Early Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Induced Hypophysitis in Melanoma Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Characteristics of Ir-hypophysitis
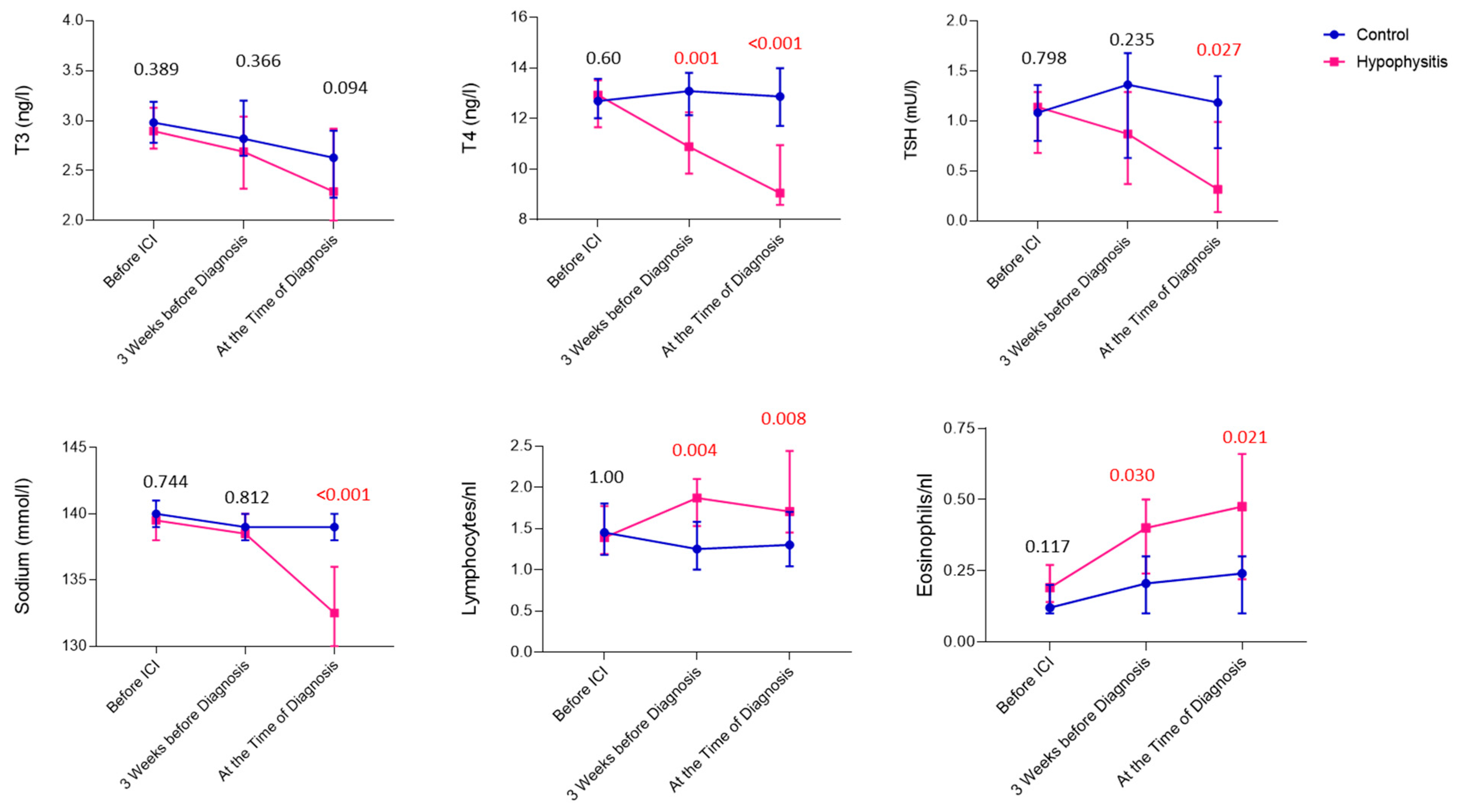
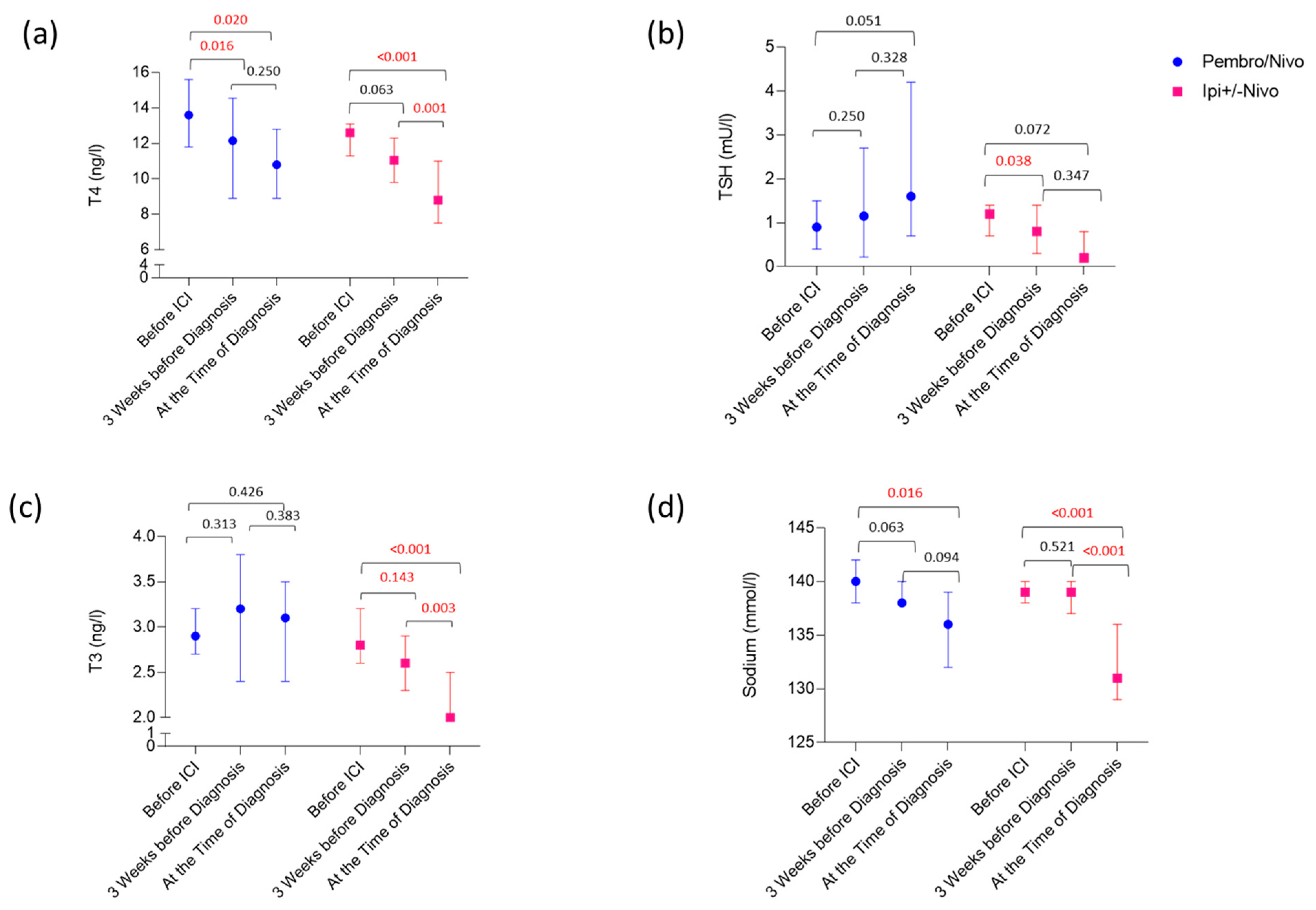
3.3. Laboratory Values Preceding and at the Time of Diagnosis of Ir-hypophysitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, E.; Newsom-Davis, T.; Morganstein, D.L. Immunotherapy-induced endocrinopathies: Assessment, management and monitoring. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 10, 2042018819896182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faje, A.; Reynolds, K.; Zubiri, L.; Lawrence, D.; Cohen, J.V.; Sullivan, R.J.; Nachtigall, L.; Tritos, N. Hypophysitis secondary to nivolumab and pembrolizumab is a clinical entity distinct from ipilimumab-associated hypophysitis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturegli, P.; Di Dalmazi, G.; Lombardi, M.; Grosso, F.; Larman, H.B.; Larman, T.; Taverna, G.; Cosottini, M.; Lupi, I. Hypophysitis Secondary to Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 Blockade: Insights into Pathogenesis from an Autopsy Series. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 3225–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Barry, W.T.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Hodi, F.S.; Min, L.; Krop, I.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filette, J.; Andreescu, C.E.; Cools, F.; Bravenboer, B.; Velkeniers, B. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Li, J.; Tan, H. Progress and Challenges of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Hypophysitis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, S.; De Remigis, A.; Callahan, M.K.; Slovin, S.F.; Wolchok, J.D.; Caturegli, P. Pituitary expression of CTLA-4 mediates hypophysitis secondary to administration of CTLA-4 blocking antibody. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 230ra45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, J.C.; Heinzerling, L.; Aberle, J.; Bähr, O.; Eigentler, T.K.; Grimm, M.O.; Grünwald, V.; Leipe, J.; Reinmuth, N.; Tietze, J.K.; et al. Combined immune checkpoint blockade (anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4): Evaluation and management of adverse drug reactions. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 57, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, D.; Johnson, J.; Goldner, W.; Addasi, N.; Desouza, C.; Kotwal, A. Adrenal Insufficiency from Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Masquerading as Sepsis. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2021, 17, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarel, F.; Gaudy, C.; Castinetti, F.; Carré, T.; Morange, I.; Conte-Devolx, B.; Grob, J.J.; Brue, T. Long-term follow-up of ipilimumab-induced hypophysitis, a common adverse event of the anti-CTLA-4 antibody in melanoma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 172, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, M.; Callahan, M.; A Postow, M.; Wolchok, J.; A Fagin, J. Endocrine-related adverse events following ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma: A comprehensive retrospective review from a single institution. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.S.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Tolaney, S.M.; Hodi, F.S.; Kaiser, U.B.; Min, L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 17–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Mahadevan, A.; Maiti, T.; Ranjan, M.; Shwetha, S.D.; Arivazhagan, A.; Saini, J. Granulomatous and lymphocytic hypophysitis–Are they immunologically distinct? APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2016, 124, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassi, E.; Angelousi, A.; Asonitis, N.; Diamantopoulos, P.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Papaxoinis, G.; Kokkinos, M.; Giovanopoulos, I.; Kyriakakis, G.; Petychaki, F.; et al. Endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors in patients with melanoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percik, R.; Shlomai, G.; Tirosh, A.; Tirosh, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Eshet, Y.; Greenberg, G.; Merlinsky, A.; Barhod, E.; Steinberg-Silman, Y.; et al. Isolated autoimmune adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency: From a rare disease to the dominant cause of adrenal insufficiency related to checkpoint inhibitors. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, Y.; Yoshino, K.; Otsuka, A.; Funakoshi, T.; Fujimura, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hata, H.; Gosho, M.; Tanaka, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Fluctuations in routine blood count might signal severe immune-related adverse events in melanoma patients treated with nivolumab. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 88, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Maruyama, H.