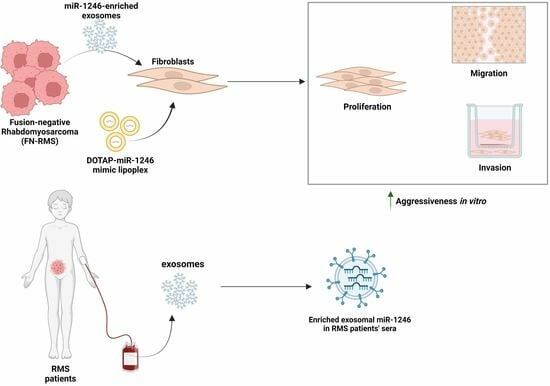
Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Signaling Unveils miR-1246 as a Driver of Aggressiveness in Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell lines and Cell Culture
2.2. MiR-1246 Functional Inhibition
2.3. Exosome Isolation
2.4. DOTAP-Mimic Lipoplex Preparation
2.5. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RTq-PCR)
2.6. Cell Proliferation
2.7. Cell Migration and Cell Invasion
2.8. Protein extraction and Western Blotting
2.9. Immunofluorescence
2.10. Pilot Clinical Study
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
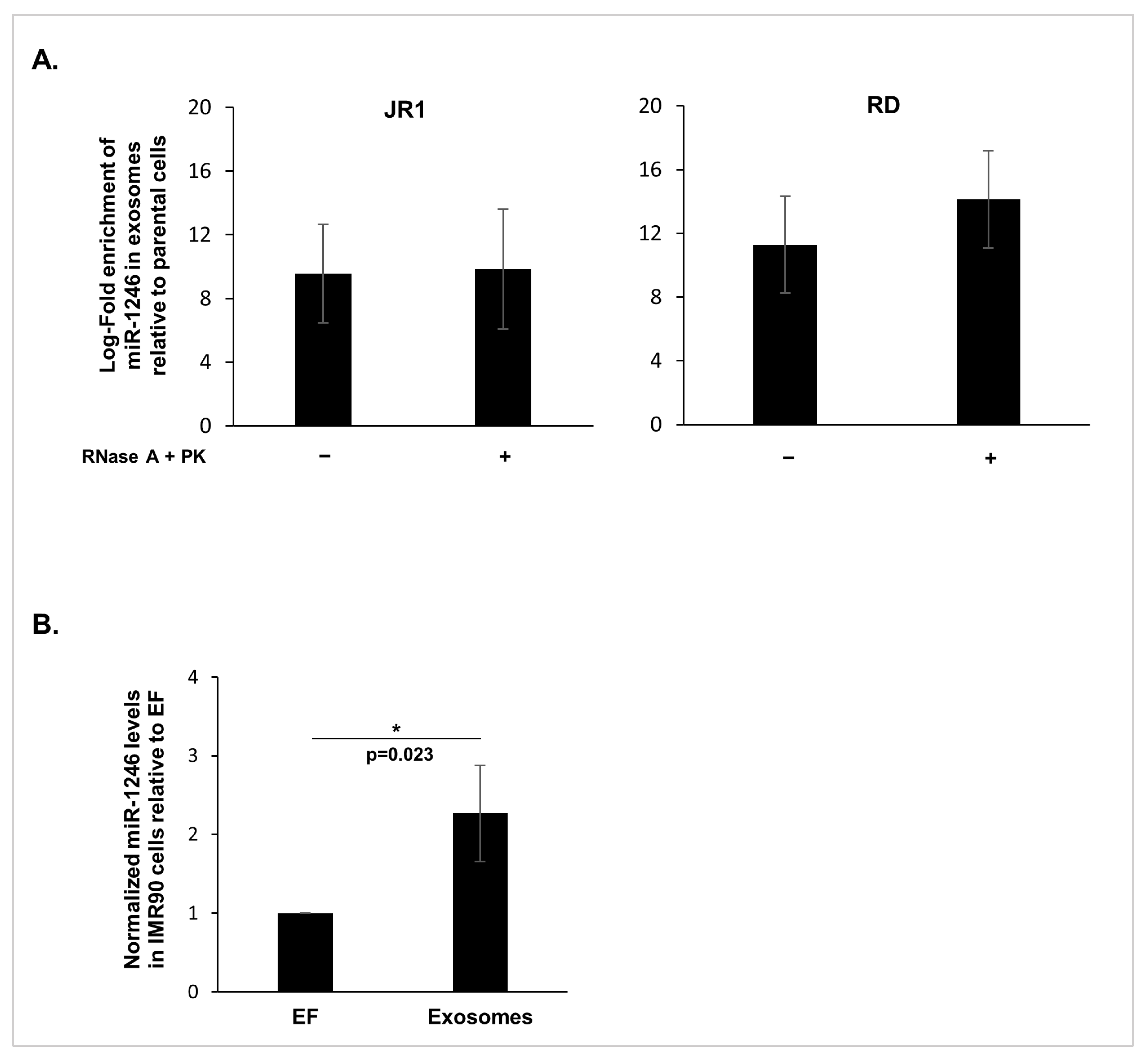
3.1. MiR-1246 Is Delivered to Recipient Fibroblasts via FN-RMS-Derived Exosomes
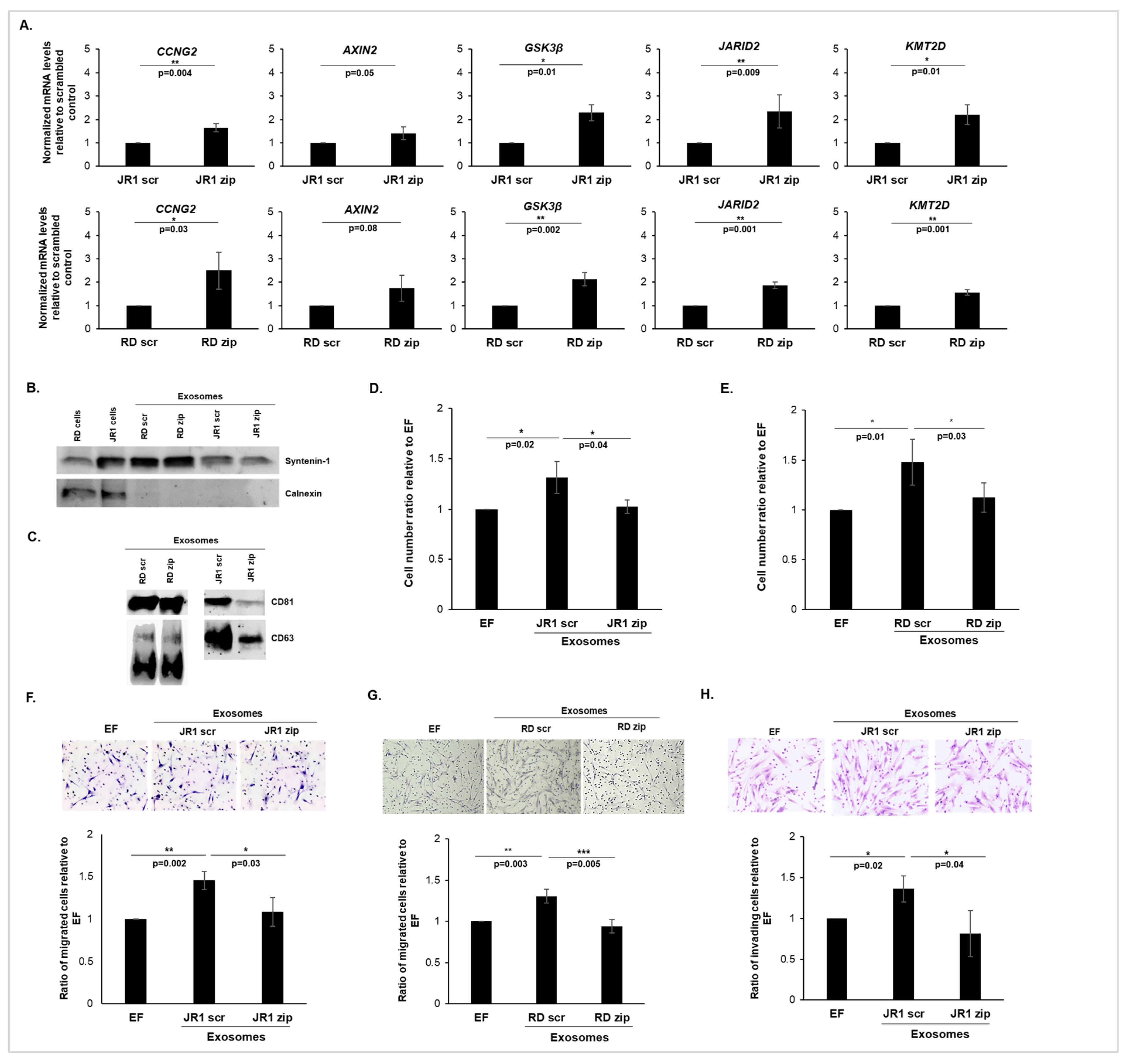
3.2. Functional Inhibition of miR-1246 in FN-RMS Cells Induces Exosome-Mediated Phenotypical Changes in Recipient Fibroblasts
3.3. Delivery of miR-1246 via DOTAP-miRNA Lipoplexes Mimics the Functional Impact of FN-RMS-Derived Exosomes on Recipient Fibroblasts
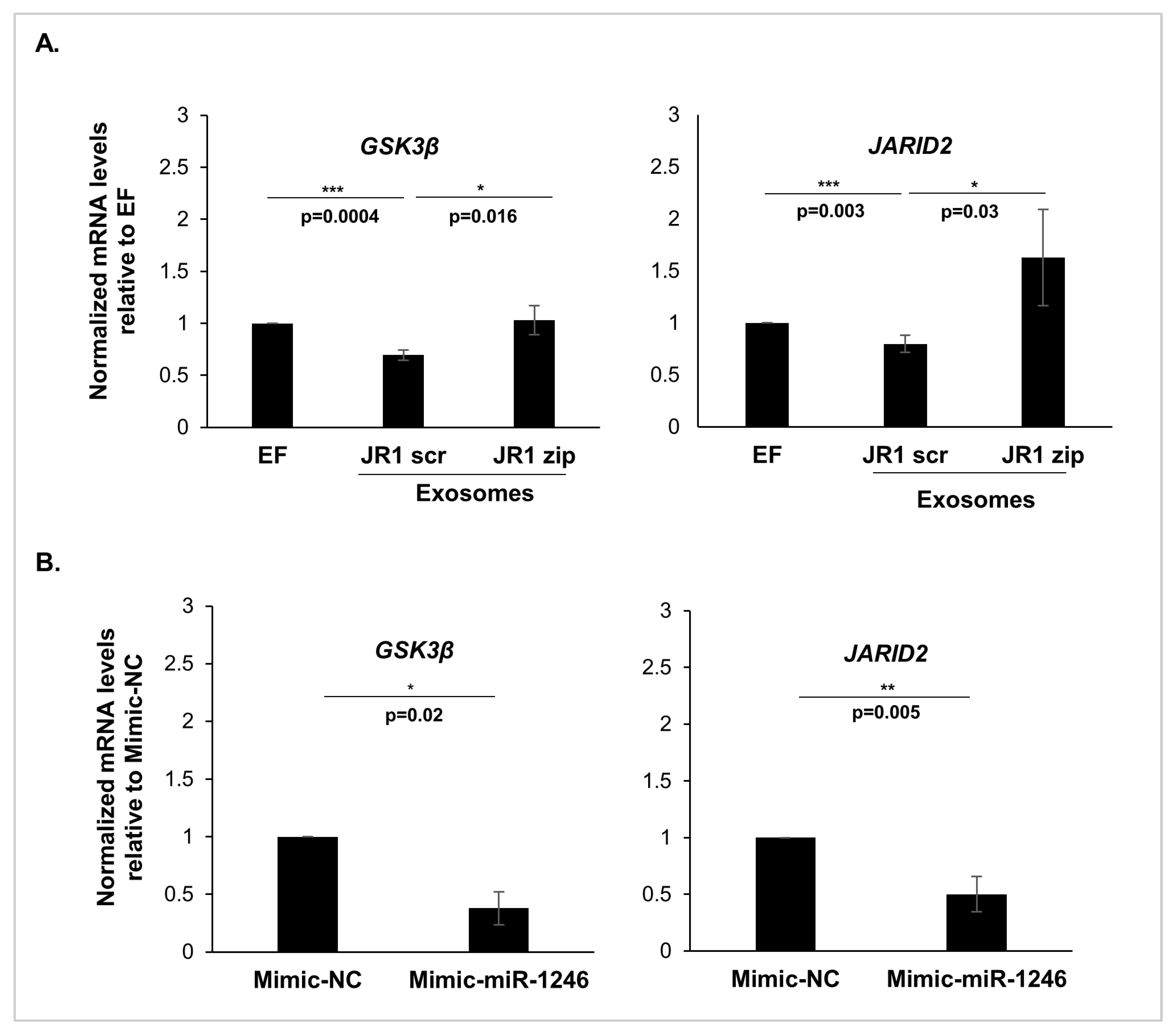
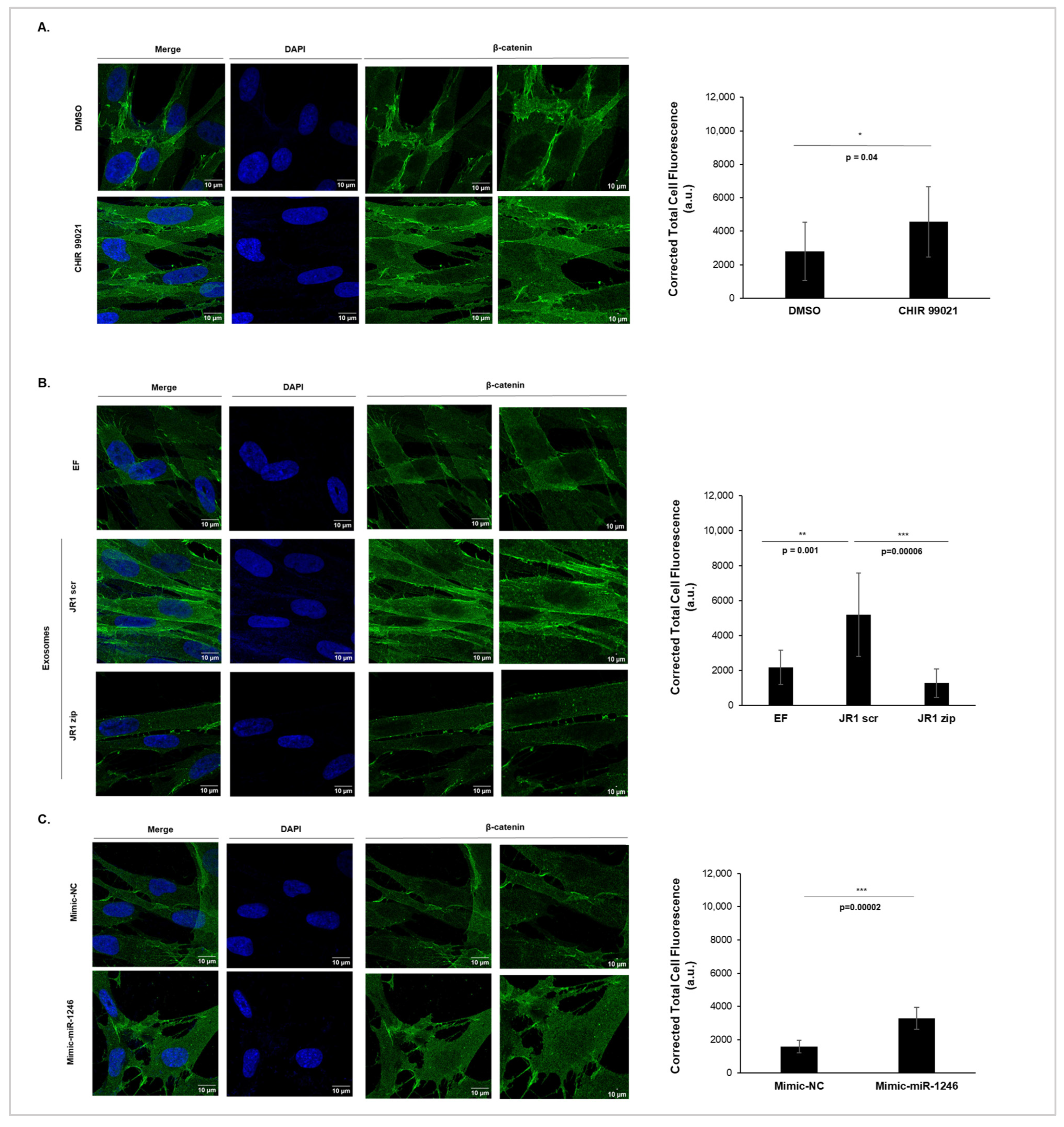
3.4. MiR-1246 Modulates Important Downstream Targets in Recipient Fibroblasts
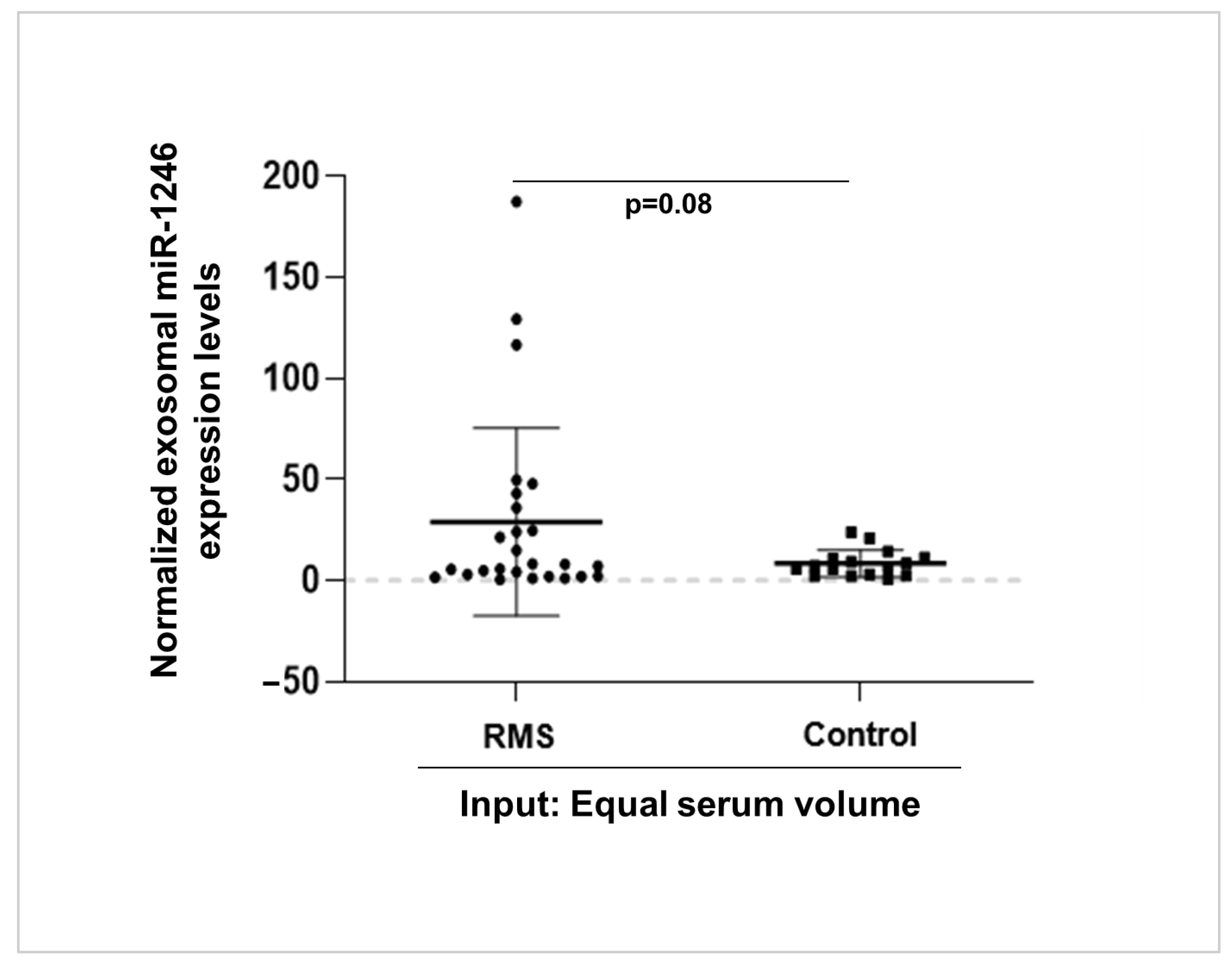
3.5. High miR-1246 Levels Are Detected in Serum-Derived Exosomes of RMS Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skapek, S.X.; Ferrari, A.; Gupta, A.A.; Lupo, P.J.; Butler, E.; Shipley, J.; Barr, F.G.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parham, D.M.; Barr, F.G. Classification of Rhabdomyosarcoma and Its Molecular Basis. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2013, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, E.R. Histology and Fusion Status in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. B 2013, 33, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Rhabdomyosarcoma Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging. Can Rhabdomyosarcoma Be Found Early? American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Dorado Garcia, H.; Scheer, M.; Henssen, A.G. Current