Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers Are Early Predictors of Disease Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
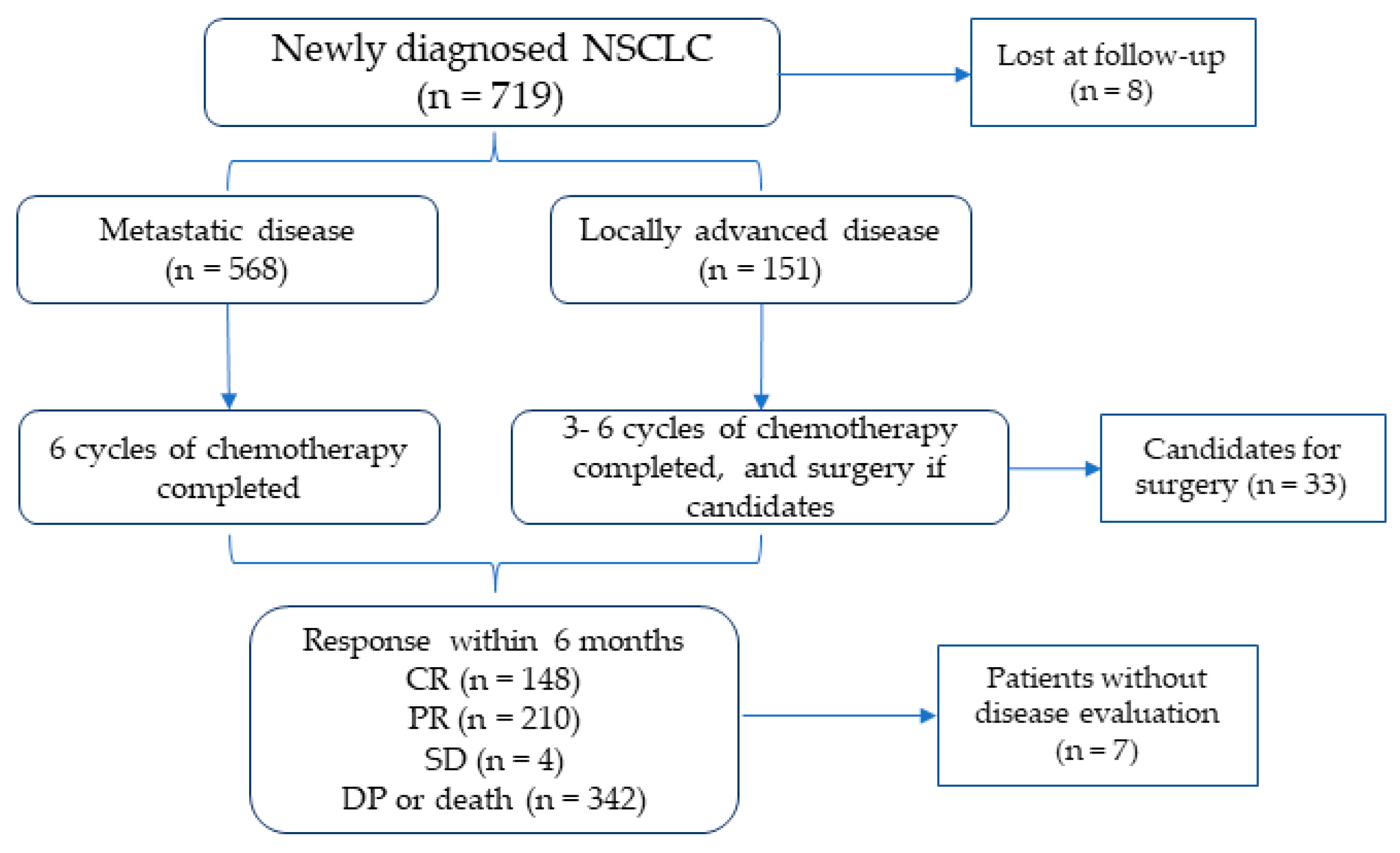
2.1. Study Design and Subjects
2.2. Blood Withdrawal and Processing
2.3. High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Analysis
2.4. Hemostatic Biomarkers Analysis
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Study Outcome
3.3. Characteristics of Patients According to DP
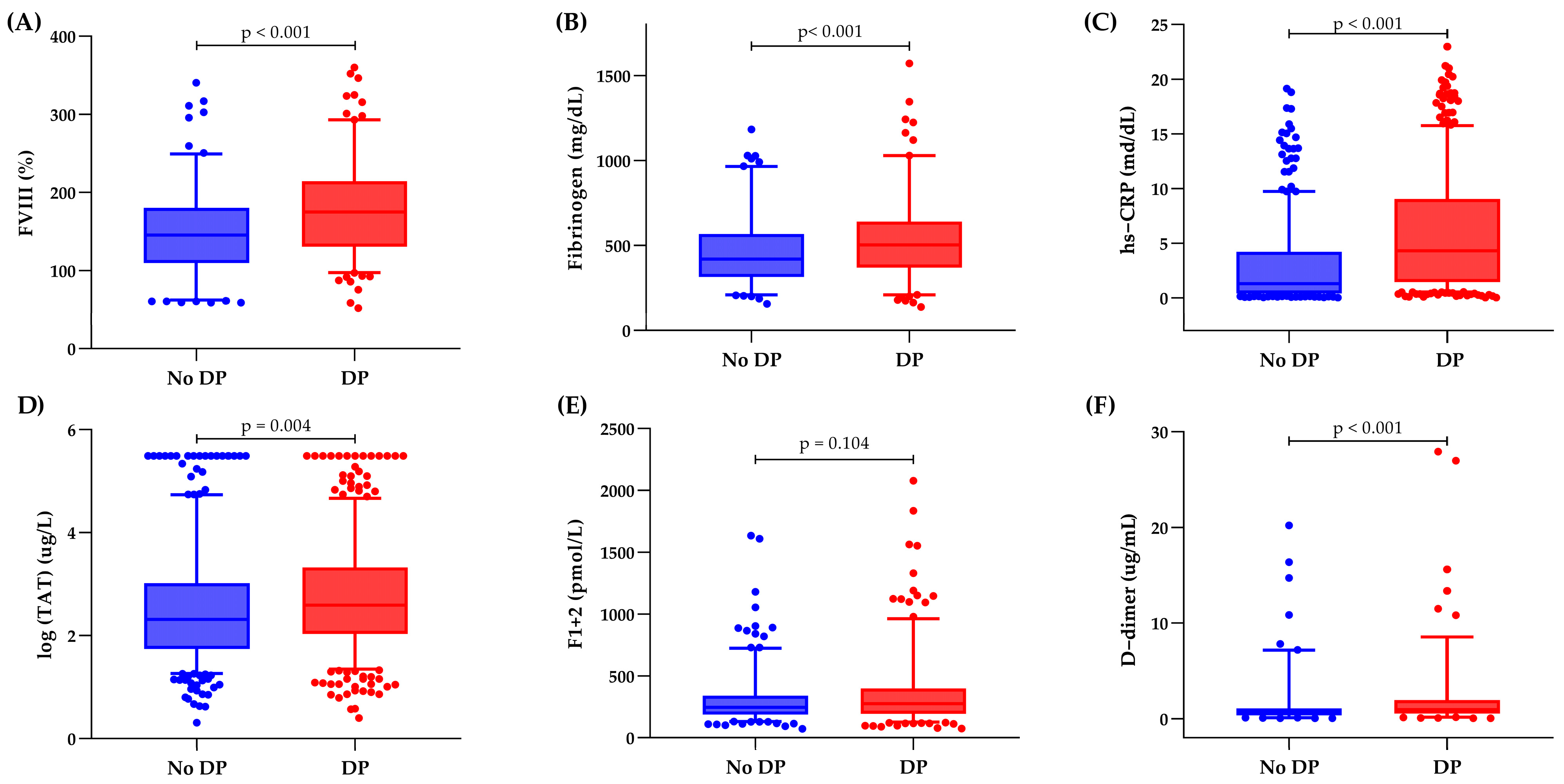
3.4. Inflammatory and Hemostatic Biomarker Distribution
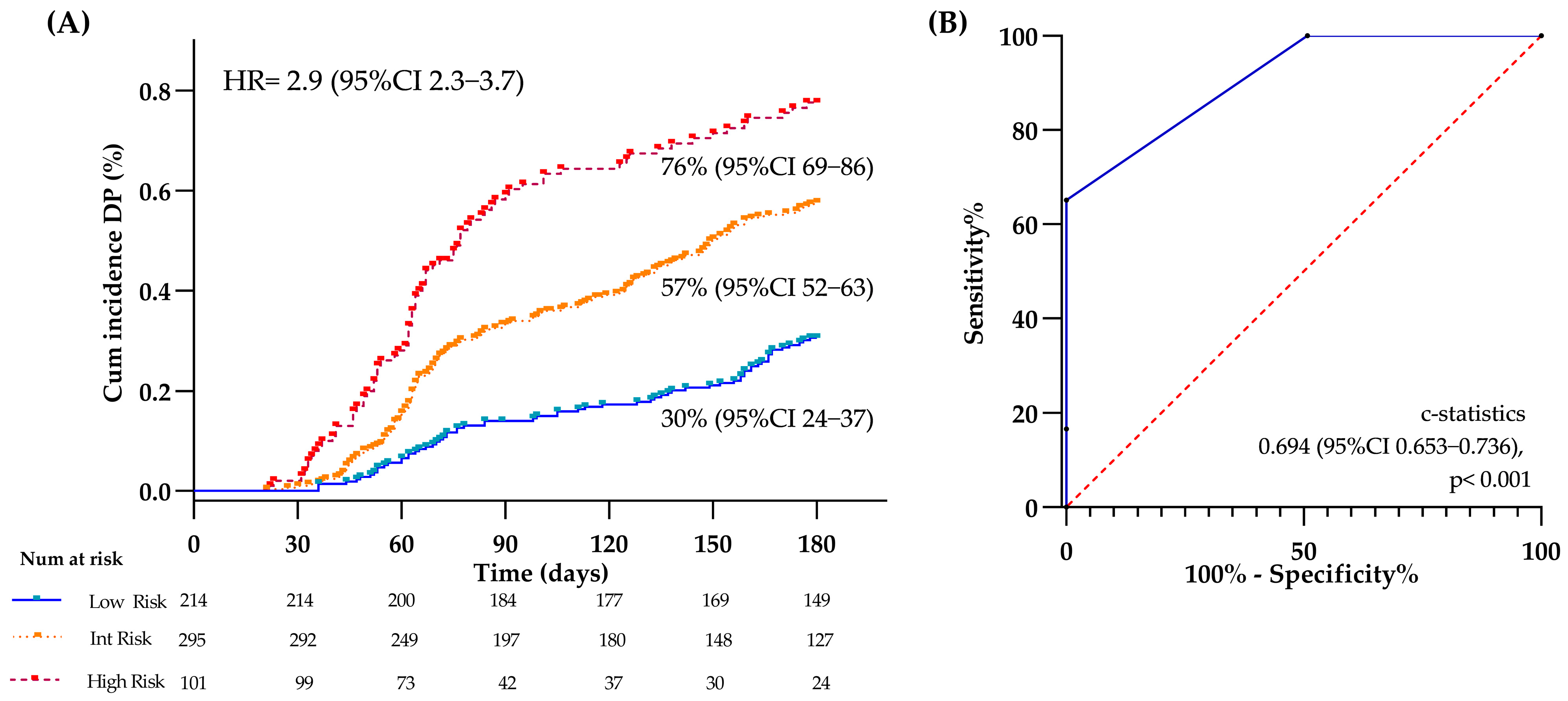
3.5. Clinical and Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers and Risk of DP
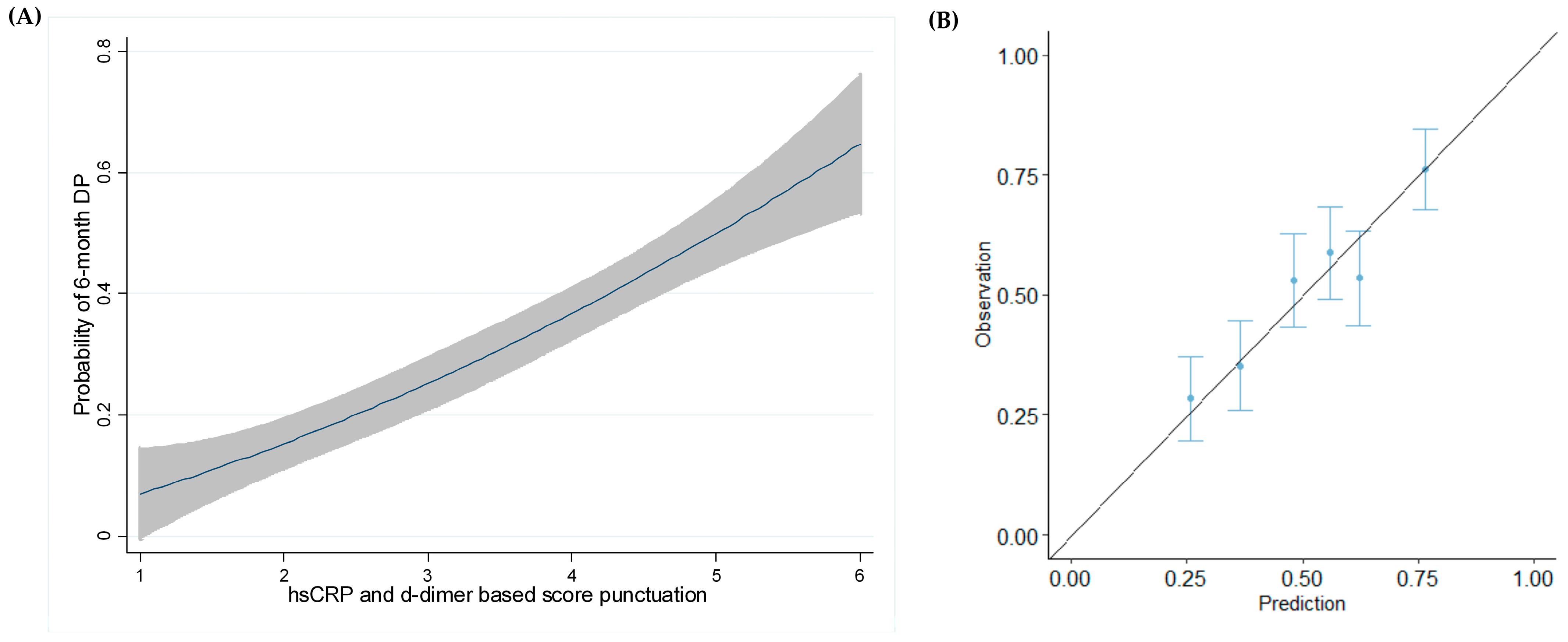
3.6. DP Modeling at 6 Months
3.7. Evaluation of the Model at Different Time Points
3.8. Relationship of VTE with DP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, D. Global burden of lung cancer in 2022 and projections to 2050: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Cancer Epidemiol. 2024, 93, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Luo, L.; Wampfler, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.-M.; Adjei, A.A.; Midthun, D.E.; Yang, P. 5-year overall survival in patients with lung cancer eligible or ineligible for screening according to US Preventive Services Task Force criteria: A prospective, observational cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, C.P.; Koinis, F.; Fallon, M.T.; Fearon, K.C.; Bowden, J.; Solheim, T.S.; Gronberg, B.H.; McMillan, D.C.; Gioulbasanis, I.; Laird, B.J. Prognosis in advanced lung cancer—A prospective study examining key clinicopathological factors. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, B.J.; Kaasa, S.; McMillan, D.C.; Fallon, M.T.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Fayers, P.; Klepstad, P. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced cancer: A comparison of clinicopathological factors and the development of an inflammation-based prognostic system. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Pekarek, L.; Navarro, F.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Álvarez-Mon, M.Á.; Diez-Pedrero, R.; Boyano-Adánez, M.d.C.; Guijarro, L.G.; Barrena-Blázquez, S.; et al. Updated Views in Targeted Therapy in the Patient with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, D.; Wampfler, J.A.; Luo, Y.-H.; Kumar, A.V.; Gu, Z.; Kosuru, N.; Yu, N.Y.; Wang, Z.; Leventakos, K.; et al. Targeted therapy-associated cardiotoxicity in patients with stage-IV lung cancer with or without cardiac comorbidities. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 53, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goussault, H.; Gendarme, S.; Assié, J.; Jung, C.; Epaud, S.; Algans, C.; Salaun-Penquer, N.; Rousseau, M.; Lazatti, A.; Chouaïd, C. Risk factors for early mortality of lung cancer patients in France: A nationwide analysis. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hei, Y.J.; O’Malley, C.D. Survival by histologic subtype in stage IV nonsmall cell lung cancer based on data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 3, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of Incidence, Prevalence, Survival, and Initial Treatment in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, G.J.; Sheu, B.; Cook, N.R.; Woodard, G.A.; Mann, M.J.; Kratz, J.R. Comparison of Conventional TNM and Novel TNMB Staging Systems for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1917062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.; Kristensen, A.F.; Falkmer, U.; Christiansen, G.; Kristensen, S.R. Increased activity of procoagulant factors in patients with small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M. Hemostatic biomarkers in cancer progression. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164 (Suppl. S1), S54–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Vignoli, A. Coagulation and cancer: Biological and clinical aspects. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moik, F.; Ay, C. Hemostasis and cancer: Impact of haemostatic biomarkers for the prediction of clinical outcomes in patients with cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2733–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.-F.; Ye, Y.-Q.; Jin, Y.-J.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Sha, M.; Liu, R.; Chen, C. Risk Factors and Impact on Outcomes of Lung Cancer Patients Concurrent with Deep Vein Thrombosis. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748221145074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopkumar, J.; Poudel, S.K.; Gervaso, L.; Reddy, C.A.; Velcheti, V.; Pennell, N.A.; McCrae, K.R.; Khorana, A.A. Risk of thromboembolism in patients with ALK- and EGFR-mutant lung cancer: A cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka-Kihara, F.; Sueta, D.; Ishii, M.; Maki, Y.; Hirakawa, K.; Tabata, N.; Ito, M.; Yamanaga, K.; Fujisue, K.; Hoshiyama, T.; et al. Validation of the Khorana Venous Thromboembolism Risk Score in Japanese Cancer Patients. JACC Asia 2021, 1, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuderer, N.M.; Culakova, E.; Lyman, G.H.; Francis, C.; Falanga, A.; Khorana, A.A. A Validated Risk Score for Venous Thromboembolism Is Predictive of Cancer Progression and Mortality. Oncologist 2016, 21, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzeroli, C.; Giaccherini, C.; Russo, L.; Bolognini, S.; Gamba, S.; Tartari, C.J.; Schieppati, F.; Ticozzi, C.; Vignoli, A.; Masci, G.; et al. Utility of the Khorana and the new-Vienna CATS prediction scores in cancer patients of the HYPERCAN cohort. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 21, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moik, F.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Posch, F.; Pabinger, I.; Ay, C. Systemic Inflammation and Activation of Haemostasis Predict Poor Prognosis and Response to Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Cao, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ye, L. The D-dimer level predicts the prognosis in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, C.; Dunkler, D.; Pirker, R.; Thaler, J.; Quehenberger, P.; Wagner, O.; Zielinski, C.; Pabinger, I. High D-dimer levels are associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Qian, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gu, W. Prognostic Value of Plasma Fibrinogen in Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Cui, P.; Hou, B.; Zhuang, C.; Wei, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Hu, Y. Predicting disease progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with circulating neutrophil-derived and platelet-derived microparticles. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Santoro, A.; Labianca, R.; De Braud, F.; Gasparini, G.; D’alessio, A.; Barni, S.; Iacoviello, L.; Barcella, L.; Brevi, S.; et al. Hypercoagulation screening as an innovative tool for risk assessment, early diagnosis and prognosis in cancer: The HYPERCAN study. Thromb. Res. 2016, 140 (Suppl. S1), S55–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, S.; Adcock, D.M.; Dauer, R.; Kristoffersen, A.; Lippi, G.; Mackie, I.; Marlar, R.A.; Nair, S. International Council for Standardization in Haematology (ICSH) recommendations for processing of blood samples for coagulation testing. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsetøy, R.; Cate, H.T.; Spronk, H.; Van Oerle, R.; Aarsetøy, H.; Staines, H.; Nilsen, D.W. Activated factor XI-antithrombin complex presenting as an independent predictor of 30-days mortality in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients. Thromb. Res. 2021, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.L. CDC/AHA Workshop on Markers of Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease: Application to Clinical and Public Health Practice: Laboratory tests