A Systematic Review of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Cancer Receiving Palliative Radiotherapy: Evidence-Based Recommendations
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Key Questions
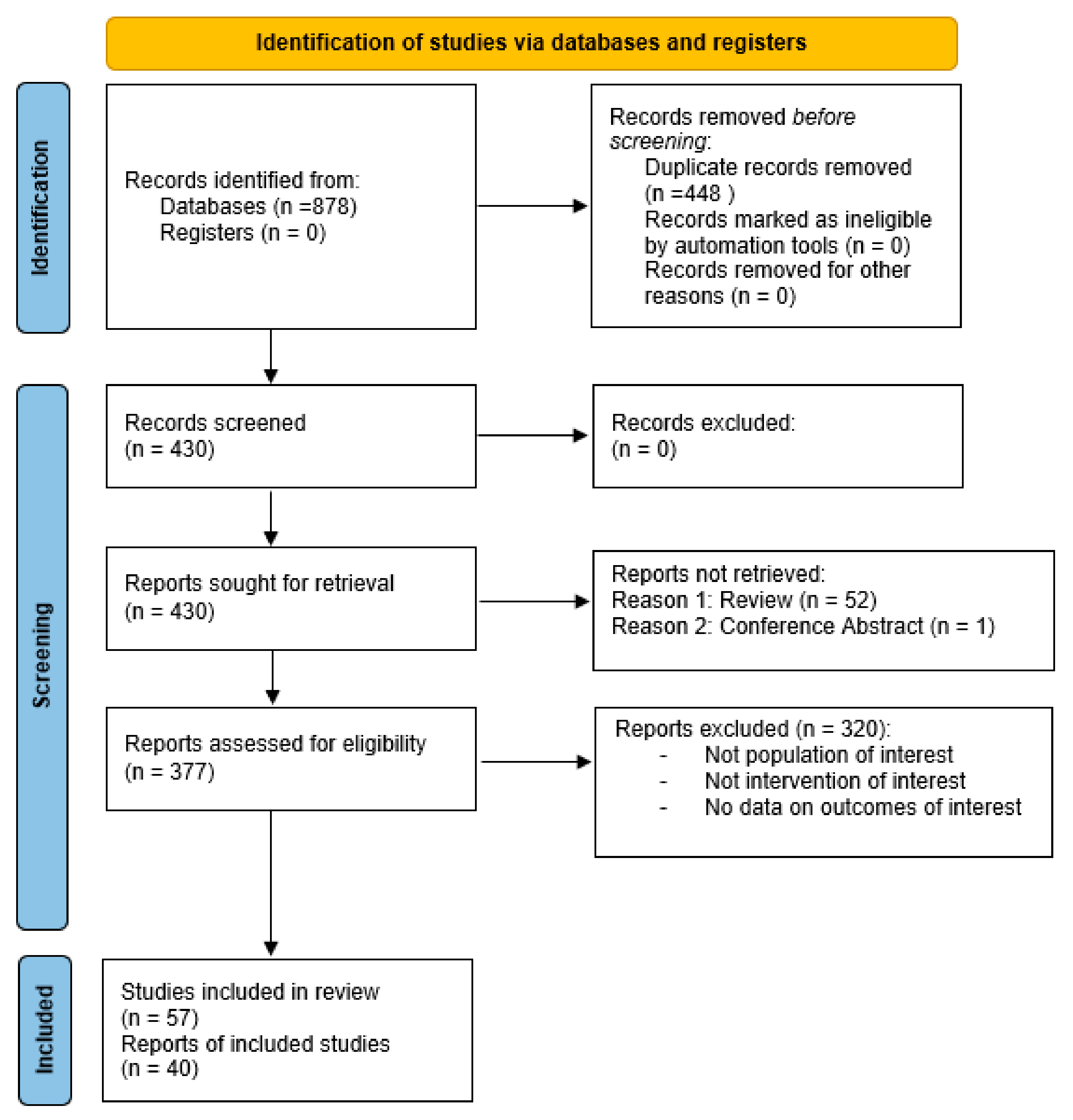
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identifying Target Population
2.2. Systematic Literature Search
2.3. Assigning the Level of Evidence to the Selected Literature
2.4. Formulating and Grading Final Recommendations
3. Results
3.1. Recommendations
3.1.1. Recommendation 1: Quality: Moderate; Strength: Moderate
- The clinical decision to recommend PRT may benefit from the use of evidence-based prognostic factors to guide decision-making.
