The Effect of Preoperative Anemia on Blood Transfusion Outcomes in Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
Patient Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolan, R.T.; Butler, J.S.; Murphy, S.M.; Cronin, K.J. Health-related quality of life, surgical and aesthetic outcomes following microvascular free flap reconstructions: An 8-year institutional review. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2012, 94, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozec, A.; Poissonnet, G.; Chamorey, E.; Casanova, C.; Vallicioni, J.; Demard, F.; Mahdyoun, P.; Peyrade, F.; Follana, P.; Bensadoun, R.-J.; et al. Free-Flap Head and Neck Reconstruction and Quality of Life: A 2-Year Prospective Study. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.; Harris, J.; Seikaly, H. Transfusion as a Predictor of Recurrence and Survival in Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Patients. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 39, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woolley, A.L.; Hogikyan, N.D.; Gates, G.A.; Haughey, B.H.; Schechtman, K.B.; Goldenberg, J.L. Effect of blood transfusion on recurrence of head and neck carcinoma: Retrospective review and meta-analysis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1992, 101, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alun-Jones, T.; Clarke, P.J.; Morrissey, S.; Hill, J. Blood transfusion and laryngeal cancer. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1991, 16, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, M.S.; Samy, R.N.; Hanasono, M.M.; Terris, D.J. Autologous and heterologous blood transfusion in head and neck cancer surgery. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 125, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, G.; Böttcher, J.; Gerken, M.; Fischer, R.; Roth, G.; Lehn, P.; Klingelhöffer, C.; Meier, J.K.; Fraccaroli, A.; Tischer, J.; et al. Prognostic value of perioperative red blood cell transfusion and anemia on survival and recurrence in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2020, 107, 104773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-L.; Tai, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-P.; Chan, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Chang, K.-Y. The Impact of Blood Transfusion on Recurrence and Mortality Following Colorectal Cancer Resection: A Propensity Score Analysis of 4030 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13345. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, Y.H.; Wu, H.L.; Mandell, M.S.; Tsou, M.Y.; Chang, K.Y. The association of allogeneic blood transfusion and the recurrence of hepatic cancer after surgical resection. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.J.; Tan, K.S.; Molena, D.; Huang, J.; Bott, M.J.; Park, B.J.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Rusch, V.W.; Bains, M.S.; Downey, R.J.; et al. Perioperative blood transfusion has a dose-dependent relationship with disease recurrence and survival in patients with non–small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 157, 2469–2477. e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodnough, L.T.; Shander, A.; Riou, B. Patient blood management. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 1367–1376, Erratum in Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, R.S. A model for predicting transfusion requirements in head and neck surgery. Laryngoscope 1995, 105, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.D.; Goldstein, D.P.; McCluskey, S.A.; Miles, B.A.; Hofer, S.O.; Brown, D.H.; Irish, J.C.; Gullane, P.J.; Gilbert, R.W. Blood transfusion prediction in patients undergoing major head and neck surgery with free-flap reconstruction. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, H.; Van Belle, S.; Barrett-Lee, P.; Birgegård, G.; Bokemeyer, C.; Gascón, P.; Kosmidis, P.; Krzakowski, M.; Nortier, J.; Olmi, P.; et al. The European Cancer Anaemia Survey (ECAS): A large, multinational, prospective survey defining the prevalence, incidence, and treatment of anaemia in cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2293–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Nutritional Anaemias: Tools for Effective Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szakmany, T.; Dodd, M.; Dempsey, G.A.; Lowe, D.; Brown, J.S.; Vaughan, E.D.; Rogers, S.N. The influence of allogenic blood transfusion in patients having free-flap primary surgery for oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, P.; Canis, M.; Reiter, M. Preoperative anemia and perioperative blood transfusion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietl, B.; Marienhagen, J.; Schäfer, C.; Kölbl, O. The Prognostic Value of Anaemia at Different Treatment Times in Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Treated with Surgery and Postoperative Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, N.B.; Tarabanis, C.; Miller, A.L.; Puram, S.V.; Varvares, M.A. Preoperative anemia displays a dose-dependent effect on complications in head and neck oncologic surgery. Head Neck 2019, 41, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, C.M. Importance of hemoglobin concentration and its modification for the outcome of head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2012, 51, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stata Statistical Software; Release 17; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2021.
