The Era of Precision Medicine: Advancing Treatment Paradigms for Small Cell Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemotherapy
2.1. First-Line Chemotherapy
2.2. Maintenance Therapy
2.3. Second-Line Therapy and Beyond
3. Radiation Therapy
3.1. LS-SCLC
3.2. ES-SCLC
3.3. Emerging Modalities in RT
4. Immunotherapy
4.1. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
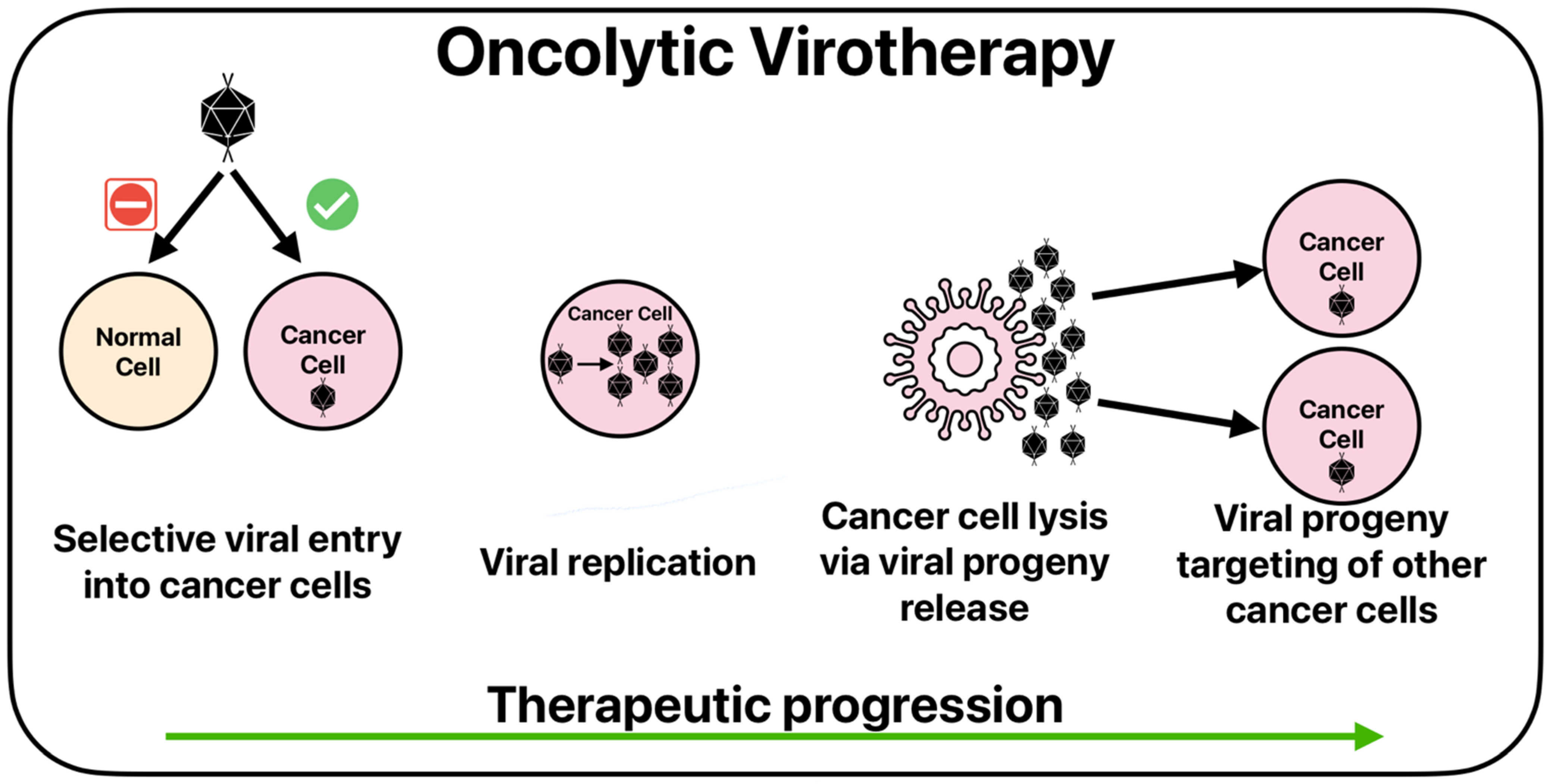
4.2. Oncolytic Viruses
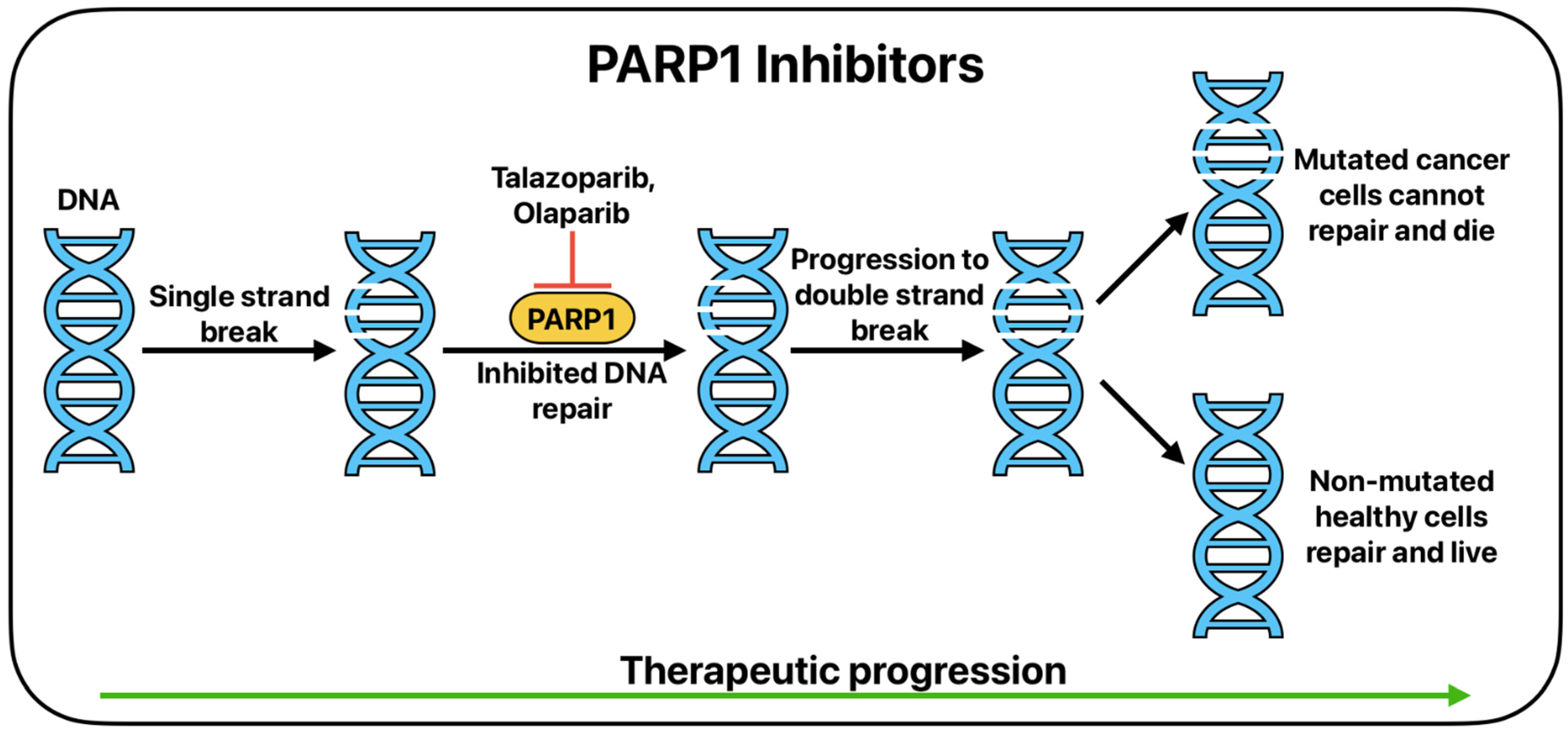
5. Targeted Therapy
6. Bispecific Antibodies
6.1. Bispecific Antibody Structure
6.2. Use in Small Cell Lung Cancer
6.3. DLL3-Targeted
6.4. LAG-3-Targeted
6.5. GD2-Targeted
7. Antibody–Drug Conjugates
7.1. DLL3
7.2. Trophoblastic Cell Surface Antigen (TROP2)
7.3. B7-H3
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer World Health Organization. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/en (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Lung and Bronchus Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, A.K.P.; Loo, B.W.; Bassetti, M.; Blakely, C.; Chiang, A.; D’Amico, T.A.; D’Avella, C.; Dowlati, A.; Downey, R.J.; Edelman, M.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 1441–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Johnson, B.E. Paraneoplastic Syndromes Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2006, 4, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barahman, M.; Shamsaei, G.; Kashipazha, D.; Bahadoram, M.; Akade, E.I. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes of small cell lung cancer. Postępy Psychiatr. Neurologii 2024, 33, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Fennell, D.A.; De Ruysscher, D.K. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megyesfalvi, Z.; Gay, C.M.; Popper, H.; Pirker, R.; Ostoros, G.; Heeke, S.; Lang, C.; Hoetzenecker, K.; Schwendenwein, A.; Boettiger, K.; et al. Clinical insights into small cell lung cancer: Tumor heterogeneity, diagnosis, therapy, and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 620–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Rudin, C.M. Small cell lung cancer: Where do we go from here? Cancer 2015, 121, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.M.; Quintanal-Villalonga, Á.; Gao, V.R.; Xie, Y.; Allaj, V.; Chaudhary, O.; Masilionis, I.; Egger, J.; Chow, A.; Walle, T.; et al. Signatures of plasticity, metastasis, and immunosuppression in an atlas of human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1479–1496.e1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demedts, I.K.; Vermaelen, K.Y.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P. Treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung carcinoma: Current status and future prospects. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Guan, X.; Bao, G.; Yao, Y.; Zhong, X. Molecular subtyping of small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, H.; Ismaila, N.; Bian, J.; Dabney, R.; Das, M.; Ellis, P.; Feldman, J.; Hann, C.; Kulkarni, S.; Laskin, J.