Simple Summary
Recurrent chromosomal translocations are particularly common in human cancers, where they promote tumorigenesis by creating fusion genes from segments of two normal genes. These rearrangements can also disrupt tumor suppressor genes and lead to the amplification of oncogenes. This review examines the ETS-gene rearrangements in prostate cancer. A deeper understanding of the gene fusions in this disease could shed light on the clinical and molecular diversity associated with this widespread disease.
Abstract
Chromosomal rearrangements are implicated in the pathogenesis of several human malignancies, but, concurrently, they also represent targetable opportunities, as exemplified by imatinib (Gleevec), which targets the BCR-ABL gene fusion in myeloid leukemia. In prostate cancer, several chromosomal rearrangements have been identified, most of them involving ETS genes, which encode key transcription factors. In this review, we explore the discovery of 5′ partners that classify ETS gene fusions into distinct groups based on the prostate specificity and androgen responsiveness. Furthermore, we try to address the relationship between gene fusion status and patient outcomes and discuss the possibility of using prostate-specific targeting of ETS gene fusions in cancer detection, stratification, and treatment.
1. Introduction
Prostate cancer (PC) is the second-most common tumor diagnosed in men after lung cancer and the fifth leading cause of cancer death worldwide [1,2,3,4]. More than 1.2 million new cases are diagnosed every year, and global PC-related deaths exceed 350,000 annually [4]. Various genetic and demographic factors, such as age, family history, genetic predisposition, and race, play a role in the high incidence of PC. Epidemiological data indicate that the incidence of PC is also related to exposure to environmental chemical compounds. The sharp rise in industrial chemical production over the past 6–7 decades parallels the increasing rates of PC and other hormone-dependent cancers. With the widespread use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening, nearly 90% of PCs can be diagnosed while still clinically localized [3]. The clinical behavior of localized PC varies significantly. Several risk stratification systems have been developed that integrate clinical and pathological factors like Gleason scores, PSA levels, and staging; however, these tools are still far from accurately predicting outcomes [1,2]. Although PSA is the primary biomarker used to detect PCa, it lacks specificity. Low PSA levels can still be present in aggressive PCa, while high levels can occur in benign cases. Additionally, prostate biopsies, the traditional detection method, are often uncomfortable and may yield false negatives if samples are taken from areas like the central or transitional zones where tumors may be absent. These limitations highlight the urgent need for better diagnostic and prognostic tools.
The natural history of PC onset and course is highly variable, making it a heterogeneous disease [5]. PCs that are detected early often advance slowly to a level where other aging-related causes/diseases pose a threat to life. Predicting the potential for early-stage cancers to progress is challenging. It is unknown whether genetic changes are linked to the onset and spread of PC despite extensive research being conducted on the molecular mechanisms underlying disease development [3]. At present, there is no infallible method to discriminate aggressive from indolent tumors. However, significant discoveries in the last century have dramatically changed the outlook for PC patients, including the hormone-dependent nature of PC [3] and the high therapeutic efficacy in targeting this key feature, specifically the high expression and frequent genetic amplification of the androgen receptor (AR). In addition, numerous studies for the genetic cause of this disease have revealed deletions of the PTEN gene and amplification of the AR in advanced disease [6].
Although AR plays a central role in PC, AR gene mutations are only observed in a minority of PCs and rarely at disease onset. This suggests that additional genetic lesions might contribute to prostate tumorigenesis. Advances in genome-wide analysis, microarrays, and high-throughput sequencing have allowed for the identification of key genes involved in the development and progression of PC, including aberrant fusion transcripts. Oncogenic chromosomal translocations involve the abnormal fusion of two genes, which can lead to deregulated or altered gene expression that are often, but not always, associated with the expression of chimeric proteins displaying transforming properties [6].
Translocations in ETS gene family members are the most common translocations implicated in PC development. It was initially reported that the 5′ untranslated region of TMPRSS2 (21q22.2), which is prostate specific and androgen inducible, replaces the 5′ end of ERG (21q22.3) and ETV1 (7p21.3) during PC development. Interestingly, the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion is often caused by a deletion [7], although a significant number of TMPRSS2-ERG fusions are formed through a translocation-like mechanism, whereas the TMPRSS2-ETV1 fusion is always the consequence of a translocation [8]. TMPRSS2 also fuses with other ETS family genes in a small percentage of PCs, such as ETV4 (17q21) and ETV5 (3q28). An interesting point of the TMPRSS2-ETS translocation is that, unlike IgH-related translocations, the product is not a chimeric protein; instead, overexpression of the oncogene occurs under the influence of a promoter element [9]. Other translocations identified in PC samples include fusions of SLC45A3, which encodes the solute carrier family 45 member 3, with ETV5 (1q32.1)(3q28); KLK2 (19q13.41) with ETV4 (17q21); C15orf21, a prostate-specific androgen-repressed gene with ETV1 (15q21.1)(7p21.3); and SLC45A3 (1q32.1) with ETV1 (7p21.3) [10]. Shan and colleagues found a translocation involving the UNC5C gene, located at the centromeric breakpoint on 4q22 [11]. This translocation directly causes the loss of the promoter region and the first exon of UNC5C, which encodes a putative tumor suppressor that is inactivated in various human cancers [12]. Notably, this translocation may contribute to PC development through the inactivation of tumor-suppressor genes rather than a gain of function by forming fusion genes [11].
This review explores the significant chromosomal translocations in PC and their involvement in the course and progression of the disease, and the therapeutic implications and opportunities.
2. The ETS Gene Family
The E26 transformation-specific (ETS) transcription factor family plays a crucial role in regulating various biological processes through its ability to bind specific DNA sequences, particularly in the promoter regions of target genes. With at least 28 genes categorized into five subfamilies [13], ETS transcription factors are involved in important pathways such as stem cell development, cell senescence, proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis [13].
All ETS transcription factors include a conserved ETS DNA-binding domain that consists of 80 amino acids and binds to the DNA core sequence 5′GGA(A/T)3′ (Figure 1A). The ETS domain is a variant of the winged helix–turn–helix motif [14], which is highly structurally conserved among the ETS family members, and contains three α-helices and four β-sheets (Figure 1A). Protein–DNA contacts occur through the third α-helix and in the ‘wing’ between β-strands 3 and 4, as shown in the crystal structure of the ETS domain of ETS2 [15].
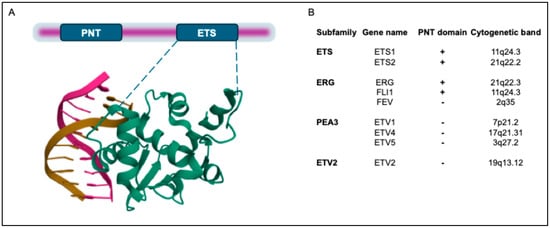
Figure 1.
Domain structure of human ETS transcription factors (TFs) involved in oncogenic chromosomal rearrangements in PC. (A). In addition to the ETS domain, ETS1 and ETS2 also contain a Pointed (PNT) domain. In the lower part, the crystal structure of the ETS domain of ETS2 is shown, which was downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (PDB; https://www.rcsb.org/; https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb4BQA/pdb) [16]. (B). ETS transcription factors (TFs) have been classified into 12 subfamilies. Herein, only the proteins involved in PC translocations are shown. In addition to the ETS domain, a subset of the ETS family also possesses a PNT domain. Coordinates of cytogenetic bands of ETS genes are indicated.
ETS-domain proteins interact with various protein partners that either inhibit or enhance DNA binding. They also bind to coactivators and corepressors, which regulate their transcriptional activity. ETS-domain family members can be further sub-classified based on the presence of the Pointed domain, which was initially identified in the Drosophila melanogaster protein pointed (Pnt) [17]. The Pnt domain contains a bundle of four α-helices, with an additional N-terminal α-helix [18] that facilitates heterodimerization with protein partners and acts as a transcriptional repressor [17].
Among the genes involved in PC, ERG belongs to the “ERG subfamily” and contains a Pnt protein-interaction domain, while ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5 belong to the “PEA3 subfamily”, so called because of their close homology with the epididymal transcription factor polyomavirus enhancer activator 3 (PEA3), who was the first member of this group to be found and whose human homolog is ETV4 [19]. The ETS family members involved in PC chromosomal rearrangements are listed in Figure 1B.
ERG proteins interact with the Fos/Jun (AP1) complex to cause transcriptional activation and can form homodimer or heterodimers with other ERG splice variants and/or other ETS family proteins for reciprocal negative regulation [20]. Under normal physiological conditions, ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5 display a role in morphogenesis; analysis of their mRNA levels revealed that these genes are widely expressed in several organs during embryonic development [19], motor coordination [21], and in fertility [22].
