Prognostic Value of PLR, SIRI, PIV, SII, and NLR in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Can Inflammatory Factors Influence Pathogenesis and Outcomes?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patients and Variables
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Cutoff Determination and ROC Analysis
3.3. Oncological Outcomes
4. Discussion
Recommendations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NMIBC | Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer |
| MIBC | Muscle-invasive bladder cancer |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| SII | Systemic immune-inflammation index |
| SIRI | Systemic inflammation |
| CIS | Carcinoma in situ |
| IFs | Inflammatory factors |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, P.; Bizzarri, F.P.; Filomena, G.B.; Marino, F.; Iacovelli, R.; Ciccarese, C.; Boccuto, L.; Ragonese, M.; Gavi, F.; Rossi, F.; et al. Relationship Between Loss of Y Chromosome and Urologic Cancers: New Future Perspectives. Cancers 2024, 16, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.S.; Steinberg, G.; Witjes, J.A.; Li, R.; Shariat, S.F.; Roupret, M.; Babjuk, M.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Psutka, S.P.; Williams, S.B.; et al. Intermediate-risk Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: Updated Consensus Definition and Management Recommendations from the International Bladder Cancer Group. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 5, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veskimäe, E.; Espinos, E.L.; Bruins, H.M.; Yuan, Y.; Sylvester, R.; Kamat, A.M.; Shariat, S.F.; Witjes, J.A.; Compérat, E.M. What Is the Prognostic and Clinical Importance of Urothelial and Nonurothelial Histological Variants of Bladder Cancer in Predicting Oncological Outcomes in Patients with Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer? A European Association of Urology Muscle Invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridhar, K.V.; Kohli, M. Management of Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Cancer and the Emerging Role of Immunotherapy in Advanced Urothelial Cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1564–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Compérat, E.M.; Escrig, J.L.D.; Gontero, P.; Liedberg, F.; Masson-Lecomte, A.; Mostafid, A.H.