Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Contact with Neurogenic Zones and Its Effects on Survival: Insights beyond Traditional Predictors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Patient Data
2.2. Image Acquisition and Post-Processing
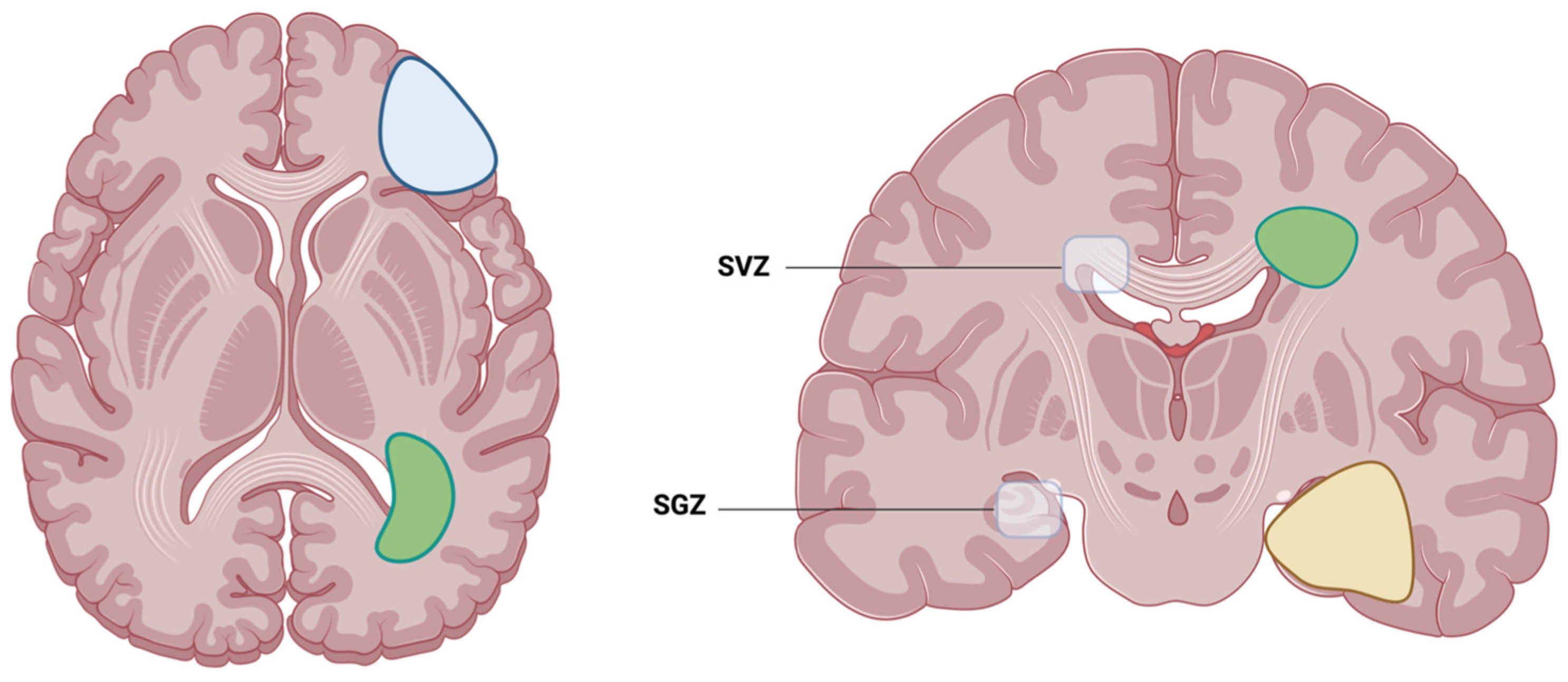
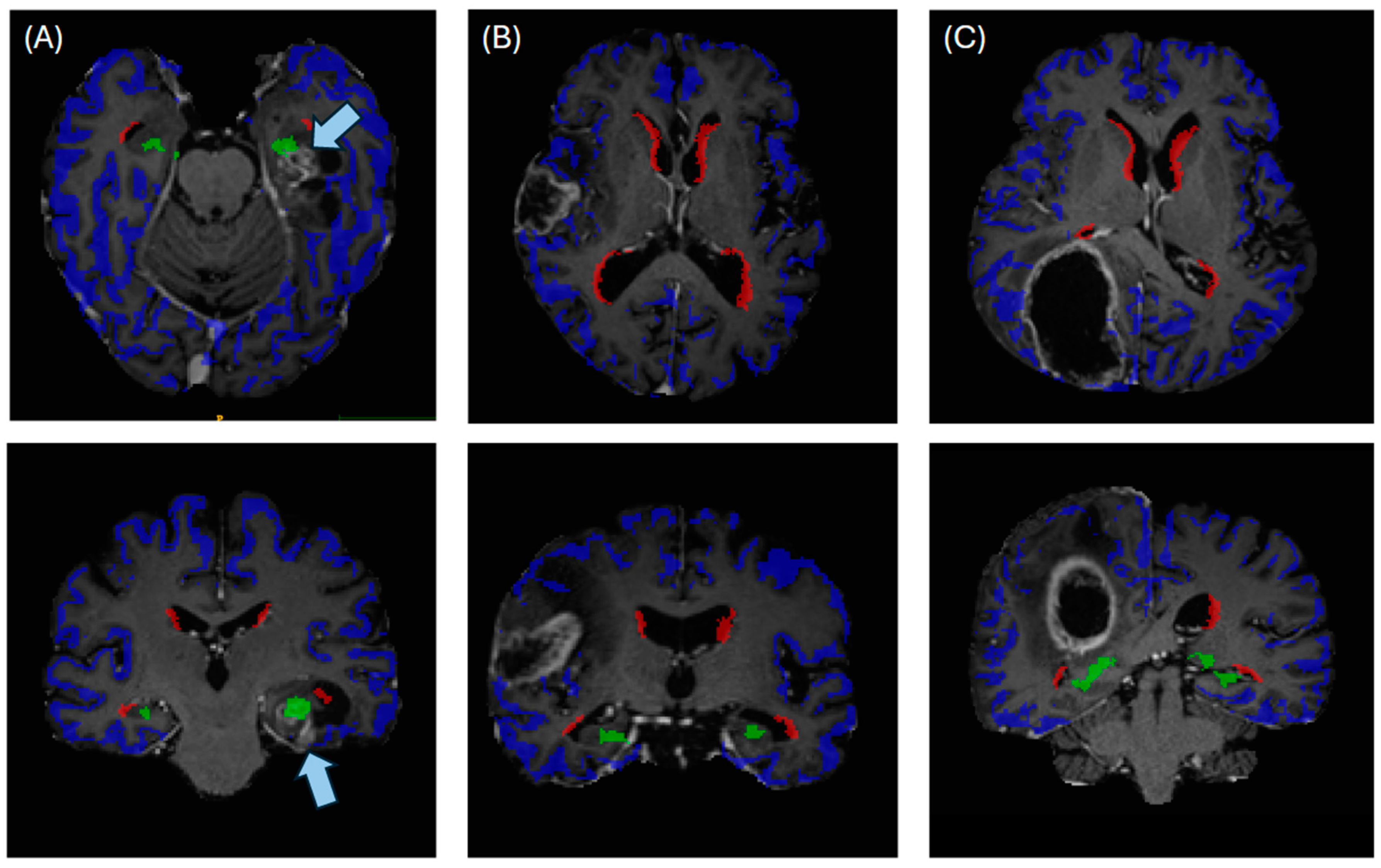
2.3. Automated Segmentation of Neurogenic Zones
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristic of the Study Population
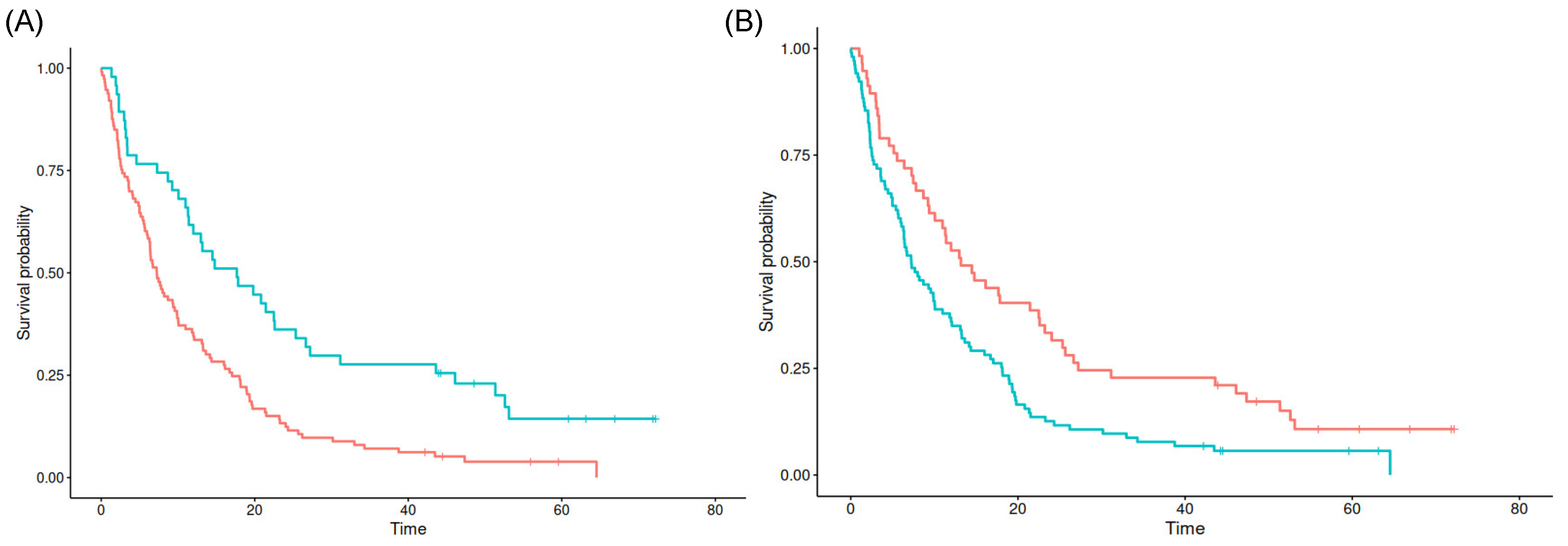
3.2. Results of Survival Analysis with Quantitative Localization Data
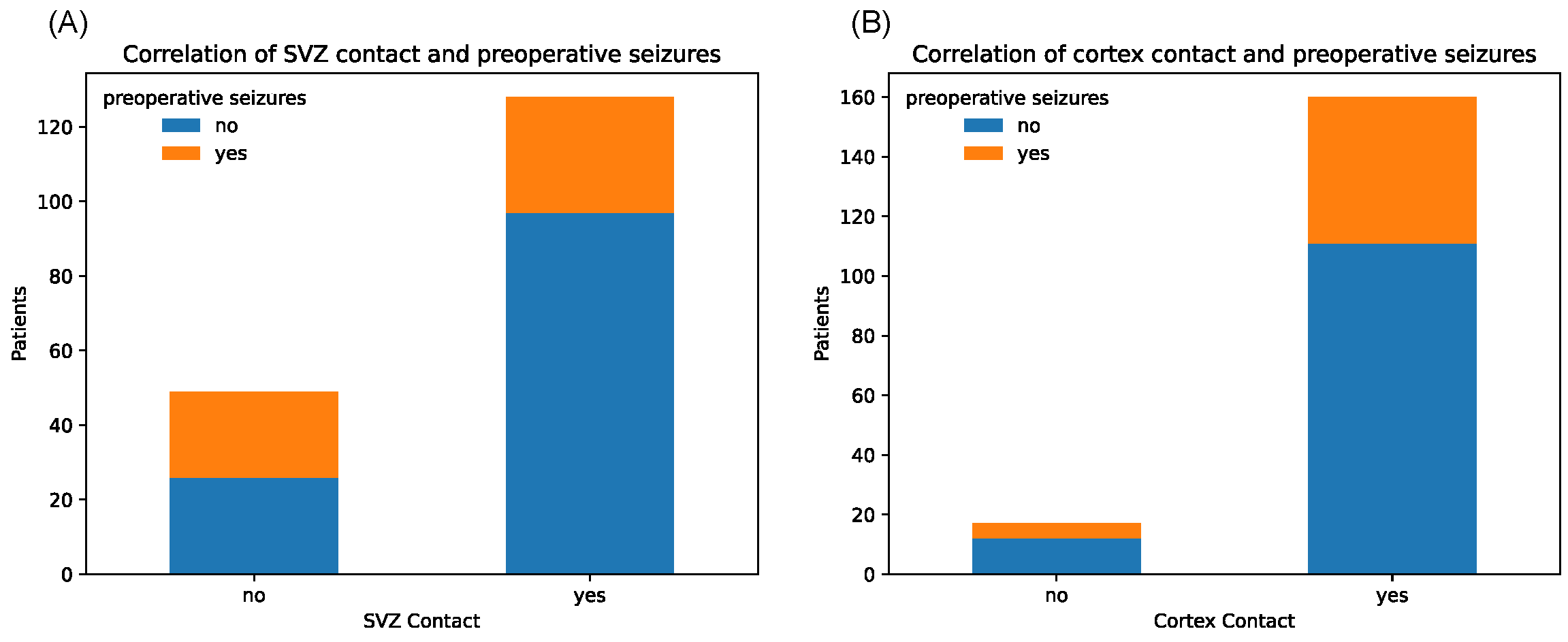
3.3. Correlations between Localization Data and Clinical Parameters
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CET | Contrast-enhancing tumor |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TMZ | temozolomide |
| OPC | oligodendrocyte precursor cells |
| APC | astrocytic precursor cells |
| NSC | neural stem cell |
| NPC | neural progenitor cell |
| SVZ | subventricular zone |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| OS | overall survival |
| IDH1 | isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| KPS | Karnofsky performance status |
| MGMT | O6-methylguanin-DNA-methyltransferase |
| CE | contrast-enhancing |
| TFE | T1-weighted Turbo Field Echo |
| FLAIR | fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| RT | radiotherapy |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| CI | confidence intervall |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| RANO | Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology |
| MPRAGE | magnetization-prepared rapid gradient-echo |
| GTR | gross total resection |
| STR | subtotal resection |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| DG | Dental gyrus |
References
- Hertler, C.; Felsberg, J.; Gramatzki, D.; Le Rhun, E.; Clarke, J.; Soffietti, R.; Wick, W.; Chinot, O.; Ducray, F.; Roth, P.; et al. Long-Term Survival with IDH Wildtype Glioblastoma: First Results from the ETERNITY Brain Tumor Funders’ Collaborative Consortium (EORTC 1419). Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 189, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, iv1–iv96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ah-Pine, F.; Khettab, M.; Bedoui, Y.; Slama, Y.; Daniel, M.; Doray, B.; Gasque, P. On the Origin and Development of Glioblastoma: Multifaceted Role of Perivascular Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sage, J.C.; Miller, M.R.