-areolar recurrence in the setting of nipple-sparing mastectomy: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, L.C.; Sellers, T.A.; Schaid, D.J.; Frank, T.S.; Soderberg, C.L.; Sitta, D.L.; Frost, M.H.; Grant, C.S.; Donohue, J.H.; Woods, J.E.; et al. Efficacy of bilateral prophylactic mastectomy in BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutation carriers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owaki, T.; Kijima, Y.; Yoshinaka, H.; Hirata, M.; Okumura, H.; Ishigami, S.; Nerome, Y.; Takezaki, T.; Natsugoe, S. Present status of endoscopic mastectomy for breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 6, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liao, J.; Tan, J.; Hu, H. Comparison of minimal access and open breast surgery: A propensity score-matched study on postoperative immune function in breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Fukuma, E.; Teraoka, K.; Hoshi, K. Local recurrence following treatment for breast cancer with an endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy. Breast Cancer 2016, 23, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flugstad, N.A.; Pozner, J.N.; Baxter, R.A.; Creasman, C.; Egrari, S.; Martin, S.; Messa, C.A., 3rd; Oliva, A.; Schlesinger, S.L.; Kortesis, B.G. Does implant insertion with a funnel decrease capsular contracture? A preliminary report. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2016, 36, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Liang, F.; Xie, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Dai, H.; Du, Z. ASO author reflections: A novel technique of transaxillary reverse-sequence endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy and direct-to-implant prepectoral breast reconstruction. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 2791–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.X.; Guan, S. A technique of endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer. JSLS 2017, 21, e2017.00028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehnke, R.D.; Groening, R.M.; Van Buskirk, E.R.; Clarke, J.M. Anatomy of the superficial fascia system of the breast: A comprehensive theory of breast fascial anatomy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.; Xie, Y.; Liang, F.; Qiu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, H.; Du, Z. Reverse-sequence endoscopic nipple-sparing mastectomy with immediate implant-based breast reconstruction: An improvement of conventional minimal access breast surgery. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1366877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Asao, T.; Uchida, N.; Yanagita, Y.; Saito, K.; Yamaki, S.; Kuwano, H. Endoscopy-assisted subcutaneous mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for breast cancer: Advantage of the posterior approach. Int. Surg. 2008, 93, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ostapenko, E.; Nixdorf, L.; Devyatko, Y.; Exner, R.; Wimmer, K.; Fitzal, F. Prepectoral versus subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarello, M.; Barone Adesi, L.; Macrì, G.; Visconti, G. When to consider prepectoral implant conversion after subpectoral implant breast reconstruction and how to plan it. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2023, 43, NP1071–NP1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Pinto, J.M.; Andresen, C.; Barbosa, J.P.; Poleri, F.; Casimiro, R.; Gonçalves, D.; Baptista, D.; Coelho, G.; Cunha, C.; Costa, H. Impact of polyurethane versus acellular dermal matrix coating on prepectoral reconstruction outcomes: Interface does matter. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2024, 91, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Kanai, T.; Gomi, K.; Watanabe, T.; Ito, T.; Komatsu, A.; Fujita, T.; Amano, J. Endoscopic-assisted skin-sparing mastectomy combined with sentinel node biopsy. ANZ J. Surg. 2008, 78, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.W.; Mok, C.W.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, D.R.; Kuo, S.J.; Chen, S.T. Endoscopic assisted breast conserving surgery for breast cancer: Clinical outcome, learning curve, and patient reported aesthetic results from preliminary 100 procedures. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leff, D.R.; Vashisht, R.; Yongue, G.; Keshtgar, M.; Yang, G.Z.; Darzi, A. Endoscopic breast surgery: Where are we now and what might the future hold for video-assisted breast surgery? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 125, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endara, M.; Chen, D.; Verma, K.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Spear, S.L. Breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy: A systematic review of the literature with pooled analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.W.; Wang, C.C.