Targeting the Undruggable: Recent Progress in PROTAC-Induced Transcription Factor Degradation
Simple Summary
Abstract
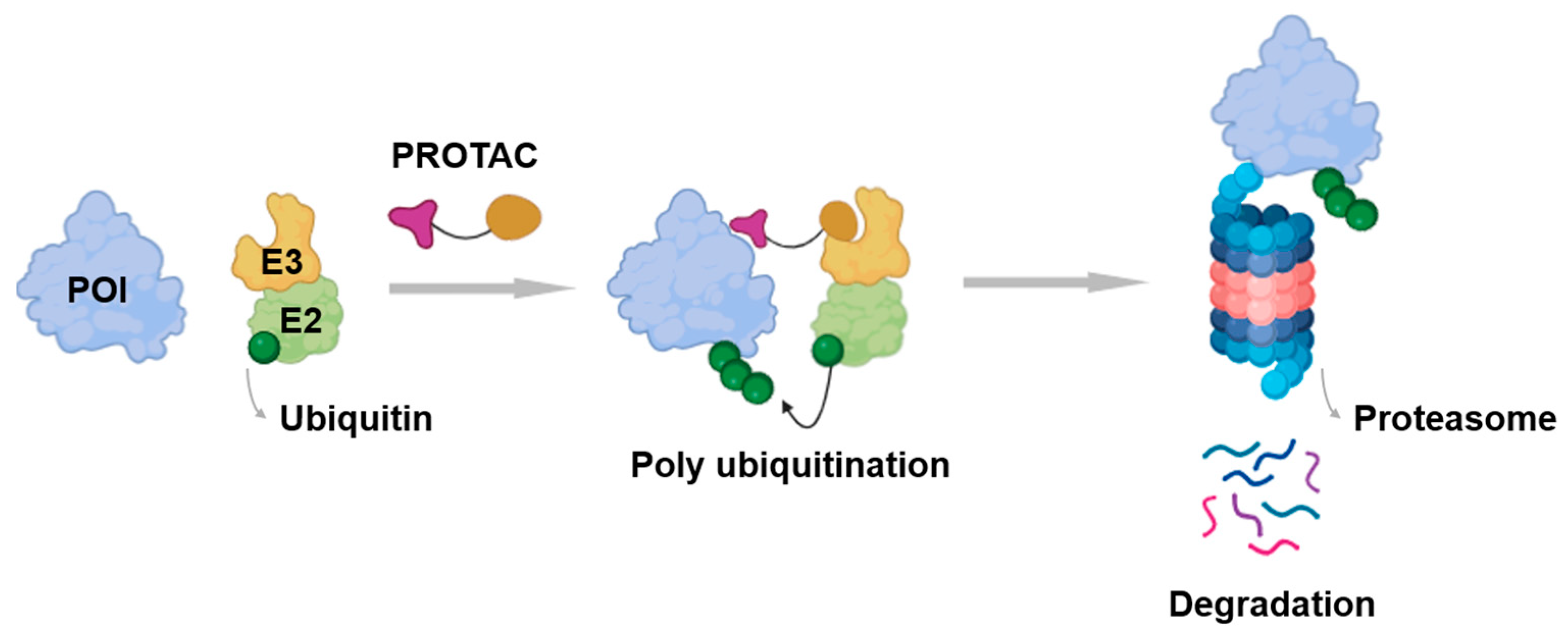
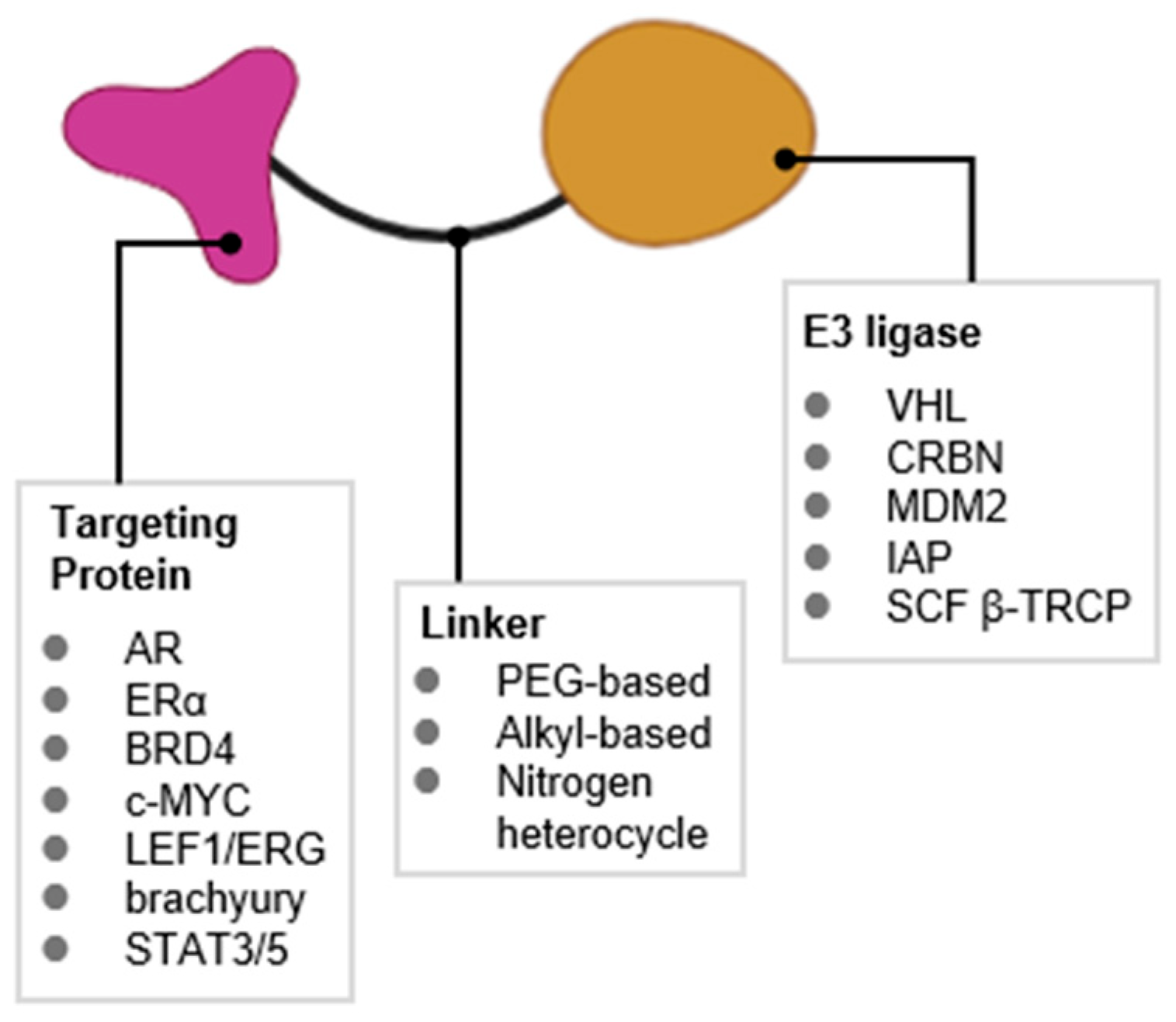
1. Introduction
2. PROTACs Targeting the Androgen Receptor (AR)
| PROTAC | E3 Ligase | Target Protein Binder | Structure | DC50 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
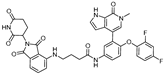
| Protac-3 | SCF β-TRCP | DHT | 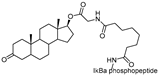 | 10 μM | [13] |
| PROTAC-5 | VHL | DHT | 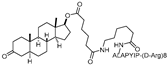 | - | [15] |
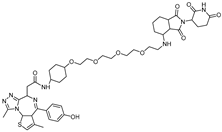
| ARCC-4 | VHL | Enzalutamide | 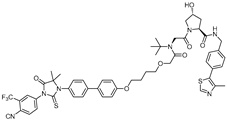 | 5 nM | [17] |
| ARD-69 | VHL | ARI-16 | 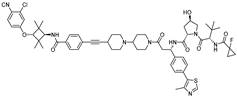 | ~1 nM | [19] |
| ARD-266 | VHL | ARI-16 | 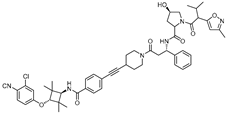 | 0.5 nM | [20] |
| A031 | VHL | ARI-16-derivatives | 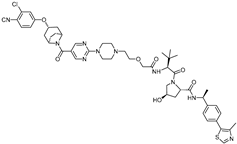 | 2 μM | [21] |
| ARD-2128 | CRBN | ARI-16 | 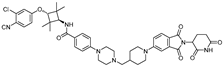 | 0.28 nM | [22] |
| ARD-2051 | CRBN | AR 4034 | 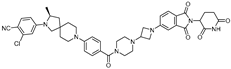 | 0.6 nM | [23] |
| ARD-1676 | CRBN | AR 4034 | 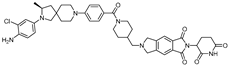 | 1.1 nM | [24] |
| ARD-2585 | CRBN | AR antagonist | 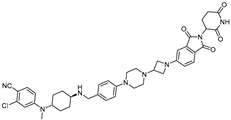 | 0.04–0.1 nM | [25] |
| BWA-522 | CRBN | Ralaniten | 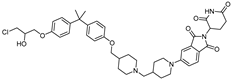 | 0.73 μM | [26] |
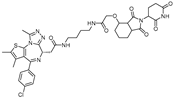
| ARV-110 | CRBN | AR ligand-30 | 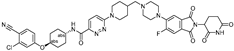 | 10 nM | [27,28] |
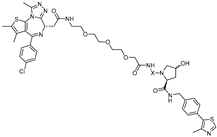
| ARV-766 | CRBN | 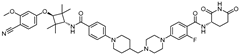 | <1 nM |
3. PROTACs Targeting Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4 (BRD4)
4. PROTACs Targeting ERα
| PROTAC | E3 Ligase | Target Protein Binder | Structure | DC50 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROTAC-2 | SCF β-TRCP | E2 | 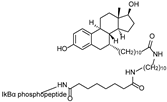 | - | [13] |
| E2-SMPI | VHL | E2 | 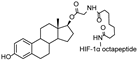 | 50 µM | [43] |
| ERD-308 | VHL | Raloxifene | 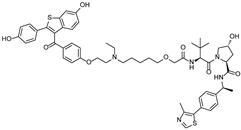 | 0.17 nM | [46] |
| ZD12 | VHL | OBSHA ligand | 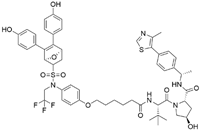 | - | [48] |
| Compound A3 | VHL | highly ER targeting NIR fluorescent probe | 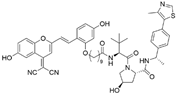 | 0.12 µM | [49] |
| SNIPER(ER)-11 | cIAP | estrone | 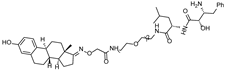 | - | [52] |
| SNIPER(ER)-87 | IAP | 4-hydroxyl tamoxifen | 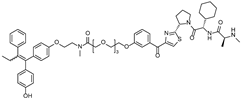 | 3 nM | [53,54] |
| ERE-PROTAC | VHL | GTCCAAAGTCAGGTCA-CAGTGACCTGATCAAAGT- (ds) | 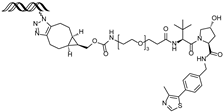 | ~5 µM | [55] |
| LCL-ER(dec) | IAP | GTCAGGTCACAGTGACCTGAT (ds) | 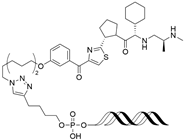 | ~3 µM | [56] |
| POM-ER(apt)D1 | POM | nucleic acid aptamers | 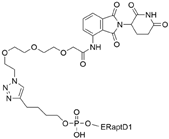 | ~5 µM | [58] |
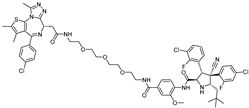
| ARV-471 | CRBN | 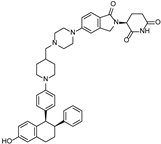 | 0.9 nM | [59,60] |
5. PROTACs Targeting Other TFs
| PROTAC | Target Protein | E3 Ligase | Target Protein Binder | Structure | DC50 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEF1 OP-V1 | LEF1 | VHL | TACAAAGATCAAAGGGTT (ds) | 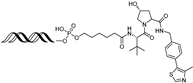 | 25 nM | [61] |
| ERG OP-C-N1 | ERG | VHL | ACGGACCGGAAATCCGGTT (ds) | 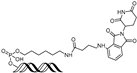 | 182.4 nM | [61] |
