Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
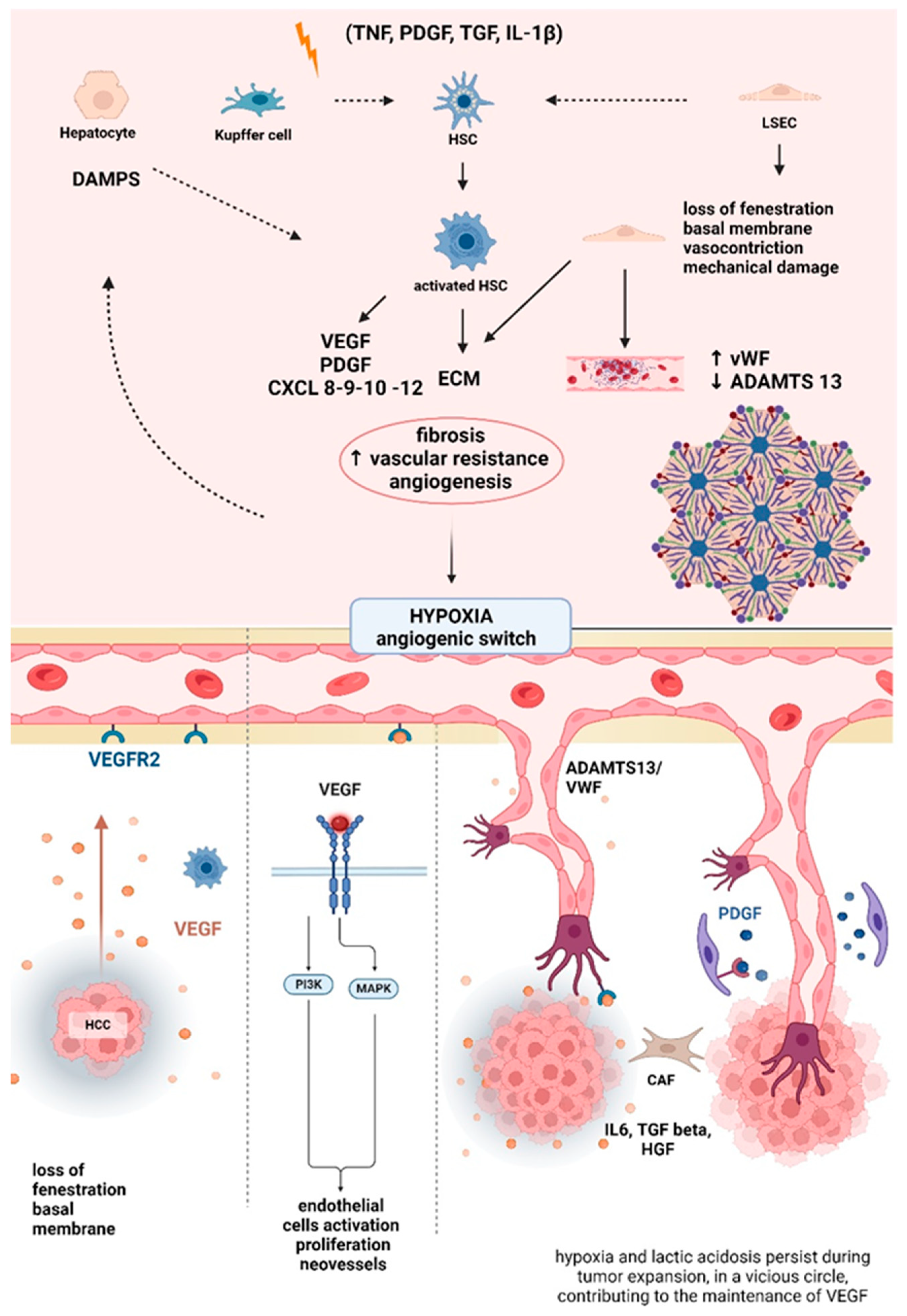
2. HCC and Portal Hypertension: Two Sides of the Same Coin
PH in Liver Cirrhosis and HCC: Physiopathology
3. How Does Systemic Therapy Affect Portal Hypertension?
3.1. Systemic Therapy in HCC: State of the Art
3.2. Effect of Sorafenib on Portal Hypertension
3.3. Effect of Lenvatinib on Portal Hypertension
3.4. Effect of Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab on Portal Hypertension
3.5. Effect of ICIs on Portal Hypertension
| Systemic Treatment | Molecular Target | PH | Risk of Bleeding | Risk of Liver Decompensation/Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | ||||
| Sorafenib | VEGFR, PDGFR, Raf/MEK/ERK pathway | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Lenvatinib | VEGFR 1-3, FGFR 1-4, PDGFR-α, RET, KIT, FGF19, FGF21 | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ (Encephalopathy) |
| Regorafenib | VEGFR-1-3, PDGFR, TIE2, FGFR c-KIT, RET, RAF-1, BRAF, V600E BRAF [88] | ↓ (Murine model) [89] | No data | Apparently none |
| Cabozantinib | MET, VEGFR 1, 2, 3, AXL (GAS6 receptor), RET, ROS1, TRKA, TRKB, TYRO3, MER, KIT, FLT-3 [90] | No data | No data | No data |
| Monoclonal antibodies | ||||
| Ramucirumab | VEGFR-2 | No data | No data | No data |
| Immunotherapy | ||||
| Atezolizumab/Bevacizumab | PD-L1, VEGF | No data | ↑ | |
| Tremelimumab/Durvalumab | CTLA-4, PD-L1 | No data | No | IRLI |
| Nivolumab | PD-1 | No data | No data | |
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | No data | No data | |
| Ipilimumab | CTLA-4 | No data | No data |
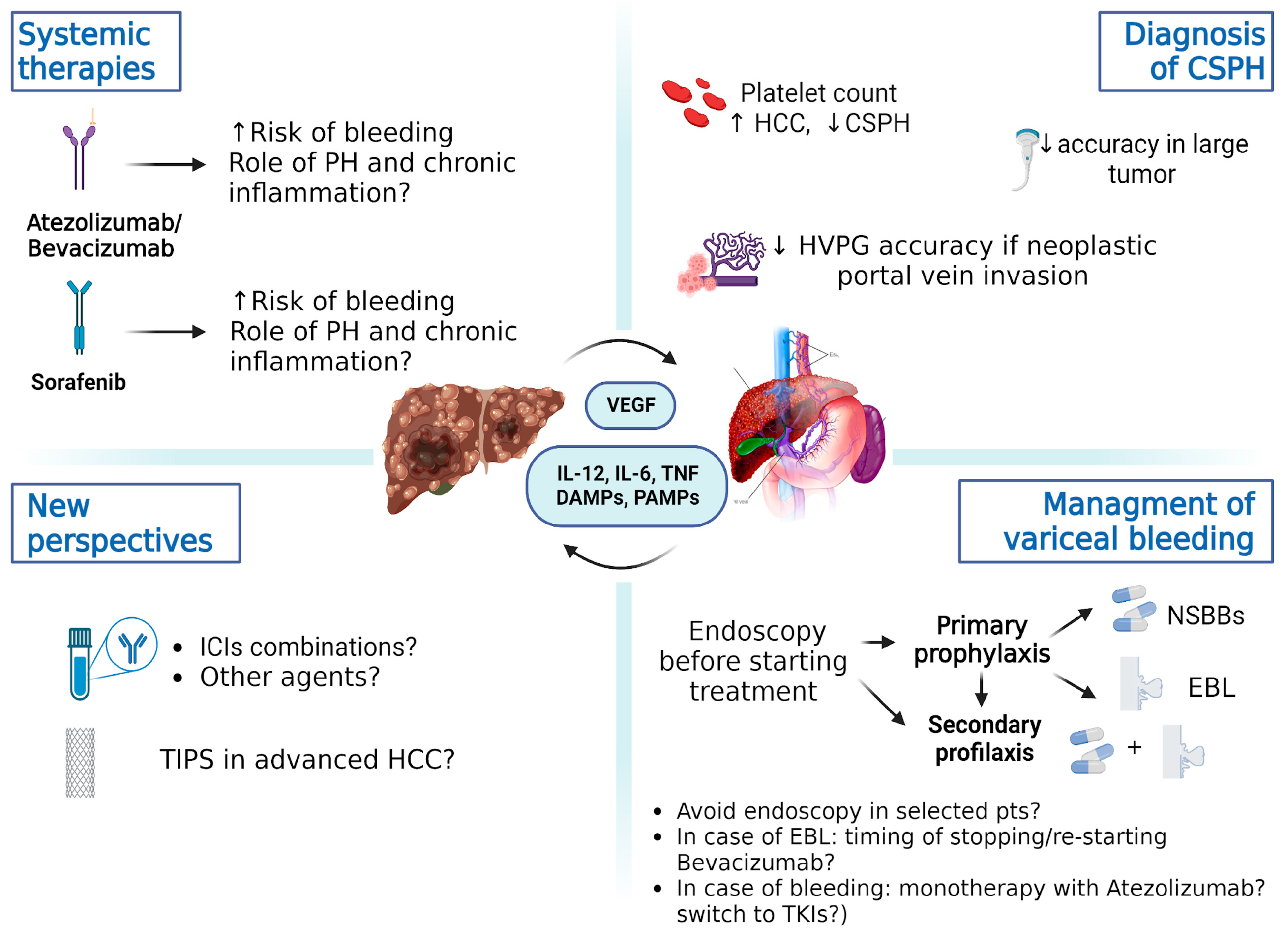
4. Real-Life Studies and Management of Portal Hypertension in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Baveno VII Criteria and Beyond
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Singal, A.G.; Kanwal, F.; Llovet, J.M. Global trends in hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology: Implications for screening, prevention and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumgay, H.; Ferlay, J.; de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Zheng, R.; Wei, W.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P.; Soerjomataram, I. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 161, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, R.R.; Liu, X.; Gu, P.; Yu, H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, C.; Ou, B.; Peng, Z. Global burden of primary liver cancer by five etiologies and global prediction by 2035 based on global burden of disease study 2019. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Masuda, H.; Miyake, H.; Takayama, T.; Yokoyama, E. Endoscopic Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Evaluation of Bleeding Esophageal Varices. Digestion 2005, 70, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripoll, C.; Groszmann, R.J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J.; Grace, N.; Burroughs, A.; Planas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Makuch, R.; et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient predicts development of hepatocellular carcinoma independently of severity of cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Park, S.Y.; Tak, W.Y. Treatment Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of Acute Variceal Bleeding in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2020, 14, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Franchis, R.; Primignani, M. Natural history of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2001, 5, 645–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C. Baveno VII—Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, G.; Gustot, T.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Fallon, M.B.; Shah, V.H.; Moreau, R.; Jalan, R. Inflammation and portal hypertension—The undiscovered country. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pagán, J.-C.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Bosch, J. Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannini, E.G.; Risso, D.; Testa, R.; Trevisani, F.; Di Nolfo, M.A.; Del Poggio, P.; Benvegnù, L.; Ludovico Rapaccini, G.; Farinati, F.; Zoli, M.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of the presence of esophageal varices in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2006, 4, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, M.; Rudler, M.; Thabut, D. Portal hypertension and hepatocellular carcinoma: Des liaisons dangereuses…. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2021, 41, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, Y.; Trebicka, J. Portal hypertension in cirrhosis: Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapy. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, D.C. The Molecular Basis of Portal Hypertension. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2017, 128, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, Á.M.; Palao, N.; Bragado, P.; Gutierrez-Uzquiza, A.; Herrera, B.; Sánchez, A.; Porras, A. New and Old Key Players in Liver Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaert, H.; Thompson, M.G.; Thomas, T.; Geerts, A. Hepatic stellate cells: Role in microcirculation and pathophysiology of portal hypertension. Gut 2002, 50, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Sancho, J.; Caparrós, E.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Francés, R. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, J.; Lemoinne, S.; Boulanger, C.; Durand, F.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Rautou, P.E. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: Physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Sancho, J.; Maeso-Díaz, R.; Fernández-Iglesias, A.; Navarro-Zornoza, M.; Bosch, J. New cellular and molecular targets for the treatment of portal hypertension. Hepatol. Int. 2015, 9, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.K.; Toruner, M.; Chung, M.K.; Groszmann, R.J. Endothelial dysfunction and decreased production of nitric oxide in the intrahepatic microcirculation of cirrhotic rats. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 1998, 28, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhence, A. Von Willebrand Factor as a Biomarker for Liver Disease—An Update. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 13, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsuyama, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iwamoto, T.A.; Mori, T.; Wanaka, A.; Fukui, H.; et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood 2005, 106, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moake, J.L.; Turner, N.A.; Stathopoulos, N.A.; Nolasco, L.H.; Hellums, J.D. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanless, I.R.; Wong, F.; Blendis, L.M.; Greig, P.; Heathcote, E.J.; Levy, G. Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: Possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 1995, 21, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Affo, S.; Yu, L.X.; Schwabe, R.F. The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Fibrosis in Liver Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 153–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Rong, D.; Song, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, X. Targeting Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of HCC: New Opportunities and Challenges. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 775462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Xiong, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, B. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote the stemness of CD24+ liver cells via paracrine signaling. J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2019, 97, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Hamberger, F.; Ravichandra, A.; Miller, M.; Nair, A.; Affo, S.; Filliol, A.; Chin, L.; Savage, T.M.; Yin, D.; et al. Tumor restriction by type I collagen opposes tumor-promoting effects of cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e146987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Wang, R.; Chen, Q.