Simple Summary
In this literature review, we explore the milestone events from the discovery of BRAF mutations to present-day clinical intervention strategies. We delve into the role of the BRAF gene in various cancer types such as melanoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and thyroid cancer. Additionally, we reviewed clinical trials that led to the FDA approval of therapeutic regimens as monotherapy or, more recently, as combinatorial approaches to treat cancer types harboring BRAF hotspot mutations.
Abstract
Since their discovery in 2002, BRAF mutations have been identified as clear drivers of oncogenesis in several cancer types. Currently, their incidence rate is nearly 7% of all solid tumors with BRAF V600E constituting approximately 90% of these diagnoses. In melanoma, thyroid cancer, and histiocytic neoplasms, BRAF hotspot mutations are found at a rate of about 50%, while in lung and colorectal cancers they range from 3% to 10% of reported cases. Though present in other malignancies such as breast and ovarian cancers, they constitute a small portion of diagnoses (<1%). Given their frequency along with advancements in screening technologies, various methods are used for the detection of BRAF-mutant cancers. Among these are targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) on tumor tissue or circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and immunohistochemistry (IHC)-based assays. With advancements in detection technologies, several approaches to the treatment of BRAF-mutant cancers have been taken. In this review, we retrace the milestones that led to the clinical development of targeted therapies currently available for these tumors.
1. Introduction
Located on chromosome 7q34, V-Raf Murine Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog B (BRAF) codes for a serine/threonine protein kinase (BRAF), which belongs to the rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) protein family that also includes ARAF and CRAF [1]. These proteins are direct activators of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway as well as effectors of rat sarcoma (RAS) proteins (Figure 1) [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Importantly, this pathway plays a key role in cell growth and fate in normal cells as well as in cancerous cells.
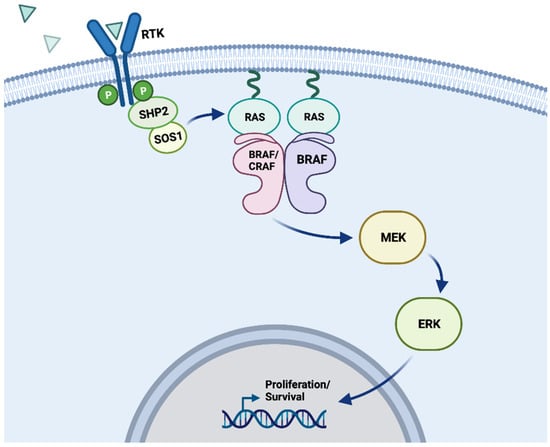
Figure 1.
MAPK signaling pathway. Schematic depicting the physiological activation of BRAF within the MAPK signaling pathway. Position of a wild-type BRAF kinase dimer (either BRAF/BRAF or BRAF/CRAF) within the MAPK signaling pathway. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) receive signaling from ligands (indicated by blue triangles), which then begin a signaling cascade that passes through RAS, RAF, MEK, ERK, and into the nucleus to impact cell proliferation and survival. In a wild-type cell, these processes can be activated and inactivated through regulation pathways that conserve typical metabolic order, but oncogenic mutations to these kinases can disrupt the cell’s ability to control these signals [10]. “Created with BioRender.com”.
RAF proteins contain three conserved regions (CR) with differing functionalities (Figure 2). The CR1 domain is divided into two subdomains: a cysteine-rich domain (CRD) involved with RAF kinase domain autoinhibition and needed for RAS protein interaction, and a RAS-binding domain which serves as the interface for RAS proteins [11]. The CR2 domain functions as an inhibitor of RAS protein binding and RAF activation [12] and the CR3 domain possesses serine and threonine-mediated kinase activity [13].

Figure 2.
Secondary structure of BRAF. [Top] Locus of BRAF gene on chromosome 7q34. [Middle] Secondary structure of the BRAF protein from amino acid 1 to 766, with conserved regions (CR) 1–3 and functional domains including the RAS-binding domain (RBD), cysteine-rich domain (CRD), phosphate binding loop (PL), catalytic loop (CL), and activation loop (AL). [Bottom] Representation of the 18 exons that make up BRAF, with the number of each exon’s first base pair specified next to the gene (only counting the translated sequence, omitting UTR and flanking sequences). “Created with BioRender.com”.
Early experiments investigating the role of BRAF in embryonic development showed that targeted disruption in the BRAF gene leads to an embryonic lethal phenotype due to vascular defects during mid-gestation [14]. Unlike ARAF or CRAF knockout mice, BRAF knockout mice display significantly enlarged blood vessels, an increased number of endothelial precursor cells, and apoptotic death of endothelial cells [14]. This revolutionary study was the first to establish BRAF as a vital signaling factor for the development of the vascular system and, in 2002, the first evidence of an association between BRAF gene mutations and human cancer was described [15] (Figure 3).
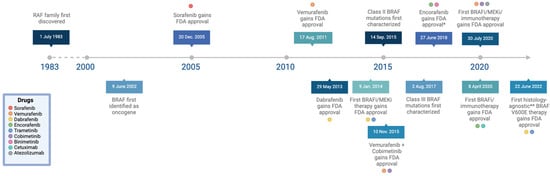
Figure 3.
Timeline of key advancements in the understanding of BRAF mutations: breakthroughs in research, FDA approvals for novel treatment options, and the discovery of the three classes of BRAF mutations [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. (* Encorafenib not approved for monotherapeutic treatment, only in combination with other drugs.) (** Histology-agnostic except for BRAF V600E-mutant CRC.) Adapted from “Icon Pack—Timelines (Horizontal)”, by BioRender.com (2024). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates.
Since then, BRAF mutations currently account for approximately 7% of all human solid tumors. Notably, BRAF mutations are seen at particularly high rates in melanoma, colorectal cancer (CRC), lung cancer, and papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) [15,26,27,28,29,30,31] (Figure 4a). Specifically, BRAF-activating mutations are primarily limited to the kinase domain, encompassing exons 11 to 15 [32] (Figure 4b). Among the various BRAF mutations, exon 15 p.V600E is by far the most prevalent [15] (Figure 4b).

Figure 4.
Frequency and types of BRAF alterations across solid tumors. (a) Prevalence of BRAF mutations across various cancer histologies (presented as absolute counts). Only published studies on solid tumors with >100 samples, available on cBioPortal [33], were included. The frequency of BRAF mutations varies from around 1% in cancer types such as esophageal, appendiceal, and gallbladder cancers to up to 35% in melanoma. (b) Lollipop diagram depicting BRAF mutations identified in several cancer types. The most prevalent mutation, V600E, is localized in the kinase domain and has been frequently reported in melanoma, thyroid, colorectal, and non-small-cell lung cancer. BRAF mutations that mapped in the RAF-like RAS binding and C1 domains are also depicted. These mutations are very rare, their oncogenic potential is mainly unclear, and they are found in a variety of histologies.
Given over 200 BRAF-mutant alleles have been identified in human tumors [25], these mutations have been divided into three classes depending on the activity of the BRAF protein present [25,31,34,35,36].
Of the three classes of mutations, class I is the most common given it includes exon 15 p.V600 alterations. By inducing elevated levels of kinase activity, these mutations lead to the activation of the MEK/ERK pathways in a manner that is independent of protein dimerization and RAS activation [25,31,34,35,36]. Class II mutations, like class I mutations, are RAS-independent and include gene fusions as well as various point mutations (exon 11 p.G464E/V, exon 11 p. G469A/R/V, exon 15 p. L597Q/V, and exon 15 p.K601E/N/T). However, unlike class I mutations, class II alterations require protein dimerization to induce MEK/ERK pathway activation and they promote both intermediate and high kinase activity [25,31,34,35,36]. In contrast, class III mutations are RAS-dependent and exhibit both increased affinity for RAS-GTP as well as increased binding with CRAF when compared to BRAF wild-type (WT), leading to hyperactivation of the MEK/ERK pathway [25] (Figure 5).
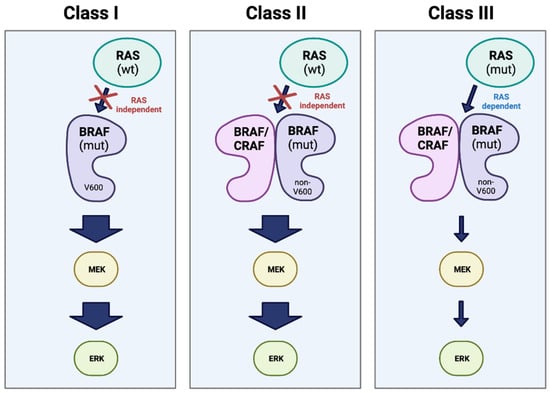
Figure 5.
Classes of BRAF mutation. Representation of the three major classes of oncogenic mutations in BRAF. Class I involves a RAS-independent, kinase-active BRAF monomer with a V600 mutation. Classes II and III are non-V600 mutations, and both act as dimers with either CRAF or a second BRAF. However, Class II is RAS-independent and results in high kinase activity, while Class III is dependent on mutant RAS and results in little to no kinase activity (represented in the figure by arrow thickness) [25,37,38]. “Created with BioRender.com”.
2. BRAF Mutations in Cancer
2.1. Melanoma
BRAF mutations are highly prevalent in melanomas, ranging from approximately 40% to 60% of all reported cases [39]. Of these alterations, 97% occur at exon 15 (codon 600) [40] with up to 90% being just the p.V600E mutant. This mutant arises from a transverse mutation in nucleotide 1799 turning a T to an A (c.1799T>A), ultimately resulting in the valine to glutamic acid substitution (p.V600E) observed [41]. From an epidemiology standpoint, BRAF-mutant melanomas often occur in younger patients, frequently possessing a superficial diffusion or nodular morphology. Unlike WT cases, BRAF-mutant melanomas are more prone to brain metastasis [26,42] and are often localized in areas with limited sun damage [43].