- ARECCI Ethics and Screening Tool Developed by the Alberta Research Ethics Community Consensus Initiative (ARECCI) Network (2005, Revised 2010). Available online: https://albertainnovates.ca/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/ARECCI-Ethics-Guideline-Tool.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Ali, M.; Dort, J.C.; Sauro, K.M. Preoperative Hemoglobin and Perioperative Blood Transfusion in Major Head and Neck Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 52, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danan, D.; Smolkin, M.E.; Varhegyi, N.E.; Bakos, S.R.; Jameson, M.J.; Shonka, D.C., Jr. Impact of blood transfusions on patients with head and neck cancer undergoing free tissue transfer. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puram, S.V.; Yarlagadda, B.B.; Sethi, R.; Muralidhar, V.; Chambers, K.J.; Emerick, K.S.; Rocco, J.W.; Lin, D.T.; Deschler, D.G. Transfusion in head and neck free flap patients: Practice patterns and a comparative analysis by flap type. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenner, M.; Vairaktaris, E.; Nkenke, E.; Weisbach, V.; Neukam, F.W.; Radespiel-Tröger, M. Prognostic impact of blood transfusion in patients undergoing primary surgery and free-flap reconstruction for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2009, 115, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Doersten, P.; Cruz, R.M.; Selby, J.V.; Hilsinger, R.L., Jr. Transfusion, recurrence, and infection in head and neck cancer surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1992, 106, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, B.; Choi, E.E.; Barlas, V.; Petersen, T.R.; Menon, N.G.; Morrell, N.T. Risk Factors for 30-Day Mortality After Head and Neck Microsurgical Reconstruction for Cancer: NSQIP Analysis. OTO Open 2021, 5, 2473974X211037257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, B.N.; Okwuegbuna, O.; Jafari, A.; Califano, J.; Brumund, K.T.; Gabriel, R.A. Association of Preoperative Anemia With 30-Day Morbidity and Mortality Among Patients With Thyroid Cancer Who Undergo Thyroidectomy. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 145, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.S.; Jabbour, N.; Martin, R.C.G. Anemia and Transfusions in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; McCluskey, S.A.; Hall, F.; Lipa, J.; Neligan, P.; Brown, D.; Irish, J.; Gullane, P.; Gilbert, R. Predictors of morbidity following free flap reconstruction for cancer of the head and neck. Head Neck 2007, 29, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, T.B.; Petrisor, D.; Li, R.; Andersen, P.; Azzi, J.E.; Thomas, W.; Wax, M.K. Reducing transfusion criteria in free flap surgery. Conference abstract. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, P83. [Google Scholar]
