Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with at Least 10 Brain Metastases at Diagnosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, M.; Xu, W.; Sahgal, A. A Meta-Analysis Evaluating Stereotactic Radiosurgery, Whole-Brain Radiotherapy, or Both for Patients Presenting with a Limited Number of Brain Metastases. Cancer 2012, 118, 2486–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiappacasse, L.; Kinj, R.; Micheli, R.D.; Mederos, N.; Tuleasca, C.; Cossu, G.; Dunet, V.; Levivier, M.; Bourhis, J.; HOTTINGER, A.F. Management of Brain Metastases in 2022. Rev. Medicale Suisse 2022, 18, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, P.; Rahman, M. Epidemiology of Brain Metastases. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 31, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamba, N.; Wen, P.Y.; Aizer, A.A. Epidemiology of Brain Metastases and Leptomeningeal Disease. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Baehring, J.; Bhatia, A.; Bloch, O.; Brem, S.; Butowski, N.; Cannon, D.M.; Chao, S.; Chheda, M.G.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Version 1.2023 Central Nervous System Cancers Continue NCCN Guidelines Panel Disclosures 2023. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1425 (accessed on 4 April 2024).
- Rhun, E.L.; Guckenberger, M.; Smits, M.; Dummer, R.; Bachelot, T.; Sahm, F.; Galldiks, N.; de Azambuja, E.; Berghoff, A.S.; Metellus, P.; et al. EANO–ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up of Patients with Brain Metastasis from Solid Tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1332–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravan, M.J.; Fecci, P.E.; Anders, C.K.; Clarke, J.M.; Salama, A.K.S.; Adamson, J.D.; Floyd, S.R.; Torok, J.A.; Salama, J.K.; Sampson, J.H.; et al. Current Multidisciplinary Management of Brain Metastases. Cancer 2020, 126, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.H.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E.L. Current Approaches to the Management of Brain Metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Górska, Z.; Duchnowska, R.; Jassem, J. Molecular Profiles of Brain Metastases: A Focus on Heterogeneity. Cancers 2021, 13, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Clavier, J.B.; Pop, M.; Schumacher, C.; Lefebvre, F.; Noël, G. Institutional, Retrospective Analysis of 777 Patients with Brain Metastases: Treatment Outcomes and Diagnosis-Specific Prognostic Factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windsor, A.A.; Koh, E.S.; Allen, S.; Gabriel, G.S.; Yeo, A.E.T.; Allison, R.; van der Linden, Y.M.; Barton, M.B. Poor Outcomes after Whole Brain Radiotherapy in Patients with Brain Metastases: Results from an International Multicentre Cohort Study. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: Analysis of Outcome and Risk of Brain Radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grinsven, E.E.; Nagtegaal, S.H.J.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; Van Zandvoort, M.J.E. The Impact of Stereotactic or Whole Brain Radiotherapy on Neurocognitive Functioning in Adult Patients with Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2021, 44, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmel, W.C.M.; Gehring, K.; Eekers, D.B.P.; Hanssens, P.E.J.; Sitskoorn, M.M. Cognitive Effects of Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Adult Patients with Brain Metastases: A Systematic Review. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorzeff, I.; Antoni, D.; Josset, S.; Noël, G.; Tallet-Richard, A. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases. Cancer/Radiothérapie 2022, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients with Multiple Brain Metastases (JLGK0901): A Multi-Institutional Prospective Observational Study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusthoven, C.G.; Yamamoto, M.; Bernhardt, D.; Smith, D.E.; Gao, D.; Serizawa, T.; Yomo, S.; Aiyama, H.; Higuchi, Y.; Shuto, T.; et al. Evaluation of First-Line Radiosurgery vs. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer Brain Metastases: The FIRE-SCLC Cohort Study. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Bauman, G.; Bradfield, L.; Burri, S.H.; Cabrera, A.R.; Cunningham, D.A.; Eaton, B.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kim, M.M.; Kotecha, R.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases: An ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Kasuya, H. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Results for Patients with 5–10 versus 11–20 Brain Metastases: A Retrospective Cohort Study Combining 2 Databases Totaling 2319 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2021, 146, e479–e491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Luy, D.D.; Jose, S.; Deng, H.; Yavan, S.; Worrell, S.; Belkhir, J.R.; Tang, L.W.; Lunsford, L.D. Single-Session Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Patients with 20 or More Brain Metastases. Neurosurgery 2023, 93, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; Kenna, W.M.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive Partitioning Analysis (Rpa) Of Prognostic Factors. In Three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (Rtog) Brain Metastases Trials; Elsevier Science Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; Volume 37, pp. 745–751. [Google Scholar]