3.1.2. Recommendation 2: Quality: Moderate; Strength: Moderate
- Certain biological factors appear to be significant in the prognosis of certain diseases.
3.1.3. Recommendation 3: Quality: Moderate; Strength: Moderate
- Prognostic models and tools developed for use in patients with advanced cancer can be used in the decision to prescribe PRT.
3.1.4. Recommendation 4: Quality: Moderate; Strength: Moderate
- SBRT/Re-irradiation decision making.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hui, D.; Paiva, C.E.; Del Fabbro, E.G.; Steer, C.; Naberhuis, J.; van de Wetering, M.; Fernández-Ortega, P.; Morita, T.; Suh, S.Y.; Bruera, E.; et al. Prognostication in advanced cancer: Update and directions for future research. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, P.; Buckle, P.; Dolan, R.; Feliu, J.; Hui, D.; Laird, B.J.A.; Maltoni, M.; Moine, S.; Morita, T.; Nabal, M.; et al. Prognostic evaluation in patients with advanced cancer in the last months of life: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, M.; Caraceni, A.; Brunelli, C.; Broeckaert, B.; Christakis, N.; Eychmueller, S.; Glare, P.; Nabal, M.; Viganò, A.; Larkin, P.; et al. Prognostic factors in advanced cancer patients: Evidence-based clinical recommendations—A study by the Steering Committee of the European Association for Palliative Care. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6240–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine. Levels of Evidence. Available online: https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/oxford-centre-for-evidence-based-medicine-levels-of-evidence-march-2009 (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, H.; Takahashi, M.; Wakai, K.; Sugiura, H.; Kataoka, T.; Nakanishi, K. Prognostic factors and a scoring system for patients with skeletal metastasis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Linden, Y.M.; Dijkstra, S.P.D.S.; Vonk, E.J.A.; Marijnen, C.A.M.; Leer, J.W.H. Prediction of survival in patients with metastases in the spinal column. Cancer 2005, 103, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.; Abdolell, M.; Panzarella, T.; Harris, K.; Bezjak, A.; Warde, P.; Tannock, I. Predictive model for survival in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5863–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, M.; Harada, H.; Asakura, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Furutani, K.; Hashii, H.; Takagi, T.; Katagiri, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishimura, T. Prognostic factors and a scoring system for survival after radiotherapy for metastases to the spinal column. Cancer 2008, 113, 2816–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, E.; Abdolell, M.; Panzarella, T.; Harris, K.; Bezjak, A.; Warde, P.; Tannock, I. Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors for survival in patients with advanced cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 73, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rades, D.; Panzner, A.; Rudat, V.; Karstens, J.H.; Schild, S.E. Dose escalation of radiotherapy for metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC) in patients with relatively favorable survival prognosis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2011, 187, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.E.; Edler, L.; Rausch, R.; Welzel, T.; Wick, W.; Debus, J. Generation and validation of a prognostic score to predict outcome after re-irradiation of recurrent glioma. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, M.S.; Epstein-Peterson, Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Tseng, Y.D.; Wright, A.A.; Temel, J.S.; Catalano, P.; Balboni, T.A. Predicting life expectancy in patients with metastatic cancer receiving palliative radiotherapy: The TEACHH model. Cancer 2014, 120, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, C.; Angelo, K.; Haukland, E.; Pawinski, A. Survival after palliative radiotherapy in geriatric cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6641–6645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bollen, L.; van der Linden, Y.M.; Pondaag, W.; Fiocco, M.; Pattynama, B.P.; Marijnen, C.A.; Nelissen, R.G.; Peul, W.C.; Dijkstra, P.D. Prognostic factors associated with survival in patients with symptomatic spinal bone metastases: A retrospective cohort study of 1043 patients. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhoff, P.G.; de Graeff, A.