Initially, tumors harboring the V600E mutation were not treated differently than those with BRAF WT. However, given the significantly shorter response to conventional chemotherapy/radiotherapy, a shift in treatment approach was necessary.
Thus came the rise of RAF inhibitors, developed to explore the possibility of targeted therapy in this context. With the onset of targeted therapies, clinical trials such as coBRIM or COLUMBUS revealed the efficacy of specialized BRAF inhibitors in cases of BRAF exon 15 p.V600-mutant melanomas [44,45]. In addition to V600E, other mutations observed at this codon are p.V600K, accounting for about 10% of cases, p.V600R (1%), p.V600M (0.3%), or p.V600D (0.1%) (Figure 4b) [41].
Though there is abundant evidence supporting the efficacy of BRAF inhibitors against the most common mutants, their effect in rarer cases has yet to be established [46]. In addition, resistance to therapy has begun to emerge in clinics. To overcome these limitations, combinatorial therapies including RAF and MEK inhibitors as well as immunotherapy have recently been explored with promising preliminary results. The COMBI-d (NCT01584648) clinical trial was the first BRAF-mutant melanoma-focused trial to evaluate the efficacy of the combination of dabrafenib plus trametinib against dabrafenib alone. Upon a 36-month follow-up, the PFS of the combination group was 22% against 12% for the dabrafenib monotherapy arm [47]. Additionally, in the phase 3 clinical trial CheckMate 067, a 6.5-year follow-up analysis revealed that the combination treatment of nivolumab and ipilimumab worked better than nivolumab alone in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma (6-year PFS 38% vs. 23% and 6.5-year overall survival (OS) of 57% vs. 43%) [48]. Currently, the standard of care for the treatment of BRAF V600E-mutant melanoma includes a combination of vemurafenib (RAFi) plus cobimetinib (MEKi) plus atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1 mAb; Table 1) [49].

Table 1.
BRAF inhibitors and combination therapies currently FDA-approved to treat BRAF mutant cancers.
2.2. Thyroid
In general, BRAF gene mutations occur more frequently in sporadic papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) such as aggressive microcarcinomas and tall-cell variant cancers in adult patients [50,51], followed by poorly differentiated carcinomas and PTC-derived anaplastic thyroid carcinomas (ATCs) [52,53,54,55]. In other thyroid lesions such as follicular or medullary carcinomas as well as benign neoplasms, BRAF mutations are very rare or never seen [52,53,54,55]. However, in general, the presence of BRAF V600E has been associated from around 18 to 87% of thyroid cancers [54,56].
Through both in vitro and in vivo work, it was believed that the V600E mutation in particular associates with an invasive thyroid cancer phenotype and promotes thyroid cancer progression [57,58]. However, a consensus on whether this can be confirmed has not been reached. Nevertheless, the presence of the BRAF exon 15p.V600E point mutation does play a critical role in the diagnostic and prognostic outlook in patients [59,60]. In addition to associated poorer outcomes and aggressive behavior [51,61,62,63] when compared to WT, BRAF mutations have been linked to a higher risk of disease recurrence and persistence [63,64]. Furthermore, other non-BRAF factors such as extrathyroidal tumor invasion, older age, lymph node and distant metastases, and being male have all been tied to poorer prognostic outcomes [53,63,65,66,67,68,69,70].
2.3. Lung Cancer
From the first report of a BRAF mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in 2011 [28], variable mutation frequencies have been reported ranging from 1.5–3.5% to 7–8% [34,71,72,73]. Among the mutations identified, class I alterations are the most prevalent, though other mutations have been reported [74]. Importantly, nearly all cases of BRAF-mutant NSCLC display strong expression of thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) and feature an adenocarcinoma morphology with a papillary growth pattern [28]. While BRAF mutations are primarily associated with a glandular morphology, some cases have been reported of these alterations in small cell carcinoma as well as varying NSCLC subtypes ranging from pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma [75,76,77].
Given the variability in the hypothesized epidemiological factors affecting the frequency and distribution of BRAF mutations in NSCLC, molecular testing through next-generation sequencing (NGS) provides the best prognostic tool for their identification [78]. In some cases, such as with smokers harboring BRAF-mutant lung cancer, the presence of such a mutation is associated with longer median progression-free survival (PFS) when compared to non-mutant groups when treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. In addition to prognostic value, BRAF mutations serve as positive predictive markers for the identification of NSCLC patients who could potentially benefit from targeted therapy [79,80,81,82]. For instance, in the lung cancer cohort of the phase II, basket, open-label AcSé trial, an objective response was observed in 43/96 patients in the BRAF V600-mutant group, while no objective response was reached in the BRAF non-V600 arm. Thus, in the case of BRAF V600-mutant NSCLC, combination therapies involving BRAF and MEK inhibitors such as dabrafenib + trametinib or encorafenib + binimetinib (currently standard of care for the management of these tumors) are effective clinical options (Table 1) [83,84].
2.4. Colorectal
Slightly more prevalent than in lung cancer, BRAF mutations are found in about 10% of CRCs [85,86]. From an epidemiology standpoint, BRAF mutations in CRCs are more commonly detected in patients aged 70 or older and in women. As for their morphology, BRAF-mutant CRCs are typically localized in the proximal colon, displaying a poorly differentiated histology characterized by serrated and mucinous components [87,88]. In contrast to the other cancer types discussed, in CRCs, non-p.V600E mutations occur at higher frequencies than BRAF p.V600E in younger patients and men, are located on the distal colon, display low-grade histology, and have a longer median OS in response to chemotherapy [89]. Lastly, BRAF-mutant CRCs often display high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) as well as a high CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP-H) [90,91,92]. Specifically, 30–50% of patients with sporadic MSI-H also possess a BRAF mutation [93]. In prognostic terms, CRC patients possessing BRAF exon 15 p.V600E mutations display lower DFS, OS, and cancer-specific survival (CSS) when compared to non-BRAF-mutant CRC regardless of disease stage or chemotherapeutic intervention [94]. Unlike the other cancer types discussed above, targeted therapy has also shown disappointing results in BRAF-mutant CRC with monotherapies being mainly inefficacious and combination therapies, including immunotherapy-based regimens, achieving ORR in just about 30% of patients [95]. Currently, the approved therapy for BRAF V600E CRC includes a combination of the second-generation RAF inhibitor encorafenib plus the anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab (Table 1) [49].
2.5. Other Cancers
Histiocytic neoplasms such as Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) and Erdheim–Chester disease (ECD) are derived from macrophage/dendritic lineages and known to be enriched for BRAF V600 mutations with frequencies up to 50% [96,97]. As such, clinical trials like the VE-BASKET study (NCT01524978), which evaluated the efficacy of vemurafenib in nonmelanoma cancers harboring BRAF V600 mutations, revealed that these mutants are highly targetable with an ORR of 61.5% in the larger cohort and an ORR of 54.5% in the ECD cohort [96].
Oncogenic mutations in BRAF are also seen at low frequencies in other cancer types (Figure 4a). For example, pediatric low-grade gliomas (PLGGs) often harbor the BRAF p.V600E point mutation. Importantly, patients with mutated tumors have poorer clinical outcomes than patients presenting with BRAF WT disease [98,99]. For example, in a longitudinal study conducted in Ontario in which PLGG patients were treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy, 69 of 405 of them were found to harbor the BRAF V600E mutation. This cohort exhibited a 10-year PFS of 27% compared to 60.2% in the BRAF WT group [99]. In contrast, the presence of the BRAF exon 15 p.V600E has no impact on prognosis in patients with glioblastoma, even when tumors harbor epithelioid morphology without isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) alterations [100].
Though frequencies are low, BRAF mutations have also been reported in both breast cancer and ovarian cancer [101].
3. Diagnostic Approaches for BRAF Mutations
3.1. Detection of Mutations
With the advancements in diagnostic technologies, a wide range of methods exist for the detection and diagnosis of BRAF-mutant cancers. Among these are sequencing-based and PCR-based methods as well as immunohistochemistry (IHC) [102,103]. Additionally, the onset of liquid biopsy testing technologies has allowed for minimally invasive genetic testing, giving the opportunity to evaluate clonal evolution as well as resistance mechanisms through the course of treatment [37,104,105,106,107]. The shift from genotyping focused on few genes with sequential testing through single-gene assays to next-generation sequencing (NGS), which scans a larger set of genes, has allowed for the detection of previously undiscovered alterations as well as increasing the likelihood of detecting rare alterations [74]. As for more frequently studied genes, NGS provides the opportunity to distinguish uncommon genotypes, which are often overlooked in hotspot PCR-based assays [108]. Furthermore, NGS allows for the identification of several classes of alterations such as fusions, amplifications, and mutations [109,110], as well as offering the potential to unveil novel alterations which have not yet been discovered.
Though DNA-based NGS is usually the main means for genotyping, its variable sensitivity to alternatively spliced transcripts and fusions renders it rather unreliable for the analysis of minute changes [111,112]. However, the exploration of RNA-based methods has allowed for the direct assessment of oncogenic RNA transcripts lacking large intronic sequences. This has enabled more sensitive and efficient analyses, leading to the detection of occult kinase fusions which are often overlooked by DNA sequencing [111,112]. In addition to being more efficient, RNA-based analysis allows for higher specificity through confirmation that some fusions produce novel chimeric transcripts while others of uncertain significance detected in DNA are not transcribed into oncogenes [113]. Given RNA sequencing can directly capture aberrant splicing byproducts, it largely outperforms DNA hybrid capture-based target enrichment, allowing for the determination of which variants lead to certain exons being skipped [114]. Though RNA-based sequencing offers many advantages when compared to DNA-based assays, RNA is often prone to clinical testing failure given its predisposition to degradation and lability [115,116]. Regarding oncogenic hotspot mutations, a DNA-based technique should be sufficient for a reliable diagnosis. RNA-based assays are instead preferable for detecting BRAF fusions which occur at low frequencies in melanoma (3%), glioma (2%) thyroid cancer (1%), pancreatic carcinoma (0.3%), NSCLC (0.2%), and colorectal cancer (0.2%) [117]. Another alternative is IHC utilizing the anti-BRAF V600E (VE1) mouse monoclonal antibody, which was generated to specifically recognize the mutated amino acid sequence from amino acids 596 to 606 [118]. Given IHC equipment is both widely available in pathology laboratories and gives much faster results than molecular biology techniques, the VE1 IHC diagnostic method provides a great alternative to conventional BRAF V600E genotyping, particularly for those tumor types in which this mutation is frequently found (e.g., melanoma, histiocytic neoplasms).
