Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT-4o in Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis Using Multi-Modality Ultrasound Imaging: Dual- vs. Triple-Modality Approaches
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Study Population
2.2. Ultrasound Imaging Procedure
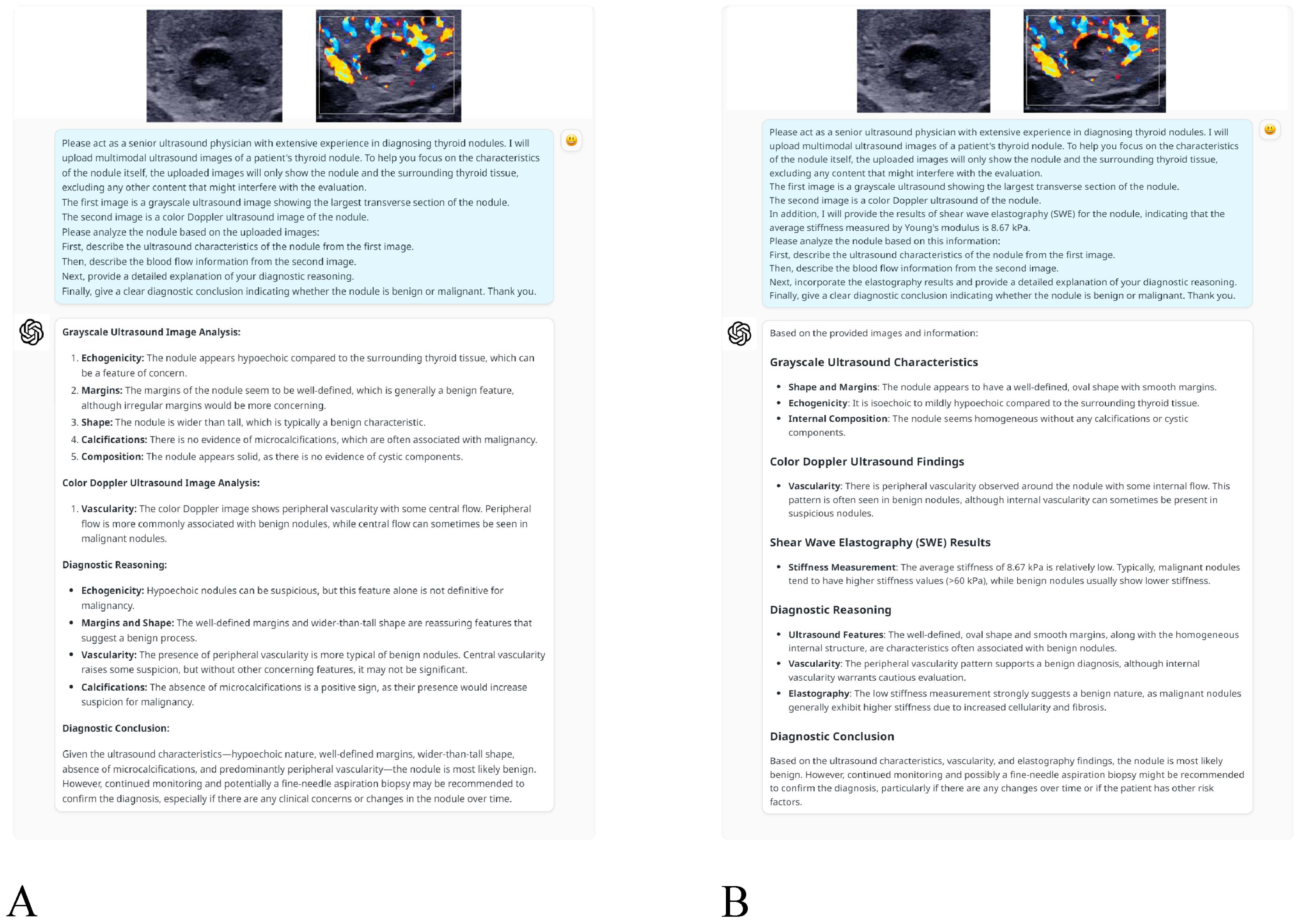
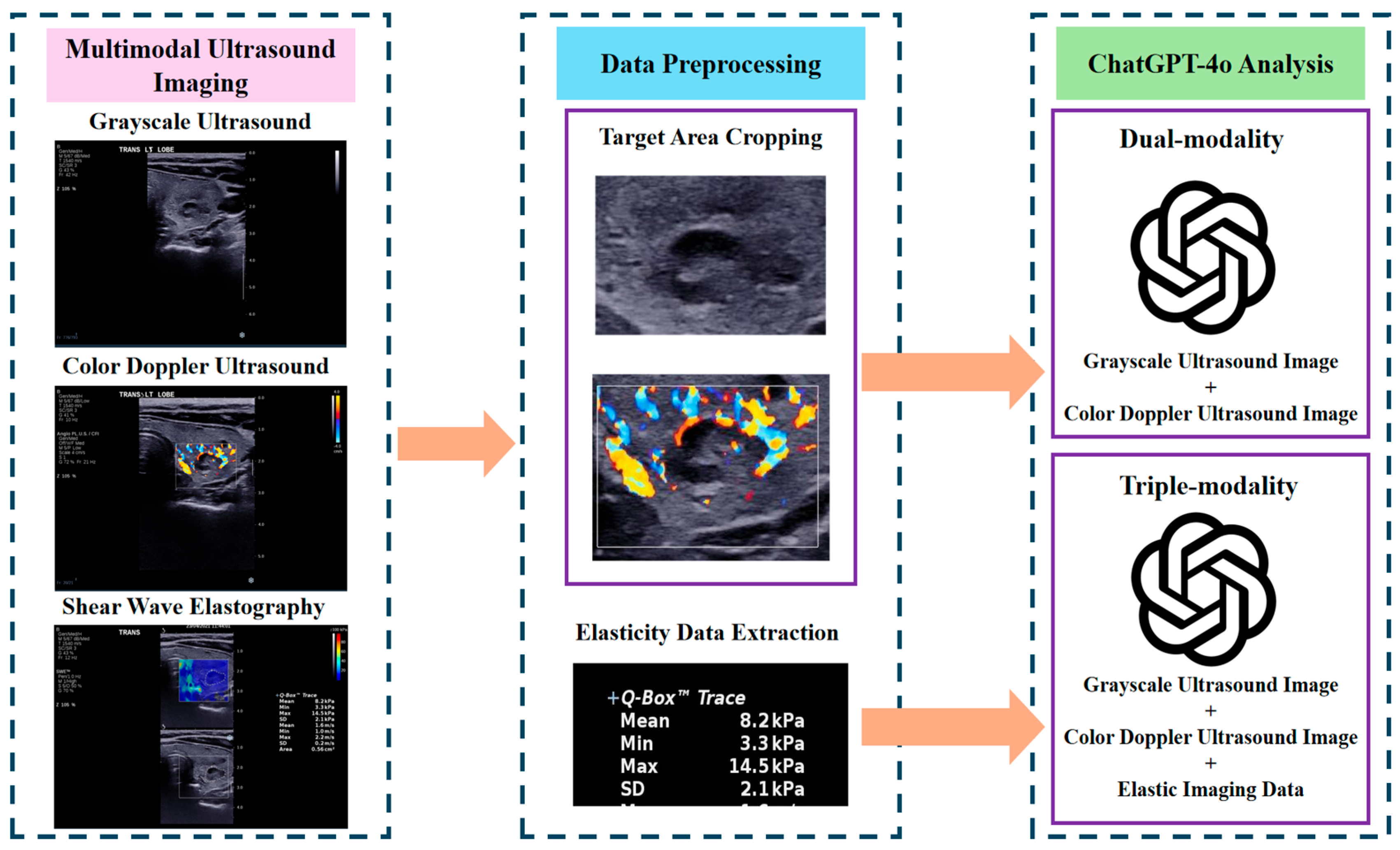
2.3. Application of ChatGPT-4o for Multi-Modality Analysis
- Dual-modality analysis: This approach used grayscale ultrasound and CDUS images only. The following prompt was provided to ChatGPT-4o to direct its analysis: “Please act as a senior ultrasound physician with extensive experience in diagnosing thyroid nodules. I will upload multimodal ultrasound images of a patient’s thyroid nodule. To help you focus on the characteristics of the nodule itself, the uploaded images will only show the nodule and the surrounding thyroid tissue, excluding any other content that might interfere with the evaluation. The first image is a grayscale ultrasound image showing the largest transverse section of the nodule. The second image is a color Doppler ultrasound image of the nodule. Please analyze the nodule based on the uploaded images: First, describe the ultrasound characteristics of the nodule from the first image. Then, describe the blood flow information from the second image. Next, provide a detailed explanation of your diagnostic reasoning. Finally, give a clear diagnostic conclusion indicating whether the nodule is benign or malignant. Thank you.”