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ASCO-Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario) Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5448–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, J.-L.; Daurès, J.-P.; Rivière, A.; Quoix, E.; Westeel, V.; Quantin, X.; Breton, J.-L.; Lemarié, E.; Poudenx, M.; Milleron, B.; et al. Etoposide Plus Cisplatin with or Without the Combination of 4′-Epidoxorubicin Plus Cyclophosphamide in Treatment of Extensive Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A French Federation of Cancer Institutes Multicenter Phase III Randomized Study. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatzer, M.; Schmid, S.; Radovic, M.; Früh, M.; Putora, P.M. The role of radiation therapy in the management of small cell lung cancer. Breathe 2017, 13, e87–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, L.A.; Huskamp, H.A.; Lamont, E.B. Survival and Toxicity After Cisplatin Plus Etoposide Versus Carboplatin Plus Etoposide for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Elderly Patients. J. Oncol. Pract. 2016, 12, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.F.; Raghavan, D.; Stuart-Harris, R.; Morstyn, G.; Aroney, R.; Kefford, R.; Yuen, K.; Lee, J.; Gianoutsos, P.; Olver, I.N. Carboplatin (CBDCA, JM-8) and VP-16-213 in previously untreated patients with small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1987, 5, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Di Maio, M.; Chiodini, P.; Rudd, R.M.; Okamoto, H.; Skarlos, D.V.; Früh, M.; Qian, W.; Tamura, T.; Samantas, E.; et al. Carboplatin- or Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment of Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The COCIS Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kunikane, H.; Yokoyama, A.; Kudoh, S.; Ishizuka, N.; Fukuda, H.; Tamura, T.; Saijo, N. Randomized phase III trial of carboplatin(C) plus etoposide (E) vs. split doses of cisplatin (P) plus etoposide (E) in elderly or poor-risk patients with extensive disease small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC): JCOG9702. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, LBA7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluomini, L.; Pilotto, S.; Avancini, A.; Insolda, J.; Sposito, M.; Menis, J.; Ciccarese, C.; Iacovelli, R.; Ferrara, M.G.; Milella, M.; et al. Maintenance or consolidation therapy in small-cell lung cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Oncol. 2022, 49, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torasawa, M.; Horinouchi, H.; Nomura, S.; Igawa, S.; Asai, M.; Ishii, H.; Wakui, H.; Ushio, R.; Asao, T.; Namba, Y.; et al. Reconsidering the Cutoff Value for Sensitive and Refractory Relapses in Extensive-Stage SCLC in the Era of Immunotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, A.M.; Howlader, N.; Krapcho, M.a.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2015; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018.
