Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation in Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Guidelines and PICO
- Participants: patients with IP malignant transformation;
- Intervention/Index: risk factor exposure;
- Comparison: IP without malignant transformation;
- Outcome: number of malignant transformations in exposed vs. non-exposed individuals.
2.2. Protocol Registration
2.3. Search Strategy
- sinonasal inverted papilloma;
- malignant transformation.
- 1.
- PubMed
- 2.
- Embase
2.4. Selection of Articles
2.5. Eligibility Criteria
- Observational and interventional studies, cohort studies, in English, with any publication date, from any country.
- Patients above 18 years of age presenting with a histologically proven diagnosis of sinonasal inverted papilloma and malignant transformation, either synchronous (present at the time of initial diagnosis) or metachronous (during follow-up).
- Documented exposure to risk factors with at least one of the following:
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Infectious agents (i.e., viruses)
- Professional exposure (i.e., exposure to chemicals or substances specifically related to a determined occupational activity, such as dusts or solvents).
- Comparison of the incidence of malignant transformation between exposed and non-exposed individuals. The comparison may be documented either by the number of individuals affected by malignancy compared to those who did not have malignancy or by odds ratio. Odds ratio values had to be clearly expressed in the main text, tables, figures, or Supplementary Tables/Materials.
- Studies reporting case series with fewer than 5 participants.
- Only malignant transformed cases with no comparison with non-transformed (benign) cases.
- No adequate comparisons with non-exposed individuals.
- Studies with unclear diagnostic methods.
- Selected populations (i.e., only geriatric cases or only cases from a specific topography)
- Studies including non-consecutive cases, but only selected cases (possible selection biases).
- Foreign language (not English).
- Discussion papers (i.e., reviews, both narrative and systematic), with no new cases described.