3. PC Chromosomal Translocations Involving ETS Family Members
Translocation of ETS genes were first reported in Ewing sarcoma (EWS-FLI1, EWS-ERG, and EWS-ETV1) and acute myeloid leukemia (TLS-ERG). The first time ETS genes were found to be involved in the development of human PC was the identification of the high expression of ERG in a large proportion of prostate tumor samples [8,23,24,25]. The most common chromosomal rearrangements involve the 5′ untranslated region of TMPRSS2 (21q22) and the coding region of ERG (21q22), ETV1 (7p21), or ETV4 (17q21), leading to overexpression of the respective ETS family member [8,25]. The TMPRSS2/ERG rearrangement can be associated with aggressive tumor features [26], with incidences varying from 15% to 72% [27]. As a result of this translocation, a TMPRSS2-ERG fusion gene is created, with the expression of the ETS protein under the control of the promoter/enhancer of the TMPRSS2 gene. Since TMPRSS2 is androgen-inducible and is highly expressed in the prostate [28], its translocations lead to the androgen-dependent expression of ETS proteins in this organ in response to androgens, thus inducing ETS protein overexpression in PCs. ERG is the most commonly rearranged ETS gene in PCs (50%), primarily due to its proximity to the TMPRSS2 gene on chromosome 21. The PEA3 family genes are localized on different chromosomes, resulting in less frequent translocations (ETV1 translocations in 5–10% cases, and ETV4 or ETV5 translocations in ~1–2%) [29].
TMPRSS2 and ERG are about 3 Mbp apart in an identical orientation on chromosome 21 (Figure 2), and in about two-thirds of cases with TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, there is a complete or partial deletion of the middle sequence. Notably, more than 50% of these fusion events join the first intron of TMPRSS2 with the third intron of ERG and lead to the most common TMPRSS2-ERG mRNA fusion transcript that juxtaposes exon 1 of TMPRSS2 with exon 4 of ERG [9]. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion has been associated with a more aggressive phenotype in both clinically localized PC and metastatic PC [30]. Tomlins et al. reported the fusion of a 5′ sequence from TMPRSS2 to a 3′ ETV1 sequence; these genes are localized in two different chromosomes (Chr. 21 and Chr. 7, respectively). In the TMPRSS2-ETV1 fusion event, exon 1 of TMPRSS2 joins exon 4 of ETV1, leading to a rearrangement very similar to that of the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion gene [25].
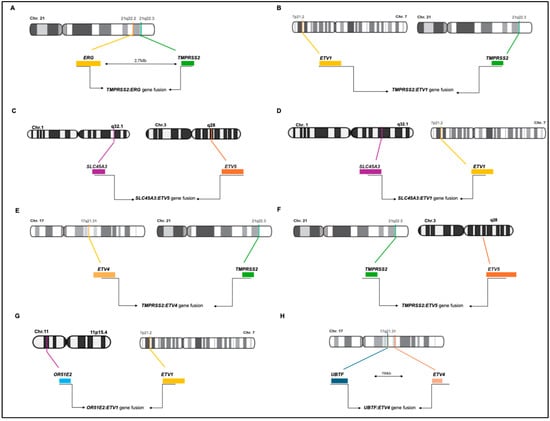
Figure 2.
Schematic representations of ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. (A). TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion; (B). TMPRSS2:ETV1 gene fusion; (C). SLC45A3:ETV5 gene fusion; (D). SLC45A3:ETV1 gene fusion; (E). TMPRSS2:ETV4 gene fusion; (F). TMPRSS2:ETV5 gene fusion; (G). OR51E2:ETV1 gene fusion; (H) UBTF:ETV4 gene fusion.
In the TMPRSS2-ETV4 fusion event, a short 8 Kb regulatory region located upstream of TMPRSS2 and characterized by an androgen-regulated enhancer is juxtaposed to an intronic region immediately upstream of exon 3 of ETV4. While the upregulation of ETV4 expression was shown in the RWPE, and PC-3 and DU145 cells, but not in LNCaP and VCaP cells, the TMPRSS2-ETV4 fusion has not been reported in PC cell lines [31]. Remarkably, the downregulation of ETV4 inhibits the proliferation and migration of PC cells and anchorage-independent growth in nude mice [31], whereas its overexpression stimulates proliferation, anchorage-independent growth, and migration of RWPE PC cells [31]. In the TMPRSS2-ETV5 fusion event, exons 1–3 of TMPRSS2 are fused with exon 2 of ETV5. ETV1 and ETV5 were also found to be fused with the androgen-induced gene solute carrier family 45 member 3 (SLC45A3). In these fusion events, exon 1 of SLC45A3 is juxtaposed with exon 5 of ETV1 and exon 8 of ETV5 [32].
Later on, Barros-Silva and colleagues reported two new 5′ fusion partners of ETS genes (OR51E2-ETV1 and UBTF-ETV4) [33]. The OR51E2 and ETV1 genes are mapped on chromosome bands 11p15 and 7p21, respectively, and share the same transcriptional orientation, indicating an origin from a chromosomal translocation. The OR51E2-ETV1 transcript comprises the untranslated exon 1 of OR51E2 with an additional 292 bp untranslated sequence downstream of exon 2 of OR51E2, which is fused to exon 8 of ETV1. The OR51E2 gene (Olfactory Receptor, Family 51, Subfamily E, Member 2) encodes a member of the G-protein-coupled receptor family derived from a single coding exon. The OR51E2-ETV1 fusion maintains the tissue specificity due to one of the two described promoters of OR51E2 (in exon 1). The UBTF-ETV4 fusion transcript comprises the untranslated exon 1 and 2 of UBTF, joined to exon 5 of ETV4. Both genes are in the same chromosomal band, 17q21, separated by about 700 kb.
Hermans and colleagues reported two other fusion genes involving ETV4 in PC: Kallikrein 2 (KLK2)-ETV4 and calcium-activated nucleotidase 1 (CANT1)-ETV4. KLK2 is an androgen-regulated and prostate-specific gene, which maps to chromosome band 19q13, while ETV4 maps to chromosome band 17q21. The KLK2-ETV4 mRNA fragment comprises KLK2 exon 1 linked to a new ETV4 exon (exon 4a) followed by the ETV4 exon 5 and 6 sequences. Because of the relative orientations of KLK2 and ETV4, the KLK2-ETV4 gene fusion cannot be accounted for by a single chromosomal translocation. The second CANT1-ETV4 transcript contains one of the two described exons 1 of CANT1 (exon 1a). This exon maps ≃4 Kbp downstream of the other first exon. Only one of the two alternative first exons of CANT1 is present in the CANT1-ETV4 fusion transcript. In contrast to most CANT1 transcripts, this mRNA is preferentially expressed in the prostate. CANT1 and ETV4 map in the same orientation on 17q, at 35 Mbp [34].
DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 5 (DDX5) has been identified as a new 5′ partner gene of ETV4 by RLM-RACE in one PCa patient. Sequence analysis of DDX5-ETV4 revealed that this fusion transcript comprises exons 1–3 of DDX5, fused in frame with exons 5–13 of ETV4 [30]. Tomlins et al. described four 5′ fusion ETV1 partners: SLC45A3; HERV-K_22q11.23, an endogenous retroviral element; C15orf21, a prostate-specific androgen-repressed gene; and HNRPA2B1, a strongly expressed housekeeping gene [25].
Although gene fusions can be considered a common feature in PC, their specific role in cancer development is still under investigation. TMPRSS2 is a prostate-specific gene that is expressed in both normal and cancerous prostate tissue, whose expression is promoted by androgens in PC cells. Thus, the 5′ untranslated region of the TMPRSS2 gene can drive the overexpression of the fused ETS gene in TMPRSS2:ETS-positive PCs in an androgen-dependent fashion [24,35]. During PC progression, ETS gene fusions likely act as genetic triggers, promoting the transition from a benign epithelium to prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and leading to adenocarcinoma and metastatic disease [35]. In fact, TMPRSS2:ERG fusion is not expressed in benign prostate tissue, whereas it is found in localized PCs and in various metastatic stages. Furthermore, overexpression of ETV1 in benign prostate cells increased cell invasion without affecting proliferation; however, transgenic mice overexpressing ETV1 developed mouse PIN (mPIN), but not carcinoma [36,37]. These findings suggest that ETS gene fusions, while important, require additional genetic lesions (such as PTEN or NKX3-1 loss) to drive invasion and carcinoma development.
