Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: A Real-World Data Study from a Resource-Limited Country
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
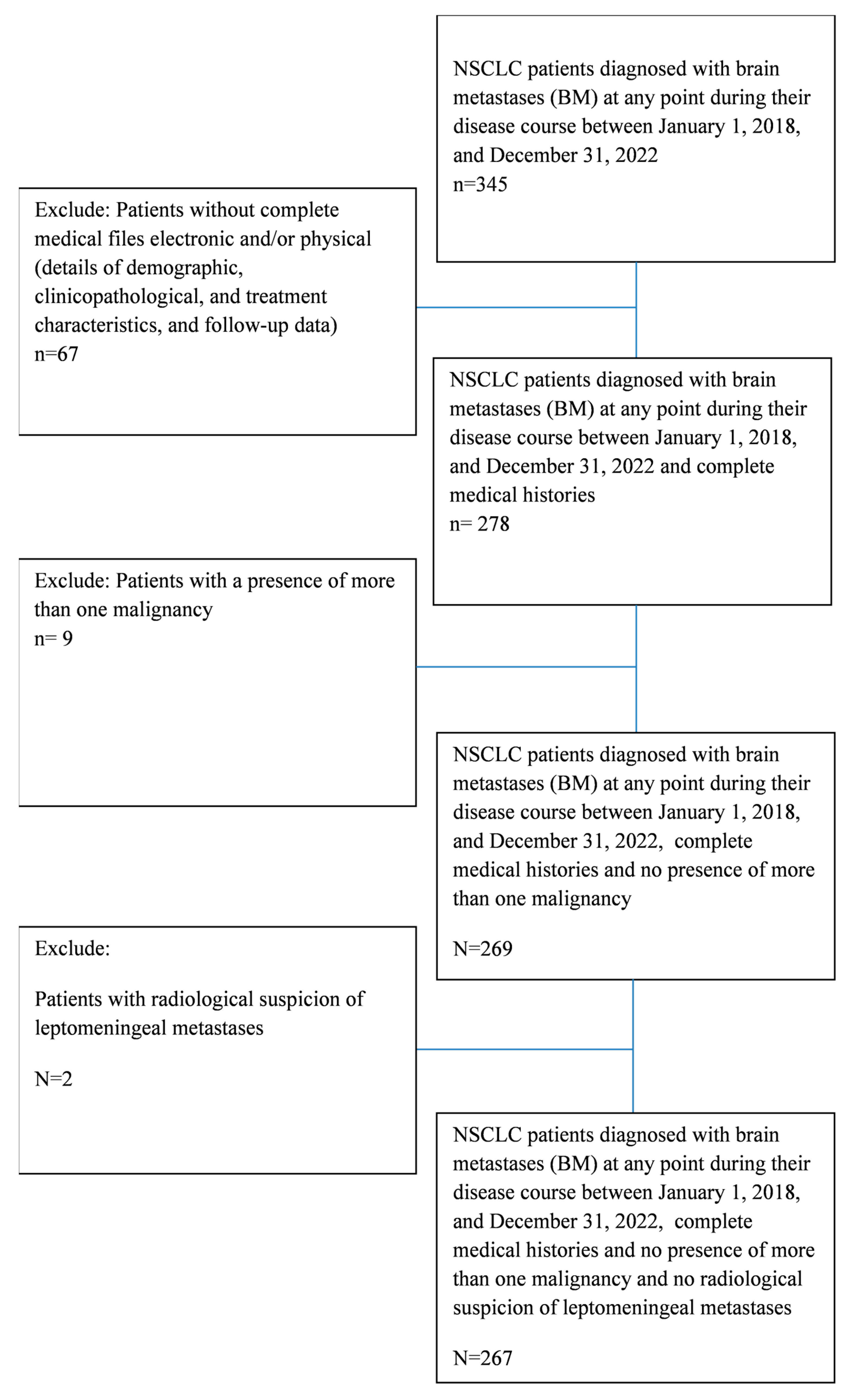
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
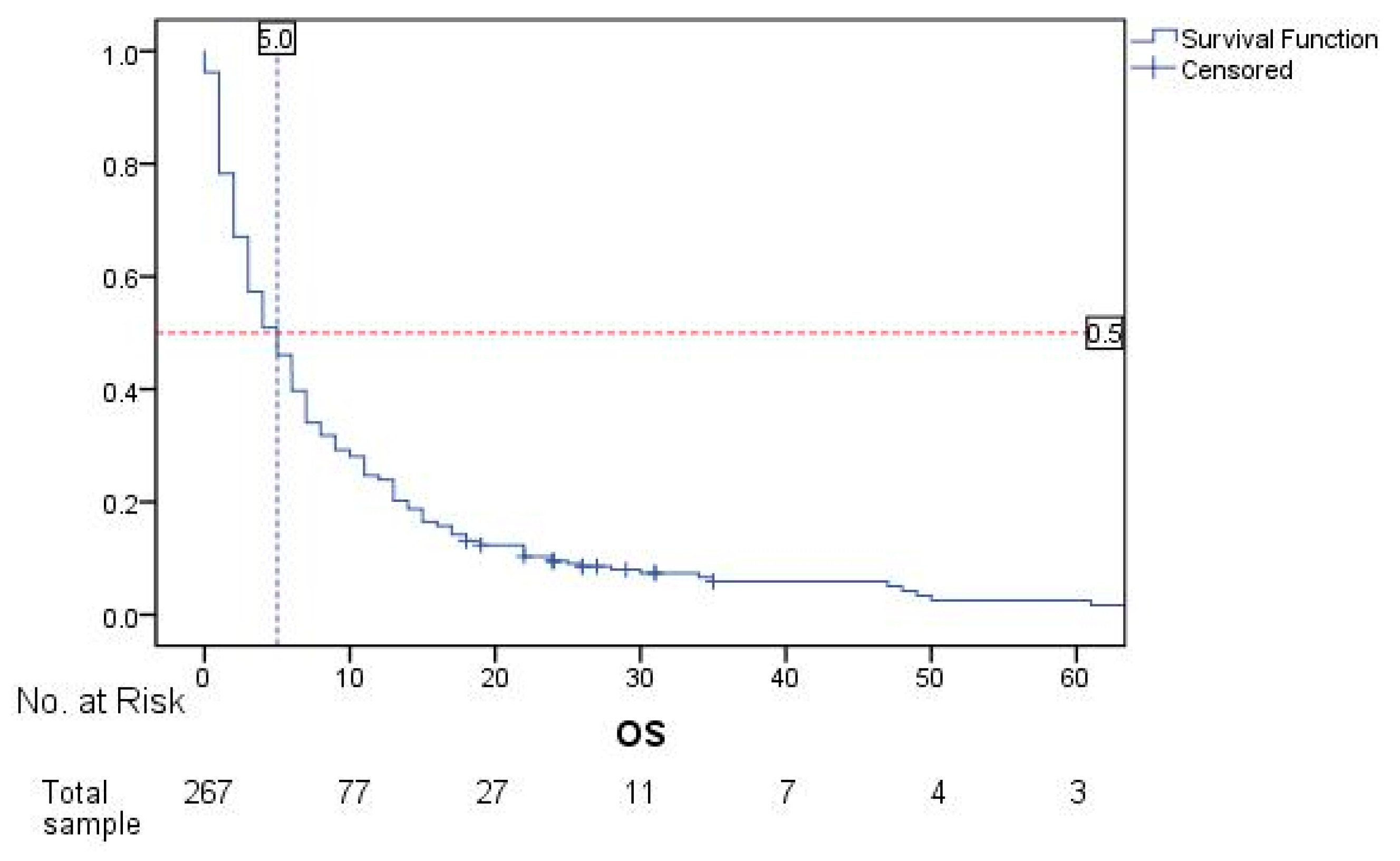
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljus, D.; ZivkovicPerisic, S.; Bozic, Z. Malignant Tumours in Republic of Serbia 2021, 1st ed.; Institute of Public Health of Serbia “Dr. Milan Jovanović Batut”: Belgrade, Serbia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Inguet, J.; Smith, K.H.; Bramlage, P. Targeted therapies for treatment of non-small cell lung cancer—Recent advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, S.; Milner-Watts, C.; Perna, M.; Janzic, U.; Vidal, N.; Kaudeer, N.; Ahmed, M.; McDonald, F.; Locke, I.; Minchom, A.; et al. Systemic treatment of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, M.; Soejima, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Brain metastases in oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, S298–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Estimating survival in patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: An update of the graded prognostic assessment for lung cancer using molecular markers (Lung-molGPA). JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in patients with brain metastases: Summary report on the updated diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment and definition of the eligibility quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Yang, T.J.; Beal, K.; Pan, H.; Brown, P.D.; Bangdiwala, A.; Shanley, R.; Yeh, N.; Gaspar, L.E.; Braunstein, S.; et al. The effect of gene alterations and tyrosine kinase inhibition on survival and cause of death in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung and brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; De, B.; Li, J.; Carpenter, D.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Milligan, M.; Shih, H.A.; Kutuk, T.; Kotecha, R.; Higaki, H.; et al. Graded Prognostic Assessment (GPA) for patients with lung cancer and brain metastases: Initial report of the small cell lung cancer GPA and update of the non-small cell lung cancer GPA including the effect of programmed death ligand 1 and other prognostic factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Targeted therapy of brain metastases: Latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2017, 9, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Bauer, T.M.