| OT17 | brachyury | VHL | TCCAATTTCACACCTAGGTGTGAAATTGGG (ds) | 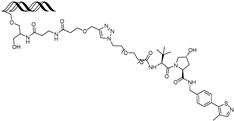 | 75 nM | [62] |
| OT7 | c-MYC | VHL | GAGCACGTGGTTGCCACGTGGTT (ds) | 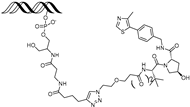 | 50 nM | [62] |
| MP-16 | c-MYC | VHL | GAGTAGCACGTGCTAC (ds) | 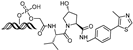 | ~0.8 µM | [63] |
| MP-17 | c-MYC | VHL | GAGTAGCACGTGCTAC (ds) | 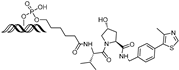 | ~0.8 µM | [63] |
| TEP | c-MYC | pomalidomide | nucleic acid aptamers | 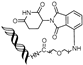 | ~100 nM | [64] |
| circPAI-ProMYC | c-MYC | CRBN | nucleic acid aptamers | 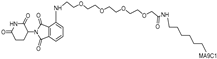 | 5.02 nM | [65] |
| SD-36 | STAT3 | CRBN | SI-109 | 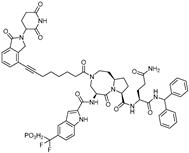 | 0.06 µM | [66] |
| AK-2292 | STAT5 | CRBN | STAT5 ligand | 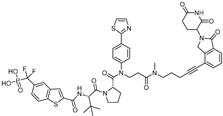 | ~1 µM | [67] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TFs | Transcription factors |
| PPIs | Protein–protein interactions |
| PROTAC | Proteolysis-targeting chimeras |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| ERα | Estrogen receptor alpha |
| BRD4 | Bromodomain 4 |
| VHL | Von Hippel-Lindau |
| DC50 | Half-maximal degradation concentration |
| CRBN | Cereblon |
| MDM2 | Murine double minute 2 |
| DHT | Dihydroxytestosterone |
| LBD | Ligand-binding domain |
| NTD | N-terminal domain |
| BET | Extra-Terminal motif |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| KLF5 | Krüppel-like factor 5 |
| BL | Burkitt’s lymphoma |
| OBHSA | Oxabicycloheptane sulfonamide |
| IAP | Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins |
| SNIPER | Specific and non-genetic IAP-dependent protein eraser |
| cIAP | Cellular IAP |
| 4-OHT | 4-hydroxytamoxifen |
| XIAP | X-linked IAP |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded DNA |
| ERE | Estrogen response element |
| O’PROTAC | Oligonucleotide-based PROTAC |
| LEF1 | Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 |
| ERG | ETS-related gene |
| TNA | Threose nucleic acid |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| STAT5 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 |
| CML | Chronic myeloid leukemia |
| Smad3 | SMAD family member 3 |
| HIF-2α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha |
References
- Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Qing, G. Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. The different roles of ER subtypes in cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushweller, J.H. Targeting transcription factors in cancer—From undruggable to reality. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarasinghe, K.T.; Samarasinghe, K.T.G.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; Burgess, M.; Nalawansha, D.A.; Dai, K.; Hu, Z.; Bebenek, A.; Holley, S.A.; Crews, C.M.; et al. Targeted degradation of transcription factors by TRAFTACs: Transcription factor targeting chimeras. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 648–661.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, D.P.; Mares, A.; Smith, I.E.D.; Ko, E.; Campos, S.; Miah, A.H.; Mulholland, K.E.; Routly, N.; Buckley, D.L.; Gustafson, J.L.; et al. Catalytic in vivo protein knockdown by small-molecule PROTACs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. Targeting Undruggable Transcription Factors with PROTACs: Advances and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10183–10194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.P.; Jeselsohn, R.M.; Vahdat, L.T.; Hurvitz, S.A. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) Estrogen Receptor Degraders for Treatment of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2025, 20, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalawansha, D.A.; Crews, C.M. PROTACs: An Emerging Therapeutic Modality in Precision Medicine. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 998–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, P.-C.; Naganuma, M.; Demizu, Y.; Naito, M. Current Status of Oligonucleotide-Based Protein Degraders. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovich, P.S. Degrader-antibody conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacino, J.; Lee, P.; Jeong, H.; Kim, Y.; Song, Y.; Permpoon, U.; Wong, W.; Bai, C.; Fishkin, N.; Takrouri, K.; et al. ORM-6151: A first-in-class, anti-CD33 antibody-enabled GSPT1 degrader for AML. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 3061–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Verma, R.; Ransick, A.; Stein, B.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Development of Protacs to target cancer-promoting proteins for ubiquitination and degradation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneekloth, J.S., Jr.; Fonseca, F.N.; Koldobskiy, M.; Mandal, A.; Deshaies, R.; Sakamoto, K.; Crews, C.M. Chemical genetic control of protein levels: Selective in vivo targeted degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3748–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, A.; Cyrus, K.; Salcius, M.; Kim, K.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J.; Sakamoto, K.M. Targeting steroid hormone receptors for ubiquitination and degradation in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7201–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schalken, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.M. Enzalutamide: Targeting the androgen signalling pathway in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salami, J.; Salami, J.; Alabi, S.; Willard, R.R.; Vitale, N.J.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Jin, M.; McDonnell, D.P.; Crew, A.P.; et al. Androgen receptor degradation by the proteolysis-targeting chimera ARCC-4 outperforms enzalutamide in cellular models of prostate cancer drug resistance. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Linton, A.; Kephart, S.; Ornelas, M.; Pairish, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Greasley, S.; Nagata, A.; Burke, B.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. Discovery of aryloxy tetramethylcyclobutanes as novel androgen receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7693–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, C.; Qin, C.; Xiang, W.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Xu, T.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ARD-69 as a Highly Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Androgen Receptor (AR) for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 941–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiang, W.; Qin, C.; Miao, B.; Xu, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chinnaswamy, K.; Stuckey, J.; et al. Discovery of Highly Potent and Efficient PROTAC Degraders of Androgen Receptor (AR) by Employing Weak Binding Affinity VHL E3 Ligase Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 11218–11231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, L.; Mao, S.; Xu, P.; Xu, X.; Zhao, R.