Initially, TMPRSS2 was the only known 5′ partner in ETS gene fusions. However, as more cancers were studied, a lower percentage of TMPRSS2:ETV1 fusions were found compared to TMPRSS2:ERG fusions, suggesting that other 5′ partners might be involved. Afterward, several new 5′ partners for ETV1 fusions were identified, including SLC45A3, HERV-K_22q11.3, C15ORF21, and HNRPA2B1. All these partners are under the regulation of androgens, leading to distinct classes of ETS gene fusions [33].
Interestingly, transcription factors can contribute to genomic rearrangements by positioning chromosomal loci and recruiting enzymes that induce DNA double-strand breaks, thereby increasing the susceptibility of the transcribed regions to rearrangements. For example, the enzyme topoisomerase-2 beta (TOP-2b) is recruited to gene promoters in response to androgen and estrogen signaling, causing DNA breaks and aiding transcription. Androgen signaling itself has been shown to promote TMPRSS2-ERG fusion by recruiting DNA break-inducing enzymes and rearrangement breakpoints are more frequent near open chromatin and AR-binding sites in TMPRSS2-ERG fusions but less common in tumors lacking these fusions [38,39]. In line with these findings, inhibitors of repair enzymes like PARP1 and DNA-PK may reduce gene fusion susceptibility, while TOP-2b inhibitors, such as etoposide or doxorubicin, could promote gene fusions by enhancing DNA breaks. Thus, gene fusion vulnerabilities open the path to novel targetable opportunities in PC.
4. Strategies for Detecting Gene Fusions in PC
The detection of significant overexpression of ETV1 or ERG genes in PC samples showing a consistent loss of the 5′ regions of the associated transcripts led to the identification of structural rearrangements involving chromosomal translocations. RNA ligase-mediated rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RLM-RACE), FISH techniques, and direct DNA sequencing have been instrumental to demonstrating that the 5′ end of ETV1 or ERG are consistently replaced with the 5′ untranslated region of the prostate-specific gene TMPRSS2 (21q22.2), generating different translocations (summarized in Table 1 and Figure 2). Remarkably, overexpression of either ETV1 or ERG is mutually exclusive and associated with fusion transcripts, occurring in 10% of PCa cases for ETV1 and 60% for ERG, thereby leading to the overexpression of their downstream targets [40,41].
The conventional methods for detecting chromosomal translocations are Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE), reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR), and real-time PCR (qPCR) [42]. FISH uses fluorescently labeled DNA probes targeting DNA sequences on chromosomes. FISH is fast, with a high resolution and it is often used to validate the results obtained from other methods. PCR methods are based on designing oligonucleotide primers on both sides of the breakpoint fusion region. This amplification allows for the identification of rearranged DNA fragments. RT-PCR is well established for identifying very small numbers of fusion transcripts. Both PCR and RT-PCR can be extremely sensitive and specific for the detection of chromosomal translocations. The application of qPCR to detect chromosomal translocation is more sensitive and rapid than RT-PCR. By using specific primers complementary to the breakpoint region, the fusion transcripts can be detected and quantified. All of these approaches, although highly sensitive, do not allow for the identification of novel chromosomal translocations. To this aim, next-generation sequencing (NGS) represents a powerful tool in the high-throughput approach for detecting translocations. Translocation detection is performed by sequencing the entire genome or specific regions of interest making it an uncommon approach in clinics due to its high cost and complexity.


Table 1.
Chromosomal rearrangements identified in PC samples.
Table 1.
Chromosomal rearrangements identified in PC samples.
| Translocation | Samples | Detection Technique(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 17/34 | [43] | |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 17/111 | qPCR; FISH | [27] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG; TMPRSS2:ETV4 | 7/19 1/19 | RT-PCR | [44] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 44/63 | RACE; RT-PCR; FISH | [45] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG TMPRSS2:ETV1 TMPRSS2:ETV4 | 36/65 1/53 1/53 | Interphase FISH | [27,46] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 120/253 | interphase FISH | [47] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 11/26 | RT-PCR; DNA sequencing | [48] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 35/58 primary 3/7 lymph node metastases | FISH | [7] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 35/86 | RT-PCR; FISH; DNA sequencing | [49] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG TMPRSS2:ETV1 | 14/18 0 | RT-PCR | [50] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG TMPRSS2:ETV1 | 35/82 1/82 | RT-PCR; FISH | [51] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 35/59 | RT-qPCR | [26] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG TMPRSS2:ETV1 | 18/50 0 | RT-PCR | [52] |
| TMPRSS2:ERG | 6/15 | RT-PCR; FISH | [53] |
| OR51E2:ETV1 | 1/14 | 5′ RACE | [33] |
| CANT1:ETV4 | 1/149 | qPCR/FISH | [34] |
| KLK2:ETV4 | 1/149 | qPCR/FISH | [34] |
| DDX5:ETV4 | 1/110 | qPCR/FISH | [30] |
| UBTF:ETV4 | 1/14 | 5′ RACE | [33] |
| SLC45A3:ETV1 | 1/14 | 5′ RACE | [33] |
| C15ORF21:ETV1 | 1/14 | 5′ RACE | [33] |
| HERVK17:ETV4 | 1/14 | 5′ RACE | [33] |
| HNRPA2B1:ETV1 | 2/194 | RT-PCR | [54] |
| FLJ35294:ETV1 | 1/110 | qPCR/FISH | [30] |
The development of new methods to detect genetic rearrangements has therefore improved the ability to identify new partners of the TMPRSS2 gene in PC. The improvement of NGS-based methods with fusion sequencing via terminator-assisted synthesis (FTAS-seq) allows for the enrichment of specific genes while profiling their 3′-terminal fusion partners. The detection of translocations based on NGS methods has several advantages compared to conventional methods, such as the detection of cryptic rearrangements and unknown partner genes, in addition to the possibility to analyze the presence of gene mutations in parallel [55]. In particular, using this semi-targeted RNA sequencing technique, 11 previously unknown TMPRSS2 fusion partners were identified (Linc00114, PPP3CA, AMACR, CASZ1, SIM2, TTC18, FGFR2, OPTN, C1orf61, TBXAS1, and RERE), with 21 different breakpoint sequences [56]. Moreover, with this method, various TMPRSS2-ERG isoforms in PC specimens were described [56]. In addition, next-generation mapping (NGM), a technology that is able to analyze megabase-length DNA sequences outside the detection range of single-base resolution NGS, allowed for the identification of large complex genome rearrangements, named chromoplexy, occurring coordinately and differently in ETS-positive and negative tumors, thus depicting the clonal progression of cancer genomes [57]. These novel approaches show promise as tools for biomarker discovery and could aid in the development of personalized cancer therapies.
Reliable detection of ETS gene fusions by immunohistochemistry (IHC) is hindered by antibody availability; while a reliable antibody exists for detecting ERG, other ETS gene fusions lack specific antibodies for cancer cells. This limitation highlights the need for more sensitive techniques, such as RNA in situ hybridization (RNA ISH). The advent of RNAscope technology has strongly improved detection sensitivity in comparison with traditional FISH techniques, while also minimizing background noise. The combination of IHC and RNA-ISH methods enables more comprehensive detections of ETS fusions. Kunju and colleagues validated the RNA-ISH method for the in situ detection of ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded PC samples [58]. By comparing RNA ISH/IHC with standard in situ techniques for detection of ETS gene rearrangements, they confirmed the reliability of the new method and demonstrated its utility in identifying rare PC subtypes with dual ETS gene rearrangements in different tumor foci of the same tumor [58].
The use of whole-mount radical prostatectomy has recently been instrumental to assessing the clonal heterogeneity of PC. This approach revealed mutually exclusive expression of various biomarkers across distinct tumor foci in multifocal tumors, with no single focus displaying the simultaneous expression of any of the other markers analyzed, indicating that the tumors likely arose through independent clonal evolution driven by distinct molecular aberrations [59]. With this technique, TMPRSS2-ERG fusion was confirmed as the most common genetic alteration in PC, with ERG overexpression in 56% of patients, followed by SPINK1, the second-most common biomarker, showing overexpression in around 10% of PC cases [59]. ERG expression was more frequently observed in younger Caucasian patients with low-grade, organ-confined tumors. In contrast, SPINK1 expression was more frequently observed in African American patients, particularly in tumors with a higher volume (>20%) and anterior localization. Interestingly, 17% of cases showed ERG and SPINK1 coexpression, either in different areas of the same tumor or in separate tumors within the same prostate gland, highlighting the heterogeneity of PC [59]. This multiclonal architecture can influence the Gleason grading, potentially affecting clinical decision-making by reclassifying patients from high-risk to intermediate-risk categories.