- Robson, A.; Sturman, J.; Williamson, P.; Conboy, P.; Penney, S.; Wood, H. Pre-treatment clinical assessment in head and neck cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2016, 130 (Suppl. S2), S13–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.V.; Nagababu, E.; Johnson, D.J.; Kebaish, K.M.; Lipsitz, J.A.; Dwyer, I.M.; Zuckerberg, G.S.; Barodka, V.M.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Frank, S.M. 2,3-Diphosphoglycerate Concentrations in Autologous Salvaged Versus Stored Red Blood Cells in Surgical Patients After Transfusion. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelubre, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Red blood cell transfusion in the critically ill patient. Ann. Intensive Care 2011, 1, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, H.; Müldür, E.; Endler, G.; Hübl, W. Prevalence of iron deficiency across different tumors and its association with poor performance status, disease status and anemia. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltzfus, R.J.; Dreyfuss, M.L. Guidelines for the Use of Iron Supplements to Prevent and Treat Iron Deficiency Anemia; Ilsi Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Crippen, M.M.; Brady, J.S.; Mozeika, A.M.; Eloy, J.A.; Baredes, S.; Park, R.C.W. Impact of Body Mass Index on Operative Outcomes in Head and Neck Free Flap Surgery. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 159, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Han, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhu, X.; Shi, J.; Lin, D. Perioperative Albumin Supplementation is Associated With Decreased Risk of Complications Following Microvascular Head and Neck Reconstruction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, J.S.L.; Seto, A.; Li, G.K.H. Association Between Preoperative Nutritional Status and Postoperative Outcome in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, U.O.; Scott, M.J.; Hubner, M.; Nygren, J.; Demartines, N.; Francis, N.; Rockall, T.A.; Young-Fadok, T.M.; Hill, A.G.; Soop, M.; et al. Guidelines for Perioperative Care in Elective Colorectal Surgery: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS®) Society Recommendations: 2018. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 659–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, N.X.; Baron, T.; Litvinchuk, S. An Economic Evaluation of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) in Alberta, Canada. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 866–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kei, T.; Mistry, N.; Curley, G.; Pavenski, K.; Shehata, N.; Tanzini, R.M.; Gauthier, M.-F.; Thorpe, K.; Schweizer, T.A.; Ward, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of erythropoietin and iron therapy to reduce red blood cell transfusion in surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Anaesth. 2019, 66, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, T.M.; Glenn, M.G.; Riley, D.; Weymuller, E.A., Jr. Blood use in head and neck tumor surgery. Potential for autologous blood. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1989, 115, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlius, J.; Schmidlin, K.; Brillant, C.; Schwarzer, G.; Trelle, S.; Seidenfeld, J.; Zwahlen, M.; Clarke, M.; Weingart, O.; Kluge, S.; et al. Recombinant human erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and mortality in patients with cancer: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2009, 373, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretiak, R.; Laupacis, A.; Rivière, M.; McKerracher, K.; Souêtre, E. Cost of allogeneic and autologous blood transfusion in Canada. Canadian Cost of Transfusion Study Group. CMAJ 1996, 154, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naoum, F.A. Iron deficiency in cancer patients. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2016, 38, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhurosy, T.; Jishan, A.; Boland, P.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Heckman, C.J. Underdiagnosis of iron deficiency anemia among patients with colorectal cancer: An examination of electronic medical records. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, E.S.; Hrycyshyn, A.; Salman, N.; Remtulla Tharani, A.; Abbruzzino, A.; Smith, J.; Kachura, J.J.; Sholzberg, M.; Mosko, J.D.; Chadi, S.A.; et al. Iron Surveillance and Management in Gastro-Intestinal Oncology Patients: A National Physician Survey. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9836–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luporsi, E.; Turpin, A.; Massard, V.; Morin, S.; Chauffert, B.; Carnot, A.; Cacoub, P. Behalf of the CARENFER Study Group. Iron deficiency in patients with cancer: A prospective cross-sectional study. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2024, 14, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, A.; Sharma, A.; Kundnani, N.R.; Mihăilescu, A.; David, V.L.; Bedreag, O.; Săndesc, D.; Dinu, A.R.; Săndesc, M.A.; Albulescu, N.; et al. Intravenous iron infusion as an alternative to minimize blood transfusion in peri-operative patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhenawy, A.M.; Meyer, S.R.; Bagshaw, S.M.; MacArthur, R.G.; Carroll, L.J. Role of preoperative intravenous iron therapy to correct anemia before major surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J.; Dekker, J.W.; Bruns, E.; Borstlap, W.; Jeekel, J.; Zwaginga, J.J.; Schipperus, M. Short-term effect of preoperative intravenous iron therapy in colorectal cancer patients with anemia: Results of a cohort study. Transfusion 2018, 58, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.D.; Simpson, J.A.; Ng, S.; Tselepis, C.; Iqbal, T.; Brookes, M.J.; Acheson, A.G. The feasibility and clinical efficacy of intravenous iron administration for preoperative anaemia in patients with colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 2014, 16, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodnough, L.T.; Shander, A.; Spence, R. Bloodless medicine: Clinical care without allogeneic blood transfusion. Transfusion 2003, 43, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, J.C.; Santiveri, F.X.; Ramos, I.; Vela, E.; Puig, L.; Escolano, F. Tranexamic acid reduces blood transfusion in total knee arthroplasty even when a blood conservation program is applied. Transfusion 2008, 48, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, M.; Engelke, W. Advantages of a new technique of neck dissection using an ultrasonic scalpel. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2007, 35, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
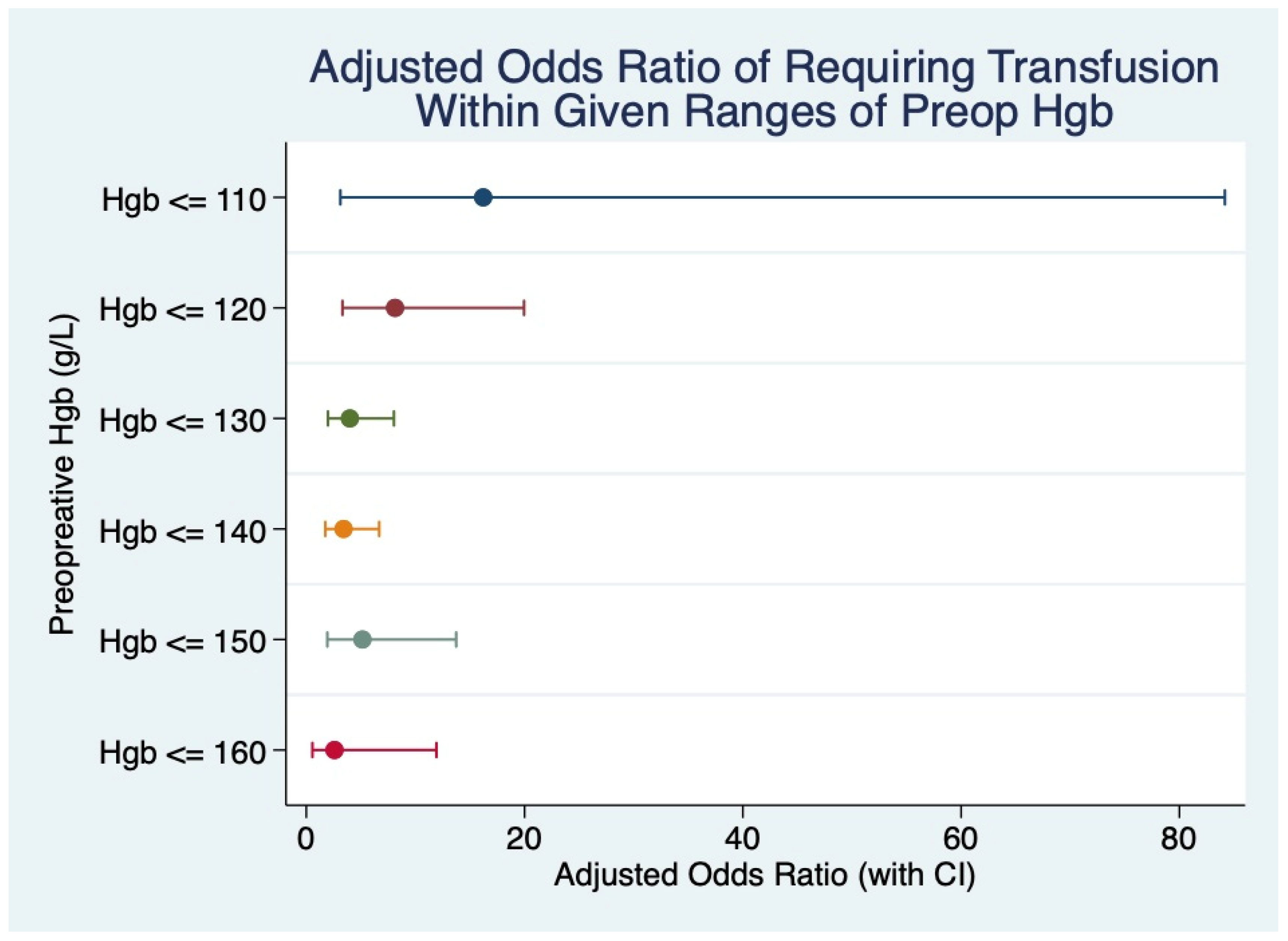
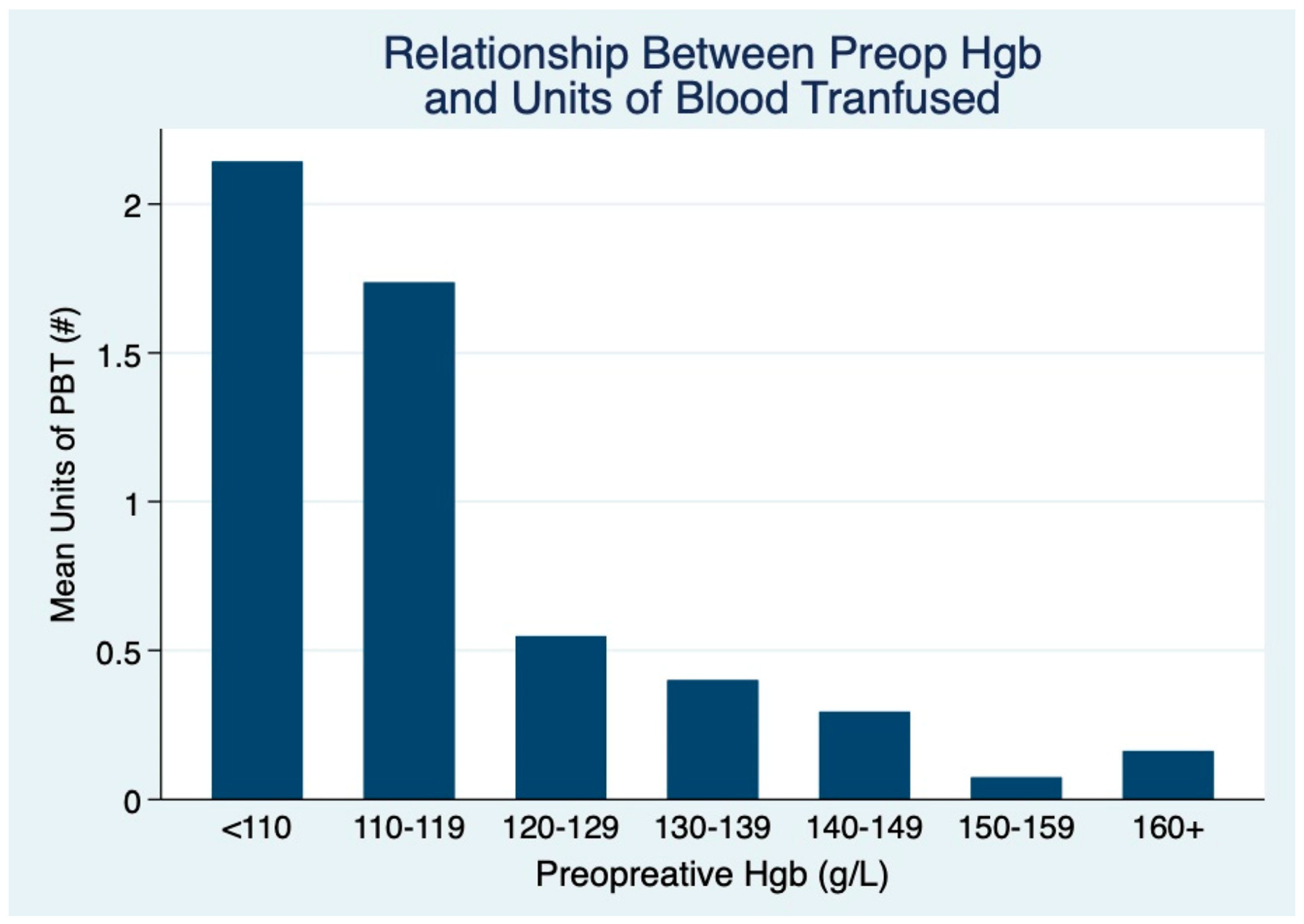
| Variable | n (%) | Transfused, n (%) | Non-Transfused, n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative Variables | ||||
| Preoperative Hgb (g/L, Mean [SD]) | 141.6 [16.90] | 128.4 [19.96] | 144.6 [14.55] | <0.0001 |
| Sex | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.008 * |
| Male | 256 (71) | 39 (15) | 217 (85) | |
| Female | 107 (29) | 29 (27) | 78 (73) | |