While adequate tumor tissue samples are pivotal to successful NGS, they are often not enough for comprehensive testing and collecting them can be invasive for the patient [119]. Through the use of around 3–10 mL of plasma followed by the analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), liquid biopsies can provide additional information supplementing tissue-based approaches or replace them altogether in certain instances [120]. While they serve as an alternative approach, liquid biopsies require ultra-deep sequencing (>10,000× depth) and often include fewer genes than tissue-based panels in order to balance sequencing depth and breadth [121]. This, along with the fact that ctDNA in plasma is rather scarce, results in the exclusion of less commonly altered genes as those alterations which are highly recurrent are prioritized.
3.2. Associated Biomarkers
In the case of CRC, MSI-H status may be indicative of the presence of a BRAF mutation, with co-occurrence of the two often leading to later presentation of disease as well as poorer prognosis [122]. BRAF mutations themselves have been identified as important biomarkers and are often used to predict a therapeutic response. In some cases such as advanced melanoma, the presence of a BRAF mutation actually improves patient prognostic outlook [123], while in other types such as colorectal cancer, the finding of a BRAF V600E mutation is associated with resistance to standard therapy and is overall a biomarker of poor prognosis [124].
The prevalence of BRAF mutations in certain cancer types varies by a range of factors including age. In some cancers such as advanced melanoma, V600 mutations occur at particularly higher rates in adolescents and young adults when compared to older adults (68% vs. 46%, p < 0.001) [125], identifying age as a potential biomarker for the presence of the BRAF V600E mutation in these tumors. As such, the therapeutic approach may vary between the two populations, with younger patients with advanced melanomas more likely than older adults to receive targeted therapy upfront based on the presence of the V600 mutation. Given this, it appears that in the case of BRAF-mutant cancers, treatments are influenced by the presence and type of BRAF mutation rather than directly by age, though precise regimens may differ by population type [126].
4. Targeted Therapies for BRAF-Mutant Cancers
Before delving into the currently available FDA-approved therapies for the treatment of BRAF-mutant tumors (summarized in Table 1), it is important to understand how BRAF inhibitors interact with the BRAF kinase itself. Like most kinases, RAFs are composed of two domains: the N-terminal and C-terminal lobes [127]. These domains are held together by a flexible hinge, and the cleft between them acts as an active site that can bind to substrates such as ATP and kinase inhibitors. Two regulatory elements of BRAF, the αC-helix and the DFG motif, are particularly relevant to the function of its inhibitors [128]. Under typical conditions, these elements can switch between inactive-OUT and active-IN conformations, but treatment with RAF inhibitors can cause allosteric structural changes that lock specific conformations into place [24,129]. These conformations can be used to categorize BRAF inhibitors into type I (αC-helix-IN/DFG-IN), type I1/2 (αC-helix-OUT/DFG-IN), and type II (αC-helix-IN/DFG-OUT) [129]. BRAF inhibitors can also be categorized by generation, with first-generation inhibitors being the least specific treatment and third-generation ones being the most recent developments.
4.1. First-Generation BRAF Inhibitors
First-generation RAF inhibitors were created prior to the discovery of the oncogenicity of BRAF mutations and were initially designed to act as ATP-competitive inhibitors of CRAF [130]. These first-generation drugs stabilize the αC-helix into the active-IN position [131]. Although several iterations of this class of drug have gone through preclinical trials, sorafenib is the only first-generation RAF inhibitor to have gained FDA approval [132]. This particular inhibitor also causes an inactive-OUT conformation of the DFG motif, meaning that it is classified as a type II inhibitor [133]. Sorafenib is not particularly effective against cells that exhibit BRAF V600E mutations; even so, its multikinase inhibition activity makes it effective enough to have been FDA-approved to treat advanced renal cell carcinoma (median overall survival [mOS] 17.8 months for the sorafenib branch vs. 15.1 months for the placebo, median progression-free survival [mPFS] 5.5 vs. 2.8 months), unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (mOS 10.7 vs. 7.9 months, mPFS 5.5 vs. 2.8 months), and metastatic differentiated thyroid carcinoma (mOS 42.8 vs. 39.4 months, mPFS 10.8 vs. 5.8 months) [16,134,135]. Even with its nonspecific approach to treatment, this pioneer drug helped break ground on a whole new approach to the treatment of BRAF-mutant cancers.
4.2. Second-Generation BRAF Inhibitors
Upon the discovery of BRAF mutations and their roles as oncogenes in 2002 by Davies et al., researchers began to develop more targeted therapies in the form of second-generation RAF inhibitors [134]. These drugs focus on inhibiting BRAF V600E, a mutation that is particularly prevalent in melanoma, thyroid cancers, and colorectal cancers [15,134]. Specifically, they bind the inactive-OUT position of the αC helix [54]. Second-generation RAF inhibitors can also be effective against other Class I BRAF mutations, which include all V600 variants and make up over 90% of all BRAF mutations [32]. Class I BRAF mutations are highly kinase-active, RAS-independent, and signal as monomers [136]. Vemurafenib became the first of these inhibitors to gain FDA approval in 2011, specifically as a monotherapy for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanomas with V600E mutations [25]. Currently, it is also used to treat BRAF V600-mutant cases of Erdheim–Chester disease [17]. Dabrafenib, which was FDA-approved as a treatment for unresectable or metastatic melanomas with V600E mutations in 2013, has a similar mechanism of action as vemurafenib and also inhibits the BRAF monomer [17]. These monotherapeutic approaches have been vital in the treatment of patients with Class I BRAF mutations. However, emerging resistance to these drugs—as well as the need for a broader range of treatment options—has led to the advent of several combination therapies [137].
4.3. Combination Therapies
A key issue with BRAF inhibitor monotherapy is that it can sometimes lead to increased activation of MEK and ERK, which are downstream of BRAF in the MAPK pathway [104]. This can reduce the efficacy of treatments and even cause secondary skin cancers to occur in some patients [138]. The development of combination therapies pairing BRAF and MEK inhibitors is meant to bypass this effect and has led to more targeted treatments for a wider range of histologies. For example, dabrafenib in combination with the MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib was first approved by the FDA in 2014 for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanomas with BRAF V600E and V600K mutations [139]. Currently, this combination is also approved to treat a variety of BRAF V600E-mutant cancers of different histologies including non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with the involvement of lymph node(s), locally advanced or metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer, pediatric low-grade glioma, and any unresectable or metastatic solid tumors with no other satisfactory treatment options. The latter of these approvals, which was granted in 2022, is an especially relevant breakthrough as it represents the first histology-agnostic treatment option for patients with BRAF V600E-mutant solid tumors [49].
Similarly, the combination of vemurafenib and the MEK1/2 inhibitor cobimetinib has been approved for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanomas with BRAF V600E and V600K mutations [18]. Despite not having been approved for monotherapeutic use, the second-generation BRAF inhibitor encorafenib is FDA-approved for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanomas with BRAF V600E and V600K mutations [140]. The combination of encorafenib and the anti-EGFR antibody cetuximab, for instance, was FDA-approved in 2020 to treat metastatic colorectal cancer with a BRAF V600E mutation after prior therapy. Combination therapies can also involve three drugs, such as in the case of vemurafenib, cobimetinib, and the PD-L1 blocking antibody atezolizumab; this trio was FDA-approved for treating unresectable or metastatic melanomas with any BRAF V600 mutation [19]. Dual BRAF and MEK inhibition is already known to improve immunity responses against tumors, so the addition of these immunotherapeutic drugs is meant to provide an additional synergistic effect for certain histologies [141]. The use of antibodies in the treatment of BRAF-mutant cancers is reflective of a growing interest in immunotherapy, both within the field of oncology and beyond it.
4.4. Third-Generation BRAF Inhibitors
Despite having promising results in the treatment of Class I BRAF mutations, second-generation RAF inhibitors are not nearly as effective against Class II and III mutations [142]. This is due to a key structural difference in the expression of these mutations; while Class I BRAF functions as a monomer, Class II and III act as homo- or hetero- and heterodimers, respectively [143]. Second-generation BRAF inhibitors such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib bind to the BRAF kinase, stabilizing the αC-helix into its inactive OUT position. This is an effective approach to inhibiting the BRAF monomers associated with Class I BRAF mutations. However, in dimers, this same αC-OUT position causes a steric strain between the inhibitor and kinase that leads to a negative allosteric effect in the second protomer [144]. As a result, the monomer-targeting second-generation inhibitors fall flat in the inhibition of dimerized non-V600 mutations. There are currently no FDA-approved BRAF inhibitors that adequately inhibit Class II and III mutations, but several third-generation BRAF inhibitors are being developed and tested in clinical trials in order to meet this need. Third-generation BRAF inhibitors are characterized by their targeting of both monomers and dimers of the BRAF kinase [142]. One example of this broader approach to treatment is the use of αC-IN RAF inhibitors, such as CEP-32496 and RAF-265 [89,145]. These drugs help to reduce steric hindrance, inhibiting both RAF protomers and reducing the overall activity of dimeric RAF [146]. Unfortunately, this same αC-IN feature also induces RAF priming, which leads to a significant increase in RAF dimerization [144]. αC-OUT inhibitors do not catalyze RAF priming to the same degree, but in cases of heightened activation of the upstream RAS, they can cause RAF priming and dimerization to increase through an effect known as inhibitor-induced paradoxical activation [147]. Future third-generation BRAF inhibitors will have to target both monomeric and dimeric BRAF, as well as avoiding paradoxical activation both upstream and downstream of BRAF.
