PAX5 Alterations in a Consecutive Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cohort Treated Using the ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Materials
2.2. DNA and RNA Isolation
2.3. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.4. Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification for CNV Detection
2.5. Sanger Sequencing for Detection of Germline PAX5 Variants
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PAX5alt and PAX5 P80R Patients
3.2. Genetic Changes Identified in PAX5alt and PAX5 P80R Patients
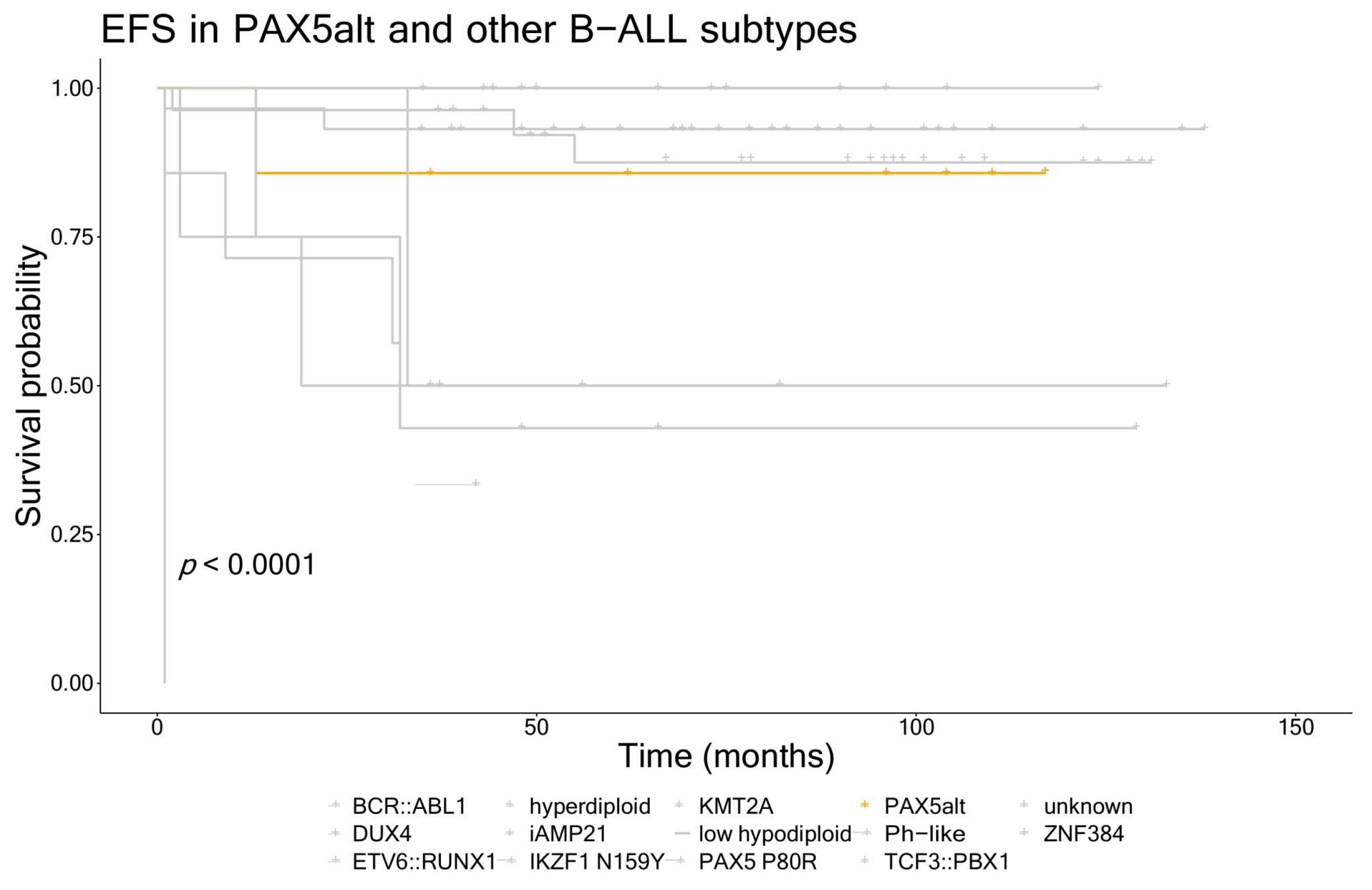
3.3. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes for Patients with the PAX5alt and PAX5 P80R Subtypes
3.4. PAX5 Variants in Other B-ALL Subtypes
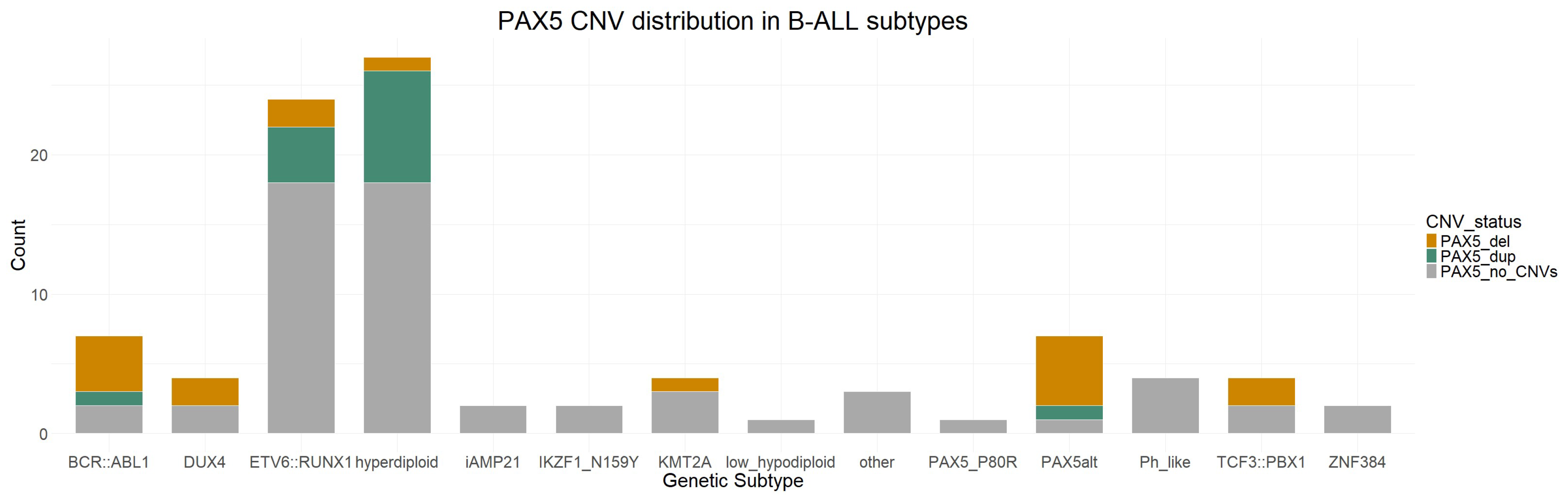
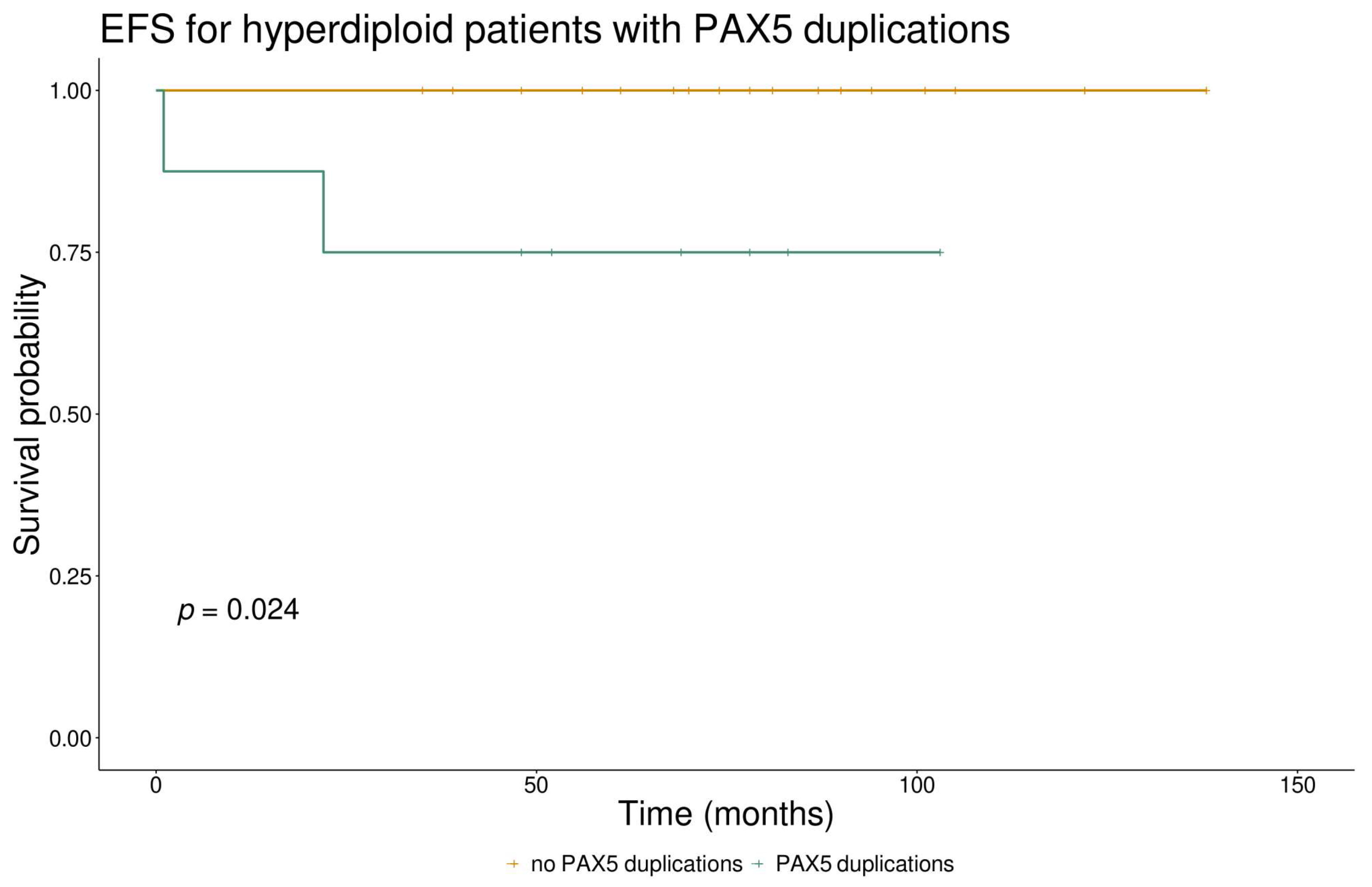
3.5. PAX5 CNVs and Their Clinical Significance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobaleda, C.; Schebesta, A.; Delogu, A.; Busslinger, M. Pax5: The Guardian of B Cell Identity and Function. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenbacher, S.; Jaritz, M.; Hill, L.; Schäfer, M.; Busslinger, M. Essential Role of the Pax5 C-Terminal Domain in Controlling B Cell Commitment and Development. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Strid, T.; Kuruvilla, J.; Somasundaram, R.; Cristobal, S.; Smith, E.; Prasad, M.; Fioretos, T.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Soneji, S.; et al. PAX5 Is Part of a Functional Transcription Factor Network Targeted in Lymphoid Leukemia. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebral, K.; Denk, D.; Attarbaschi, A.; König, M.; Mann, G.; Haas, O.A.; Strehl, S. Incidence and Diversity of PAX5 Fusion Genes in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Goorha, S.; Radtke, I.; Miller, C.B.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Dalton, J.D.; Girtman, K.; Mathew, S.; Ma, J.; Pounds, S.B.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Genetic Alterations in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nature 2007, 446, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familiades, J.; Bousquet, M.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M.; Béné, M.-C.; Beldjord, K.; De Vos, J.; Dastugue, N.; Coyaud, E.; Struski, S.; Quelen, C.; et al. PAX5 Mutations Occur Frequently in Adult B-Cell Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and PAX5 Haploinsufficiency Is Associated with BCR-ABL1 and TCF3-PBX1 Fusion Genes: A GRAALL Study. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.L.; Roberts, K.G.; Moore, I.; Zhou, X.; Nakitandwe, J.; Hagiwara, K.; Pelletier, S.; Gingras, S.; Berns, H.; et al. PAX5-Driven Subtypes of B-Progenitor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duployez, N.; Jamrog, L.A.; Fregona, V.; Hamelle, C.; Fenwarth, L.; Lejeune, S.; Helevaut, N.; Geffroy, S.; Caillault, A.; Marceau-Renaut, A.; et al. Germline PAX5 Mutation Predisposes to Familial B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 1424–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Schrader, K.A.; Waanders, E.; Timms, A.E.; Vijai, J.; Miething, C.; Wechsler, J.; Yang, J.; Hayes, J.; Klein, R.J.; et al. A Recurrent Germline PAX5 Mutation Confers Susceptibility to Pre-B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lee, S.H.R.; Chin, W.H.N.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Lim, E.H.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Chiew, K.H.; Oh, B.L.Z.; Koh, G.S.; et al. Distinct Clinical Characteristics of DUX4- and PAX5-Altered Childhood B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5226–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinnerl, D.; Fortschegger, K.; Kauer, M.; M Marchante, J.R.; Kofler, R.; Den Boer, M.L.; Strehl, S. The Role of the Janus-Faced Transcription Factor PAX5-JAK2 in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, G.; Bresolin, S.; Silvestri, D.; Quadri, M.; Saitta, C.; Vendramini, E.; Buldini, B.; Palmi, C.; Bardini, M.; Grioni, A.; et al. PAX5 Fusion Genes Are Frequent in Poor Risk Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia and Can Be Targeted with BIBF1120. EBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Heyne, S.; Sikora, K.; Rabbani, L.; Rauer, M.; Kilpert, F.; Richter, A.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Manke, T. SnakePipes: Facilitating Flexible, Scalable and Integrative Epigenomic Analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4757–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences From High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beder, T.; Hansen, B.T.; Hartmann, A.M.; Zimmermann, J.; Amelunxen, E.; Wolgast, N.; Walter, W.; Zaliova, M.; Antić, Ž.; Chouvarine, P.; et al. The Gene Expression Classifier ALLCatchR Identifies B-Cell Precursor ALL Subtypes and Underlying Developmental Trajectories Across Age. Hemasphere 2023, 7, E939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Jia, Z.; Liu, J.; Mao, A.; Han, H.; Gu, Z. MD-ALL: An Integrative Platform for Molecular Diagnosis of B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica, 2023; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renevey, A.; Proks, M.; Garcia, M.U.; Peltzer, A.; Praveen, R.S.; Ziff, O.; Ewels, P.; De Smet, M.; Moran, B.; Saad, C.; et al. Nf-Core/Rnafusion: 2.3.4 (2.3.4). Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, S.; Ellermann, J.; Walther, T.; Burkhardt, P.; Fröhlich, M.; Hutter, B.; Toprak, U.H.; Neumann, O.; Stenzinger, A.; Scholl, C.; et al. Accurate and Efficient Detection of Gene Fusions from RNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsted, P.; Hateley, S.; Joseph, I.C.; Pimentel, H.; Bray, N.; Pachter, L. Fusion Detection and Quantification by Pseudoalignment. BioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Dobin, A.; Stransky, N.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; Tickle, T.; Bankapur, A.; Ganote, C.; Doak, T.G.; Pochet, N.; et al. STAR-Fusion: Fast and Accurate Fusion Transcript Detection from RNA-Seq. BioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Shao, M.; Kingsford, C. SQUID: Transcriptomic Structural Variation Detection from RNA-Seq. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicorici, D.; Şatalan, M.; Edgren, H.; Kangaspeska, S.; Murumägi, A.; Kallioniemi, O.; Virtanen, S.; Kilkku, O. FusionCatcher—A Tool for Finding Somatic Fusion Genes in Paired-End RNA-Sequencing Data. BioRxiv 2014, 011650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, Y.; Edmonson, M.N.; Zhou, X.; Newman, S.; McLeod, C.; Thrasher, A.; Liu, Y.; Tang, B.; Rusch, M.C.; et al. CICERO: A Versatile Method for Detecting Complex and Diverse Driver Fusions Using Cancer RNA Sequencing Data. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen, R.S.; Garcia, M.U.; Menden, K. Nf-Core/Rnavar: Nf-Core/Rnavar v1.0.0—Tiny Firefly (1.0.0). Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From FastQ Data to High-Confidence Variant Calls: The Genome Analysis Toolkit Best Practices Pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional Annotation of Genetic Variants from High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for General Users and for Biologist Programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, C. In Silico PCR Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 760, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Schieck, M.; Hofmann, W.; Tauscher, M.; Lentes, J.; Bergmann, A.; Stelter, M.; Möricke, A.; Alten, J.; Schlegelberger, B.; et al. Frequency and Prognostic Impact of PAX5 p.P80R in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients Treated on an AIEOP-BFM Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Protocol. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020, 59, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migita, N.A.; Jotta, P.Y.; do Nascimento, N.P.; Vasconcelos, V.S.; Centoducatte, G.L.; Massirer, K.B.; de Azevedo, A.C.; Brandalise, S.R.; Yunes, J.A. Classification and Genetics of Pediatric B-Other Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Targeted RNA Sequencing. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2957–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Dai, Y.T.; Lilljebjörn, H.; Shen, S.H.; Cui, B.W.; Bai, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Qian, M.X.; Kubota, Y.; Kiyoi, H.; et al. Transcriptional Landscape of B Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Based on an International Study of 1223 Cases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11711–E11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passet, M.; Boissel, N.; Sigaux, F.; Saillard, C.; Bargetzi, M.; Ba, I.; Thomas, X.; Graux, C.; Chalandon, Y.; Leguay, T.; et al. PAX5 P80R Mutation Identifies a Novel Subtype of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Favorable Outcome. Blood 2019, 133, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeha, S.; Choi, J.; Roberts, K.G.; Pei, D.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Inaba, H.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Gruber, T.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Clinical Significance of Novel Subtypes of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the Context of Minimal Residual Disease-Directed Therapy. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobucci, I.; Kimura, S.; Mullighan, C.G. Clinical Medicine Biologic and Therapeutic Implications of Genomic Alterations in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Boeree, A.; de Haas, V.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; Horstmann, M.A.; Escherich, G.; Pieters, R.; den Boer, M.L. Copy Number Alterations in B-Cell Development Genes, Drug Resistance, and Clinical Outcome in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour Feizi, A.H.; Zeinali, S.; Toporski, J.; Sheervalilou, R.; Mehranfar, S. Frequency and Correlation of Common Genes Copy Number Alterations in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Prognosis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 3493–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C.; Nebral, K.; Chilton, L.; Leschi, C.; Waanders, E.; Boer, J.M.; Žaliová, M.; Sutton, R.; Öfverholm, I.I.; Ohki, K.; et al. Intragenic Amplification of PAX5: A Novel Subgroup in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia? Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, J.; Chen, S. Emerging Molecular Subtypes and Therapeutic Targets in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Med. 2021, 15, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, F.; Rüschendorf, F.; Gombert, M.; Husemann, P.; Ginzel, S.; Izraeli, S.; Harit, M.; Weintraub, M.; Weinstein, O.Y.; Lerer, I.; et al. Inherited Susceptibility to Pre B-ALL Caused by Germline Transmission of PAX5 c.547G>A. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.W.; Roberts, K.G.; Gu, Z.; Shi, L.; Pounds, S.; Pei, D.; Cheng, C.; Dai, Y.; Devidas, M.; Qu, C.