| Age (yrs, Mean [SD]) | 61.4 [12.27] | 62.0 [12.94] | 61.3 [12.13] | 0.6856 ‡ |
| Comorbidity | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.170 † |
| 0 | 149 (41) | 29 (20) | 120 (81) | |
| 1 | 112 (31) | 17 (15) | 95 (85) | |
| 2+ | 72 (20) | 19 (26) | 53 (74) | |
| Missing | 30 (8) | 3 (10) | 27 (90) | |
| T stage | 332 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.007 † |
| T0/Tis | 39 (11) | 9 (23) | 30 (77) | |
| T1 | 45 (12) | 4 (9) | 41 (91) | |
| T2 | 89 (25) | 11 (12) | 78 (88) | |
| T3 | 40 (11) | 6 (15) | 34 (85) | |
| T4 | 119 (33) | 35 (29) | 84 (71) | |
| Missing | 31 (9) | 3 (10) | 28 (9) | |
| N stage | 291 | 52 (18) | 0.467 * | |
| N0 | 149 (41) | 29 (19) | 120 (81) | |
| N+ | 142 (39) | 23 (16) | 119 (84) | |
| Missing | 72 (20) | 16 (24) | 56 (19) | |
| Cancer stage | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.123 † |
| Stage 0–II | 95 (26) | 12 (13) | 83 (87) | |
| Stage III–IV | 238 (66) | 52 (22) | 186 (78) | |
| Missing | 30 (8) | 4 (6) | 26 (9) | |
| Smoking | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.719 * |
| Current | 111 (31) | 19(17) | 98 (83) | |
| Former | 123 (34) | 21 (17) | 102 (83) | |
| Never | 87 (24) | 18 (21) | 69 (23) | |
| Missing | 42 (12) | 10 (24) | 32 (76) | |
| EtOH | 363 | 68 (19) | 195 (81) | 0.546 * |
| Current | 201 (55) | 35 (17) | 166 (83) | |
| Former | 42 (12) | 7 (17) | 35 (12) | |
| Never | 71 (20) | 16 (24) | 55 (19) | |
| Missing | 49 (14) | 10 (15) | 39 (13) | |
| BMI (categorical) | 333 | 65 (20) | 268 (80) | 0.001 * |
| Underweight | 24 (7) | 11 (46) | 13 (54) | |
| Normal weight | 142 (43) | 33 (23) | 109 (41) | |
| Overweight | 103 (31) | 13 (12) | 90 (34) | |
| Obese | 64 (19) | 8 (13) | 56 (21) | |
| BMI (continuous, Mean [SD]) | 25.7 [5.93] | 23.7 [6.04] | 26.2 [5.80] | 0.0002 ¶ |
| Cancer recurrence | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.738 * |
| Yes | 54 (15) | 11 (20) | 252 (82) | |
| No | 301 (85) | 57 (18) | 43 (80) | |
| Primary cancer site | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.339 † |
| Oral cavity | 237 (65) | 41 (17) | 196 (83) | |
| Oropharynx | 16 (4) | 4 (25) | 12 (75) | |
| Hypopharynx | 8 (2) | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | |
| Larynx | 9 (2) | 1 (11) | 8 (89) | |
| Paranasal sinus | 23 (6) | 9 (39) | 14 (61) | |
| Skin | 36 (10) | 4 (11) | 32 (89) | |
| Salivary gland | 14 (4) | 3 (21) | 11 (79) | |
| Thyroid | 2 (1) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | |
| Unknown | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) | |