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, K.; Yu, G.; Wang, X. Discovery of A031 as effective proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) androgen receptor (AR) degrader for the treatment of prostate cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiang, W.; Qin, C.; Miao, B.; McEachern, D.; Wang, Y.; Metwally, H.; Wang, L.; Matvekas, A.; et al. Strategies toward Discovery of Potent and Orally Bioavailable Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Degraders of Androgen Receptor for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 12831–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhao, L.; Xiang, W.; Miao, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, M.; Xu, T.; McEachern, D.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Discovery of ARD-2051 as a Potent and Orally Efficacious Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Androgen Receptor for the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 8822–8843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhao, L.; Han, X.; Xu, T.; Kregel, S.; Wang, M.; Miao, B.; Qin, C.; Wang, M.; McEachern, D.; et al. Discovery of ARD-1676 as a Highly Potent and Orally Efficacious AR PROTAC Degrader with a Broad Activity against AR Mutants for the Treatment of AR + Human Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 13280–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Zhao, L.; Han, X.; Qin, C.; Miao, B.; McEachern, D.; Wang, Y.; Metwally, H.; Kirchhoff, P.D.; Wang, L.; et al. Discovery of ARD-2585 as an Exceptionally Potent and Orally Active PROTAC Degrader of Androgen Receptor for the Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 13487–13509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Li, B.; Mao, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.; et al. Discovery of BWA-522, a first-in-class and orally bioavailable PROTAC degrader of the androgen receptor targeting N-terminal domain for the treatment of prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 11158–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Burris, H.A., III; Vuky, J.; Dreicer, R.; Sartor, A.O.; Sternberg, C.N.; Percent, I.J.; Hussain, M.H.A.; Kalebasty, A.R.; Shen, J.; et al. Phase 1/2 study of ARV-110, an androgen receptor (AR) PROTAC degrader, in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, S.M.; Flanagan, J.J.; Teh, J.; Andreoli, M.; Rousseau, E.; Pannone, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Willard, R.; Davenport, K.; Bortolon, E.; et al. Oral estrogen receptor PROTAC vepdegestrant (ARV-471) is highly efficacious as monotherapy and in combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors in preclinical ER+ breast cancer models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3549–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Dong, M.; Pan, X.; Bian, J.; Zhou, Q. BRD4 inhibitor JQ1 inhibits and reverses mechanical injury-induced corneal scarring. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.E.; Buckley, D.L.; Paulk, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Souza, A.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Bradner, J.E. DRUG DEVELOPMENT. Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation. Science 2015, 348, 1376–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengerle, M.; Chan, K.H.; Ciulli, A. Selective Small Molecule Induced Degradation of the BET Bromodomain Protein BRD4. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Ciulli, A. E3 ligase ligands for PROTACs: How they were found and how to discover new ones. Slas Discov. Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2021, 26, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, T.; Luo, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Ronai, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ruppin, E.; Han, L. Expanding PROTACtable genome universe of E3 ligases. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Heo, J.; Jeong, H.; Hong, K.T.; Kwon, D.H.; Shin, M.H.; Oh, M.; Sable, G.A.; Ahn, G.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Targeted degradation of transcription coactivator SRC-1 through the N-degron pathway. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17548–17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.; Lartigue, S.; Dong, H.; Qian, Y.; Crews, C.M. MDM2-Recruiting PROTAC Offers Superior, Synergistic Antiproliferative Activity via Simultaneous Degradation of BRD4 and Stabilization of p53. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Jin, H.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, X. The therapeutic effect of the BRD4-degrading PROTAC A1874 in human colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Qian, Y.; Altieri, M.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Raina, K.; Hines, J.; Winkler, J.D.; Crew, A.P.; Coleman, K.; et al. Hijacking the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cereblon to Efficiently Target BRD4. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, K.F.; Wang, L.; Soltwedel, T.; Fidanze, S.D.; Hasvold, L.A.; Liu, D.; Mantei, R.A.; Pratt, J.K.; Sheppard, G.S.; Bui, M.H.; et al. Discovery of N-(4-(2, 4-Difluorophenoxy)-3-(6-methyl-7-oxo-6, 7-dihydro-1 H-pyrrolo [2, 3-c] pyridin-4-yl) phenyl) ethanesulfonamide (ABBV-075/Mivebresib), a Potent and Orally Available Bromodomain and Extraterminal Domain (BET) Family Bromodomain Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8369–8384. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Lan, T.; Wang, L.; Gong, C.; Lv, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; et al. BRD4-specific PROTAC inhibits basal-like breast cancer partially through downregulating KLF5 expression. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lee, Y. Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) in Breast Cancer Therapy. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Baek, S.-H.; Ho, A.; Kim, K. Degradation of target protein in living cells by small-molecule proteolysis inducer. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyrus, K.; Wehenkel, M.; Choi, E.-Y.; Lee, H.; Swanson, H.; Kim, K.-B. Jostling for position: Optimizing linker location in the design of estrogen receptor-targeting PROTACs. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrus, K.; Wehenkel, M.; Choi, E.-Y.; Swanson, H.; Kim, K.-B. Two-headed PROTAC: An effective new tool for targeted protein degradation. Chembiochem A Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2010, 11, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Miao, B.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Hayes, D.F.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ERD-308 as a Highly Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Estrogen Receptor (ER). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1420–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, C.; Huang, S.; Zhou, H.