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hippenmeyer, S.; Vogel, H.; Foreman, O.; Bronson, R.T.; Nishiyama, A.; Luo, L.; et al. Mosaic Analysis with Double Markers (MADM) Reveals Tumor Cell-of-Origin in Glioma. Cell 2011, 146, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungk, C.; Warta, R.; Mock, A.; Friauf, S.; Hug, B.; Capper, D.; Abdollahi, A.; Debus, J.; Bendszus, M.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Location-Dependent Patient Outcome and Recurrence Patterns in IDH1-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Lee, Y.; Miller, R.; Castillo, M. Glioblastoma Multiforme: Relationship to Subventricular Zone and Recurrence. Neuroradiol. J. 2013, 26, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, C.; Keller, S.; Schmidt, M.H.H. The Role of SVZ Stem Cells in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.S.; Perfilieva, E.; Björk-Eriksson, T.; Alborn, A.-M.; Nordborg, C.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the Adult Human Hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lois, C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Proliferating Subventricular Zone Cells in the Adult Mammalian Forebrain Can Differentiate into Neurons and Glia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2074–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.A.; Cha, S.; Mayo, M.C.; Chen, M.-H.; Keles, E.; VandenBerg, S.; Berger, M.S. Relationship of Glioblastoma Multiforme to Neural Stem Cell Regions Predicts Invasive and Multifocal Tumor Phenotype. Neuro-Oncology 2007, 9, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. The Adult Ventricular–Subventricular Zone (V-SVZ) and Olfactory Bulb (OB) Neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a018820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016–2020. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, iv1–iv99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.F.; Ottaviani, D.; Tazare, J.; Gregson, J.; Kitchen, N.; Brandner, S.; Fersht, N.; Mulholland, P. Survival Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of Radiotherapy with Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide versus Radiotherapy Alone on Survival in Glioblastoma in a Randomised Phase III Study: 5-Year Analysis of the EORTC-NCIC Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamutdinov, D.; Dandashi, J.A.; Stock, E.M.; Vasquez, E.A.; Mao, Y.; Dayawansa, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, E.; Fonkem, E.; Huang, J.H. Survival Outcomes Prognostication in Glioblastoma Diagnosed Patients. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, e67–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, J.R.; Horton, J.; Scott, C.; Curran, W.J.; Rubin, P.; Fischbach, J.; Isaacson, S.