Endoscopic Immuno-Oncology: A New Frontier in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Endoscopic Platforms Enabling Ablation Therapy in PDAC
3. Endoscopic Pancreatic Ablation: Techniques and Clinical Implementation
3.1. Photodynamic Therapy
3.2. Cryothermal Ablation
3.3. Irreversible Electroporation
3.4. Microwave Ablation
3.5. Radiofrequency Ablation
| Modality | Mechanism | Delivery Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) | Light-activated photosensitizer generates cytotoxic species causing apoptosis and necrosis | EUS-guided (via 19G FNA needle) or percutaneous approach | Minimally invasive, allows for localized and targeted therapy | Limited light penetration |
| Cryothermal Ablation | Freeze–thaw cycles create ice crystals and vascular injury causing cell death | EUS-guided cryoprobe | Less collateral structure damage, safer when operating near vessels | Potential for minor adverse events, evidence remains limited to small studies and early-phase trials |
| Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) | High-voltage electric fields create nanopores disrupting cell membranes, leading to apoptosis | Percutaneous approach, or open approach with ECG synchronization. Electrodes are placed around target tissue to deliver therapy | Non-thermal (minimizes damage to surrounding structures), safer near vessels | Requires general anesthesia and ECG sync, potential arrhythmias |
| Microwave Ablation (MWA) | Microwave-induced water molecule oscillation produces heat and coagulative necrosis | Open approach, laparoscopic, or percutaneous approach. Heat is delivered through ablation probe | Higher intratumoral temperatures, larger and more uniform ablation zones | Limited large-scale data, variable outcomes |
| Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) | Alternating current generates heat causing coagulative necrosis via frictional heating | EUS-guided insulated needle electrodes | Minimally invasive, potential for immune activation and increased effectiveness with adjunctive chemotherapy | Complication risks (mild pancreatitis, vessel injury), requires precise targeting |
4. Radiofrequency Ablation Effects on the Local Tumor Microenvironment
4.1. RFA as an Immune Primer in Pancreatic Cancer
4.2. DAMP Release and Activation of Innate Immunity
4.3. Neutrophil Infiltration and the Innate–Adaptive Bridge
4.4. Neutrophil-Driven Immune Activation
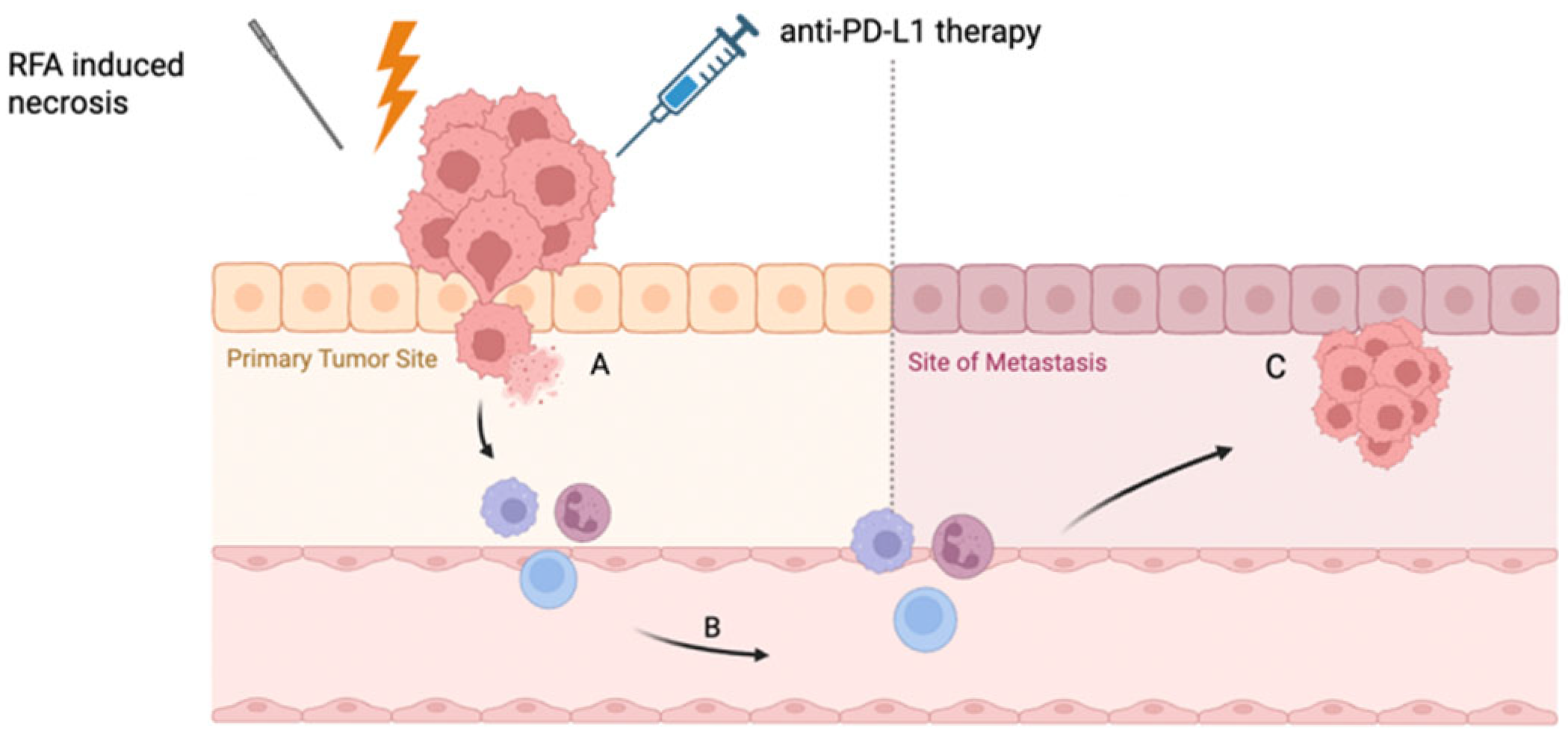
4.5. The Abscopal Effect: Local Ablation, Systemic Response
4.6. RFA-Induced PD-L1 Expression: A Rationale for Immune Checkpoint Inhibition
4.7. Adenosine and CD73: A Targetable Immunosuppressive Escape
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosein, A.N.; Brekken, R.A.; Maitra, A. Pancreatic cancer stroma: An update on therapeutic targeting strategies. Nat. reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Chowdhury, S.; Zhang, M.; Bajaj, V.; Dhir, M.; Are, C. Trends in the Global Incidence of Pancreatic Cancer and a Brief Review of its Histologic and Molecular Subtypes. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2025, 56, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słodkowski, M.; Wroński, M.; Karkocha, D.; Kraj, L.; Śmigielska, K.; Jachnis, A. Current Approaches for the Curative-Intent Surgical Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempero, M.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Al-Hawary, M.; Asbun, H.; Bain, A.; Behrman, S.W.; Benson, A.B.; Binder, E.; Cardin, D.B.; Cha, C.; et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2. 2017, nccn clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 1028–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintziras, I.; Wächter, S.; Manoharan, J.; Kanngiesser, V.; Maurer, E.; Bartsch, D.K. Postoperative morbidity following pancreatic cancer surgery is significantly associated with worse overall patient survival; systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 38, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberstein, P.E.; Olive, K.P. Pancreatic cancer: Why is it so hard to treat? Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2013, 6, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Xu, S.; Gao, Y.X.; Zhao, Z.M.; Zhao, G.D.; Hu, M.G.; Tan, X.L.; Lau, W.Y.; Liu, R. Early and late recurrence patterns of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A multicenter study. Int. J. Surg. 2023, 109, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Zheng, L. The tumour microenvironment in pancreatic cancer—Clinical challenges and opportunities. Nat. reviews. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcidiacono, P.G.; Carrara, S.; Reni, M.; Petrone, M.C.; Cappio, S.; Balzano, G.; Boemo, C.; Cereda, S.; Nicoletti, R.; Enderle, M.D.; et al. Feasibility and safety of EUS-guided cryothermal ablation in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, L.A.; Tyberg, A. EUS-RFA of the pancreas: Where are we and future directions. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Truong, V.G.; Choi, J.; Jeong, H.J.; Oh, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Kang, H.W. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Laser Ablation Using a Diffusing Applicator for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2022, 14, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Chun, H.J.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Seo, Y.S.; Jeen, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; Um, S.H.; Kim, C.D.; et al. EUS-guided irreversible electroporation using endoscopic needle-electrode in porcine pancreas. Surg. Endosc. 2019, 33, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harne, P.S.; Harne, V.; Wray, C.; Thosani, N. Endoscopic innovations in diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer: A narrative review and future directions. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2024, 17, 17562848241297434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.; Thosani, N.; Kothari, S. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation in Pancreatic Lesions: Where Are We Now and What Does the Future Hold? Cancers 2024, 16, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Serikawa, M.; Tsuboi, T.; Kawamura, R.; Tsushima, K.; Nakamura, S.; Hirano, T.; Fukiage, A.; Mori, T.; Ikemoto, J.; et al. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braden, B.; Gupta, V.; Dietrich, C.F. Therapeutic EUS: New tools, new devices, new applications. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kato, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; Otsuka, M. Current status of endoscopic ultrasound-guided antitumor treatment for pancreatic cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2025, 37, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Jaruvongvanich, V.; Chandrasekhara, V. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided injectable therapy for pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, Y.; Pereira, S.P.; Pogue, B.; Maytin, E.V.; Hasan, T.; Linn, B.; Mangels-Dick, T.; Wang, K.K. EUS-guided verteporfin photodynamic therapy for pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, S.G. Photodynamic therapy for cancer of the pancreas. Gut 2002, 50, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Oh, D.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lim, Y.-S.; Song, T.J.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Initial human experience of endoscopic ultrasound-guided photodynamic therapy with a novel photosensitizer and a flexible laser-light catheter. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWitt, J.M.; Sandrasegaran, K.; O’Neil, B.; House, M.G.; Zyromski, N.J.; Sehdev, A.; Perkins, S.M.; Flynn, J.; McCranor, L.; Shahda, S. Phase 1 study of EUS-guided photodynamic therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Progress in the cryoablation and cryoimmunotherapy for tumor. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Clark, T.W.I. Cryoablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S187–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusceddu, C.; Mascia, L.; Ninniri, C.; Ballicu, N.; Zedda, S.; Melis, L.; Deiana, G.; Porcu, A.; Fancellu, A. The Increasing Role of CT-Guided Cryoablation for the Treatment of Liver Cancer: A Single-Center Report. Cancers 2022, 14, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aycock, K.N.; Davalos, R.V. Irreversible electroporation: Background, theory, and review of recent developments in clinical oncology. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, K.R.; Kavnoudias, H.; Neal, R.E. Introduction to irreversible electroporation—Principles and techniques. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, N.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Pandit, H.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pulliam, Z.R.; Tan, M.; Martin, R.C.G. Electrochemotherapy with irreversible electroporation and folfirinox improves survival in murine models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 4348–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.C.G.; Kwon, D.; Chalikonda, S.; Sellers, M.; Kotz, E.; Scoggins, C.; McMasters, K.M.; Watkins, K. Treatment of 200 locally advanced (Stage iii) pancreatic adenocarcinoma patients with irreversible electroporation: Safety and efficacy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, S. Irreversible electroporation after induction chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, F.E.F.; Geboers, B.; Ruarus, A.H.; Vroomen, L.G.P.H.; Schouten, E.A.C.; van der Lei, S.; Vos, D.J.W.; Dijkstra, M.; Schulz, H.H.; Bakker, J.; et al. MRI-guided stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy versus CT-guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (CROSSFIRE): A single-centre, open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska-Naryniecka, A.; Szwedowicz, U.; Łapińska, Z.; Rudno-Rudzińska, J.; Kielan, W.; Kulbacka, J. Irreversible electroporation in pancreatic cancer—An evolving experimental and clinical method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Arevalo-Mora, M.; Oleas, R.; Alcivar-Vasquez, J.; Del Valle, R. Novel EUS-guided microwave ablation of an unresectable pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. VideoGIE 2022, 7, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshna, D.R.; Leupold, M.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Pawlik, T.M.; Cloyd, J.M.; Ejaz, A.; Shah, H.; Burlen, J.; Krishna, S.G. Advancements in microwave ablation techniques for managing pancreatic lesions. Life 2023, 13, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, A.; Dupuy, D.; Pereira, P.L. Microwave ablation. In Percutaneous Tumor Ablation in Medical Radiology; Vogl, T.J., Helmberger, T.K., Mack, M.G., Reiser, M.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Mayo-Smith, W.W. Microwave ablation: Principles and applications. RadioGraphics 2005, 25 (Suppl. 1), S69–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Gruber-Rouh, T.; Koitka, K.; Lehnert, T.; Nour-Eldin, N.-E.A. Microwave ablation therapy: Clinical utility in treatment of pulmonary metastases. Radiology 2011, 261, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lygidakis, N.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Papastratis, P.; Zivanovic, V.; Kefalourous, H.; Koshariya, M.; Lintzeris, I.; Porfiris, T.; Koutsiouroumba, D. Microwave ablation in locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma—A new look. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2007, 54, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Carrafiello, G.; Ierardi, A.M.; Fontana, F.; Petrillo, M.; Floridi, C.; Lucchina, N.; Cuffari, S.; Dionigi, G.; Rotondo, A.; Fugazzola, C. Microwave ablation of pancreatic head cancer: Safety and efficacy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. JVIR 2013, 24, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moond, V.; Maniyar, B.; Harne, P.S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Thosani, N.C. Harnessing endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation to reshape the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma microenvironment and elicit systemic immunomodulation. Explor. Target. Anti-Tumor Ther. 2024, 5, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaisz, F.G.; Elkelany, O.O.; Davies, B.; Lozanski, G.; Krishna, S.G. A review on endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (Eus-rfa) of pancreatic lesions. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Georgiades, C. Radiofrequency ablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S179–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, W.J.; Brugge, W.R. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided tumor ablation. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, S.G.; Healey, A.; Dietrich, C.; Arcidiacono, P. Systematic review of endoscopy ultrasound-guided thermal ablation treatment for pancreatic cancer. Endosc. Ultrasound 2020, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Brace, C.L.; Lee, F.T.; Goldberg, S.N. Principles of and advances in percutaneous ablation. Radiology 2011, 258, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhtakia, S. Therapy of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Fine needle intervention including ethanol and radiofrequency ablation. Clin. Endosc. 2017, 50, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, B.; Pirici, D.; Mărgăritescu, C.; Larisa, S.; Fronie, S.; Pătraşcu, Ş.; Şurlin, V.; Săftoiu, A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of the pancreas: An experimental study with pathological correlation. Endosc. Ultrasound 2015, 4, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.N.; Mallery, S.; Gazelle, G.S.; Brugge, W.R. EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation in the pancreas: Results in a porcine model. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 50, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Seo, D.-W.; Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.-H. Clinical outcomes of EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation for unresectable pancreatic cancer: A prospective observational study. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegrachi, S.; Besselink, M.G.; Van Santvoort, H.C.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; Molenaar, I.Q. Radiofrequency ablation for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. HPB 2014, 16, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thosani, N.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Guha, S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Bhakta, D.; Patil, P.; Wray, C.J. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (Eus-rfa) for advanced pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Del Valle, R.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Arevalo-Mora, M.; Cunto, D.; Egas-Izquierdo, M.; Estrada-Guevara, L.; Bunces-Orellana, O.; Moreno-Zambrano, D.; Alcivar-Vasquez, J.; et al. Assessing EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation in unresectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A single-center historic cohort study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 100, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieranu, C.G.; Balaban, D.V.; Tabacelia, D.; Klimko, A.; Gheorghe, C.; Pereira, S.P.; Jinga, M.; Saftoiu, A. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Scoping Review with Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seelen, L.W.F.; Brada, L.J.H.; Walma, M.S.; Rombouts, S.J.E.; Bruijnen, R.C.G.; Busch, O.R.; Cirkel, G.A.; Van Dam, R.M.; Van Delden, O.M.; Festen, S.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation and chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (The pelican trial): An international randomized controlled trial. HPB 2024, 26, S36–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, A.M.; Lucchina, N.; Bacuzzi, A.; Marco, D.C.; Bracchi, E.; Cocozza, E.; Dionigi, G.; Tsetis, D.; Floridi, C.; Carrafiello, G. Percutaneous ablation therapies of inoperable pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Imperatore, N.; de Nucci, G.; Mandelli, E.D.; de Leone, A.; Zito, F.P.; Lombardi, G.; Manes, G. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A systematic review of the literature. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1759–E1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthet, M.; Giovannini, M.; Lesavre, N.; Boustiere, C.; Napoleon, B.; Koch, S.; Gasmi, M.; Vanbiervliet, G.; Gonzalez, J.M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, E.; Hassan, J.; Chan Wah Hak, C.; Sivamanoharan, N.; Wilkins, A.; Samson, A.; Ono, M.; Harrington, K.J.; Melcher, A.; Wennerberg, E. Kickstarting immunity in cold tumours: Localised tumour therapy combinations with immune checkpoint blockade. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 754436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wei, Z.; Ye, X. Immunostimulatory effects of thermal ablation: Challenges and future prospects. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2024, 20, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Shen, Y.; Xie, J.; Meng, Z. Immunomodulatory effects of ablation therapy on tumors: Potentials for combination with immunotherapy. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Duan, Y.; Yang, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Si, T. The analysis of immunogenic cell death induced by ablation at different temperatures in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1146195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosova, J.; Macinga, P.; Krupickova, L.; Fialova, M.; Hujova, A.; Mares, J.; Urban, O.; Hajer, J.; Spicak, J.; Striz, I.; et al. Impact of endoluminal radiofrequency ablation on immunity in pancreatic cancer and cholangiocarcinoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, E.Y.; Thosani, N.C.; O’Brien, B.; Strickland, L.N.; Mota, V.; Chaney, J.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Cardenas, J.; Poulsen, K.L.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation remodels the tumor microenvironment and promotes systemic immunomodulation in pancreatic cancer. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Q.; Pan, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Hou, Z.; Yu, X.; Lin, X.; Lin, R.; Lu, F.; et al. High-dimensional single-cell analysis delineates radiofrequency ablation induced immune microenvironmental remodeling in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, T.; Pop, L.M.; Laine, A.; Iyengar, P.; Vitetta, E.S.; Hannan, R. Key role for neutrophils in radiation-induced antitumor immune responses: Potentiation with G-CSF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11300–11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, J.S.S.; Ray, P.; Hayashi, T.; Whisenant, T.C.; Vicente, D.; Carson, D.A.; Miller, A.M.; Schoenberger, S.P.; White, R.R. Irreversible electroporation combined with checkpoint blockade and tlr7 stimulation induces antitumor immunity in a murine pancreatic cancer model. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1714–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Mou, G.Z.; Li, T.Z.; Xu, W.T.; Zhang, T.; Xue, H.; Zuo, W.B.; Li, Y.N.; Luo, Y.H.; Jin, C.H. PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Malignant Tumor Based on Monotherapy and Combined Treatment Research. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211004942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraoni, E.Y.; O’Brien, B.J.; Strickland, L.N.; Osborn, B.K.; Mota, V.; Chaney, J.; Atkins, C.L.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Cardenas, J.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation remodels the tumor microenvironment and promotes neutrophil-mediated abscopal immunomodulation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Zheng, X.; Sun, M.; Wen, W.; Dai, X.; Yang, M.; et al. Pd-1 blockade boosts radiofrequency ablation–elicited adaptive immune responses against tumor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.-Y.; Pagacz, J.; Averbek, S.; Scholten, D.; Liu, Y.; Kron, S.J. Timing Anti-PD-L1 Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy to Enhance Tumor Irradiation. Cancers 2025, 17, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, B.; Allard, D.; Buisseret, L.; Stagg, J. The adenosine pathway in immuno-oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraoni, E.Y.; Ju, C.; Robson, S.C.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M. Purinergic and adenosinergic signaling in pancreatobiliary diseases. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 849258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, F.; S Evans, S. Pre-resectional radiofrequency ablation as a neoadjuvant in situ tumor vaccine. J. Vaccines Vaccin. 2016, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vemulapalli, V.; Natha, C.; Thosani, N. Endoscopic Immuno-Oncology: A New Frontier in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132091
Vemulapalli V, Natha C, Thosani N. Endoscopic Immuno-Oncology: A New Frontier in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132091
Chicago/Turabian StyleVemulapalli, Varun, Cristina Natha, and Nirav Thosani. 2025. "Endoscopic Immuno-Oncology: A New Frontier in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132091
APA StyleVemulapalli, V., Natha, C., & Thosani, N. (2025). Endoscopic Immuno-Oncology: A New Frontier in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 17(13), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132091