available to assess inflammation—Performance and standardization: A background paper. Circulation 2004, 110, e572–e576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Rosas, P.; Giaccherini, C.; Russo, L.; Verzeroli, C.; Gamba, S.; Tartari, C.J.; Bolognini, S.; Ticozzi, C.; Schieppati, F.; Barcella, L.; et al. A New Risk Prediction Model for Venous Thromboembolism and Death in Ambulatory Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaroussi, Y.; Bouteiller, F.; Bellera, C.; Pasquier, D.; Perol, M.; Debieuvre, D.; Filleron, T.; Girard, N.; Schott, R.; Mathoulin-Pélissier, S.; et al. Survival outcomes of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy or immunotherapy as first-line in a real-life setting. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Arrondeau, J.; Gervais, C.; Durand, J.-P.; Fabre, E.; De Percin, S.; Villeminey, C.V.; Piketty, A.-C.; Rassy, N.; Ulmann, G.; et al. Development and validation of a host-dependent, PDL1-independent, biomarker to predict 6-month progression-free survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) patients treated with anti-PD1 immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in the CERTIM Cohort: The ELY study. EBioMedicine 2021, 73, 103630. [Google Scholar]
- Simeone, J.C.; Nordstrom, B.L.; Patel, K.; Klein, A.B. Treatment patterns and overall survival in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer in a real-world, US setting. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 3491–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Boshoff, C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, Y.; Abe, R.; Sumito, N.; Tanaka, T.; Ishige, Y.; Shionoya, I.; Yamamura, K.; Nishiki, K.; Nojiri, M.; Kato, R.; et al. Disease control in patients with non-small cell lung cancer using pemetrexed: Investigating the best treatment strategy. Thorac. Cancer 2024, 15, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e493–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswalt, C.; Liu, Y.; Pang, H.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Wang, X.; Crawford, J. Associations between body mass index, weight loss and overall survival in patients with advanced lung cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y. Weight loss as a predictor of reduced survival in patients with lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiyesimi, I.A.; Leighl, N.B.; Ismaila, N.; Alluri, K.; Florez, N.; Gadgeel, S.; Masters, G.; Schenk, E.L.; Schneider, B.J.; Sequist, L.; et al. Therapy for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Without Driver Alterations: ASCO Living Guideline, Version 