4.5. Current Efforts in Targeting Resistance to Therapy
In response to the prevalence of patients with BRAF mutations developing resistance to treatments through the paradoxical re-activation of MEK/ERK detailed above, researchers have been working on a new class of RAF inhibitors referred to as “paradox breakers” [49]. These drugs, which were designed by making structural modifications to vemurafenib, are meant to lessen the re-activation effect that would otherwise allow tumors to develop resistance to treatment [49]. Two promising examples of this are plixorafenib and PLX904; they not only inhibit monomeric BRAF V600E-mutant cancers but can also inhibit BRAF homodimers and BRAF-CRAF heterodimers [144,148]. Plixorafenib is already undergoing testing in a phase I/IIa clinical trial on patients with BRAF class I and II mutated solid tumors [NCT02428712]. Unfortunately, these two drugs have not been found to be effective inhibitors of CRAF homodimers and ARAF dimers, which means they will most likely not be effective against class III BRAF mutations [49,149,150]. Even so, they are capable of inhibiting a wide range of targets and offer physicians a novel approach to treatment [49,149,150].
Another important aspect of treating resistance to therapy is having effective tools to use if a patient’s tumor spreads beyond the organ in which it originated. Brain metastases are particularly common for patients with melanoma, which is one of the major histologies in which BRAF mutations are found [151]. A new brain-penetrant RAF inhibitor called Compound 1a is currently being tested in preclinical research as a potential treatment option for these metastases, and is already showing promising results compared to approved BRAF and MEK inhibitors [152,153].
5. Resistance Mechanisms and Overcoming Challenges
5.1. BRAF and the MAPK Signaling Pathway
BRAF, whether wild-type or mutated, is an inextricable part of the larger MAPK signaling pathway. This means that any attempt at targeting it without disrupting other parts of the pathway can present a challenge. For example, one of the most common resistance mechanisms that tumors develop against BRAF inhibitors is the reactivation of various components of the MAPK pathway [154]. Monotherapeutic administration of BRAF inhibitors often leads to the reactivation of the MEK/ERK effector cascade, which is downstream of BRAF [155]. This is why BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination therapy has become prominent in research efforts and has led to significant improvements in patient response rates, progression-free survival, and median duration of response when compared to monotherapy [156]. As with monotherapy, the administration of combination therapies is also subject to the emergence of various mechanisms of resistance. Most of these mechanisms are again MEK/ERK-dependent, although MEK/ERK-independent variations have also been identified [157].
5.2. MEK/ERK-Dependent Resistance
MEK/ERK-dependent forms of BRAF inhibitor resistance can be further subdivided based on whether they are adaptive or acquired. Adaptive resistance occurs without new mutations arising, and its prevalence varies by tumor histology due to the unique variations in receptor expression that these cancers already possess [158]. For example, EGFR is active in both colon cancer and melanoma, but the comparatively higher levels of EGFR expression in colon cancer cause it to develop drug resistance significantly faster than in melanoma. In a similar mechanism involving HER2 and HER3 ligands, V600E thyroid cancers are able to form resistance to vemurafenib more quickly than melanoma can [159,160]. These variations in resistance highlight the importance of taking tumor histology into account when considering treatment options for BRAF-mutant cancers.
In contrast to adaptive resistance, acquired MEK/ERK-dependent resistance arises when changes are made to actual molecular switches of the MAPK pathway [161]. These changes occur as a result of selective pressures caused by treatment with kinase inhibitors. Dependent resistance can arise through alterations directly at the BRAF level, or it can begin upstream or downstream of BRAF such as at RAS, MEK1/2, and ERK 1/2 [162,163]. Similar to adaptive resistance, acquired MEK/ERK-dependent resistance can vary based on tumor histology [164]; this mechanism is more commonly found in skin, colon, and thyroid cancers, though it has also been found to occur in pancreatic, lung, and ovarian tumors [161].
As part of acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors, emerging alterations in the BRAF gene itself can also occur [165]. For example, the amplification of BRAF has been observed in dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy-resistant melanoma and colon cancer patients, with additional variations in BRAF splicing found in the melanoma patients [163,165,166,167]. Of the dabrafenib and trametinib-resistant melanoma patients, one out of five were found to have a BRAF splicing alteration associated with a lack of exons 2–10 [163]. A rarer alteration, found in 0.4% of this same subset of dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy-resistant melanomas, possessed in-frame deletion mutations related to exons 2–8 that are associated with the RAS-binding domain [168]. Deleterious mutations resulting in BRAF activation were also found in 0.6–1% of lung, pancreatic, thyroid, and ovarian cancers [161,169]. These mutations lock the αC-helix into the active-in conformation by shortening the β3/αC-helix loop, thereby facilitating the formation of BRAF dimers [161,169]. Lastly, a β3-αC deletion mutation has been found to diminish the binding abilities of BRAF inhibitors AZ628, dabrafenib, and vemurafenib by increasing the flexibility of the αC-helix [170]. These relatively novel findings show that not all acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors appears upstream or downstream of BRAF, and that some alterations are capable of directly affecting the structure and function of BRAF itself.
5.3. MEK/ERK-Independent Resistance
Although it is comparatively less common, MEK/ERK-independent resistance can also arise due to treatment with BRAF inhibitors [157]. Preclinical research has helped expand our current understanding of this category of resistance, with mechanisms ranging from the loss of phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) to changes in metabolic processes [164,171]. However, not much is known about MEK/ERK-independent resistance mechanisms in the context of BRAF/MEK inhibitor combination therapy, making this an important area for future research to target [159].
5.4. Potential New Targets for Overcoming Mechanisms of Resistance
Along with investigating BRAF and MEK/ERK in the treatment of BRAF-mutant cancers, researchers are looking into the role of other factors that may affect the emergence of resistance to BRAF inhibitors. For example, the stem cell-associated transcriptional factor POU4F1 was found to play a part in the development of malignant BRAF-activated tumors [172]. In melanoma, POU4F1 is also able to promote acquired resistance to vemurafenib through paradoxical re-activation of MEK/ERK [172]. These findings suggest that POU4F1 could be a potential new target in the treatment of BRAF-mutant melanoma, but further studies must be conducted in order to determine its therapeutic potential.
Another potential target, a PTEN pseudogene transcript called PTENP1-AS, is expressed in high levels in BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma [173]. When PTENP1-AS was targeted by investigators, the melanoma cells were resensitized to the BRAF inhibitors they had previously developed resistance to [173]. This promising relationship shows potential for future use, both as a diagnostic measure and as a method of overcoming drug resistance.
There has also been some headway on incorporating theranostic treatment options, such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), into the arsenal of approaches that can be used to treat BRAF-mutant cancers [174]. PDT involves activating a photosensitizer with a specific wavelength of light, which then interacts with molecular oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species that kill targeted cells [175]. The specificity of PDT could prove to be useful in the treatment of BRAF-mutant cancers, especially in combination with other treatment strategies. Antibody–drug conjugates can also be used in the context of BRAFi resistance tumors to target specific antigens found on tumors, which help to reduce adverse effects in apoptosis-resistant histologies such as melanoma [174].
6. Clinical Implications and Patient Outcomes
Understanding the various pathways and molecular mechanisms that affect BRAF is crucial for understanding diseases associated with its mutations. However, it is the clinical trials in which these concepts are put into practice that actually dictate their translational value in patient care. Clinical trials on BRAF-mutant cancers and associated conditions have been the basis on which FDA approvals, new standards of treatment, and novel approaches to research have been made. A table summarizing clinical trials to date concerning BRAF mutations, further subdivided by phase classification, is presented in Supplementary Table S1.
Another crucial part of patient care is understanding how well treatments can be tolerated, as this factor often dictates whether or not a person can continue medication. Often, adverse effects are dictated by how many off-target effects a drug causes, so more targeted treatments are typically associated with lower toxicity profiles than their more general counterparts [176,177]. BRAF and MEK inhibitors target their respective kinases, but their close association with the larger MAPK signaling pathway means that these treatments can impact several outcomes of cellular signaling, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and even apoptosis [178,179,180]. These effects can manifest as a variety of different symptoms in varying intensities depending on histology, dosage, mutations, and the specific drug being used [181]. For example, as mentioned previously in this review, the monotherapeutic use of BRAF inhibitors can sometimes lead to re-activation of the MAPK pathway that can lead to paradoxical oncogenesis [182]. This is the reasoning behind the development of combination therapies, but these too come with their own set of symptoms [57]. Clinical trials often report the tolerability of treatments by grading the adverse effects. However, due to variations in several aspects of clinical trials such as patient populations and types of reporting, these metrics are not meant to be directly compared across studies [183]. It is important that healthcare providers be able to consider how treatments will affect their patients, which is why many studies use meta-analyses of clinical trials in order to find a reliable way to compare treatments [184]. Below is a table summarizing the results of one such meta-analysis on the grades of adverse effects associated with BRAF mono- and combination therapies (Table 2).

Table 2.
BRAF inhibitor adverse effects. Overall incidence rate of grade 3 to grade 5 (G3–G5), and any grade, adverse effects of BRAFi and BRAFi + MEK1/2i treatments (0–50% in green, 51–75% in orange, 76–100% in red).
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
BRAF hotspot mutations are oncogenic drivers in multiple cancer types. While current approaches for treating BRAF V600-mutant solid tumors vary based on cancer type, the FDA granted accelerated approval for the use of BRAFi dabrafenib in combination with MEKi trametinib for the treatment of all unresectable or metastatic BRAF V600E-mutant solid tumors except for CRC in June 2022. For BRAF V600E-mutant CRC, the current standard of care involves targeting BRAF and EGFR through the use of encorafenib in combination with cetuximab. While BRAF inhibitors work very well in the context of class I mutations, they often lose efficacy against class I mutations as a result of ERK reactivation through RAF dimer induction. Though this ERK reactivation can be moderated through the use of vertical pathway targeting (i.e., using a BRAFi in combination with a MEKi), the formation of RAF dimers still poses a formidable challenge in clinical intervention.
