The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of Refractory Thrombocytopenia: ITP or MDS with Isolated Thrombocytopenia?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Isolated Thrombocytopenia
3. Immune Thrombocytopenia, ITP
3.1. Clinical Definitions
3.2. Pathophysiology of ITP
3.3. Diagnosis of ITP
Diagnosis of ITP in Childhood
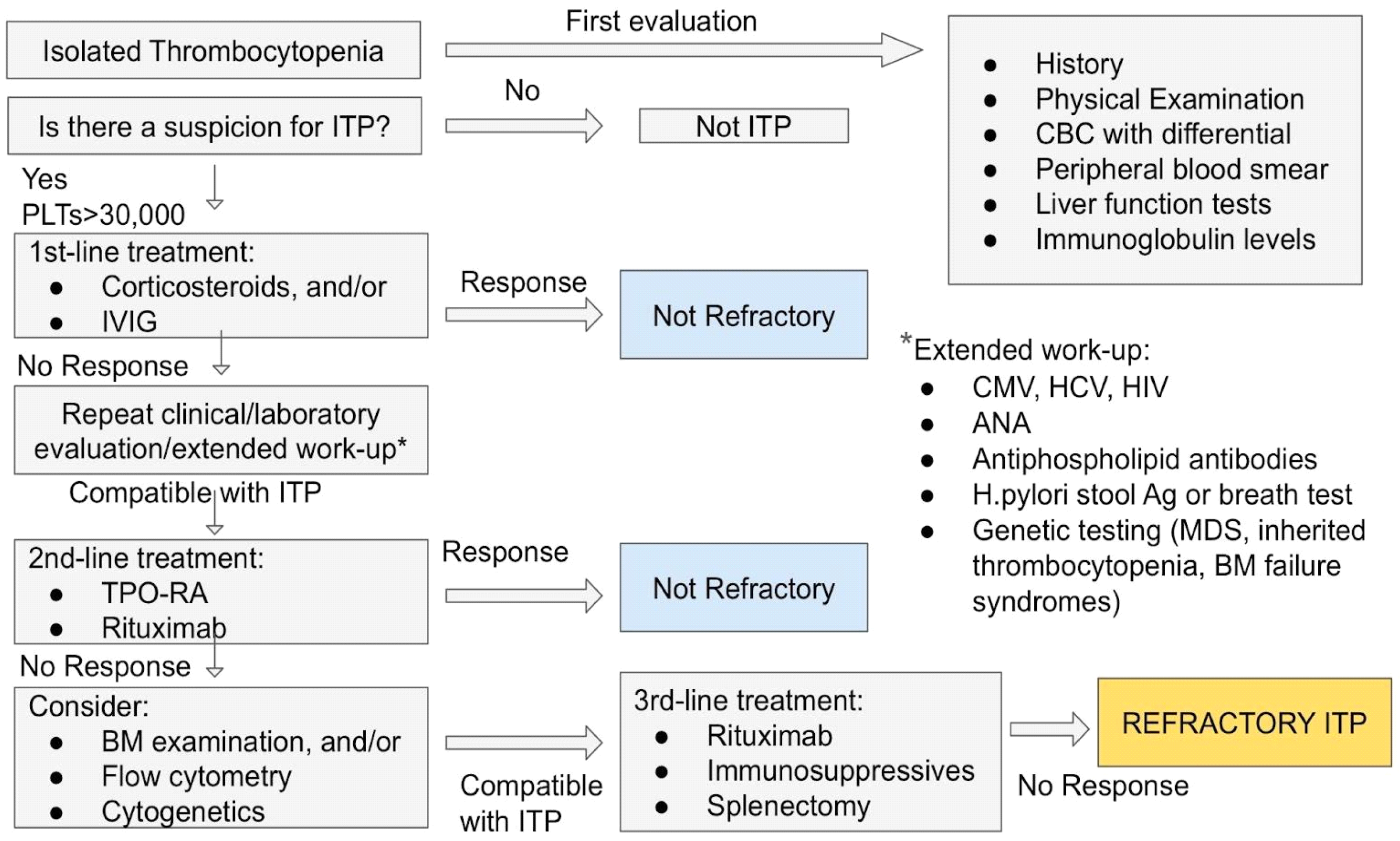
3.4. Treatment of ITP
3.4.1. First-Line Treatment
Corticosteroids
Rituximab
3.4.2. Second-Line Treatment
Thrombopoietin-Receptor Agonists, TPO-RAs
Splenectomy
3.4.3. Emergency Treatment
4. Refractory ITP: The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of ITP
5. Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Isolated Thrombocytopenia, MDS-IT
5.1. Challenges in Diagnosis of MDS-IT
5.1.1. Blood and Bone Marrow Examination
5.1.2. Cytogenetic Findings
5.2. Prognostic Factors
6. Misdiagnosed Thrombocytopenia
7. Refractory Cytopenia of Childhood, RCC
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANA | antinuclear antibodies |
| ANC | absolute neutrophil count |
| ASH | American Society of Hematology |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CR | complete response |
| DIC | disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| EBV | epstein–barr virus |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GPs | Glycoproteins |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| HBV | hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| HELLP | hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| HUS | hemolytic uremic syndrome |
| IPSS | international prognostic scoring system |
| IPSS-R | revised international prognostic scoring system |
| ITP | immune thrombocytopenia |
| IVIG | intravenous immune globulin |
| MDS | myelodysplastic syndrome |
| MDS-IT | myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated thrombocytopenia |
| NR | no response |
| PNH | paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria |
| R | response |
| RBCs | red blood cells |
| RCC | refractory cytopenia of childhood |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TMA | thrombotic microangiopathies |
| TPO | thrombopoietin |
| TPO-RA | thrombopoietin-receptor agonists |
| TTP | thrombotic thrombopenic purpura |
| WBCs | white blood cells |
References
- Cheng, C.K.; Chan, J.; Cembrowski, G.S.; van Assendelft, O.W. Complete blood count reference interval diagrams derived from NHANES III: Stratification by age, sex, and race. Lab Hematol. 2004, 10, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, R. How to approach thrombocytopenia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2012, 2012, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.M.; Cuker, A. Diagnostic Approach to Thrombocytopenia in Adults. UpToDate 2023. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/diagnostic-approach-to-thrombocytopenia-in-adults (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Jinna, S.; Khandhar, P.B. Thrombocytopenia; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, F.; Bird, R. How I approach new onset thrombocytopenia. Platelets 2020, 31, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veneri, D.; Franchini, M.; Randon, F.; Nichele, I.; Pizzolo, G.; Ambrosetti, A. Thrombocytopenias: A clinical point of view. Blood Transfus. 2009, 7, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stasi, R. Immune thrombocytopenia: Pathophysiologic and clinical update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2012, 38, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, D.M.; Cuker, A. Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia. UpToDate 2023. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/drug-induced-immune-thrombocytopenia (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Franchini, M.; Veneri, D.; Lippi, G. Thrombocytopenia and infections. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuker, A.; George, J.N. Pathophysiology of TTP and Other Primary Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMAs). UpToDate 2022. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pathophysiology-of-ttp-and-other-primary-thrombotic-microangiopathies-tmas (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Aster, R.H. Pooling of platelets in the spleen: Role in the pathogenesis of “hypersplenic” thrombocytopenia. J. Clin. Investig. 