- Simos, D.; Sajjady, G.; Sergi, M.; Liew, M.S.; Califano, R.; Ho, C.; Leighl, N.; White, S.; Summers, Y.; Petrcich, W.; et al. Third-Line Chemotherapy in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An International Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriggi, F. Second-Line Treatment Options for Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Light at The End of the Tunnel. Cancers 2024, 16, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Salgia, R. Managing Patients with Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Oncol. Pract. 2018, 14, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Ismaila, N.; Hann, C.L.; Malhotra, N.; Movsas, B.; Norris, K.; Pietanza, M.C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Turrisi, A.T.; Giaccone, G. Treatment of Small-Cell Lung Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the American College of Chest Physicians Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4106–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, A.; Sforza, V.; Carillio, G.; Palumbo, G.; Montanino, A.; Sandomenico, C.; Costanzo, R.; Esposito, G.; Laudato, F.; Mercadante, E.; et al. Lurbinectedin in small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 932105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, M.K.; Alghazwni, M.K.; Alharbi, A.S.; Alqurashi, G.G.; Kamal, M.; Alnufaie, S.R.; Alshammari, S.S.; Alshehri, B.A.; Tayeb, R.H.; Bougeis, R.J.M.; et al. Nanoplatform for the Delivery of Topotecan in the Cancer Milieu: An Appraisal of its Therapeutic Efficacy. Cancers 2023, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles, A.; Calvo, E.; Santamaría Nuñez, G.; Costanzo, F.; José Guillén, M.; Martinez Diez, M.; Gupta, A.; Cuevas, C.; Egly, J.M.; Aviles, P. Unveiling the Mechanism of Lurbinectedin’s Action and Its Potential in Combination Therapies in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde, P.; Payne, D. Does thoracic irradiation improve survival and local control in limited-stage small-cell carcinoma of the lung? A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 10, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignon, J.-P.; Arriagada, R.; Ihde Daniel, C.; Johnson David, H.; Perry Michael, C.; Souhami Robert, L.; Brodin, O.; Joss Rudolf, A.; Kies Merrill, S.; Lebeau, B.; et al. A Meta-Analysis of Thoracic Radiotherapy for Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 327, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Früh, M.; De Ruysscher, D.; Popat, S.; Crinò, L.; Peters, S.; Felip, E. Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, vi99–vi105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Pijls-Johannesma, M.; Bentzen, S.M.; Minken, A.; Wanders, R.; Lutgens, L.; Hochstenbag, M.; Boersma, L.; Wouters, B.; Lammering, G.; et al. Time Between the First Day of Chemotherapy and the Last Day of Chest Radiation Is the Most Important Predictor of Survival in Limited-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijls-Johannesma, M.; De Ruysscher, D.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Kester, A.; Rutten, I.; Lambin, P. Timing of chest radiotherapy in patients with limited stage small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrisi Andrew, T.; Kim, K.; Blum, R.; Sause William, T.; Livingston Robert, B.; Komaki, R.; Wagner, H.; Aisner, S.; Johnson David, H. Twice-Daily Compared with Once-Daily Thoracic Radiotherapy in Limited Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated Concurrently with Cisplatin and Etoposide. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faivre-Finn, C.; Snee, M.; Ashcroft, L.; Appel, W.; Barlesi, F.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bezjak, A.; Cardenal, F.; Fournel, P.; Harden, S.; et al. Concurrent once-daily versus twice-daily chemoradiotherapy in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer (CONVERT): An open-label, phase 3, randomised, superiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maalouf, G.; Rodier, J.-M.; Faivre, S.; Raymond, E. Could we expect to improve survival in small cell lung cancer? Lung Cancer 2007, 57, S30–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotman, B.J.; van Tinteren, H.; Praag, J.O.; Knegjens, J.L.; El Sharouni, S.Y.; Hatton, M.; Keijser, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Senan, S. Use of thoracic radiotherapy for extensive stage small-cell lung cancer: A phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotman, B.J.; Mauer, M.E.; Bottomley, A.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Kramer, G.W.P.M.; Rankin, E.M.; Snee, M.; Hatton, M.; Postmus, P.E.; Collette, L.; et al. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation in Extensive Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Short-Term Health-Related Quality of Life and Patient Reported Symptoms—Results of an International Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial by the EORTC Radiation Oncology and Lung Cancer Groups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Seto, T.; Harada, H.; Nokihara, H.; Saka, H.; Nishio, M.; Kaneda, H.; Takayama, K.; Ishimoto, O.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez De Dios, N. Current and future strategies in radiotherapy for small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2020, 6, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, A.; Botticella, A.; Le Péchoux, C.; Faivre-Finn, C. Thoracic radiotherapy in small cell lung cancer—A narrative review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.; Lang, S.; Rowbottom, C.; Guckenberger, M.; Faivre-Finn, C. Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Developments. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.; Ackerson, B.; Gu, L.; Kelsey, C.R. Dosimetric advantages of intensity modulated radiation therapy in locally advanced lung cancer. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Hui, B.; Ma, X.; Yan, Y.; Xue, C.; Shi, X.; Drokow, E.K.; Ren, J. Dosimetric comparison between IMRT and VMAT in irradiation for peripheral and central lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunte, S.O.; Clark, C.H.; Zyuzikov, N.; Nisbet, A. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT): A review of clinical outcomes—What is the clinical evidence for the most effective implementation? Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20201289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Glatstein, E.; Marks, L.B.; Emami, B.; Grimm, J.; Sperduto, P.W.; Kim, M.-S.; Hui, S.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Cho, L.C. Biological Principles of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) and Stereotactic Radiation Surgery (SRS): Indirect Cell Death. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.; Dieckmann, K.; Hoogeman, M.S.; Hoyer, M.; Hurkmans, C.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Lartigau, E.; Méndez Romero, A.; Senan, S.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on implementation and practice of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, O.; Dincoglan, F.; Demiral, S.; Uysal, B.; Gamsiz, H.; Ozcan, F.; Colak, O.; Elcim, Y.; Gundem, E.; Dirican, B.; et al. Adaptive radiation therapy (ART) for patients with limited-stage small cell lung cancer (LS-SCLC): A dosimetric evaluation. Indian J. Cancer 2023, 60, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Frank, V.; John, W.; Alvaro, M. Adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Qin, Y.; Gao, W.; Tao, L.; Su, W.; Zhong, J. Neoantigen: A New Breakthrough in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massarelli, E.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Welsh, J.; Tang, C.; Tsao, A.S. Immunotherapy in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Wang, X.J. Harnessing the power of the immune system in cancer immunotherapy and cancer prevention. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: From tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D. Does the immune system see tumors as foreign or self? Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 807–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, A.; Maji, A.; Potdar, P.D.; Singh, N.; Parikh, P.; Bisht, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Paul, M.K. Lung cancer immunotherapy: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Chan, L.C.; Song, M.S.; Hung, M.C. New Approaches on Cancer Immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a036863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.; Ustoyev, Y. Cancer and the Immune System: The History and Background of Immunotherapy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 35, 150923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, A.; Mohammed, R.N.; Raji, A.; Chupradit, S.; Yumashev, A.V.; Suksatan, W.; Shalaby, M.N.; Thangavelu, L.; Kamrava, S.; Shomali, N.; et al. Tumor immunotherapies by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs); the pros and cons. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoos, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Korman, A.; Abdallah, K.; Berman, D.; Shahabi, V.; Chin, K.; Canetta, R.; Humphrey, R. Development of ipilimumab: Contribution to a new paradigm for cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Oncol. 2010, 37, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2012, 24, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; Mcdermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Gharibi, T.; Marofi, F.; Babaloo, Z.; Baradaran, B. CTLA-4: From mechanism to autoimmune therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.M.; Ma, Y.; Yin, Z.; Xia, Y.; Du, J.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, J.J.; Zou, L.; Ye, Z.; Huang, Z. Current understanding of CTLA-4: From mechanism to autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1198365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozalo-Sanmillan, S.; Mcnally, J.M.; Lin, M.Y.; Chambers, C.A.; Berg, L.J. Cutting Edge: Two Distinct Mechanisms Lead to Impaired T Cell Homeostasis in Janus Kinase 3- and CTLA-4-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.B.; Yuan, J.; Wolchok, J.D. Targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 in immunotherapies for melanoma and other cancers. Immunotherapy 2010, 2, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, S.I. Role of anti-CTLA-4 therapies in the treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2004, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Hodi, F.S.; Weber, J.S.; Allison, J.P.; Urba, W.J.; Robert, C.; O’Day, S.J.; Hoos, A.; Humphrey, R.; Berman, D.M.; et al. Development of ipilimumab: A novel immunotherapeutic approach for the treatment of advanced melanoma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1291, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriola, E.; Wheater, M.; Galea, I.; Cross, N.; Maishman, T.; Hamid, D.; Stanton, L.; Cave, J.; Geldart, T.; Mulatero, C.; et al. Outcome and Biomarker Analysis from a Multicenter Phase 2 Study of Ipilimumab in Combination with Carboplatin and Etoposide as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Luft, A.; Serwatowski, P.; Barlesi, F.; Chacko, R.; Sebastian, M.; Lu, H.; Cuillerot, J.-M.; Lynch, T.J. Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in extensive-disease-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 2 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Luft, A.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Kim, S.W.; Akerley, W.; Pietanza, M.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Zielinski, C.; Thomas, M.; et al. Phase III Randomized Trial of Ipilimumab Plus Etoposide and Platinum Versus Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z. PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitors in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 731798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezayi, M.; Hosseini, A. Structure of PD1 and its mechanism in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Spigel, D.R.; Cho, B.C.; Laktionov, K.K.; Fang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zenke, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Wang, Q.; Navarro, A.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Limited-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, N.; Farago, A.F.; De Braud, F.; Atmaca, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Schneider, J.G.; Spigel, D.R.; Moreno, V.; Chau, I.; Hann, C.L.; et al. Third-Line Nivolumab Monotherapy in Recurrent SCLC: CheckMate 032. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.C.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Lopez-Martin, J.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Kao, S.; Miller, W.H.; Delord, J.-P.; Gao, B.; Planchard, D.; Gottfried, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab After Two or More Lines of Previous Therapy in Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic SCLC: Results From the KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 Studies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Withdrawn Cancer Accelerated Approvals; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/withdrawn-cancer-accelerated-approvals (accessed on 18 May 2025).