-B. Exploring the PROTAC degron candidates: OBHSA with different side chains as novel selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 172, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Yin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Lv, J.; Du, C.; Deng, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Liang, K. Discovery of a novel class of PROTACs as potent and selective estrogen receptor α degraders to overcome endocrine-resistant breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 6631–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xin, L.; Deng, X.; Dong, C.; Hu, G.; Zhou, H.-B. Fluorescence theranostic PROTACs for real-time visualization of ERalpha degradation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 267, 116184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ji, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liang, D. Specific non-genetic IAP-based protein erasers (SNIPERs) as a potential therapeutic strategy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, M.; Ohoka, N.; Shibata, N. SNIPERs—Hijacking IAP activity to induce protein degradation. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y.; Kitaguchi, R.; Ishikawa, M.; Naito, M.; Hashimoto, Y. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of nuclear receptor-degradation inducers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6768–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disch, J.S.; Duffy, J.M.; Lee, E.C.Y.; Gikunju, D.; Chan, B.; Levin, B.; Monteiro, M.I.; Talcott, S.A.; Lau, A.C.; Zhou, F.; et al. Bispecific estrogen receptor α degraders incorporating novel binders identified using DNA-encoded chemical library screening. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 5049–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohoka, N.; Morita, Y.; Nagai, K.; Shimokawa, K.; Ujikawa, O.; Fujimori, I.; Ito, M.; Hayase, Y.; Okuhira, K.; Shibata, N.; et al. Derivatization of inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) ligands yields improved inducers of estrogen receptor α degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6776–6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, X.; Fan, T.; Tan, C.; Liu, F.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y. PROTAC degrader of estrogen receptor α targeting DNA-binding domain in breast cancer. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2022, 5, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganuma, M.; Ohoka, N.; Tsuji, G.; Tsujimura, H.; Matsuno, K.; Inoue, T.; Naito, M.; Demizu, Y. Development of chimeric molecules that degrade the estrogen receptor using decoy oligonucleotide ligands. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 13, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sett, A.; Borthakur, B.B.; Sharma, J.D.; Kataki, A.C.; Bora, U. DNA aptamer probes for detection of estrogen receptor α positive carcinomas. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 104–120.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, H.; Naganuma, M.; Ohoka, N.; Inoue, T.; Naito, M.; Tsuji, G.; Demizu, Y. Development of DNA aptamer-based PROTACs that degrade the estrogen receptor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synder, L.B.; Flanagan, J.J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.M.