In addition, since class II and III BRAF mutations also function as dimers, no approved BRAF inhibitors are currently active against these mutant tumors. As such, BRAF drug discovery seems to be moving in the direction of RAF dimer targeting, beginning with the use of “paradox breakers” designed to avoid the paradoxical induction of ERK signaling. Moreover, the recent inclusion of immunotherapy as part of the standard of care for the treatment of BRAF-mutant melanoma will be instrumental in not only understanding the effect of ERK inhibition on the tumor-immune microenvironment, but also in determining the impact of the combination of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy with MAPK inhibition. Though these advancements have shown great promise, more work is needed to assess its clinical translatability based on biomarkers and patient selection criteria.
In summary, it is clear that our understanding of BRAF and ways to target it is progressing rapidly as a result of a joint collaboration between scientists and medical professionals. In order to continue to advance in this field, it is imperative that this system be maintained to better the lives of patients with BRAF-mutant cancers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers16061215/s1, Table S1: Clinical trials on BRAF mutated cancers organized by phase.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: P.R., N.V.B. and E.C.; writing: P.R., N.V.B., V.F. and E.C.; visualization: P.R., N.V.B. and E.C.; supervision: E.C.; funding acquisition: E.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Woman’s Cancer Association Madelon Ravlin Memorial Grant Award (E.C.), the SCCC Tumor Biology Programmatic Award (E.C.), and the Lung Cancer Research Foundation (LCRF) (E.C.).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fabrizio De André, Franco Battiato, Francesco Guccini, Vinicio Capossela, Lucio Dalla, and Francesco De Gregori for their constant support. E.C. also thanks the LCRF for the 2022 William C. Rippe Award.
Conflicts of Interest
E.C. has acted as a consultant for ENTOS Inc., and has received research funding from ERASCA, InnoCare pharma, and Prelude. E.C. is also a committee member of the Clinical Biosafety Service.
References
- Matallanas, D.; Birtwistle, M.; Romano, D.; Zebisch, A.; Rauch, J.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Kolch, W. Raf family kinases: Old dogs have learned new tricks. Genes. Cancer 2011, 2, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, P.; Haser, W.; Haystead, T.A.; Vincent, L.A.; Roberts, T.M.; Sturgill, T.W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science 1992, 257, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; App, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Banerjee, P.; Brautigan, D.L.; Rapp, U.R.; Avruch, J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature 1992, 358, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodie, S.A.; Willumsen, B.M.; Weber, M.J.; Wolfman, A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science 1993, 260, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aelst, L.; Barr, M.; Marcus, S.; Polverino, A.; Wigler, M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6213–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojtek, A.B.; Hollenberg, S.M.; Cooper, J.A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell 1993, 74, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, P.H.; Viciana, P.R.; Downward, J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature 1993, 364, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Settleman, J.; Kyriakis, J.M.; Takeuchi-Suzuki, E.; Elledge, S.J.; Marshall, M.S.; Bruder, J.T.; Rapp, U.R.; Avruch, J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature 1993, 364, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Sullivan, R.J.; Yaeger, R. Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms of BRAF in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4618–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Wu, X.; Frost, J.A. B-Raf and Raf-1 are regulated by distinct autoregulatory mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16244–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Meikle, S.; Yazici, Z.; Eulitz, M.; Kolch, W. Regulation of Raf-1 activation and signalling by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.; Lee, J.; Guan, K.L. Positive and negative regulation of Raf kinase activity and function by phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3716–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, L.; Zimmer, A.M.; Beck, T.W.; Hahn, H.; Bernal, R.; Rapp, U.R.; Zimmer, A. Endothelial apoptosis in Braf-deficient mice. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecentriq [Package Insert]; Genentech, Inc.: South San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023.
- Zelboraf [Package Insert]; Hoffmann La Roche: Basel, Switzerland, 2017.
- Mekinist [Package Insert]; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Basel, Switzerland, 2023.
- Braftovi [Package Insert]; Array Biopharma Inc.: Boulder, CO, USA, 2023.
- Nexavar [Package Insert]; Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2023.
- Tafinlar [Package Insert]; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Basel, Switzerland, 2023.
- Erbitux [Package Insert]; ImClone Systems Incorporated: Bridgewater, NJ, USA, 2021.
- Rapp, U.R.; Goldsborough, M.D.; Mark, G.E.; Bonner, T.I.; Groffen, J.; Reynolds, F.H., Jr.; Stephenson, J.R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 4218–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, J. Identification and Characterization of Small-Molecule Inhibitors to Selectively Target the DFG-in over the DFG-out Conformation of the B-Raf Kinase V600E Mutant in Colorectal Cancer. Arch. Pharm. 2016, 349, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Yaeger, R.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.S.; Tao, A.; Torres, N.M.; Chang, M.T.; Drosten, M.; Zhao, H.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS. Nature 2017, 548, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Massari, F.; MacLennan, G.T.; Montironi, R. Molecular testing for BRAF mutations to inform melanoma treatment decisions: A move toward precision medicine. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhomen, N.; Marais, R. New insight into BRAF mutations in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2007, 17, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, A.; Felicioni, L.; Malatesta, S.; Grazia Sciarrotta, M.; Guetti, L.; Chella, A.; Viola, P.; Pullara, C.; Mucilli, F.; Buttitta, F. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring BRAF mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3574–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G. BRAF Mutations in Lung Cancer. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirripa, M.; Biason, P.; Lonardi, S.; Pella, N.; Pino, M.S.; Urbano, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Cremolini, C.; Corallo, S.; Pietrantonio, F.; et al. Class 1, 2, and 3 BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Detailed Clinical, Pathologic, and Molecular Characterization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3954–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Sonawane, P.; Kumar, A.; Singh, H.; Naumovich, V.; Pathak, P.; Grishina, M.; Khalilullah, H.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A.H.; et al. Challenges and Opportunities in the Crusade of BRAF Inhibitors: From 2002 to 2022. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 27819–27844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.T.; Mitchell, T.N.; Zehir, A.; Shah, R.H.; Benayed, R.; Syed, A.; Chandramohan, R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Won, H.H.; Scott, S.N.; et al. Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT): A Hybridization Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Clinical Assay for Solid Tumor Molecular Oncology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisone, D.; Friedlaender, A.; Malapelle, U.; Banna, G.; Addeo, A. A BRAF new world. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 152, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracht, J.W.P.; Karachaliou, N.; Bivona, T.; Lanman, R.B.; Faull, I.; Nagy, R.J.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Berenguer, J.; Fernandez-Bruno, M.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; et al. BRAF Mutations Classes I, II, and III in NSCLC Patients Included in the SLLIP Trial: The Need for a New Pre-Clinical Treatment Rationale. Cancers 2019, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankner, M.; Rose, A.A.N.; Rajkumar, S.; Siegel, P.M.; Watson, I.R. Classifying BRAF alterations in cancer: New rational therapeutic strategies for actionable mutations. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3183–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.G.; Malapelle, U.; Andre, F.; Paz-Ares, L.; Schuler, M.; Thomas, D.M.; Vainer, G.; Yoshino, T.; Rolfo, C. Practical Considerations for the Use of Circulating Tumor DNA in the Treatment of Patients With Cancer: A Narrative Review. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiech, M.; Leszczynski, P.; Kono, H.; Wardell, C.; Taniguchi, H. Emerging BRAF Mutations in Cancer Progression and Their Possible Effects on Transcriptional Networks. Genes 2020, 11, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, N.K.; Wilmott, J.S.; Waddell, N.; Johansson, P.A.; Field, M.A.; Nones, K.; Patch, A.M.; Kakavand, H.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Burke, H.; et al. Whole-genome landscapes of major melanoma subtypes. Nature 2017, 545, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle, M.A.; Fassunke, J.; Konig, K.; Grunewald, I.; Schlaak, M.; Kreuzberg, N.; Tietze, L.; Schildhaus, H.U.; Buttner, R.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S. Comparison of high resolution melting analysis, pyrosequencing, next generation sequencing and immunohistochemistry to conventional Sanger sequencing for the detection of p.V600E and non-p.V600E BRAF mutations. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradish, J.R.; Cheng, L. Molecular pathology of malignant melanoma: Changing the clinical practice paradigm toward a personalized approach. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Flaherty, K.T. BRAF targeted therapy changes the treatment paradigm in melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M.; Nagrial, A.M.; Haydu, L.E.; Hamilton, A.L.; Mann, G.J.; Hughes, T.M.; Thompson, J.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Kefford, R.F. Prognostic and clinicopathologic associations of oncogenic BRAF in metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Encorafenib plus binimetinib versus vemurafenib or encorafenib in patients with BRAF-mutant melanoma (COLUMBUS): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Dreno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Maio, M.; Mandala, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Combined vemurafenib and cobimetinib in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, A.; Haidar, A.; Anghel, R.M. Treating malignant melanoma when a rare BRAF V600M mutation is present: Case report and literature review. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 56, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Flaherty, K.T.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; de Braud, F.; Larkin, J.