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.O.; Nelson, J.S. Influence of Location and Extent of Surgical Resection on Survival of Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme: Results of Three Consecutive Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) Clinical Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1993, 26, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallud, J.; Roux, A.; Moiraghi, A.; Aboubakr, O.; Elia, A.; Guinard, E.; Oppenheim, C.; Tauziede-Espariat, A.; Parraga, E.; Gavaret, M.; et al. Characteristics and Prognosis of Tumor-Related Epilepsy During Tumor Evolution in Patients with IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma. Neurology 2024, 102, e207902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, A.; Roca, P.; Edjlali, M.; Sato, K.; Zanello, M.; Dezamis, E.; Gori, P.; Lion, S.; Fleury, A.; Dhermain, F.; et al. MRI Atlas of IDH Wild-Type Supratentorial Glioblastoma: Probabilistic Maps of Phenotype, Management, and Outcomes. Radiology 2019, 293, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, A.; Armocida, D.; Paglia, F.; Palmieri, M.; Frati, A.; D’Andrea, G.; Salvati, M.; Santoro, A. IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma Presenting with Seizure: Clinical Specificity, and Oncologic and Surgical Outcomes. J. Neurol. Surg. Part Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2022, 83, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skardelly, M.; Brendle, E.; Noell, S.; Behling, F.; Wuttke, T.V.; Schittenhelm, J.; Bisdas, S.; Meisner, C.; Rona, S.; Tatagiba, M.S.; et al. Predictors of Preoperative and Early Postoperative Seizures in Patients with Intra-Axial Primary and Metastatic Brain Tumors: A Retrospective Observational Single Center Study. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, S.; van Bodegraven, E.; Seute, T.; Spliet, W.G.M.; Geurts, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Schoysman, L.; Huiszoon, W.B.; Varkila, M.; Rouss, S.; et al. Adverse Prognosis of Glioblastoma Contacting the Subventricular Zone: Biological Correlates. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallaert, G.; Pinson, H.; Van den Broecke, C.; Sweldens, C.; Van Roost, D.; Kalala, J.-P.; Boterberg, T. Survival Impact of Incidental Subventricular Zone Irradiation in IDH-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Liu, M.; Sun, G.; Xu, B. MR Imaging, MGMT Promoter Methylation Features and Prognostic Analysis of Subventricular Zone Contacting IDH Wild-Type Glioblastoma. Curr. Med. Imaging 2023, 19, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Z.; Wu, W.; Sun, G.; Xu, B. The Imaging Features and Prognosis of Gliomas Involving the Subventricular Zone: An MRI Study. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 222, 107465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas, S.; Luguera, E.; Molero, J.; Balaña, C.; Estival, A.; Castañer, S.; Carrato, C.; Hostalot, C.; Teixidor, P.; Villà, S. Influence of Glioblastoma Contact with the Subventricular Zone on Survival and Recurrence Patterns. Clin. Transl. Oncol. Off. Publ. Fed. Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Inst. Mex. 2021, 23, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isensee, F.; Schell, M.; Pflueger, I.; Brugnara, G.; Bonekamp, D.; Neuberger, U.; Wick, A.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Heiland, S.; Wick, W.; et al. Automated Brain Extraction of Multisequence MRI Using Artificial Neural Networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4952–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlfing, T.; Zahr, N.M.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. The SRI24 Multichannel Atlas of Normal Adult Human Brain Structure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 798–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofler, F.; Berger, C.; Waldmannstetter, D.; Lipkova, J.; Ezhov, I.; Tetteh, G.; Kirschke, J.; Zimmer, C.; Wiestler, B.; Menze, B.H. BraTS Toolkit: Translating BraTS Brain Tumor Segmentation Algorithms Into Clinical and Scientific Practice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.F.; Kofler, F.; Grundl, L.; Finck, T.; Li, H.; Zimmer, C.; Menze, B.; Wiestler, B. Improving Automated Glioma Segmentation in Routine Clinical Use Through Artificial Intelligence-Based Replacement of Missing Sequences with Synthetic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans. Invest. Radiol. 2022, 57, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruil, D.E.; David, S.; Nagtegaal, S.H.J.; de Sonnaville, S.F.A.M.; Verhoeff, J.J.C. Irradiation of the Subventricular Zone and Subgranular Zone in High- and Low-Grade Glioma Patients: An Atlas-Based Analysis on Overall Survival. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdab193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baheti, B.; Waldmannstetter, D.; Chakrabarty, S.; Akbari, H.; Bilello, M.; Wiestler, B.; Schwarting, J.; Calabrese, E.; Rudie, J.; Abidi, S.; et al. The Brain Tumor Sequence Registration Challenge: Establishing Correspondence between Pre-Operative and Follow-up MRI Scans of Diffuse Glioma Patients. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.06979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunts, K.; Mohlberg, H.; Bludau, S.; Zilles, K. Julich-Brain: A 3D Probabilistic Atlas of the Human Brain’s Cytoarchitecture. Science 2020, 369, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kahng, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, S.J.; Um, J.