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Bollen, L.; Dijkstra, S.P.; van der Steen-Banasik, E.M.; van Vulpen, M.; Leer, J.W.; Marijnen, C.A.; van der Linden, Y.M. An easy tool to predict survival in patients receiving radiation therapy for painful bone metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 90, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oorschot, B.; Assenbrunner, B.; Schuler, M.; Beckmann, G.; Flentje, M. Survival and prognostic factors after moderately hypofractionated palliative thoracic radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, K.; Dalhaug, A.; Pawinski, A.; Haukland, E.; Nieder, C. Survival Prediction Score: A simple but age-dependent method predicting prognosis in patients undergoing palliative radiotherapy. ISRN Oncol. 2014, 2014, 912865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leth, T.; Von Oettingen, G.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.A.; Lukacova, S.; Høyer, M. Survival and prognostic factors in patients treated with stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Angelo, K.; Dalhaug, A.; Pawinski, A.; Haukland, E.; Norum, J. Palliative radiotherapy during the last month of life: Predictability for referring physicians and radiation oncologists. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3043–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieder, C.; Mannsåker, B.; Dalhaug, A.; Pawinski, A.; Haukland, E. Palliative radiotherapy in cancer patients with increased serum c-reactive protein level. In Vivo 2016, 30, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Zwirner, K.; Paulsen, F.; Schittenhelm, J.; Borchers, C.; Skardelly, M.; Zips, D.; Eckert, F. Prognostic parameters and outcome after re-irradiation for progressive glioblastoma. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2017, 136, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, C.; Tollåli, T.; Haukland, E.; Reigstad, A.; Randi Flatøy, L.; Dalhaug, A. A four-tiered prognostic score for patients receiving palliative thoracic radiotherapy for lung cancer. Cancer Investig. 2018, 36, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, C.; Kämpe, T.A. Frequency and prognostic impact of consistently low Edmonton Symptom Assessment System score in the patients treated with palliative radiotherapy. Cureus 2018, 10, e2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willeumier, J.J.; van der Linden, Y.M.; van der Wal, C.W.P.G.; Jutte, P.C.; van der Velden, J.M.; Smolle, M.A.; van der Zwaal, P.; Koper, P.; Bakri, L.; de Pree, I.; et al. An easy-to-use prognostic model for survival estimation for patients with symptomatic long bone metastases. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, D.; Ochoa, M.; Piulats, J.M.; Gutiérrez, C.; Arias, L.; Català, J.; Grau, M.; Peñafiel, J.; Cobos, E.; Garcia-Bru, P.; et al. Prognostic factors and decision tree for long-term survival in metastatic uveal melanoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syadwa, A.S.; Anita, Z.B. Palliative radiotherapy for advanced cancer: Are we giving it to the right patient at the right time? Med. J. Malaysia 2018, 73, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gensheimer, M.F.; Henry, A.S.; Wood, D.J.; Hastie, T.J.; Aggarwal, S.; Dudley, S.A.; Pradhan, P.; Banerjee, I.; Cho, E.; Ramchandran, K.; et al. Automated survival prediction in metastatic cancer patients using high-dimensional electronic medical record data. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Wu, Z.J.; Xu, H.; Wu, C.H.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.R.; Fan, L.L.; Sun, G.P. Nomograms for predicting survival in patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma who undergo palliative gastrectomy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Ke, W.; Wang, R.; Mu, X.; Sun, F.; Wang, X.; Garg, S.; Shi, W.; He, Y. Prognostic nomogram for bladder cancer with brain metastases: A National Cancer Database analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzese, C.; Nicosia, L.; Facondo, G.; Lo Faro, L.; Cuccia, F.; Vullo, G.; Osti, M.F.; Alongi, F.; Scorsetti, M. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for adrenal gland metastases: Outcome and predictive factors from a multicenter analysis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2021, 38, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, T.; Xue, J. Prognostic factors of survival of advanced liver cancer patients treated with palliative radiotherapy: A retrospective study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaorsky, N.G.; Liang, M.; Patel, R.; Lin, C.; Tchelebi, L.T.; Newport, K.B.; Fox, E.J.; Wang, M. Survival after palliative radiation therapy for cancer: The METSSS model. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 158, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Maeda, K.; Fukami, Y.; Matsuyama, R.; Nonogaki, T.; Kato, R.; Ishida, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Ueshima, J.; Nagano, A. High SARC-F score predicts poor survival of patients with cancer receiving palliative care. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.; Bassale, S.; Shukla, R.; Dai Kubicky, C. A prognostic index for predicting survival of patients undergoing radiation therapy for spine metastasis using recursive partitioning analysis. J. Palliat. Med. 2022, 25, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, K.; Norum, J.; Dalhaug, A.; Pawinski, A.; Aandahl, G.; Haukland, E.; Engljähringer, K.; Nieder, C. Development and validation of a model predicting short survival (death within 30 days) after palliative radiotherapy. Anticancer. Res. 2014, 34, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, E.; Abdolell, M.; Panzarella, T.; Harris, K.; Bezjak, A.; Warde, P.; Tannock, I. Validation of a predictive model for survival in metastatic cancer patients attending an outpatient palliative radiotherapy clinic. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 73, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buergy, D.; Siedlitzki, L.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Wenz, F.; Lohr, F. Overall survival after reirradiation of spinal metastases—Independent validation of predictive models. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, K.A.; Hesse, J.; Straube, C.; Zimmer, C.; Schmidt-Graf, F.; Schlegel, J.; Meyer, B.; Combs, S.E. Validation of an established prognostic score after re-irradiation of recurrent glioma. Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, M.; Bennett, H.; Yi, M.; Robinson, B.; James, M. 30-day mortality following palliative radiotherapy. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 64, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, S.M.; Schettle, M.; Willmann, J.; Ahmadsei, M.; Seiler, A.; Blum, D.; Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.; Hertler, C. Validation and extension of the METSSS score in a metastatic cancer patient cohort after palliative radiotherapy within the last phase of life. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 34, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, M.; Scarpi, E.; Dall’Agata, M.; Micheletti, S.; Pallotti, M.C.; Pieri, M.; Ricci, M.; Romeo, A.; Tenti, M.V.; Tontini, L.; et al. Prognostication in palliative radiotherapy—ProPaRT: Accuracy of prognostic scores. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 918414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Takamatsu, S.; Shimoyachi, N.; Shibata, S.; Makino, M.; Ohashi, S.; Taima, Y.; Minamikawa, R.; Kumano, T.; Gabata, T. Prediction of post-radiotherapy survival for bone metastases: A comparison of the 3-variable number of risk factors model with the new Katagiri scoring system. J. Radiat. Res. 2022, 63, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmann, D.; Paelecke-Habermann, Y.; Geinitz, H.; Aschoff, R.; Bayerl, A.; Bölling, T.; Bosch, E.; Bruns, F.; Eichenseder-Seiss, U.; Gerstein, J.; et al. Prospective evaluation of quality of life effects in patients undergoing palliative radiotherapy for brain metastases. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goutam, S.; Ghosh, S.; Stosky, J.; Tam, A.; Quirk, S.; Fairchild, A.; Wu, J.; Kerba, M. An analysis of clinical and systemic factors associated with palliative radiotherapy delivery and completion at the end of life in Alberta, Canada. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 10043–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahgal, A.; Myrehaug, S.D.; Siva, S.; Masucci, G.L.; Maralani, P.J.; Brundage, M.; Butler, J.; Chow, E.; Fehlings, M.G.; Foote, M.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy versus conventional external beam radiotherapy in patients with painful spinal metastases: An open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Area Considered | No. of Articles Selected | Selected Studies | No. of Pts | Criteria Quality Checklist Filled [3] | Study Classification Type [3] | Evidence Grade [4] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Year | ||||||
