Effectiveness of Systemic Corticosteroids in Managing Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Longitudinal Assessment of CR-NP
2.3. General Baseline Assessment, Analgesic Medications, and Adverse Events
2.4. Data Analyses
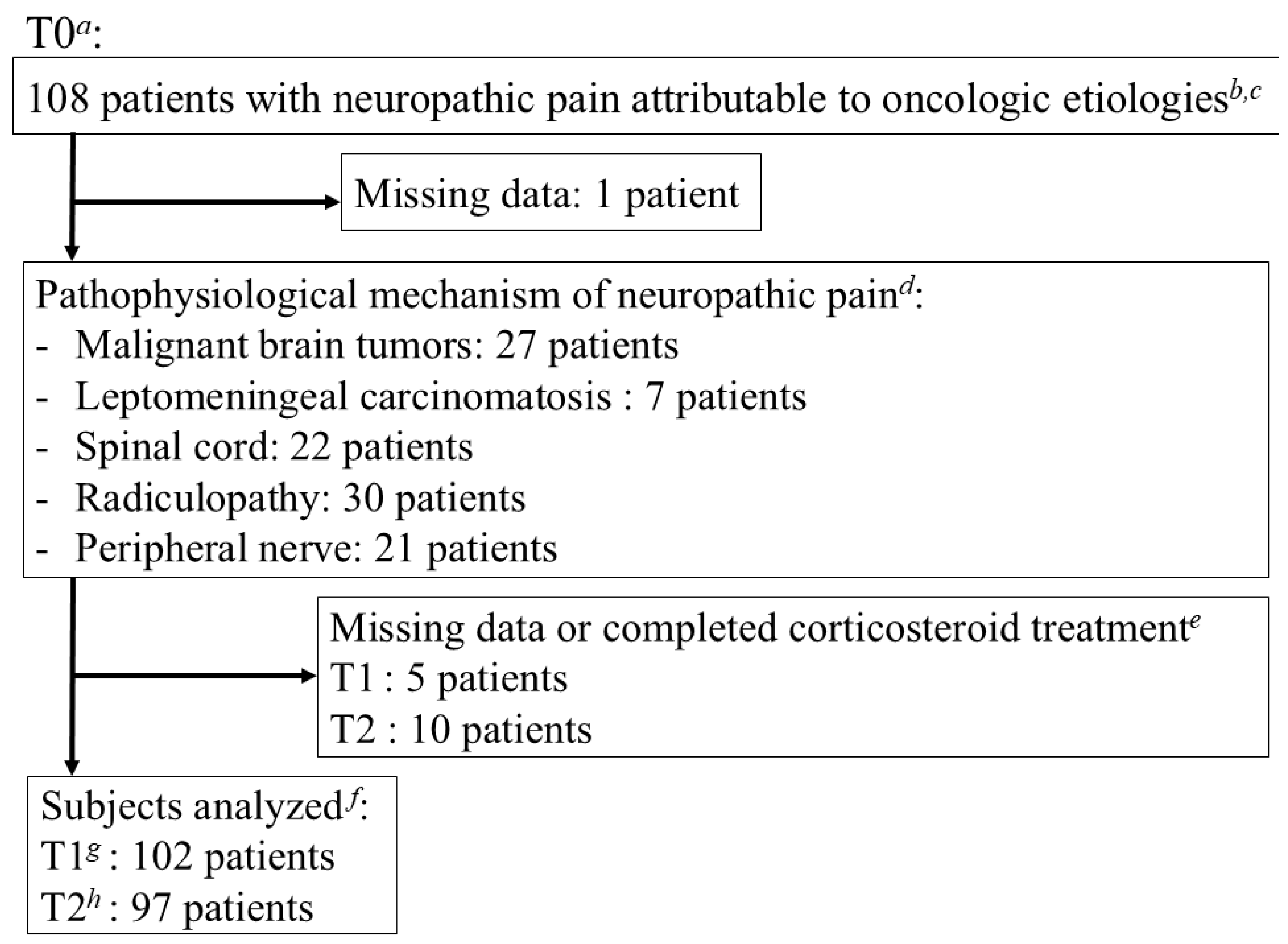
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Baseline Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Changes in CR-NP Intensity and Pain Interference with Activities and Sleep
3.3. Proportions of Pain Reduction (33%, 50%, and 100%) and Achievement of PPG and Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC)
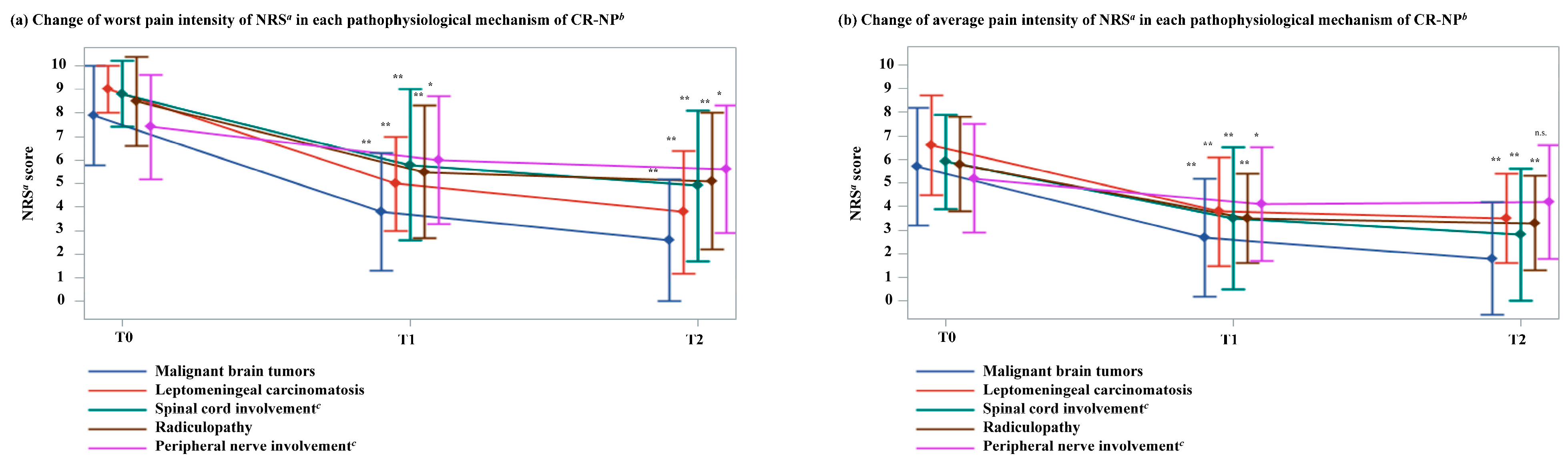
3.4. Changes in CR-NP Intensity by Pathological Mechanism
3.5. Opioid Dose Adjustments and the Correlation Between Pain Intensity and Changes in Analgesics and Adjuvant Analgesics
3.6. Relationship Between CR-NP Intensity and ADLs on the AKPS
3.7. Changes in Corticosteroid Dosage
3.8. Adverse Events Related to Corticosteroid Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADL | Activities of daily living |
| AKPS | Australian Karnofsky Performance Scale |
| BFI-SF | Brief pain inventory–short form |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CR-NP | Cancer-related neuropathic pain |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CTCAE | Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events |
| DEDD | Dexamethasone-equivalent daily dose |
| DSIS | Daily sleep interference score |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MEDD | Morphine equivalent daily dose |
| NNT | Number-needed-to-treat |
| NRS | Numerical rating scale |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PGIC | Patient global impression of change |
| PPG | Personalized pain goals |
| PROs | Patient-reported outcome |
| QOL | Quality of life |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SE | Standard error |
| SLANSS | Self-Reported Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs |
| SPC | Specialized palliative care |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Outcome (Compared to T0 NRS) | T1 (n, %) | T2 (n, %) |
|---|---|---|
| 33% reduction in worst pain | 56 b, 54.9% | 64 c, 66.0% |
| 33% reduction in average pain | 58 d, 56.3% | 70 e, 71.4% |
| 50% reduction in worst pain | 40 b, 39.2% | 54 c, 55.7% |
| 50% reduction in average pain | 48 d, 46.6% | 55 e, 56.1% |
| 100% reduction in average pain | 12 d, 11.7% | 20 e, 20.4% |
| PPG score achieved | 51 f, 51.0% | 57 g, 60.0% |
Appendix A.2
| PGIC a | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very Much Improved | Much Improved | Minimally Improved | No Change | Minimally Worse | Much Worse | Very Much Worse | |
| T1 cases (%) b | 17 (16.5) | 35 (34.0) | 30 (29.1) | 16 (15.5) | 3 (2.9) | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.0) |
| T2 cases (%) c | 21 (21.2) | 37 (37.4) | 21 (21.2) | 12 (12.1) | 5 (5.1) | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.0) |
Appendix A.3
| Symptom b | Grade b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two or Less | Three or More | |||
| Insomnia | 10 | 0 | ||
| Delirium | 7 | 1 | ||
| Hyperglycemia | 2 | 1 | ||
| Other symptoms c | 0 | 0 | ||