As mentioned above, biological differences across ethnicities were documented in PC, particularly in the frequency of ERG oncogenic activation. Notably, men of European descent have the highest rates of ERG alterations, while men of African or Asian descent have significantly lower rates [60]. Although these findings must be interpreted with caution due to variations in testing methods, sample types, and ethnic or geographical classifications, addressing these issues is crucial for realizing precision medicine for all PC patients [60]. These interesting observations highlight socioeconomic status as a contributing factor in the observed disparities; nevertheless, these emerging findings on ethnic differences in ERG frequencies could offer an objective way to assess ethnicity-based cancer biology to improve clinical diagnoses and enable tailored therapies.
5. Relevance of ETS Fusions in PC Prognosis
ERG gene rearrangements have been studied in various clinical settings, but no clear consensus on their significance has emerged. Some studies suggested that ERG fusions are linked to favorable outcomes, while others found no association, or even a connection to poor prognosis and more aggressive cancer [7,23,26,27,46,52,53,61]. ERG rearrangements involving deletions between TMPRSS2 and ERG, as well as duplications of the deleted allele, have been linked to aggressive disease [7,46,62]. Further studies support this finding, documenting that duplication of the rearranged allele correlates with worse outcomes, including increased metastasis. However, in a subsequent study on a cohort of 521 patients undergoing radical prostatectomy, ERG rearrangements alone were not associated with disease stage or recurrence but were linked to a lower grade of cancer [63]. Additionally, research into other genetic alterations, like those involving ETV1 rearrangements, has failed to show strong associations with poor survival [64]. This variability suggests that factors other than the ERG status, such as PTEN deletions and/or the expression/deletion of other factors, may contribute in determining PC progression and prognosis. PTEN gene deletion plays a major role in the development of PC. Yoshimoto and colleagues, in a small set of cases, observed that cancers with both ERG rearrangements and PTEN deletions had the worst prognosis [65]. These findings were supported by two in vivo studies involving transgenic mouse models. Carver and colleagues reported that PC samples with the TMPRSS2-ERG rearrangement often exhibited loss of the tumor suppressor PTEN [36]. Consistently, transgenic overexpression of ERG in mouse prostate tissue accelerated the progression of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) to prostatic adenocarcinoma in a heterozygous Pten background. Therefore, ERG seems to play a specific role in PC progression, working together with PTEN haploinsufficiency to drive the transition from HGPIN to invasive adenocarcinoma [36]. In parallel, King and colleagues demonstrated that transgenic TMPRSS2-ERG mice develop prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) only in the context of PI3-kinase pathway activation when PTEN is inhibited or genetically ablated. They also showed that TMPRSS2-ERG-positive human tumors often exhibit PTEN loss, suggesting cooperation of these factors in prostate tumorigenesis [37].
Thus, the prognostic significance of these translocations remains unclear, although specific variants may have more predictive value. A key open question is whether the molecular understanding of ETS translocations can help in developing a new molecular classification of PC that differentiates cancers with distinct clinical behaviors. In this context, ERG overexpression alone does not seem to trigger PC; in vitro studies have shown that overexpressing ERG or ETV1 increases cell migration and invasion [25,34,66,67]. Conversely, knocking down these genes in PC cells slows invasion [24,25,67,68]. In genetically modified mice, ERG or ETV1 overexpression leads to prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) but not invasive cancer and crossbreeding with Pten-knockout mice results in PIN and micro-invasive cancer. Thus, ERG appears to cooperate with other oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes in PC development.
Gene expression studies have identified pathways linked to ERG overexpression, such as the WNT and transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) pathways, as well as genes like CACNA1D, TDRD1, PLA2G7, and NCALD [44,69,70,71]. These genes may not be direct ERG targets but could be indirectly regulated or could mark cells where TMPRSS2-ERG fusion occurred. TDRD1 has been identified as a direct ERG target [71]. Remarkably, ERG overexpression interferes with the AR gene expression program, potentially promoting dedifferentiation through EZH2 [72].
The role of ETV1 in PC is less understood. In vitro studies showed that the full-length protein is a strong transcriptional activator, whereas the truncated form lacking the N-terminal TAD domain seems less active [73,74]. Both variants increase migration and invasion, but only the full-length protein induces anchorage-independent growth [73]. However, clinical samples displaying ETV1 overexpression are rare, thus limiting a comprehensive understanding of ETV1-regulated genes in PC.
Thus, although ERG and ETV1 both belong to the ETS family and may share some binding sites, they likely affect PC development through different mechanisms. ERG inhibits AR-regulated gene expression, while ETV1 appears to stimulate it, as evidenced by their opposite effects on PSA expression [72,75]. By using knock-in mouse models and genome-wide analyses, Baena and colleagues explored the distinct roles of ERG and ETV1 translocations in PC. While both transcription factors regulate a shared set of genes, including AR targets, they perform this transcriptional regulation in opposite ways. ETV1 upregulates AR target genes and genes involved in steroid biosynthesis and metabolism, pushing for other oncogenic events, like PTEN loss, which contribute to more aggressive PC in both mice and humans [76]. These reported findings highlight biologically distinct PC subtypes defined by different ETS transcription factor signatures. Clinical outcome analyses confirmed that ETV1-regulated pathways are strongly linked to the progression of invasive prostate adenocarcinoma [76]. Specifically, gene sets defined by ETV1, but not by ERG, are associated with higher Gleason scores and metastatic disease. Consistently, ERG expression has shown no correlation with poor outcomes, and no significant association with Gleason scores, disease recurrence, or clinical prognoses [77].
Overall, the molecular evidence suggests that ERG and ETV1 have both shared and distinct targets, and clinical samples with ETV1-positive and ERG-positive tumors cluster separately [71,78], indicating limited evidence for a common mechanism in PC.
6. Therapeutic Approaches Targeting ETS Fusions
In PC cells, the overexpression of ETS factors enhances cell invasion and leads to the development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) in transgenic mouse models [24]. Conversely, reducing ETS factors in vitro decreases cell motility and invasiveness. In line with these observations, depletion of ERG and ETV1 was shown to be sufficient to slow tumor growth in vivo [25]. Recent studies have shown that TMPRSS2-ERG expression is reactivated in castration-resistant prostate cancer [35]. From these reported findings, ETS proteins have emerged as promising targets for preventing or treating metastatic PC. Several small molecule inhibitors have been identified in the past decade through in vitro screens (e.g., YK-4-279, BRD32048, and ERGi-USU) [79,80,81] and computer-aided drug design (e.g., VPC-18005) [82]. Since many ETS factors have known 3D protein structures, they represent suitable targets for structure-based drug discovery. However, while the protein sequences of ETS factors are conserved, limiting the development of oligonucleotides that mimic ETS1-binding sites [83], the 3D structures of their DNA-binding pockets and the homodimerization domains differ, with unique polar and hydrophobic regions, as well as amino acid variations. This diversity allows for the development of specific small molecule inhibitors for each ETS factor, expanding the potential for anti-ETS therapies, as discussed below (Table 2).

Table 2.
List of small molecule inhibitors targeting ETS transcription factors in PC cells.
6.1. The Small Molecule Inhibitor YK-4-279
A small molecule inhibitor targeting the interaction between the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1 and its transcriptional partner DHX9 was developed for Ewing sarcoma treatment [79,89]. The RNA/DNA helicase DHX9 was shown to interact with EWS-FLI1 and enhance its oncogenic properties [89,90,91]. The YK-4-279 molecule was shown to target the chimeric protein EWS-FLI1 in Ewing sarcoma and impairs EWS-FLI1 activity and slow down tumor growth in mouse xenograft models [79,92]. Thus, YK-4-279 treatment, as well as DHX9 downregulation, could represent a targetable opportunity for Ewing sarcoma [92,93,94], and the TK-216 derivative has recently concluded phase I/II trial as a monotherapy and in combination with vincristine in relapsed or refractory Ewing sarcoma patients [95].
Since FLI1, ERG, and ETV1 are Class I ETS factors, sharing over 60% identity and 80% homology in their amino acid sequences [96], the YK-4-279 molecule was also tested in PC cell lines with androgen-dependent ERG and ETV1 expression [84]. Remarkably, the small molecule YK-4-279 effectively inhibited ERG- and ETV1-driven transcriptional activity, leading to decreased cell motility and invasion [84] and reduced primary tumor growth and metastasis of fusion-positive PC xenografts [85].