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Chandler, J.; et al. The discovery of ARV-471, an orally bioavailable estrogen receptor degrading PROTAC for the treatment of patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, J.J.; Qian, Y.; Gough, S.M.; Andreoli, M.; Bookbinder, M.; Cadelina, G.; Bradley, J.; Rousseau, E.; Willard, R.; Pizzano, J.; et al. Abstract P5-04-18: ARV-471, an oral estrogen receptor PROTAC degrader for breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79 (Suppl. 4), P5-04-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Yan, Y.; Ding, D.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yan, W.; Kharbanda, A.; Li, H.; Huang, H. Destruction of DNA-binding proteins by programmable oligonucleotide PROTAC (O’PROTAC): Effective targeting of LEF1 and ERG. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarasinghe, U.T.G.; An, E.; Genuth, M.A.; Chu, L.; Holley, S.A.; Crews, C.M. OligoTRAFTACs: A generalizable method for transcription factor degradation. RSC Chem. Biol. 2022, 3, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, M.; Ma, H.; He, J.; Xu, F.; Ming, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, D.; Yang, K.; Li, J.; et al. Targeting oncogenic transcriptional factor c-myc by oligonucleotide PROTAC for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 280, 116978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Ma, Y.; Wei, D.; Lu, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; et al. c-Myc-Targeting PROTAC Based on a TNA-DNA Bivalent Binder for Combination Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9334–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X.; Bai, R.; Yuan, D.; Gao, D.; He, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kou, J.; et al. Antitumor effect of anti-c-myc aptamer-based protac for degradation of the c-myc protein. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2309639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Bai, L.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; McEachern, D.; Chinnaswamy, K.; Wen, B.; Dai, L.; Kumar, P.; et al. Structure-Based Discovery of SD-36 as a Potent, Selective, and Efficacious PROTAC Degrader of STAT3 Protein. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 11280–11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneshige, A.; Bai, L.; Wang, M.; McEachern, D.; Meagher, J.L.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Metwally, H.; Kirchhoff, P.D.; et al. A selective small-molecule STAT5 PROTAC degrader capable of achieving tumor regression in vivo. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, D.; Fan, J.; Luo, N.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. VHL-recruiting PROTAC attenuates renal fibrosis and preserves renal function via simultaneous degradation of Smad3 and stabilization of HIF-2α. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, H.; Lee, Y. Targeting the Undruggable: Recent Progress in PROTAC-Induced Transcription Factor Degradation. Cancers 2025, 17, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111871
Jung H, Lee Y. Targeting the Undruggable: Recent Progress in PROTAC-Induced Transcription Factor Degradation. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111871
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Hyein, and Yeongju Lee. 2025. "Targeting the Undruggable: Recent Progress in PROTAC-Induced Transcription Factor Degradation" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111871
APA StyleJung, H., & Lee, Y. (2025). Targeting the Undruggable: Recent Progress in PROTAC-Induced Transcription Factor Degradation. Cancers, 17(11), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111871