Inter- and Intra-Patient Repeatability of Radiomic Features from Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Imaging Acquisition
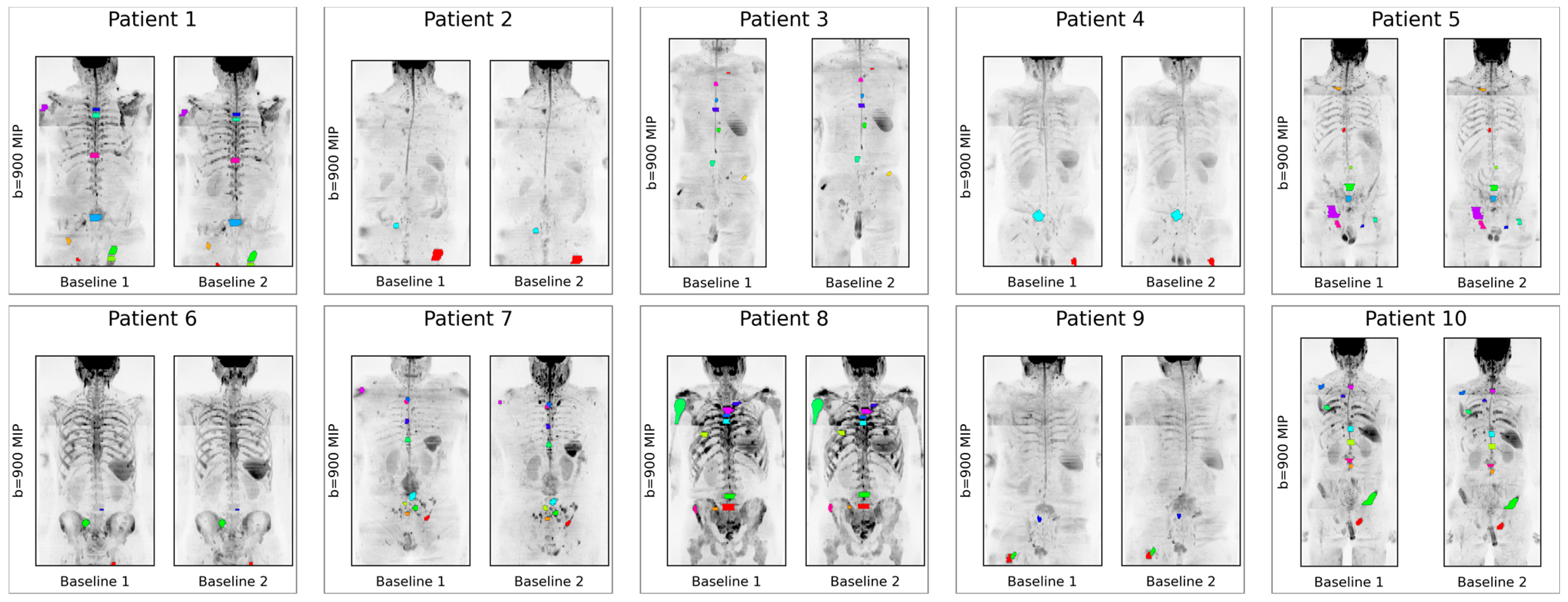
2.3. Disease Delineation
2.4. Extraction of Radiomics Features
2.5. Repeatability Model
| Equation | Description |
| Repeatability coefficient. Useful in the context of assessing response after treatment. Any change above or below is considered to be statistically significant and thus might be a direct result of treatment rather than due to measurement error (assuming a p-value of 0.05). | |
| Intra-patient intraclass correlation. Compares the magnitude of the inter-measurement error with intra-patient variation in lesion values. A value closer to 1 indicates better measurement repeatability in the context of measuring changes to individual lesions. | |
| Inter-patient intraclass correlation. Compares the magnitude of the inter-measurement error with inter-patient variation in lesion values. A value closer to 1 indicates better measurement repeatability in the context of measuring changes with groups of lesions within each patient. | |
| Average within-lesion coefficient of variation. Describes the magnitude of inter-measurement error in the context of true lesion values. A large value represents potentially poor repeatability compared with the expected values for each lesion. | |
| Average between-lesion coefficient of variation. Describes the magnitude of inter-lesion variation in the context of average patient values. A large value represents higher intra-patient heterogeneity. | |
| Between-patient coefficient of variation. Describes the magnitude of inter-patient variation in the context of the average population value. A large value represents higher inter-patient heterogeneity. | |
| Limits of agreement (log-transformed features only). Defines the percentage difference after treatment needed to deem that change significantly different. |
2.6. Model Fitting
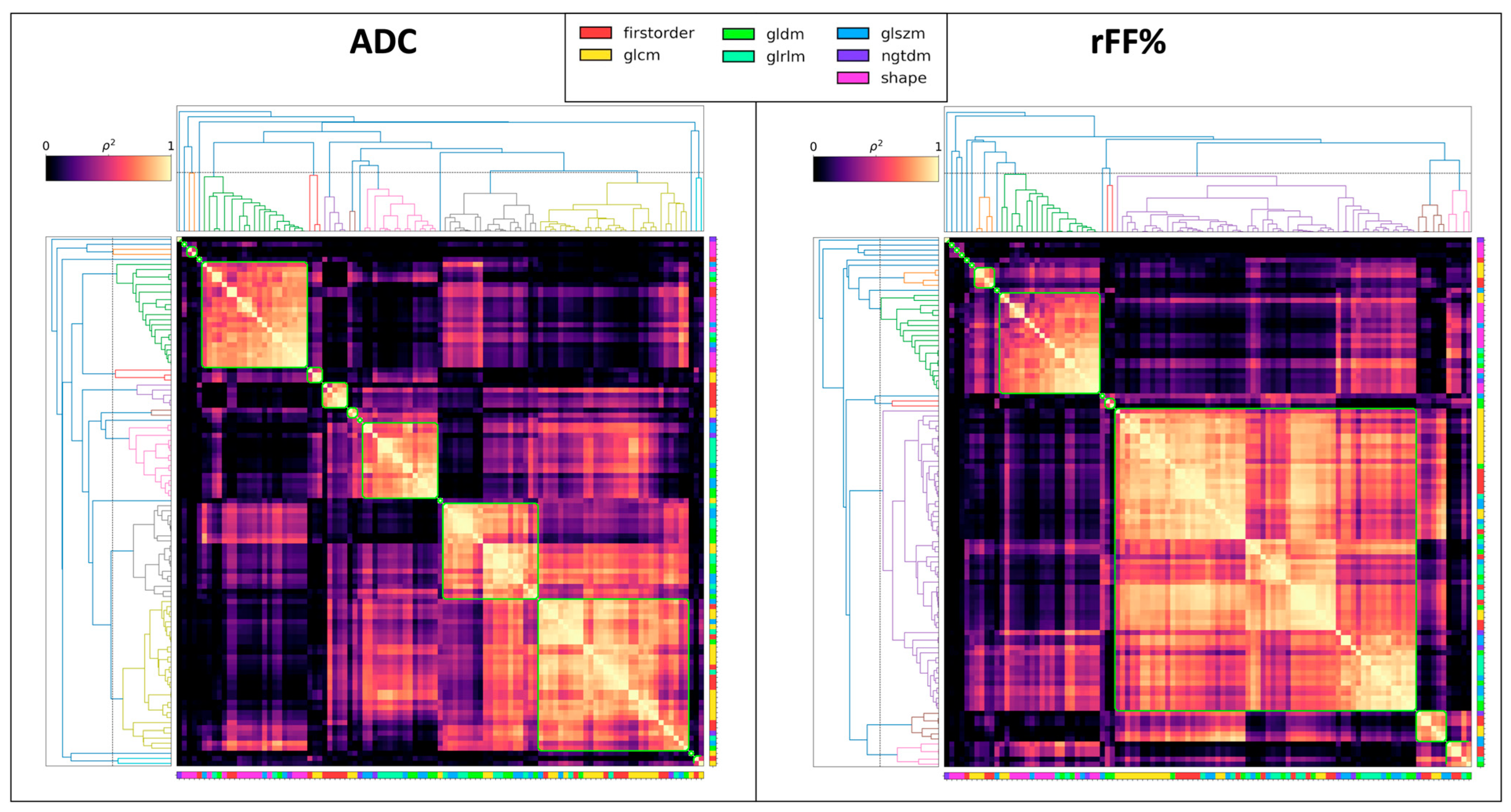
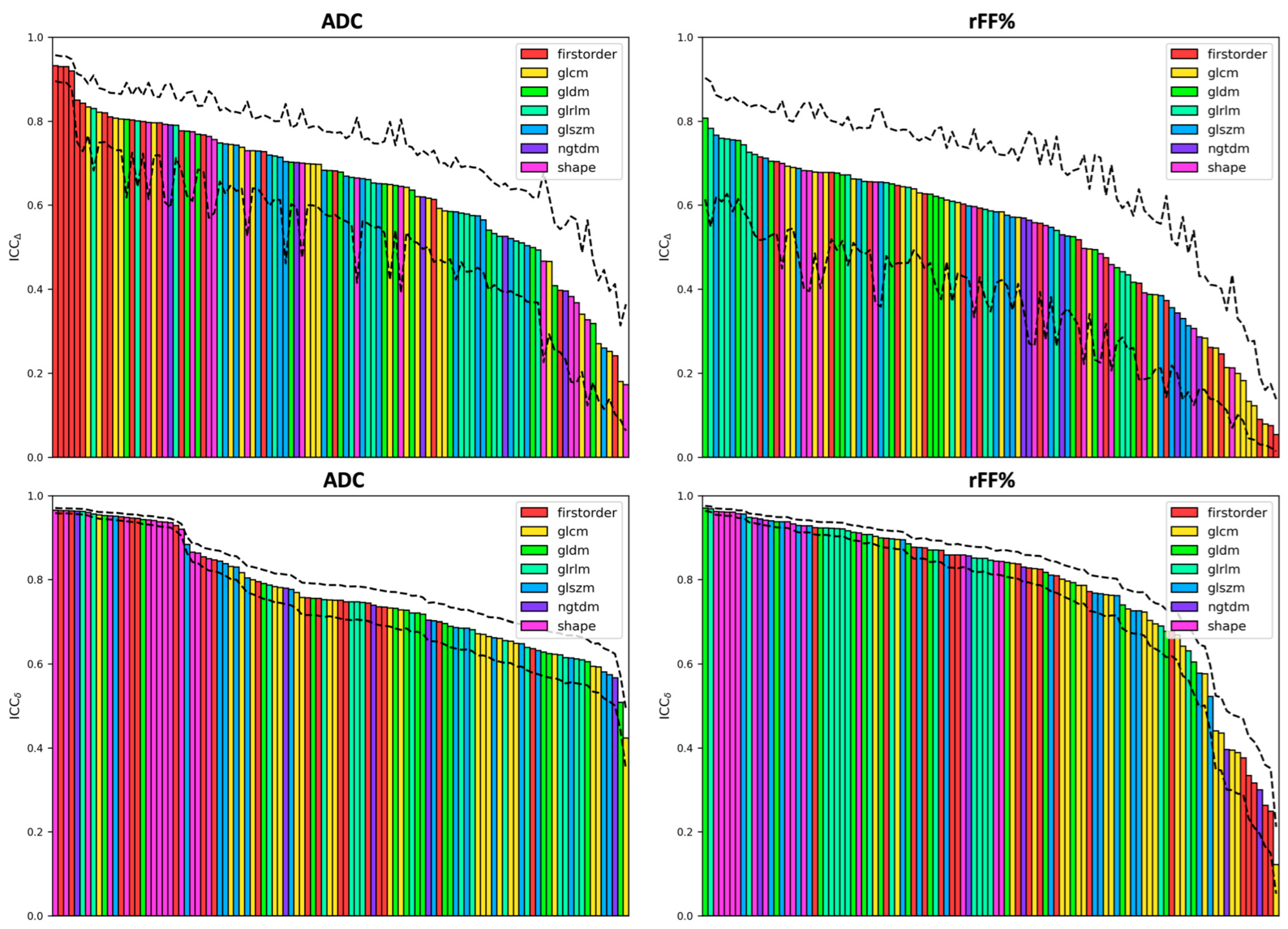
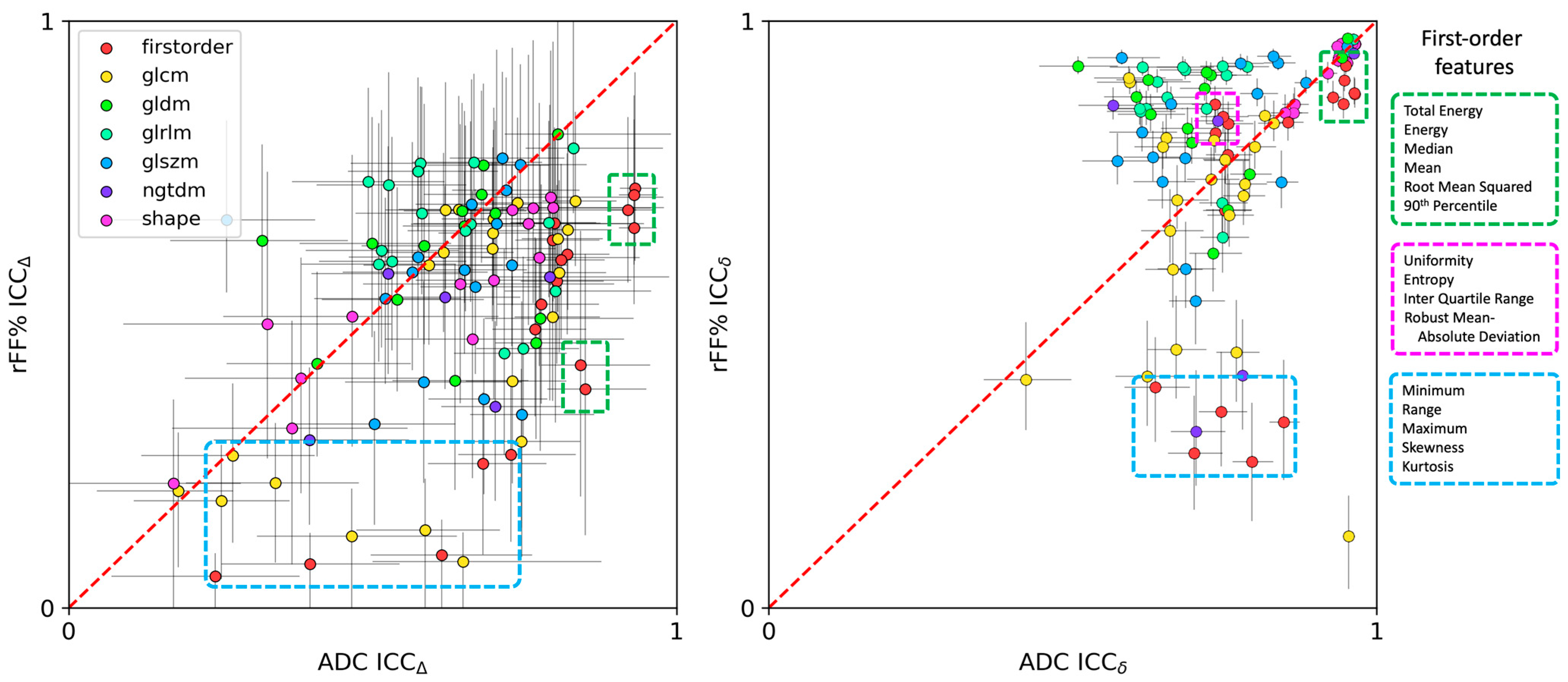
3. Results