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Goto, Y.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, D.W.; Mok, T.; Polli, A.; et al. First-line lorlatinib or crizotinib in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, A.S.; Herbst, R.S.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Hui, R.; Peled, N.; Kim, D.W.; Novello, S.; Satouchi, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Garon, E.B.; et al. Outcomes with pembrolizumabmonotherapy in patients with programmed death-ligand 1-positive NSCLC with brain metastases: Pooled analysis of KEYNOTE-001, 010, 024, and 042. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, E.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Simó, M.; Massutí, B.; Juan, O.; Huidobro, G.; López, R.; De Castro, J.; Estival, A.; Mosquera, J.; et al. Phase II trial of atezolizumab combined with carboplatin and pemetrexed for patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer with untreated brain metastases (Atezo-Brain, GECP17/05). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4478–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Li, H.; Yu, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, K.; Pan, G.; Xie, M.; Li, N.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, Y. Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastases: A real-world retrospective study in China. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 3019–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowley, A.; Phiri, K.; Multani, J.K.; Casey, V.; Mpima, S.; Yasuda, M.; Chen, C.C.; Manuguid, F.; Chao, J.; Aziez, A.; et al. Real-world treatment patterns and clinical outcomes after introduction of immune checkpoint inhibitors: Results from a retrospective chart review of patients with advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer in the EU5. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, N.; Samuel, R.; Riaz, M.; Johnson, C.; Cheeseman, S.L.; Snee, M. A study of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with brain metastasis: A single-centre experience. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2023, 34, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janžič, U.; Turnšek, N.; Dediu, M.; Donev, I.S.; Lupu, R.; Teodorescu, G.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Pluzanski, A. Real-world testing practices, treatment patterns, and clinical outcomes in patients from Central Eastern Europe with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective chart review study (REFLECT). Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5833–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Berkey, B.; Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.; Curran, W. A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: An analysis of 1,960 patients in the RTOG database. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Cheng, G. Lung-molGPA index predicts survival outcomes of non-small-cell lung cancer patients with synchronous or metachronous brain metastases. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 8837–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Tostivint, E.; Hulo, P.; Guardiolle, V.; Bodot, L.; Rabeau, A.; Porte, M.; Hiret, S.; Demontrond, P.; Curcio, H.; Boudoussier, A.; et al. Correction to: Real-world multicentre cohort of first-line pembrolizumab alone or in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer PD-L1 ≥ 50. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 1891–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.N.; John, J.; Tiu, R.V.; Willard, M.D.; Beyrer, J.K.; Bowman, L.; Sheffield, K.M.; Han, Y.; Brastianos, P.K. Clinicogenomic factors and treatment patterns among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with or without brain metastases in the United States. Oncologist 2023, 28, e1075–e1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Q.; Yap, M.L.; Cheng, E.S.; Ngo, P.J.; Vaneckova, P.; Karikios, D.; Canfell, K.; Weber, M.F. Evaluating prognostic factors for sex differences in lung cancer survival: Findings from a large Australian cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Pang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Er, P.; Wang, Y.; You, J.; Wang, P. A nomogram for predicting brain metastases of EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma patients and estimating the efficacy of therapeutic strategies. J. Thorac. Dis. 2021, 13, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Li, J.; Song, L.; He, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Li, W. The number of brain metastases predicts the survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutation status. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wang, W.X.; Wang, D.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Y.C.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.P.; Zhuang, W.; Fang, M.Y.; Wan, B.; et al. A real-world study in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with de novo brain metastasis. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindl, A.; Yadavalli, S.; Gruber, K.A.; Seiwald, M.; Gatterbauer, B.; Dieckmann, K.; Frischer, J.M.; Klikovits, T.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Grisold, A.; et al. Neurological symptom burden impacts survival prognosis in patients with newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 4341–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, G.; Thomas, P.; Breton, J.L.; Léna, H.; Gouva, S.; Dabouis, G.; Bennouna, J.; Souquet, P.J.; Balmes, P.; Thiberville, L.; et al. Results of a phase III study of early versus delayed whole brain radiotherapy with concurrent cisplatin and vinorelbine combination in inoperable brain metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer: GroupeFrançais de Pneumo-Cancérologie (GFPC) protocol 95-1. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.T.; Yoon, S.J.; Pyo, H.R.; Cho, K.H.; Shin, S.H.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Primary chemotherapy for newly diagnosed nonsmall cell lung cancer patients with synchronous brain metastases compared with whole-brain radiotherapy administered first: Results of a randomised pilot study. Cancer 2008, 113, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvenna, P.; Nankivell, M.; Barton, R.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Wilson, P.; McColl, E.; Moore, B.; Brisbane, I.; Ardron, D.; Holt, T.; et al. Dexamethasone and supportive care with or without whole brain radiotherapy in treating patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer with brain metastases unsuitable for resection or stereotactic radiotherapy (QUARTZ): Results from a phase 3, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.R.G.; Miao, E.; Boe, L.A.; Patil, T.; Imber, B.S.; Myall, N.J.; Pollom, E.L.; Hui, C.; Qu, V.; Langston, J.; et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors with and without up-front stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from EGFR and ALK oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer (TURBO-NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3606–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.J.; Pan, S.M.; Lai, S.Z.; Xu, X.N.; Deng, M.L.; Wang, X.H.; Yao, D.C.; Wu, S.X. Upfront cranial radiotherapy vs. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone for the treatment of brain metastases from nonsmall cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of 1465 patients. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, K.; Liang, W.; Zhao, S.; Guo, M.; He, Q.; Li, C.; Song, H.; He, J.; Xia, X. EGFR-TKI plus brain radiotherapy versus EGFR-TKI alone in the management of EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients with brain metastases. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Franchi, M.; Zaffaroni, M.; Vincini, M.G.; de Marinis, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Orecchia, R.; Marvaso, G.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A. Upfront advanced radiotherapy and new drugs for NSCLC patients with synchronous brain metastases: Is the juice worth the squeeze? A real-world analysis from Lombardy, Italy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Niu, L.; Xiao, G.; Peng, H.; Deng, F.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. The long-term and short-term efficacy of immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 875488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, F.; Althoff, F.C.; Sebastian, M. Systemic treatment for brain metastases in NSCLC: A new chapter. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Wu, Y.L.; Hirsh, V.; O’Byrne, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Mok, T.; Popat, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Massey, D.; Zazulina, V.; et al. First-line afatinib versus chemotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and common epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations and brain metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, L.; Corso, F.; Baili, P.; Scotti, F.; Torri, V.; Ganzinelli, M.; Mišković, V.; Leporati, R.; Provenzano, L.; Spagnoletti, A.; et al. Data analytics for real-world data integration in TKI-treated NSCLC patients using electronic health records. ESMO Real World Data Digit. Oncol. 2025, 7, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Henon, C.; Auclin, E.; Mezquita, L.; Ferrara, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Mazieres, J.; Lefebvre, C.; Rabeau, A.; Le Moulec, S.; et al. Outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastases treated with checkpoint inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Patients | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage | ||
| Age | <65 | 161 | 60.3 |
| ≥65 | 106 | 39.7 | |
| Gender | Male | 162 | 60.7 |
| Female | 105 | 39.3 | |
| Smoking status | Smokers and ex-smokers | 197 | 73.8 |
| Non-smokers | 70 | 26.2 | |
| Histologic type | Squamous cell lung cancer | 49 | 18.4 |
| Non-squamous cell lung cancer | 218 | 81.6 | |
| ECOG performance status | PS 0–1 | 110 | 41.2 |
