Long-Term Oral Tamoxifen Administration Decreases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus of Female Long-Evans Rats
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Tamoxifen Self-Administration
2.3. Blood Analysis
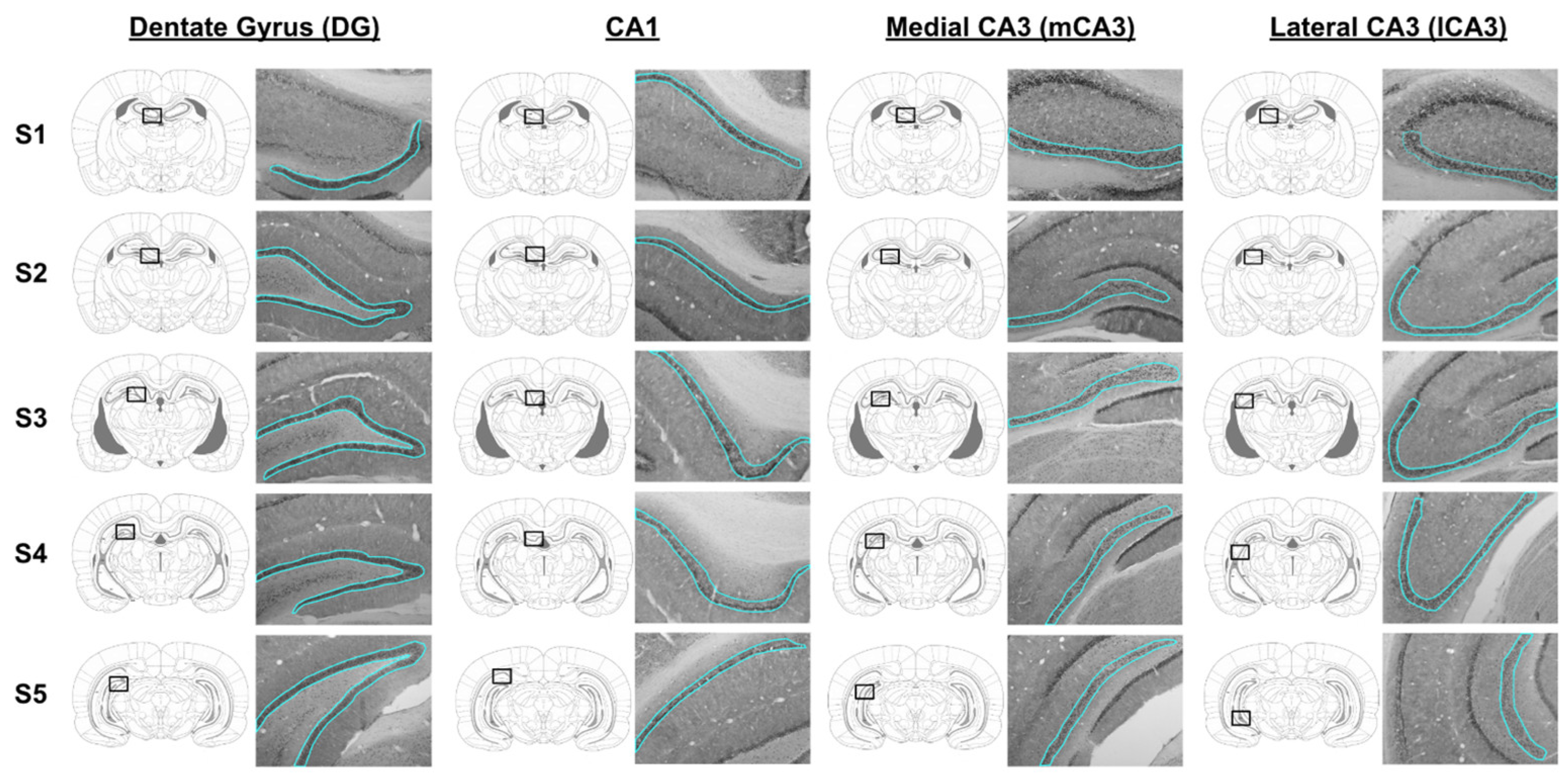
2.4. Tissue Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. BDNF Densitometry Analysis in Hippocampus
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight
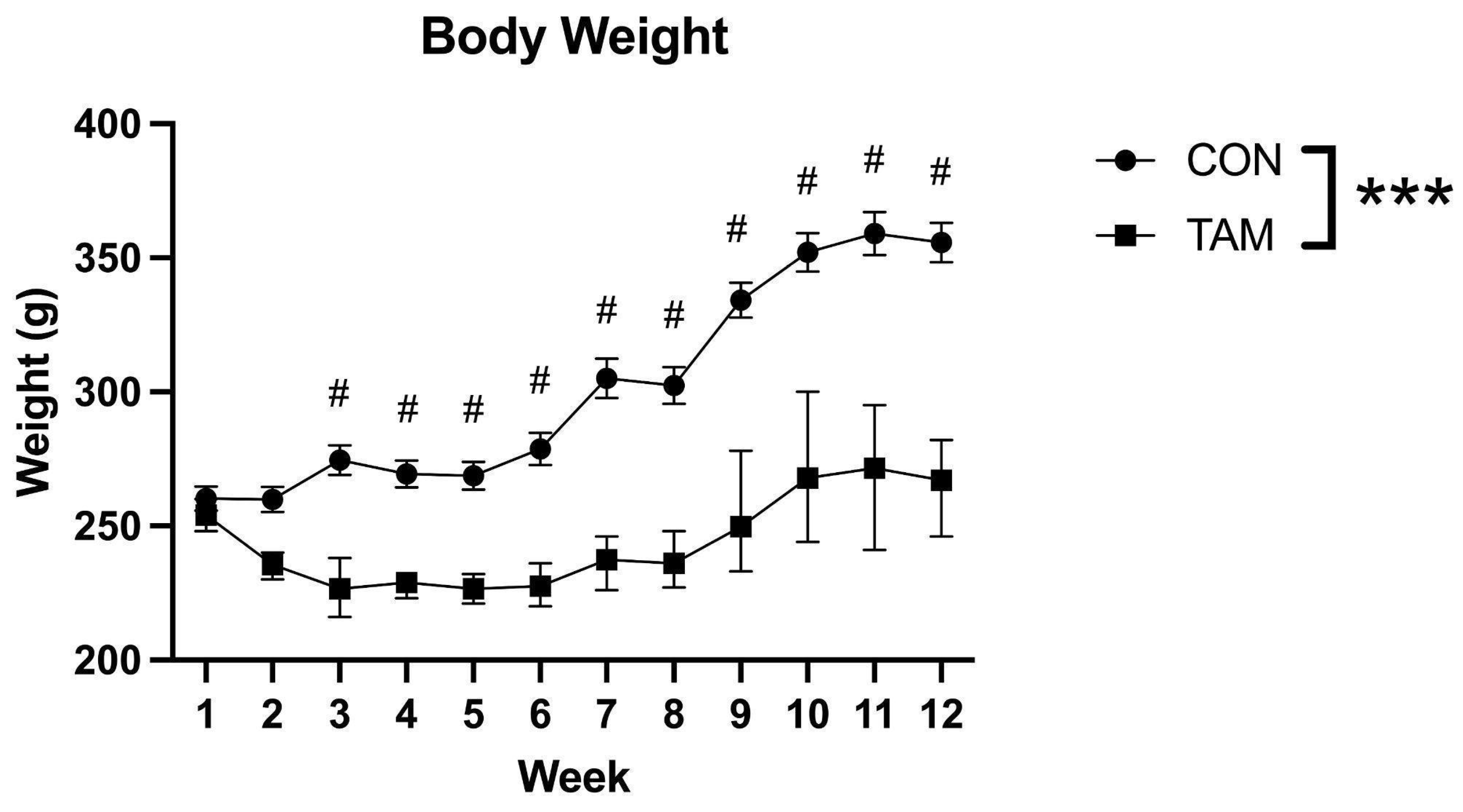
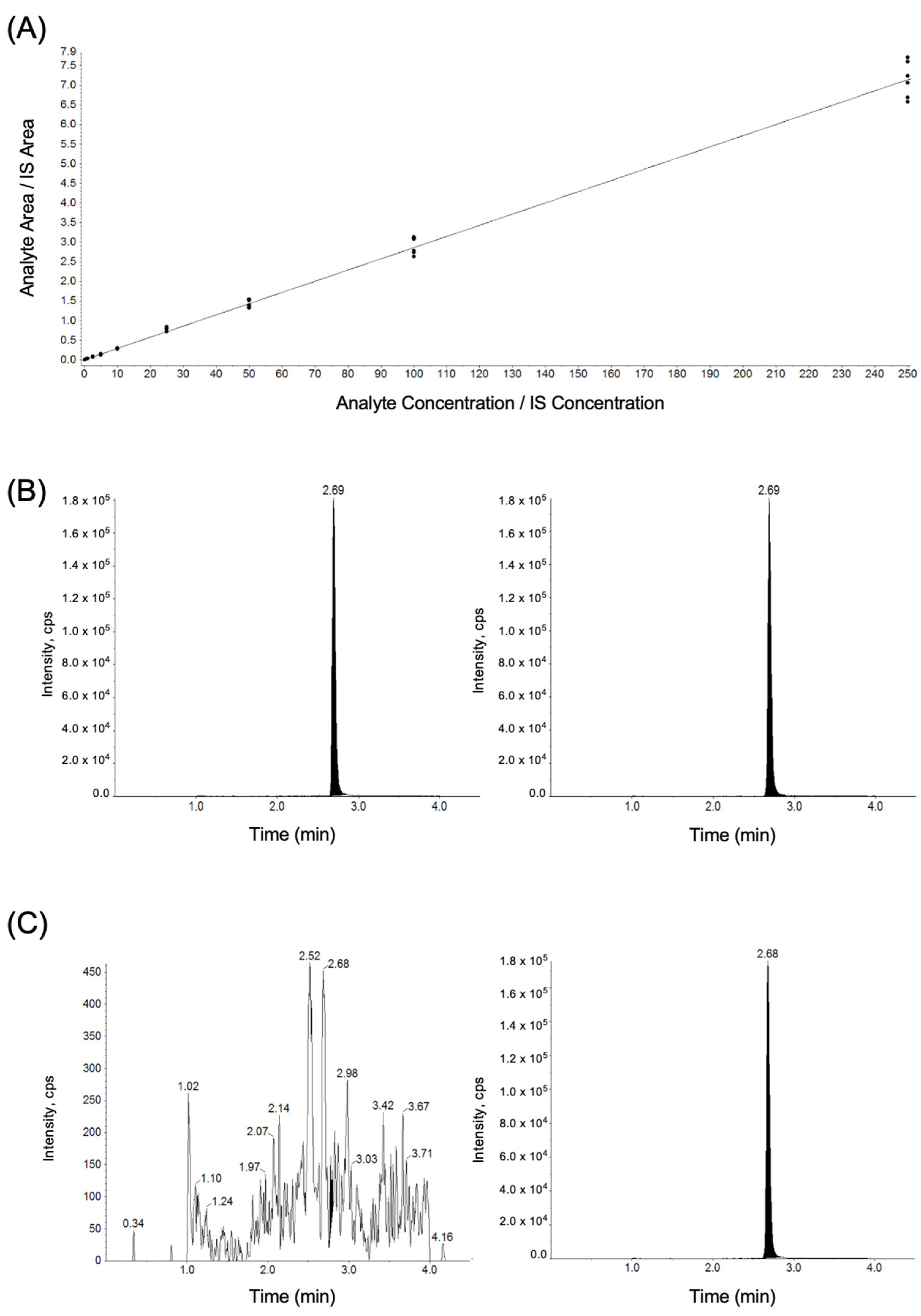
3.2. Plasma Tamoxifen Levels
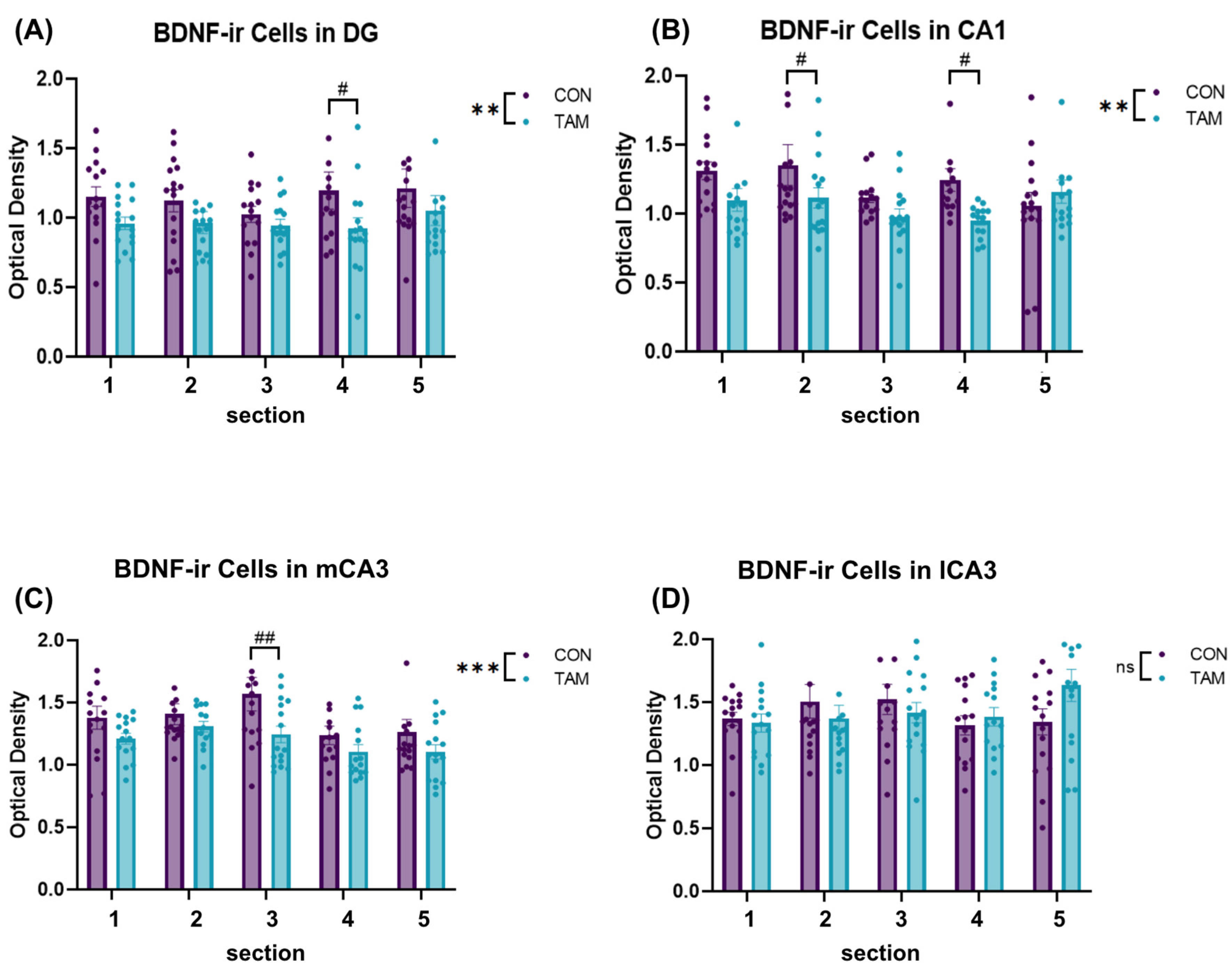
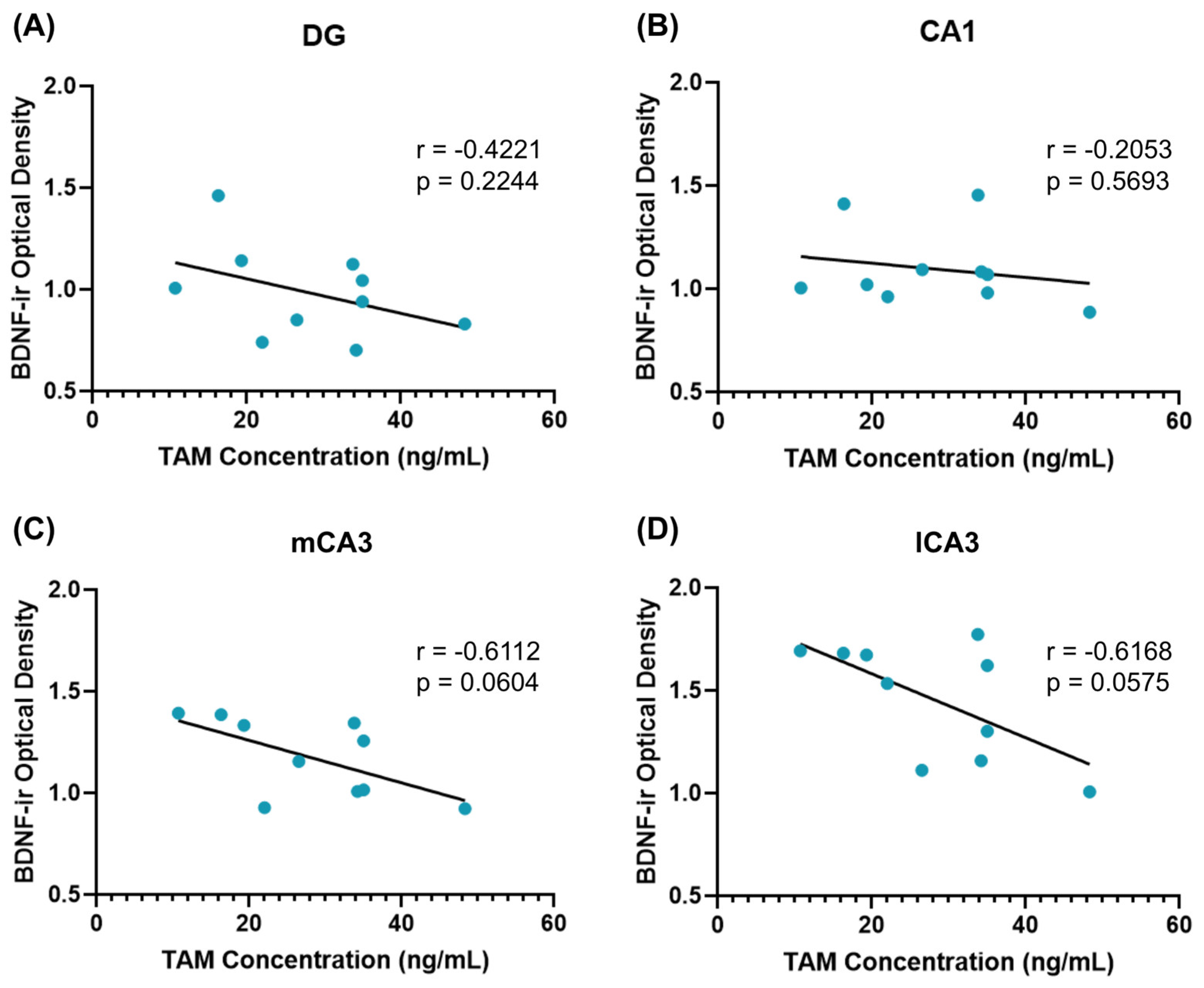
3.3. BDNF Immunoreactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jebahi, F.; Sharma, S.; Bloss, J.E.; Wright, H.H. Effects of tamoxifen on cognition and language in women with breast cancer: A systematic search and a scoping review. Psycho-Oncol. 2021, 30, 1262–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakia, K.C.; Henry, N.L. Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy in Premenopausal Women with Breast Cancer. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. H&O 2015, 13, 663–672. [Google Scholar]
- Novick, A.M.; Scott, A.T.; Epperson, C.N.; Schneck, C.D. Neuropsychiatric Effects of Tamoxifen: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 59, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi-Malekabadi, H.; Pourganji, M.; Zabihi, H.; Saeedjalali, M.; Hosseini, M. Tamoxifen antagonizes the effects of ovarian hormones to induce anxiety and depression-like behavior in rats. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2015, 73, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.E.; Tierney, M.C.; Wu, W.; Pritchard, K.I.; Rochon, P.A. Endocrine treatment-associated cognitive impairment in breast cancer survivors: Evidence from published studies. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, E.A.; Rochon, P.A.; Moineddin, R.; Lee, P.E.; Wu, W.; Pritchard, K.I.; Tierney, M.C. Cognitive sequelae of endocrine therapy in women treated for breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 168, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boele, F.W.; Schilder CM, T.; de Roode, M.