2023.3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, e23–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; He, J.; Ning, R.; Tan, L.; Zeng, A.; Zhou, S. Pretreatment plasma d-dimer levels as an independent prognostic factor for overall survival among patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520962661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Du, N.; Ren, L. Application of an elevated plasma D-dimer cut-off value improves prognosis prediction of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Russo, L. Hemostatic Biomarkers and Cancer Prognosis: Where Do We Stand? Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 47, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, J.M.; Barth, D.A.; Brueckl, W.M.; Zeitler, G.; Foris, V.; Mollnar, S.; Stotz, M.; Rossmann, C.H.; Terbuch, A.; Balic, M.; et al. C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Levels in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response and Progression in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Bi-Center Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeghaian, M.; Tareco Bucho, T.M.; de Bruin, M.; Schmitz, A.; Bodalal, Z.; Smit, E.F.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; van den Broek, D.; Trebeschi, S. Can blood-based markers predict RECIST progression in non-small cell lung cancer treated with immunotherapy? J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Xu, H.; Tang, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhou, D.; Chen, C.; Cao, D. Inflammatory factors are associated with prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, S.H.; Shi, R.; Mills, G. Advance lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) at diagnosis is a prognostic marker in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A retrospective review. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, F.T.; Hocazade, C.; Kos, M.; Uncu, D.; Karakas, E.; Dogan, M.; Uncu, H.G.; Ozdemir, N.; Zengin, N. Assessment of Prognostic Value of “Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio” and “Prognostic Nutritional Index” as a Sytemic Inflammatory Marker in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3997–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.M.; McMillan, D.C.; McArdle, C.S.; Angerson, W.J.; Dunlop, D.J. Comparison of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) with performance status (ECOG) in patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy for inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkaya, Y.; Köstek, O.; Sakin, A.; Özyükseler, D.T.; Şakalar, T.; Çil, I. Is the prognostic nutritional index a prognostic and predictive factor in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line chemotherapy? Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Y.; Topkan, E.; Mertsoylu, H.; Selek, U. Low Prognostic Nutritional Index Predicts Poor Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Stage IIIB Non-small-cell Lung Carcinoma Undergoing Chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ahn, H.J.; Yang, M.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.J. The prognostic nutritional index and postoperative complications after curative lung cancer resection: A retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 160, 276–285.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Park, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Suh, B.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, Y.W.; Heo, D.S. Nutritional status in the era of target therapy: Poor nutrition is a prognostic factor in non-small cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Gao, M.-Q.; Jiang, X.-C.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Pang, B. Research progress and value of albumin-related inflammatory markers in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of clinical evidence. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, M.; Ball, D.; Solomon, B.; MacManus, M.; Manser, R.; Riedel, B.; Westerman, D.; Evans, S.M.; Wolfe, R.; Burbury, K. Dynamic Thromboembolic Risk Modelling to Target Appropriate Preventative Strategies for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálffy, G.; Morócz, É.; Korompay, R.; Hécz, R.; Bujdosó, R.; Puskás, R.; Lovas, T.; Gáspár, E.; Yahya, K.; Király, P.; et al. Targeted therapeutic options in early and metastatic NSCLC-overview. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2024, 30, 1611715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingy, N.E.; Tromp, V.N.M.F.; Hurk, C.J.G.v.D.; Becker-Commissaris, A.; Walraven, I. Health-Related Quality of Life and Survival in Metastasized Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with and without a Targetable Driver Mutation. Cancers 2021, 13, 4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccherini, C.; Verzeroli, C.; Russo, L.; Gamba, S.; Tartari, C.J.; Bolognini, S.; Schieppati, F.; Ticozzi, C.; Sarmiento, R.; Celio, L.; et al. Thrombin Generation and D-Dimer for Prediction of Disease Progression and Mortality in Patients with Metastatic Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccherini, C.; Marchetti, M.; Masci, G.; Verzeroli, C.; Russo, L.; Celio, L.; Sarmiento, R.; Gamba, S.; Tartari, C.J.; Diani, E.; et al. Thrombotic biomarkers for risk prediction of malignant disease recurrence in patients with early stage breast cancer. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Gomez-Rosas, P.; Pesenti, M.; Verzeroli, C.; Giaccherini, C.; Russo, L.; Sarmiento, R.; Masci, G.; Celio, L.; Minelli, M.; et al. Validation of the Role of Thrombin Generation Potential by a Fully Automated System in the Identification of Breast Cancer Patients at High Risk of Disease Recurrence. TH Open 2021, 5, e56–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, M.; Giaccherini, C.; Masci, G.; Verzeroli, C.; Russo, L.; Celio, L.; Sarmiento, R.; Gamba, S.; Tartari, C.J.; Diani, E.; et al. Thrombin generation predicts early recurrence in breast cancer patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.C.; Rajab, I.M.; Alebraheem, M.; Potempa, L.A. C-Reactive Protein and Cancer-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Insights. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 595835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 6-Month DCR (n = 362) | 6-Month DP (n = 342) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex (n, %) Age (years, mean [SD]) BMI (kg/m2, mean [SD]) Metastatic disease (n, %) Locally advanced disease (n, %) ECOG (n, %)
| 237 (66) 65 (8.7) 25 (4.5) 264 (73) 98 (27) 190 (53) 138 (38) 9 (3) | 243 (71) 66 (10.2) 24 (4.2) 297 (87) 45 (13) 120 (35) 159 (47) 43 (13) | 0.066 0.061 0.121 <0.001 <0.001 |
Smoking (n, %)
| 118 (33) 160 (44) | 119 (35) 155 (45) | 0.367 |
CV risk factors ≥ 1 (n, %)
| 267 (74) 40 (11) 148 (41) 65 (18) 36 (10) 6 (2) | 262 (77) 47 (14) 151 (44) 51 (15) 27 (8) 3 (1) | 0.390 0.165 0.187 0.161 0.205 0.506 |
Histological subtypes (n, %)
| 88 (24) 241 (67) 10 (3) 5 (1) 18 (5) | 70 (21) 224 (66) 21 (6) 9 (3) 18 (5) | 0.060 |
Blood Count (median [IQR])
| 8.8 (6.9–11.1) 13.4 (12.3–14.5) 40.5 (37.8–43.3) 272 (213–335) | 9.5 (7.3–12.7) 13.0 (11.8–14.1) 39.7 (35.9–42.3) 289 (218–379) | 0.001 0.001 0.001 0.042 |
Chemotherapy (n, %)
Target therapy (n, %) * Radiotherapy (n, %)
| 362 (100) 20 (6) 159 (44) 105 (29) 21 (6) 2 (1) 15 (4) 6 (2) 34 (9) 18 (5) 13 (4) 195 (54) 52 (14) 145 (40) | 342 (100) 10 (3) 157 (46) 94 (26) 13 (4) 0 (0) 32 (9) 21 (6) 15 (4) 43 (13) 17 (5) 153 (45) 16 (5) 135 (40) | 0.122 <0.001 |
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Age, years | 1.008 (0.997–1.020) | 0.166 | ||
| Male sex | 0.890 (0.754–1.051) | 0.171 | ||
| Metastatic status | 1.644 (1.316–2.052) | <0.001 | ||
| BMI | 0.973 (0.949–0.999) | 0.038 | ||
| CV risk factors | 1.000 (0.837–1.195) | 0.997 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma vs. squamous | 1.129 (0.934–1.365) | 0.209 | ||