Since the 1940s, androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has been the primary treatment for metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer [3]. However, its initial effectiveness is short-lived, and most men eventually develop castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), which leads to rapid deterioration and death [3]. For patients with CRPC, docetaxel-based chemotherapy is often used to extend survival and maintain quality of life. Prolonged use of high-dose docetaxel can lead to toxicity and resistance, leaving few treatment options for those who progress after or during treatment. Recently, drugs such as abiraterone, cabazitaxel, and enzalutamide have been approved for CRPC patients who no longer respond to docetaxel, but their effectiveness remains limited [97], thus highlighting the critical need to enhance the overall effectiveness of treatments while minimizing side effects. The combination of low-dose docetaxel and YK-4-279 was shown to significantly inhibit growth, trigger apoptosis, and reduce the migration and invasion capabilities of human PC cells [98].
6.2. Inhibition of ERG-DNA Binding Through DB1255 and the VPC-18005 Antagonist
DB1255 is a di-(phenyl-thiophene-amidine) compound and a DNA-binding modulator that specifically targets the ERG/DNA complex. It was identified in a screen of molecules affecting ERG/DNA binding [86]. The ETS domain binds to DNA by direct recognition (through conserved arginine residues) of the core 5′-GGA(A/T)-3′ sequence within the major groove, along with interactions with the phosphate backbone in the minor groove, that flanks the 5′-GGA(A/T)-3′ sequence [99]. Inhibition of ERG’s binding to DNA can be achieved by targeting a sequence that partially covers the minimal ERG-binding site and blocking ERG/DNA binding.
The search for antagonists designed to sterically prevent ERG DNA binding through its ETS domain to impair its transcriptional activity led to identification of the VPC-18005 inhibitor. A structure-based virtual screening approach was applied to the ERG-ETS domain crystal structure, identifying a druggable surface pocket overlapping with the ERG–DNA interface and adjacent to the DNA recognition helix (α3). The predicted small molecule would competitively block DNA binding. The identified lead compound, VPC-18005, directly binds to the ERG ETS domain and was shown to reduce migration and invasion of PC cells expressing ERG. Remarkably, VPC-18005 also decreased metastasis in a zebrafish xenograft model [82]. These results provide evidence that small molecules targeting the ERG-ETS domain can suppress transcriptional activity and reverse the transformed characteristics of PC with abnormal ERG expression [82].
6.3. Degradation of ERG by WP1130
The development of the WP1130 inhibitor stems from the rationale of targeting the ERG oncogenic program through inducing its degradation. The ubiquitin-specific peptidase 9, X-linked (USP9X), which is a deubiquitinase enzyme, binds to ERG in PC cells expressing TMPRSS2:ERG and deubiquitinates ERG in vitro. Knockdown of USP9X led to increased levels of ubiquitinated ERG, which was accompanied by a reduction in ERG levels. Remarkably, treatment with the USP9X inhibitor WP1130 was sufficient to achieve ERG degradation both in vivo and in vitro, thus decreasing the expression of genes associated with ERG, resulting in the inhibition of ERG-positive tumor growth in mouse xenografts [87]. Interestingly, the USP9X inhibitor WP1130 was also able to induce the degradation of pre-B cell leukemia homeobox-1 (PBX1) protein, which promotes PCa cell proliferation and confers resistance to doxorubicin and cisplatin [100]. The combined treatment with multiple deubiquitinase inhibitors, including betulinic acid or WP1130 and enzalutamide, reduced AR protein stability and mRNA expression in PC cells, making it an attractive strategy for CRPC treatment [101].
6.4. Inhibition of ETV1 by BRD32048
By utilizing small-molecule microarray screens, Pop and colleagues identified compounds able to affect the biological function of ETV1. In particular, BRD32048, a 1,3,5-triazine small molecule, was the leading candidate for modulating ETV1 activity. The authors found that BRD32048 directly binds to ETV1, influencing both its transcriptional activity and the ETV1-driven invasion of cancer cells. In addition, BRD32048 also inhibited the p300-dependent acetylation of ETV1, which, in turn, caused its degradation [80].
6.5. Inhibition of ERG Expression by ERGi-USU Inhibitor
To identify inhibitor small molecule compounds that can decrease ERG protein levels, a collection of 2407 small molecules, including natural products and approved oncology drugs, was used in a primary screen with a Western assay platform. The screening identified the ERGi-USU inhibitor, which inhibited the cell growth of ERG-harboring PC cells, whereas non-ERG-expressing cell lines were not affected [81]. Importantly, ERGi-USU significantly inhibited the growth of ERG-positive tumor xenografts in nude mice [81]. From the parent ERGi-USU compound, the more potent ERG inhibitor ERGi-USU-6 was developed by improving the synthesis procedure [102].
6.6. TNIK Kinase Inhibition by NCB-0846
By using mass spectrometry-based kinomic profiling, Lee and colleagues identified kinases that were differentially expressed and/or phosphorylated in DU145 cells engineered to express ERG. Among them, the authors identified Traf2 and Nck-interacting kinase (TNIK) as being markedly upregulated and phosphorylated upon ERG overexpression. This screen opened the path to the use of the TNIK inhibitor NCB-0846, which was able to reduce cell viability, colony formation, and anchorage-independent growth in ERG-positive PC cells [88].
6.7. Splice-Switching Oligonucleotides Targeting ERG Alternative Splicing
With the aim of inhibiting ERG activity, Li and colleagues developed splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs) targeting ERG alternative splicing [103]. Alternative splicing amplifies the coding potential of the eukaryotic genome and increases the diversity of mRNA and protein products [104]. Regulation of splicing is essential for maintaining tissue homeostasis and is critically involved in development and various diseases, including cancer, suggesting that targeting this process could represent a promising strategy for therapeutic intervention [104]. Exon 7b of ERG is 72 bp long and adds, in frame, 24 amino acids to the transcriptional transactivation domain, whose inclusion is associated with advanced PC [105]. Reducing the inclusion of exon 7b through SSOs reduced cell proliferation and migration, and increased apoptosis, confirming the contribution of exon 7b to ERG’s oncogenic properties [105] (Figure 3). Treatment with a single dose of the SSO resulted in a marked drop in the ERG protein levels in both ERG-positive VCaP and MG63 cell lines and in mouse models. This led to decreased expression of key downstream target of ERG, including cyclin D1, c-Myc, and Wnt/β-catenin, thus reducing cell proliferation and migration, and promoting apoptosis [103]. These findings highlight SSOs as a potential therapeutic strategy for PC, like the successful Eteplirsen, which was developed for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy treatment [106], and Nusinersen, developed for Spinal Muscular Atrophy treatment [107].
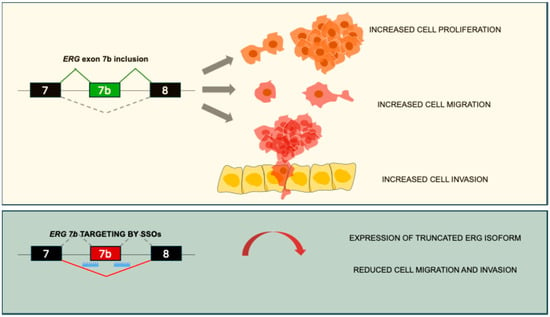
Figure 3.
Splice-switching oligonucleotides targeting ERG alternative splicing represent a novel therapeutic approach for targeting ERG-positive PC. In the upper panel, ERG exon 7 inclusion leads to PC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In the lower panel, SSOs targeting exon 7b acceptor and donor sites lead to the exclusion of the alternative exon and recognition of a premature stop codon, leading to a truncated ERG protein [103,105].
7. Conclusions
Genomic rearrangements represent a nonrandom and locus-specific feature of PC. Since its discovery in 2005, ERG overexpression through fusion with androgen-regulated genes has been linked to PC [8,23]. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion is present in about 50% of PCs and seems to be linked to disease progression. However, while its prognostic value remains unclear, ERG fusion shows promise as a diagnostic biomarker. Fusion genes can be detected via blood samples, enabling non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring. Moreover, gene-editing strategies targeting fusion breakpoints hold promise for future treatments. Overall, fusion gene profiling represents a valuable addition to PC management, improving prediction, guiding therapy, and offering mechanistic insights into disease progression.
Accurately predicting the clinical course of PC remains difficult, especially in identifying patients at risk of recurrence. While Gleason scores and serum PSA levels are commonly used prognostic tools, incorporating fusion gene profiling could significantly enhance the prediction accuracy for PC recurrence [108]. Machine-learning models combining fusion gene data with PSA and/or Gleason scores were able to achieve high levels of accuracy [108], proving their robustness and applicability in managing the molecular and phenotypic heterogeneity of PC.
Another issue to consider is that most genomic studies examine a single tumor focus, yet PC is often multifocal, with significant molecular heterogeneity across different regions of the prostate gland. This intra-tumoral heterogeneity should be considered in future genomic analyses, therapeutic development, and biomarker design.