1966, 45, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, D.; McMillan, R.; Nichol, J.L.; Slichter, S.J. Pathogenesis of chronic immune thrombocytopenia: Increased platelet destruction and/or decreased platelet production. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, R.; Chaturvedi, S. Epidemiology and Clinical Manifestations of Immune Thrombocytopenia. Hamostaseologie 2019, 39, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelburg, R.A.; Carbaat-Ham, J.C.; Hesam, H.; Ragusi, M.A.A.D.; Zwaginga, J.J. Platelet function in adult ITP patients can be either increased or decreased, compared to healthy controls, and is associated with bleeding risk. Hematology 2016, 21, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodeghiero, F.; Stasi, R.; Gernsheimer, T.; Michel, M.; Provan, D.; Arnold, D.M.; Bussel, J.B.; Cines, D.B.; Chong, B.H.; Cooper, N.; et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: Report from an international working group. Blood 2009, 113, 2386–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, I.C.; Liebman, H.A. Complement in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP): The role of complement in refractory ITP. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 203, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoemberg, M.; Stahl, D.; Schlenke, P.; Sibrowski, W.; Pachmann, U.; Cassens, U. The Isotype of Autoantibodies Influences the Phagocytosis of Antibody-Coated Platelets in Autoimmune Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 74, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwana, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Ikeda, Y. Splenic macrophages maintain the anti-platelet autoimmune response via uptake of opsonized platelets in patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, R.; Cooper, N.; Del Poeta, G.; Stipa, E.; Evangelista, M.L.; Abruzzese, E.; Amadori, S. Analysis of regulatory T-cell changes in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura receiving B cell-depleting therapy with rituximab. Blood 2008, 112, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Peng, J.; Hou, M. CD8+ T cells suppress autologous megakaryocyte apoptosis in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, R.; Abe, R.; Oku, K.; Tanaka, T.; Matsueda, Y.; Wada, T.; Arinuma, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Ikenoue, T.; Miyakawa, Y.; et al. Involvement of the complement system in immune thrombocytopenia: Review of the literature. Immunol. Med. 2023, 46, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Osch, T.L.J.; Oosterhoff, J.J.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; Nouta, J.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Geerdes, D.M.; Mok, J.Y.; Heidt, S.; Mulder, A.; van Esch, W.J.E.; et al. Fc galactosylation of anti-platelet human IgG1 alloantibodies enhances complement activation on platelets. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezger, M.; Nording, H.; Sauter, R.; Graf, T.; Heim, C.; von Bubnoff, N.; Ensminger, S.M.; Langer, H.F. Platelets and Immune Responses During Thromboinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- British Committee for Standards in Haematology General Haematology Task Force. Guidelines for the investigation and management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults, children and in pregnancy. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 120, 574–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provan, D.; Arnold, D.M.; Bussel, J.B.; Chong, B.H.; Cooper, N.; Gernsheimer, T.; Ghanima, W.; Godeau, B.; González-López, T.J.; Grainger, J.; et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3780–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottayam, R.; Rozenberg, G.; Brighton, T.; Cohn, R.J. Isolated thrombocytopenia in children: Thinking beyond idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura and leukaemia. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2007, 43, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, R.J.; Doyle, J.J.; Krahn, M.D.; Blanchette, V.S.; Naglie, G. Initial bone marrow aspiration in childhood idiopathic thrombocytopenia: Decision analysis. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2001, 23, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, N.; Ghanima, W. Immune Thrombocytopenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neunert, C.; Lim, W.; Crowther, M.; Cohen, A.; Solberg, L., Jr.; Crowther, M.A. The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2011, 117, 4190–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchens, C.S.; Weiss, L. Ultrastructural changes of endothelium associated with thrombocytopenia. Blood 1975, 46, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neunert, C.; Terrell, D.R.; Arnold, D.M.; Buchanan, G.; Cines, D.B.; Cooper, N.; Cuker, A.; Despotovic, J.M.; George, J.N.; Grace, F.N.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3829–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucconi, M.G.; Fazi, P.; Bernasconi, S.; De Rossi, J.; Leone, G.; Gugliotta, L.; Vianelli, N.; Avvisati, G.; Rodeghiero, F.; Amendola, A.; et al. Therapy with high-dose dexamethasone (HD-DXM) in previously untreated patients affected by idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A GIMEMA experience. Blood 2007, 109, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.L.; Mahévas, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Stasi, R.; Cunningham-Rundles, S.; Godeau, B.; Kanter, J.; Neufeld, E.; Taube, T.; Ramenghi, U.; et al. Outcomes 5 years after response to rituximab therapy in children and adults with immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2012, 119, 5989–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanima, W.; Khelif, A.; Waage, A.; Michel, M.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Romdhan, N.B.; Kahrs, J.; Darne, B.; Holme, P.A. Rituximab as second-line treatment for adult immune thrombocytopenia (the RITP trial): A multicentre, randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Porras, J.R.; Mingot-Castellano, M.E.; Andrade, M.M.; Alonso, R.; Caparrós, I.; Arratibel, M.C.; Fernández-Fuertes, F.; Cortti, M.J.; Pascual, C.; Sánchez-González, B.; et al. Use of eltrombopag after romiplostim in primary immune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newland, A.; Godeau, B.; Priego, V.; Viallard, J.-F.; Fernández, M.F.L.; Orejudos, A.; Eisen, M. Remission and platelet responses with romiplostim in primary immune thrombocytopenia: Final results from a phase 2 study. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojouri, K.; Vesely, S.K.; Terrell, D.R.; George, J.N. Splenectomy for adult patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A systematic review to assess long term platelet count responses, prediction of response, and surgical complications. Blood 2004, 104, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khellaf, M.; Michel, M.; Schaeffer, A.; Bierling, P.; Godeau, B. Assessment of a therapeutic strategy for adults with severe autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura based on a bleeding score rather than platelet count. Haematologica 2005, 90, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Psaila, B.; Bussel, J.B. Refractory immune thrombocytopenic purpura: Current strategies for investigation and management. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 143, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Chung, J.H. Long-term results of laparoscopic splenectomy in pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2014, 86, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miltiadous, O.; Hou, M.; Bussel, J.B. Identifying and treating refractory ITP: Difficulty in diagnosis and role of combination treatment. Blood 2020, 135, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.M.; Nazy, I.; Clare, R.; Jaffer, A.M.; Aubie, B.; Li, N.; Kelton, J.G. Misdiagnosis of primary immune thrombocytopenia and frequency of bleeding: Lessons from the McMaster ITP Registry. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2414–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianelli, N.; Auteri, G.; Buccisano, F.; Carrai, V.; Baldacci, E.; Clissa, C.; Bartoletti, D.; Giuffrida, G.; Magro, D.; Rivolti, E.; et al. Refractory primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP): Current clinical challenges and therapeutic perspectives. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aster, J.C.; Stone, R.M. Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Classification of Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS). UpToDate 2023. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-classification-of-myelodysplastic-syndromes-mds (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Ma, X. Epidemiology of myelodysplastic syndromes. Am. J. Med. 2012, 125 (Suppl. S7), S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, R.; Steensma, D.P. Recent developments in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2014, 124, 2793–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.-M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisbren, J.; Dinner, S.; Altman, J.; Frankfurt, O.; Helenowski, I.; Gao, J.; McMahon, B.J.; Stein, B.L. Disease characteristics and prognosis of myelodysplastic syndrome presenting with isolated thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 105, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Moran, M.S.; Arenillas, L.; Ferrer, A.; Lopez-Cadenas, F.; Garcia-Avila, S.; Fernández, C.; Salar, A.; Calvo, X. Myelodysplastic Syndromes Presenting with Isolated Thrombocytopenia: A Less Aggressive Form of Presentation and with Better Prognosis. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. S1), 6960–6961. [Google Scholar]
- Sashida, G.; Takaku, T.; Shoji, N.; Nishimaki, J.; Ito, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Kimura, Y.; Ohyashiki, J.H.; Ohyashiki, K. Clinico-hematologic Features of Myelodysplastic Syndrome Presenting as Isolated Thrombocytopenia: An Entity with a Relatively Favorable Prognosis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liapis, K.; Papadopoulos, V.; Vrachiolias, G.; Stavroulaki, E.; Misidou, C.; Kourakli, A.; Galanopoulos, A.; Papoutselis, M.K.; Papageorgiou, S.; Diamantopoulos, S.T.; et al. Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) Presenting with Isolated Thrombocytopenia: Characteristics, Outcomes, and Clinical Presentation Differences from Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP). Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. S1), 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Xue, Y.; Pan, J.; Cen, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z. Refractory Thrombocytopenia, an Unusual Myelodysplastic Syndrome with an Initial Presentation Mimicking Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Int. J. Hematol. 2005, 81, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurodaa, J.; Kimurab, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Wada, K.; Uoshima, N.; Yoshikawa, T. Unusual Myelodysplastic Syndrome with the Initial Presentation Mimicking Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Acta Haematol. 2002, 108, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, D.M.; Colon-Otero, G.; Cockerill, K.J.; Jenkins, R.B.; Noel, P.; Pierre, R.V. Refractory Thrombocytopenia. A Myelodysplastic Syndrome That May Mimic Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1992, 98, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Soupir, C.P.; Johari, V.; Johari, V.; Hasserjian, R.P. Myelodysplastic syndrome with isolated deletion of chromosome 20q: An indolent disease with minimal morphological dysplasia and frequent thrombocytopenic presentation. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 139, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soupir, C.P.; Vergilio, J.A.; Kelly, E.; Kelly, E.; Dal Cin, P.; Kuter, D.; Hasserjian, R.P. Identification of del(20q) in a subset of patients diagnosed with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.L.; Tuechler, H.; Schanz, J.; Sanz, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Solé, F.; Bennett, J.M.; Bowen, D.; Fenaux, P.; Dreyfus, F.; et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012, 120, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adès, L.; Itzykson, R.; Fenaux, P. Myelodysplastic syndromes. Lancet 2014, 383, 2239–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, C.M. Pediatric MDS Including Refractory Cytopenia and Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia. In The EBMT Handbook: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies, 7th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Chapter 74. [Google Scholar]