and Future Treatment Strategies for Rhabdomyosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappo, A.S.; Anderson, J.R.; Crist, W.M.; Wharam, M.D.; Breitfeld, P.P.; Hawkins, D.; Raney, R.B.; Womer, R.B.; Parham, D.M.; Qualman, S.J. Survival after Relapse in Children and Adolescents with Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 3487–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Lam, E.W.F.; Sun, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in the Tumor Microenvironment: Old Stories, but New Tales. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Greening, D.W.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer—Implications for Future Improvements in Cancer Care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Sandvig, K.; Llorente, A. Exosomal MiRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahs, A.; Hussein, N.; Zalzali, H.; Ramadan, F.; Ghamloush, F.; Tamim, H.; El Homsi, M.; Badran, B.; Boulos, F.; Tawil, A.; et al. CD147 Promotes Tumorigenesis via Exosome-Mediated Signaling in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Qian, N.; Ling, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Du, R.; Zhong, G.; Liu, C.; Yu, G.; et al. Breast Cancer Exosomes Contribute to Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation and Promote Bone Metastasis of Tumor Cells. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayad, S.E.; Rammal, G.; Ghamloush, F.; Basma, H.; Nasr, R.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Chelala, C.; Saab, R. Exosomes Derived from Embryonal and Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Carry Differential MiRNA Cargo and Promote Invasion of Recipient Fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusachenko, O.N.; Zenkova, M.A.; Vlassov, V.V. Nucleic Acids in Exosomes: Disease Markers and Intercellular Communication Molecules. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.D.; Cheng, P.