| PS ≥ 2 | 157 | 58.8 | |
| Stage IV | At first diagnosis | 196 | 73.4 |
| During the disease course | 71 | 26.6 | |
| Timing of brain metastases verification | At first diagnosis | 167 | 62.5 |
| At later stage IV diagnosis | 61 | 22.8 | |
| During the stage IV treatment | 39 | 14.6 | |
| Number of brain metastases | 1 | 90 | 33.7 |
| >1 | 177 | 66.3 | |
| Symptoms | Yes | 145 | 54.3 |
| No | 122 | 45.7 | |
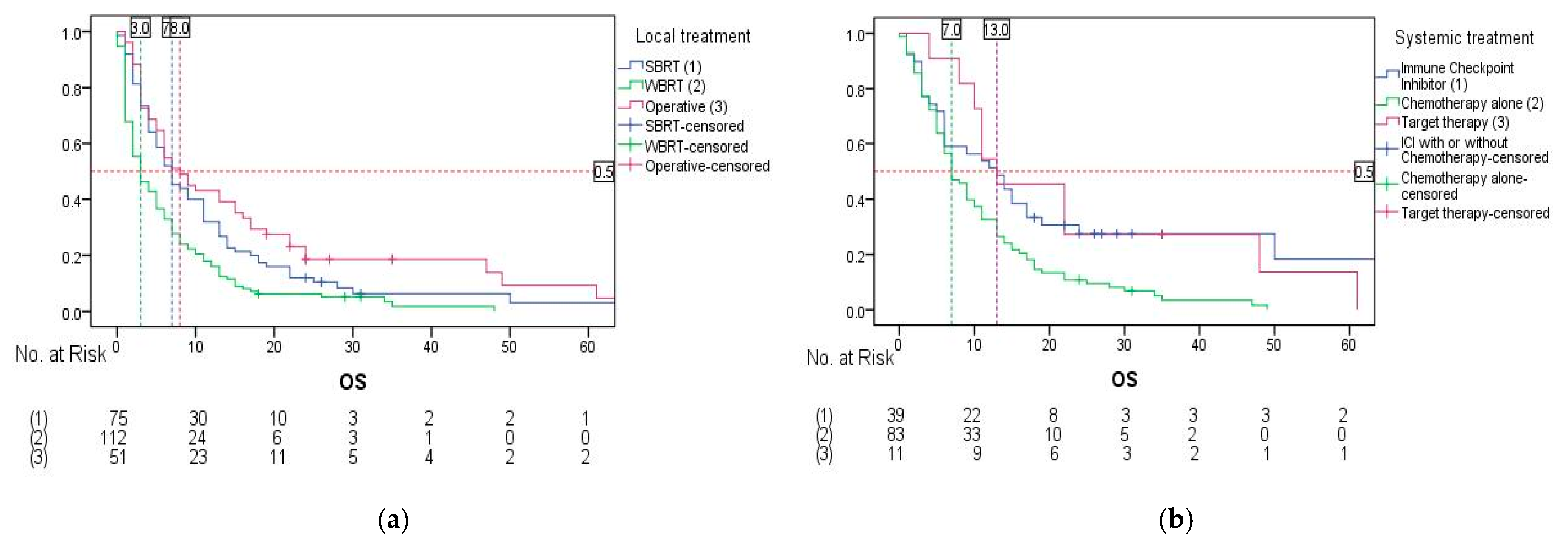
| Brain metastases treatment | BSC | 29 | 10.9 |
| Systemic + local | 133 | 49.4 | |
| Local treatment only | 105 | 39.3 | |
| Local treatment 1 | SBRT | 75 | 28.1 |
| WBRT | 112 | 41.6 | |
| Operative | 51 | 19.1 | |
| Systemic treatment 2 | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor | 39 | 14.6 |
| Chemotherapy alone | 83 | 31.1 | |
| Target therapy | 11 | 4.1 | |
| Molecular Test | Test Results | Patients | Systemic Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor | Chemotherapy Alone | Target Therapy | |||
| PD-L1 | ≥50% | 39 (14.6%) | 39 (29.4%) | 0 | 0 |
| 1–49% | 24 (9.0%) | 0 | 12 (9.0%) | 3 (2.3%) | |
| <1% | 57 (21.3%) | 0 | 28 (21.1%) | 2 (1.5%) | |
| Not tested | 147 (55.1%) | 0 | 43 (32.3%) | 6 (4.5%) | |
| EGFR | Wild-type | 132 (49.4%) | 30 (22.6%) | 54 (40.6%) | 0 |
| Mutated | 19 (7.1%) | 0 | 4 (3.0%) | 11 (8.3%) | |
| Not tested | 116 (43.4%) | 9 (6.8%) | 25 (18.8%) | 0 | |
| ALK | Positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Negative | 99 (37.1%) | 28 (21.1%) | 37 (27.8%) | 5 (3.8%) | |
| Not tested | 168 (62.9%) | 9 (6.8%) | 83 (62.4%) | 0 | |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mOS in Months (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | ||
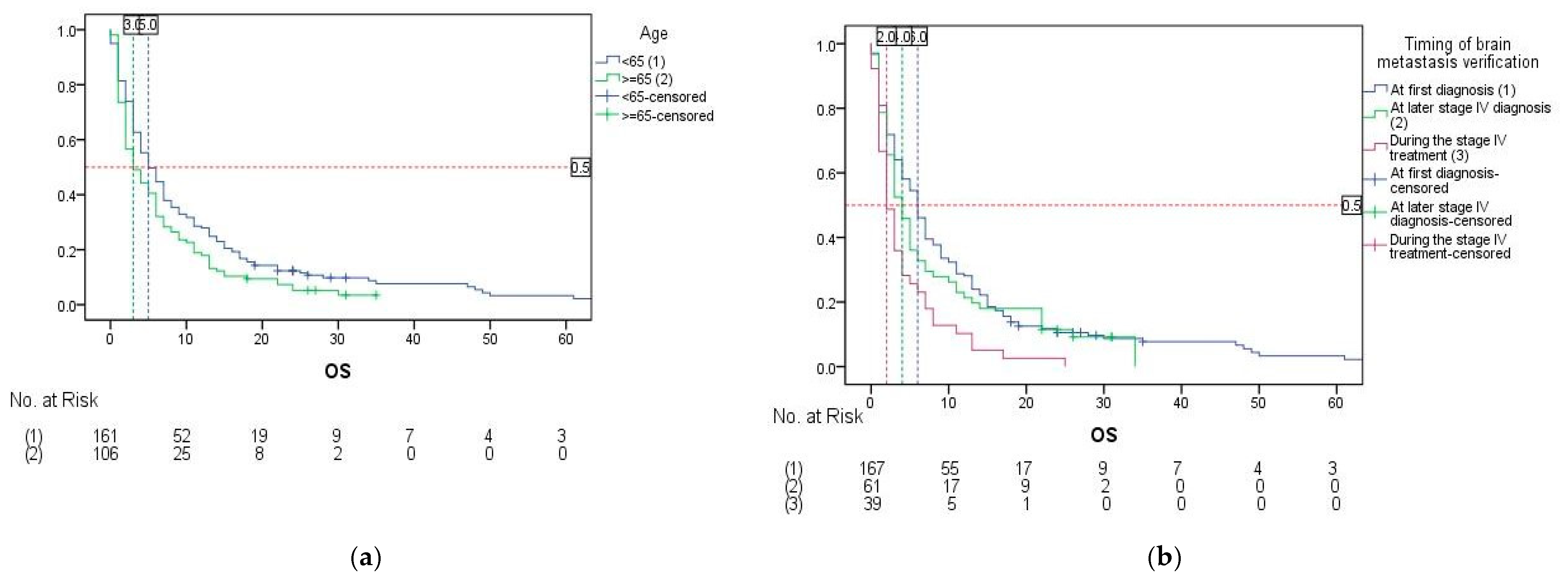
| Age | <65 | 5.0 (3.537–6.463) | 0.752 (0.583–0.971) | 0.029 | 0.760 (0.580–0.994) | 0.045 |
| ≥65 | 3.0 (1.448–4.552) | 1 | ||||
| Gender | Male | 4.0 (3.066–4.934) | 0.762 (0.590–0.985) | 0.038 | 1 | 0.135 |
| Female | 6.0 (4.661–7.339) | 0.815 (0.623–1.066) | ||||
| Smoking status | Smokers and ex-smokers | 5.0 (3.791–6.209) | 0.859 (0.651–1.134) | 0.285 | - | - |
| Non-smokers | 4.0 (2.277–5.723) | - | ||||
| Histologic type | Squamous cell lung cancer | 3.0 (1.753–4.247) | 0.814 (0.592–1.120) | 0.207 | - | - |
| Non-squamous cell lung cancer | 6.0 (4.807–7.193) | - | ||||
| ECOG performance type | PS 0–1 | 9.0 (5.979–12.021) | 0.478 (0.368–0.621) | <0.001 | 0.676 (0.418–1.093) | 0.110 |
| PS ≥2 | 3.0 (2.060–3.940) | 1 | ||||