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, A.; Abbas, A.; Chan, T.; Henick, B.; Wang, X.; Doshi, P.; Fu, P.; Patel, J.; Kuo, F.; Chang, H.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Outcome in Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Its Relationship With Retinoblastoma Mutation Status and Function. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Pluzanski, A.; Lee, J.S.; Otterson, G.A.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Minenza, E.; Linardou, H.; Burgers, S.; Salman, P.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Lung Cancer with a High Tumor Mutational Burden. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Kravets, S.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Umeton, R.; Albayrak, A.; Subegdjo, S.J.; Johnson, B.E.; Nishino, M.; Sholl, L.M.; Awad, M.M. Use of targeted next generation sequencing to characterize tumor mutational burden and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition in small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zuo, M.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y. Oncolytic virotherapy in cancer treatment: Challenges and optimization prospects. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1308890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Li, Z.; Chiocca, E.A.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Yu, J. The emerging field of oncolytic virus-based cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Guo, H.; Lin, L.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, J. Application of oncolytic virus in tumor therapy. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Tian, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, R.; Dong, W.; Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Antonio Chiocca, E.; Kaur, B.; et al. An oncolytic virus expressing a full-length antibody enhances antitumor innate immune response to glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jou, T.H.-T.; Hsin, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Ye, J.; Yin, H.; Xing, Y. Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC): A Review of the Recent Advances in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. Teserpaturev/G47Δ: First Approval. BioDrugs 2022, 36, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fang, J.; Chu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Xiu, Z.; Jin, N.; Zhu, G.; et al. In vivo and in vitro inhibition of SCLC by combining dual cancer-specific recombinant adenovirus with Etoposide. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellish, P.; Shabashvili, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Nawab, A.; Guijarro, M.V.; Zhang, M.; Cao, C.; Moussatche, N.; Boyle, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. Oncolytic virotherapy for small-cell lung cancer induces immune infiltration and prolongs survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.S.; Burroughs, K.D.; Hales, L.M.; Ganesh, S.; Jones, B.H.; Idamakanti, N.; Hay, C.; Li, S.S.; Skele, K.L.; Vasko, A.-J.; et al. Seneca Valley Virus, a Systemically Deliverable Oncolytic Picornavirus, and the Treatment of Neuroendocrine Cancers. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Poirier, J.T.; Senzer, N.N.; Stephenson, J.; Loesch, D.; Burroughs, K.D.; Reddy, P.S.; Hann, C.L.; Hallenbeck, P.L. Phase I Clinical Study of Seneca Valley Virus (SVV-001),a Replication-Competent Picornavirus, in Advanced Solid Tumors with Neuroendocrine Features. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, W.J.; Paz-Ares, L. Emerging Strategies for the Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Barayan, R.; Louie, A.; Lok, B. Novel therapeutic combinations with PARP inhibitors for small cell lung cancer: A bench-to-bedside review. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Evers, G.; Kerkhoff, A.; Mohr, M.; Schliemann, C.; Berdel, W.; Schmidt, L. Future Options of Molecular-Targeted Therapy in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barayan, R.; Ran, X.; Lok, B. PARP inhibitors for small cell lung cancer and their potential for integration into current treatment approaches. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6240–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, C.; Guo, X.; Feng, L.; Yu, Z. PARP inhibitors in small cell lung cancer: The underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, A.; Hage Chehade, C.; Ozay, Z.I.; Nordblad, B.; Swami, U.; Agarwal, N. Talazoparib for the treatment of prostate cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2024, 25, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Talazoparib: First global approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, C.; Rienzo, A.; Piscopo, G.; Barbieri, A.; Arra, C.; Maurea, N. Management of QT prolongation induced by anti-cancer drugs: Target therapy and old agents. Different algorithms for different drugs. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 63, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, G.; Howie, L.; Amiri-Kordestani, L.; Zhang, L.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Pierre, V.; Charlab, R.; Ramamoorthy, A.; Song, P.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Niraparib for the Maintenance Treatment of Patients with Recurrent Ovarian Cancer in Response to Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatore, C.; Lareau, S. Lung Cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, P19–P20. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, A.; Attili, I.; Pasello, G.; Guarneri, V.; Conte, P.F.; Bonanno, L. Immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: From molecular promises to clinical challenges. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenova, E.; Nagel, R.; Berns, A. Origins, genetic landscape, and emerging therapies of small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1447–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, J.; Lok, B.; Laird, J.; Poirier, J.; Rudin, C. Unravelling the biology of SCLC: Implications for therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, B.H.; Gardner, E.E.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Ni, A.; Desmeules, P.; Rekhtman, N.; de Stanchina, E.; Teicher, B.A.; Riaz, N.; Powell, S.N.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Activity Correlates with SLFN11 Expression and Demonstrates Synergy with Temozolomide in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erice, O.; Smith, M.; White, R.; Goicoechea, I.; Barriuso, J.; Jones, C.; Margison, G.; Acosta, J.; Wellbrock, C.; Arozarena, I. MGMT Expression Predicts PARP-Mediated Resistance to Temozolomide. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Mina, L.; Chugh, R.; Glaspy, J.; Rafii, S.; Kaye, S.; Sachdev, J.; Heymach, J.; Smith, D.C.; et al. Phase I, Dose-Escalation, Two-Part Trial of the PARP Inhibitor Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Germline BRCA1/2 Mutations and Selected Sporadic Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Mortimer, P.G.; Smith, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. The clinical efficacy of olaparib monotherapy or combination with ceralasertib (AZD6738) in relapsed small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Pan, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, N.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; He, J.; Li, X.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Niraparib as Maintenance Treatment in Patients With Extensive-Stage SCLC After First-Line Chemotherapy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegaki, N.; Katsumata, M.; Minna, J.; Tsujimoto, Y. Expression of bcl-2 in small cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.X.; Sato, Y.; Kuwao, S.; Kameya, T. Expression of bcl-2 oncogene protein is prevalent in small cell lung carcinomas. J. Pathol. 1995, 177, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ezra, J.M.; Kornstein, M.J.; Grimes, M.M.; Krystal, G. Small cell carcinomas of the lung express the Bcl-2 protein. Am. J. Pathol. 1994, 145, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Lochmann, T.L.; Bouck, Y.M.; Faber, A.C. BCL-2 inhibition is a promising therapeutic strategy for small cell lung cancer. Oncoscience 2018, 5, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.K.; Yang, X.; Anderson, M.G.; Morgan-Lappe, S.E.; Sarthy, A.V.; Chen, J.; Warner, R.B.; Ng, S.-C.; Fesik, S.W.; Elmore, S.W. Influence of Bcl-2 family members on the cellular response of small-cell lung cancer cell lines to ABT-737. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, A.; Mitten, M.; Adickes, J.; Ackler, S.; Refici, M.; Ferguson, D.; Oleksijew, A.; O’Connor, J.; Wang, B.; Frost, D.; et al. Activity of the Bcl-2 Family Inhibitor ABT-263 in a Panel of Small Cell Lung Cancer Xenograft Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3268–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisonoff, A.; Rivers, M.M. Recombination of a mixture of univalent antibody fragments of different specificity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1961, 93, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milstein, C.; Cuello, A.C. Hybrid Hybridomas and Their Use in Immunohistochemistry. Nature 1983, 305, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Minari, R.; Cortellini, A.; Rolfo, C.D.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Notch Pathway in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: From Preclinical Evidence to Therapeutic Challenges. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 42, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Borghaei, H.; Champiat, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Govindan, R.; Boyer, M.; Johnson, M.L.; Udagawa, H.; Hummel, H.-D.; Salgia, R.; et al. Phase I Study of AMG 757, a Half-Life Extended Bispecific T-Cell Engager (HLE BiTE Immune Therapy) Targeting DLL3, in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Champiat, S.; Lai, W.V.; Izumi, H.; Govindan, R.; Boyer, M.; Hummel, H.-D.; Borghaei, H.; Johnson, M.L.; Steeghs, N.; et al. Tarlatamab, a First-in-Class DLL3-Targeted Bispecific T-Cell Engager, in Recurrent Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipp, S.; Voynov, V.; Drobits-Handl, B.; Giragossian, C.; Trapani, F.; Nixon, A.E.; Scheer, J.M.; Adam, P.J. A Bispecific DLL3/CD3 IgG-Like T-Cell Engaging Antibody Induces Antitumor Responses in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5258–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermke, M.; Felip, E.; Kuboki, Y.; Morgensztern, D.; Sayehli, C.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Arriola, E.; Oum’Hamed, Z.; Song, E.; Studeny, M.; et al. First-in-Human Dose-Escalation Trial of BI 764532, a Delta-like Ligand 3 (DLL3)/CD3 IgG-like T-Cell Engager in Patients (Pts) with DLL3-Positive (DLL3+) Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) and Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (NEC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Fang, D.; Lobsinger, M.; Long, Y.; Chen, K.; Lam, A.; Guo, Y.; Selesniemi, K.; Wang, M.; Zou, H. Abstract 2908: PT217, an Anti-DLL3/Anti-CD47 Bispecific Antibody, Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity through Novel Mechanisms of Action. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Du, Q.; Jin, J.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Q. LAG3 and Its Emerging Role in Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solinas, C.; Migliori, E.; De Silva, P.; Willard-Gallo, K. LAG3: The Biological Processes That Motivate Targeting This Immune Checkpoint Molecule in Human Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triebel, F.; Jitsukawa, S.; Baixeras, E.; Roman-Roman, S.; Genevee, C.; Viegas-Pequignot, E.; Hercend, T. LAG-3, a Novel Lymphocyte Activation Gene Closely Related to CD4. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, S.D.; Shin, H.; Haining, W.N.; Zou, T.; Workman, C.J.; Polley, A.; Betts, M.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Vignali, D.A.A.; Wherry, E.J. Coregulation of CD8+ T Cell Exhaustion by Multiple Inhibitory Receptors during Chronic Viral Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.K.; Sugiura, D.; Okazaki, I.; Maruhashi, T.; Okazaki, T. Atypical Motifs in the Cytoplasmic Region of the Inhibitory Immune Co-Receptor LAG-3 Inhibit T Cell Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 6017–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, G.; Cheresh, D.A.; Varki, N.M.; Yu, A.; Staffileno, L.K.; Reisfeld, R.A. Detection of Ganglioside GD2 in Tumor Tissues and Sera of Neuroblastoma Patients. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esaki, N.; Ohkawa, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Tsuda, Y.; Ohmi, Y.; Bhuiyan, R.H.; Kotani, N.; Honke, K.; Enomoto, A.; Takahashi, M.; et al. ASC Amino Acid Transporter 2, Defined by Enzyme-Mediated Activation of Radical Sources, Enhances Malignancy of GD2-Positive Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Tarlatamab-Dlle for Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Baine, M.K.