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z. BMSC-Derived Exosomal MiR-29a Promotes Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 608521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghamloush, F.; Ghayad, S.E.; Rammal, G.; Fahs, A.; Ayoub, A.J.; Merabi, Z.; Harajly, M.; Zalzali, H.; Saab, R. The PAX3-FOXO1 Oncogene Alters Exosome MiRNA Content and Leads to Paracrine Effects Mediated by Exosomal MiR-486. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahs, A.; Ramadan, F.; Ghamloush, F.; Ayoub, A.J.; Ahmad, F.A.; Kobeissy, F.; Mechref, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, R.; Hussein, N.; et al. Effects of the Oncoprotein PAX3-FOXO1 on Modulation of Exosomes Function and Protein Content: Implications on Oxidative Stress Protection and Enhanced Plasticity. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammal, G.; Fahs, A.; Kobeissy, F.; Mechref, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, R.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Saab, R.; Ghayad, S.E. Proteomic Profiling of Rhabdomyosarcoma-Derived Exosomes Yield Insights into Their Functional Role in Paracrine Signaling. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3567–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. A Review on the Role of MiR-1246 in the Pathoetiology of Different Cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 771835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; Konno, M.; Tomimaru, Y.; Wada, H.; Hama, N.; Kawamoto, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Nishida, N.; et al. MicroRNA-1246 Expression Associated with CCNG2-Mediated Chemoresistance and Stemness in Pancreatic Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Li, J.; Chen, R.; Gu, Q.; Yang, P.; Qian, W.; Ji, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, J.; et al. Upregulated METTL3 Promotes Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer via MiR-1246/SPRED2/MAPK Signaling Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xiong, H.; Duan, L.; Li, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. MiR-1246 Promotes Metastasis and Invasion of A549 Cells