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib versus dabrafenib monotherapy in patients with metastatic BRAF V600E/K-mutant melanoma: Long-term survival and safety analysis of a phase 3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone Versus Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, A.J.; Chen, Z.; Rosen, N.; Solit, D.B. BRAF—A tumour-agnostic drug target with lineage-specific dependencies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniran, A.J.; Zhu, Z.; Gandhi, M.; Steward, D.L.; Fidler, J.P.; Giordano, T.J.; Biddinger, P.W.; Nikiforov, Y.E. Correlation between genetic alterations and microscopic features, clinical manifestations, and prognostic characteristics of thyroid papillary carcinomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Ugolini, C.; Viola, D.; Lupi, C.; Biagini, A.; Giannini, R.; Romei, C.; Miccoli, P.; Pinchera, A.; Basolo, F. BRAF(V600E) mutation and outcome of patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: A 15-year median follow-up study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Y.; Rosenbaum, E.; Clark, D.P.; Zeiger, M.A.; Umbricht, C.B.; Tufano, R.P.; Sidransky, D.; Westra, W.H. Mutational analysis of BRAF in fine needle aspiration biopsies of the thyroid: A potential application for the preoperative assessment of thyroid nodules. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Kimura, E.T.; Gandhi, M.; Biddinger, P.W.; Knauf, J.A.; Basolo, F.; Zhu, Z.; Giannini, R.; Salvatore, G.; Fusco, A.; et al. BRAF mutations in thyroid tumors are restricted to papillary carcinomas and anaplastic or poorly differentiated carcinomas arising from papillary carcinomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5399–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M.; Vasko, V.; Tallini, G.; Larin, A.; Wu, G.; Udelsman, R.; Ringel, M.D.; Ladenson, P.W.; Sidransky, D. BRAF T1796A transversion mutation in various thyroid neoplasms. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovisco, V.; Soares, P.; Sobrinho-Simoes, M. B-RAF mutations in the etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis of thyroid carcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauf, J.A.; Ma, X.; Smith, E.P.; Zhang, L.; Mitsutake, N.; Liao, X.H.; Refetoff, S.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Fagin, J.A. Targeted expression of BRAFV600E in thyroid cells of transgenic mice results in papillary thyroid cancers that undergo dedifferentiation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4238–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesa, C., Jr.; Mirza, M.; Mitsutake, N.; Sartor, M.; Medvedovic, M.; Tomlinson, C.; Knauf, J.A.; Weber, G.F.; Fagin, J.A. Conditional activation of RET/PTC3 and BRAFV600E in thyroid cells is associated with gene expression profiles that predict a preferential role of BRAF in extracellular matrix remodeling. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6521–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellevicine, C.; Migliatico, I.; Sgariglia, R.; Nacchio, M.; Vigliar, E.; Pisapia, P.; Iaccarino, A.; Bruzzese, D.; Fonderico, F.; Salvatore, D.; et al. Evaluation of BRAF, RAS, RET/PTC, and PAX8/PPARg alterations in different Bethesda diagnostic categories: A multicentric prospective study on the validity of the 7-gene panel test in 1172 thyroid FNAs deriving from different hospitals in South Italy. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellevicine, C.; Sgariglia, R.; Malapelle, U.; Vigliar, E.; Nacchio, M.; Ciancia, G.; Eszlinger, M.; Paschke, R.; Troncone, G. Young investigator challenge: Can the Ion AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2 be used for next-generation sequencing of thyroid FNA samples? Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, Y.J.; Lim, J.A.; Ahn, H.Y.; Lee, E.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Hahn, S.K.; Youn, Y.K.; Kim, K.H.; et al. The association of the BRAF(V600E) mutation with prognostic factors and poor clinical outcome in papillary thyroid cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer 2012, 118, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, Y.S. Clinicopathologic significance of BRAF V600E mutation in papillary carcinomas of the thyroid: A meta-analysis. Cancer 2007, 110, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, M.; Westra, W.H.; Tufano, R.P.; Cohen, Y.; Rosenbaum, E.; Rhoden, K.J.; Carson, K.A.; Vasko, V.; Larin, A.; Tallini, G.; et al. BRAF mutation predicts a poorer clinical prognosis for papillary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 6373–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebebew, E.; Weng, J.; Bauer, J.; Ranvier, G.; Clark, O.H.; Duh, Q.Y.; Shibru, D.; Bastian, B.; Griffin, A. The prevalence and prognostic value of BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 466–470, discussion 470–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.S.; Li, S.; Song, J.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Lee, J.C.; Rha, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Sul, J.Y.; Kweon, G.R.; Ro, H.K.; et al. Influence of the BRAF V600E mutation on expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in papillary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3667–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Giuliano, A.E.; Turner, R.R.; Gaffney, R.E.; Umetani, N.; Kitago, M.; Elashoff, D.; Hoon, D.S. Lymphatic mapping establishes the role of BRAF gene mutation in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Kim, W.B.; Rhee, Y.S.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Gong, G.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Hong, S.J.; et al. The BRAF mutation is useful for prediction of clinical recurrence in low-risk patients with conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Endocrinol. 2006, 65, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, H.; Nakashima, M.; Hayashi, T.; Hayashida, N.; Maeda, S.; Rogounovitch, T.I.; Ohtsuru, A.; Saenko, V.A.; Kanematsu, T.; Yamashita, S. Clinical implication of hot spot BRAF mutation, V599E, in papillary thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4393–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovisco, V.; Soares, P.; Preto, A.; de Castro, I.V.; Lima, J.; Castro, P.; Maximo, V.; Botelho, T.; Moreira, S.; Meireles, A.M.; et al. Type and prevalence of BRAF mutations are closely associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma histotype and patients’ age but not with tumour aggressiveness. Virchows Arch. 2005, 446, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Quiros, R.M.; Gattuso, P.; Ain, K.B.; Prinz, R.A. High prevalence of BRAF gene mutation in papillary thyroid carcinomas and thyroid tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4561–4567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imielinski, M.; Berger, A.H.; Hammerman, P.S.; Hernandez, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Hodis, E.; Cho, J.; Suh, J.; Capelletti, M.; Sivachenko, A.; et al. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell 2012, 150, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Rossi, G.; Minari, R.; Conti, A.; Friboulet, L.; Tiseo, M.; Planchard, D. BRAF in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Pickaxing another brick in the wall. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 66, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, G.; Yang, S.R.; Cocco, E.; Drilon, A. Rare molecular subtypes of lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustugun, O.T.; Khattak, A.M.; Tromborg, A.K.; Beigi, M.; Beiske, K.; Lund-Iversen, M.; Helland, A. BRAF-mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 84, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretic, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrock, A.B.; Li, S.D.; Frampton, G.M.; Suh, J.; Braun, E.; Mehra, R.; Buck, S.C.; Bufill, J.A.; Peled, N.; Karim, N.A.; et al. Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinomas Commonly Harbor Either Potentially Targetable Genomic Alterations or High Tumor Mutational Burden as Observed by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Remon, J.; Mateo, J.; Westphalen, C.B.; Barlesi, F.; Lolkema, M.P.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; Robson, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Pauli, C.; Strobel, K.; Hirschmann, A.; Printzen, G.; Aebi, S.; Diebold, J. A patient with BRAF V600E lung adenocarcinoma responding to vemurafenib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, e23–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Michielin, O.; Zimmermann, S. Dramatic response induced by vemurafenib in a BRAF V600E-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e341–e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; O’Shaughnessy, J.A.; Cowey, C.L.; Konduri, K. BRAF V600E-mutated lung adenocarcinoma with metastases to the brain responding to treatment with vemurafenib. Lung Cancer 2014, 85, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, S.; Siano, M.; Joerger, M.; Rodriguez, R.; Muller, J.; Fruh, M. Response to dabrafenib after progression on vemurafenib in a patient with advanced BRAF V600E-mutant bronchial adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2015, 87, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Cropet, C.; Montane, L.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.J.; Quantin, X.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Otto, J.; Favier, L.; Avrillon, V.; et al. Vemurafenib in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with BRAF(V600) and BRAF(nonV600) mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, T.M.; Quoix, E.; Souquet, P.J.; Barlesi, F.; Baik, C.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With BRAF V600E-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC: Updated 5-Year Survival Rates and Genomic Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Garcia, E.; Argiles, G.; Elez, E.; Tabernero, J. BRAF mutant colorectal cancer: Prognosis, treatment, and new perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malapelle, U.; Pisapia, P.; Sgariglia, R.; Vigliar, E.; Biglietto, M.; Carlomagno, C.; Giuffre, G.; Bellevicine, C.; Troncone, G. Less frequently mutated genes in colorectal cancer: Evidences from next-generation sequencing of 653 routine cases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.N.; Kopetz, E.S. BRAF mutant colorectal cancer as a distinct subset of colorectal cancer: Clinical characteristics, clinical behavior, and response to targeted therapies. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Mahoney, M.R.; Sargent, D.J.; Nelson, G.D.; Alberts, S.R.; Sinicrope, F.A.; Goldberg, R.M.; Limburg, P.J.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Grothey, A.; et al. Patient and tumor characteristics and BRAF and KRAS mutations in colon cancer, NCCTG/Alliance N0147. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.C.; Renfro, L.A.; Al-Shamsi, H.O.; Schrock, A.B.; Rankin, A.; Zhang, B.Y.; Kasi, P.M.; Voss, J.S.; Leal, A.D.; Sun, J.; et al. (Non-V600) BRAF Mutations Define a Clinically Distinct Molecular Subtype of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, E.; Benhamida, J.; Middha, S.; Zehir, A.; Mullaney, K.; Shia, J.; Yaeger, R.; Zhang, L.; Wong, D.; Villafania, L.; et al. Colorectal Carcinomas Containing Hypermethylated MLH1 Promoter and Wild-Type BRAF/KRAS Are Enriched for Targetable Kinase Fusions. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; de Reynies, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missiaglia, E.; Jacobs, B.; D’Ario, G.; Di Narzo, A.F.; Soneson, C.; Budinska, E.; Popovici, V.; Vecchione, L.; Gerster, S.; Yan, P.; et al. Distal and proximal colon cancers differ in terms of molecular, pathological, and clinical features. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, B.; Kopetz, S.; Tie, J.; Gibbs, P.