The Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Breast Cancer
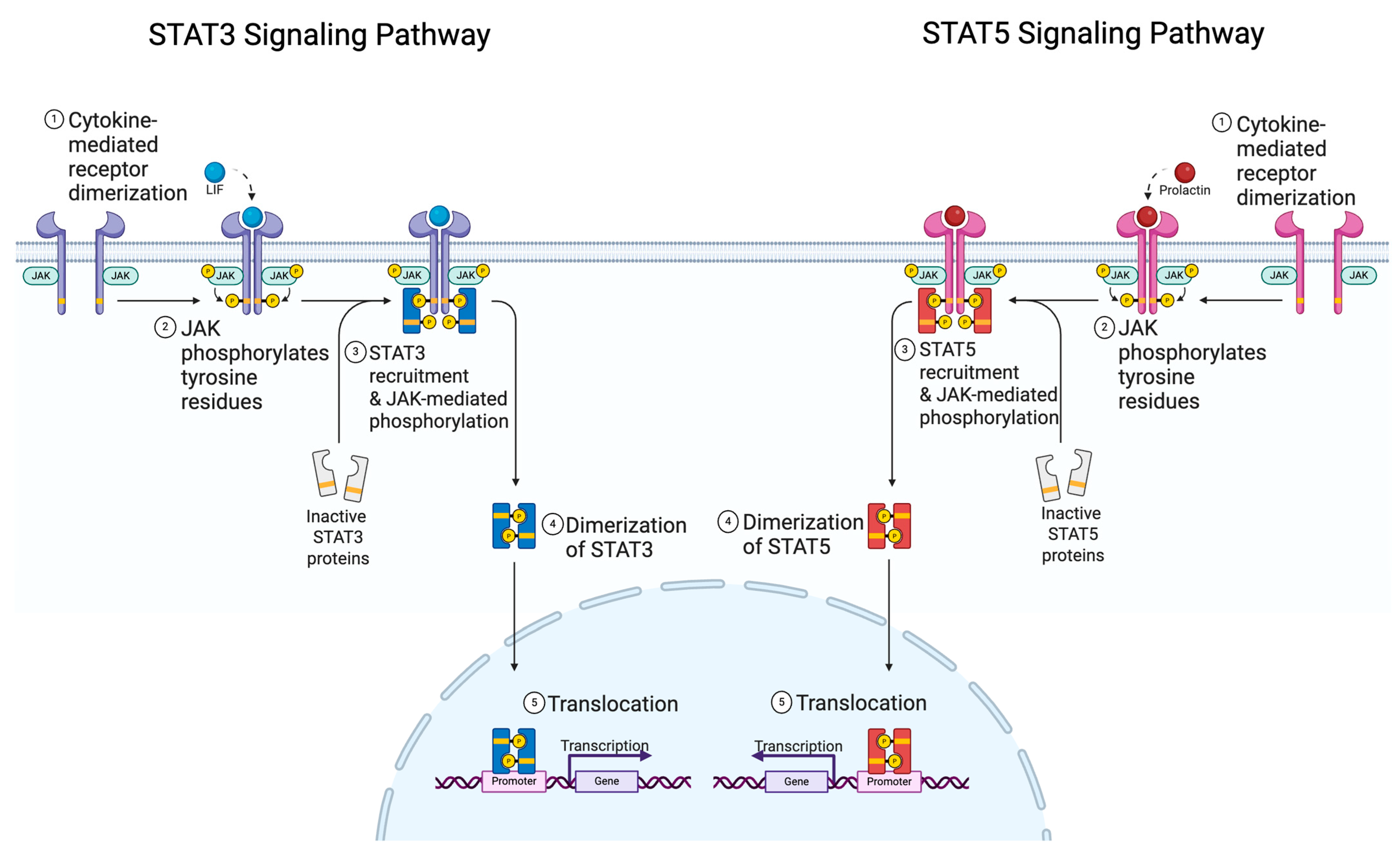
1.2. STAT Family and Function
1.3. JAK Specificity and Targetability
2. STAT3 and STAT5 in Normal Breast Physiology
2.1. STAT3 and STAT5 in Embryogenesis, Puberty, and Menopause
2.2. Role of STAT5 in Pregnancy and Lactation
2.3. Role of STAT3 in Involution and Post-Lactational Remodeling
3. STAT5 in Breast Cancer
3.1. Role of STAT5 in Breast Cancer
3.2. STAT5 Transcriptional Regulation of Genes
3.3. STAT5 Protein Interactions in Breast Cancer

| Name | Target Gene or Cofactor | Clinical Relevance | STAT5 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOX5-L [41] | Target gene | Proliferation, migration, invasion | Upregulates |
| ABCB1 [42] | Target gene | Chemoresistance | Upregulates |
| FYN [43] | Target gene | Metastatic potential | Upregulates |
| ISG20/miR-17-92 [45,46] | Target gene | Metastatic potential | Downregulates |
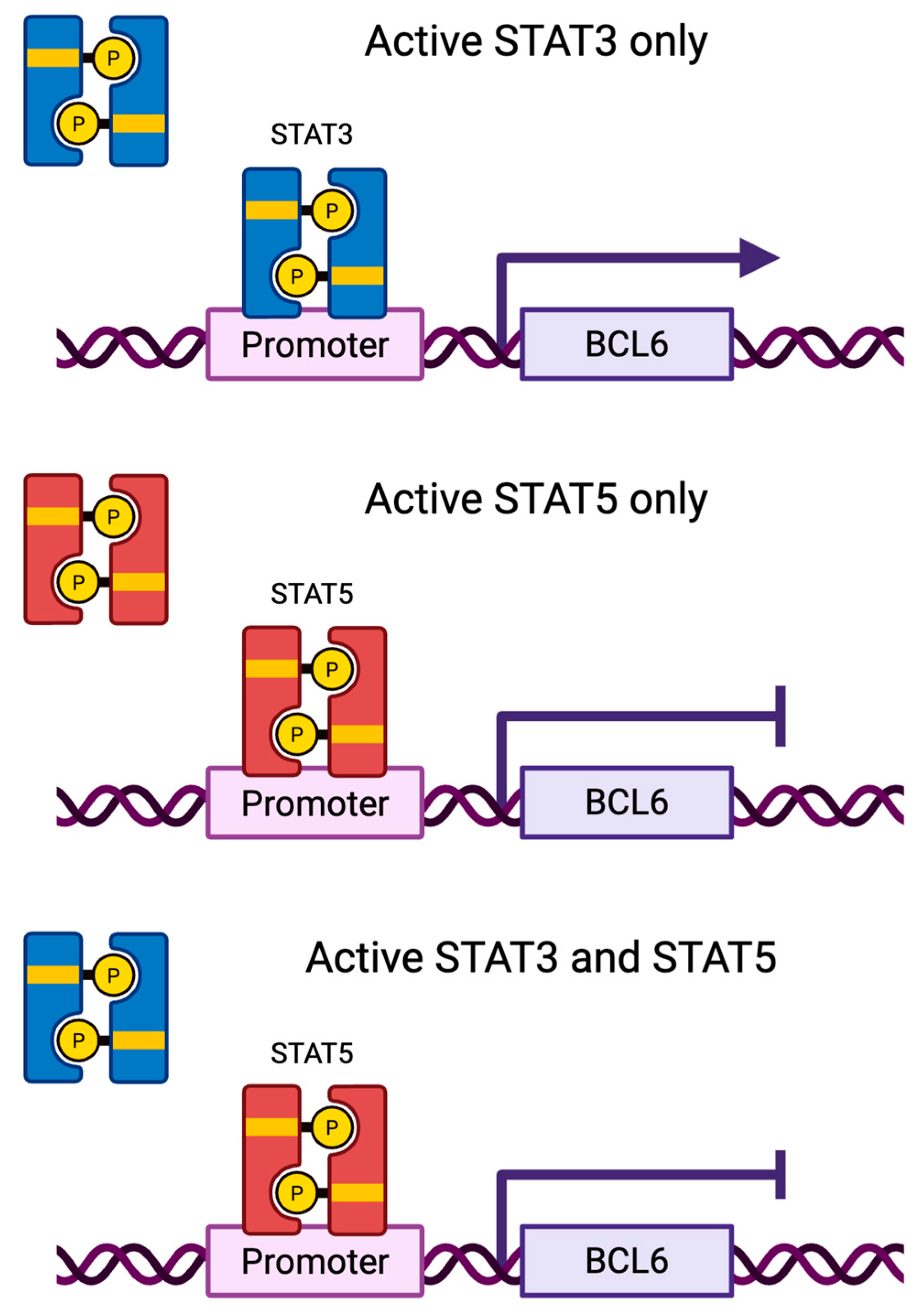
| BCL6 [47,48] | Target gene | Proliferation, cell cycle progression | Downregulates |
| OCT1 [58,59] | Cofactor | Cell cycle progression | Promotes |
| METTL3 [60] | Cofactor | Cell cycle progression | Promotes |
| FGFR-2 [61] | Cofactor | Proliferation | Promotes |
| PR [61] | Cofactor | Proliferation | Promotes |
| Naa10p [62] | Cofactor | Inhibits migration, STAT5-mediated ID1 expression | Inhibitory |
| HMGN2 [63,64] | Not established | Facilitates chromatin accessibility | Promotes |
4. STAT3 in Breast Cancer
4.1. Role of STAT3 in Breast Cancer
4.2. STAT3 Transcriptional Regulation of Genes
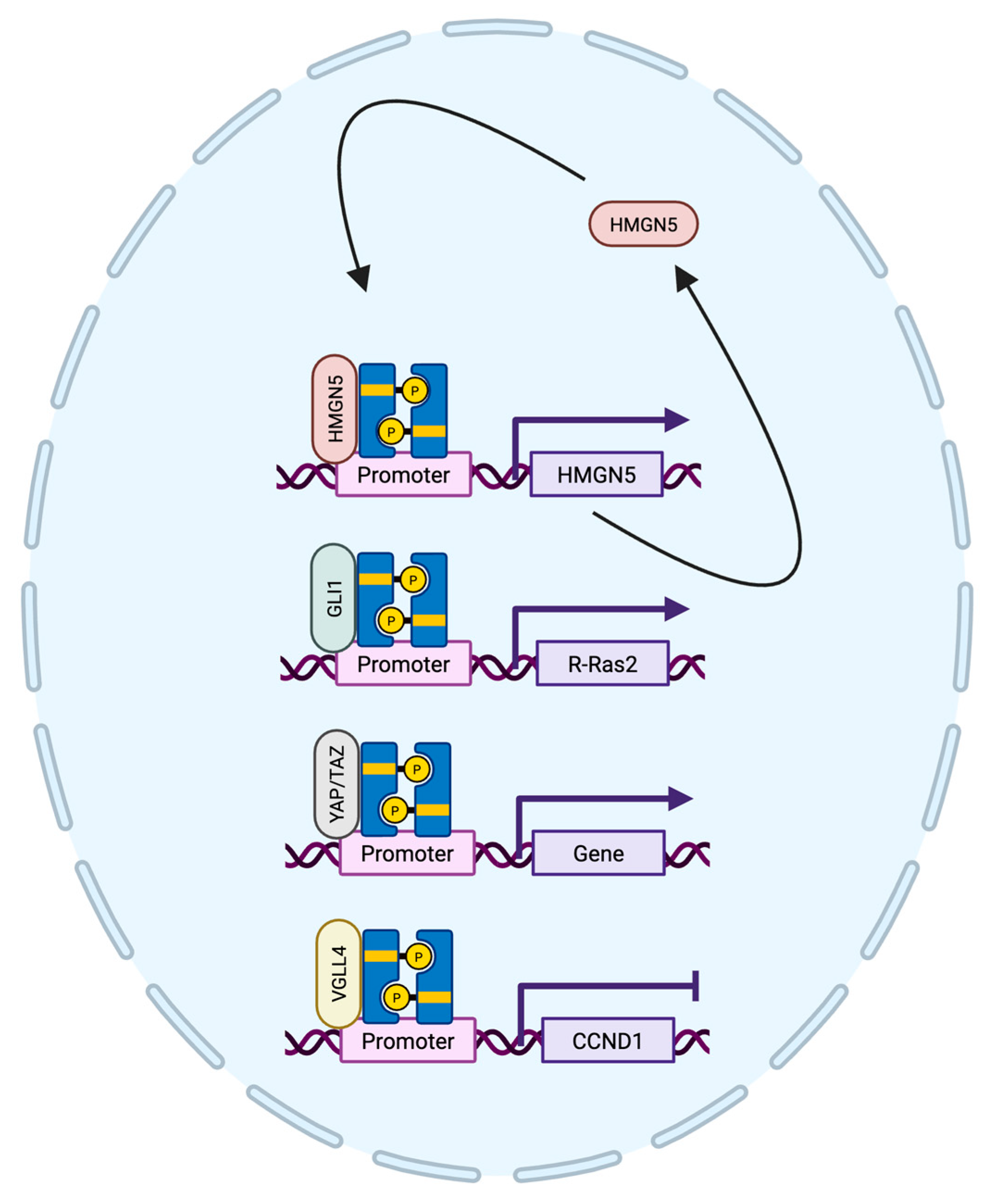
4.3. STAT3 Protein Interactions in Breast Cancer
| Name | Target Gene or Cofactor | Clinical Relevance | STAT3 Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD-L1 [76,77,89] | Target gene | Tumor growth | Upregulates |
| Twist [78,90] | Target gene | Invasion, metastasis | Upregulates |
| ERRα [79] | Target gene | EMT, metastasis | Upregulates |
| TNFRSF1A [80] | Target gene | Survival, proliferation | Upregulates |
| HMGN5 [81] | Target gene/cofactor | Facilitates chromatin accessibility | Upregulates/promotes |
| CPT1B [82] | Target gene | Chemoresistance | Upregulates |
| BCL6 [47] | Target gene | Proliferation, cell cycle progression | Upregulates |
| GRN [84] | Cofactor | Maximal STAT3 activity | Promotes |
| GLI1 [71] | Cofactor | Worse metastasis-free survival | Promotes |
| YAP1/TAZ [85] | Cofactor | STAT3 coactivators in TNBC | Promotes |
| VGLL4 [86] | Cofactor | Suppress STAT3 activity | Inhibitory |
5. STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer
5.1. Connection to Clinical Outcome
5.2. STAT3 and STAT5 Can Compete for DNA-Binding in Breast Cancer
5.3. STAT3 and STAT5 Relationship in Other Cell Types
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCB1 | ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 1 |
| BCL6 | B-cell lymphoma 6 |
| CPT1B | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1B |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| EMT | Epithelial mesenchymal transition |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ERRα | Estrogen-related receptor α |
| FGFR-2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 |
| GLI | Glioma associated oncogene homolog 1 |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HMGN2 | High mobility group nucleosome binding domain 2 |
| HMGN5 | High mobility group nucleosome binding domain 5 |