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada, B.; Guerra, J.A.; Malón, D.; Jara, C.; Rodriguez, L.; Del Barco, S. Pretreatment neutrophil/lymphocyte, platelet/lymphocyte, lymphocyte/monocyte, and neutrophil/monocyte ratios and outcome in elderly breast cancer patients. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Basso, M.; Strippoli, A.; Schinzari, G.; D’Argento, E.; Larocca, M.; Cassano, A.; Barone, C. Are Markers of Systemic Inflammation Good Prognostic Indicators in Colorectal Cancer? Clin. Color. Cancer 2017, 16, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, M.; Yamashita, H.; Watanabe, T.; Seto, Y. Comparison of Prognostic Abilities Among Preoperative Laboratory Data Indices in Patients with Resectable Gastric and Esophagogastric Junction Adenocarcinoma. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Jeong, M.J.; Cha, J.; Lee, J.S.; Yoo, J.G.; Song, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, H.N.; Yoon, J.H.; et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte, platelet-to-lymphocyte and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in non-endometrioid endometrial cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3712–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Palermo, G.; Iacovelli, R.; Ragonese, M.; Ciccarese, C.; Maioriello, G.; Fantasia, F.; Bizzarri, F.P.; Marino, F.; Moosavi, K.; et al. Comparison of PIV and Other Immune Inflammation Markers of Oncological and Survival Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy. Cancers 2024, 16, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, P.; Marino, F.; Rossi, F.; Bizzarri, F.P.; Ragonese, M.; Dibitetto, F.; Filomena, G.B.; Marafon, D.P.; Ciccarese, C.; Iacovelli, R.; et al. Is Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index a Real Non-Invasive Biomarker to Predict Oncological Outcomes in Patients Eligible for Radical Cystectomy? Medicina 2023, 59, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, P.; Foschi, N.; Palermo, G.; Maioriello, G.; Lentini, N.; Iacovelli, R.; Ciccarese, C.; Ragonese, M.; Marino, F.; Bizzarri, F.P.; et al. SIRI as a biomarker for bladder neoplasm: Utilizing decision curve analysis to evaluate clinical net benefit. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2025, 43, 393.e1–393.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arıman, A.; Merder, E. The prognostic importance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in testicular cancer. Urol. J. 2021, 88, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Bentzen, S.; Rout, A.; Miller, K. Predicting if lung cancer will relapse—The role of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio. Hematol. Stem Cell Ther. 2021, 16, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Ai, K.; Xu, R. Pretreatment Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor in Bladder Cancer and Metastatic or Unresectable Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Pooled Analysis of Comparative Studies. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojerholm, E.; Smith, A.; Hwang, W.T.; Baumann, B.C.; Tucker, K.N.; Lerner, S.P.; Mamtani, R.; Boursi, B.; Christodouleas, J.P. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a bladder cancer biomarker: Assessing prognostic and predictive value in SWOG 8710. Cancer 2017, 123, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, A.G.; Bruins, H.M.; Carrion, A.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Kailavasan, M.; Lorch, A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2025 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2025, 87, 582–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Aoki, T.; Tsuruyama, T.; Narumiya, S. Definition of Prostaglandin E2–EP2 Signals in the Colon Tumor Microenvironment That Amplify Inflammation and Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2822–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clatot, F.; Gouérant, S.; Mareschal, S.; Cornic, M.; Berghian, A.; Choussy, O.; El Ouakif, F.; François, A.; Bénard, M.; Ruminy, P.; et al. The gene expression profile of inflammatory, hypoxic and metabolic genes predicts the metastatic spread of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneim, M.A.; Abdel-Latif, M.; El-Mekresh, M.; Abol-Enein, H.; Mosbah, A.; Ashamallah, A.; El-Baz, M.A. Radical Cystectomy for Carcinoma of the Bladder: 2,720 Consecutive Cases 5 Years Later. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caini, S.; Del Riccio, M.; Vettori, V.; Francolini, G.; D’ecclesiis, O.; Cai, T.; Gaeta, A.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Zanna, I.; Palli, D.; et al. Prognostic Impact of Post-Diagnosis Smoking Cessation among Bladder Cancer Patients: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Wen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, L.; Yang, J. The Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of NLR, PLR and MLR in Non-Muscular Invasive Bladder Cancer. Arch. Espanoles Urol. 2022, 75, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cinar, N.B.; Avci, I.E.; Telli, E.; Uslubas, A.K.; Teke, K.; Dillioglugil, O. The systemic inflammation response index: An independent predictive factor for survival outcomes of bladder cancer stronger than other inflammatory markers. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2023, 41, 256.e1–256.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prijovic, N.; Acimovic, M.; Santric, V.; Stankovic, B.; Nikic, P.; Vukovic, I.; Soldatovic, I.; Nale, D.; Kovacevic, L.; Nale, P.; et al. Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2582–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Tasaki, S.; Asakuma, J.; Horiguchi, A.; Ito, K. Preoperative risk stratification using plasma fibrinogen levels can predict lymphovascular invasion and poor prognosis in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, A.; Ghahari, M.; Bitaraf, M.; Fard, E.S.; Haddad, M.; Momeni, S.A.; Inanloo, S.H.; Ghahari, P.; Mohamoud, M.M.; Mohamadzadeh, M.; et al. Prognostic Value of NLR, PLR, SII, and dNLR in Urothelial Bladder Cancer Following Radical Cystectomy. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2024, 22, 102144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Xu, S.; Mao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, P. Systemic Immune-Inflammatory Index as a Predictor of Lymph Node Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 7131–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Shao, Y.; Zou, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, J. Prognostic significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e30380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, K.W.; Kim, B.H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.I.; Chang, H.S. The Efficacy of the EORTC Scoring System and Risk Tables for the Prediction of Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Instillation. Korean J. Urol. 2010, 51, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jobczyk, M.; Stawiski, K.; Kaszkowiak, M.; Rajwa, P.; Różański, W.; Soria, F.; Shariat, S.F.; Fendler, W. Deep Learning-based Recalibration of the CUETO and EORTC Prediction Tools for Recurrence and Progression of Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 5, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hong, G.; Xu, A.; Zeng, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wu, P.; Liu, C.; Jiang, N.; et al. Artificial intelligence-based model for lymph node metastases detection on whole slide images in bladder cancer: A retrospective, multicentre, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
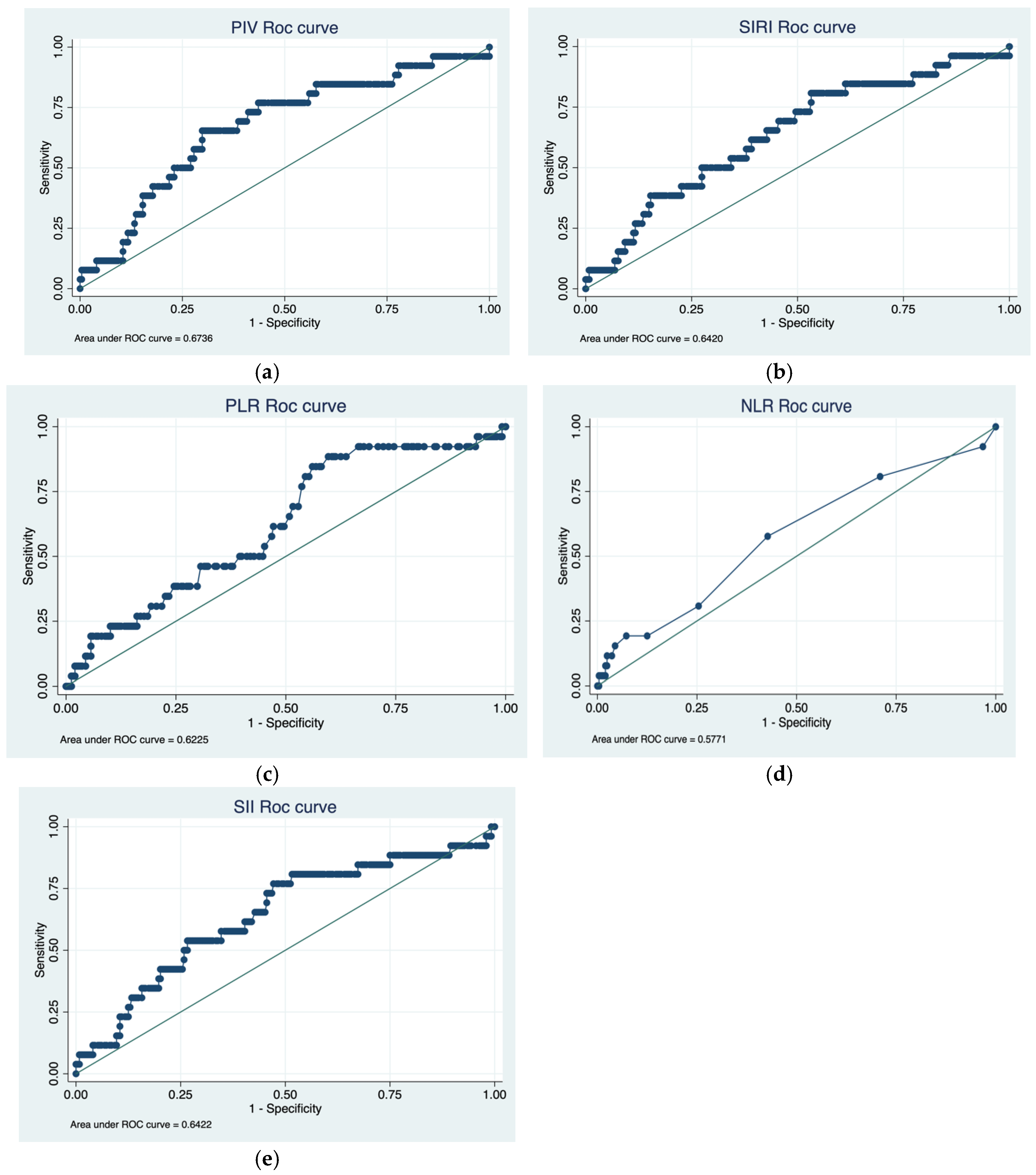

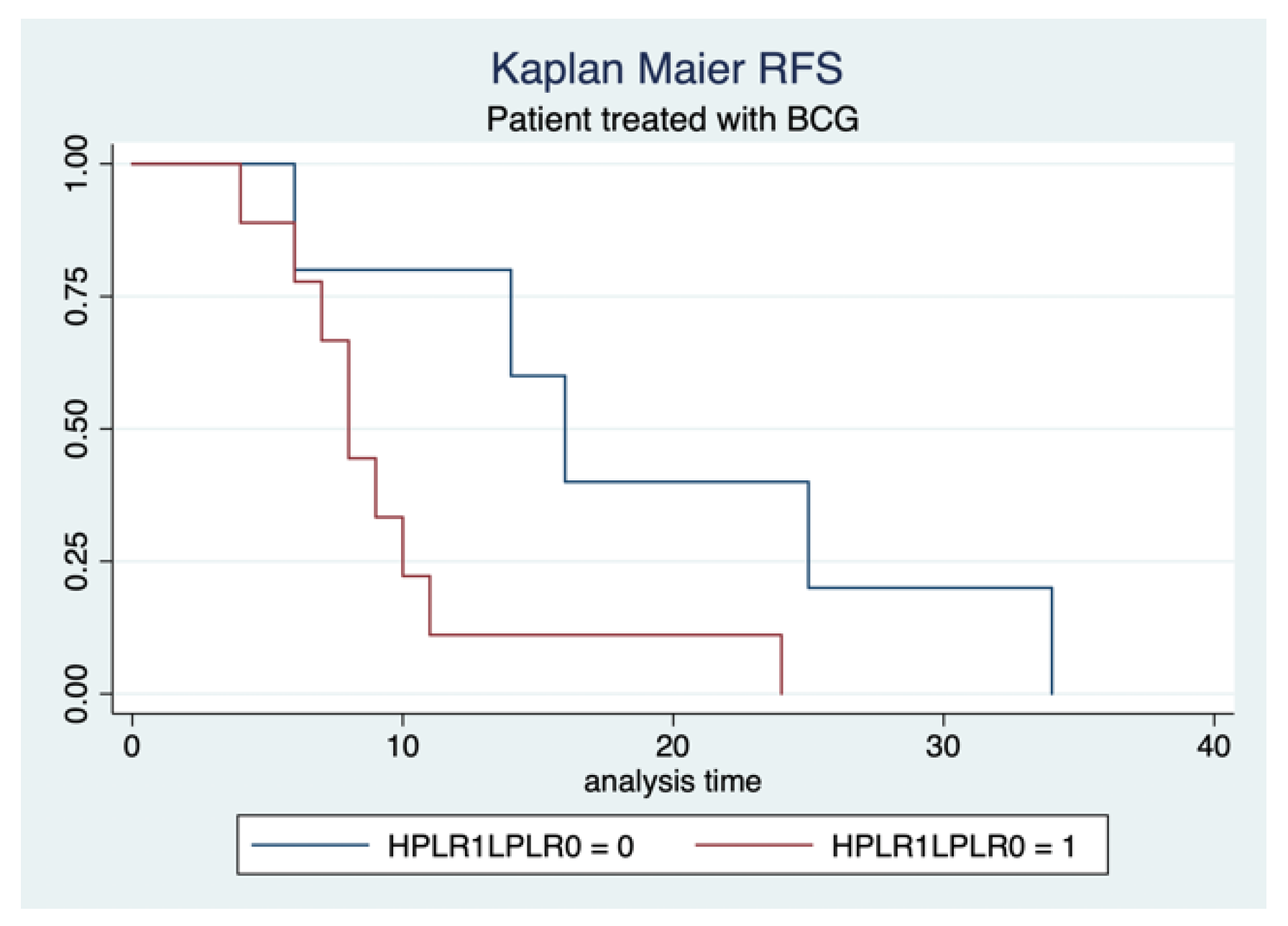
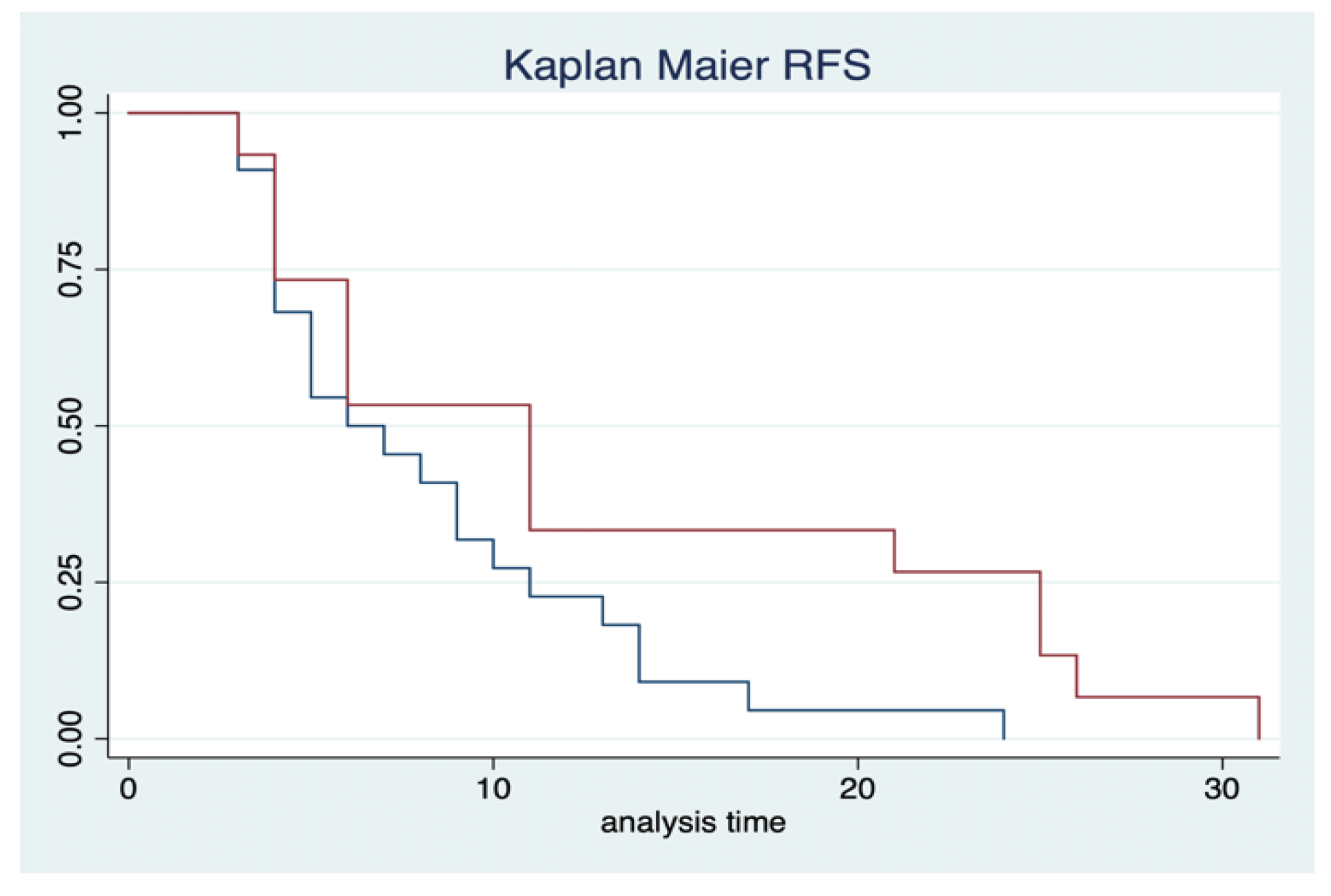
| Characteristics | Total |
|---|---|
| Patients | 285 |
| Age (mean) | 73.2 (34–97) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 226 (79.8%) |
| Female | 67 (20.14%) |
| Body mass index, median (IQR) | 25.74 (23.44–28.08) |
| Tobacco smoking, n (%) | |
| Never smoker | 54 (19%) |
| Active smoker | 76 (26.86%) |
| Previous smoker | 107 (37.81) |
| Charlson comorbidity index, n (%) | |
| CCI < 2 | 25 (9%) |
| CCI ≥ 2 | 259 (91%) |
| T stage, n (%) | |
| Tx | 45 (15.8%) |
| Ta | 63 (22.18%) |
| T1 | 92 (32.39%) |
| CIS | 14 (4.9%) |
| Concomitant CIS | 42 (14.8%) |
| Prostatic urethra invasion | 35 (12%) |
| Pathological grade 1973 | |
| G1 | 15 (5.4) |
| G2 | 59 (21.2) |
| G3 | 190 (68.35) |
| Pathological grade 2004 | |
| LG | 71 (25.62) |
| HG | 209 (74.38) |
| Size of largest lesion (cm), median | 4.4 cm (2.2–6) |