- Galaverna, F.; Ruggeri, A.; Locatelli, F. Myelodysplastic syndromes in children. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Differential Diagnosis of Isolated Thrombocytopenia |
|---|
| Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) 1 |
| Drug-Induced Immune Thrombocytopenia |
| Infections |
| HIV 2 |
| HCV 3 |
| CMV 4 |
| Helicobacter pylori |
| Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Isolated Thrombocytopenia (MDS-IT) 5 |
| Acquired Amegakaryocytic Thrombocytopenia |
| Nutritional Deficiency |
| Secondary Causes of ITP 1 | |
|---|---|
| Disease | Findings Confirmative of Disease |
| Certain drugs (e.g., acetaminophen, abciximab, carbamazepine, rifampicin and vancomycin) | Initiation of new medication |
| Infection (e.g., HIV 2, HBV 3, HCV 4, CMV 5, EBV 6, Helicobacter pylori) | Constitutional symptoms and signs; positive serological and PCR 7 tests for HCV 4, HBV 3, CMV 5, EBV 6, HIV 2, urea breath test for H. pylori |
| Evans syndrome | Thrombocytopenia; positive direct antiglobulin test for hemolytic anemia |
| Lymphoproliferative disorders | Weight loss, night sweats, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly; abnormal complete blood count and bone marrow aspirate/biopsy |
| Systemic autoimmune disease (e.g., SLE 8, rheumatoid arthritis, antiphospholipid syndrome) | Arthralgias/arthritis, hair loss, sun sensitivity, mouth ulcers, rash, thromboembolism |
| Main Findings of Studies on MDS-IT 1 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Number of Patients | Median Age of Diagnosis, Years | Median PLT 2 Count, ×109/L | Median Hb 3 Count, g/dL | Median WBC 4 Count, ×109/L | Median BM 5 Blasts Count, % | IPSS 6/IPSS-R Risk Score, % | Cytogenetics Risk Score, % | Karyotype | Median OS 7, Months |
| Flores-Moran MS et al. (2022) [49] | 20 | 74 | 84 | – | – | – | Very Low (45%)/Low (45%) | – | Normal (60%) | 104 (range 28–206) |
| Liapis K. et al. (2021) [51] | 77 | 66 | 87 | 13.6 | 4.6 | 2 | Low (73.5%) | Favorable (83.1%) | Normal (51.9%) | 109 (95% CI 8 103–115) |
| Waisbren J. et al. (2016) [48] | 50 | 72 | 64 | 12 | 4.4 | 4 | Very Low + Low (46%) | – | Normal (56%) | 29 (range 2.7–74.5) |
| Sashida G. et al. (2009) [50] | 13 | 57 | 55 | 12.6 | 5.5 | 1.6 | Low + Intermediate (100%) | – | Normal (38.5%) | 32.2 (range 5–72) |
| Directed Approach of Isolated Thrombocytopenia | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary ITP 1 | MDS 2 | ||
| Clinical characteristics | Age at presentation | Any age, median age of diagnosis 56 years old | Most common in older adults |
| Incidence | 1–6.4:100,000 | 1–4:1,000,000 | |
| Distinguishing features | Isolated thrombocytopenia with petechiae/bruising in a healthy-looking patient | Other abnormalities on CBC 3/dysplasia in BM 4, possibly associated with trisomy 8 or 21, etc. | |
| Diagnostic tests | CBC 3, peripheral-blood smear:
|
| |
| Rule out viral infections: CMV 9, HCV 10, HIV 11 Rule out drugs/toxins Rule out renal, hepatic, thyroid dysfunction | |||
| Molecular characteristics | None identified | Monosomy 7, trisomy 8 or 21 | |
| Clinical approach | Standard first- and second-line treatment | Chemotherapy, HSCT 12, TPO-RA 13 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosmidou, A.; Gavriilaki, E.; Tragiannidis, A. The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of Refractory Thrombocytopenia: ITP or MDS with Isolated Thrombocytopenia? Cancers 2024, 16, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081462
Kosmidou A, Gavriilaki E, Tragiannidis A. The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of Refractory Thrombocytopenia: ITP or MDS with Isolated Thrombocytopenia? Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081462
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosmidou, Aikaterini, Eleni Gavriilaki, and Athanasios Tragiannidis. 2024. "The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of Refractory Thrombocytopenia: ITP or MDS with Isolated Thrombocytopenia?" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081462
APA StyleKosmidou, A., Gavriilaki, E., & Tragiannidis, A. (2024). The Challenge for a Correct Diagnosis of Refractory Thrombocytopenia: ITP or MDS with Isolated Thrombocytopenia? Cancers, 16(8), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081462