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Lai, W.V.; Egger, J.V.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Daneshbod, Y.; Beras, A.; Spencer, R.S.; Lopardo, J.; Bodd, F.M.; et al. SCLC Subtypes Defined by ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1: A Comprehensive Immunohistochemical and Histopathologic Characterization. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Park, E.M.; Diao, L.; Groves, S.M.; Heeke, S.; Nabet, B.Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis, L.M.; Lu, W.; et al. Patterns of Transcription Factor Programs and Immune Pathway Activation Define Four Major Subtypes of SCLC with Distinct Therapeutic Vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, P.; Tang, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, N. The current status and future of ADC therapy for small cell Lung Cancer: A promising approach. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.; Giffin, M.; Bailis, J.; Smit, M.-A.; Carbone, D.; He, K. DLL3: An emerging target in small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluomini, L.; Sposito, M.; Avancini, A.; Insolda, J.; Milella, M.; Rossi, A.; Pilotto, S. Unlocking New Horizons in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treatment: The Onset of Antibody–Drug Conjugates. Cancers 2023, 15, 5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cao, D.; Sha, J.; Zhu, X.; Han, S. DLL3 is regulated by LIN28B and miR-518d-5p and regulates cell proliferation, migration and chemotherapy response in advanced small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (BBRC) 2019, 514, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, B.; Vallatharasu, Y.; Kolandra, L.; Hamid, M.; Uprety, D. Rovalpituzumab Tesirine: A Novel DLL3-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate. Drugs R D 2018, 18, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.; Reck, M.; Johnson, M.; Blackhall, F.; Hann, C.; Yang, J.-H.; Bailis, J.; Bebb, G.; Goldrick, A.; Umejiego, J.; et al. Emerging therapies targeting the delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3) in small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.; Pietanza, M.; Bauer, T.; Ready, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Glisson, B.; Byers, L.; Johnson, M.; Burris, H.; Robert, F.; et al. Rovalpituzumab tesirine, a DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate, in recurrent small-cell lung cancer: A first-in-human, first-in-class, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgensztern, D.; Besse, B.; Greillier, L.; Santana-Davila, R.; Ready, N.; Hann, C.; Glisson, B.; Farago, A.; Dowlati, A.; Rudin, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in Third-Line and Beyond Patients with DLL3-Expressing, Relapsed/Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the Phase II TRINITY Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6958–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackhall, F.; Jao, K.; Greillier, L.; Cho, B.; Penkov, K.; Reguart, N.; Majem, M.; Nackaerts, K.; Syrigos, K.; Hansen, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine Compared With Topotecan as Second-Line Therapy in DLL3-High SCLC: Results From the Phase 3 TAHOE Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zvirbule, Z.; Laktionov, K.; Helland, A.; Cho, B.; Gutierrez, V.; Colinet, B.; Lena, H.; Wolf, M.; Gottfried, M.; et al. Rovalpituzumab Tesirine as a Maintenance Therapy After First-Line Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Patients With Extensive-Stage–SCLC: Results From the Phase 3 MERU Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.; Remon, J.; Adjei, A. All That Glitters Is Not Gold: The Story of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shvartsur, A.; Bonavida, B. Trop2 and its overexpression in cancers: Regulation and clinical/ therapeutic implications. Genes Cancer 2014, 6, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; Yu, M.; Li, L.; Liang, Y.; Kong, F. Antibody–drug conjugates treatment of small cell lung cancer: Advances in clinical research. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Messersmith, W.A.; Kio, E.A.; Berlin, J.D.; Vahdat, L.; Masters, G.A.; Moroose, R.; Santin, A.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Picozzi, V.; et al. Sacituzumab govitecan, a Trop-2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, for patients with epithelial cancer: Final safety and efficacy results from the phase I/II IMMU-132-01 basket trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, A.; Cervantes, A.; Babu, S.; Hamilton, E.P.; Wong, S.F.; Tazbirkova, A.; Sullivan, I.G.; Van Marcke de Lummen, C.; Italiano, A.; Patel, J.; et al. 1990MO Sacituzumab govitecan (SG) as second-line (2L) treatment for extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC): Preliminary results from the phase II TROPiCS-03 basket trial. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1061–S1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, T.; Zalath, M.; Arrojo, R.; Sharkey, R.; Govindan, S.; Chang, C.-H.; Goldenberg, D. Sacituzumab govitecan plus platinum-based chemotherapy mediates significant antitumor effects in triple-negative breast, urinary bladder, and small-cell lung carcinomas. Oncotarget 2024, 15, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabrizio, F.; Muscarella, L.; Rossi, A. B7-H3/CD276 and small-cell lung cancer: What’s new? Transl. Oncol. 2024, 39, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Patel, M.; Falchook, G.S.; Koyama, T.; Friedman, C.F.; Piha-Paul, S.; Gutierrez, M.E.; Abdul-Karim, R.; Awad, M.; Adkins, D.R.; et al. 453O DS-7300 (B7-H3 DXd antibody-drug conjugate [ADC]) shows durable antitumor activity in advanced solid tumors: Extended follow-up of a phase I/II study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S744–S745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Awad, M.; Koyama, T.; Gutierrez, M.; Falchook, G.S.