-Y.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, J.-K.; Park, J.; et al. Human Glioblastoma Arises from Subventricular Zone Cells with Low-Level Driver Mutations. Nature 2018, 560, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steed, T.C.; Treiber, J.M.; Taha, B.; Engin, H.B.; Carter, H.; Patel, K.S.; Dale, A.M.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Glioblastomas Located in Proximity to the Subventricular Zone (SVZ) Exhibited Enrichment of Gene Expression Profiles Associated with the Cancer Stem Cell State. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 148, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, A.M.; Dewan, M.C.; White-Dzuro, G.A.; Brinson, P.R.; Weaver, K.D.; Thompson, R.C.; Ihrie, R.A.; Chambless, L.B. Decreased Survival in Glioblastomas Is Specific to Contact with the Ventricular-Subventricular Zone, Not Subgranular Zone or Corpus Callosum. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 132, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Tomé, W.A.; Mehta, M.P. Why Avoid the Hippocampus? A Comprehensive Review. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallaert, G.; Pinson, H.; Van den Broecke, C.; Vanhauwaert, D.; Van Roost, D.; Boterberg, T.; Kalala, J.P. Subventricular Zone Contacting Glioblastoma: Tumor Size, Molecular Biological Factors and Patient Survival. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palpan Flores, A.; Vivancos Sanchez, C.; Roda, J.M.; Cerdán, S.; Barrios, A.J.; Utrilla, C.; Royo, A.; Gandía González, M.L. Assessment of Pre-Operative Measurements of Tumor Size by MRI Methods as Survival Predictors in Wild Type IDH Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, A.M.; Mummareddy, N.; Salwi, S.; Davis, L.T.; Ihrie, R.A. Glioblastoma Distance From the Subventricular Neural Stem Cell Niche Does Not Correlate with Survival. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 564889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, A.; Frisén, J. Adult Neurogenesis in Humans- Common and Unique Traits in Mammals. PLoS Biol. 2015, 13, e1002045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Tramontin, A.D.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Barbaro, N.M.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, S.; Lawton, M.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; Manuel-García Verdugo, J.; et al. Unique Astrocyte Ribbon in Adult Human Brain Contains Neural Stem Cells but Lacks Chain Migration. Nature 2004, 427, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsa, A.T.; Wachhorst, S.; Lamborn, K.R.; Prados, M.D.; McDermott, M.W.; Berger, M.S.; Chang, S.M. Prognostic Significance of Intracranial Dissemination of Glioblastoma Multiforme in Adults. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, W.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms and Functional Implications of Adult Neurogenesis. Cell 2008, 132, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeberg, S.; König, L.; Bostel, T.; Harrabi, S.; Welzel, T.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Glioblastoma Recurrence Patterns after Radiation Therapy with Regard to the Subventricular Zone. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT Gene Silencing and Benefit from Temozolomide in Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumakova, A.; Lathia, J.D. Outlining Involvement of Stem Cell Program in Regulation of O6-Methylguanine DNA Methyltransferase and Development of Temozolomide Resistance in Glioblastoma. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malley, D.S.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Kocialkowski, S.; Pearson, D.M.; Collins, V.P.; Ichimura, K. A Distinct Region of the MGMT CpG Island Critical for Transcriptional Regulation Is Preferentially Methylated in Glioblastoma Cells and Xenografts. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollapalli, K.; Ghantasala, S.; Kumar, S.; Srivastava, R.; Rapole, S.; Moiyadi, A.; Epari, S.; Srivastava, S. Subventricular Zone Involvement in Glioblastoma—A Proteomic Evaluation and Clinicoradiological Correlation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, S.; Wehner, T.; Miller, D.; Wellmer, J.; Schlegel, U.; Grönheit, W. Brain Tumor Related Epilepsy: Pathophysiological Approaches and Rational Management of Antiseizure Medication. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2022, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, A.; Digregorio, M.; Delcamp, C.; Rogister, B.; Piette, C.; Coppieters, N. The Subventricular Zone, a Hideout for Adult and Pediatric High-Grade Glioma Stem Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 614930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients Characteristics | Total (n = 177) |
|---|---|
| Age at time of initial diagnosis (mean) | |
| male | 63.99 years |
| female | 62.68 years |
| all | 65.51 years |
| Gender (absolute and in percent) | |
| male | 95 (53.67%) |
| female | 82 (46.33%) |
| Preoperative seizures (absolute and in percent) | 54 (30.51%) |
| KPS at diagnosis (median) | 80 |
| Resection status (absolute and in percent) | |
| biopsy | 69 (38.98%) |
| resection (subtotal or gross total) | 107 (60.45%) |