| Stage IV | At first diagnosis | 5.0 (3.789–6.211) | 0.917 (0.691–1.217) | 0.548 | - | - |
| During the disease course | 4.0 (2.826–5.174) | - | ||||
| Timing of brain metastases verification | At first diagnosis | 6.0 (4.778–7.222) | 0.533 (0.373–0.761) | 0.002 | 0.610 (0.424–0.878) | 0.022 1 |
| At later stage IV diagnosis | 4.0 (2.729–5.271) | 0.614 (0.406–0.927) | 0.594 (0.389–0.910) | |||
| During the stage IV treatment | 2.0 (0.980–3.020) | 1 | 1 | |||
| Number of brain metastases | 1 | 7.0 (5.366–8.634) | 0.569 (0.434–0.745) | <0.001 | 0.576 (0.432–0.769) | <0.001 |
| >1 | 3.0 (2.069–3.931) | 1 | ||||
| Symptoms | Yes | 3.0 (2.351–3.649) | 0.511 (0.396–0.659) | <0.001 | 1 | 0.428 |
| No | 8.0 (5.540–10.460) | 1.218 (0.748–1.983) | ||||
| Brain metastases treatment | BSC | 2.0 (1.317–2.683) | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | <0.001 1 |
| Systemic + local | 9.0 (6.828–11.172) | 0.237 (0.154–0.366) | 0.320 (0.197–0.520) | |||
| Local treatment only | 2.0 (1.352–2.648) | 0.610 (0.402–0.928) | 0.746 (0.486–1.145) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Randjelovic, N.; Petronijevic, M.; Calamac, M.; Peulic, M.; Filipovic, B.; Mutavdzic, V.; Djuric, A.; Rankovic, T.; Bugarcic, M.; Canak, I.; et al. Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: A Real-World Data Study from a Resource-Limited Country. Cancers 2025, 17, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101603
Randjelovic N, Petronijevic M, Calamac M, Peulic M, Filipovic B, Mutavdzic V, Djuric A, Rankovic T, Bugarcic M, Canak I, et al. Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: A Real-World Data Study from a Resource-Limited Country. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101603
Chicago/Turabian StyleRandjelovic, Nevena, Marina Petronijevic, Marina Calamac, Marija Peulic, Biljana Filipovic, Vladan Mutavdzic, Aleksandar Djuric, Teodora Rankovic, Milos Bugarcic, Ivana Canak, and et al. 2025. "Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: A Real-World Data Study from a Resource-Limited Country" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101603
APA StyleRandjelovic, N., Petronijevic, M., Calamac, M., Peulic, M., Filipovic, B., Mutavdzic, V., Djuric, A., Rankovic, T., Bugarcic, M., Canak, I., Mikov, J., Igrutinovic, N., Novak, S., Marjanovic, M., Perovic, J., Urosevic, T., & Cufer, T. (2025). Outcomes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: A Real-World Data Study from a Resource-Limited Country. Cancers, 17(10), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101603