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, C.J.; Lin, S.L.; Chen, S.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, D.R.; Kuo, S.J. The learning curve of robotic nipple sparing mastectomy for breast cancer: An analysis of consecutive 39 procedures with cumulative sum plot. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, G.; Visconti, G.; Garganese, G.; Barone-Adesi, L.; Di Leone, A.; Sanchez, A.M.; Terribile, D.; Salgarello, M.; Masetti, R. Nipple-sparing mastectomy combined with endoscopic immediate reconstruction via axillary incision for breast cancer: A preliminary experience of an innovative technique. Breast J. 2020, 26, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallory, M.A.; Losk, K.; Camuso, K.; Caterson, S.; Nimbkar, S.; Golshan, M. Does “two is better than one” apply to surgeons? Comparing single-surgeon versus co-surgeon bilateral mastectomies. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

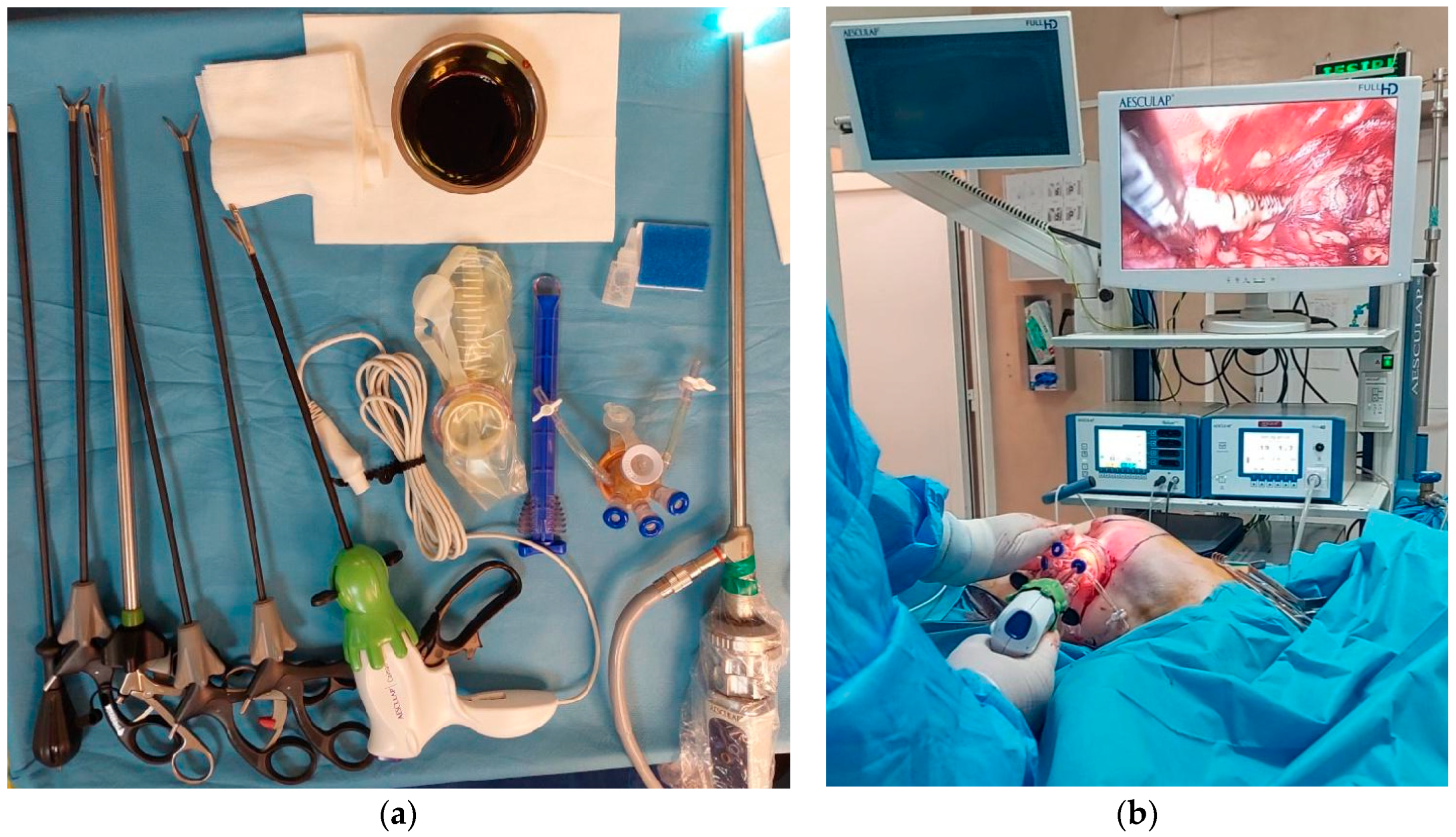
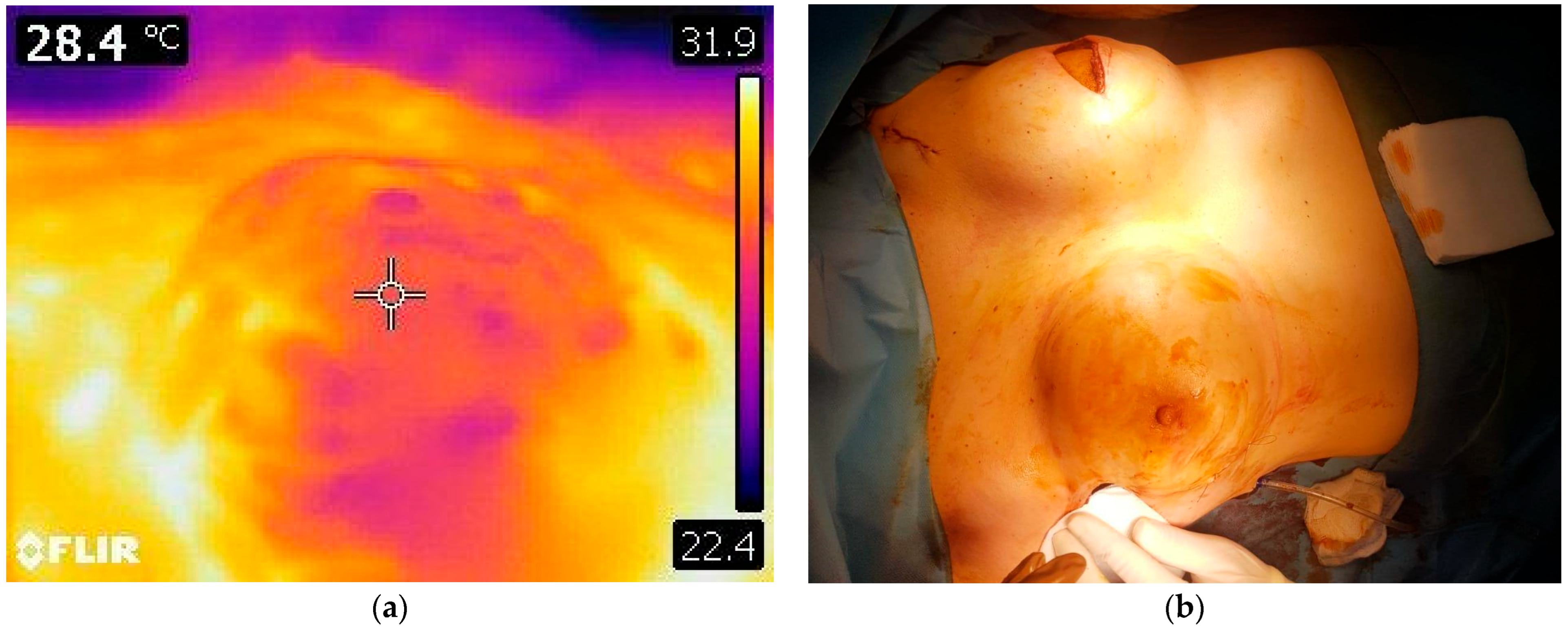
| Oncologic Characteristic | Subtype | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor location | Contralateral breast (operated) | 15 | 83.33% |
| Ipsilateral breast (TM) | 3 | 16.67% | |
| Breast cancer type | Ductal carcinoma | 12 | 66.67% |
| Lobular carcinoma | 5 | 27.78% | |
| Lobular carcinoma (in situ) | 1 | 11.11% | |
| Grading | G1 | 6 | 33.33% |
| G2 | 10 | 55.56% | |
| G3 | 12 | 11.11% | |
| Staging | IA | 4 | 22.22% |
| IB | 2 | 11.11% | |
| IIA | 4 | 22.22% | |
| IIB | 3 | 16.67% | |
| IIIA | 5 | 27.78% | |
| Chemotherapy | Pre-VAM | 13 | 72.22% |
| Radiotherapy | Pre-VAM | 10 | 55.56% |
| Hormonal therapy | Pre-/post-VAM | 18 | 100% |
| Herceptin therapy | Pre-VAM | 5 | 27.78% |
| Post-mastectomy breast volume | None | 5 | 27.78% |
| Expander/implant (mean volume) | 268.13 mL (range: 175–450 mL) | ||
| First mastectomy to VAM interval | (mean) | 21.75 months (range: 6–60 months) | |
| Previous ipsilateral breast surgery | Quadrantectomy | 2 | 11.11% |
| Breast reduction/mastopexy | 4 | 22.22% | |
| Patient | Incision (cm) | Implant Type | Implant Volume (mL) | Mastectomy Volume (mL) | Difference (mL) | Skin Perfusion (After Implant Placement) | Concomitant Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | P | 330 | 157.87 | 0 | Good | EI |