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Lieu, C.H.; Agarwal, A.; Maru, D.M.; Sieber, O.; Desai, J. Impact of BRAF mutation and microsatellite instability on the pattern of metastatic spread and prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 4623–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina-Sarasqueta, A.; van Lijnschoten, G.; Moerland, E.; Creemers, G.J.; Lemmens, V.; Rutten, H.J.T.; van den Brule, A.J.C. The BRAF V600E mutation is an independent prognostic factor for survival in stage II and stage III colon cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J.; Ros, J.; Elez, E. The Evolving Treatment Landscape in BRAF-V600E-Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2022, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, E.L.; Subbiah, V.; Lockhart, A.C.; Blay, J.Y.; Puzanov, I.; Chau, I.; Raje, N.S.; Wolf, J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; Torrisi, J.; et al. Vemurafenib for BRAF V600-Mutant Erdheim-Chester Disease and Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: Analysis of Data From the Histology-Independent, Phase 2, Open-label VE-BASKET Study. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, E.L.; Durham, B.H.; Ulaner, G.A.; Drill, E.; Buthorn, J.; Ki, M.; Bitner, L.; Cho, H.; Young, R.J.; Francis, J.H.; et al. Efficacy of MEK inhibition in patients with histiocytic neoplasms. Nature 2019, 567, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbinski, C.; Nikiforova, M.N.; Hagenkord, J.M.; Hamilton, R.L.; Pollack, I.F. Interplay among BRAF, p16, p53, and MIB1 in pediatric low-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassaletta, A.; Zapotocky, M.; Mistry, M.; Ramaswamy, V.; Honnorat, M.; Krishnatry, R.; Guerreiro Stucklin, A.; Zhukova, N.; Arnoldo, A.; Ryall, S.; et al. Therapeutic and Prognostic Implications of BRAF V600E in Pediatric Low-Grade Gliomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2934–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling, F.; Schittenhelm, J. Oncogenic BRAF Alterations and Their Role in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2019, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; Iaccarino, A.; Sgariglia, R.; Nacchio, M.; Russo, G.; Gragnano, G.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G. BRAF: A Two-Faced Janus. Cells 2020, 9, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Barros, A.V.; Anjos, R.S.D.; Silva, C.C.G.; Silva, E.; Araujo, F.; Carvalho, M.V. Diagnostic accuracy of immunohistochemistry compared with molecular tests for detection of BRAF V600E mutation in ameloblastomas: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanni, I.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F.; Andreotti, V.; Bruno, W.; Ghiorzo, P. The Current State of Molecular Testing in the BRAF-Mutated Melanoma Landscape. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.A.; Ong, E.; Huang, H.J.; McPhaul, L.W.; Yoon, S.; Janku, F.; Gianoukakis, A.G. Ultrasensitive detection of BRAF V600E mutations in circulating tumor DNA of patients with metastatic thyroid cancer. Endocrine 2022, 76, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.A.; Polivka, J.; Huang, H.J.; Treskova, I.; Pivovarcikova, K.; Fikrle, T.; Woznica, V.; Dustin, D.J.; Call, S.G.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Ultrasensitive detection of BRAF mutations in circulating tumor DNA of non-metastatic melanoma. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.A.; Subbiah, V. Precision oncology for biliary tract tumors: It’s written in blood! Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, P.C.; Cote, G.J.; Hai, T.; Gule-Monroe, M.; Bui-Griffith, J.; Williams, M.D.; Hess, K.; Hofmann, M.C.; Dadu, R.; Zafereo, M.; et al. Circulating BRAF V600E Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in the Management of Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, PO.18.00173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passiglia, F.; Malapelle, U.; Normanno, N.; Pinto, C. Optimizing diagnosis and treatment of EGFR exon 20 insertions mutant NSCLC. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 109, 102438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Cappuzzo, F.; Ou, S.I.; Camidge, D.R. Targeting MET in Lung Cancer: Will Expectations Finally Be MET? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Luo, J.; Chang, J.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Drilon, A. MET-dependent solid tumours—Molecular diagnosis and targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benayed, R.; Offin, M.; Mullaney, K.; Sukhadia, P.; Rios, K.; Desmeules, P.; Ptashkin, R.; Won, H.; Chang, J.; Halpenny, D.; et al. High Yield of RNA Sequencing for Targetable Kinase Fusions in Lung Adenocarcinomas with No Mitogenic Driver Alteration Detected by DNA Sequencing and Low Tumor Mutation Burden. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4712–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, K.D.; Le, A.T.; Sheren, J.; Nijmeh, H.; Gowan, K.; Jones, K.L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Aisner, D.L.; Doebele, R.C. Comparison of Molecular Testing Modalities for Detection of ROS1 Rearrangements in a Cohort of Positive Patient Samples. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.R.; Aypar, U.; Rosen, E.Y.; Mata, D.A.; Benayed, R.; Mullaney, K.; Jayakumaran, G.; Zhang, Y.; Frosina, D.; Drilon, A.; et al. A Performance Comparison of Commonly Used Assays to Detect RET Fusions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Offin, M.; Brannon, A.R.; Chang, J.; Chow, A.; Delasos, L.; Girshman, J.; Wilkins, O.; McCarthy, C.G.; Makhnin, A.; et al. MET Exon 14-altered Lung Cancers and MET Inhibitor Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.; Hondelink, L.M.; Solleveld-Westerink, N.; Uljee, S.M.; Ruano, D.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; von der Thusen, J.H.; Ramai, S.R.S.; Postmus, P.E.; Graadt van Roggen, J.F.; et al. Optimizing Mutation and Fusion Detection in NSCLC by Sequential DNA and RNA Sequencing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmeules, P.; Boudreau, D.K.; Bastien, N.; Boulanger, M.C.; Bosse, Y.; Joubert, P.; Couture, C. Performance of an RNA-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Assay for Combined Detection of Clinically Actionable Fusions and Hotspot Mutations in NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.S.; Wang, K.; Chmielecki, J.; Gay, L.; Johnson, A.; Chudnovsky, J.; Yelensky, R.; Lipson, D.; Ali, S.M.; Elvin, J.A.; et al. The distribution of BRAF gene fusions in solid tumors and response to targeted therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Preusser, M.; Habel, A.; Sahm, F.; Ackermann, U.; Schindler, G.; Pusch, S.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Zentgraf, H.; von Deimling, A. Assessment of BRAF V600E mutation status by immunohistochemistry with a mutation-specific monoclonal antibody. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kateb, H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Steger-May, K.; Pfeifer, J.D. Identification of major factors associated with failed clinical molecular oncology testing performed by next generation sequencing (NGS). Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighl, N.B.; Page, R.D.; Raymond, V.M.; Daniel, D.B.; Divers, S.G.; Reckamp, K.L.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Dix, D.; Odegaard, J.I.; Lanman, R.B.; et al. Clinical Utility of Comprehensive Cell-free DNA Analysis to Identify Genomic Biomarkers in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose Brannon, A.; Jayakumaran, G.; Diosdado, M.; Patel, J.; Razumova, A.; Hu, Y.; Meng, F.; Haque, M.; Sadowska, J.; Murphy, B.J.; et al. Enhanced specificity of clinical high-sensitivity tumor mutation profiling in cell-free DNA via paired normal sequencing using MSK-ACCESS. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, S.; Sun, W.; Madan, R.; Lamsal, K.; Schmitt, S.; Godwin, A.K.; Kasi, A. Microsatellite Instability with BRAF V600E Associated with Delayed Presentation but Poor Survival in Stage III Colorectal Cancer. Fortune J. Health Sci. 2023, 6, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, U.; Rossi, G.; Pisapia, P.; Barberis, M.; Buttitta, F.; Castiglione, F.; Cecere, F.L.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Iaccarino, A.; Marchetti, A.; et al. BRAF as a positive predictive biomarker: Focus on lung cancer and melanoma patients. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 156, 103118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Carbonero, N.; Martinez-Useros, J.; Li, W.; Orta, A.; Perez, N.; Carames, C.; Hernandez, T.; Moreno, I.; Serrano, G.; Garcia-Foncillas, J. KRAS and BRAF Mutations as Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers for Standard Chemotherapy Response in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Single Institutional Study. Cells 2020, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooij, M.K.; Wetzels, M.; Aarts, M.J.B.; van den Berkmortel, F.; Blank, C.U.; Boers-Sonderen, M.J.; Dierselhuis, M.P.; de Groot, J.W.B.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Piersma, D.; et al. Age Does Matter in Adolescents and Young Adults versus Older Adults with Advanced Melanoma; A National Cohort Study Comparing Tumor Characteristics, Treatment Pattern, Toxicity and Response. Cancers 2020, 12, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.A.; Subbiah, V. Precision oncology for BRAF-mutant cancers with BRAF and MEK inhibitors: From melanoma to tissue-agnostic therapy. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, H.; Therrien, M. Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornev, A.P.; Taylor, S.S. Dynamics-Driven Allostery in Protein Kinases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoulia, Z.; Gavathiotis, E.; Poulikakos, P.I. New perspectives for targeting RAF kinase in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Jackson, C.A.; Eyers, P.A.; Cohen, P.; Goedert, M.; Boyle, F.T.; Hewitt, N.; Plant, H.; Hedge, P. Paradoxical activation of Raf by a novel Raf inhibitor. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. FDA-approved small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adnane, L.; Trail, P.A.; Taylor, I.; Wilhelm, S.M. Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006, Nexavar), a dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases VEGFR/PDGFR in tumor vasculature. Methods Enzymol. 2006, 407, 597–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, R.S.; He, P.; Modi, V.; Duong-Ly, K.C.; Ma, H.; Peterson, J.R.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr.; Levy, R.M. Conformational analysis of the DFG-out kinase motif and biochemical profiling of structurally validated type II inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer; Amgen. Study of BAY43-9006 in Patients with Unresectable and/or Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer; Bayer: Bayer Leverkusen, Germany; Amgen: Southend Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tabernero, J.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Cassidy, J.; Sobrero, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Kohne, C.H.; Tejpar, S.; Gladkov, O.; Davidenko, I.; Salazar, R.; et al. Sorafenib in combination with oxaliplatin, leucovorin, and fluorouracil (modified FOLFOX6) as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: The RESPECT trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Puzanov, I.; Kim, K.B.; Ribas, A.; McArthur, G.A.; Sosman, J.A.; O’Dwyer, P.J.; Lee, R.J.; Grippo, J.F.; Nolop, K.; et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraiso, K.H.; Fedorenko, I.V.; Cantini, L.P.; Munko, A.C.; Hall, M.; Sondak, V.K.; Messina, J.L.; Flaherty, K.T.; Smalley, K.S. Recovery of phospho-ERK activity allows melanoma cells to escape from BRAF inhibitor therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussemart, L.; Routier, E.; Mateus, C.; Opletalova, K.; Sebille, G.; Kamsu-Kom, N.; Thomas, M.; Vagner, S.; Favre, M.; Tomasic, G.; et al. Prospective study of cutaneous side-effects associated with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib: A study of 42 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotellic [Package Insert], Genentech, Inc.: South San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015.