-L.; Deijen, J.B.; Schagen, S.B. Cognitive functioning during long-term tamoxifen treatment in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Menopause 2015, 22, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellon, S.A.; Ganz, P.A.; Bower, J.E.; Petersen, L.; Abraham, L.; Greendale, G.A. Neurocognitive Performance in Breast Cancer Survivors Exposed to Adjuvant Chemotherapy and Tamoxifen. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2004, 26, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejbak, L.; Vrbancic, M.; Crossley, M. Endocrine therapy is associated with low performance on some estrogen-sensitive cognitive tasks in postmenopausal women with breast cancer. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2010, 32, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, D.; Ye, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K. Decision-making impairments in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Horm. Behav. 2014, 66, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, V.; Shilling, V.; Fallowfield, L.; Howell, A.; Hutton, S. Does hormone therapy for the treatment of breast cancer have a detrimental effect on memory and cognition? A pilot study. Psycho-Oncol. 2004, 13, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breckenridge, L.M.; Bruns, G.L.; Todd, B.L.; Feuerstein, M. Cognitive limitations associated with tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors in employed breast cancer survivors. Psycho-Oncol. 2012, 21, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahles, T.A.; Root, J.C.; Ryan, E.L. Cancer- and Cancer Treatment–Associated Cognitive Change: An Update on the State of the Science. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wu, C.F.; Shi, B.; Xu, Y.M. Tamoxifen and toremifene cause impairment of learning and memory function in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 71, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvassori, S.S.; Borges, C.P.; Varela, R.B.; Bavaresco, D.V.; Bianchini, G.; Mariot, E.; Arent, C.O.; Resende, W.R.; Budni, J.; Quevedo, J. The different effects of lithium and tamoxifen on memory formation and the levels of neurotrophic factors in the brain of male and female rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 134, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Zamora, D.A.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; González-Burgos, I. Effects of selective estrogen receptor modulators on allocentric working memory performance and on dendritic spines in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons of ovariectomized rats. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechinel-Recco, K.; Valvassori, S.S.; Varela, R.B.; Resende, W.R.; Arent, C.O.; Vitto, M.F.; Luz, G.; de Souza, C.T.; Quevedo, J. Lithium and tamoxifen modulate cellular plasticity cascades in animal model of mania. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kight, K.E.; McCarthy, M.M. Sex differences and estrogen regulation of BDNF gene expression, but not propeptide content, in the developing hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, K.M.; Kim, J.; Tuscher, J.J.; Fortress, A.M. Sex steroid hormones matter for learning and memory: Estrogenic regulation of hippocampal function in male and female rodents. Learn. Mem. 2015, 22, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harte-Hargrove, L.C.; MacLusky, N.J.; Scharfman, H.E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor–estrogen interactions in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway: Implications for normal brain function and disease. Neuroscience 2013, 239, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.L.; Waters, E.M.; Romeo, R.D.; Wood, G.E.; Milner, T.A.; McEwen, B.S. Uncovering the Mechanisms of Estrogen Effects on Hippocampal Function. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 29, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolley, C.S. Estrogen-mediated structural and functional synaptic plasticity in the female rat hippocampus. Horm. Behav. 1998, 34, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Day, M.; Muñiz, L.C.; Bitran, D.; Arias, R.; Revilla-Sanchez, R.; Grauer, S.; Zhang, G.; Kelley, C.; Pulito, V.; et al. Activation of estrogen receptor-β regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity and improves memory. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.D.; Galea LA, M. Adult hippocampal cell proliferation is suppressed with estrogen withdrawal after a hormone-simulated pregnancy. Horm. Behav. 2008, 54, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. A Review and Update of Mechanisms of Estrogen in the Hippocampus and Amygdala for Anxiety and Depression Behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; MacLusky, N.J. Estrogen and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in hippocampus: Complexity of steroid hormone-growth factor interactions in the adult CNS. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2006, 27, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohrabji, F.; Lewis, D.K. Estrogen–BDNF interactions: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2006, 27, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luine, V.; Frankfurt, M. Interactions between estradiol, BDNF and dendritic spines in promoting memory. Neuroscience 2013, 239, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; MacLusky, N.J. Differential regulation of BDNF, synaptic plasticity and sprouting in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway of male and female rats. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Akaishi, T.; Matsuki, N.; Ohno, Y.; Nakazawa, K. β-Estradiol induces synaptogenesis in the hippocampus by enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor release from dentate gyrus granule cells. Brain Res. 2007, 1150, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, M.C.; Jacobs, T.F. Tamoxifen. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532905/ (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Hickman, D.; Swan, M. Use of a Body Condition Score Technique to Assess Health Status in a Rat Model of Polycystic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2010, 49, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bobin-Dubigeon, C.; Campone, M.; Rossignol, E.; Salaun, E.; Amiand, M.-B.; Bard, J.-M. New UPLC–MS/MS assay for the determination of tamoxifen and its metabolites in human plasma, application to patients. Future Science OA 2019, 5, FSO374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Raju, K.S.; Taneja, I.; Singh, S.P.; Tripathi, A.; Mishra, D.P.; Hussain, K.M.; Gayen, J.R.; Singh, S.K.; Wahajuddin, M. Simultaneous determination of centchroman and tamoxifen along with their metabolites in rat plasma using LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Krimm, R.; Hill, D.L. Maintenance of Mouse Gustatory Terminal Field Organization Is Dependent on BDNF at Adulthood. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6873–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taliaz, D.; Stall, N.; Dar, D.E.; Zangen, A. Knockdown of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in specific brain sites precipitates behaviors associated with depression and reduces neurogenesis. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 7th ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/books/the-rat-brain-in-stereotaxic-coordinates/paxinos/978-0-12-391949-6 (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, E.A.; Solheim, E.; Ueland, P.M. Distribution of tamoxifen and its metabolites in rat and human tissues during steady-state treatment. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4837–4844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pareto, D.; Alvarado, M.; Hanrahan, S.M.; Biegon, A. In vivo occupancy of female rat brain estrogen receptors by 2004, 17beta-estradiol and tamoxifen. NeuroImage 2004, 23, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klann, I.P.; Fulco BC, W.; Nogueira, C.W. Subchronic exposure to tamoxifen modulates the hippocampal BDNF/ERK/Akt/CREB pathway and impairs memory in intact female rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.M.; Saulsbery, A.I.; Sarchet, P.; Devasthali, N.; Einstein, D.; Kirby, E.D. Oral and Injected Tamoxifen Alter Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Female and Male Mice. eNeuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0422-21.2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, C.; Arcego, D.M.; Laureano, D.P.; Diehl, L.A.; Da Costa Lima, I.F.; Krolow, R.; Pettenuzzo, L.F.; Dalmaz, C.; Vendite, D. Effect of chronic administration of tamoxifen and/or estradiol on feeding behavior, palatable food and metabolic parameters in ovariectomized rats. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 119, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.M.; Schrock, S.; Bishop, M. Estrogens and antiestrogens: Actions and interactions with fluphenazine on food intake and body weight in rats. Am. J. Physiol. -Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 264, R1214–R1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Lelliott, C.J.; Tovar, S.; Kimber, W.; Gallego, R.; Virtue, S.; Blount, M.; Vázquez, M.J.; Finer, N.; Powles, T.J.; et al. Tamoxifen-Induced Anorexia Is Associated with Fatty Acid Synthase Inhibition in the Ventromedial Nucleus of the Hypothalamus and Accumulation of Malonyl-CoA. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, G.N.; Heller, H.W. Tamoxifen mimics the effects of estradiol on food intake, body weight, and body composition in rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 264, R1219–R1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, E.A.; Foley, J.J.; Clark-Vetri, R.; Raffa, R.B. Effects of repeated administration of chemotherapeutic agents tamoxifen, methotrexate, and 5-fluorouracil on the acquisition and retention of a learned response in mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 217, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, C.J.; Burgoon, L.D.; Williams, K.J.; Forgacs, A.L.; Zacharewski, T.R. Comparative temporal and dose-dependent morphological and transcriptional uterine effects elicited by tamoxifen and ethynylestradiol in immature, ovariectomized mice. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Park, J.W.; Ahn, I.S.; Diamante, G.; Sivakumar, N.; Arneson, D.; Yang, X.; Veen, J.E.; Correa, S.M. Estrogen receptor alpha in the brain mediates tamoxifen-induced changes in physiology in mice. eLife 2021, 10, e63333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, J.M.; Lauterborn, J.C.; Yan, Q.; Gall, C.M.; Varon, S. Distribution of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Protein and mRNA in the Normal Adult Rat CNS: Evidence for Anterograde Axonal Transport. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieni, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Dekkers, M.; Rauskolb, S.; Ionescu, M.S.; Deogracias, R.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Kojima, M.; Nestel, S.; Frotscher, M.; et al. BDNF and its pro-peptide are stored in presynaptic dense core vesicles in brain neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, T.; Döhring, J.; Rohr, A.; Jansen, O.; Deuschl, G. CA1 neurons in the human hippocampus are critical for autobiographical memory, mental time travel, and autonoetic consciousness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17562–17567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, E.; Miles, R. The CA3 region of the hippocampus: How is it? what is it for? how does it do it? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesner, R.P. A behavioral analysis of dentate gyrus function. In Progress in Brain Research; Scharfman, H.E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 163, pp. 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, R.F.; Stevenson, C.H.; Wilson, C.L.; Saunders, I.; Wood, E.R. The role of hippocampal subregions in memory for stimulus associations. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 215, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.-W. Are The Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Xie, X. Neurotrophic factor control of satiety and body weight. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.P.; Langan-Fahey, S.M.; Johnson, D.A.; Jordan, V.C. Metabolites, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of tamoxifen in rats and mice compared to the breast cancer patient. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 1991, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donocoff, R.S.; Teteloshvili, N.; Chung, H.; Shoulson, R.; Creusot, R.J. Optimization of tamoxifen-induced Cre activity and its effect on immune cell populations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffner, C. Intraperitoneal Injection of Tamoxifen for Inducible Cre-Driver Lines; The Jackson Laboratory: Bar Harbor, ME, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Di Giacomo, D.; Cannita, K.; Ranieri, J.; Cocciolone, V.; Passafiume, D.; Ficorella, C. Breast cancer and psychological resilience among young women. J. Psychopatology 2016, 3, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Fafouti, M.; Paparrigopoulos, T.; Zervas, Y.; Rabavilas, A.; Malamos, N.; Liappas, I.; Tzavara, C. Depression, Anxiety and General Psychopathology in Breast Cancer Patients: A Cross-sectional Control Study. In Vivo 2010, 24, 803–810. [Google Scholar]
| Tamoxifen Diet (g/Kg) | Control Diet (g/Kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| 2016, Teklad Global 16% Protein Rodent Diet 1 | 949.75 | 1000 |
| Sucrose | 49.96 | 0.00 |
| Tamoxifen USP | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| Red Food Color | 0.25 | 0.00 |
| Calibration Curve (n = 6) | Tamoxifen Concentration (ng/mL) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 250 | |
| 1 | 0.108 | 0.528 | 1.00 | 2.61 | 5.11 | 10.5 | 29.4 | 46.4 | 108 | 270 |
| 2 | 0.117 | 0.533 | 1.11 | 2.61 | 4.84 | 10.3 | 27.4 | 48.4 | 107 | 253 |
| 3 | 0.104 | 0.484 | 0.95 | 2.69 | 4.79 | 10.2 | 29.2 | 54.0 | 109 | 247 |
| 4 | 0.090 | 0.479 | 0.88 | 2.08 | 4.25 | 9.55 | 25.2 | 47.9 | 95.6 | 266 |
| 5 | 0.091 | 0.566 | 0.922 | 2.49 | 5.06 | 10.5 | 27.9 | 52.9 | 92.1 | 234 |
| 6 | 0.092 | 0.467 | 0.841 | 2.18 | 4.25 | 9.38 | 24.8 | 46.5 | 97.2 | 230 |