- Cases including only carcinoma in situ with no invasive component in the evaluation of malignant transformation.
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
- Selection (four items with a maximum of four stars).
- Is the case definition adequate?
- Representativeness of the cases
- Selection of controls
- Definition of controls
- Comparability (one item with a maximum of two stars)
- Comparability of cases and controls on the basis of the design or analysis
- Exposure (three items with a maximum of three stars)
- Ascertainment of exposure
- Same method of ascertainment for cases and controls
- Non-response rate
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Quality of Evidence
3. Results
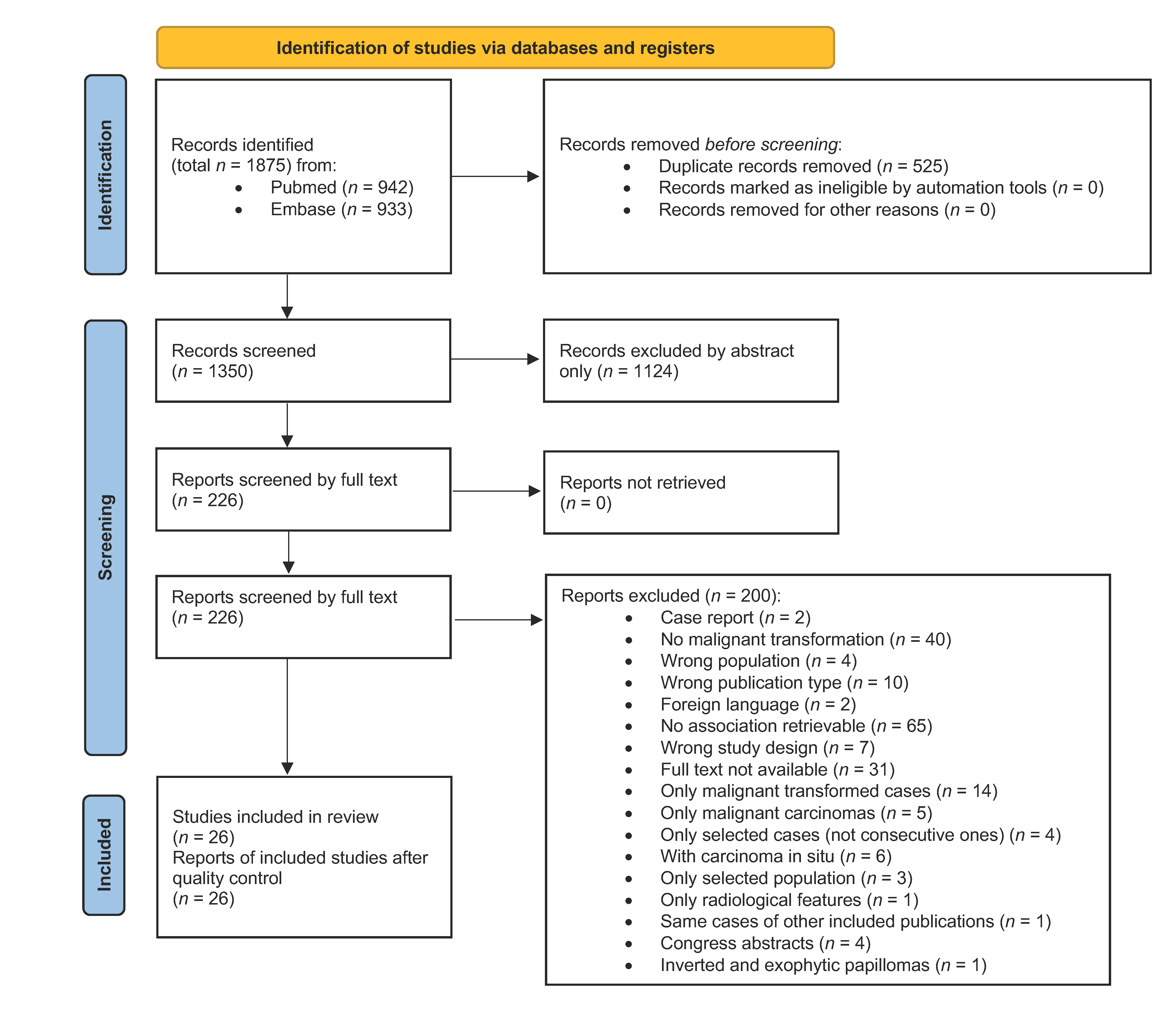
3.1. Article Selection
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Population Examined
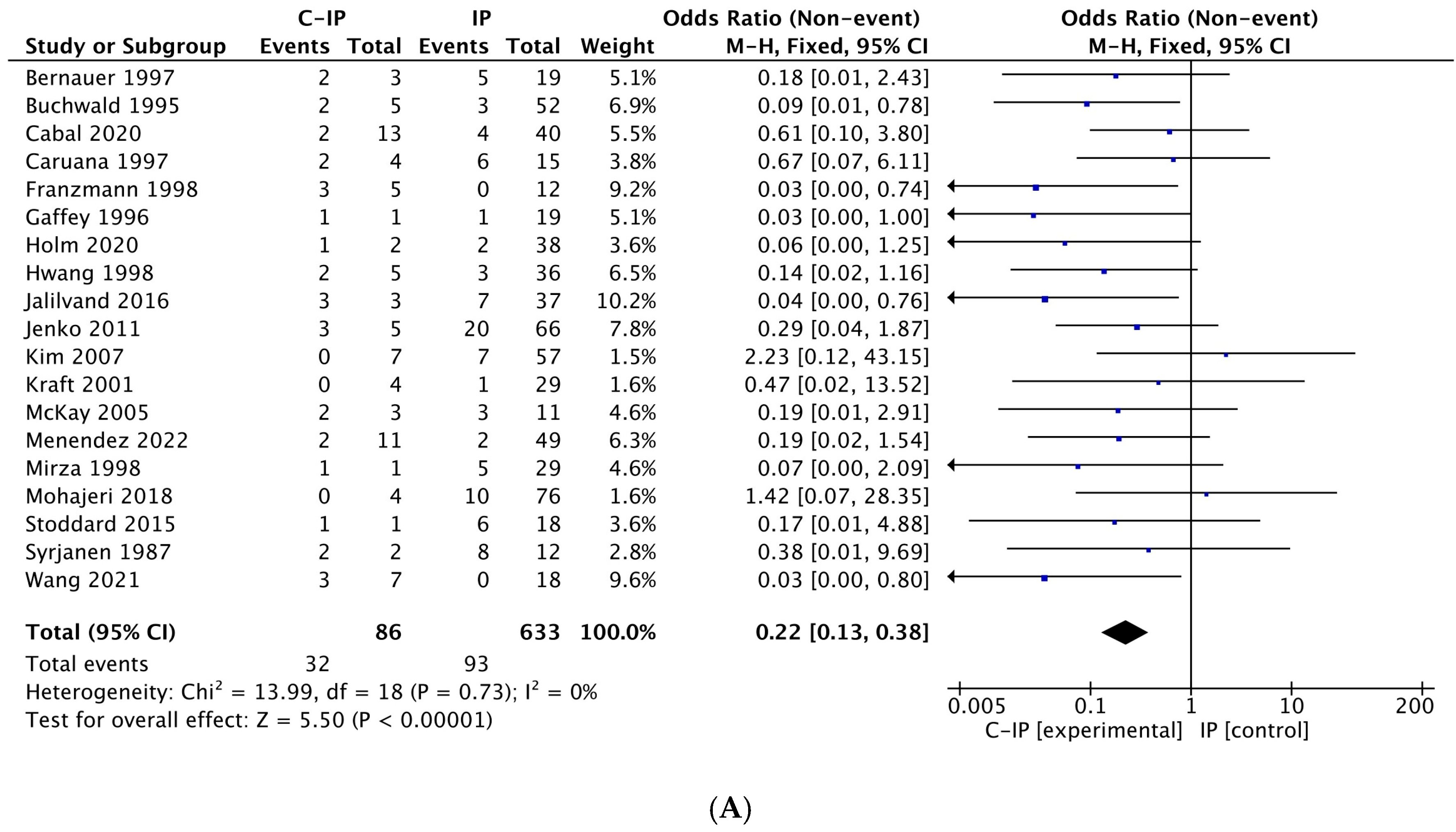
3.4. Meta-Analysis Results
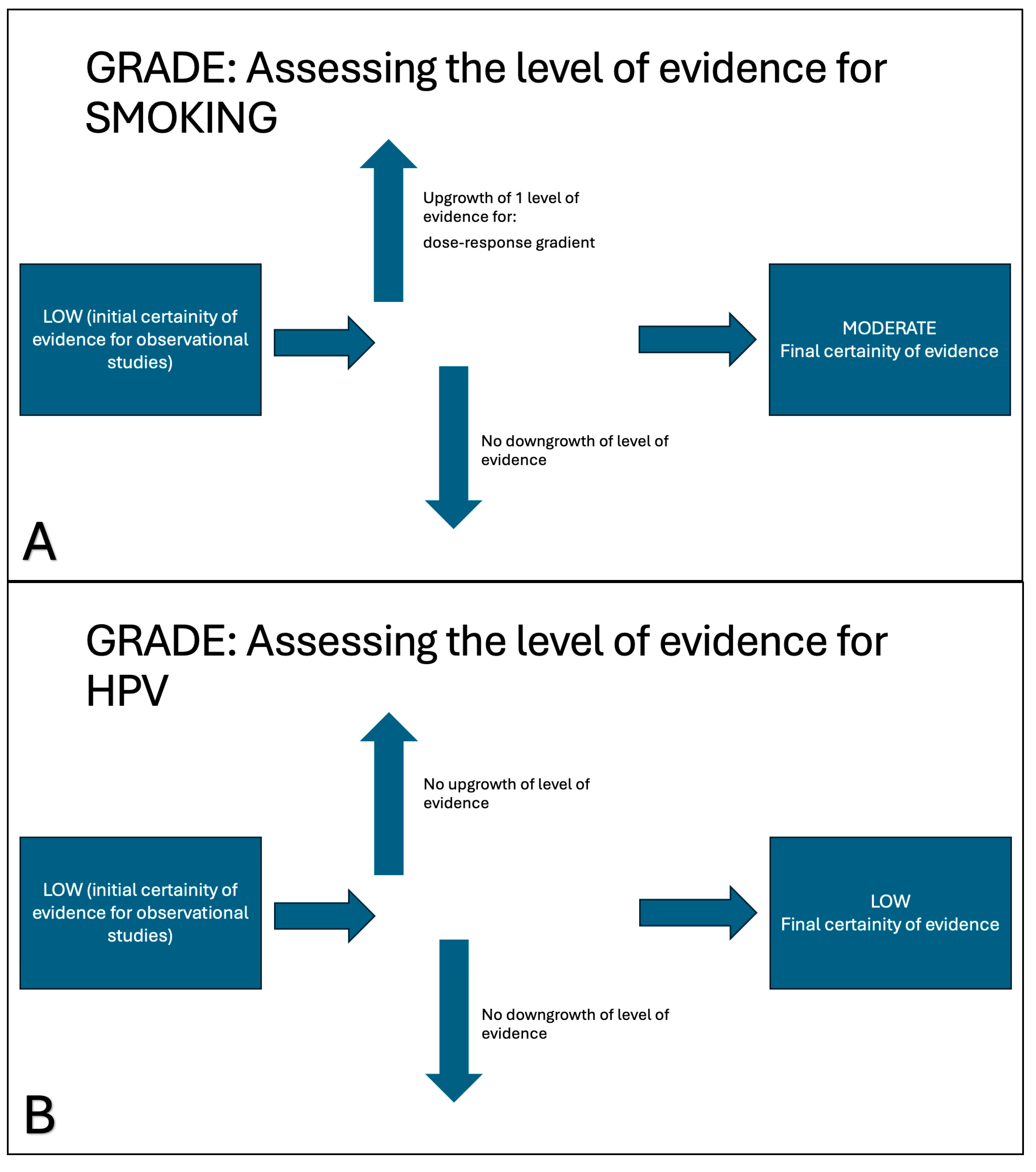
- The evidence for HPV as a significant risk factor is robust, with the lack of heterogeneity further strengthening confidence in its oncogenic role.