- Triple-modality analysis: This analysis used SWE measurements, grayscale ultrasound and CDUS images to offer an integrated evaluation approach. The prompt was adapted as follows: “Please act as a senior ultrasound physician with extensive experience in diagnosing thyroid nodules. I will upload multimodal ultrasound images of a patient’s thyroid nodule. To help you focus on the characteristics of the nodule itself, the uploaded images will only show the nodule and the surrounding thyroid tissue, excluding any content that might interfere with the evaluation. The first image is a grayscale ultrasound showing the largest transverse section of the nodule. The second image is a color Doppler ultrasound of the nodule. In addition, I will provide the results of shear wave elastography (SWE) for the nodule, indicating that the average stiffness measured by Young’s modulus is XX kPa. Please analyze the nodule based on this information: First, describe the ultrasound characteristics of the nodule from the first image. Then, describe the blood flow information from the second image. Next, incorporate the elastography results and provide a detailed explanation of your diagnostic reasoning. Finally, give a clear diagnostic conclusion indicating whether the nodule is benign or malignant. Thank you.”
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population Characteristics
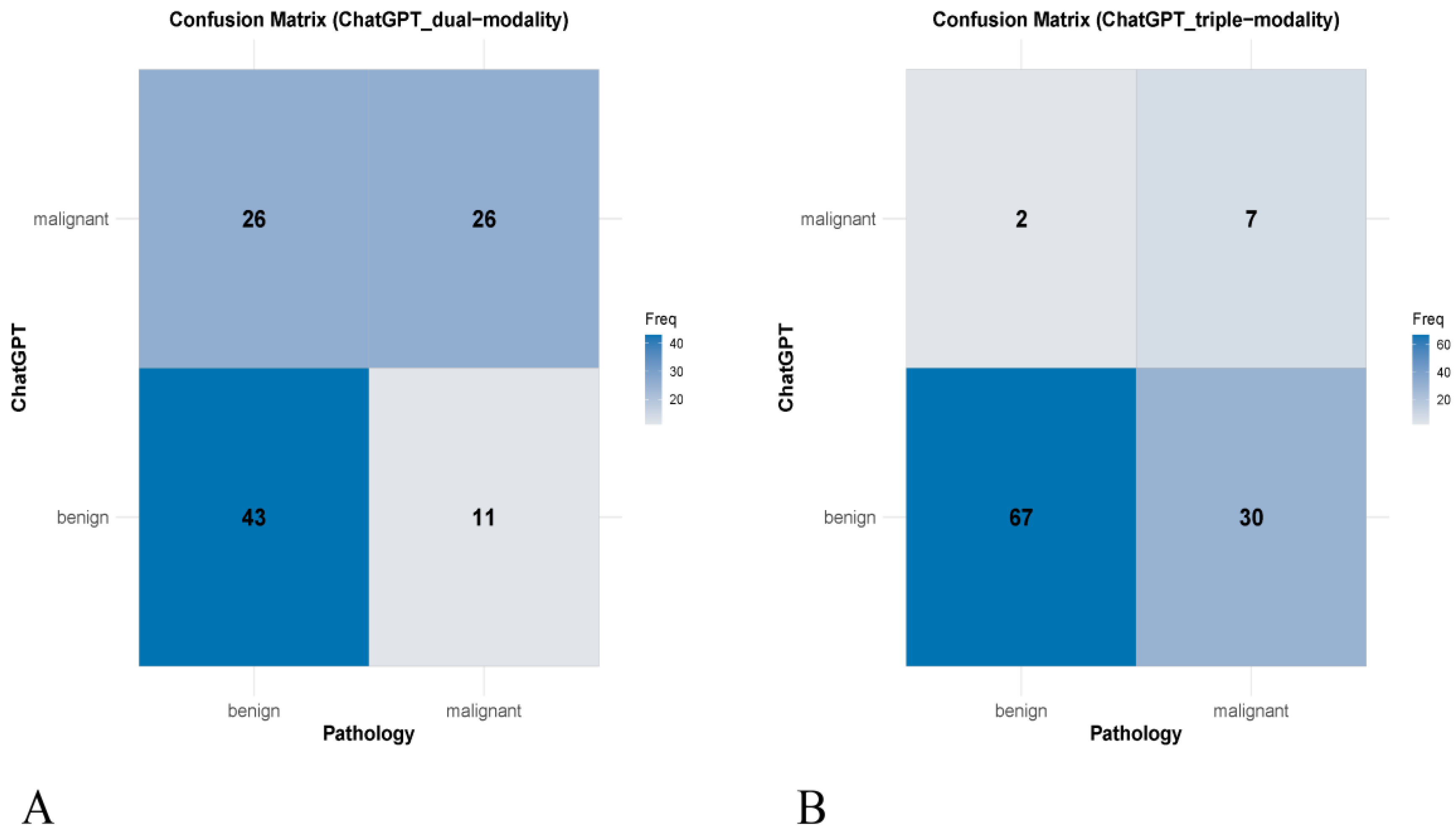
3.2. Concordance with Pathological Diagnosis
3.3. Diagnostic Performance Comparison
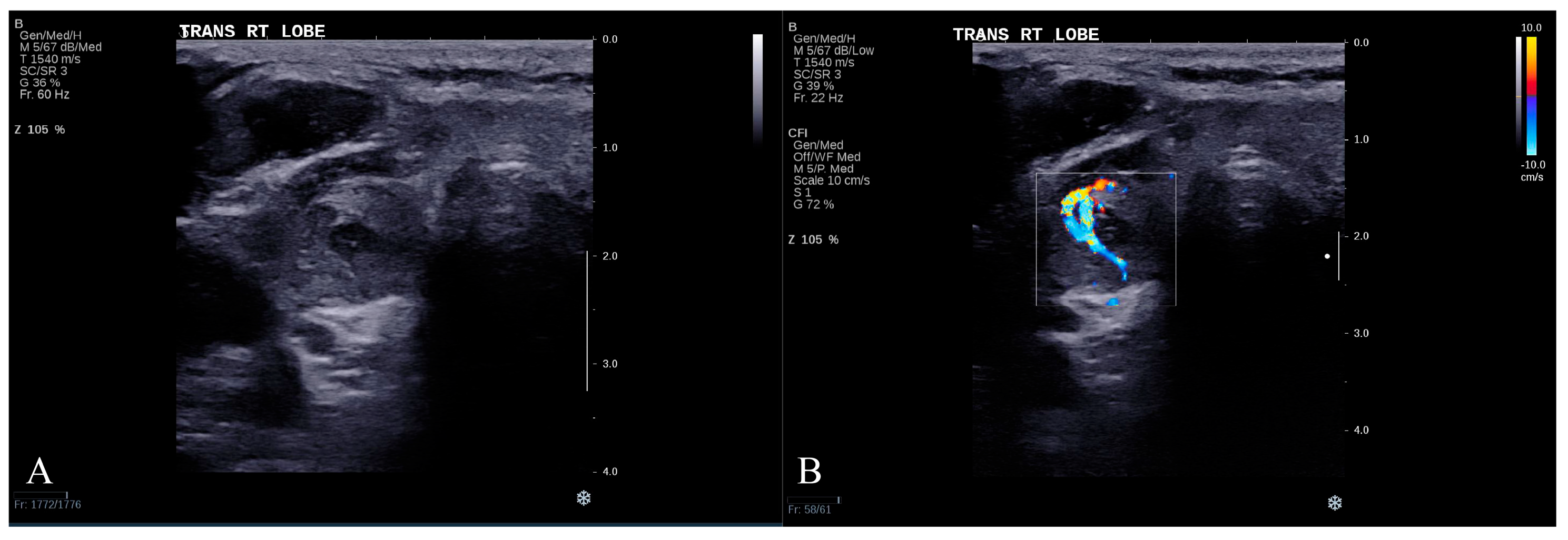
3.4. Representative Misclassified Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patil, R.; Gudivada, V. A Review of Current Trends, Techniques, and Challenges in Large Language Models (LLMs). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Du, W. From text to image: Challenges in integrating vision into ChatGPT for medical image interpretation. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhong, T.; Dong, P.; Xie, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; et al. Potential of multimodal large language models for data mining of medical images and free-text reports. Meta-Radiology 2024, 2, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Lund, B.D.; Mannuru, N.R.; Arshad, M.A.; Hayawi, K.; Bevara, R.V.K.; Mannuru, A.; Batool, L. Putting GPT-4o to the Sword: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Language, Vision, Speech, and Multimodal Proficiency. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Bao, P.; Yuan, J.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Large language models illuminate a progressive pathway to artificial intelligent healthcare assistant. Med. Plus 2024, 1, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, E.; Ong, J.; Masalkhi, M.; Zaman, N.; Sarker, P.; Lee, A.G.; Tavakkoli, A. GPT-4 and medical image analysis: Strengths, weaknesses and future directions. J. Med. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Cui, L.; Tu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L. A Systematic Evaluation of GPT-4V’s Multimodal Capability for Chest X-ray Image Analysis. Meta-Radiology 2024, 2, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, E.K.; Doherty, G.M.; Barletta, J.A. Management of thyroid nodules. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, R.; Zhong, J.; Chen, W.; Shuai, J.; Chen, M.; Deng, F.; Wei, T.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; et al. A multicenter cohort study of thyroidectomy-related decision regret in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Nong, D.; Xin, M.; Lin, L. Accuracy of Ultrasound Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 5056082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, B.; Brigante, G.; Ansaloni, A.; Taliani, E.; Kaleci, S.; Monzani, M.L.; Simoni, M.; Rochira, V. The Added Value of Operator’s Judgement in Thyroid Nodule Ultrasound Classification Arising From Histologically Based Comparison of Different Risk Stratification Systems. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itani, M.; Assaker, R.; Moshiri, M.; Dubinsky, T.J.; Dighe, M.K. Inter-observer Variability in the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System: In-Depth Analysis and Areas for Improvement. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carlos, J.; Garcia, J.; Basterra, F.J.; Pineda, J.J.; Dolores Ollero, M.; Toni, M.; Munarriz, P.; Anda, E. Interobserver variability in thyroid ultrasound. Endocrine 2024, 85, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y. The role of large language models in medical image processing: A narrative review. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSaad, R.; Abd-Alrazaq, A.; Boughorbel, S.; Ahmed, A.; Renault, M.A.; Damseh, R.; Sheikh, J. Multimodal Large Language Models in Health Care: Applications, Challenges, and Future Outlook. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. Interactive computer-aided diagnosis on medical image using large language models. Commun. Eng. 2024, 3, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, L.R.; Mohamed, M.K.; Andronikou, S. ChatGPT-4: A breakthrough in ultrasound image analysis. Radiol. Adv. 2024, 1, umae006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chambara, N.; Wu, C.; Lo, X.; Liu, S.Y.W.; Gunda, S.T.; Han, X.; Qu, J.; Chen, F.; Ying, M.T.C. Assessing the feasibility of ChatGPT-4o and Claude 3-Opus in thyroid nodule classification based on ultrasound images. Endocrine 2024, 87, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Ha, E.J.; Suh, C.H.; Choi, M.; Baek, J.H.; Na, D.G.; Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Clinical applications of Doppler ultrasonography for thyroid disease: Consensus statement by the Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Ultrasonography 2020, 39, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.; Barr, R.; Bojunga, J.; Cantisani, V.; Chammas, M.C.; Dighe, M.; Vinayak, S.; Xu, J.M.; Dietrich, C.F. WFUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Use of Ultrasound Elastography: Part 4. Thyroid. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, K.Z.; Bonnema, S.J.; Jespersen, M.L.; Nielsen, V.E. Reappraisal of shear wave elastography as a diagnostic tool for identifying thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; He, D. The Potential Applications and Challenges of ChatGPT in the Medical Field. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdush, J.; Begum, M.; Hossain, S.T. ChatGPT and Clinical Decision Support: Scope, Application, and Limitations. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corazza, G.R.; Lenti, M.V.; Howdle, P.D. Diagnostic reasoning in internal medicine: A practical reappraisal. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, K.I.; Tselikas, N.D. ChatGPT and Open-AI Models: A Preliminary Review. Future Internet 2023, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Total | Benign | Malignant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 102 | 69 | 33 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 18/84 | 11/58 | 7/26 |