| unknown | 1 (0.56 %) |
| Tumor location (absolute and in percent) | |
| frontal | 34 (19.21%) |
| central | 20 (11.30%) |
| temporal | 59 (33.33%) |
| parietal | 28 (15.82%) |
| occipital | 8 (4.52%) |
| multifocal | 20 (11.30%) |
| others | 8 (4.52%) |
| Overall survival (median) | 8.10 months |
| PFS (median) | 3.97 months |
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor volume (main component) in mm3 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | <0.005 |
| Patient age at diagnosis | 1.06 (1.04–1.07) | <0.005 |
| Resection (at any time) | 0.26 (0.17–0.41) | <0.005 |
| MGMT Promotor Methylation | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.18 |
| KPS score | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.01 |
| Multifocality at initial diagnosis | 1.67 (0.98–2.86) | 0.06 |
| Relative tumor fraction in SVZ in % | 117.77 (0.08–1.80 × 105) | 0.20 |
| Relative tumor fraction in SGZ in % | 0.51 (0.00–1.46 × 105) | 0.92 |
| Relative tumor fraction in cortex in % | 0.26 (0.17–0.41) | 0.87 |
| _________________________________________ | ||
| Tumor volume (main component) in mm3 | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | <0.005 |
| Patient age at diagnosis | 1.06 (1.04–1.07) | <0.005 |
| Resection (at any time) | 0.24 (0.16–0.36) | <0.005 |
| MGMT promotor methylation | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.21 |
| KPS score | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.01 |
| Multifocality at initial diagnosis | 1.51 (0.89–2.57) | 0.12 |
| Minimal distance to SVZ in mm | 0.97 (0.95–0.99) | 0.01 |
| Minimal distance to SGZ in mm | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.08 |
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p value |
| Tumor Contact with SVZ | Tumor Contact with SGZ | Tumor Contact with Cortex | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | SVZ Contact | No SVZ Contact | p Value | SGZ Contact | No SGZ Contact | p Value | Cortex Contact | No Cortex Contact | p Value | |
| Total Counts | 128 (72.3%) | 49 (27.7%) | 54 (30.5%) | 123(69.5%) | 160 (90.4%) | 17 (9.6%) | ||||
| Overall survival | Median | 6.97 | 12.49 | 0.008 | 7.28 | 9.25 | 0.690 | 8.10 | 10.20 | 0.824 |
| Multifocality | Preoperative | |||||||||
| Yes | 13 (10.2%) | 7 (14.3%) | 0.609 | 2 (3.7%) | 18 (14.6%) | 0.063 | 18 (11.2%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1.00 | |
| No | 115 (89.8%) | 42 (85.7%) | 52 (96.3%) | 105(85.4%) | 142 (88.8%) | 15 (88.2%) | ||||
| In total | ||||||||||
| Yes | 40 (31.2%) | 19 (38.8%) | 0.440 | 14 (25.9%) | 45 (36.6%) | 0.225 | 52 (32.5%) | 7 (41.1%) | 0.652 | |