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Pharmacological and Radiotherapeutic Management of Cancer Pain in Adults and Adolescents; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fallon, M.; Giusti, R.; Aielli, F.; Hoskin, P.; Rolke, R.; Sharma, M.; Ripamonti, C.I.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of cancer pain in adult patients: ESMO clinical practice guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 4), iv166–iv191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagami, K.; Chiu, S.W.; Kosugi, K.; Ishiki, H.; Hiratsuka, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Mori, M.; Kubo, E.; Ikari, T.; Arakawa, S.; et al. Cancer pain management in patients receiving inpatient specialized palliative care services. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2024, 67, 27–38.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijders, R.A.H.; Brom, L.; Theunissen, M.; van den Beuken-van Everdingen, M.H.J. Update on prevalence of pain in patients with cancer 2022: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberto, A.; Deandrea, S.; Greco, M.T.; Corli, O.; Negri, E.; Pizzuto, M.; Ruggeri, F. Prevalence of neuropathic pain in cancer patients: Pooled estimates from a systematic review of published literature and results from a survey conducted in 50 Italian palliative care centers. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2016, 51, 1091–1102.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H.; Tagami, K.; Ariyoshi, K.; Oyamada, S.; Kizawa, Y.; Inoue, A.; Koyama, A. Attitude of Japanese palliative care specialists towards adjuvant analgesics cancer-related neuropathic pain refractory to opioid therapy: A nationwide cross-sectional survey. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, C.; Bennett, M.I.; Kaasa, S.; Fainsinger, R.; Sjgren, P.; Mercadante, S.; Løhre, E.T.; Caraceni, A.; European Association for Palliative Care (EAPC) Research Network and International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) Cancer Pain Special Interest Group. Classification of neuropathic pain in cancer patients: A Delphi Expert survey report and EAPC/IASP proposal of an algorithm for diagnostic criteria. Pain 2014, 155, 2707–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portenoy, R.K.; Ahmed, E.; Keilson, Y.Y. Cancer Pain Management: Adjuvant Analgesics (Coanalgesics). Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/cancer-pain-management-role-of-adjuvant-analgesics-coanalgesics (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Tagami, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Ariyoshi, K.; Oyamada, S.; Hiratsuka, Y.; Kizawa, Y.; Koyama, A.; Inoue, A. The current clinical use of adjuvant analgesics for refractory cancer pain in Japan: A nationwide cross-sectional survey. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 50, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawatari, H.; Shinjo, T.; Morita, T.; Kohara, H.; Yomiya, K. Revision of pharmacological treatment recommendations for cancer pain: Clinical guidelines from the Japanese society of palliative medicine. J. Palliat. Med. 2022, 25, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryken, T.C.; Kuo, J.S.; Prabhu, R.S.; Sherman, J.H.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Olson, J.J. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the role of steroids in the treatment of adults with metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, E189–E191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.M.; Messersmith, H.; Ahluwalia, M.; Andrews, D.; Brastianos, P.K.