| Age (years) | 53.71 ± 12.46 | 53.23 ± 12.22 | 54.70 ± 13.08 |
| Nodules | 106 | 69 (65.1) | 37 (34.9) |
| Nodule elastic value (kPa) | 14.64 (10.30–21.24) | 14.30 (9.73–18.27) | 17.47 (12.00–30.74) |
| Index | Pathological Result | Cohen’s Kappa Value (95% CI) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | ||||
| Dual-modality | Benign | 43 | 11 | 0.298 (0.123–0.473) | 0.001 |
| Malignant | 26 | 26 | |||
| Triple-modality | Benign | 67 | 30 | 0.194 (0.038–0.350) | 0.014 |
| Malignant | 2 | 7 | |||
| Index | Sensitivity% (95% CI) | Specificity% (95% CI) | Accuracy% (95% CI) | PPV% (95% CI) | NPV% (95% CI) | AUC% (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual-modality | 70.3 (53.0–84.1) | 62.3 (49.8–73.7) | 65.1 (55.2–74.1) | 50.0 (40.9–59.1) | 79.6 (69.7–86.9) | 66.3 (56.5–75.2) |
| Triple-modality | 18.9 (8.0–35.2) | 97.1 (89.9–99.6) | 69.8 (60.1–78.4) | 77.8 (43.4–94.1) | 69.1 (65.5–72.4) | 58.0 (48.0–67.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Chambara, N.; Liu, S.Y.W.; Chow, T.C.M.; Lai, C.M.S.; Ying, M.T.C. Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT-4o in Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis Using Multi-Modality Ultrasound Imaging: Dual- vs. Triple-Modality Approaches. Cancers 2025, 17, 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132068
Chen Z, Chambara N, Liu SYW, Chow TCM, Lai CMS, Ying MTC. Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT-4o in Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis Using Multi-Modality Ultrasound Imaging: Dual- vs. Triple-Modality Approaches. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132068
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ziman, Nonhlanhla Chambara, Shirley Yuk Wah Liu, Tom Chi Man Chow, Carol Man Sze Lai, and Michael Tin Cheung Ying. 2025. "Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT-4o in Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis Using Multi-Modality Ultrasound Imaging: Dual- vs. Triple-Modality Approaches" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132068
APA StyleChen, Z., Chambara, N., Liu, S. Y. W., Chow, T. C. M., Lai, C. M. S., & Ying, M. T. C. (2025). Exploring the Potential of ChatGPT-4o in Thyroid Nodule Diagnosis Using Multi-Modality Ultrasound Imaging: Dual- vs. Triple-Modality Approaches. Cancers, 17(13), 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132068