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Okiyama, N.; Watanabe, R.; Fujimoto, M.; Fujisawa, Y. Correlation between blood cell count and outcome of melanoma patients treated with anti-PD-1 antibodies. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyasu, R.; Horiike, A.; Yoshizawa, T.; Dotsu, Y.; Koyama, J.; Saiki, M.; Sonoda, T.; Nishikawa, S.; Kitazono, S.; Yanagitani, N.; et al. adrenal insufficiency related to anti-programmed Death-1 therapy. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4229–4232. [Google Scholar]
- Torino, F.; Barnabei, A.; Paragliola, R.M.; Marchetti, P.; Salvatori, R.; Corsello, S.M. Endocrine side-effects of anti-cancer drugs: mAbs and pituitary dysfunction: Clinical evidence and pathogenic hypotheses. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, R153–R164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Dalmazi, G.; Ippolito, S.; Lupi, I.; Caturegli, P. Hypophysitis induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: A 10-year assessment. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 14, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessel, S.; Weiss, S.A.; Austin, M.; Mahajan, A.; Etts, K.; Zhang, L.; Aizenbud, L.; Perdigoto, A.L.; Hurwitz, M.; Sznol, M.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Hypophysitis and Patterns of Loss of Pituitary Function. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 836859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Lai, Z.M.; Spain, L.; Greener, V.; Turajlic, S.; Larkin, J.; Morganstein, D.L. Predicting development of ipilimumab-induced hypophysitis: Utility of T4 and TSH index but not TSH. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwama, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Okada, N.; Okuji, T.; Ito, M.; Onoue, T.; Goto, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsunekawa, T.; et al. Pituitary dysfunction induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors is associated with better overall survival in both malignant melanoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma: A prospective study. J. Immuno Ther. Cancer 2020, 8, e000779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyders, T.; Chakos, D.; Swami, U.; Latour, E.; Chen, Y.; Fleseriu, M.; Milhem, M.; Zakharia, Y.; Zahr, R. Ipilimumab-induced hypophysitis, a single academic center experience. Pituitary 2019, 22, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizaki, T.; Kameda, H.; Oba, C.; Yong Cho, K.; Nakamura, A.; Miyoshi, H.; Osawa, T.; Shinohara, N.; Atsumi, T. Nivolumab-induced hypophysitis causing secondary adrenal insufficiency after transient ACTH elevation. Endocr. J. 2019, 66, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Urai, S.; Motomura, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Ohmachi, Y.; Kobatake, M.