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, B. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote stem cell-like properties of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through IL-6/STAT3/Notch signaling. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Sun, W.; Kim, R.; He, A.R.; Abada, P.B.; Mynderse, M.; Finn, R.S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 912–920. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, C. The role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in cancer liver metastasis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1845–1860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kostallari, E.; Shah, V.H. Pericytes in the Liver. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1122, 153–167. [Google Scholar]
- Corpechot, C.; Barbu, V.; Wendum, D.; Kinnman, N.; Rey, C.; Poupon, R.; Housset, C.; Rosmorduc, O. Hypoxia-induced VEGF and collagen I expressions are associated with angiogenesis and fibrogenesis in experimental cirrhosis. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2002, 35, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiani, C.; Garcia-Pras, E.; Mejias, M.; de Gottardi, A.; Berzigotti, A.; Bosch, J.; Fernandez, M. Apelin signaling modulates splanchnic angiogenesis and portosystemic collateral vessel formation in rats with portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis: An organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-C.; Tang, Z.-Y. Angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: The retrospectives and perspectives. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 130, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Duda, D.G.; Sahani, D.V.; Jain, R.K. HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Incio, J.; Soares, R. Angiogenesis and chronic inflammation: Cause or consequence? Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouaib, S.; Messai, Y.; Couve, S.; Escudier, B.; Hasmim, M.; Noman, M.Z. Hypoxia promotes tumor growth in linking angiogenesis to immune escape. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, J.; Groszmann, R.J.; Shah, V.H. Evolution in the understanding of the pathophysiological basis of portal hypertension: How changes in paradigm are leading to successful new treatments. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S121–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Marschall, Z.; Cramer, T.; Höcker, M.; Finkenzeller, G.; Wiedenmann, B.; Rosewicz, S. Dual mechanism of vascular endothelial growth factor upregulation by hypoxia in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2001, 48, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, C.; Heymach, J.; Overman, M.; Tran, H.; Kopetz, S. Beyond VEGF: Inhibition of the fibroblast growth factor pathway and antiangiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6130–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, A.; Masoumi Moghaddam, S.; Morris, D.L.; Pourgholami, M.H. The critical role of vascular endothelial growth factor in tumor angiogenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2012, 12, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Hu, H.; Zhang, D.; Hu, P.; Yang, Y.; Ren, H. The role of von Willebrand factor as a biomarker of tumor development in hepatitis B virus-associated human hepatocellular carcinoma: A quantitative proteomic based study. J. Proteomics 2014, 106, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, H.; Namisaki, T.; Kitade, M.; Kaji, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Shimozato, N.; Moriya, K.; Seki, K.; Sawada, Y.; et al. VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio as a potential biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Tsuji, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Saikawa, S.; Sato, S.; Sawada, Y.; Kaji, K.; Okura, Y.; Shimozato, N.; et al. von Willebrand factor is a useful biomarker for liver fibrosis and prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with hepatitis B and C. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Tateishi, R.; Enooku, K.; Yoshida, H.; Nakagawa, H.; Masuzaki, R.; Kondo, Y.; Goto, T.; Shiina, S.; Kume, Y.; et al. Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development by Plasma ADAMTS13 in Chronic Hepatitis B and C. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simonetto, D.A.; Yang, H.Y.; Yin, M.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Kwon, J.H.; Hilscher, M.; Pan, S.; Yang, L.; Bi, Y.; Beyder, A.; et al. Chronic Passive Venous Congestion drives Hepatic Fibrogenesis via Sinusoidal Thrombosis and Mechanical Forces. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2015, 61, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, L.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Portal Hypertension: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 23, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, V.; Schepis, T.; Coppola, G.; Chiappetta, M.F.; Del Vecchio, L.E.; Rozera, T.; Quero, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Alfieri, S.; Papa, A. The Role of Microbiota in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, S.J. Tremelimumab: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nivolumab Approved for Liver Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, OF3. [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saung, M.T.; Pelosof, L.; Casak, S.; Donoghue, M.; Lemery, S.; Yuan, M.; Rodriguez, L.; Schotland, P.; Chuk, M.; Davis, G.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab for the Treatment of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated with Sorafenib. Oncologist 2021, 26, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Pembrolizumab for Hepatocellular Carcinoma; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019.
- Fukumura, D.; Kloepper, J.; Amoozgar, Z.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamba, T.; McDonald, D.M. Mechanisms of adverse effects of anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliche, S.; Waltenberger, J. VEGF receptor signaling and endothelial function. IUBMB Life 2001, 52, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Ross, J.; Awad, H.; Hurwitz, H.; Klitzman, B. The Effects of ZD6474, an Inhibitor of VEGF Signaling, on Cutaneous Wound Healing in Mice1. J. Surg. Res. 2005, 129, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilickap, S.; Abali, H.; Celik, I. Bevacizumab, bleeding, thrombosis, and warfarin. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3542, author reply 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, Y.; Schutz FA, B.; Choueiri, T.K. Risk of bleeding with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitors sunitinib and sorafenib: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnane, L.; Trail, P.A.; Taylor, I.; Wilhelm, S.M. Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006, Nexavar®), a Dual-Action Inhibitor That Targets RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway in Tumor Cells and Tyrosine Kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in Tumor Vasculature. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 407, pp. 597–612. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; McNabola, A.; Wilkie, D.; Wilhelm, S.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Revisiting Antiangiogenic Multikinase Inhibitors in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Blockade: The Case of Sorafenib. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3665–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejias, M.; Garcia-Pras, E.; Tiani, C.; Miquel, R.; Bosch, J.; Fernandez, M. Beneficial effects of sorafenib on splanchnic, intrahepatic, and portocollateral circulations in portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M.; Mejias, M.; Garcia-Pras, E.; Mendez, R.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Bosch, J. Reversal of portal hypertension and hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation by combined vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor blockade in rats. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiberger, T.; Angermayr, B.; Schwabl, P.; Rohr-Udilova, N.; Mitterhauser, M.; Gangl, A.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Sorafenib attenuates the portal hypertensive syndrome in partial portal vein ligated rats. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coriat, R.; Gouya, H.; Mir, O.; Ropert, S.; Vignaux, O.; Chaussade, S.; Sogni, P.; Pol, S.; Blanchet, B.; Legmann, P.; et al. Reversible decrease of portal venous flow in cirrhotic patients: A positive side effect of sorafenib. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Sieghart, W.; Reiberger, T.; Rohr-Udilova, N.; Ferlitsch, A.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. The effects of sorafenib on the portal hypertensive syndrome in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma—A pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, H.; Nishijima, N.; Nasu, A.; Komekado, H.; Kita, R.; Kimura, T.; Kudo, M.; Osaki, Y. Long-term antitumor effect of lenvatinib on unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.C.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Hung, Y.P.; Liu, C.A.; Lee, R.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Chao, Y.; Chen, S.C. Lenvatinib combined with nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma-real-world experience. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, J.; Wu, T.; Lei, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Safadi, R.; Li, Y.; Si, T.; et al. Risk Factors for Hepatic Encephalopathy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Sorafenib or Lenvatinib Treatment: A Real-World Study. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 4429–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, H.; Uojima, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Shao, X.; Hara, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Wada, N.; Kubota, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Shibuya, A.; et al. Portal hemodynamic effects of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective cohort study. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maesaka, K.; Sakamori, R.; Yamada, R.; Urabe, A.; Tahata, Y.; Oshita, M.; Ohkawa, K.; Mita, E.; Hagiwara, H.; Tamura, S.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal hypertension. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrey, E.; Campion, B.; Evain, M.; Sultanik, P.; Blaise, L.; Giudicelli, H.; Wagner, M.; Cluzel, P.; Rudler, M.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; et al. A history of variceal bleeding is associated with further bleeding under atezolizumab-bevacizumab in patients with HCC. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabut, D.; Kudo, M. Treatment of portal hypertension in patients with HCC in the era of Baveno VII. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Nishida, N.; Schönlein, M.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Wege, H.; Gaillard, V.E.; Saeed, A.; Wietharn, B.; et al. Preliminary evidence of safety and tolerability of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis: A real-world study. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, Y.; Shibata, M.; Gohda, T.; Matsumiya, H.; Kumamoto, K.; Miyama, A.; Morino, K.; Koya, Y.; Taira, A.; Shinohara, S.; et al. Rapid Progression of Liver Fibrosis Induced by Acute Liver Injury Due to Immune-related Adverse Events of Atezolizumab. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, A.; Naganuma, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Hoshino, T.; Yasuoka, H.; Tamura, Y.; Naruse, H.; Hatanaka, T.; Kakizaki, S. Two cases of rapid progression of esophageal varices after atezolizumab-bevacizumab treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; van Hyfte, G.; Özbek, U.; Reincke, M.; Gampa, A.; Mohamed, Y.I.; Nishida, N.; Wietharn, B.; Amara, S.; Lee, P.C.; et al. Outcomes of beta blocker use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1128569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangro, B.; Chan, S.L.; Meyer, T.; Reig, M.