by Targeting GSK-3β–Mediated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 51, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Pan, Y.; Fu, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, C. Extracellular MiR-1246 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Enhances Radioresistance by Directly Targeting DR5. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32707–32722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Exosomal MiR-1246 Is Involved in Tumorigenesis by Targeting THRB in Breast Cancer. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, P.; Gahurova, L.; Mašek, T.; Hauserova, A.; Potěšil, D.; Jansova, D.; Susor, A.; Zdráhal, Z.; Ajduk, A.; Pospíšek, M.; et al. P38-MAPK-Mediated Translation Regulation during Early Blastocyst Development Is Required for Primitive Endoderm Differentiation in Mice. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Graves-Deal, R.; Trinh, V.Q.; Ramirez, M.A.; Sohn, Y.; Neininger, A.C.; Taneja, N.; McKinley, E.T.; et al. Supermeres Are Functional Extracellular Nanoparticles Replete with Disease Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 1240–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, J.M.; Nie, S.L.; Peng, Q.; Gong, J.; Huo, J.R. MicroRNA-1246 Promotes Growth and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer Cells Involving CCNG2 Reduction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.; Peng, C.Y.; Liao, Y.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Hsieh, P.L.; Yu, C.C. MiR-1246 Targets CCNG2 to Enhance Cancer Stemness and Chemoresistance in Oral Carcinomas. Cancers 2018, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Ng, K.Y.; Tong, M.; Lau, E.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Chan, K.W.; Yuan, Y.F.; Cheung, T.T.; Cheung, S.T.; Wang, X.Q.; et al. Octamer 4/MicroRNA-1246 Signaling Axis Drives Wnt/β-Catenin Activation in Liver Cancer Stem Cells. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, J.