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Oi-Yo, Y.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Fluctuations in serum adrenocorticotropic hormone concentration may predict the onset of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related hypophysitis. J. Immuno Ther. Cancer 2024, 12, e008634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control (40) | Ir-Hypophysitis (40) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | |||
| Median (Range) | 59 (17–77) | 59 (20–77) | 0.8 |
| n(%) | n(%) | ||
| Gender | 1.0 | ||
| Male | 27 (68) | 27 (68) | |
| Female | 13 (32) | 13 (32) | |
| Type of ICI | 1.0 | ||
| Pembro/Nivo | 9 (23) | 9 (23) | |
| Ipi+/−Nivo | 31 (77) | 31 (77) | |
| Other irAEs | 1.0 | ||
| Yes | 20 (50) | 20 (50) | |
| No | 20 (50) | 20 (50) | |
| CRP at Baseline | 0.06 | ||
| Normal | 19 (48) | 27 (68) | |
| Elevated | 20 (50) | 11 (28) | |
| Missing | 1 (2) | 2 (4) | |
| LDH at Baseline | 1.0 | ||
| Normal | 33 (83) | 33 (83) | |
| Elevated | 7 (17) | 6 (15) | |
| Missing | 1 (2) | ||
| PFS (Months) | 0.2 | ||
| Median (95%CI) | 7 (15–36) | 17 (19–41) | |
| OS (Months) | 0.3 | ||
| Median (95%CI) | 32 (30–51) | 48 (38–60) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitri, F.; Machiraju, D.; Naoum, C.; Hassel, J.C. Early Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Induced Hypophysitis in Melanoma Patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071340
Mitri F, Machiraju D, Naoum C, Hassel JC. Early Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Induced Hypophysitis in Melanoma Patients. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitri, Fouad, Devayani Machiraju, Christina Naoum, and Jessica C. Hassel. 2024. "Early Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Induced Hypophysitis in Melanoma Patients" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071340
APA StyleMitri, F., Machiraju, D., Naoum, C., & Hassel, J. C. (2024). Early Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Induced Hypophysitis in Melanoma Patients. Cancers, 16(7), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071340