| Guiding clinical decision making (prediction of survival for RT suitability) | 30 | Katagiri [6] | 2005 | 350 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| Van der Linden [7] | 2005 | 342 | 5 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Chow [8] | 2008 | 1307 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Mizumoto [9] | 2008 | 544 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Chow [10] | 2009 | 1307 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Rades [11] | 2011 | 382 | 3 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Combs [12] | 2012 | 233 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Krishnan [13] | 2014 | 862 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Nieder [14] | 2014 | 539 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Bollen [15] | 2014 | 1385 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Westhoff [16] | 2014 | 2091 | 5 | 2–3 | 2 | ||
| Oorschot [17] | 2014 | 120 | 4 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Angelo [18] | 2014 | 412 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Leth [19] | 2015 | 198 | 5 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Nieder [20] | 2015 | 873 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Nieder [21] | 2016 | 781 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Zwirner [22] | 2016 | 51 | 5 | 2 | 5 | ||
| Nieder [23] | 2018 | 232 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Nieder [24] | 2018 | 94 | 4 | 1–2 | 4 | ||
| Willeumier [25] | 2018 | 1750 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Lorenzo [26] | 2018 | 99 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Syadwa [27] | 2018 | 585 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Gensheimer [28] | 2019 | 12,987 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Ma [29] | 2019 | 1593 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Yao [30] | 2019 | 234 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Franzese [31] | 2021 | 142 | 5 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Hua [32] | 2021 | 159 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Zaorsky [33] | 2021 | 68,505 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Mori [34] | 2022 | 304 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Walker [35] | 2022 | 269 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Biological factors that influence prognosis | 2 | Zwirner [22] | 2016 | 51 | 5 | 2 | 5 |
| Hua [32] | 2021 | 159 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Prognostic tools | 19 | Katagiri [6] | 2005 | 350 | 6 | 2 | 4 |
| Van der Linden [7] | 2005 | 342 | 5 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Chow [8] | 2008 | 1307 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Mizumoto [9] | 2008 | 544 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Chow [10] | 2009 | 1307 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Combs [12] | 2012 | 233 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Angelo [36] | 2014 | 412 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Krishnan [13] | 2014 | 862 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Bollen [15] | 2014 | 1043 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Westhoff [16] | 2014 | 1157 | 5 | 2–3 | 2 | ||
| Nieder [23] | 2018 | 232 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Willeumier [25] | 2018 | 1520 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Lorenzo [26] | 2018 | 99 | 4 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Gensheimer [28] | 2019 | 12,987 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Ma [29] | 2019 | 1593 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Yao [30] | 2019 | 234 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Hua [32] | 2021 | 159 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Zaorsky [33] | 2021 | 68,505 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Walker [35] | 2022 | 269 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Validation | 8 | Chow [37] | 2009 | 445 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Angelo [36] | 2014 | 412 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Buergy [38] | 2016 | 52 | 4 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Kessel [39] | 2017 | 199 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Kain [40] | 2020 | 862 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Christ [41] | 2022 | 274 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Maltoni [42] | 2022 | 255 | 6 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Sakurai [43] | 2022 | 485 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| SBRT/Re-irradiation | 12 | Rades [11] | 2011 | 191 | 5 | 2 | 3 |