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Yi, J.; et al. MicroRNA-1246 by Targeting AXIN2 and GSK-3β Overcomes Drug Resistance and Induces Apoptosis in Chemo-Resistant Leukemia Cells. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4196–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralimanoharan, S.; Kwak, Y.T.; Mendelson, C.R. Redox-Sensitive Transcription Factor NRF2 Enhances Trophoblast Differentiation via Induction of MiR-1246 and Aromatase. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2022–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Y.; Cheng, C.C.; Chiang, Y.S.; Cheng, W.T.K.; Liu, I.H.; Wu, S.C. Exosomal MiR-10a Derived from Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells Preserves Ovarian Follicles after Chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Amerongen, R.; Nawijn, M.C.; Lambooij, J.P.; Proost, N.; Jonkers, J.; Berns, A. Frat Oncoproteins Act at the Crossroad of Canonical and Noncanonical Wnt-Signaling Pathways. Oncogene 2010, 29, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, C.; Baarsma, H.A.; Wagner, D.E.; Hilgendorff, A.; Königshoff, M. Linking Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia to Adult Chronic Lung Diseases: Role of WNT Signaling. Mol. Cell. Pediatr. 2016, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baarsma, H.A.; Königshoff, M.; Gosens, R. The WNT Signaling Pathway from Ligand Secretion to Gene Transcription: Molecular Mechanisms and Pharmacological Targets. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; He, Y.; Jin, X.; Xie, J.; Yu, P.; Gao, G.; Chang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chang, Y.-Z. CHIR99021 Maintenance of the Cell Stemness by Regulating Cellular Iron Metabolism. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.A.; Barr, F.G. Molecular Diagnostics in the Management of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučuk, N.; Primožič, M.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. Exosomes Engineering and Their Roles as Therapy Delivery Tools, Therapeutic Targets, and Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-F.; Xu, X.; Gin, A.; Nshimiyimana, J.D.; Mooers, B.H.M.; Caputi, M.; Hannafon, B.N.; Ding, W.