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Jordan, J.T.; Khasraw, M.; Lassman, A.B.; et al. Anticonvulsant prophylaxis and steroid use in adults with metastatic brain tumors: ASCO and SNO endorsement of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons guidelines. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, D.; Hanneman, S.K.; Jennings, K.; Ontai, A.; Cron, S.; Bruera, E. Predictive biomarkers of dyspnea response to dexamethasone and placebo in cancer patients. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2024, 68, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, A.; Good, P.; Khan, S.; Leupp, A.; Jenkins-Marsh, S.; Rickett, K.; Hardy, J.R. Corticosteroids for the management of cancer-related pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD010756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uki, J.; Mendoza, T.; Cleeland, C.S.; Nakamura, Y.; Takeda, F. A brief Cancer pain assessment tool in Japanese: The utility of the Japanese brief pain inventory—BPI-J. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1998, 16, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.I.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N.; Potter, J. The S-LANSS Score for identifying pain of predominantly neuropathic origin: Validation for use in clinical and postal research. J. Pain 2005, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, O.; Klepstad, P.; Rosland, J.H.; Aass, N.; Albert, E.; Fayers, P.; Kaasa, S. Efficacy of methylprednisolone on pain, fatigue, and appetite loss in patients with advanced cancer using opioids: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3221–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yennurajalingam, S.; Frisbee-Hume, S.; Palmer, J.L.; Delgado-Guay, M.O.; Bull, J.; Phan, A.T.; Tannir, N.M.; Litton, J.K.; Reddy, A.; Hui, D.; et al. Reduction of cancer-related fatigue with dexamethasone: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3076–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, M.K.; Brandenburg, N.A.; Alvir, J.M.J.; Griesing, T.; Revicki, D.A. Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the daily sleep interference scale among diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia patients. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2008, 36, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merante, D.; Rosenstock, J.; Sharma, U.; Feins, K.; Hsu, C.; Vinik, A.; DS-5565-A-U201 US Phase 2 Study Investigators. Efficacy of mirogabalin (DS-5565) on patient-reported pain and sleep interference in patients with diabetic neuropathic pain: Secondary outcomes of a Phase II proof-of-concept study. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Matsui, N.; Kuroha, M.; Wasaki, Y.; Ohwada, S. Mirogabalin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III study in Asian patients. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Matsui, N.; Kakehi, Y.; Murayama, E.; Ohwada, S.; Sugihara, M. Mirogabalin for the management of postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 3 study in Asian patients. Pain 2019, 160, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, S.; Hui, D.; Nguyen, L.; Chacko, R.; Scott, C.; Roberts, L.; Bruera, E. Achievement of personalized pain goal in cancer patients referred to a supportive care clinic at a Comprehensive Cancer Center. Cancer 2012, 118, 3869–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Bruera, E. A personalized approach to assessing and managing pain in patients with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.S.; Miura, T.; Okizaki, A.; Tagami, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fujimori, M.; Morita, T.; Kinoshita, H. Comparison of indicators for achievement of pain control with a personalized pain goal in a Comprehensive Cancer Center. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2018, 55, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagami, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Miura, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Watanabe, Y.S.; Uehara, Y.; Okizaki, A.; Inoue, A.; Morita, T.; et al. The association between health-related quality of life and achievement of personalized symptom goal. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 4737–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.; Bolton, J. Assessing the clinical significance of change scores recorded on subjective outcome measures. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 2004, 27, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.X.; Lin, Z.; Lei, D.; Bao, J. The role of glucocorticoids for spiral ganglion neuron survival. Brain Res. 2009, 1277, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Swarm, R.A.; Dans, M. NCCN frameworks for resource stratification of NCCN guidelines: Adult cancer pain and palliative care. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainsinger, R.L.; Nekolaichuk, C.; Lawlor, P.; Hagen, N.; Bercovitch, M.; Fisch, M.; Galloway, L.; Kaye, G.; Landman, W.; Spruyt, O.; et al. An international multicentre validation study of a pain classification system for cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2896–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abernethy, A.P.; Shelby-James, T.; Fazekas, B.S.; Woods, D.; Currow, D.C. The Australia-modified Karnofsky Performance Status (AKPS) scale: A revised scale for contemporary palliative care clinical practice [ISRCTN81117481]. BMC Palliat. Care 2005, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), v5.0. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_50 (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Ashar, A.; Hardy, J.; Good, P.; Fischer, A. Corticosteroids as co-analgesics with opioids for cancer-related pain: A feasibility study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2017, 54, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paulsen, Ø.; Aass, N.; Kaasa, S.; Dale, O. Do corticosteroids provide analgesic effects in cancer patients? A systematic literature review. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2013, 46, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Haywood, A.; Rickett, K.; Sallnow, L.; Good, P. Practice review: Evidence-based quality use of corticosteroids in the palliative care of patients with advanced cancer. Palliat. Med. 2021, 35, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Masala, S.; Banna, G.; Cotta, E.; Cavalli, M.; Fiumara, P.; Di Raimondo, F.; Mundo, E.; Scavone, G.; Granata, A.; et al. Intrasomatic injection of corticosteroid followed by vertebroplasty increases early pain relief Rather than vertebroplasty alone in vertebral bone neoplasms: Preliminary experience. Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 41, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, A.A.A.M.; El-Mashad, N.M. Pre-emptive value of methylprednisolone intravenous infusion in patients with vertebral metastases. A double-blind randomized study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2014, 48, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Meyer, R.M.; Ding, K.; Nabid, A.; Chabot, P.; Wong, P.; Ahmed, S.; Kuk, J.; Dar, A.R.; Mahmud, A.; et al. Dexamethasone in the prophylaxis of radiation-induced pain flare after palliative radiotherapy for bone metastases: A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadante, S.L.; Berchovich, M.; Casuccio, A.; Fulfaro, F.; Mangione, S. A prospective randomized study of corticosteroids as adjuvant drugs to opioids in advanced cancer patients. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2007, 24, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yennurajalingam, S.; Williams, J.L.; Chisholm, G.; Bruera, E. Effects of dexamethasone and placebo on symptom clusters in advanced cancer patients: A preliminary report. Oncologist 2016, 21, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: Molecular mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998, 94, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryken, T.C.; McDermott, M.; Robinson, P.D.; Ammirati, M.; Andrews, D.W.; Asher, A.L.; Burri, S.H.; Cobbs, C.S.; Gaspar, L.E.; Kondziolka, D.; et al. The role of steroids in the management of brain metastases: A systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 96, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Chang, S.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.F.; Wu, A.C.; Huang, J.L.; Tsai, H.J. Association of oral corticosteroid bursts with severe adverse events in children. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, A.W.; Chen, X.; Urbauer, D.L.; Bruera, E.; Hui, D. Impact of dosing and duration of dexamethasone on serious corticosteroid-related adverse events. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2024, 67, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables (n = 107) | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Mean (standard deviation) | 62.6 (13.2) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 50 (46.7) |
| Female | 57 (53.3) |
| Primary cancer sites | |
| Lung | 27 (25.2) |
| Gastrointestinal a | 18 (16.8) |
| Breast | 13 (12.1) |
| Gynecological b | 13 (12.1) |
| Head and neck | 10 (9.3) |
| Urinary c | 7 (6.5) |
| Pancreas | 4 (3.7) |
| Brain | 4 (3.7) |
| Others | 11 (10.3) |
| Charlson comorbidity index d | |
| None | 78 (72.9) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 (9.3) |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 4 (3.7) |
| Liver disease | 4 (3.7) |
| Hemiplegia | 4 (3.7) |
| Others | 11 |
| Anticancer treatment | |
| Ongoing d,e | 34 (31.8) |
| Only observation or forgoing anticancer treatment | 73 (68.2) |
| Starting of new anticancer treatment e during the observation period | 0 (0) |
| Variables (n = 107) | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Most painful site | |
| Head and neck | 37 (34.6) |
| Arm and shoulder | 21 (19.6) |
| Leg | 15 (14.0) |