| Muscle invasion after Re TURB, (n, %) | 6 (2%) |
| Instillation therapy, (n, %) | |
| Chemotherapy (MMC) | 80 (28%) |
| Immunotherapy (BCG) | 197 (69%) |
| BC recurrences | 80 (28%) |
| HG | 64 (80%) |
| LG | 16 (20%) |
| (a) | |||
| Characteristics (PLR > 139) | Recurrence-Free Survival | ||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age | 0.95 | 0.82–1 | 0.47 |
| Gender (reference male) | |||
| Female | 4.85 | 0.98–9 | 0.6 |
| Smoke (reference no) | 1.87 | 1.2–3.5 | 0.43 |
| LVi | 1.6 | 1.25–5 | 0.04 |
| Tumor size (>3 cm) | 1.4 | 1.16–3.87 | 0.05 |
| BCG therapy | 0.5 | 0.32–0.9 | 0.003 |
| Multifocal disease | 1.12 | 0.7–3 | 0.9 |
| T stage | |||
| CIS | 2.8 | 1.76–6 | 0.004 |
| pTa/T1HG | 1.2 | 0.8–2.5 | 0.89 |
| PUI | 0.54 | 0.36–5.2 | 0.1 |
| Urinary cytology | |||
| HG | 1.7 | 1.43–4.3 | 0.03 |
| (b) | |||
| Characteristics (SIRI > 1.12) | Recurrence-Free Survival | ||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age | 0.73 | 0.35–1 | 0.7 |
| Gender (reference male) | |||
| Female | 2.46 | 1.98–6 | 0.04 |
| Smoke (reference no) | 3.12 | 1.2–7.4 | 0.002 |
| LVi | 0.93 | 0.33–2.65 | 0.9 |
| Tumor size (>3 cm) | 1.4 | 1.16–3.87 | 0.05 |
| BCG Therapy | 0.5 | 0.32–0.9 | 0.003 |
| Multifocal disease | 2.13 | 0.97–3.9 | 0.8 |
| T stage | |||
| CIS | 0.95 | 0.55–1.66 | 0.86 |
| pTa/T1HG | 1.16 | 0.88–1.5 | 0.7 |
| PUI | 3.7 | 2.12–14 | 0.02 |
| Urinary cytology | |||
| HG | 1.31 | 0.79–2.18 | 0.3 |
| (c) | |||
| Characteristics (PIV > 248) | Recurrence-Free Survival | ||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age | 2.4 | 0.3–20 | 0.4 |
| Gender (reference male) | |||
| Female | 1.3 | 0.7–2.4 | 0.4 |
| Smoke (reference no) | 1.1 | 0.3–3.37 | 0.9 |
| LVi | 2.9 | 1.5–9 | 0.02 |
| Tumor size (>3 cm) | 1.4 | 1.16–3.87 | 0.05 |
| BCG therapy | 0.8 | 0.4–1.8 | 0.3 |
| Multifocal disease | 2.13 | 0.97–3.9 | 0.8 |
| T stage | |||
| CIS | 2.59 | 1.5–9.3 | 0.6 |
| pTa/T1HG | 2.7 | 1.4–4.46 | 0.001 |
| PUI | 4.1 | 2.3–9 | 0.2 |
| Urinary cytology | |||
| HG | 3.3 | 2–4.4 | 0.004 |
| (d) | |||
| Characteristics (SII > 327) | Recurrence-Free Survival | ||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| Age | 0.8 | 0.7–3 | 0.9 |
| Gender (reference male) | |||