- Nieder, C.; Andratschke, N.H.; Geinitz, H.; Grosu, A.L. Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment Score Is Valid in Patients with Brain Metastases Treated in Routine Clinical Practice in Two European Countries. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2012, 18, CR450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Berkey, B.; Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.; Curran, W. A New Prognostic Index and Comparison to Three Other Indices for Patients with Brain Metastases: An Analysis of 1960 Patients in the RTOG Database. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Institute, N. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.0 (CTCAE). Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, T.J.; Smits, M.; Boxerman, J.; Huang, R.; Barboriak, D.P.; Weller, M.; Chung, C.; Tsien, C.; Brown, P.D.; Shankar, L.; et al. Consensus Recommendations for a Standardized Brain Tumor Imaging Protocol for Clinical Trials in Brain Metastases. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 22, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Kondziolka, D.; Lobato-Polo, J.; Zorro, O.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. T1/T2 Matching to Differentiate Tumor Growth from Radiation Effects after Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Lin, N.U.; Lee, E.Q.; Aoyama, H.; Barani, I.J.; Barboriak, D.P.; Baumert, B.G.; Bendszus, M.; Brown, P.D.; Camidge, R.; et al. Response Assessment Criteria for Brain Metastases: Proposal from the RANO Group. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, J.; Goel, M.; Khanna, P. Understanding Survival Analysis: Kaplan-Meier Estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistics Notes The Logrank Test. BMJ 2004, 328, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessai, S.; Patil, V. Testing and Interpreting Assumptions of COX Regression Analysis. Cancer Res. Stat. Treat. 2019, 2, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.T.; Masters, A.H.; McTyre, E.R.; Farris, M.K.; Chung, C.; Page, B.R.; Kleinberg, L.R.; Hepel, J.; Contessa, J.N.; Chiang, V.; et al. Initial SRS for Patients With 5 to 15 Brain Metastases: Results of a Multi-Institutional Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Hirshman, B.R.; Wilson, B.; Carroll, K.T.; Proudfoot, J.A.; Goetsch, S.J.; Alksne, J.F.; Ott, K.; Aiyama, H.; Nagano, O.; et al. Survival Patterns of 5750 Stereotactic Radiosurgery–Treated Patients with Brain Metastasis as a Function of the Number of Lesions. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 944–951.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatineni, V.; O’Shea, P.J.; Saxena, S.; Khosla, A.A.; Ozair, A.; Kotecha, R.R.; Jia, X.; Rauf, Y.; Murphy, E.S.; Chao, S.T.; et al. Combination of EGFR-Directed Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (EGFR-TKI) with Radiotherapy in Brain Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A 2010–2019 Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozuka, T.; Noro, R.; Mizutani, H.; Kurimoto, F.; Hakozaki, T.; Hisakane, K.; Naito, T.; Takahashi, S.; Taniuchi, N.; Yajima, C.; et al. Osimertinib plus Local Treatment for Brain Metastases versus Osimertinib Alone in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2024, 191, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, E.; Gehring, K.; Hanssens, P.E.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Sitskoorn, M.M. Health-Related Quality of Life in Adult Patients with Brain Metastases after Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Systematic, Narrative Review. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korytko, T.; Radivoyevitch, T.; Colussi, V.; Wessels, B.W.; Pillai, K.; Maciunas, R.J.; Einstein, D.B. 12 Gy Gamma Knife Radiosurgical Volume Is a Predictor for Radiation Necrosis in Non-AVM Intracranial Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flickinger, J.C.; Kondziolka, D.; Lunsford, L.D.; Pollock, B.E.; Yamamoto, M.; Gorman, D.A.; Schomberg, P.J.; Sneed, P.; Larson, D.; Smith, V.; et al. PII S0360-3016(98)00518-5 clinical investigation central nervous system a multi-institutional analysis of complication outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 44, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandhi, R.; Kondziolka, D.; Panczykowski, D.; Monaco, E.A.; Kano, H.; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Stereotactic Radiosurgery Using the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion Unit in the Management of Patients with 10 or More Brain Metastases: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 117, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raldow, A.C.; Chiang, V.L.; Knisely, J.P.; Yu, J.B. Survival and Intracranial Control of Patients with 5 or More Brain Metastases Treated with Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Clin. Trials 2013, 36, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rava, P.; Leonard, K.; Sioshansi, S.; Curran, B.; Wazer, D.E.; Cosgrove, G.R.; Norén, G.; Hepel, J.T. Survival among Patients with 10 or More Brain Metastases Treated with Stereotactic Radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Chang, J.W.; Park, Y.G.; Chang, J.H. Analysis of Radiosurgical Results in Patients with Brain Metastases According to the Number of Brain Lesions: Is Stereotactic Radiosurgery Effective for Multiple Brain Metastases? J. Neurosurg. 