| Mean | 0.100 | 0.511 | 0.949 | 2.44 | 4.72 | 10.1 | 27.3 | 49.4 | 101 | 250 |
| SD | 0.011 | 0.040 | 0.096 | 2.53 | 0.382 | 0.487 | 1.95 | 3.29 | 7.35 | 16.3 |
| Accuracy (%) | 100 | 102 | 94.9 | 97.7 | 94.3 | 101 | 109 | 98.7 | 101 | 100 |
| CV (%) | 11.1 | 7.79 | 10.1 | 10.4 | 8.09 | 4.84 | 7.15 | 6.66 | 7.25 | 6.52 |
| Concentration (ng/mL) | Mean ± SD | % CV | % Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human Plasma | 100 | 101 ± 7.35 | 7.25 | 101 |
| Rat Plasma | 100 | 97.62 ± 2.01 | 2.06 | 97.6 |
| Subject | Measured Tamoxifen Concentration (ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| TAM 1 | 48.3 |
| TAM 2 | 33.8 |
| TAM 3 | 26.5 |
| TAM 4 | 35.0 |
| TAM 5 | 22.0 |
| TAM 6 | 34.2 |
| TAM 9 | 16.3 |
| TAM 10 | 10.7 |
| TAM 11 | 35.0 |
| TAM 12 | 19.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Been, L.E.; Halliday, A.R.; Blossom, S.M.; Bien, E.M.; Bernhard, A.G.; Roth, G.E.; Domenech Rosario, K.I.; Pollock, K.B.; Abramenko, P.E.; Behbehani, L.M.; et al. Long-Term Oral Tamoxifen Administration Decreases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus of Female Long-Evans Rats. Cancers 2024, 16, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071373
Been LE, Halliday AR, Blossom SM, Bien EM, Bernhard AG, Roth GE, Domenech Rosario KI, Pollock KB, Abramenko PE, Behbehani LM, et al. Long-Term Oral Tamoxifen Administration Decreases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus of Female Long-Evans Rats. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071373
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeen, Laura E., Amanda R. Halliday, Sarah M. Blossom, Elena M. Bien, Anya G. Bernhard, Grayson E. Roth, Karina I. Domenech Rosario, Karlie B. Pollock, Petra E. Abramenko, Leily M. Behbehani, and et al. 2024. "Long-Term Oral Tamoxifen Administration Decreases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus of Female Long-Evans Rats" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071373
APA StyleBeen, L. E., Halliday, A. R., Blossom, S. M., Bien, E. M., Bernhard, A. G., Roth, G. E., Domenech Rosario, K. I., Pollock, K. B., Abramenko, P. E., Behbehani, L. M., Pascal, G. J., & Kelly, M. E. (2024). Long-Term Oral Tamoxifen Administration Decreases Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus of Female Long-Evans Rats. Cancers, 16(7), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071373