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1376–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-M.; Jung, S.-H.; Kim, M.S.; Baek, I.-P.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, S.S.; Chung, Y.-J.; Lee, S.H. The Mutational Burdens and Evolutionary Ages of Early Gastric Cancers Are Comparable to Those of Advanced Gastric Cancers. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauthammer, M.; Kong, Y.; Bacchiocchi, A.; Evans, P.; Pornputtapong, N.; Wu, C.; McCusker, J.P.; Ma, S.; Cheng, E.; Straub, R.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Recurrent Mutations in NF1 and RASopathy Genes in Sun-Exposed Melanomas. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Mouw, K.W.; Kim, P.; Iyer, G.; Wagle, N.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Zhu, C.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Kryukov, G.V.; O’connor, K.W.; et al. Somatic ERCC2 Mutations Correlate with Cisplatin Sensitivity in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, L.; Schroeder, M.P.; Eckert, C.; Schlee, C.; Tanchez, J.O.; Kämpf, S.; Wagner, D.L.; Schulze, V.; Isaakidis, K.; Lázaro-Navarro, J.; et al. PAX5 Biallelic Genomic Alterations Define a Novel Subgroup of B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1895–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Put, N.; Deeren, D.; Michaux, L.; Vandenberghe, P. FOXP1 and PAX5 Are Rare but Recurrent Translocations Partners in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, A.; Valsecchi, L.; Quadri, M.; Watrin, T.; Scharov, K.; Procopio, S.; Tu, J.-W.; Vogt, M.; Savino, A.M.; Silvestri, D.; et al. High-Throughput Screening as a Drug Repurposing Strategy for Poor Outcome Subgroups of Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 217, 115809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskiy, Y.; Kuznetsova, V.; Kudriaeva, A.; Zmievskaya, E.; Bulatov, E. Neglected, yet Significant Role of FOXP1 in T-Cell Quiescence, Differentiation and Exhaustion. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 971045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, M.; Zaliova, M.; Fiser, K.; Vakrmanova, B.; Slamova, L.; Musilova, A.; Brüggemann, M.; Ritgen, M.; Fronkova, E.; Kalina, T.; et al. DUX4r, ZNF384r and PAX5-P80R Mutated B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Frequently Undergo Monocytic Switch. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novakova, M.; Vakrmanova, B.; Slamova, L.; Musilova, A.; Brüggemann, M.; Ritgen, M.; Fronkova, E.; Kalina, T.; Trka, J.; Stary, J.; et al. Switching Towards Monocytic Lineage and Discordancy between Flow Cytometric and PCR Minimal Residual Disease Results Is a Hallmark Feature of DUX4 Rearranged B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. S1), 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Mysliwski, M.; Serio, J.; Ropa, J.; Abulwerdi, F.A.; Chan, R.J.; Patel, J.P.; Tallman, M.S.; Paietta, E.; et al. Mutated Ptpn11 Alters Leukemic Stem Cell Frequency and Reduces the Sensitivity of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to Mcl1 Inhibition. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, M.; Martinelli, S.; Iavarone, I.; Cazzaniga, G.; Spinelli, M.; Giarin, E.; Petrangeli, V.; Carta, C.; Masetti, R.; Aricò, M.; et al. Somatic PTPN11 Mutations in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 129, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Smith, A.J.; Ojha, J.; Francis, S.S.; Sanders, E.; Endicott, A.A.; Hansen, H.M.; Smirnov, I.; Termuhlen, A.M.; Walsh, K.M.; Metayer, C.; et al. Clonal and Microclonal Mutational Heterogeneity in High Hyperdiploid Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 72733–72745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, A.; Schebesta, A.; Sun, Q.; Aschenbrenner, K.; Perlot, T.; Busslinger, M. Gene Repression by Pax5 in B Cells Is Essential for Blood Cell Homeostasis and Is Reversed in Plasma Cells. Immunity 2006, 24, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Nr. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| Predicted subtype | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5alt | PAX5 P80R |
| Genetic variants in PAX5 | / | / | / | c.1045_1048del | c.101C>T | / | c.725A>G | [c.239C>G]; [c.596G>A, c.826G>A, c.1102T>A] |
| Protein change | / | / | / | p.P349Sfs*53 | p.P34L | / | p.E242G | p.P80R, p.R199K, p.D276N, p.S368T |
| ACMG classification | / | / | / | LP | LP | / | VUS | LP, VUS, VUS, VUS |
| Fusion genes involving PAX5 | PAX5::FKBP15 | PAX5::FOXP1 | PAX5::FOXP1 | / | / | PAX5::FKBP15 | / | / |
| CNVs | IKZF1 del, CDKN2A/2B del., PAX5 ex. 10 del. (IKZF1plus) | CDKN2A/2B del. | PAX5 del., CDKN2A/2B del. | PAX5 del., CDKN2A/2B del. | PAX5 ex. 8 dup., CDKN2A/2B del. | PAX5 ex. 8 and 10 del., CDKN2A/2B del. | IKZF1 del., PAX5 del., CDKN2A/2B del. (IKZF1plus) | / |
| Gender | male | female | female | male | male | male | male | male |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 4 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 19 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| WBC at diagnosis (×109/L) | 22.6 | 8.7 | 1.1 | 17.2 | 5 | 32.2 | 372.3 | 1.98 |
| CNS involvement | neg. | neg. | neg. | pos. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. |
| Day 8 prednisone response (blasts/mm3) | 280 | 1750 | 45 | 78 | 0 | 0 | 1078 | 0 |
| MRD day 15 (%) | 0 | 50 | 0.019 | 0.6 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 0.43 | 0 |