The transrectal, ultrasound-guided 12-core systematic biopsy is currently the standard method for the initial diagnosis and grading of PC. Unlike diagnostic biopsies in other cancers, which usually target visible abnormalities, this method samples the prostate in a uniform but non-targeted manner. This approach often leads to missed cancer diagnoses and inaccurate grading at biopsy, with frequent changes in cancer classification after radical prostatectomy. Such diagnostic imprecision can result in overtreatment of low-grade disease or initial undertreatment of missed aggressive cancers. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-targeted biopsies can better detect high-grade PC compared to standard biopsies, but it is still debated whether they should replace or supplement systematic biopsies [109]. Hence, future investigations should focus on cross-disciplinary approaches, integrating genomic profiling with artificial intelligence-driven digital pathology evaluations and high-throughput image analysis to facilitate precise, subtype-specific predictions of clinical outcomes and therapeutic responses. Harnessing interdisciplinary collaborations will deepen our understanding of the biological complexity of PC and expedite the discovery of robust predictive biomarkers to guide precision oncology strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.D.C. and M.P.P.; writing—original draft preparation, F.D.C., V.R., L.C. and M.P.P.; writing—review and editing, L.C. and M.P.P.; supervision, M.P.P.; project administration, M.P.P.; funding acquisition, M.P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of University and Research (MUR; grant number PRIN202224MK8Z to M.P.P.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Verze, P.; Cai, T.; Lorenzetti, S. The role of the prostate in male fertility, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, N.D.; Tannock, I.; N’Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; et al. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: Planning for the surge in cases. Lancet 2024, 403, 1683–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J.; Fisher, G.; Kattan, M.W.; Berney, D.; Oliver, T.; Foster, C.S.; Møller, H.; Reuter, V.; Fearn, P.; Eastham, J.; et al. Long-term outcome among men with conservatively treated localised prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cooper, C.S. Translocations in solid tumours. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1996, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Beroukhim, R.; Schmidt, F.H.; Mosquera, J.M.; Setlur, S.; Tchinda, J.; Tomlins, S.A.; Hofer, M.D.; Pienta, K.G.; et al. TMPRSS2:ERG fusion-associated deletions provide insight into the heterogeneity of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8337–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Perner, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Mehra, R.; Sun, X.W.; Varambally, S.; Cao, X.; Tchinda, J.; Kuefer, R.; et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 2005, 310, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weier, C.; Haffner, M.C.; Mosbruger, T.; Esopi, D.M.; Hicks, J.; Zheng, Q.; Fedor, H.; Isaacs, W.B.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, W.G.; et al. Nucleotide resolution analysis of TMPRSS2 and ERG rearrangements in prostate cancer. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambiar, M.; Kari, V.; Raghavan, S.C. Chromosomal translocations in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1786, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Ambroisine, L.; Clark, J.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J.; Fisher, G.; Kudahetti, S.C.; Yang, J.; Kia, S.; Mao, X.; Fletcher, A.; et al. The identification of chromosomal translocation, t(4;6)(q22;q15), in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010, 13, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebault, K.; Mazelin, L.; Pays, L.; Llambi, F.; Joly, M.O.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Saurin, J.C.; Romeo, G.; Mehlen, P. The netrin-1 receptors UNC5H are putative tumor suppressors controlling cell death commitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4173–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudet, V.; Hänni, C.; Stéhelin, D.; Duterque-Coquillaud, M. Molecular phylogeny of the ETS gene family. Oncogene 1999, 18, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Mao, X.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Nettesheim, D.G.; Yu, L.; Meadows, R.P.; Thompson, C.B.; Fesik, S.W. Solution structure of the ets domain of Fli-1 when bound to DNA. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1994, 1, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.A.; Cooper, C.D.; Aitkenhead, H.; Gileadi, O. Structural insights into the autoregulation and cooperativity of the human transcription factor Ets-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8539–8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.D.; Newman, J.A.; Aitkenhead, H.; Allerston, C.K.; Gileadi, O. Structures of the Ets Protein DNA-binding Domains of Transcription Factors Etv1, Etv4, Etv5, and Fev: DETERMINANTS OF DNA BINDING AND REDOX REGULATION BY DISULFIDE BOND FORMATION. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13692–13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klämbt, C. The Drosophila gene pointed encodes two ETS-like proteins which are involved in the development of the midline glial cells. Development 1993, 117, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackereth, C.D.; Schärpf, M.; Gentile, L.N.; MacIntosh, S.E.; Slupsky, C.M.; McIntosh, L.P. Diversity in structure and function of the Ets family PNT domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 1249–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotteau-Lelièvre, A.; Desbiens, X.; Pelczar, H.; Defossez, P.A.; de Launoit, Y. Differential expression patterns of the PEA3 group transcription factors through murine embryonic development. Oncogene 1997, 15, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.P.; Cooper, C.S. ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2009, 6, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, S.; Ladle, D.R.; Lin, J.H.; Frank, E.; Jessell, T.M. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell 2000, 101, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesser, H.N.; Simon, L.; Hofmann, M.C.; Murphy, K.M.; Murphy, T.; Hess, R.A.; Cooke, P.S. Effects of ETV5 (ets variant gene 5) on testis and body growth, time course of spermatogonial stem cell loss, and fertility in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovics, G.; Liu, A.; Shaheduzzaman, S.; Furusato, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Nau, M.; Ravindranath, L.; Dobi, A.; Srikantan, V.; et al. Frequent overexpression of ETS-related gene-1 (ERG1) in prostate cancer transcriptome. Oncogene 2005, 24, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Laxman, B.; Varambally, S.; Cao, X.; Yu, J.; Helgeson, B.E.; Cao, Q.; Prensner, J.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Shah, R.B.; et al. Role of the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Laxman, B.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Helgeson, B.E.; Cao, X.; Morris, D.S.; Menon, A.; Jing, X.; Cao, Q.; Han, B.; et al. Distinct classes of chromosomal rearrangements create oncogenic ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Ren, C.; Ittmann, M. Expression of variant TMPRSS2/ERG fusion messenger RNAs is associated with aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8347–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demichelis, F.; Fall, K.; Perner, S.; Andrén, O.; Schmidt, F.; Setlur, S.R.; Hoshida, Y.; Mosquera, J.M.; Pawitan, Y.; Lee, C.; et al. TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion associated with lethal prostate cancer in a watchful waiting cohort. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4596–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Ferguson, C.; White, J.T.; Wang, S.; Vessella, R.; True, L.D.; Hood, L.; Nelson, P.S. Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4180–4184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Shin, S.; Janknecht, R. ETV1, 4 and 5: An oncogenic subfamily of ETS transcription factors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Mehra, R.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Yu, J.; Menon, A.; Lonigro, R.J.; Wang, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, L.; Shankar, S.; et al. A fluorescence in situ hybridization screen for E26 transformation-specific aberrations: Identification of DDX5-ETV4 fusion protein in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7629–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellecchia, A.; Pescucci, C.; De Lorenzo, E.; Luceri, C.; Passaro, N.; Sica, M.; Notaro, R.; De Angioletti, M. Overexpression of ETV4 is oncogenic in prostate cells through promotion of both cell proliferation and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgeson, B.E.; Tomlins, S.A.; Shah, N.; Laxman, B.; Cao, Q.; Prensner, J.R.; Cao, X.; Singla, N.; Montie, J.E.; Varambally, S.; et al. Characterization of TMPRSS2:ETV5 and SLC45A3:ETV5 gene fusions in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Silva, J.D.; Paulo, P.; Bakken, A.C.; Cerveira, N.; Løvf, M.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C.; Lothe, R.A.; Skotheim, R.I.; Teixeira, M.R. Novel 5’ fusion partners of ETV1 and ETV4 in prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, K.G.; Bressers, A.A.; van der Korput, H.A.; Dits, N.F.; Jenster, G.; Trapman, J. Two unique novel prostate-specific and androgen-regulated fusion partners of ETV4 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3094–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Balk, S.P. Reactivation of androgen receptor-regulated TMPRSS2:ERG gene expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6027–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carver, B.S.; Tran, J.; Gopalan, A.; Chen, Z.; Shaikh, S.; Carracedo, A.; Alimonti, A.; Nardella, C.; Varmeh, S.; Scardino, P.T.; et al. Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.C.; Xu, J.; Wongvipat, J.; Hieronymus, H.; Carver, B.S.; Leung, D.H.; Taylor, B.S.; Sander, C.; Cardiff, R.D.; Couto, S.S.; et al. Cooperativity of TMPRSS2-ERG with PI3-kinase pathway activation in prostate oncogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Yang, L.; Tanasa, B.; Hutt, K.; Ju, B.G.; Ohgi, K.; Zhang, J.; Rose, D.W.; Fu, X.D.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Nuclear receptor-induced chromosomal proximity and DNA breaks underlie specific translocations in cancer. Cell 2009, 139, 1069–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.S.; Tomlins, S.A.; Callahan, K.; Ghosh, A.; Nyati, M.K.; Varambally, S.; Palanisamy, N.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Induced chromosomal proximity and gene fusions in prostate cancer. Science 2009, 326, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Sinha, C.; Tomlins, S.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.A.; Maher, C.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Common gene rearrangements in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montironi, R.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Scarpelli, M. Molecular techniques and prostate cancer diagnostic. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveira, N.; Ribeiro, F.R.; Peixoto, A.; Costa, V.; Henrique, R.; Jerónimo, C.; Teixeira, M.R. TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion causing ERG overexpression precedes chromosome copy number changes in prostate carcinomas and paired HGPIN lesions. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iljin, K.; Wolf, M.; Edgren, H.; Gupta, S.; Kilpinen, S.; Skotheim, R.I.; Peltola, M.; Smit, F.; Verhaegh, G.; Schalken, J.; et al. TMPRSS2 fusions with oncogenic ETS factors in prostate cancer involve unbalanced genomic rearrangements and are associated with HDAC1 and epigenetic reprogramming. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10242–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Miller, M.A.; Li, C.; Kaygusuz, G.; van de Rijn, M.; Huntsman, D.G.; Brooks, J.D.; Pollack, J.R. A variant TMPRSS2 isoform and ERG fusion product in prostate cancer with implications for molecular diagnosis. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Tomlins, S.A.; Shen, R.; Nadeem, O.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.T.; Pienta, K.J.; Ghosh, D.; Rubin, M.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of TMPRSS2 and ETS family gene aberrations in clinically localized prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera, J.M.; Perner, S.; Demichelis, F.; Kim, R.; Hofer, M.D.; Mertz, K.D.; Paris, P.L.; Simko, J.; Collins, C.; Bismar, T.A.; et al. Morphological features of TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion prostate cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 212, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, R.K.; Sugar, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Kitching, R.; Klotz, L.H.; Venkateswaran, V.; Narod, S.A.; Seth, A. Expression of TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion in prostate cancer cells is an important prognostic factor for cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.B.; Miller, M.A.; De Luca, A.; Boyd, N.; Leung, S.; Hurtado-Coll, A.; Fazli, L.; Jones, E.C.; Palmer, J.B.; Gleave, M.E.; et al. Frequency of the TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusion is increased in moderate to poorly differentiated prostate cancers. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soller, M.J.; Isaksson, M.; Elfving, P.; Soller, W.; Lundgren, R.; Panagopoulos, I. Confirmation of the high frequency of the TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene in prostate cancer. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.J.; Rohan, S.; Kao, J.; Kitabayashi, N.; Mathew, S.; Chen, Y.T. Gene fusions between TMPRSS2 and ETS family genes in prostate cancer: Frequency and transcript variant analysis by RT-PCR and FISH on paraffin-embedded tissues. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnes, M.; Lissbrant, E.; Damber, J.E.; Stenman, G. Molecular genetic analyses of the TMPRSS2-ERG and TMPRSS2-ETV1 gene fusions in 50 cases of prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Joshua, A.M.; Chilton-Macneill, S.; Bayani, J.; Selvarajah, S.; Evans, A.J.; Zielenska, M.; Squire, J.A. Three-color FISH analysis of TMPRSS2/ERG fusions in prostate cancer indicates that genomic microdeletion of chromosome 21 is associated with rearrangement. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Kawai, M.; Kimura, E.; Ogata, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takada, H.; Kuru, S.; Mikata, T.; Matsumura, T.; et al. Study of Duchenne muscular dystrophy long-term survivors aged 40 years and older living in specialized institutions in Japan. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2017, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncavage, E.J.; Abel, H.J.; Szankasi, P.; Kelley, T.W.; Pfeifer, J.D. Targeted next generation sequencing of clinically significant gene mutations and translocations in leukemia. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazdauskienė, U.; Kapustina, Ž.; Medžiūnė, J.; Dubovskaja, V.; Sabaliauskaitė, R.; Jarmalaitė, S.; Lubys, A. Fusion sequencing via terminator-assisted synthesis (FTAS-seq) identifies TMPRSS2 fusion partners in prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baca, S.C.; Prandi, D.; Lawrence, M.S.; Mosquera, J.M.; Romanel, A.; Drier, Y.; Park, K.; Kitabayashi, N.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Ghandi, M.; et al. Punctuated evolution of prostate cancer genomes. Cell 2013, 153, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunju, L.P.; Carskadon, S.; Siddiqui, J.; Tomlins, S.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Palanisamy, N. Novel RNA hybridization method for the in situ detection of ETV1, ETV4, and ETV5 gene fusions in prostate cancer. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2014, 22, e32–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Williamson, S.R.; Carskadon, S.; Arachchige, P.D.; Dhamdhere, G.; Schultz, D.S.; Stricker, H.; Peabody, J.O.; Jeong, W.; Chitale, D.A.; et al. Clonal evaluation of early onset prostate cancer by expression profiling of ERG, SPINK1, ETV1, and ETV4 on whole-mount radical prostatectomy tissue. Prostate 2020, 80, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedarsky, J.; Degon, M.; Srivastava, S.; Dobi, A. Ethnicity and ERG frequency in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramäki, O.R.; Harjula, A.E.; Martikainen, P.M.; Vessella, R.L.; Tammela, T.L.; Visakorpi, T. TMPRSS2:ERG fusion identifies a subgroup of prostate cancers with a favorable prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3395–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Clark, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Fisher, G.; Kovacs, G.; Flohr, P.; Berney, D.; Foster, C.S.; Fletcher, A.; Gerald, W.L.; et al. Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, A.; Leversha, M.A.; Satagopan, J.M.; Zhou, Q.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Fine, S.W.; Eastham, J.A.; Scardino, P.T.; Scher, H.I.; Tickoo, S.K.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion is not associated with outcome in patients treated by prostatectomy. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Clark, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Mills, I.G.; Fisher, G.; Flohr, P.; Reid, A.; Edwards, S.; Kovacs, G.; Berney, D.; et al. Heterogeneity and clinical significance of ETV1 translocations in human prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, M.; Joshua, A.M.; Cunha, I.W.; Coudry, R.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Ludkovski, O.; Zielenska, M.; Soares, F.A.; Squire, J.A. Absence of TMPRSS2:ERG fusions and PTEN losses in prostate cancer is associated with a favorable outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klezovitch, O.; Risk, M.; Coleman, I.; Lucas, J.M.; Null, M.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S.; Vasioukhin, V. A causal role for ERG in neoplastic transformation of prostate epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cai, Y.; Yu, W.; Ren, C.; Spencer, D.M.; Ittmann, M. Pleiotropic biological activities of alternatively spliced TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene transcripts. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8516–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dobi, A.; Mohamed, A.; Li, H.; Thangapazham, R.L.; Furusato, B.; Shaheduzzaman, S.; Tan, S.H.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Whitman, E.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, a common genomic alteration in prostate cancer activates C-MYC and abrogates prostate epithelial differentiation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5348–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, J.C.; Johannes, M.; Mannsperger, H.; Fälth, M.; Metzger, J.; Kacprzyk, L.A.; Andrasiuk, T.; Gade, S.; Meister, M.; Sirma, H.; et al. TMPRSS2-ERG -specific transcriptional modulation is associated with prostate cancer biomarkers and TGF-β signaling. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boormans, J.L.; Korsten, H.; Ziel-van der Made, A.J.; van Leenders, G.J.; de Vos, C.V.; Jenster, G.; Trapman, J. Identification of TDRD1 as a direct target gene of ERG in primary prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Mani, R.S.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, C.J.