Comparison of Features with the Reference Metrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bubendorf, L.; Schöpfer, A.; Wagner, U.; Sauter, G.; Moch, H.; Willi, N.; Gasser, T.C.; Mihatsch, M.J. Metastatic patterns of prostate cancer: An autopsy study of 1589 patients. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Seymour, L.; Litière, S.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1—Standardisation and disease-specific adaptations: Perspectives from the RECIST Working Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Morris, M.J.; Stadler, W.M.; Higano, C.; Basch, E.; Fizazi, K.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Beer, T.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Trial Design and Objectives for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Updated Recommendations From the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhani, A.R.; Lecouvet, F.E.; Tunariu, N.; Koh, D.M.; De Keyzer, F.; Collins, D.J.; Sala, E.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Petralia, G.; Vargas, H.A.; et al. METastasis Reporting and Data System for Prostate Cancer: Practical Guidelines for Acquisition, Interpretation, and Reporting of Whole-body Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Evaluations of Multiorgan Involvement in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Figueiredo, I.; Mateo, J.; Collins, D.J.; Koh, D.M.; de Bono, J.S.; Tunariu, N. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Prostate Cancer Bone Disease: Correlation With Bone Biopsy Histological and Molecular Features. Invest. Radiol. 2018, 53, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, R.; Mateo, J.; Mossop, H.; Blackledge, M.D.; Collins, D.J.; Rata, M.; Morgan, V.A.; Macdonald, A.; Sandhu, S.; Lorente, D.; et al. Diffusion-weighted Imaging as a Treatment Response Biomarker for Evaluating Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study. Radiology 2017, 283, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Lopez, R.; Lorente, D.; Blackledge, M.D.; Collins, D.J.; Mateo, J.; Bianchini, D.; Omlin, A.; Zivi, A.; Leach, M.O.; de Bono, J.S.; et al. Volume of Bone Metastasis Assessed with Whole-Body Diffusion-weighted Imaging Is Associated with Overall Survival in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Radiology 2016, 280, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.; Gogbashian, A. Bony metastases: Assessing response to therapy with whole-body diffusion MRI. Cancer Imaging 2011, 11, S129–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costelloe, C.M.; Madewell, J.E.; Kundra, V.; Harrell, R.K.; Bassett, R.L.; Ma, J. Conspicuity of bone metastases on fast Dixon-based multisequence whole-body MRI: Clinical utility per sequence. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhani, A.R.; Makris, A.; Gall, P.; Collins, D.J.; Tunariu, N.; de Bono, J.S. Therapy monitoring of skeletal metastases with whole-body diffusion MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 1049–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donners, R.; Blackledge, M.; Tunariu, N.; Messiou, C.; Merkle, E.M.; Koh, D.M. Quantitative Whole-Body Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2018, 26, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. Diagnostic Performance of DWI for Differentiating High- From Low-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, W374–W381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Tong, T.; Cai, S.; Bi, R.; Xin, C.; Gu, Y. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) value: A potential imaging biomarker that reflects the biological features of rectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Park, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, S.S.; Seo, D.Y. Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficiency values on diffusion-weighted imaging with prognostic factors for breast cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e474–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, M.; Belli, P.; Rinaldi, P.; Bufi, E.; Giardina, G.; Franceschini, G.; Petrone, G.; Bonomo, L. Diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer: Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficient and tumour aggressiveness. Clin. Radiol. 2010, 65, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.E.; Yaghmai, V.; Nikolaidis, P.; McCarthy, R.J.; Merrick, L.; Miller, F.H. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in pancreatic endocrine tumors correlated with histopathologic characteristics. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 33, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donners, R.; Hirschmann, A.; Gutzeit, A.; Harder, D. T2-weighted Dixon MRI of the spine: A feasibility study of quantitative vertebral bone marrow analysis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donners, R.; Obmann, M.M.; Boll, D.; Gutzeit, A.; Harder, D. Dixon or DWI—Comparing the utility of fat fraction and apparent diffusion coefficient to distinguish between malignant and acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 132, 109342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalco, E.; Rizzo, G. Texture analysis of medical images for radiotherapy applications. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidli, S.; McQuaid, S.; South, C.; Prakash, V.; Evans, P.; Nisbet, A. The role of texture analysis in imaging as an outcome predictor and potential tool in radiotherapy treatment planning. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20140369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, K.A.; Ganeshan, B.; Hayball, M.P. CT texture analysis using the filtration-histogram method: What do the measurements mean? Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Gillies, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Runarsson, T.P.; Sigurdsson, S. Test-retest reliability and feature selection in physiological time series classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 105, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donners, R.; Candito, A.; Blackledge, M.; Rata, M.; Messiou, C.; Koh, D.-M.; Tunariu, N. Repeatability of quantitative individual lesion and total disease multiparametric whole-body MRI measurements in prostate cancer bone metastases. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, L.; Costaridou, L.; Bidaut, L.; Michoux, N.; Lecouvet, F.E.; de Geus-Oei, L.F.; Boellaard, R.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Caroli, A.; et al. Incorporating radiomics into clinical trials: Expert consensus endorsed by the European Society of Radiology on considerations for data-driven compared to biologically driven quantitative biomarkers. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6001–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euser, A.M.; Dekker, F.W.; le Cessie, S. A practical approach to Bland-Altman plots and variation coefficients for log transformed variables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan Development Team. Stan Modeling Language Users Guide and Reference Manual, 2.33. Available online: https://mc-stan.org/docs/2_33/stan-users-guide-2_33.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Raunig, D.L.; McShane, L.M.; Pennello, G.; Gatsonis, C.; Carson, P.L.; Voyvodic, J.T.; Wahl, R.L.; Kurland, B.F.; Schwarz, A.J.; Gönen, M.