2010, 113, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, R.; Tian, Y. Dose-Response Relationship for Radiation-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, S727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. A Multi-Institutional Prospective Observational Study of Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Patients With Multiple Brain Metastases (JLGK0901 Study Update): Irradiation-Related Complications and Long-Term Maintenance of Mini-Mental State Examination Scores. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tini, P.; Marampon, F.; Giraffa, M.; Bucelli, S.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; Minniti, G. Current Status and Perspectives of Interventional Clinical Trials for Brain Metastases: Analysis of ClinicalTrials.Gov. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
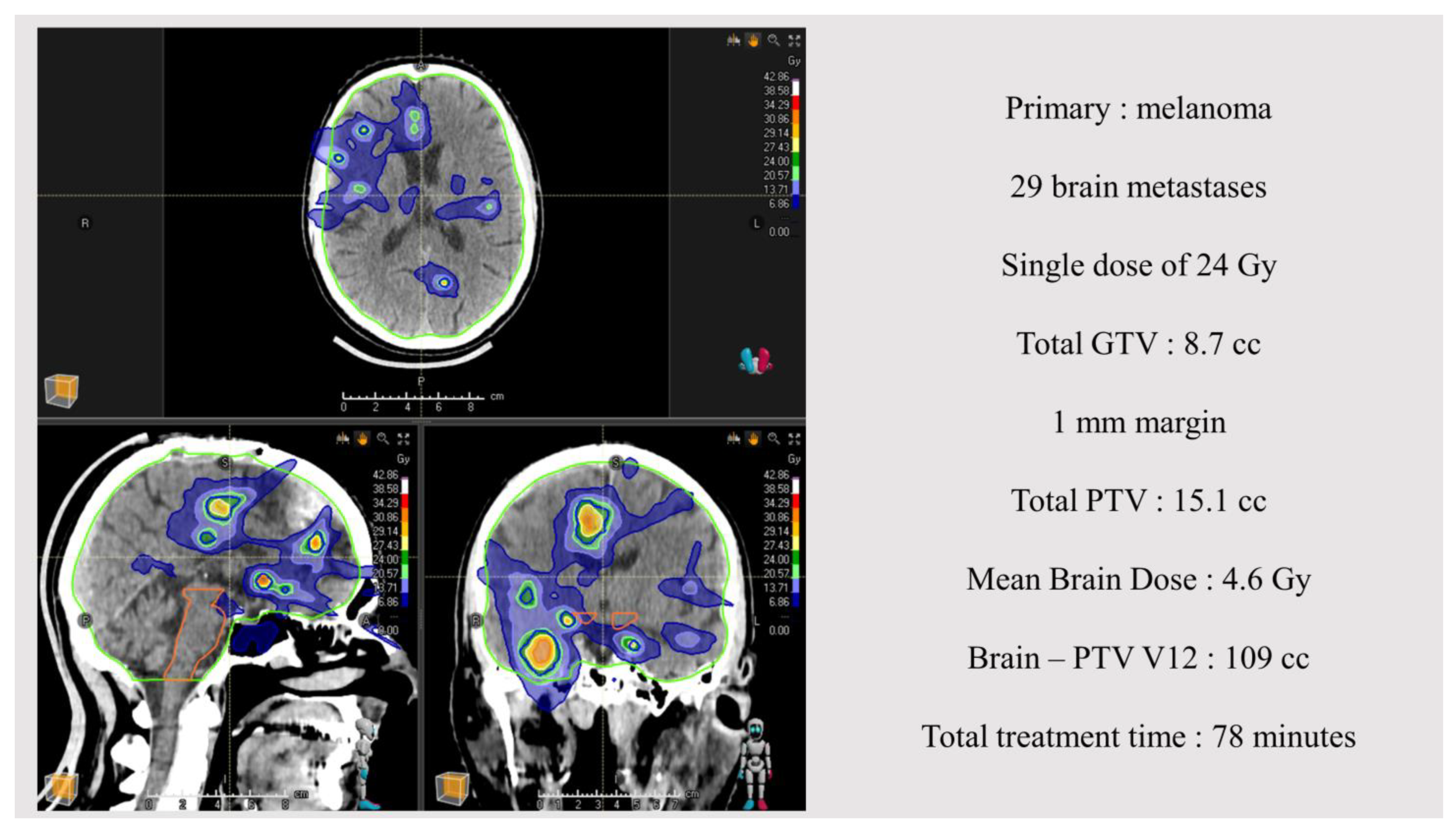
| Demographics | N = 70 (%) |
|---|---|
| Median Age, years (range; min–max) | 64.4 (24.8–86.1) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 33 (47.1) |
| Female | 37 (52.8) |
| Primary cancer | |
| NSCLC | 36 (51.4) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 33 (47.1) |
| Squamous cell | 2 (2.9) |
| Giant cell | 1 (1.4) |
| Melanoma | 12 (17.0) |
| SCLC | 8 (11.4) |
| Kidney | 5 (7.1) |
| Breast | 4 (5.8) |
| Other | 5 (7.1) |
| Brain metastases | |
| Metachronous | 41 (58.6) |
| Synchronous | 29 (41.4) |
| ECOG PS | |
| 0 | 18 (25.7) |
| 1 | 38 (54.3) |
| ≥2 | 14 (20) |
| RPA class | |
| 1 | 11 (15.7) |
| 2 | 45 (64.3) |
| 3 | 14 (20) |
| Ds-GPA class | |
| 2 | 2 (2.9) |
| 3 | 40 (57.1) |
| 4 | 28 (40.0) |
| Controlled primary | |
| Yes | 18 (25.7) |
| No | 52 (74.3) |
| Concomitant treatment | |
| None | 19 (27.1) |
| Immunotherapy | 21 (30.0) |
| Chemotherapy | 10 (14.2) |
| Chemo-immunotherapy combination | 6 (7.1) |
| Molecular targeted therapy | 11 (15.7) |
| Initial treatment | (range; min–max) |
| Total number of metastases | N = 1174 |
| Median number of metastases | 14 (10–64) |
| Number of post-operative cavities | 6 (0.5%) |
| Median PTV, cm3 | 7.0 (1.0–48.3) |
| Median GTV, cm3 | 3.0 (0.3–36.1) |
| Mean brain Dose, Gy | 3.8 (1.3–8.9) |
| Median brain-PTV V12, cm3 | 29.1 (1.7–422) |
| Median treatment dose | 20 (15–35) |
| Median number of fractions | 1 (1–5) |
| Treatment regimen | |
| 20 Gy in 1 fraction | 775 (66.0%) |