- Smoking is confirmed as a significant risk factor, although the moderate degree of variability warrants careful consideration, especially given the limited number of studies.
- Alcohol consumption is not a relevant risk factor in this context.
3.5. Quality of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IP | Inverted Papilloma |
| C-IP | Carcinoma in Inverted Papilloma |
| HPV | Human Papillomavirus |
| EBV | Epstein-Barr Virus |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| NOS | Newcastle–Ottawa Scale |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation |
References
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Head and Neck Tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 9, ISBN 978-92-832-4514-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Noel, J.E. Etiology of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Narrative Review. World J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2017, 3, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Jabarin, B.; Harvey, A.; Ham, J.; Javer, A.; Janjua, A.; Thamboo, A. Clinical Evidence Based Review and Systematic Scientific Review in the Identification of Malignant Transformation of Inverted Papilloma. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2020, 49, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudell, J.; Chiosea, S.; Thompson, L.D.R. Carcinoma Ex-Schneiderian Papilloma (Malignant Transformation): A Clinicopathologic and Immunophenotypic Study of 20 Cases Combined with a Comprehensive Review of the Literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2014, 8, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun Sham, C.; Lee, D.L.Y.; Van Hasselt, C.A.; Tong, M.C.F. A Case-Control Study of the Risk Factors Associated with Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, e37–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Suh, M.-W.; Han, D.H.; Kim, S.-T.; Min, Y.-G.; Lee, C.H.; Rhee, C.-S. Cigarette Smoking Increases Risk of Recurrence for Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, W.H.; Farzal, Z.; Kimple, A.J.; Ebert, C.S.; Senior, B.A.; Zanation, A.M.; Thorp, B.D. HPV in the Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papillomas: A Meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.-W.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Zhang, R.-X. Human Papillomavirus Infection and the Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 79, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreli, F.; Di Bari, M.; Moya-Plana, A.; Canzano, F.; Morenghi, E.; De Virgilio, A.; Mercante, G.; Spriano, G.; Colombo, G. Association between Human Papillomavirus Infection and Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer Program]. Version 5.4. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2020. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/online-learning/core-software/revman (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Higgins, J.P.T. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M. Introduction to the GRADE Tool for Rating Certainty in Evidence and Recommendations. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2024, 25, 101484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.C.L.; Lin, X.; Seckar, T.; Koptyra, M.; Kohanski, M.A.; Cohen, N.A.; Kennedy, D.W.; Adappa, N.D.; Papagiannopoulos, P.; Kuan, E.C.; et al. A Metagenomic Analysis of the Virome of Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023, 13, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eavey, R.D. Inverted Papilloma of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses in Childhood and Adolescence. Laryngoscope 1985, 95, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elner, V.M.; Burnstine, M.A.; Goodman, M.L.; Dortzbach, R.K. Inverted Papillomas That Invade the Orbit. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1995, 113, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valibeigi, B.; Ashraf, M.J.; Kerdegari, N.; Safai, A.; Abedi, E.; Khademi, B.; Azarpira, N. Prevalence of Human Papilloma Virus in Sinonasal Papilloma in Southern Iranian Population. J. Dent. 2017, 18, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrad, M.; Stelow, E.; Lewis, J. Transcriptionally-Active Low-Risk HPV in Sinonasal Inverted Papillomas; Closing the Chapter. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Ottini, G.; Facco, C.; Sahnane, N.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; Cerutti, R.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Karligkiotis, A.; Albeni, C.; Lettig, L.; Catselnuovo, P.; et al. HPV and EGFR Mutation in Schneiderian Papillomas and Related SCC: Who Plays the Games? Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 482. [Google Scholar]
- Stepp, W.H.; Kimple, A.J.; Ebert, C.S.; Senior, B.; Thorp, B.D. The Role of Integration and HPV Status in Malignant Transformation of Inverted Papillomas. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2022, 83, A016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Deng, Z.; Hasegawa, M. Importance of Human Papillomavirus Integration in Malignant Transformation of Inverted Papilloma. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2014, 151, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archang, M.; Chew, L.; Han, A.Y.-K.; Sajed, D.; Vorasubin, N.; Wang, M. Sinonasal Papillomas: 10-Year Retrospective Analysis of Etiology, Epidemiology, and Recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 36, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, H.S.; Welkoborsky, H.-J.; Tilling, A.; Amedee, R.G.; Mann, W.J. Inverted Papillomas of the Paranasal Sinuses and the Nasal Cavity: DNA Indices and HPV Infection. Am. J. Rhinol. 1997, 11, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchwald, C.; Franzmann, M.; Jacobsen, G.K.; Lindeberg, H. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in Sinonasal Papillomas: A Study of 78 Cases Using in Situ Hybridization and Polymerase Chain Reaction. Laryngoscope 1995, 105, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabal, V.N.; Menendez, M.; Vivanco, B.; Potes-Ares, S.; Riobello, C.; Suarez-Fernandez, L.; Garcia-Marin, R.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Lopez, F.; Alvarez-Marcos, C.; et al. EGFR Mutation and HPV Infection in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Rhinology 2020, 58, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, S.M.; Zwiebel, N.; Cocker, R.; McCormick, S.A.; Eberle, R.C.; Lazarus, P. P53 Alteration and Human Papilloma Virus Infection in Paranasal Sinus Cancer. Cancer 1997, 79, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzmann, M.-B.; Buchwald, C.; Jacobsen, G.K.; Lindeberg, H. Expression of P53 in Normal Nasal Mucosa and in Sinonasal Papillomas with and without Associated Carcinoma and the Relation to Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Cancer Lett. 1998, 128, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffey, M.J.; Frierson, H.F.; Weiss, L.M.; Barber, C.M.; Baber, G.B.; Stoler, M.H. Human Papillomavirus and Epstein-Barr Virus in Sinonasal Schneiderian Papillomas: An In Situ Hybridization and Polymerase Chain Reaction Study. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 106, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, A.; Allard, A.; Eriksson, I.; Laurell, G.; Nylander, K.; Olofsson, K. Absence of High-Risk Human Papilloma Virus in P16 Positive Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2020, 137, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.; Cho, K.; Roh, H. Smoking and Malignancy in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.S.; Yang, H.S.; Hong, M.K. Detection of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in Sinonasal Inverted Papillomas Using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Am. J. Rhinol. 