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers: A review of statistical methods for technical performance assessment. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2015, 24, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Bao, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, J. The correlation between apparent diffusion coefficient and tumor cellularity in patients: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElGendy, K.; Barwick, T.D.; Auner, H.W.; Chaidos, A.; Wallitt, K.; Sergot, A.; Rockall, A. Repeatability and test-retest reproducibility of mean apparent diffusion coefficient measurements of focal and diffuse disease in relapsed multiple myeloma at 3T whole body diffusion-weighted MRI (WB-DW-MRI). Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20220418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinzpeter, R.; Baumann, L.; Guggenberger, R.; Huellner, M.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics for detecting prostate cancer bone metastases invisible in CT: A proof-of-concept study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhong, F.; Guo, Q.; Li, K.; Hou, Y.; Lin, N. MRI-based texture analysis of the primary tumor for pre-treatment prediction of bone metastases in prostate cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 60, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Mao, N.; Wang, Y.; Xie, H.; Duan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B. A Radiomics nomogram for predicting bone metastasis in newly diagnosed prostate cancer patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 128, 109020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitto, S.; Bologna, M.; Corino, V.D.A.; Emili, I.; Albano, D.; Messina, C.; Armiraglio, E.; Parafioriti, A.; Luzzati, A.; Mainardi, L.; et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI radiomics of spine bone tumors: Feature stability and machine learning-based classification performance. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, J.; Chow, D.; Chang, P.; Yu, H.J.; Yuan, H.; Su, M.Y. Differentiation of spinal metastases originated from lung and other cancers using radiomics and deep learning based on DCE-MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 64, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianca, V.; Cuocolo, R.; Gitto, S.; Albano, D.; Merli, I.; Badalyan, J.; Cortese, M.C.; Messina, C.; Luzzati, A.; Parafioriti, A.; et al. Radiomic Machine Learning Classifiers in Spine Bone Tumors: A Multi-Software, Multi-Scanner Study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 137, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreher, C.; Kuder, T.A.; König, F.; Mlynarska-Bujny, A.; Tenconi, C.; Paech, D.; Schlemmer, H.P.; Ladd, M.E.; Bickelhaupt, S. Radiomics in diffusion data: A test-retest, inter- and intra-reader DWI phantom study. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 798.e13–798.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, R.J. Editorial: Avoid being tripped up by statistics: Statistical guidance for a successful research paper. Gait Posture 2019, 72, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | DWI | rFF |
|---|---|---|
| b-values | B50, b600 b900 | |
| TE | 69 | 2.39 |
| TR | 11,300 | 7.63 |
| Slice | 6 mm | 5 mm |
| Inversion | STIR 180 | |
| Averages | 3-5-5 | 1 |
| Slice spacing | 6 | 6 |
| Px bandwidth | 1955 | 400 |
| Aqu Matrix | 128 × 104 | 256 × 156 |
| Image matrix | 256 × 208 | 256 × 208 |
| Flip angle | 90 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donners, R.; Candito, A.; Rata, M.; Sharp, A.; Messiou, C.; Koh, D.-M.; Tunariu, N.; Blackledge, M.D. Inter- and Intra-Patient Repeatability of Radiomic Features from Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091647
Donners R, Candito A, Rata M, Sharp A, Messiou C, Koh D-M, Tunariu N, Blackledge MD. Inter- and Intra-Patient Repeatability of Radiomic Features from Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091647
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonners, Ricardo, Antonio Candito, Mihaela Rata, Adam Sharp, Christina Messiou, Dow-Mu Koh, Nina Tunariu, and Matthew D. Blackledge. 2024. "Inter- and Intra-Patient Repeatability of Radiomic Features from Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091647
APA StyleDonners, R., Candito, A., Rata, M., Sharp, A., Messiou, C., Koh, D.-M., Tunariu, N., & Blackledge, M. D. (2024). Inter- and Intra-Patient Repeatability of Radiomic Features from Multiparametric Whole-Body MRI in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 16(9), 1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091647