| IGF | Insulin-like growth factor |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| ISG20 | Interferon stimulated exonuclease gene 20 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| LIF | Leukemia inhibitory factor |
| LIFR | Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor |
| Naa10p | N-a-acetyltransferase 10 protein |
| NOX5-L | NADPH oxidase 5 long form |
| OCT1 | Octamer transcription factor 1 |
| OSM | Oncostatin M |
| OSMR | Oncostatin M receptor |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| PIAS | Protein inhibitor of activated STATs |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| SOCS | Suppressor of cytokine signaling |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| STAT5 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| TNFRSF1A | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A |
| VGLL4 | Vestigial like family member 4 |
| YAP1 | Yes-associated protein 1 |
References
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Newman, L.A.; Freedman, R.A.; Smith, R.A.; Star, J.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeagu, E.I.; Obeagu, G.U. Breast Cancer: A Review of Risk Factors and Diagnosis. Medicine 2024, 103, e36905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.-N.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.-J.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Yao, P.-P.; Zhu, H.-P. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlands, F.E.; Horgan, K.; Dodwell, D.D.; Smith, L. Breast Cancer Subtypes: Response to Radiotherapy and Potential Radiosensitisation. Br. J. Radiol. 2013, 86, 20120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, K.; Spruck, C. Triple-negative Breast Cancer Therapy: Current and Future Perspectives (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, M.; Bekele, F.; Fekadu, G. Treatment Strategies Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: An Updated Review. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2022, 14, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, D.; Simpson, P.T.; Green, B.; Cummings, M.C.; Lakhani, S.R. Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer. Virchows Arch. 2014, 465, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrivières, S.; Kunz, C.; Barash, I.; Vafaizadeh, V.; Borghouts, C.; Groner, B. The Biological Functions of the Versatile Transcription Factors STAT3 and STAT5 and New Strategies for Their Targeted Inhibition. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2006, 11, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, K.; Watson, C.J. The Spectrum of STAT Functions in Mammary Gland Development. JAK-STAT 2012, 1, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.-U.; Rui, H. Jak2/Stat5 Signaling in Mammogenesis, Breast Cancer Initiation and Progression. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Role of STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.-U.; Schmidt, J. The Two Faces of Janus Kinases and Their Respective STATs in Mammary Gland Development and Cancer. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balko, J.M.; Schwarz, L.J.; Luo, N.; Estrada, M.V.; Giltnane, J.M.; Dávila-González, D.; Wang, K.; Sánchez, V.; Dean, P.T.; Combs, S.E.; et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancers with Amplification of JAK2 at the 9p24 Locus Demonstrate JAK2-Specific Dependence. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 334ra53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Fei, X.; Chen, L.; Yao, L.; Lei, X. Potential Therapeutic Targets of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1381251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlin, I.; McAndrew, N.P.; Wileyto, E.P.; Clark, A.S.; Holmes, R.; Bottalico, L.N.; Mesaros, C.; Blair, I.A.; Jeschke, G.R.; Fox, K.R.; et al. Ruxolitinib and Exemestane for Estrogen Receptor Positive, Aromatase Inhibitor Resistant Advanced Breast Cancer. Npj Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, D.G.; Gil Del Alcazar, C.R.; Brock, J.; Guo, H.; Overmoyer, B.; Balko, J.; Xu, Q.; Bardia, A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Gelman, R.; et al. Phase II Study of Ruxolitinib, a Selective JAK1/2 Inhibitor, in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, J.; DeMichele, A.; Ma, C.X.; Richards, P.; Yardley, D.A.; Wright, G.S.; Kalinsky, K.; Steis, R.; Diab, S.; Kennealey, G.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 2 Study of Ruxolitinib or Placebo in Combination with Capecitabine in Patients with Advanced HER2-Negative Breast Cancer and Elevated C-Reactive Protein, a Marker of Systemic Inflammation. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-D. STAT3 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Noguchi, K.; Shi, W.; Tanaka, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Yoshida, N.; Kishimoto, T.; Akira, S. Targeted Disruption of the Mouse Stat3 Gene Leads to Early Embryonic Lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3801–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepicka, P.F.; Somasundara, A.V.H.; Dos Santos, C.O. The Molecular Basis of Mammary Gland Development and Epithelial Differentiation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 114, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Ye, S.; Ke, H.; Lin, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, M.; Jiao, B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, L. Changes in the Mammary Gland during Aging and Its Links with Breast Diseases. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2023, 55, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, I. Stat5 in Breast Cancer: Potential Oncogenic Activity Coincides with Positive Prognosis for the Disease. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furth, P.A.; Nakles, R.E.; Millman, S.; Diaz-Cruz, E.S.; Cabrera, M.C. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5 as a Key Signaling Pathway in Normal Mammary Gland Developmental Biology and Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, D.; Na, R.; Feuermann, Y.; Pechhold, S.; Chen, W.; Robinson, G.W.; Hennighausen, L. Development of Mammary Luminal Progenitor Cells Is Controlled by the Transcription Factor STAT5A. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2382–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.J.; Kreuzaler, P.A. Remodeling Mechanisms of the Mammary Gland during Involution. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikou, E.A.; Sharkey, A.; Abell, K.; Came, P.J.; Anderson, E.; Clarkson, R.W.E.; Watson, C.J. A Dual, Non-Redundant, Role for LIF as a Regulator of Development and STAT3-Mediated Cell Death in Mammary Gland. Development 2003, 130, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schere-Levy, C. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Induces Apoptosis of the Mammary Epithelial Cells and Participates in Mouse Mammary Gland Involution. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 282, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Watson, C.J. The Multifaceted Role of STAT3 in Mammary Gland Involution and Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffen, P.G.; Omidvar, N.; Marquez-Almuina, N.; Croston, D.; Watson, C.J.; Clarkson, R.W.E. A Dual Role for Oncostatin M Signaling in the Differentiation and Death of Mammary Epithelial Cells in Vivo. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Wickenden, J.A.; Allen, J.E.; Watson, C.J. Conditional Deletion of Stat3 in Mammary Epithelium Impairs the Acute Phase Response and Modulates Immune Cell Numbers during Post-Lactational Regression. J. Pathol. 2012, 227, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, T.; Morris, J.S.; Davies, C.R.; Weber-Hall, S.J.; Duffy, M.-A.; Heath, V.J.; Bell, A.K.; Ferrier, R.K.; Sandilands, G.P.; Gusterson, B.A. Involution of the Mouse Mammary Gland Is Associated with an Immune Cascade and an Acute-Phase Response, Involving LBP, CD14 and STAT3. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2004, 6, R75–R91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.S.; Lourenco, P.C.; Tonner, E.; Flint, D.J.; Selbert, S.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Clarke, A.R.; Watson, C.J. Suppression of Epithelial Apoptosis and Delayed Mammary Gland Involution in Mice with a Conditional Knockout of Stat3. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2604–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevalainen, M.T.; Xie, J.; Torhorst, J.; Bubendorf, L.; Haas, P.; Kononen, J.; Sauter, G.; Rui, H. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-5 Activation and Breast Cancer Prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.R.; Nelson, E.A.; Zou, L.; Chaudhury, M.; Signoretti, S.; Richardson, A.; Frank, D.A. Reciprocal Effects of STAT5 and STAT3 in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-N.; Fang, Z.-X.; Wu, Z.; Bai, J.-W.; Li, R.-H.; Wen, X.-F.; Zhang, G.-J.; Liu, J. Notch3 Restricts Metastasis of Breast Cancers through Regulation of the JAK/STAT5A Signaling Pathway. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Ku, A.T.; Dong, J.; Yue, F.; Jiang, W.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Peng, F.; Creighton, C.J.; Nagi, C.; Gutierrez, C.; et al. STAT5 Confers Lactogenic Properties in Breast Tumorigenesis and Restricts Metastatic Potential. Oncogene 2022, 41, 5214–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, A.R.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Liu, C.; Stringer, G.A.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Pequignot, E.; Freydin, B.; Tran, T.H.; Yang, N.; Rosenberg, A.L.; et al. Loss of Nuclear Localized and Tyrosine Phosphorylated Stat5 in Breast Cancer Predicts Poor Clinical Outcome and Increased Risk of Antiestrogen Therapy Failure. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ozuna, V.M.; Hachim, I.Y.; Hachim, M.Y.; Lebrun, J.-J.; Ali, S. Prolactin Modulates TNBC Aggressive Phenotype Limiting Tumorigenesis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, B.; Rafiee-Pour, H.-A.; Khosravi, M.-R.; Kefayat, A.; Baradaran, A.; Amjadi, E.; Goli, P. Prolactin Receptor Expression as a Novel Prognostic Biomarker for Triple Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 46, 151507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dho, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.-P.; Kwon, E.-S.; Lim, J.C.; Kim, C.-J.; Jeong, D.; Kwon, K.-S. STAT5A-Mediated NOX5-L Expression Promotes the Proliferation and Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 351, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, L.; Hu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, M.; et al. STAT5a Confers Doxorubicin Resistance to Breast Cancer by Regulating ABCB1. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 697950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-H.; Yoo, K.