| No | 88 (68.8%) | 30 (61.2%) | 40 (74.0%) | 78 (63.4%) | 108 (67.5%) | 10 (58.8%) | ||||
| MGMT promotor methylation | Yes | 48 (37.5%) | 21 (42.8%) | 17 (31.5%) | 52 (42.3%) | 63 (39.4%) | 6 (35.3%) | |||
| No | 76 (59.4%) | 27 (55.1%) | 0.666 | 35 (64.8%) | 68 (55.3%) | 0.255 | 92 (57.5%) | 11 (64.7%) | 0.868 | |
| Not evaluated | 4 (3.1%) | 1 (2.0%) | 2 (3.7%) | 3 (2.4%) | 5 (3.1%) | 0 (0%) | ||||
| Ki-67 Proliferation index | >30% | 49 (38.3%) | 22 (44.9%) | 22 (40.7%) | 49 (39.9%) | 64 (40.0%) | 7 (41.1%) | |||
| <30% | 37 (28.9%) | 19 (38.7%) | 0.872 | 15 (27.8%) | 41 (33.3%) | 0.749 | 48 (30.0%) | 8 (47.1%) | 0.624 | |
| Not evaluated | 42 (32.8%) | 8 (16.3%) | 17 (31.5%) | 33 (26.8%) | 48 (30.0%) | 2 (11.8%) | ||||
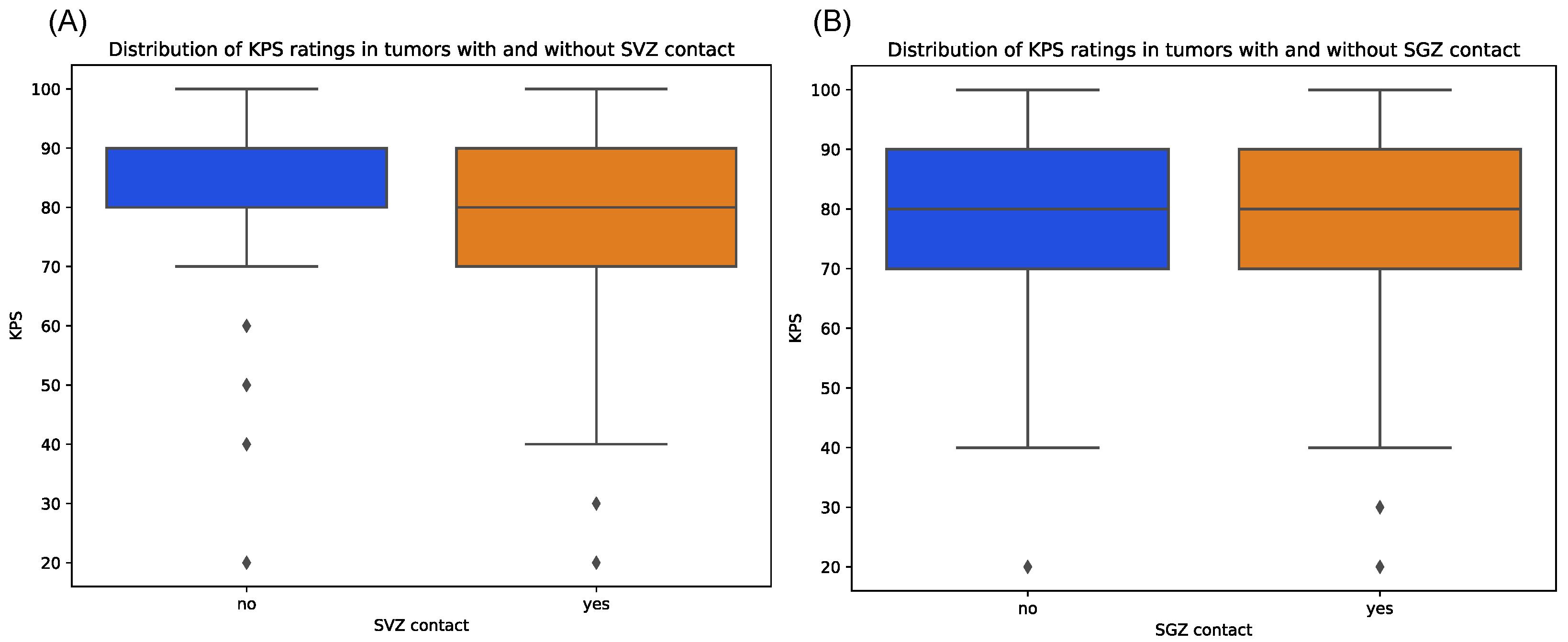
| KPS score | Median | 80 | 90 | 0.666 | 80 | 80 | 0.749 | 80 | 80 | |
| Epilepsy | Yes | 31 (24.2%) | 23 (46.9%) | 17 (31.5%) | 37 (30.1%) | 49 (30.6%) | 5 (29.4%) | |||
| No | 97 (75.8%) | 26 (53.1%) | 0.006 | 37 (68.5%) | 86 (69.9%) | 0.993 | 111 (69.4%) | 12 (70.6%) | 1.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, K.; Kempter, J.; Prokop, G.; Herrmann, T.; Griessmair, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Delbridge, C.; Meyer, B.; Bernhardt, D.; Combs, S.E.; et al. Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Contact with Neurogenic Zones and Its Effects on Survival: Insights beyond Traditional Predictors. Cancers 2024, 16, 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091743
Jung K, Kempter J, Prokop G, Herrmann T, Griessmair M, Kim S-H, Delbridge C, Meyer B, Bernhardt D, Combs SE, et al. Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Contact with Neurogenic Zones and Its Effects on Survival: Insights beyond Traditional Predictors. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091743
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Kirsten, Johanna Kempter, Georg Prokop, Tim Herrmann, Michael Griessmair, Su-Hwan Kim, Claire Delbridge, Bernhard Meyer, Denise Bernhardt, Stephanie E. Combs, and et al. 2024. "Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Contact with Neurogenic Zones and Its Effects on Survival: Insights beyond Traditional Predictors" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091743
APA StyleJung, K., Kempter, J., Prokop, G., Herrmann, T., Griessmair, M., Kim, S.-H., Delbridge, C., Meyer, B., Bernhardt, D., Combs, S. E., Zimmer, C., Wiestler, B., Schmidt-Graf, F., & Metz, M.-C. (2024). Quantitative Assessment of Tumor Contact with Neurogenic Zones and Its Effects on Survival: Insights beyond Traditional Predictors. Cancers, 16(9), 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091743