- Ribas, A.; Lawrence, D.; Atkinson, V.; Agarwal, S.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Carlino, M.S.; Fisher, R.; Long, G.V.; Hodi, F.S.; Tsoi, J.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition with PD-1 blockade immunotherapy in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, H.; Ding, H.; Qian, J.; Lizaso, A.; Lin, J.; Han-Zhang, H.; Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H. The association between BRAF mutation class and clinical features in BRAF-mutant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoulia, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ahmed, T.A.; Xin, Q.; Bollard, J.; Krepler, C.; Wu, X.; Zhang, C.; Bollag, G.; Herlyn, M.; et al. An Integrated Model of RAF Inhibitor Action Predicts Inhibitor Activity against Oncogenic BRAF Signaling. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertazza, L.; Barollo, S.; Radu, C.M.; Cavedon, E.; Simioni, P.; Faggian, D.; Plebani, M.; Pelizzo, M.R.; Rubin, B.; Boscaro, M.; et al. Synergistic antitumour activity of RAF265 and ZSTK474 on human TT medullary thyroid cancer cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Henry, J.R.; Kaufman, M.D.; Lu, W.P.; Smith, B.D.; Vogeti, S.; Rutkoski, T.J.; Wise, S.; Chun, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Inhibition of RAF Isoforms and Active Dimers by LY3009120 Leads to Anti-tumor Activities in RAS or BRAF Mutant Cancers. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Lavoie, H.; Sahmi, M.; David, M.; Hilt, C.; Hammell, A.; Therrien, M. RAF inhibitors promote RAS-RAF interaction by allosterically disrupting RAF autoinhibition. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Spevak, W.; Zhang, Y.; Burton, E.A.; Ma, Y.; Habets, G.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Ewing, T.; Matusow, B.; et al. RAF inhibitors that evade paradoxical MAPK pathway activation. Nature 2015, 526, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsough, E.J.; Kugel, C.H., 3rd; Vido, M.J.; Berger, A.C.; Purwin, T.J.; Goldberg, A.; Davies, M.A.; Schiewer, M.J.; Knudsen, K.E.; Bollag, G.; et al. Response and Resistance to Paradox-Breaking BRAF Inhibitor in Melanomas In Vivo and Ex Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Su, W.; Yaeger, R.; Tao, J.; Na, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Rymar, A.; Tao, A.; et al. RAF inhibitor PLX8394 selectively disrupts BRAF dimers and RAS-independent BRAF-mutant-driven signaling. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Saiag, P.; Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Arance, A.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Thomas, L.; Lesimple, T.; Mortier, L.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAF(V600)-mutant melanoma brain metastases (COMBI-MB): A multicentre, multicohort, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfill-Teixidor, E.; Iurlaro, R.; Handl, C.; Wichmann, J.; Arias, A.; Cuartas, I.; Emmenegger, J.; Romagnani, A.; Mangano, L.; Lorber, T.; et al. Activity and Resistance of a Brain-Permeable Paradox Breaker BRAF Inhibitor in Melanoma Brain Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, J.; Rynn, C.; Friess, T.; Petrig-Schaffland, J.; Kornacker, M.; Handl, C.; Emmenegger, J.; Eckmann, J.; Herting, F.; Frances, N.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of a Next-Generation Brain Permeable, Paradox Breaker BRAF Inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.H.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Zhao, X.X.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y.L. Development of small-molecule therapeutics and strategies for targeting RAF kinase in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazarian, R.; Shi, H.; Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Koya, R.C.; Lee, H.; Chen, Z.; Lee, M.K.; Attar, N.; Sazegar, H.; et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature 2010, 468, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Zhang, C.; Bollag, G.; Shokat, K.M.; Rosen, N. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010, 464, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Infante, J.R.; Daud, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Kefford, R.F.; Sosman, J.; Hamid, O.; Schuchter, L.; Cebon, J.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Hugo, W.; Kong, X.; Hong, A.; Koya, R.C.; Moriceau, G.; Chodon, T.; Guo, R.; Johnson, D.B.; Dahlman, K.B.; et al. Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Conde, C.; Ruiz-Llorente, S.; Dominguez, J.M.; Knauf, J.A.; Viale, A.; Sherman, E.J.; Ryder, M.; Ghossein, R.A.; Rosen, N.; Fagin, J.A. Relief of feedback inhibition of HER3 transcription by RAF and MEK inhibitors attenuates their antitumor effects in BRAF-mutant thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahallad, A.; Sun, C.; Huang, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Salazar, R.; Zecchin, D.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Bardelli, A.; Bernards, R. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature 2012, 483, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Park, J.I. Tumor Cell Resistance to the Inhibition of BRAF and MEK1/2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidorn, S.J.; Milagre, C.; Whittaker, S.; Nourry, A.; Niculescu-Duvas, I.; Dhomen, N.; Hussain, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Springer, C.J.; Pritchard, C.; et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 2010, 140, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP kinase pathway alterations in BRAF-mutant melanoma patients with acquired resistance to combined RAF/MEK inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Bi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qin, F.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signaling pathway in human cancer: Current status in clinical trials. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Fung, C.; Menzies, A.M.; Pupo, G.M.; Carlino, M.S.; Hyman, J.; Shahheydari, H.; Tembe, V.; Thompson, J.F.; Saw, R.P.; et al. Increased MAPK reactivation in early resistance to dabrafenib/trametinib combination therapy of BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahronian, L.G.; Sennott, E.M.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Kwak, E.L.; Faris, J.E.; Godfrey, J.T.; Nishimura, K.; Lynch, K.D.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Clinical Acquired Resistance to RAF Inhibitor Combinations in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer through MAPK Pathway Alterations. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddo, D.; Sennott, E.M.; Barault, L.; Valtorta, E.; Arena, S.; Cassingena, A.; Filiciotto, G.; Marzolla, G.; Elez, E.; van Geel, R.M.; et al. Molecular Landscape of Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapy Combinations in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4504–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Childress, M.A.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Ali, S.M.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Fabrizio, D.; Ross, J.S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Miller, V.A.; et al. BRAF internal deletions and resistance to BRAF/MEK inhibitor therapy. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.A.; Whalen, D.M.; Ozen, A.; Wongchenko, M.J.; Yin, J.; Yen, I.; Schaefer, G.; Mayfield, J.D.; Chmielecki, J.; Stephens, P.J.; et al. Activation Mechanism of Oncogenic Deletion Mutations in BRAF, EGFR, and HER2. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Resistance mechanism of the oncogenic beta3-alphaC deletion mutation in BRAF kinase to dabrafenib and vemurafenib revealed by molecular dynamics simulations and binding free energy calculations. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Q.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Qin, Y.; Hawley, T.; Seo, C.; Merlino, G.; Yu, Y. AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3275–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yue, Q.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guo, W.; Zhu, G.; Guo, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, T.; et al. POU4F1 promotes the resistance of melanoma to BRAF inhibitors through MEK/ERK pathway activation and MITF up-regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarsdottir, L.; Azimi, A.; Das, I.; Sigvaldadottir, I.; Suryo Rahmanto, A.; Petri, A.; Kauppinen, S.; Ingvar, C.; Jonsson, G.; Olsson, H.; et al. PTENP1-AS contributes to BRAF inhibitor resistance and is associated with adverse clinical outcome in stage III melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malindi, Z.; Barth, S.; Abrahamse, H. The Potential of Antibody Technology and Silver Nanoparticles for Enhancing Photodynamic Therapy for Melanoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biteghe, F.A.N.; Chalomie, N.E.T.; Mungra, N.; Vignaux, G.; Gao, N.; Vergeade, A.; Okem, A.; Naran, K.; Ndong, J.C.; Barth, S. Antibody-Based Immunotherapy: Alternative Approaches for the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabner, B.A.; Roberts, T.G., Jr. Timeline: Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Salomone, S.; Libra, M. Evolution of Cancer Pharmacological Treatments at the Turn of the Third Millennium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W. Meaningful relationships: The regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem. J. 2000, 351 Pt 2, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, G.C.; Falzone, L.; Salemi, R.; Zanghi, A.; Spandidos, D.A.; McCubrey, J.A.; Candido, S.; Libra, M. Cutaneous melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.K. MAP kinase pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoadley, K.A.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Cherniack, A.D.; Tamborero, D.; Ng, S.; Leiserson, M.D.M.; Niu, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Uzunangelov, V.; et al. Multiplatform analysis of 12 cancer types reveals molecular classification within and across tissues of origin. Cell 2014, 158, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, G.T.; Messina, J.L.; Fedorenko, I.V.; Sondak, V.K.; Smalley, K.S. Paradoxical oncogenesis--the long-term effects of BRAF inhibition in melanoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCC MERP. Statement on Medication Error Rates [WWW Document]. National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. 2008. Available online: https://www.nccmerp.org/statement-medication-error-rates (accessed on 24 January 2024).
- Garutti, M.; Bergnach, M.; Polesel, J.; Palmero, L.; Pizzichetta, M.A.; Puglisi, F. BRAF and MEK Inhibitors and Their Toxicities: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).