| Combs [12] | 2012 | 233 | 5 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Steinmann [44] | 2012 | 151 | 6 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Leth [19] | 2015 | 198 | 5 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Zwirner [22] | 2016 | 51 | 5 | 2 | 5 | ||
| Buergy [38] | 2016 | 52 | 4 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Kessel [39] | 2017 | 199 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Gensheimer [28] | 2019 | 12,987 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Franzese [31] | 2021 | 142 | 5 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Hua [32] | 2021 | 159 | 4 | 2–3 | 3 | ||
| Walker [35] | 2022 | 269 | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Sakurai [43] | 2022 | 485 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Reference | Disease Site | Pts (n =) | RT Details (RT Treatment Type */ Retreatment) | Prediction Forecast | Prognostic Factors | Model Results and Accuracy | Validating Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment Site: Bone | |||||||
| Bollen [15] | Symptomatic spinal metastases | 1043 | Unspecified Unspecified | <36 Months | Primary tumor, clinical profile, performance status, presence of visceral/brain mets | Four groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (31.2, 15.4, 4.8, 1.6). C Stat: 0.69. | |
| Katagiri [6] | Skeletal metastases | 350 | Unspecified Unspecified | <12 Months | Site of primary lesion, performance status, presence of visceral/brain metastases, previous chemotherapy, multiple skeletal metastases | Predictive model using prognostic factor weights. % likelihood of survival after 6 months based on scoring system (98%, 31%). | Sakurai 2022 [43] |
| Mizumoto [9] | Spinal metastases | 544 | Unspecified Unspecified | <24 Months | Unfavourable tumor type, bad performance status, hypercalcemia, visceral metastases, previous chemotherapy, multiple bone metastases, age >71 | Three groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (27.1, 5.4, 1.8). | |
| Van der Linden [7] | Symptomatic spinal metastases | 342 | Unspecified No | <24 months | KPS, primary tumor, visceral metastases | Three groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (3.0, 9.0, 18.7). | |
| Walker [34] | Spinal metastases | 269 | CRT Including Re-irradiation | <12 months | KPS, histology, stability of disease | Three groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (11.4, 6.3, 2.0). | |
| Westhoff [16] | Symptomatic bone metastases | 1157 | Unspecified Unspecified | <24 months | Sex, primary tumor, visceral mets, KPS, visual analog scale general health, valuation of life verbal rating scale | Predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS 21 weeks. C stat: 0.72. | |
| Willeumier [25] | Symptomatic long bone mets | 1770 | Unspecified Unspecified | <24 months | Clinical profile, KPS, evidence of visceral/brain met, solitary bone metastasis, and sex | Four groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (21.9, 10.5, 4.6, 2.2). C stat. 0.70. | |
| Brain | |||||||
| Yao [30] | Bladder cancer with brain metastases | 468 | Unspecified Unspecified | <9 months | Brain metastasis, surgery of the primary site, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, palliative care, brain confinement of metastatic sites, and the Charlson/Deyo score | Predictive model using prognostic factor weights. High- and low-risk groups based on model. Median OS in months (1.68, 8.05), respectively. AUC for 0.5- and 1-year survival (0.838, 0.809), respectively | |
| Multiple Sites | |||||||
| Angelo [18] | Metastatic/ incurable cancer | 412 | Unspecified Unspecified | <1 month | ECOG PS 3–4, opioid analgesic use, low Hb, steroid use, known progressive disease outside PRT target volume | RPA classification tool using prognostic factor weights. Median OS 6.3 months. Model correctly identified 75% of PRT courses administered during the final 30 days of life. | |
| Chow [10] | Advanced cancer | 1308 | Unspecified Unspecified | <12 months | KPS, interval from diagnosis, analgesic consumption, ESAS symptoms | Three groups based on RPA classification tool using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in weeks (32, 23, 11). | |