-Q. SRSF1 Regulates Exosome MicroRNA Enrichment in Human Cancer Cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, T.; Tomofuji, T.; Maruyama, T.; Yoneda, T.; Ekuni, D.; Azuma, T.; Miyai, H.; Mizuno, H.; Kato, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; et al. MiR-1246 and MiR-4644 in Salivary Exosome as Potential Biomarkers for Pancreatobiliary Tract Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2375–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, T. The Risks of MiRNA Therapeutics: In a Drug Target Perspective. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-P.; Lin, Z.-X.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Yu, X.-Y. Exosomal Cargo-Loading and Synthetic Exosome-Mimics as Potential Therapeutic Tools. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Jenkins, L.M.; Patel, K.M.; Robles, A.I.; Morris, J.; Forshew, T.; Appella, E.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Harris, C.C. Mutant P53 Cancers Reprogram Macrophages to Tumor Supporting Macrophages via Exosomal MiR-1246. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchartre, Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kahn, M. The Wnt Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 99, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T.; Hlubek, F.; Spaderna, S.; Schmalhofer, O.; Hiendlmeyer, E.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T. Invasion and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer: Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition, Stem Cells and Beta-Catenin. Cells. Tissues. Organs 2005, 179, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Gao, B.; Jin, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Song, B. Small Interfering RNA-Mediated Downregulation of Beta-Catenin Inhibits Invasion and Migration of Colon Cancer Cells in Vitro. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2012, 18, BR273–BR280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanulli, S.; Justin, N.; Teissandier, A.; Ancelin, K.; Portoso, M.; Caron, M.; Michaud, A.; Lombard, B.; da Rocha, S.T.; Offer, J.; et al. Jarid2 Methylation via the PRC2 Complex Regulates H3K27me3 Deposition during Cell Differentiation. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.J.; Moorehead, R.A. Polycomb Repressor Complex 2 Function in Breast Cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngollo, M.; Lebert, A.; Daures, M.; Judes, G.; Rifai, K.; Dubois, L.; Kemeny, J.L.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bignon, Y.J.; Guy, L.; et al. Global Analysis of H3K27me3 as an Epigenetic Marker in Prostate Cancer Progression. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, Z.S.; Villarejo-Balcells, B.; Olmos, D.; Buist, T.W.S.; Missiaglia, E.; Allen, R.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Garrett, M.D.; Blagg, J.; Shipley, J. JARID2 Is a Direct Target of the PAX3-FOXO1 Fusion Protein and Inhibits Myogenic Differentiation of Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xie, F.; Wei, H.; Cui, D. Identification of Key Circulating Exosomal MicroRNAs in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. Exosomal MiR-1246 in Serum as a Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannafon, B.N.; Trigoso, Y.D.; Calloway, C.L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Lum, D.H.; Welm, A.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; Blick, K.E.; Dooley, W.C.; Ding, W.Q. Plasma Exosome MicroRNAs Are Indicative of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Colon Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, N.; Hoshino, I.; Mori, M.; Akutsu, Y.; Hanari, N.; Yoneyama, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Isozaki, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Akanuma, N.; et al. Serum MicroRNA Expression Profile: MiR-1246 as a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Sugimachi, K.; Iinuma, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Sawada, G.; Ueda, M.; Uchi, R.; Ueo, H.; Takano, Y.; et al. Exosomal MicroRNA in Serum Is a Novel Biomarker of Recurrence in Human Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan, B.; Yue, S.; Galli, U.; Rana, S.; Gross, W.; Müller, M.; Giese, N.A.