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Galle, P.R. Diagnosis and management of toxicities of immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celsa, C.; Cabibbo, G.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Scheiner, B.; D’Alessio, A.; Manfredi, G.F.; Nishida, N.; Ang, C.; Marron, T.U.; Saeed, A.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of immunotherapy-related liver injury in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma versus other advanced solid tumours. J. Hepatol. 2024, 80, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambhampati, S.; Bauer, K.E.; Bracci, P.M.; Keenan, B.P.; Behr, S.C.; Gordan, J.D.; Kelley, R.K. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh class B cirrhosis: Safety and clinical outcomes in a retrospective case series. Cancer 2019, 125, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.M.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, H.C.; Yoo, C.; Park, S.R.; Ryu, M.H.; Ryoo, B.Y.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Lau, G.; Kudo, M.; Chan, S.L.; Kelley, R.K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.K.; Van Dao, T.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Tremelimumab plus Durvalumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Tak, W.Y.; Gasbarrini, A.; Santoro, A.; Colombo, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Mazzaferro, V.; Wiest, R.; Reig, M.; Wagner, A.; et al. Regorafenib as second-line therapy for intermediate or advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicentre, open-label, phase II safety study. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uschner, F.E.; Schueller, F.; Nikolova, I.; Klein, S.; Schierwagen, R.; Magdaleno, F.; Gröschl, S.; Loosen, S.; Ritz, T.; Roderburg, C.; et al. The multikinase inhibitor regorafenib decreases angiogenesis and improves portal hypertension. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36220–36237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Personeni, N.; Pressiani, T.; Bozzarelli, S.; Rimassa, L. Targeted agents for second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 11, 788–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, N.; Rani, B.; Gerwins, P.; Heindryckx, F. Platelets as Key Factors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnpreecha, K.; Li, F.; Xiang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.; Maroufy, V.; Wang, Q.; Tao, W.; Dang, Y.; Pham, H.A.; et al. Nonselective beta-blockers are associated with a lower risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among cirrhotic patients in the United States. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udumyan, R.; Montgomery, S.; Duberg, A.S.; Fang, F.; Valdimarsdottir, U.; Ekbom, A.; Smedby, K.E.; Fall, K. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers and liver cancer mortality in a national cohort of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, B.H.; Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, J. Outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma presenting with variceal bleeding. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.; Rimassa, L.; Sun, H.-C.; Vogel, A.; Kaseb, A.O. Immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Evaluation and management of adverse events associated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211031141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaire, M.; Manfredi, S.; Lerosey, L.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Thabut, D. Screening and management of portal hypertension in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A French practice survey. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas, E.; Cachero, A.; Amador, A.; Rota, R.; Salord, S.; Gornals, J.; Xiol, X.; Castellote, J. Ulcer bleeding after band ligation of esophageal varices: Risk factors and prognosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohi MP Fidelman, N.; Naeger, D.M.; LaBerge, J.M.; Gordon, R.L.; Kerlan, R.K., Jr. Hepatotoxicity after Transarterial Chemoembolization and Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: Do Two Rights Make a Wrong? J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nicoară-Farcău, O.; Han, G.; Rudler, M.; Angrisani, D.; Monescillo, A.; Torres, F.; Casanovas, G.; Bosch, J.; Lv, Y.; Thabut, D.; et al. Effects of Early Placement of Transjugular Portosystemic Shunts in Patients With High-Risk Acute Variceal Bleeding: A Meta-analysis of Individual Patient Data. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 193–205.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, W.J.; Hwang, W.-T.; Karasic, T.B.; McCarthy, A.M.; Kaplan, D.E. Comparison of nivolumab and sorafenib for first systemic therapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh B cirrhosis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kudo, M.; Merle, P.; Meyer, T.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Xu, R.; Edeline, J.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Ren, Z.; et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab versus lenvatinib plus placebo for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (LEAP-002): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Biolato, M.; Della Corte, C.; Maida, M.; Barbara, M.; Basso, M.; Vavassori, S.; Craxì, A.; Grieco, A.; et al. Predictors of survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who permanently discontinued sorafenib. Hepatology 2015, 62, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, F.; Anders, M.; Bermudez, C.; Demirdjian, E.; Varón, A.; Palazzo, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Beltrán, O.; da Fonseca, L.G.; Ridruejo, E.; et al. Liver decompensation is a frequent cause of treatment discontinuation and prognostic factor in intermediate-advanced HCC. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 28, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Koroki, K.; Kanzaki, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Kiyono, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kanogawa, N.; Saito, T.; Ogasawara, S.; Ooka, Y.; et al. Impact of acute decompensation on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kudo, M.; Venook, A.P.; Ye, S.L.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Chen, X.P.; Dagher, L.; Furuse, J.; Geschwind, J.H.; de Guevara, L.L.; et al. Observational registry of sorafenib use in clinical practice across Child-Pugh subgroups: The GIDEO study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara MG Slagter, A.E.; Nuttall, C.; Frizziero, M.; Pihlak, R.; Lamarca, A.; Tariq, N.; Valle, J.W.; Hubner, R.A.; Knox, J.J.; Amir, E. Sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced Child-Pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma—A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampaki, M.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Cholongitas, E. Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Decompensated Cirrhotic Patients: A Comprehensive Overview. Cancers 2023, 15, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Gaetano, V.; Pallozzi, M.; Cerrito, L.; Santopaolo, F.; Stella, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2024, 16, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071388
De Gaetano V, Pallozzi M, Cerrito L, Santopaolo F, Stella L, Gasbarrini A, Ponziani FR. Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071388
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Gaetano, Valeria, Maria Pallozzi, Lucia Cerrito, Francesco Santopaolo, Leonardo Stella, Antonio Gasbarrini, and Francesca Romana Ponziani. 2024. "Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071388
APA StyleDe Gaetano, V., Pallozzi, M., Cerrito, L., Santopaolo, F., Stella, L., Gasbarrini, A., & Ponziani, F. R. (2024). Management of Portal Hypertension in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Systemic Treatment: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Cancers, 16(7), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071388







