Biphasic Regulation of Apoptosis Following Gastric Irreversible Electroporation Using Tissue Immunohistochemistry of Activated Caspase-3 with TUNEL Method
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
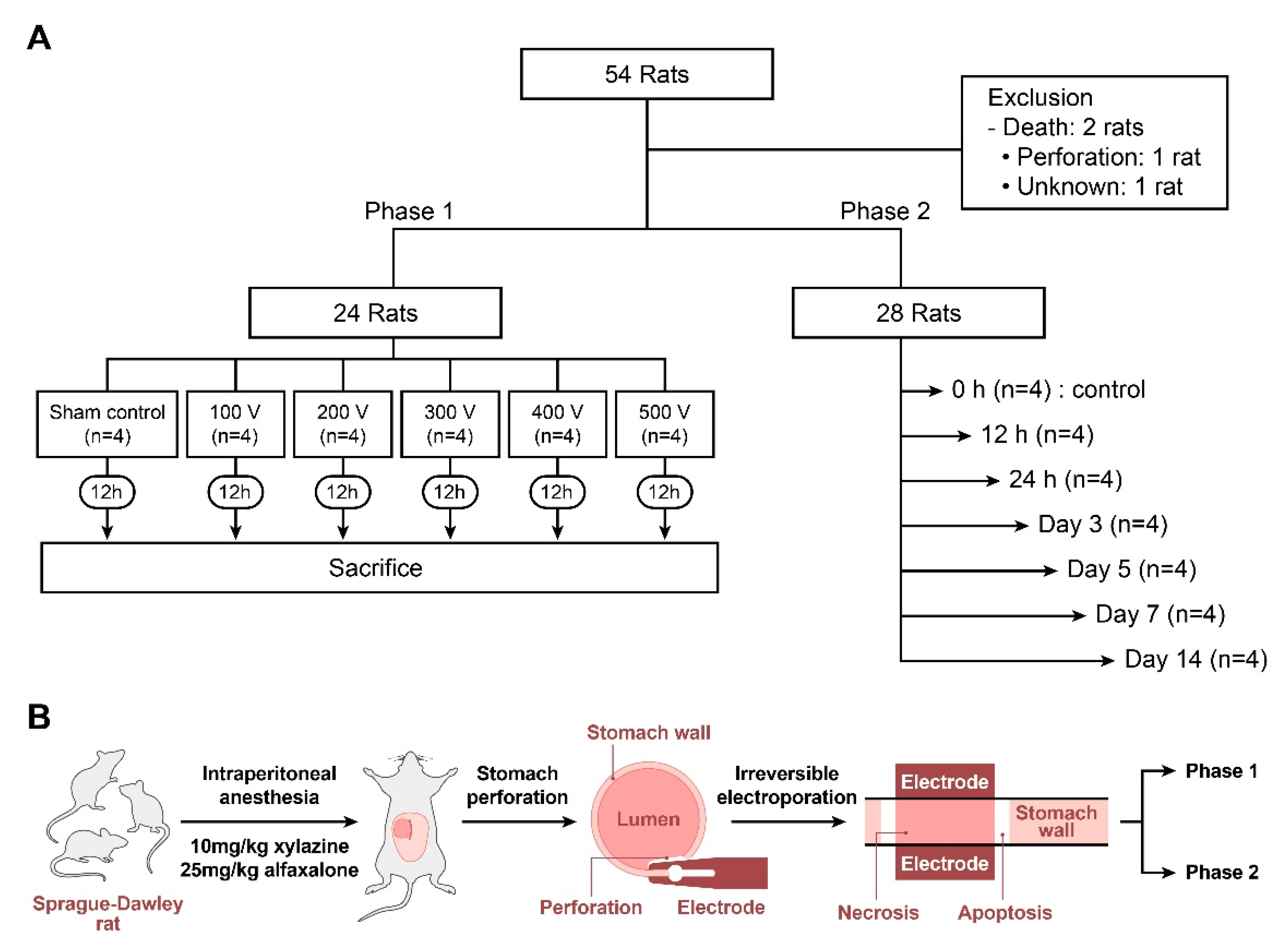
2.2. Study Design
2.3. IRE Rat Model
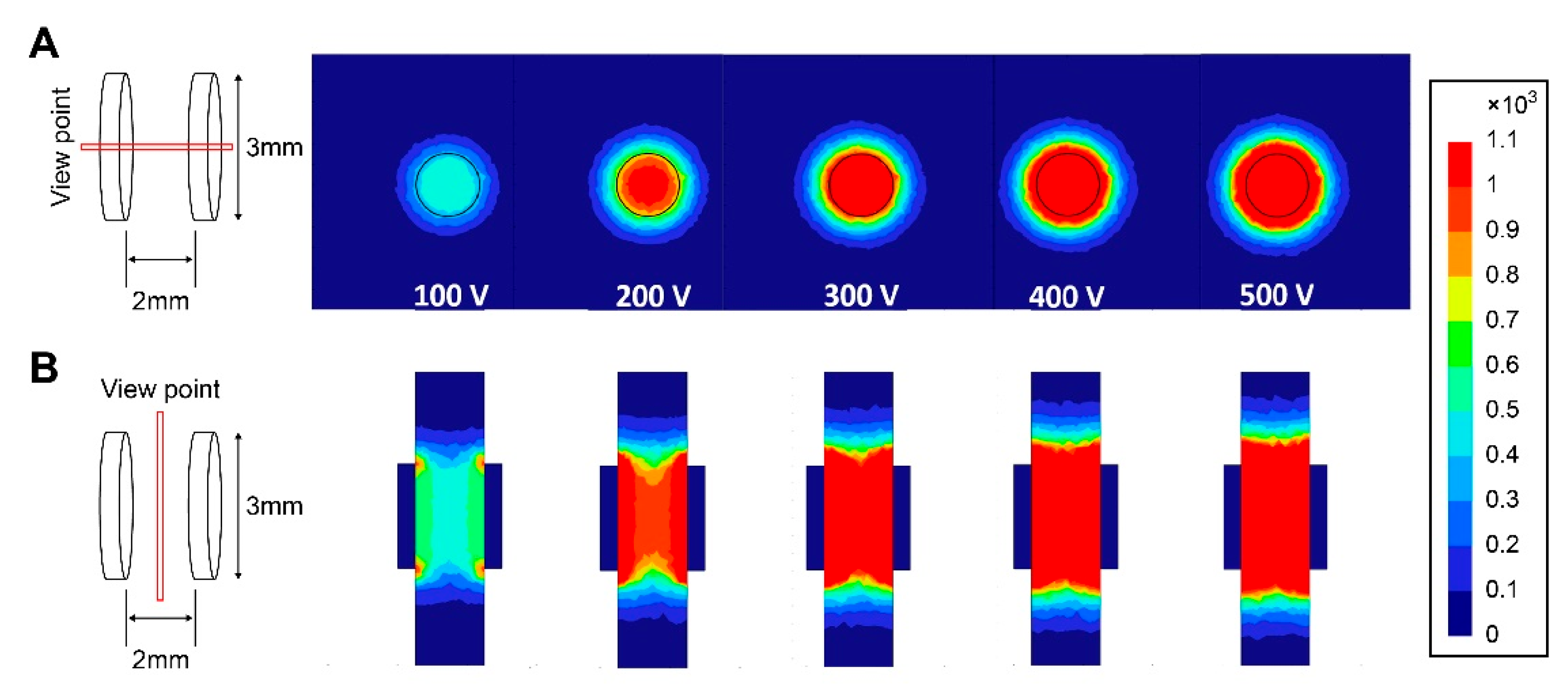
2.4. IRE Protocol and Modeling
2.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.6. TUNEL Assay
2.7. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of Cleaved Caspase-3
2.8. Masson Trichrome (MT) Staining
2.9. Digital Image Analysis
2.10. Apoptosis, Necrosis, Apoptosis/NECROSIS Ratio Definition
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phase 1 Study
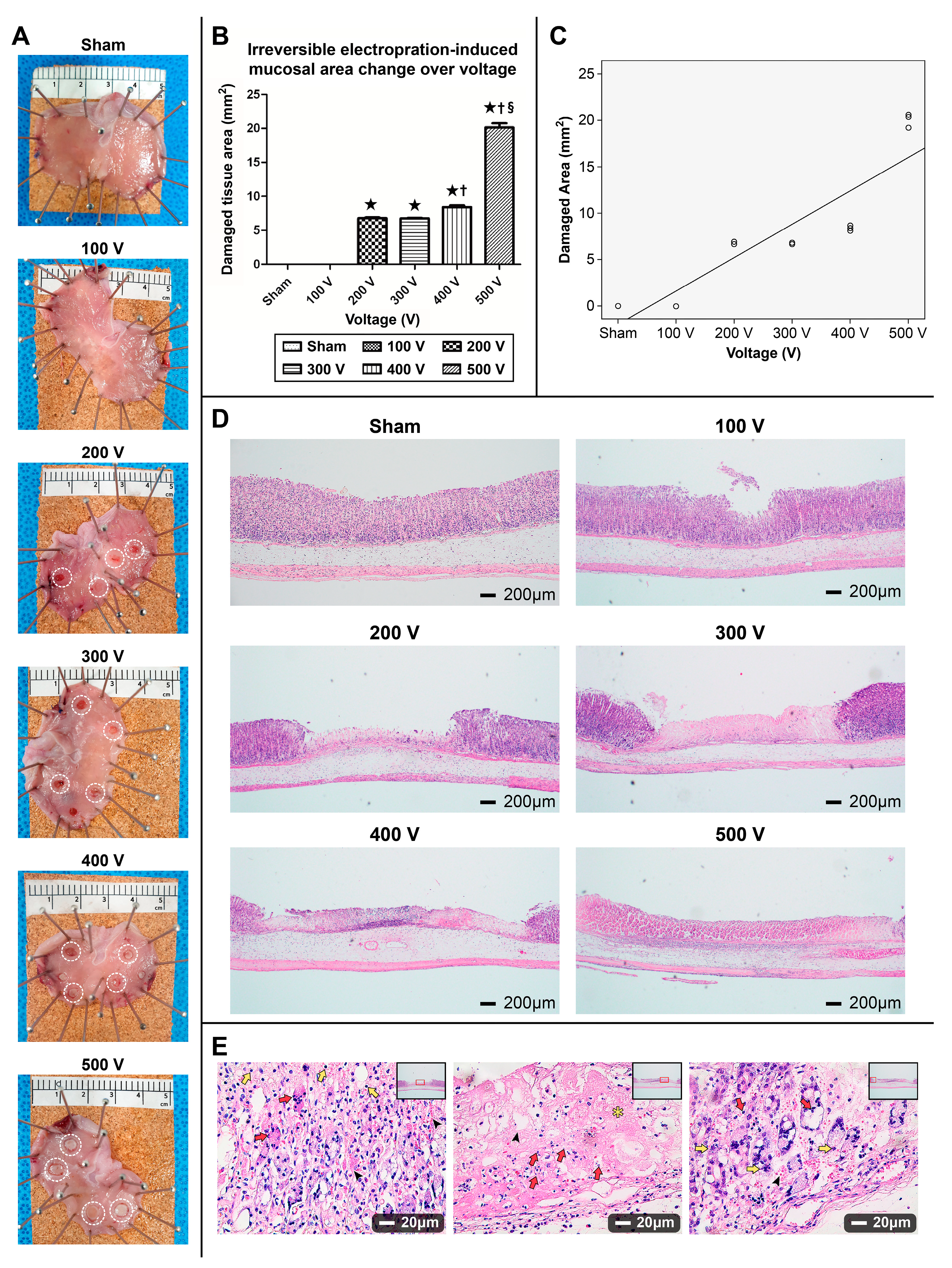
3.1.1. Gross Appearance of the Ablated Stomach
3.1.2. Damaged Gastric Tissue Area Varying by Electrical Field Intensity and Correlation between Area of the Ablation Zone and Electrical Voltage
3.1.3. H&E Staining
3.1.4. TUNEL Assay
3.1.5. Cleaved Caspase-3 Immunohistochemistry
3.1.6. Staining Pattern upon Electrical Energy Intensity
3.1.7. Apoptosis/Necrosis (TUNEL+/Casp+ over TUNEL+/Casp-) Ratio
3.2. Phase 2 Study
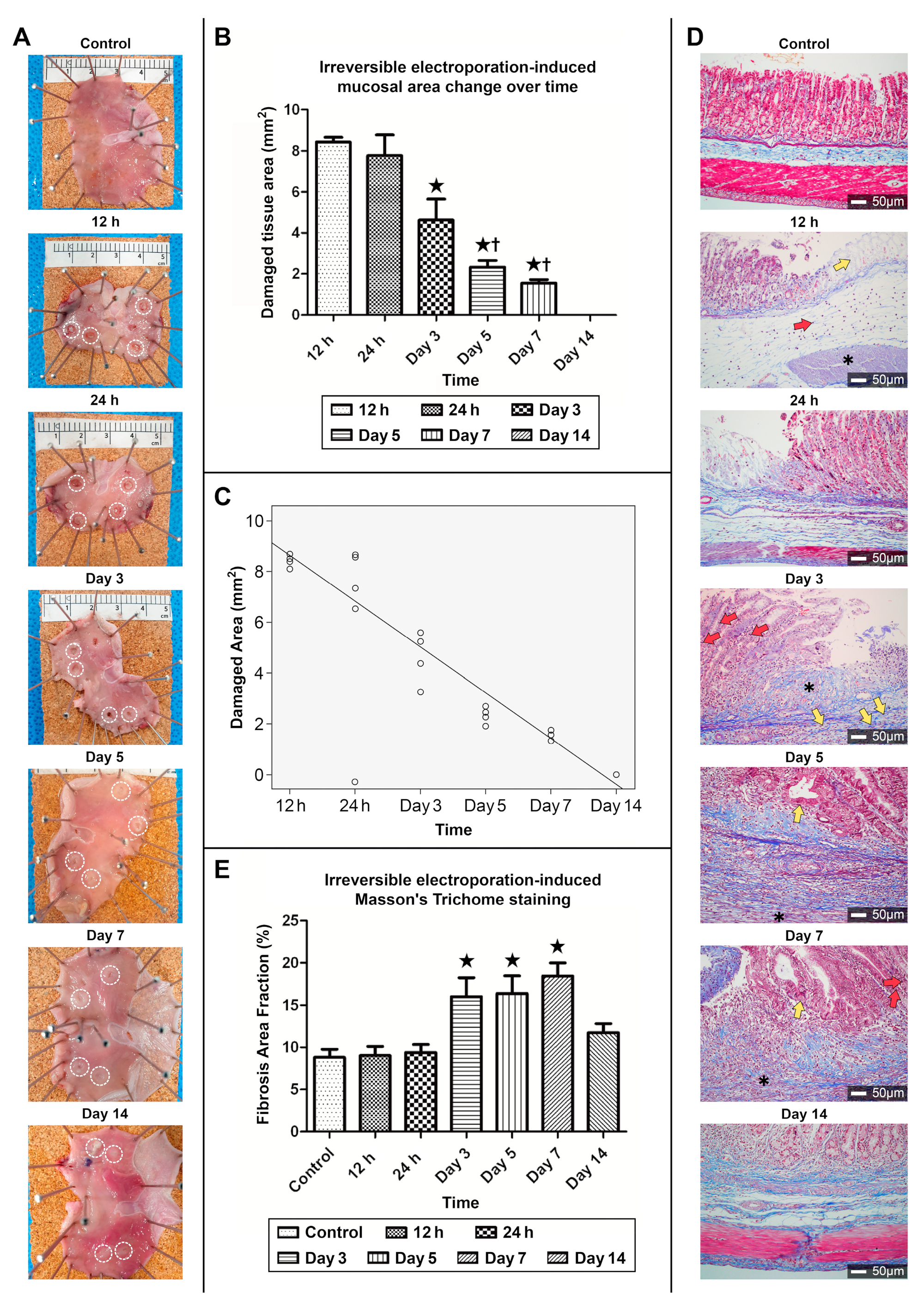
3.2.1. Gross Appearance of Recovery in the Ablated Zone
3.2.2. Correlation between the Area of the Ablation Zone and Time
3.2.3. MT Staining of the Collagen Fibers in the Ablation Zone
3.2.4. Fibrosis Area Fraction Changes in MT Staining upon Ulcer Healing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavčič, D. Membrane Electroporation and Electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasson, E.M.; Alinezhadbalalami, N.; Brock, R.M.; Allen, I.C.; Verbridge, S.S.; Davalos, R.V. Understanding the role of calcium-mediated cell death in high-frequency irreversible electroporation. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 131, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, L.G.; Edhemovic, I.; Soden, D.; Perrone, A.M.; Scarpa, M.; Campanacci, L.; Cemazar, M.; Valpione, S.; Miklavčič, D.; Mocellin, S.; et al. Electrochemotherapy—Emerging applications technical advances, new indications, combined approaches, and multi-institutional collaboration. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aycock, K.N.; Davalos, R.V. Irreversible Electroporation: Background, Theory, and Review of Recent Developments in Clinical Oncology. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sakere, B.; André, F.; Bernat, C.; Connault, E.; Opolon, P.; Davalos, R.V.; Rubinsky, B.; Mir, L.M. Tumor ablation with irreversible electroporation. PLoS ONE 2007, 11, e1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista Napotnik, T.; Polajžer, T.; Miklavčič, D. Cell death due to electroporation—A review. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 141, 107871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsky, B.; Onik, G.; Mikus, P. Irreversible electroporation: A new ablation modality—Clinical implications. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 6, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, R.V.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edd, J.F.; Horowitz, L.; Dávalos, R.F.; Mir, L.M.; Rubinsky, B. In vivo results of a new focal tissue ablation technique: Irreversible electroporation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geboers, B.; Scheffer, H.J.; Graybill, P.M.; Ruarus, A.H.; Nieuwenhuizen, S.; Puijk, R.S.; van den Tol, P.M.; Davalos, R.V.; Rubinsky, B.; de Gruijl, T.D.; et al. High-Voltage Electrical Pulses in Oncology: Irreversible Electroporation, Electrochemotherapy, Gene Electrotransfer, Electrofusion, and Electroimmunotherapy. Radiology 2020, 295, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, C.B.; Sano, M.B.; Rossmeisl, J.H., Jr.; Caldwell, J.L.; Garcia, P.A.; Rylander, M.N.; Davalos, R.V. High-frequency irreversible electroporation (H-FIRE) for non-thermal ablation without muscle contraction. Biomed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyanju, O.; Al-Angari, H.M.; Sahakian, A.V. The optimization of needle electrode number and placement for irreversible electroporation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiol. Oncol. 2012, 46, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golberg, A.; Bruinsma, B.G.; Uygun, B.E.; Yarmush, M.L. Tissue heterogeneity in structure and conductivity contribute to cell survival during irreversible electroporation ablation by “electric field sinks”. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogenes, A.M.; Overduin, C.G.; Slump, C.H.; van Laarhoven, C.J.H.M.; Fütterer, J.J.; Broek, R.P.G.T.; Stommel, M.W.J. The Influence of Irreversible Electroporation Parameters on the Size of the Ablation Zone and Thermal Effects: A Systematic Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338221125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.; Tait, S.W.G. Mitochondrial apoptosis: Killing cancer using the enemy within. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Witzig, T.E.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Huang, Y.; Krajina, B.A.; McBirney, M.; Doak, A.E.; Qu, S.; Wang, C.L.; Haffner, M.C.; Cheung, K.J. Metastasis from the tumor interior and necrotic core formation are regulated by breast cancer-derived angiopoietin-like 7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214888120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-G.; Jiao, D. Necroptosis, tumor necrosis and tumorigenesis. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hua, Y.; Cai, Z. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy: Present and emerging inducers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4854–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, S. T-cell activation and immune memory enhancement induced by irreversible electroporation in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Meng, Z. Immunomodulatory effect of locoregional therapy in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 951–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriarchavatana, P.; Ayers, J.D.; Kendall, L.V. Anesthetic activity of alfaxalone compared with ketamine in mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flatow, E.A.; Komegae, E.N.; Fonseca, M.T.; Brito, C.F.; Musteata, F.M.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Steiner, A.A. Elucidating the role of leptin in systemic inflammation: A study targeting physiological leptin levels in rats and their macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 313, R572–R582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. Physiological and histopathological effects of electroporation pulse on stomach of rats. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Jeen, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; Chun, H.J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.B.; et al. Assessment of efficacy and safety of advanced endoscopic irreversible electroporation catheter in the esophagus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.R.; Yue, W. Semi-quantitative determination of protein expression using immunohistochemistry staining and analysis: An integrated protocol. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrity, M.M.; Burgart, L.J.; Riehle, D.L.; Hill, E.M.; Sebo, T.J.; Witzig, T. Identifying and Quantifying Apoptosis: Navigating Technical Pitfalls. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kari, S.; Subramanian, K.; Altomonte, I.A.; Murugesan, A.; Yli-Harja, O.; Kandhavelu, M. Programmed cell death detection methods: A systematic review and a categorical comparison. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 482–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.R.; Garner, D.S.; Williams, S.D.; Funckes-Shippy, C.L.; Spath, I.S.; Blomme, E.A. Comparison of immunohistochemistry for activated caspase-3 and cleaved cytokeratin 18 with the TUNEL method for quantification of apoptosis in histological sections of PC-3 subcutaneous xenografts. J. Pathol. 2003, 199, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayans, R.; Murray, D. Do TUNEL and Other Apoptosis Assays Detect Cell Death in Preclinical Studies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janke, L.J.; Ward, J.M.; Vogel, P. Classification, Scoring, and Quantification of Cell Death in Tissue Sections. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grusch, M.; Polgar, D.; Gfatter, S.; Leuhuber, K.; Huettenbrenner, S.; Leisser, C.; Fuhrmann, G.; Kassie, F.; Steinkellner, H.; Smid, K.; et al. Maintenance of ATP favours apoptosis over necrosis triggered by benzamide riboside. Cell Death Differ. 2002, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailleux, A.A.; Overholtzer, M.; Schmelzle, T.; Bouillet, P.; Strasser, A.; Brugge, J.S. BIM regulates apoptosis during mammary ductal morphogenesis, and its absence reveals alternative cell death mechanisms. Dev. Cell 2007, 12, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Bsc, M.F.B.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, M.I.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.-W.; Kang, M.J.; Park, E.H.; Yun, E.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kong, H.-J.; Im, J.-S.; Seo, H.G. Prediction of Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Korea, 2023. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Yun, E.H.; Jung, K.-W. Epidemiology of Gastric Cancer in Korea: Trends in Incidence and Survival Based on Korea Central Cancer Registry Data (1999–2019). J. Gastric Cancer 2022, 22, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, P.W.-Y.; Sung, J.J.-Y. Endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer: One piece is better than dash to pieces. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Japanese gastric cancer treatment guidelines 2014 (ver. 4). Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, L.; Shen, Z.; Mao, D.; Khadaroo, P.A.; Su, H. A meta-analysis of comparison of proximal gastrectomy with double-tract reconstruction and total gastrectomy for proximal early gastric cancer. BMC Surg. 2019, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-J.; Chen, G.-M.; Wei, Y.-C.; Yu, H.; Wang, X.-C.; Zhao, Z.-K.; Luo, T.-Q.; Nie, R.-C.; Zhou, Z.-W. Palliative Gastrectomy versus Gastrojejunostomy for advanced Gastric cancer with outlet obstruction: A propensity score matching analysis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Luo, X.; Fang, G.; Chai, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Niu, L. Evaluation of the safety of irreversible electroporation on the stomach wall using a pig model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Seo, Y.S.; Jeen, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; Chun, H.J.; Um, S.H.; Kim, C.D.; et al. Characterization of irreversible electroporation on the stomach: A feasibility study in rats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9094, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Li, Q.; Hu, L.; Yan, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, P.; Chen, X.; et al. Safety and efficacy of magnetic anchoring electrode-assisted irreversible electroporation for gastric tissue ablation. Surg. Endosc. 2020, 34, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, L.; Chu, D.; Wu, Z.; et al. Magnetic anchoring and guidance-assisted endoscopic irreversible electroporation for gastric mucosal ablation: A preclinical study in canine model. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 5665–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Keum, B.; Bang, E.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.H.; Yim, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, E.S.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Feasibility and effectiveness of endoscopic irreversible electroporation for the upper gastrointestinal tract: An experimental animal study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Beebe, S.J. An apoptosis targeted stimulus with nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) in E4 squamous cell carcinoma. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Sain, N.M.; Harlow, K.T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Shires, P.K.; Heller, R.; Beebe, S.J. A protective effect after clearance of orthotopic rat hepatocellular carcinoma by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.; Sain, N.M.; Beebe, S.J. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) activate intrinsic caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death in Jurkat cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, S.J.; Sain, N.M.; Ren, W. Induction of Cell Death Mechanisms and Apoptosis by Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Fields (nsPEFs). Cells 2013, 2, 136–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, A.; Saczko, J.; Kulbacka, J. Apoptosis as the main type of cell death induced by calcium electroporation in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 136, 107592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, E.H.; Schoenbach, K.H.; Beebe, S.J. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in p53-wildtype and p53-null HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, X.; Cui, G.; Yin, S.; Chen, L.; Jiang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, L. Nanosecond pulsed electric field inhibits cancer growth followed by alteration in expressions of NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling molecules. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuccitelli, R.; Chen, X.; Pakhomov, A.G.; Baldwin, W.H.; Sheikh, S.; Pomicter, J.L.; Ren, W.; Osgood, C.; Swanson, R.J.; Kolb, J.F.; et al. A new pulsed electric field therapy for melanoma disrupts the tumor’s blood supply and causes complete remission without recurrence. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Mechanisms of Caspase Activation and Inhibition during Apoptosis. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramuz, O.; Isnardon, D.; Devilard, E.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Hassoun, J.; Birg, F.; Xerri, L. Constitutive nuclear localization and initial cytoplasmic apoptotic activation of endogenous caspase-3 evidenced by confocal microscopy. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2003, 84, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, X.; Tao, D.; Hu, J.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Gardner, K.; Judge, S.I.; et al. Timing of apoptosis onset depends on cell cycle progression in peripheral blood lymphocytes and lymphocytic leukemia cells. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saraste, A.; Pulkki, K. Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 45, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faroja, M.; Ahmed, M.; Appelbaum, L.; Ben-David, E.; Moussa, M.; Sosna, J.; Nissenbaum, I.; Goldberg, S.N. Irreversible electroporation ablation: Is all the damage nonthermal? Radiology 2013, 266, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gemert, M.J.C.; Wagstaff, P.G.K.; de Bruin, D.M.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; van der Wal, A.C.; Heger, M.; van der Geld, C.W.M. Irreversible electroporation: Just another form of thermal therapy? Prostate 2015, 75, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, E.; Appelbaum, L.; Sosna, J.; Nissenbaum, I.; Goldberg, S.N. Characterization of irreversible electroporation ablation in in vivo porcine liver. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 198, W62–W68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnawski, A.; Szabo, I.L.; Husain, S.S.; Soreghan, B. Regeneration of gastric mucosa during ulcer healing is triggered by growth factors and signal transduction pathways. J. Physiol. Paris 2001, 95, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ypsilantis, P.; Pitiakoudis, M.; Souftas, V.D.; Lambropoulou, M.; Tsalikidis, C.; Foutzitzi, S.; Tsigalou, C.; Prassopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Simopoulos, C. Liver regeneration following radiofrequency ablation. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 150, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakushima, N.; Fujishiro, M.; Kodashima, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Tateishi, A.; Iguchi, M.; Imagawa, A.; Motoi, T.; Yahagi, N.; Omata, M. Histopathologic characteristics of gastric ulcers created by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Endoscopy 2006, 38, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.; Henke, C.A.; Bitterman, P.B. Extracellular matrix as a driver of progressive fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQuitty, C.E.; Williams, R.; Chokshi, S.; Urbani, L. Immunomodulatory role of the extracellular matrix within the liver disease microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Bai, X.; Ding, Y.; Lee, I.-S. Electrical stimulation as a novel tool for regulating cell behavior in tissue engineering. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.; DiPietro, L.A. Apoptosis and angiogenesis: An evolving mechanism for fibrosis. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 3893–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenbach, K.H.; Katsuki, S.; Stark, R.H.; Buescher, E.S.; Beebe, S.J. Bioelectrics-new applications for pulsed power technology. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2002, 30, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.K.; Kim, H.B.; Jung, J.H.; Baik, K.Y.; Moon, K.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Yi, J.-H.; Chung, J.H. Histological and mathematical analysis of the irreversibly electroporated liver tissue. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertel, A.; Verghese, A.; Byers, S.W.; Ochs, M.; Tozeren, A. Pathway-specific differences between tumor cell lines and normal and tumor tissue cells. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



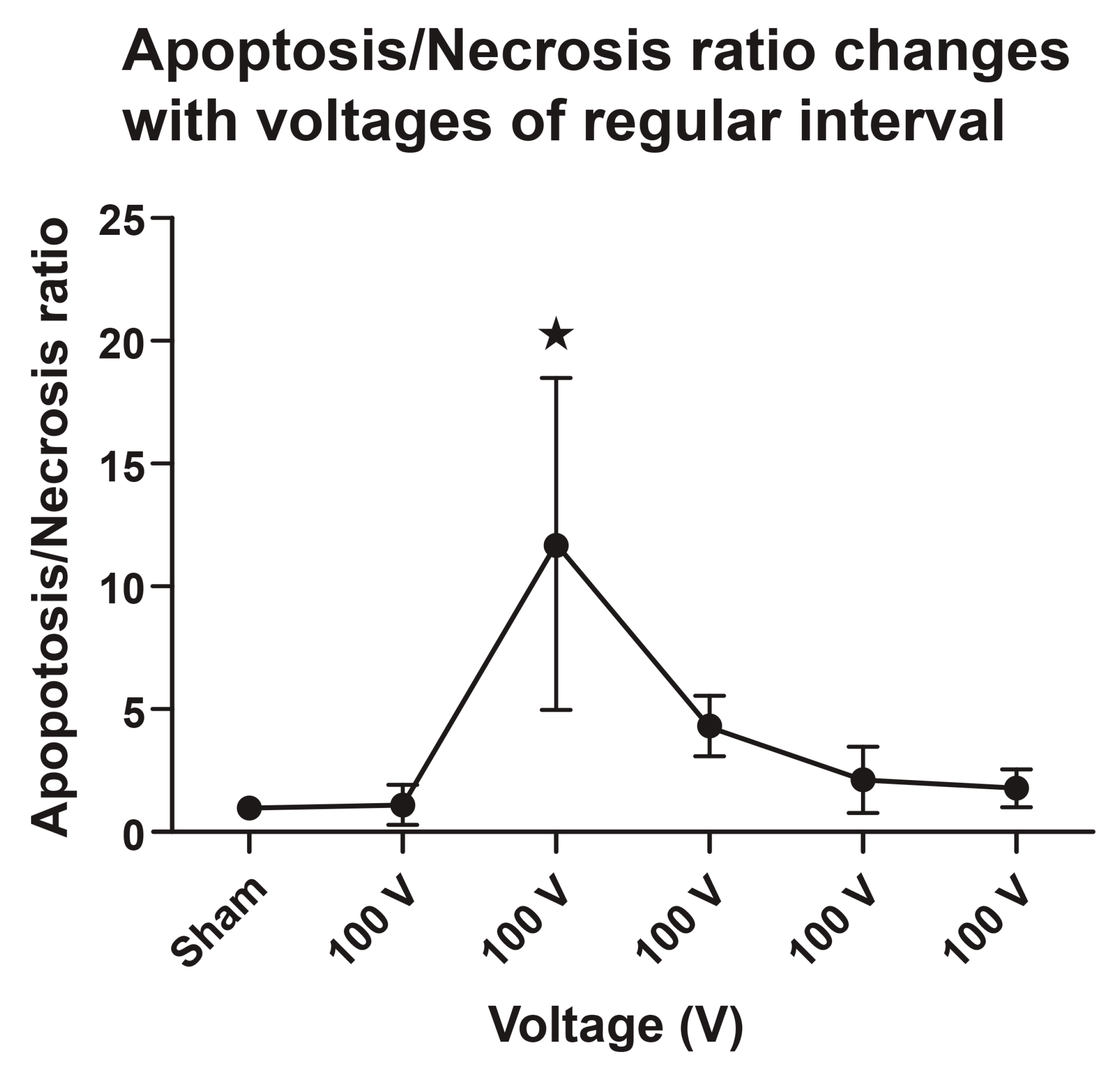
| Sham Control (n = 4) | 100 V (n = 4) | 200 V (n = 4) | 300 V (n = 4) | 400 V (n = 4) | 500 V (n = 4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TUNEL+/Casp+ over TUNEL+/Casp- ratio | 1.00 | 0.455 | 10.8 | 3.29 | 1.42 | 0.959 |
| 1.00 | 0.564 | 4.32 | 3.50 | 0.811 | 1.34 | |
| 1.00 | 2.27 | 20.7 | 5.90 | 2.74 | 2.29 | |
| 1.00 | 1.23 | 11.2 | 4.73 | 3.73 | 2.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.J.; Chun, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Keum, B.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, J.H. Biphasic Regulation of Apoptosis Following Gastric Irreversible Electroporation Using Tissue Immunohistochemistry of Activated Caspase-3 with TUNEL Method. Cancers 2024, 16, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071389
Jeon HJ, Chun HJ, Choi HS, Keum B, Kim HB, Kim JH. Biphasic Regulation of Apoptosis Following Gastric Irreversible Electroporation Using Tissue Immunohistochemistry of Activated Caspase-3 with TUNEL Method. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071389
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Han Jo, Hoon Jai Chun, Hyuk Soon Choi, Bora Keum, Hong Bae Kim, and Jong Hyuk Kim. 2024. "Biphasic Regulation of Apoptosis Following Gastric Irreversible Electroporation Using Tissue Immunohistochemistry of Activated Caspase-3 with TUNEL Method" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071389
APA StyleJeon, H. J., Chun, H. J., Choi, H. S., Keum, B., Kim, H. B., & Kim, J. H. (2024). Biphasic Regulation of Apoptosis Following Gastric Irreversible Electroporation Using Tissue Immunohistochemistry of Activated Caspase-3 with TUNEL Method. Cancers, 16(7), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071389