| Chow [8] | Metastatic cancer | 1307 | Unspecified Unspecified | <18 months | Non-breast cancer, metastases other than bone, KPS < 60 | Three groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in weeks (64, 29, 10). C stat: 0.63 | Chow 2009 [10] |
| Chow [8] | Metastatic cancer | 1307 | Unspecified Unspecified | <18 months | Non-breast cancer, metastases other than bone, KPS < 60 | Three groups based on predictive model using number of prognostic factors. Median OS in weeks (64, 29, 10). C stat: 0.63. | Sakurai 2022 [43] |
| Gensheimer [28] | Metastatic cancer | 12,987 | CRT/SBRT/SRS Unspecified | < 12 months | Fully automatic (4126 variables) | Predictive model using automated prognostic factor weights. Median OS 20.9 months C stat: 0.745 | |
| Krishnan [13] | Metastatic cancer | 862 | Unspecified No | < 24 months | Type of cancer, ECOG, age, prior palliative chemotherapy, prior hospitalizations, and hepatic metastases | Three groups based on predictive model using number of prognostic factors. Median OS in months (19.9, 5, 1.7). | Kain 2020 [40], Maltoni 2022 [42] |
| Zaorsky [33] | Metastatic cancer | 68,505 | Unspecified Unspecified | < 48 months | Metastasis location, age, primary tumor, gender, Charlson comorbidity score, RT site | Three groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (11.66, 5.09, 3.28). C stat: 0.71. | Christ 2022 [41] |
| Other Sites | |||||||
| Combs [12] | Recurrent glioma | 233 | SRS Inclusive of re-irradiation | < 24 months | Histology, age, time between initial RT and re-irradiation | Four groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. % likelihood of survival after 6 months (89%, 82%, 68%, 70%). | Kessel 2017 [39] |
| Hua [32] | Advanced liver cancer | 159 | CRT/SBRT Unspecified | < 24 months | Bone metastasis, portal vein tumor thrombus, alpha-fetoprotein, radiation dose | Predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS 14.8 months. C stat: 0.735. | |
| Lorenzo [26] | Metastatic uveal melanoma | 99 | Unspecified Unspecified | <12 months | Age > 65, lactate dehydrogenase, size of liver metastasis, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase | RPA classification tool based on prognostic factor weights. Two survival patterns observed (>12 months, <12 months). | |
| Ma [29] | Metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma | 1593 | Unspecified Unspecified | <40 months | Age, tumor size, location, grade, T stage, N stage, metastatic site, scope of gastrectomy, number of examined lymph node(s), chemotherapy and radiotherapy | Two groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months (5.0, 12.0). C stat (Pre-Operative): 0.607. C stat (Post-Operative): 0.699. | |
| Nieder [23] | Lung cancer | 232 | Unspecified No | <12 months | Performance status, lactate dehydrogenase, C-reactive protein, liver/adrenal gland metastases, and extrathoracic disease status | Four groups based on predictive model using prognostic factor weights. Median OS in months: (0.8, 1.6, 3.3, 10.5). | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tam, A.; Scarpi, E.; Maltoni, M.C.; Rossi, R.; Fairchild, A.; Dennis, K.; Vaska, M.; Kerba, M. A Systematic Review of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Cancer Receiving Palliative Radiotherapy: Evidence-Based Recommendations. Cancers 2024, 16, 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091654
Tam A, Scarpi E, Maltoni MC, Rossi R, Fairchild A, Dennis K, Vaska M, Kerba M. A Systematic Review of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Cancer Receiving Palliative Radiotherapy: Evidence-Based Recommendations. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091654
Chicago/Turabian StyleTam, Alexander, Emanuela Scarpi, Marco Cesare Maltoni, Romina Rossi, Alysa Fairchild, Kristopher Dennis, Marcus Vaska, and Marc Kerba. 2024. "A Systematic Review of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Cancer Receiving Palliative Radiotherapy: Evidence-Based Recommendations" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091654
APA StyleTam, A., Scarpi, E., Maltoni, M. C., Rossi, R., Fairchild, A., Dennis, K., Vaska, M., & Kerba, M. (2024). A Systematic Review of Prognostic Factors in Patients with Cancer Receiving Palliative Radiotherapy: Evidence-Based Recommendations. Cancers, 16(9), 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091654