-C.; An, Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, M.; Uddin, N.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, I.-G.; Suh, Y.; Lee, S.-J. FYN Promotes Mesenchymal Phenotypes of Basal Type Breast Cancer Cells through STAT5/NOTCH2 Signaling Node. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.S.; Xie, J.; LeBaron, M.J.; Ealley, E.L.; Nevalainen, M.T.; Rui, H. Stat5 Promotes Homotypic Adhesion and Inhibits Invasive Characteristics of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2005, 24, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsheikh, H.A.M.; Metge, B.J.; Pruitt, H.C.; Kammerud, S.C.; Chen, D.; Wei, S.; Shevde, L.A.; Samant, R.S. Disruption of STAT5A and NMI Signaling Axis Leads to ISG20-Driven Metastatic Mammary Tumors. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuermann, Y.; Robinson, G.W.; Zhu, B.; Kang, K.; Raviv, N.; Yamaji, D.; Hennighausen, L. The miR-17/92 Cluster Is Targeted by STAT5 but Dispensable for Mammary Development. Genesis 2012, 50, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.R.; Nelson, E.A.; Yeh, J.E.; Pinello, L.; Yuan, G.-C.; Frank, D.A. STAT5 Outcompetes STAT3 To Regulate the Expression of the Oncogenic Transcriptional Modulator BCL6. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Utama, F.E.; Lin, J.; Yang, N.; Sjolund, A.B.; Ryder, A.; Johnson, K.J.; Neilson, L.M.; Liu, C.; Brill, K.L.; et al. Prolactin Inhibits BCL6 Expression in Breast Cancer through a Stat5a-Dependent Mechanism. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, A.; Binothman, N.; Boudreault, J.; Wang, N.; Shams, F.; Hamam, D.; Tian, J.; Moamer, A.; Dai, M.; Lebrun, J.-J.; et al. Prolactin Receptor-Driven Combined Luminal and Epithelial Differentiation in Breast Cancer Restricts Plasticity, Stemness, Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ozuna, V.M.; Hachim, I.Y.; Hachim, M.Y.; Lebrun, J.-J.; Ali, S. Prolactin Pro-Differentiation Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Impact on Prognosis and Potential Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Mahesutihan, G.; Meng, J.; Chen, Y.; Lv, J. Identification of STAT5B as a Biomarker Associated with Prognosis and Immune Infiltration in Breast Cancer. Medicine 2023, 102, e32972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-T.; Liu, J.; Li, G.-W.; Shen, J.-X.; Huang, Y.-T. The Transcriptional STAT3 Is a Potential Target, Whereas Transcriptional STAT5A/5B/6 Are New Biomarkers for Prognosis in Human Breast Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 36279–36288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.-Z.; Zuo, Z.-H.; Kong, X.-J.; Steiner, M.; Yin, Z.; Perry, J.K.; Zhu, T.; Liu, D.-X.; Lobie, P.E. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT)-5A and STAT5B Differentially Regulate Human Mammary Carcinoma Cell Behavior. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, A.R.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Liu, C.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Stringer, G.A.; Pequignot, E.; Freydin, B.; Yang, N.; Ertel, A.; Tran, T.H.; et al. Low Levels of Stat5a Protein in Breast Cancer Are Associated with Tumor Progression and Unfavorable Clinical Outcomes. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, F.; Brockman, J.L.; Helzer, K.T.; Rugowski, D.E.; Goffin, V.; Alarid, E.T.; Schuler, L.A. 17β-Estradiol and ICI182,780 Differentially Regulate STAT5 Isoforms in Female Mammary Epithelium, With Distinct Outcomes. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernaciak, T.M.; Zareno, J.; Parsons, J.T.; Silva, C.M. A Novel Role for Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5b (STAT5b) in Β1-Integrin-Mediated Human Breast Cancer Cell Migration. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, R52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Able, A.A.; Burrell, J.A.; Stephens, J.M. STAT5-Interacting Proteins: A Synopsis of Proteins That Regulate STAT5 Activity. Biology 2017, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockman, J.L.; Schuler, L.A. Prolactin Signals via Stat5 and Oct-1 to the Proximal Cyclin D1 Promoter. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2005, 239, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magné, S.; Caron, S.; Charon, M.; Rouyez, M.-C.; Dusanter-Fourt, I. STAT5 and Oct-1 Form a Stable Complex That Modulates Cyclin D1 Expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8934–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, P.Y.; Kim, G.; Lim, S.-C.; Choi, H.S. METTL3-STAT5B Interaction Facilitates the Co-Transcriptional m6A Modification of mRNA to Promote Breast Tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2024, 603, 217215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerliani, J.P.; Guillardoy, T.; Giulianelli, S.; Vaque, J.P.; Gutkind, J.S.; Vanzulli, S.I.; Martins, R.; Zeitlin, E.; Lamb, C.A.; Lanari, C. Interaction between FGFR-2, STAT5, and Progesterone Receptors in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3720–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Min, L.; Han, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Dong, B.; Wang, L.; Jiang, B.; Xu, H.; et al. Inhibition of STAT5a by Naa10p Contributes to Decreased Breast Cancer Metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2244–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwecker, S.M.; Kim, J.J.; Licht, J.D.; Clevenger, C.V. Histone H1 and Chromosomal Protein HMGN2 Regulate Prolactin-Induced STAT5 Transcription Factor Recruitment and Function in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 2237–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medler, T.R.; Craig, J.M.; Fiorillo, A.A.; Feeney, Y.B.; Harrell, J.C.; Clevenger, C.V. HDAC6 Deacetylates HMGN2 to Regulate Stat5a Activity and Breast Cancer Growth. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 994–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.R.; Xiang, M.; Frank, D.A. Distinct Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in the Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, P.; Rezaeian, A.H.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Gupta, S.; Liang, H.; Lin, H.-K.; Hung, M.-C.; et al. LIFR Is a Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor Upstream of the Hippo-YAP Pathway and a Prognostic Marker. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Santhamma, B.; Pratap, U.P.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Altwegg, K.A.; Tang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; et al. LIFR Inhibition Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of HDAC Inhibitors in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighid, N.; El Akil, S.; Izaabel, E.H. STAT3 Gene Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Breast Cancer in the Moroccan Population. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, L.L.C.; Almendro, V.; Marusyk, A.; Shipitsin, M.; Schemme, J.; Walker, S.R.; Bloushtain-Qimron, N.; Kim, J.J.; Choudhury, S.A.; Maruyama, R.; et al. The JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway Is Required for Growth of CD44+CD24– Stem Cell–like Breast Cancer Cells in Human Tumors. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.S.; Giehl, N.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J.V. STAT3 Activation in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cell Traits. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkisoon, S.R.; Carpenter, R.L.; Rimkus, T.; Anderson, A.; Harrison, A.; Lange, A.M.; Jin, G.; Watabe, K.; Lo, H.-W. Interaction between STAT3 and GLI1/tGLI1 Oncogenic Transcription Factors Promotes the Aggressiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers and HER2-Enriched Breast Cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2502–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, C.-H.; Chen, H.-D.; Hu, G.-N.; Shao, J.-K.; Dong, X.-F.; Jin, L.-L.; Wang, C.-Q. P-STAT3 Expression in Breast Cancer Correlates Negatively with Tumor Size and HER2 Status. Medicine 2021, 100, e25124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariboldi, M.B.; Ravizza, R.; Molteni, R.; Osella, D.; Gabano, E.; Monti, E. Inhibition of Stat3 Increases Doxorubicin Sensitivity in a Human Metastatic Breast Cancer Cell Line. Cancer Lett. 2007, 258, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Hong, J.H.; Chun, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kang, K.; Kim, H.S.; Won, H.S.; Ko, Y.H. Inhibition of STAT3 Enhances Sensitivity to Tamoxifen in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vining, D.J.; Arora, S.P.; De Achaval, S.; Larson, J.; Kauh, J.; Cartwright, C.; Avritscher, R.; Alibhai, I.; Tweardy, D.J.; et al. Phase I Trial of TTI-101, a First-in-Class Oral Inhibitor of STAT3, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan Nair, V.; Toor, S.M.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Dual Inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 Activation Downregulates Expression of PD-L1 in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerdes, I.; Wallerius, M.; Sifakis, E.; Wallmann, T.; Betts, S.; Bartish, M.; Tsesmetzis, N.; Tobin, N.; Coucoravas, C.; Bergh, J.; et al. STAT3 Activity Promotes Programmed-Death Ligand 1 Expression and Suppresses Immune Responses in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.Z.; Zhang, W.; Sun, M.; Wang, Q.; Coppola, D.; Mansour, M.; Xu, L.; Costanzo, C.; Cheng, J.Q.; Wang, L.-H. Twist Is Transcriptionally Induced by Activation of STAT3 and Mediates STAT3 Oncogenic Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 14665–14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-H.; Qi, J.; Lin, S.-Q.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Liu, F.; Xie, W.-D.; Li, X. STAT3 Targets ERR-α to Promote Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition, Migration, and Invasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusquiaguirre, S.P.; Yeh, J.E.; Walker, S.R.; Liu, S.; Frank, D.A. The STAT3 Target Gene TNFRSF1A Modulates the NF-κB Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, H.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Kong, W.; Chen, J.; et al. HMGN5 Escorts Oncogenic STAT3 Signaling by Regulating the Chromatin Landscape in Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2022, 20, 1724–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fahrmann, J.F.; Lee, H.; Li, Y.-J.; Tripathi, S.C.; Yue, C.; Zhang, C.; Lifshitz, V.; Song, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. JAK/STAT3-Regulated Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Is Critical for Breast Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Chemoresistance. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 136–150.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudisi, F.; Cherubini, F.; Monteleone, G.; Stolfi, C. STAT3 Interactors as Potential Therapeutic Targets for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.E.; Kreimer, S.; Walker, S.R.; Emori, M.M.; Krystal, H.; Richardson, A.; Ivanov, A.R.; Frank, D.A. Granulin, a Novel STAT3-Interacting Protein, Enhances STAT3 Transcriptional Function and Correlates with Poorer Prognosis in Breast Cancer. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Pratt, H.; Gao, M.; Wei, F.; Weng, Z.; Struhl, K. YAP and TAZ Are Transcriptional Co-Activators of AP-1 Proteins and STAT3 during Breast Cellular Transformation. eLife 2021, 10, e67312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Luo, Q.; Deng, X.; Ji, C.; Li, D.; Munankarmy, A.; Jian, W.; Zhao, J.; Fang, L. VGLL4 Interacts with STAT3 to Function as a Tumor Suppressor in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, R.; Chen, R.; Cao, T.; Zeng, F.; Liu, Q. The Hippo Pathway in Breast Cancer: The Extracellular Matrix and Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, C.J.; Izzo, F.; Díaz Flaqué, M.C.; Cordo Russo, R.; Venturutti, L.; Mercogliano, M.F.; De Martino, M.; Pineda, V.; Muñoz, S.; Guzmán, P.; et al. Heregulin Co-Opts PR Transcriptional Action Via Stat3 Role As a Coregulator to Drive Cancer Growth. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1468–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Seo, E.-B.; Jeong, A.J.; Lee, S.-H.; Noh, K.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, C.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Shin, H.M.; Kim, H.-R.; et al. The Acidic Tumor Microenvironment Enhances PD-L1 Expression via Activation of STAT3 in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Besser, A.H.; Wander, S.A.; Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Ince, T.; Durante, M.A.; Guo, W.; Mills, G.; et al. Cytoplasmic P27 Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Metastasis via STAT3-Mediated Twist1 Upregulation. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5447–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-P.; Ghoreschi, K.; Steward-Tharp, S.M.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Zhu, J.; Grainger, J.R.; Hirahara, K.; Sun, H.-W.; Wei, L.; Vahedi, G.; et al. Opposing Regulation of the Il17 Locus through Direct, Reciprocal Actions of STAT3 and STAT5. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; He, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Dery, K.J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z. Correction: PRMT1 Plays a Critical Role in Th17 Differentiation by Regulating Reciprocal Recruitment of STAT3 and STAT5. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2021–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Meng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, D. Selective Activation of STAT3 and STAT5 Dictates the Fate of Myeloid Progenitor Cells. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Temple, A.E.; Walker, S.R. The Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111781
Temple AE, Walker SR. The Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111781
Chicago/Turabian StyleTemple, Alexandra E., and Sarah R. Walker. 2025. "The Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111781
APA StyleTemple, A. E., & Walker, S. R. (2025). The Roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 17(11), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111781