| 2 | 3.5 | M | 350 | 115 | 25 | Good | EI |
| 3 | 4 | M | 450 | 422 | 20 | Suboptimal | EI |
| 4 | 3 | P | 350 | 298.02 | 50 | Good | LD |
| 5 | 4,5 | P | 295 | 245.56 | 5 1 | Good | None |
| 6 | 3 | P | 220 | 147.98 | 0 | Suboptimal | IR + HBSO |
| 7 | 3.5 | P | 320 | 256.67 | 0 | Good | None |
| 8 | 2.5 | P | 195 | 113.68 | 20 | Good | None |
| 9 | 3 | M | 315 | 315 | 0 | Suboptimal | EI |
| 10 | 3 | P | 320 | 267.84 | 0 | Good | EI |
| 11 | 3 | P | 340 | 246.23 | 0 | Suboptimal | IR + HBSO |
| 12 | 2.5P | P | 220 | 138.4 | 20 | Suboptimal | IR |
| 13 | 3 | M | 265 | 225.43 | 15 | Good | None |
| 14 | 2.5 | P | 195 | 150.12 | 0 | Good | IR |
| 15 | 3 | P | 320 | 304.83 | 10 1 | Good | None |
| 16 | 3.5 | M | 380 | 324.55 | 0 | Good | EI |
| 17 | 3 | M | 340 | 288.61 | 15 | Suboptimal | EI |
| 18 | 3 | P | 280 | 233.41 | 0 | Good | HBSO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tulin, A.D.; Ion, D.-E.; Avino, A.; Gheoca-Mutu, D.-E.; Abu-Baker, A.; Țigăran, A.-E.; Timofan, T.; Ostafi, I.; Jecan, C.R.; Răducu, L. Video-Assisted Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: First Clinical Experience and Outcomes in an Eastern European Medical Center. Cancers 2025, 17, 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132267
Tulin AD, Ion D-E, Avino A, Gheoca-Mutu D-E, Abu-Baker A, Țigăran A-E, Timofan T, Ostafi I, Jecan CR, Răducu L. Video-Assisted Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: First Clinical Experience and Outcomes in an Eastern European Medical Center. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132267
Chicago/Turabian StyleTulin, Adrian Daniel, Daniela-Elena Ion, Adelaida Avino, Daniela-Elena Gheoca-Mutu, Abdalah Abu-Baker, Andrada-Elena Țigăran, Teodora Timofan, Ileana Ostafi, Cristian Radu Jecan, and Laura Răducu. 2025. "Video-Assisted Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: First Clinical Experience and Outcomes in an Eastern European Medical Center" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132267
APA StyleTulin, A. D., Ion, D.-E., Avino, A., Gheoca-Mutu, D.-E., Abu-Baker, A., Țigăran, A.-E., Timofan, T., Ostafi, I., Jecan, C. R., & Răducu, L. (2025). Video-Assisted Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: First Clinical Experience and Outcomes in an Eastern European Medical Center. Cancers, 17(13), 2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132267