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Doi, T.; Satoh, T.; Okamoto, N.; Singh, J.; et al. OA05.05 Ifinatamab Deruxtecan (I-DXd; DS-7300) in Patients with Refractory SCLC: A Subgroup Analysis of a Phase 1/2 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S54–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serani, S. Phase 2 Study Reveals Encouraging Results for i-DXD in ES-SCLC; Targeted Oncology: East Windsor, NJ, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.targetedonc.com/view/phase-2-study-reveals-encouraging-results-for-i-dxd-in-es-sclc (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Chan, A. IFINATAMAB Deruxtecan Shows Improved Clinical Activity at Higher Dose in ES-SCLC; OncLive: Cranbury, NJ, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.onclive.com/view/ifinatamab-deruxtecan-shows-improved-clinical-activity-at-higher-dose-in-es-sclc (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Owonikoko, T.; Byers, L.; Cheng, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Perol, M.; Turner, J.; Qian, M.; Garcia, C.; Godard, J.; et al. IDeate-Lung02: A phase 3, randomized, open-label study of ifinatamab deruxtecan (I-DXd) vs treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) in relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. (JCO) 2024, 42, TPS8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Trial Identifier/Authors | Treatment Modality | Clinical Setting | Treatment Setting | Outcome(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02763579/Horn et al. [22] | Atezolizumab plus carboplatin and etoposide | Patients with ES-SCLC with previous treatment failure | 1200 mg atezolizumab on day 1 of each 21 day cycle for 4 cycles, followed by atezolizumab until toxicity or progression | Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy achieved a median PFS of 12.3 months compared to 10.9 months in the chemotherapy plus placebo |
| NCT03043872/Paz-Ares et al. [23] | Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in combination with EP | Patients with untreated ES-SCLC | 1500 mg durvalumab with or without tremelimumab 75 mg EP every 3 weeks for 4 cycles followed by 1500 mg durvalumab | Durvalumab plus chemotherapy achieved a median OS of 13.0 months versus 10.3 months in the chemotherapy group |
| NCT01331525/Arriola et al. [75] | Ipilimumab plus carboplatin and etoposide | Chemotherapy naïve ES-SCLC | 10 mg/kg ipilimumab day 1 of chemotherapy cycles 3 and 6, then once every 12 weeks after week 30 | Ipilimumab had an objective response rate of 84.8% and a median immune-related progression free survival of 7.3 months |
| NCT00527735/Reck et al. [76] | Ipilimumab plus paclitaxel and carboplatin (PC) | Chemotherapy naïve ES-SCLC | Phased or concurrent 10 mg/kg ipilimumab with PC every 3 weeks for 18 weeks, followed by ipilimumab every 12 weeks | Phased ipilimumab had an OS of 12.9 months vs. control of 9.9 months. Concurrent ipilimumab had a median OS of 9.1 months |
| NCT01450761/Reck et al. [77] | Ipilimumab plus EP | Patients with ES-SCLC | 10 mg/kg ipilimumab with EP every three weeks for four cycles | Ipilimumab plus chemotherapy had a median OS of 11.0 months compared to 10.9 months in control group |
| NCT03703297/ Cheng et al. [80] | Durvalumab plus tremelimumab vs. placebo | LS-SCLC that displayed resistance to chemoradiotherapy | 1500 mg durvalumab plus 75 mg tremelimumab or placebo every four weeks for 24 months | Durvalumab plus tremelimumab had a median OS of 55.5 months vs. 33.4 months in placebo |
| NCT01928394/Ready et al. [81] | Nivolumab monotherapy | LS-SCLC and ES-SCLC with disease progression who failed two or more chemotherapy regimens | 3 mg/kg nivolumab every two weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity | Nivolumab monotherapy achieved an 11.9% objective response rate and a median duration of response of 17.9 months |
| NCT02054806/NCT02628067/Chung et al. [82] | Pembrolizumab monotherapy | Recurrent or metastatic SCLC who failed two or more previous treatment methods | 10 mg/kg pembrolizumab every 2 weeks or 200 mg every 3 weeks for up to 2 years | Pembrolizumab monotherapy achieved a 19.3% objective response rate with two patients achieving a complete response |
| NCT03066778/Rudin et al. [84] | Pembrolizumab plus EP | Stage IV SCLC not previously treated with systemic therapy | 200 mg pembrolizumab once every 3 weeks for up to 35 cycles with 4 cycles of EP | 12-month PFS estimates in pembrolizumab plus EP was 13.6% vs. 3.1% in control plus EP |
| Clinical Trial Identifier/Authors | Treatment Modality | Clinical Setting | Treatment Setting | Outcome(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01286987/Bono et al. [114] | Talazoparib based monotherapy | Recurrent SCLC patients | Administered 1.0 mg talazoparib daily. | Talazoparib gave SCLC patients with BRCA mutations the highest objective response rate of 40%. 9% of patients had a partial response for 3–4 months. |
| NCT03009682/Park et al. [115] | Olaparib based monotherapy | Patients who failed prior platinum-based regimen with mutations harboring homologous recombination pathway gene mutation | Olaparib 300 mg twice a day every 12 h administered daily. | Olaparin monotherapy gave an objective response rate of 6.7%. Disease control rate was 26.7%. Median progression-free survival was 1.25 months and median overall survival was 8.56 months. |
| NCT03516084/Ai et al. [116] | Niraparib based monotherapy | Patients with complete response or partial response to standardized, platinum-based first-line chemotherapy | 300 mg niraparib if baseline body weight ≥ 77 kg or platelet count ≥ 150,000/μL. Otherwise, 200 mg niraparib once daily until progression or unacceptable toxicity. | Median progression free survival was 1.54 months. Median overall survival was 9.92 months. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corica, D.A.; Bell, S.D.; Zhao, L.; Lawler, N.J.; Poirier, M.A.; Miller, P.J.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The Era of Precision Medicine: Advancing Treatment Paradigms for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111847
Corica DA, Bell SD, Zhao L, Lawler NJ, Poirier MA, Miller PJ, Wakefield MR, Fang Y. The Era of Precision Medicine: Advancing Treatment Paradigms for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111847
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorica, Derek A., Scott D. Bell, Lei Zhao, Nicholas J. Lawler, McKade A. Poirier, Peyton J. Miller, Mark R. Wakefield, and Yujiang Fang. 2025. "The Era of Precision Medicine: Advancing Treatment Paradigms for Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111847
APA StyleCorica, D. A., Bell, S. D., Zhao, L., Lawler, N. J., Poirier, M. A., Miller, P. J., Wakefield, M. R., & Fang, Y. (2025). The Era of Precision Medicine: Advancing Treatment Paradigms for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(11), 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111847