| 24 Gy in 1 fraction | 348 (29.6%) |
| 35 Gy in 5 fractions | 18 (1.5%) |
| Other | 33 (2.8%) |
| Patient Outcome | N = 70 (%) |
|---|---|
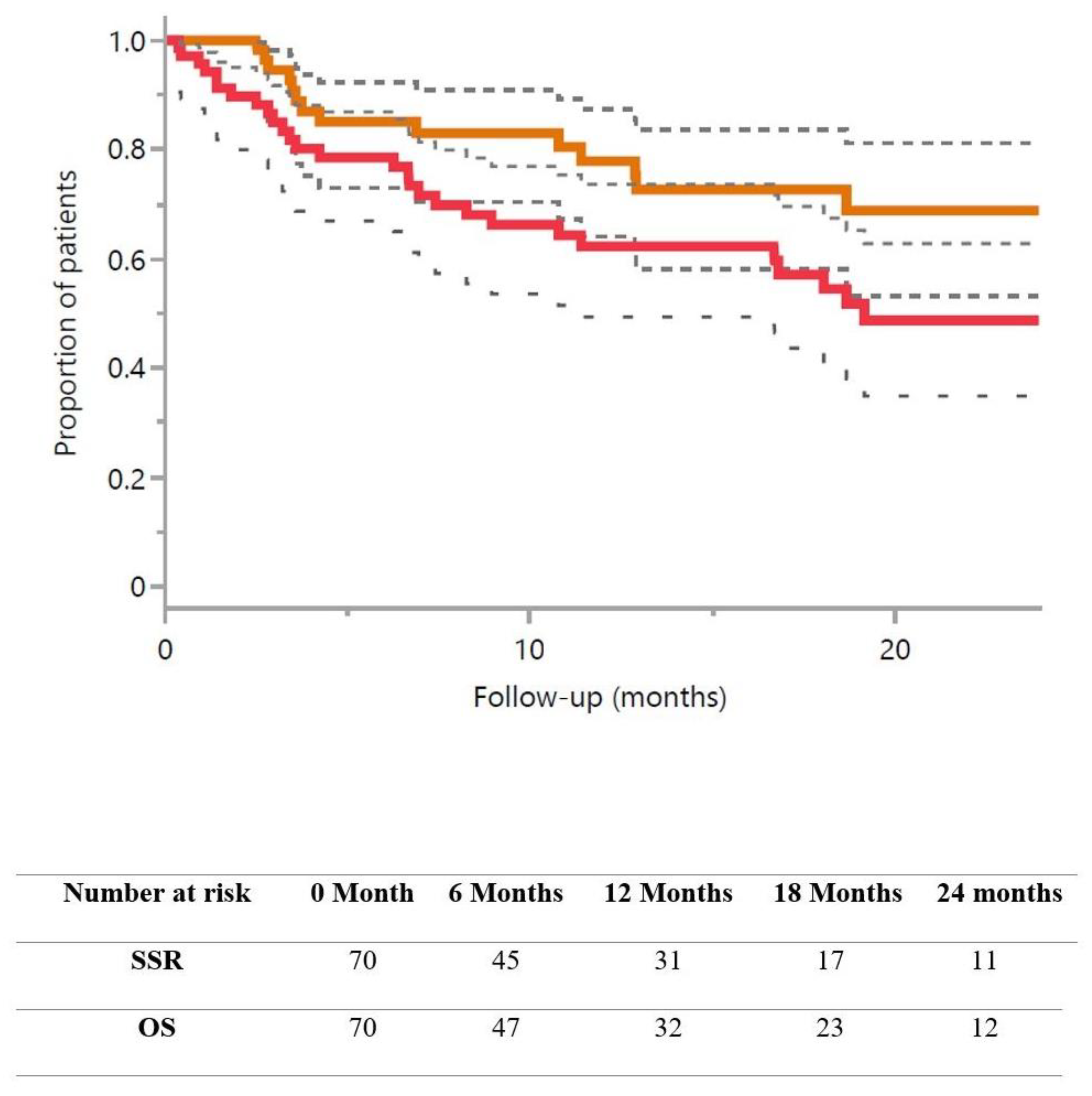
| Median follow-up (months) | 18.8 (3.6–55.1) |
| Overall survival | |
| At 1 year | 62.3% (50.0–74.6) |
| At 2 years | 48.7% (34.1–63.0) |
| Strategy success rate * | |
| At 1 year | 77.8% (66.1–89.5) |
| At 2 years | 68.8% (54.2–83.3) |
| Freedom from WBRT | |
| At 1 year | 87.8% (78.8–96.8) |
| At 2 years | 78.7% (66.0–91.5) |
| Cumulative number of brain treatments | |
| 1 | 39 (55.7%) |
| 2 | 15 (21.4%) |
| 3 | 7 (10.0%) |
| ≥4 | 9 (12.8%) |
| At least one radio-necrosis | |
| No | 60 (85.7%) |
| Yes | 10 (14.2%) |
| Grade 1 | 9 (12.8%) |
| Grade 2 | 1 (1.4%) |
| ≥Grade 2 Toxicity | |
| No | 67 (95.7%) |
| Yes | 3 (4.3%) |
| Lesions outcome | (range) |
| Cumulative number of metastases | N = 1537 |
| Local control rate | |
| At 1 year | 97.3% (96.4–98.2) |
| At 2 years | 96.4% (95.0–97.8) |
| Necrosis rate | |
| At 1 year | 2.1% (1.0–3.1) |
| At 2 years | 2.9% (1.5–4.3) |
| Median cumulative number of metastases | 16 (10–105) |
| Median cumulative PTV, cm3 | 7.7 (0.9–54.7) |
| Cumulative mean brain dose, Gy | 4.9 (1.3–11.0) |
| Cumulative number of brainstem metastases | 25 (1.6%) |
| Median cumulative brain-PTV V12**, cm3 | 37.3 (1.7–529.3) |
| Treatment Sequence | Number of Treated Patients | Total Number of Treated Lesions | Median Number of Lesions per Patient (Min–Max Range) | Median Time from the Previous Sequence in Months (Min–Max Range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N°1 | 70 | 1174 | 14 (10–64) | - |
| N°2 | 31 | 157 | 3(1–29) | 4.3 (2.3–24.7) |
| N°3 | 16 | 100 | 4 (1–22) | 8.2 (5.3–25.1) |
| N°4 | 9 | 69 | 3 (1–34) | 12.0 (8.3–26.2) |
| N°5 | 4 | 17 | 4 (2–17) | 22.1 (14.7–23.4) |
| N°6 | 3 | 21 | 8 (1–12) | 17.4 (17.2–23.4) |
| N°7 | 1 | 1 | 1 (1–1) | 12.3 (12.3–12.3) |
| Variable (N) | Overall Survival (95% CI) | Log Rank p-Value/Cox Regression | Strategy Success Rate (95% CI) | Log Rank p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | p = 0.82/NI | p = 0.63 | ||
| <64 y-o (35) | 65.3% (47.7–82.9) | 76.0% (59.0–93.0) | ||
| ≥64 y-o (35) | 59.5% (76.8–42.2) | 80.0% (62.0–98.0) | ||
| Sex | p = 0.023/NS | p = 0.35 | ||
| Female (37) | 69.3% (52.4–86.4) | 80.0% (65.5–95.7) | ||
| Male (33) | 55.3% (37.7–72.9) | 75.3% (58.1–92.5) | ||
| ECOG PS | p = 0.002/NI ** | p = 0.63 | ||
| 0–1 (56) | 70.9% (58.0–83.8) | 76.8% (64.1–89.5) | ||
| ≥2 (14) | 25.4% (0–52.4) | 87.5% (65.0–100) | ||
| RPA class | p = 0.002/p = 0.0004 | p = 0.63 | ||