1998, 12, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilvand, S.; Saidi, M.; Shoja, Z.; Ghavami, N.; Hamkar, R. The Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Infection in Iranian Patients with Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenko, K.; Kocjan, B.; Zidar, N.; Poljak, M.; Strojan, P.; Žargi, M.; Blatnik, O.; Gale, N. In Inverted Papillomas HPV More Likely Represents Incidental Colonization than an Etiological Factor. Virchows Arch. 2011, 459, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Yoon, J.-K.; Citardi, M.J.; Batra, P.S.; Roh, H.-J. The Prevalence of Human Papilloma Virus Infection in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma Specimens Classified by Histological Grade. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, M.; Simmen, D.; Casas, R.; Pfaltz, M. Significance of Human Papillomavirus in Sinonasal Papillomas. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2001, 115, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D. ErbB1 and ErbB2 Overexpression in Patients with Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Inverted Papilloma with Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2019, 139, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, S.P.; Grégoire, L.; Lonardo, F.; Reidy, P.; Mathog, R.H.; Lancaster, W.D. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Transcripts in Malignant Inverted Papilloma Are from Integrated HPV DNA. Laryngoscope 2005, 115, 1428–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez Del Castro, M.; Naves Cabal, V.; Vivanco, B.; Suárez-Fernández, L.; López, F.; Llorente, J.L.; Hermsen, M.A.; Álvarez-Marcos, C. Loss of P16 Expression Is a Risk Factor for Recurrence in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Rhinology 2022, 60, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, N.; Montone, K.; Sato, Y.; Kroger, H.; Kennedy, D.W. Identification of P53 and Human Papilloma Virus in Schneiderian Papillomas. Laryngoscope 1998, 108, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, S.; Lai, C.; Purgina, B.; Almutairi, D.; Baghai, T.; Dimitroulakos, J.; Kilty, S. Human Papillomavirus: An Unlikely Etiologic Factor in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, M.; Tomasetti, M.; Monaco, F.; Amati, M.; Rubini, C.; Foschini, M.P.; Sollini, G.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Pasquini, E.; Santarelli, L. NGS-Based miRNome Identifies miR-449 Cluster as Marker of Malignant Transformation of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Oral Oncol. 2021, 122, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, D.G.; Keeney, M.G.; Gao, G.; Smith, D.I.; García, J.J.; O’Brien, E.K. Transcriptional Activity of HPV in Inverted Papilloma Demonstrated by In Situ Hybridization for E6/E7 mRNA. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjänen, S.; Happonen, R.-P.; Virolainen, E.; Siivonen, L.; Syrjänen, K. Detection of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Structural Antigens and DNA Types in Inverted Papillomas and Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Nasal Cavities and Paranasal Sinuses. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1987, 104, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Overexpression of FoxM1 in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma and Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, W. Expression of Sp100 Protein in Human Papillomavirus-Associated Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP21–NP25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Piao, Y.; Wang, C.; Xian, J.; Zhang, L. Microvessel Barrier Dysfunction in Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma-associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Manifestation in Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2024, 14, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.H.; Tong, C.C.L.; Penta, M.; Patel, V.S.; Palmer, J.N.; Adappa, N.D.; Nayak, J.V.; Hwang, P.H.; Patel, Z.M. Imaging Predictors for Malignant Transformation of Inverted Papilloma. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.H.; Verbeek, J.; Schwingshackl, L.; Filippini, T.; Vinceti, M.; Akl, E.A.; Morgan, R.L.; Mustafa, R.A.; Zeraatkar, D.; Senerth, E.; et al. GRADE GUIDANCE 38: Updated Guidance for Rating up Certainty of Evidence Due to a Dose-Response Gradient. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2023, 164, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitmer, T.; Wiener, C. Is There an Occupational Etiology of Inverted Papilloma of the Nose and Sinuses? Acta Oto-Laryngol. 1996, 116, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.E.; Becker, G.L.; Jackson, J.B.; Rysavy, M.B. Human Papillomavirus and Associated Cancers: A Review. Viruses 2024, 16, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, N.R.; Windon, M.J.; Amanian, A.; Zamuner, F.T.; Bishop, J.; Fakhry, C.; Rooper, L.M. Evaluation of the Incidence of Human Papillomavirus–Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Sinonasal Tract Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2255971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang Sing Pang, K.J.W.; Mur, T.; Collins, L.; Rao, S.R.; Faden, D.L. Human Papillomavirus in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2020, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, P.R.; Saraswathula, A.; Ramanathan, M. Etiology of Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: An Update. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsentemeidou, A.; Fyrmpas, G.; Stavrakas, M.; Vlachtsis, K.; Sotiriou, E.; Poutoglidis, A.; Tsetsos, N. Human Papillomavirus Vaccine to End Oropharyngeal Cancer. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2021, 48, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Credico, G.; Polesel, J.; Dal Maso, L.; Pauli, F.; Torelli, N.; Luce, D.; Radoï, L.; Matsuo, K.; Serraino, D.; Brennan, P.; et al. Alcohol Drinking and Head and Neck Cancer Risk: The Joint Effect of Intensity and Duration. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Errico, A.; Zajacova, J.; Cacciatore, A.; Baratti, A.; Zanelli, R.; Alfonzo, S.; Beatrice, F. Occupational Risk Factors for Sinonasal Inverted Papilloma: A Case–Control Study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
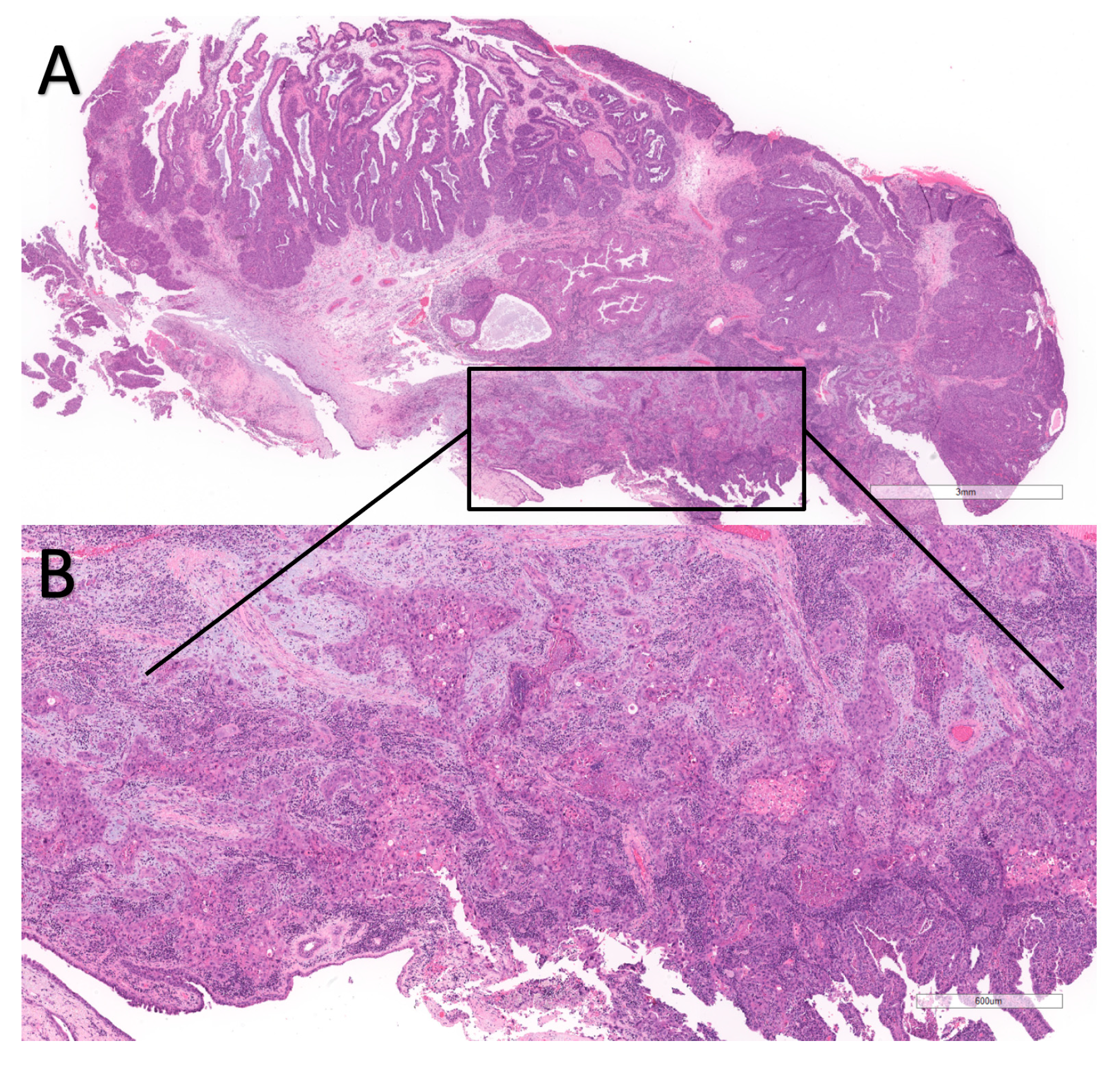




| Author | 1. Selection | 2. Comparability | 3. Exposure | Total Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archang [23] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Bernauer [24] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Buchwald [25] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Cabal [26] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Caruana [27] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Franzmann [28] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Gaffey [29] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Holm [30] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Hong [31] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Hwang [32] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Jalilvand [33] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Jenko [34] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Kim [35] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Kraft [36] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Li [37] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| McKay [38] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Menendez [39] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Mirza [40] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Mohajeri [41] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Re [42] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Stoddard [43] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Syrjanen [44] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Wang [45] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Wang [46] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Xian [47] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Yan [48] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Average | 4 | 1 | 2.3 | 7.3 |