| ECOG = 2 | 1.114 (0.919–1.349) | 0.271 | ||
| Radical vs. palliative radiotherapy | 0.622 (0.522–0.741) | <0.001 | ||
| Leukocytes, 109/L | 1.032 (1.018–1.045) | <0.001 | ||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 0.894 (0.841–0.949) | <0.001 | ||
| Platelets, 109/L | 1.001 (1.000–1.002) | 0.051 | ||
| hs-CRP, mg/dL | 1.070 (1.050–1.089) | <0.001 | 1.083 (1.055–1.111) | <0.001 |
| FVIII, % | 1.003 (1.002–1.005) | <0.001 | ||
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL | 1.001 (1.000–1.001) | <0.001 | ||
| TAT, µg/L | 1.122 (1.027–1.225) | 0.011 | ||
| F1+2, pmol/L | 1.000 (1.000–1.001) | 0.223 | ||
| D-dimer, µg/mL | 1.001 (1.000–1.002) | <0.001 | 1.001 (1.000–1.002) | 0.018 |
| hs-CRP (mg/dL) | Points |
|---|---|
| <1.0 | 1 |
| 1.0–3.0 | 2 |
| >3.0 | 3 |
| D-dimer (µg/mL) | |
| <0.5 | 0 |
| 0.5–1.5 | 1 |
| >1.5–4.0 | 2 |
| >4.0 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomez-Rosas, P.; Tartari, C.J.; Russo, L.; Bolognini, S.; Ticozzi, C.; Romeo, D.; Schieppati, F.; Barcella, L.; Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M., on behalf of the HYPERCAN Investigators. Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers Are Early Predictors of Disease Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2025, 17, 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121932
Gomez-Rosas P, Tartari CJ, Russo L, Bolognini S, Ticozzi C, Romeo D, Schieppati F, Barcella L, Falanga A, Marchetti M on behalf of the HYPERCAN Investigators. Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers Are Early Predictors of Disease Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2025; 17(12):1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121932
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomez-Rosas, Patricia, Carmen Julia Tartari, Laura Russo, Silvia Bolognini, Chiara Ticozzi, Debora Romeo, Francesca Schieppati, Luca Barcella, Anna Falanga, and Marina Marchetti on behalf of the HYPERCAN Investigators. 2025. "Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers Are Early Predictors of Disease Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients" Cancers 17, no. 12: 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121932
APA StyleGomez-Rosas, P., Tartari, C. J., Russo, L., Bolognini, S., Ticozzi, C., Romeo, D., Schieppati, F., Barcella, L., Falanga, A., & Marchetti, M., on behalf of the HYPERCAN Investigators. (2025). Thromboinflammatory Biomarkers Are Early Predictors of Disease Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers, 17(12), 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121932