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Gong, Y.; et al. An integrated network of androgen receptor, polycomb, and TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusions in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, K.G.; van der Korput, H.A.; van Marion, R.; van de Wijngaart, D.J.; Ziel-van der Made, A.; Dits, N.F.; Boormans, J.L.; van der Kwast, T.H.; van Dekken, H.; Bangma, C.H.; et al. Truncated ETV1, fused to novel tissue-specific genes, and full-length ETV1 in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7541–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasi, D.; van der Korput, H.A.; Douben, H.C.; de Klein, A.; de Ridder, C.M.; van Weerden, W.M.; Trapman, J. Overexpression of full-length ETV1 transcripts in clinical prostate cancer due to gene translocation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, T.D.; Jin, F.; van Deursen, J.M.; Dehm, S.M.; Tindall, D.J.; Grande, J.P.; Munz, J.M.; Vasmatzis, G.; Janknecht, R. Induction of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and modulation of androgen receptor by ETS variant 1/ETS-related protein 81. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8102–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena, E.; Shao, Z.; Linn, D.E.; Glass, K.; Hamblen, M.J.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kim, J.; Nguyen, M.; Zhang, X.; Godinho, F.J.; et al. ETV1 directs androgen metabolism and confers aggressive prostate cancer in targeted mice and patients. Genes. Dev. 2013, 27, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Graff, R.E.; Bauer, S.R.; Pitt, M.J.; Lis, R.T.; Stack, E.C.; Martin, N.E.; Kunz, L.; Penney, K.L.; Ligon, A.H.; et al. The TMPRSS2:ERG rearrangement, ERG expression, and prostate cancer outcomes: A cohort study and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasi Tandefelt, D.; Boormans, J.L.; van der Korput, H.A.; Jenster, G.W.; Trapman, J. A 36-gene signature predicts clinical progression in a subgroup of ERG-positive prostate cancers. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkizan, H.V.; Kong, Y.; Merchant, M.; Schlottmann, S.; Barber-Rotenberg, J.S.; Yuan, L.; Abaan, O.D.; Chou, T.H.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Brown, M.L.; et al. A small molecule blocking oncogenic protein EWS-FLI1 interaction with RNA helicase A inhibits growth of Ewing’s sarcoma. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, M.S.; Stransky, N.; Garvie, C.W.; Theurillat, J.P.; Hartman, E.C.; Lewis, T.A.; Zhong, C.; Culyba, E.K.; Lin, F.; Daniels, D.S.; et al. A small molecule that binds and inhibits the ETV1 transcription factor oncoprotein. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Xavier, C.P.; Sukumar, G.; Tan, S.H.; Ravindranath, L.; Seraj, N.; Kumar, V.; Sreenath, T.; McLeod, D.G.; Petrovics, G.; et al. Identification of a Small Molecule That Selectively Inhibits ERG-Positive Cancer Cell Growth. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3659–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.S.; Roshan-Moniri, M.; Hsing, M.; Lau, D.; Kim, A.; Yen, P.; Mroczek, M.; Nouri, M.; Lien, S.; Axerio-Cilies, P.; et al. Discovery and characterization of small molecules targeting the DNA-binding ETS domain of ERG in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42438–42454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Doki, Y.; Sugita, Y.; Sohma, I.; Miyata, H.; Takiguchi, S.; Yasuda, T.; Tomita, N.; Morishita, R.; et al. Gene therapy using ets-1 transcription factor decoy for peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahim, S.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Kong, Y.; Brown, M.L.; Toretsky, J.A.; Üren, A. YK-4-279 inhibits ERG and ETV1 mediated prostate cancer cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, S.; Minas, T.; Hong, S.H.; Justvig, S.; Çelik, H.; Kont, Y.S.; Han, J.; Kallarakal, A.T.; Kong, Y.; Rudek, M.A.; et al. A small molecule inhibitor of ETV1, YK-4-279, prevents prostate cancer growth and metastasis in a mouse xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhili, R.; Peixoto, P.; Depauw, S.; Flajollet, S.; Dezitter, X.; Munde, M.M.; Ismail, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Farahat, A.A.; Stephens, C.E.; et al. Targeting the DNA-binding activity of the human ERG transcription factor using new heterocyclic dithiophene diamidines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kollipara, R.K.; Srivastava, N.; Li, R.; Ravindranathan, P.; Hernandez, E.; Freeman, E.; Humphries, C.G.; Kapur, P.; Lotan, Y.; et al. Ablation of the oncogenic transcription factor ERG by deubiquitinase inhibition in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4251–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.S.; Zhang, L.; Berger, A.; Lawrence, M.G.; Song, J.; Niranjan, B.; Davies, R.G.; Lister, N.L.; Sandhu, S.K.; Rubin, M.A.; et al. Characterization of the ERG-regulated Kinome in Prostate Cancer Identifies TNIK as a Potential Therapeutic Target. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toretsky, J.A.; Erkizan, V.; Levenson, A.; Abaan, O.D.; Parvin, J.D.; Cripe, T.P.; Rice, A.M.; Lee, S.B.; Uren, A. Oncoprotein EWS-FLI1 activity is enhanced by RNA helicase A. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5574–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidaleo, M.; Svetoni, F.; Volpe, E.; Miñana, B.; Caporossi, D.; Paronetto, M.P. Genotoxic stress inhibits Ewing sarcoma cell growth by modulating alternative pre-mRNA processing of the RNA helicase DHX9. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31740–31757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidaleo, M.; De Paola, E.; Paronetto, M.P. The RNA helicase A in malignant transformation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 28711–28723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercatelli, N.; Fortini, D.; Palombo, R.; Paronetto, M.P. Small molecule inhibition of Ewing sarcoma cell growth via targeting the long non coding RNA HULC. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombo, R.; Verdile, V.; Paronetto, M.P. Poison-Exon Inclusion in DHX9 Reduces Its Expression and Sensitizes Ewing Sarcoma Cells to Chemotherapeutic Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellini, L.; Scarfò, M.; Bonvissuto, D.; Sette, C.; Paronetto, M.P. The DNA/RNA helicase DHX9 orchestrates the KDM2B-mediated transcriptional regulation of YAP1 in Ewing sarcoma. Oncogene 2024, 43, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A.; Federman, N.; Daw, N.; Anderson, P.M.; Davis, L.E.; Kim, A.; Macy, M.E.; Pietrofeso, A.; Ratan, R.; Riedel, R.F.; et al. Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase I/II, First-in-Human Trial of TK216: A First-Generation EWS::FLI1 Fusion Protein Antagonist in Ewing Sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.H.; Badis, G.; Berger, M.F.; Kivioja, T.; Palin, K.; Enge, M.; Bonke, M.; Jolma, A.; Varjosalo, M.; Gehrke, A.R.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Nakazawa, M.; Roeser, J.C.; Chen, Y.; Mohammad, T.A.; Fedor, H.L.; Lotan, T.L.; et al. AR-V7 and resistance to enzalutamide and abiraterone in prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, M.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Du, Z.; Zhang, K.; Goodin, S.; et al. The Effects and Mechanism of YK-4-279 in Combination with Docetaxel on Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyna, B.R.; Arrowsmith, C.H. DNA binding specificity studies of four ETS proteins support an indirect read-out mechanism of protein-DNA recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28363–28370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Lin, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Sethi, G.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. Inhibition of the deubiquitinase USP9x induces pre-B cell homeobox 1 (PBX1) degradation and thereby stimulates prostate cancer cell apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4572–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Las Pozas, A.; Reiner, T.; De Cesare, V.; Trost, M.; Perez-Stable, C. Inhibiting Multiple Deubiquitinases to Reduce Androgen Receptor Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldhose, B.; Pandrala, M.; Xavier, C.; Mohamed, A.A.; Srivastava, S.; Sunkara, A.D.; Dobi, A.; Malhotra, S.V. New Selective Inhibitors of ERG Positive Prostate Cancer: ERGi-USU-6 Salt Derivatives. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hobson, L.; Perry, L.; Clark, B.; Heavey, S.; Haider, A.; Sridhar, A.; Shaw, G.; Kelly, J.; Freeman, A.; et al. Targeting the ERG oncogene with splice-switching oligonucleotides as a novel therapeutic strategy in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paronetto, M.P.; Passacantilli, I.; Sette, C. Alternative splicing and cell survival: From tissue homeostasis to disease. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumbe, S.L.; Porazinski, S.R.; Oltean, S.; Mansell, J.P.; Vahabi, B.; Wilson, I.D.; Ladomery, M.R. The Evolutionarily Conserved Cassette Exon 7b Drives ERG’s Oncogenic Properties. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, Y.Y. Eteplirsen: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aartsma-Rus, A. FDA Approval of Nusinersen for Spinal Muscular Atrophy Makes 2016 the Year of Splice Modulating Oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid. Ther. 2017, 27, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.P.; Liu, S.; Ren, B.G.; Nelson, J.; Jarrard, D.; Brooks, J.D.; Michalopoulos, G.; Tseng, G.; Luo, J.H. Fusion Gene Detection in Prostate Cancer Samples Enhances the Prediction of Prostate Cancer Clinical Outcomes from Radical Prostatectomy through Machine Learning in a Multi-Institutional Analysis. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, M.; Jäderling, F.; Discacciati, A.; Bergman, M.; Annerstedt, M.; Aly, M.; Glaessgen, A.; Carlsson, S.; Grönberg, H.; Nordström, T.; et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 908–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).