| Authors | Year | N. of All IP | N. of IP Without Carcinoma | N. of C-IP | Rate of Malignancy (%) | HPV N. of Cases in IP vs. C-IP (p-Value) | Smoking Status N. of Cases in IP vs. C-IP (p-Value) | Alcohol N. of Cases in IP vs. C-IP (p-Value) | EBV N. of Cases in IP vs. C-IP (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Archang [23] | 2022 | 100 | 96 | 4 | 4/100 (4%) | 39/106 vs. 5/12 (0.281) | 32/106 vs. 4/12 (0.035) | ||
| Bernauer [24] | 1997 | 22 | 19 | 3 | 3/22 (13.6%) | 5/19 vs. 2/3 (NA) | |||
| Buchwald [25] | 1995 | 57 | 52 | 5 | 5/57 (8.8%) | 3/52 vs. 2/5 (NA) | |||
| Cabal [26] | 2020 | 55 | 41 | 14 | 14/55 (25.5%) | 4/40 vs. 2/13 (NA) | |||
| Caruana [27] | 1997 | 19 | 15 | 4 | 4/19 (21.1%) | 6/15 vs. 2/4 (NA) | 3/15 vs. 2/4 (NA) | 3/15 vs. 0/4 (NA) | |
| Franzmann [28] | 1998 | 17 | 12 | 5 | 5/17 (29.4%) | 0/12 vs. 3/5 (NA) | |||
| Gaffey [29] | 1996 | 20 | 19 | 1 | 1/20 (5%) | 1/19 vs. 1/1 (NA) | 1/12 vs. 1/1 | ||
| Holm [30] | 2020 | 53 | 50 | 3 | 3/53 (5.7%) | 2/38 vs. 1/2 (NA) | |||
| Hong [31] | 2013 | 162 | 145 | 17 | 17/162 (10.5%) | 39/145 vs. 17/17 (<0.001) | |||
| Hwang [32] | 1998 | 42 | 36 | 6 | 6/42 (14.3%) | 3/36 vs. 2/5 (NA) | |||
| Jalivand [33] | 2016 | 40 | 37 | 3 | 3/40 (7.5%) | 7/37 vs. 3/3 (0.002) | |||
| Jenko [34] | 2011 | 71 | 66 | 5 | 5/71 (7.0%) | 20/66 vs. 3/5 (NA) | |||
| Kim [35] | 2007 | 57 | 50 | 7 | 7/57 (12.3%) | 7/57 vs. 0/7 (NA) | |||
| Kraft [36] | 2001 | 34 | 30 | 4 | 4/34 (11.8%) | 1/29 vs. 0/4 (NA) | |||
| Li [37] | 2019 | 25 | 16 | 9 | 9/25 (36.0%) | 4/12 vs. 3/6 (NA) | |||
| McKay [38] | 2005 | 14 | 11 | 3 | 3/14 (21.4%) | 3/11 vs. 2/3 (NA) | |||
| Menendez [39] | 2022 | 60 | 49 | 11 | 11/60 (18.3%) | 2/49 vs. 2/11 (0.034 0.006 *) | |||
| Mirza [40] | 1998 | 30 | 29 | 1 | 1/30 (3.3%) | 5/29 vs. 1/1 (NA) | |||
| Mohajeri [41] | 2018 | 76 | 72 | 4 | 4/76 (5.3%) | 10/76 VS. 0/4 (NA) | |||
| Re [42] | 2021 | 50 | 33 | 17 | 17/50 (34.0%) | 18/33 VS. 9/17 (NA) | |||
| Stoddard [43] | 2015 | 19 | 18 | 1 | 1/19 (5.3%) | 6/18 VS. 1/1 (≥5 mRNA) (NA) | |||
| Syrjanen [44] | 1987 | 14 | 12 | 2 | 2/14 (14.3%) | 8/12 vs. 2/2 (NA) | |||
| Wang [45] | 2019 | 25 | 17 | 8 | 8/25 (32.0%) | 4/17 vs. 2/8 (NA) | |||
| Wang [46] | 2021 | 25 | 18 | 7 | 7/25 (28.0%) | 0/18 vs. 3/7 (NA) | |||
| Xian [47] | 2024 | 42 | 22 | 20 | 20/42 (47.6%) | 8/22 vs. 6/20 (0.662) | |||
| Yan [48] | 2019 | 142 | 76 | 66 | 66/142 (46.5%) | 7/76 vs. 8/66 (0.596) | |||
| Total | 1271 | 1041 | 230 | 230/1271 (18.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ambrosini-Spaltro, A.; Querzoli, G.; Leucci, A.C.; Camagni, A.; Farneti, P.; D’Angelo, E.; Donini, E.; Tosoni, A.; Pasquini, E.; Galli, P.; et al. Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation in Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111798
Ambrosini-Spaltro A, Querzoli G, Leucci AC, Camagni A, Farneti P, D’Angelo E, Donini E, Tosoni A, Pasquini E, Galli P, et al. Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation in Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111798
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmbrosini-Spaltro, Andrea, Giulia Querzoli, Anna Caterina Leucci, Angela Camagni, Paolo Farneti, Elisa D’Angelo, Elisa Donini, Alicia Tosoni, Ernesto Pasquini, Paolo Galli, and et al. 2025. "Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation in Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111798
APA StyleAmbrosini-Spaltro, A., Querzoli, G., Leucci, A. C., Camagni, A., Farneti, P., D’Angelo, E., Donini, E., Tosoni, A., Pasquini, E., Galli, P., & Foschini, M. P. (2025). Risk Factors for Malignant Transformation in Inverted Sinonasal Papilloma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(11), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111798