| Back | 13 (12.2) |
| Hip and genitals | 9 (8.4) |
| Others | 12 (11.2) |
| SLANSS a,b score | |
| Median (IQR) | 15 (12–18) |
| AKPS c | |
| Mean (SD) | 47.3 (18.4) |
| PPG | |
| Median (IQR) i | 3 (2–4) |
| Initial corticosteroid administration Dosage d,e | |
| Median (IQR) | 6.6 (4–8) |
| Type of corticosteroids | |
| Dexamethasone | 78 (72.9) |
| Betamethasone | 21 (19.6) |
| Prednisolone | 8 (7.5) |
| Route of corticosteroids | |
| Intravenous | 53 (49.5) |
| Oral | 50 (46.7) |
| Subcutaneous | 4 (3.7) |
| Regular analgesic, analgesic adjuvants, and diuretics medication at T0 f,g,h | |
| Opioids | 72 (67.3) |
| NSAIDs | 47 (43.9) |
| Acetaminophen | 46 (43.0) |
| Gabapentinoids k,j | 28 (26.2) |
| Osmotic diuretics | 16 (15.0) |
| Antidepressants | 5 (4.7) |
| Ketamine | 2 (1.9) |
| Others | 2 (1.9) |
| Dosage of regular opioids at T0 j,k | |
| Median (IQR) | 47.5 (30–120) |
| BPI and DSIS Items a | From T0 b to T1 c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0, Mean (SD) | T1, Mean (SD) | Difference in Means (95% CI) | p | |
| Worst pain intensity in the last 24 h | 8.2 (1.9) | 5.2 (2.9) | −3.0 (−3.6 to −2.4) | <0.01 |
| Average pain intensity in the last 24 h | 5.8 (2.2) | 3.5 (2.4) | −2.3(−2.8 to −1.7) | <0.01 |
| Pain interference general activities | 6.9 (2.5) | 4.1 (2.7) | −2.7 (−3.3 to −2.1) | <0.01 |
| Pain interference sleep | 5.8 (3.1) | 3.1 (2.7) | −2.7 (−3.2 to −1.9) | <0.01 |
| BPI and DSIS Items a | From T0 to T2 d | |||
| T0, Mean (SD) | T2, Mean (SD) | Difference in Means (95% CI) | p | |
| Worst pain intensity in the last 24 h | 8.2 (1.9) | 4.4 (3.0) | −3.8 (−4.5 to −3.3) | <0.01 |
| Average pain intensity in the last 24 h | 5.8 (2.2) | 3.0 (2.5) | −2.8(−3.3 to −2.2) | <0.01 |
| Pain interference general activities | 6.9 (2.5) | 3.4 (2.8) | −3.4 (−4.0 to −2.8) | <0.01 |
| Pain interference sleep | 5.8 (3.1) | 2.4 (2.6) | −3.4 (−4.0 to −2.6) | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagami, K.; Kessoku, T.; Hasuo, H.; Ishiki, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Mori, M.; Hiratsuka, Y.; Kosugi, K.; Okuda, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Effectiveness of Systemic Corticosteroids in Managing Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101630
Tagami K, Kessoku T, Hasuo H, Ishiki H, Yamaguchi T, Mori M, Hiratsuka Y, Kosugi K, Okuda Y, Yamaguchi T, et al. Effectiveness of Systemic Corticosteroids in Managing Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101630
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagami, Keita, Takaomi Kessoku, Hideaki Hasuo, Hiroto Ishiki, Takashi Yamaguchi, Masanori Mori, Yusuke Hiratsuka, Kazuhiro Kosugi, Yuka Okuda, Takeya Yamaguchi, and et al. 2025. "Effectiveness of Systemic Corticosteroids in Managing Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101630
APA StyleTagami, K., Kessoku, T., Hasuo, H., Ishiki, H., Yamaguchi, T., Mori, M., Hiratsuka, Y., Kosugi, K., Okuda, Y., Yamaguchi, T., Miyamoto, S., Oya, K., Nishijima, K., Koinuma, Y., Morikawa, N., Oyamada, S., Ariyoshi, K., Higuchi, M., Mawatari, H., ... Inoue, A. (2025). Effectiveness of Systemic Corticosteroids in Managing Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain: A Multicenter Prospective Observational Study. Cancers, 17(10), 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101630