| Other | 17 (5) | 4 (24) | 13 (76) | |
| Type of cancer | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | 0.913 † |
| SCC | 290 (80) | 54 (19) | 236 (81) | |
| NSCC | 73 (20) | 14 (19) | 59 (81) | |
| Intraoperative variables | ||||
| Type of flap | 363 | 68 (19) | 295 (81) | <0.0001 * |
| RFFF | 184 (51) | 17 (9) | 167 (91) | |
| FFF | 80 (22) | 25 (31) | 55 (69) | |
| ALT | 55 (15) | 11 (20) | 44 (80) | |
| Other | 44 (12) | 15 (34) | 29 (66) | |
| Neck dissection | 360 | 67 (19) | 293 (81) | 0.392 * |
| None | 67 (19) | 16 (24) | 51 (76) | |
| Right | 107 (30) | 15 (14) | 92 (86) | |
| Left | 89 (25) | 16 (18) | 73 (82) | |
| Bilateral | 97 (27) | 20 (21) | 77 (79) | |
| Clavien-Dindo class | 332 | 65 (20) | 267 (80) | <0.001 † |
| 0–IIIa | 280 (84) | 46 (16) | 234 (84) | |
| IIIb–V | 52 (16) | 19 (37) | 33 (63) | |
| Predictor | p-Value | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Preoperative Hgb | <0.0001 | 0.94 |
| Sex | ns | 0.90 |
| Cancer Stage | 0.049 | 2.07 |
| BMI | 0.040 | 5.53 |
| Clavien-Dindo Class | 0.007 | 3.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, M.; Nakoneshny, S.C.; Dort, J.C.; Sauro, K.M.; Matthews, T.W.; Chandarana, S.P.; Wilson, T.A.; McKenzie, D.C.; Schrag, C.; Matthews, J.; et al. The Effect of Preoperative Anemia on Blood Transfusion Outcomes in Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery. Cancers 2025, 17, 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132136
Ali M, Nakoneshny SC, Dort JC, Sauro KM, Matthews TW, Chandarana SP, Wilson TA, McKenzie DC, Schrag C, Matthews J, et al. The Effect of Preoperative Anemia on Blood Transfusion Outcomes in Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132136
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Munib, Steven C. Nakoneshny, Joseph C. Dort, Khara M. Sauro, Thomas Wayne Matthews, Shamir P. Chandarana, Todd A. Wilson, David C. McKenzie, Christiaan Schrag, Jennifer Matthews, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Preoperative Anemia on Blood Transfusion Outcomes in Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132136
APA StyleAli, M., Nakoneshny, S. C., Dort, J. C., Sauro, K. M., Matthews, T. W., Chandarana, S. P., Wilson, T. A., McKenzie, D. C., Schrag, C., Matthews, J., & Hart, R. D. (2025). The Effect of Preoperative Anemia on Blood Transfusion Outcomes in Major Head and Neck Cancer Surgery. Cancers, 17(13), 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132136