| Female | 3.2 | 1.4–8 | 0.65 |
| Smoke (reference no) | 2.5 | 1.2–15 | 0.2 |
| LVi | 1.93 | 0.98–3.5 | 0.05 |
| Tumor size (>3 cm) | 4.3 | 1.6–9 | 0.03 |
| BCG therapy | 0.9 | 0.2–3 | 0.6 |
| Multifocal disease | 4.12 | 1.56–7 | 0.03 |
| T stage | |||
| CIS | 2.14 | 1.55–12.3 | 0.6 |
| pTa/T1HG | 1.56 | 0.97–4.76 | 0.4 |
| PUI | 4.5 | 1.24–12 | 0.04 |
| Urinary cytology | |||
| HG | 2.21 | 1.18–15 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizzarri, F.P.; Campetella, M.; Russo, P.; Palermo, G.; Moosavi, S.K.; Rossi, F.; D’Amico, L.; Cretì, A.; Gavi, F.; Panio, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of PLR, SIRI, PIV, SII, and NLR in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Can Inflammatory Factors Influence Pathogenesis and Outcomes? Cancers 2025, 17, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132189
Bizzarri FP, Campetella M, Russo P, Palermo G, Moosavi SK, Rossi F, D’Amico L, Cretì A, Gavi F, Panio E, et al. Prognostic Value of PLR, SIRI, PIV, SII, and NLR in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Can Inflammatory Factors Influence Pathogenesis and Outcomes? Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132189
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizzarri, Francesco Pio, Marco Campetella, Pierluigi Russo, Giuseppe Palermo, Seyed Koosha Moosavi, Francesco Rossi, Lorenzo D’Amico, Antonio Cretì, Filippo Gavi, Enrico Panio, and et al. 2025. "Prognostic Value of PLR, SIRI, PIV, SII, and NLR in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Can Inflammatory Factors Influence Pathogenesis and Outcomes?" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132189
APA StyleBizzarri, F. P., Campetella, M., Russo, P., Palermo, G., Moosavi, S. K., Rossi, F., D’Amico, L., Cretì, A., Gavi, F., Panio, E., Presutti, S., Bellavia, F., Ragonese, M., Ciccarese, C., Iacovelli, R., Sighinolfi, M. C., Racioppi, M., Sacco, E., & Rocco, B. (2025). Prognostic Value of PLR, SIRI, PIV, SII, and NLR in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Can Inflammatory Factors Influence Pathogenesis and Outcomes? Cancers, 17(13), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132189