| 1–2 (56) | 70.9% (58.0–83.8) | 76.8% (64.1–89.5) | ||
| 3 (14) | 25.4% (0–52.4) | 87.5% (65.0–100) | ||
| Ds-GPA class | p = 0.24/NI | p = 0.56 | ||
| ≤3 (42) | 69.7% (54.8–84.7) | 80.3% (66.0–94.6) | ||
| 4 (28) | 52.1% (32.2–72.0) | 75.3% (56.4–94.3) | ||
| Metastases | p = 0.33/NI | p = 0.16 | ||
| Metachronous (41) | 61.6% (45.5–77.3) | 72.0% (55.4–88.6) | ||
| Synchronous (29) | 64.4% (45.4–83.4) | 84.5% (68.0–100) | ||
| Number of brain metastases | p = 0.50/NI | p = 0.31 | ||
| <14 (35) | 64.6% (46.8–82.2) | 79.6% (63.3–95.9) | ||
| ≥14 (35) | 60.4% (43.6–77.2) | 76.1% (60.4–92.3) | ||
| Tumor volume | p = 0.38/NI | p = 0.47 | ||
| <PTV 7 cm3 (35) | 70.4% (53.9–86.9) | 72.5% (54.9–90.1) | ||
| ≥PTV 7 cm3 (35) | 65.0% (52.5–77.6) | 86.5% (72.2–100) | ||
| Primary | p = 0.0375/NS | p = 0.34 | ||
| SCLC (36) | 46.7% (10.2–83.3) | 80.0% (44,9–100) | ||
| Other Primary (34) | 64.3% (51.2–77.4) | 77.2% (64.0–90.1) | ||
| Controlled Primary | p = 0.08/NS | p = 0.88 | ||
| Yes (18) | 80.7% (64.7–96.6) | 75.1% (53.9–96.3) | ||
| No (52) | 55.9% (41.2–70.6) | 80.1% (66.8–93.0) | ||
| Concomitant Treatment | p = 0.055/NS | p = 0.92 | ||
| Molecular targeted therapy (11) | 87.5% (64.5–100) | 75.0% (45.0–100) | ||
| Other treatment (59) | 58.5% (45.2–71.8) | 78.0% (65.0–91.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinj, R.; Hottinger, A.F.; Böhlen, T.T.; Ozsahin, M.; Vallet, V.; Dunet, V.; Bouchaab, H.; Peters, S.; Tuleasca, C.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with at Least 10 Brain Metastases at Diagnosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091742
Kinj R, Hottinger AF, Böhlen TT, Ozsahin M, Vallet V, Dunet V, Bouchaab H, Peters S, Tuleasca C, Bourhis J, et al. Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with at Least 10 Brain Metastases at Diagnosis. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091742
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinj, Rémy, Andreas Felix Hottinger, Till Tobias Böhlen, Mahmut Ozsahin, Véronique Vallet, Vincent Dunet, Hasna Bouchaab, Solange Peters, Constantin Tuleasca, Jean Bourhis, and et al. 2024. "Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with at Least 10 Brain Metastases at Diagnosis" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091742
APA StyleKinj, R., Hottinger, A. F., Böhlen, T. T., Ozsahin, M., Vallet, V., Dunet, V., Bouchaab, H., Peters, S., Tuleasca, C., Bourhis, J., & Schiappacasse, L. (2024). Long-Term Results of Stereotactic Radiotherapy in Patients with at Least 10 Brain Metastases at Diagnosis. Cancers, 16(9), 1742. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091742