| MRD day 33 (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.016 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| End of induction risk classification | HR | HR | SR | IR | IR | IR | IR | IR |
| Event | no | no | no | no | no | relapse with AML switch, death | no | no |
| Patient Characteristics | PAX5alt or PAX5 P80R (n = 8) | Other (n = 91) |
| Gender | ||
| male | 6 | 48 |
| female | 2 | 43 |
| Age at diagnosis | ||
| ˂1 year | 0 | 3 |
| 1–5 years | 5 | 52 |
| ≥6 years | 3 | 36 |
| WBC at diagnosis | ||
| ˂20 × 109/L | 5 | 71 |
| ≥20 × 109/L | 3 | 20 |
| CNS involvement | ||
| yes | 1 | 6 |
| no | 7 | 83 |
| unknown | 0 | 2 |
| Day 8 prednisone response | ||
| ˂1000 blasts/µL | 6 | 79 |
| ≥1000 blasts/µL | 2 | 10 |
| unknown | 0 | 2 |
| MRD day 15 | ||
| ˂0.1% | 4 | 31 |
| 0.1–10% | 3 | 45 |
| ˃10% | 1 | 12 |
| unknown | 0 | 3 |
| MRD day 33 | ||
| ˂0.01% | 7 | 66 |
| ≥0.01% | 1 | 22 |
| unknown | 0 | 3 |
| End of induction risk classification | ||
| standard | 1 | 16 |
| intermediate | 5 | 54 |
| high | 2 | 21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Črepinšek, K.; Klobučar, N.; Tesovnik, T.; Šket, R.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Kovač, J.; Kavčič, M.; Prelog, T.; Kitanovski, L.; Jazbec, J.; et al. PAX5 Alterations in a Consecutive Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cohort Treated Using the ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol. Cancers 2024, 16, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061164
Črepinšek K, Klobučar N, Tesovnik T, Šket R, Jenko Bizjan B, Kovač J, Kavčič M, Prelog T, Kitanovski L, Jazbec J, et al. PAX5 Alterations in a Consecutive Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cohort Treated Using the ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol. Cancers. 2024; 16(6):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061164
Chicago/Turabian StyleČrepinšek, Klementina, Nika Klobučar, Tine Tesovnik, Robert Šket, Barbara Jenko Bizjan, Jernej Kovač, Marko Kavčič, Tomaž Prelog, Lidija Kitanovski, Janez Jazbec, and et al. 2024. "PAX5 Alterations in a Consecutive Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cohort Treated Using the ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol" Cancers 16, no. 6: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061164
APA StyleČrepinšek, K., Klobučar, N., Tesovnik, T., Šket, R., Jenko Bizjan, B., Kovač, J., Kavčič, M., Prelog, T., Kitanovski, L., Jazbec, J., & Debeljak, M. (2024). PAX5 Alterations in a Consecutive Childhood B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cohort Treated Using the ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol. Cancers, 16(6), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061164