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Büchler, M.W.; et al. Combined Evaluation of a Panel of Protein and MiRNA Serum-Exosome Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis Increases Sensitivity and Specificity. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fu, Z.; Wen, S.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Zhou, W.; Lin, Y.; Lv, Y. Expression and Diagnostic Value of MiR-497 and MiR-1246 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramadan, F.; Saab, R.; Ghamloush, F.; Khoueiry, R.; Herceg, Z.; Gomez, L.; Badran, B.; Clezardin, P.; Hussein, N.; Cohen, P.A.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Signaling Unveils miR-1246 as a Driver of Aggressiveness in Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091652
Ramadan F, Saab R, Ghamloush F, Khoueiry R, Herceg Z, Gomez L, Badran B, Clezardin P, Hussein N, Cohen PA, et al. Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Signaling Unveils miR-1246 as a Driver of Aggressiveness in Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091652
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamadan, Farah, Raya Saab, Farah Ghamloush, Rita Khoueiry, Zdenko Herceg, Ludovic Gomez, Bassam Badran, Philippe Clezardin, Nader Hussein, Pascale A. Cohen, and et al. 2024. "Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Signaling Unveils miR-1246 as a Driver of Aggressiveness in Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091652
APA StyleRamadan, F., Saab, R., Ghamloush, F., Khoueiry, R., Herceg, Z., Gomez, L., Badran, B., Clezardin, P., Hussein, N., Cohen, P. A., & Ghayad, S. E. (2024). Exosome-Mediated Paracrine Signaling Unveils miR-1246 as a Driver of Aggressiveness in Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers, 16(9), 1652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091652