Super-Enhancer Dysregulation in Rhabdoid Tumor Cells Is Regulated by the SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and PROTAC Generation
2.2. Western Blotting and Antibodies
2.3. CUT&RUN
2.4. RNA-seq and ATAC-seq
2.5. CUT&RUN Analysis
2.6. ATAC-seq Analysis
2.7. RNA-seq Analysis
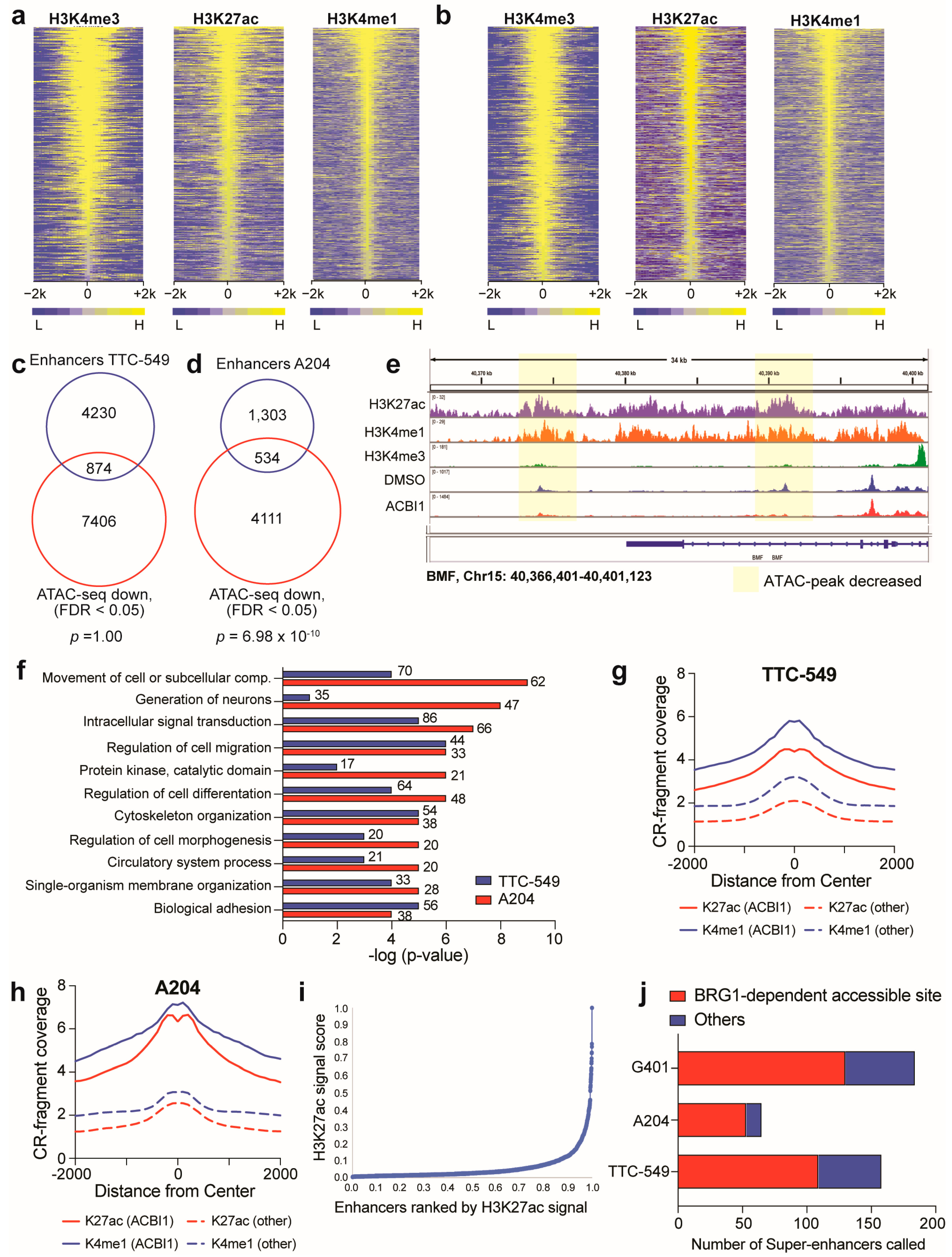
3. Results
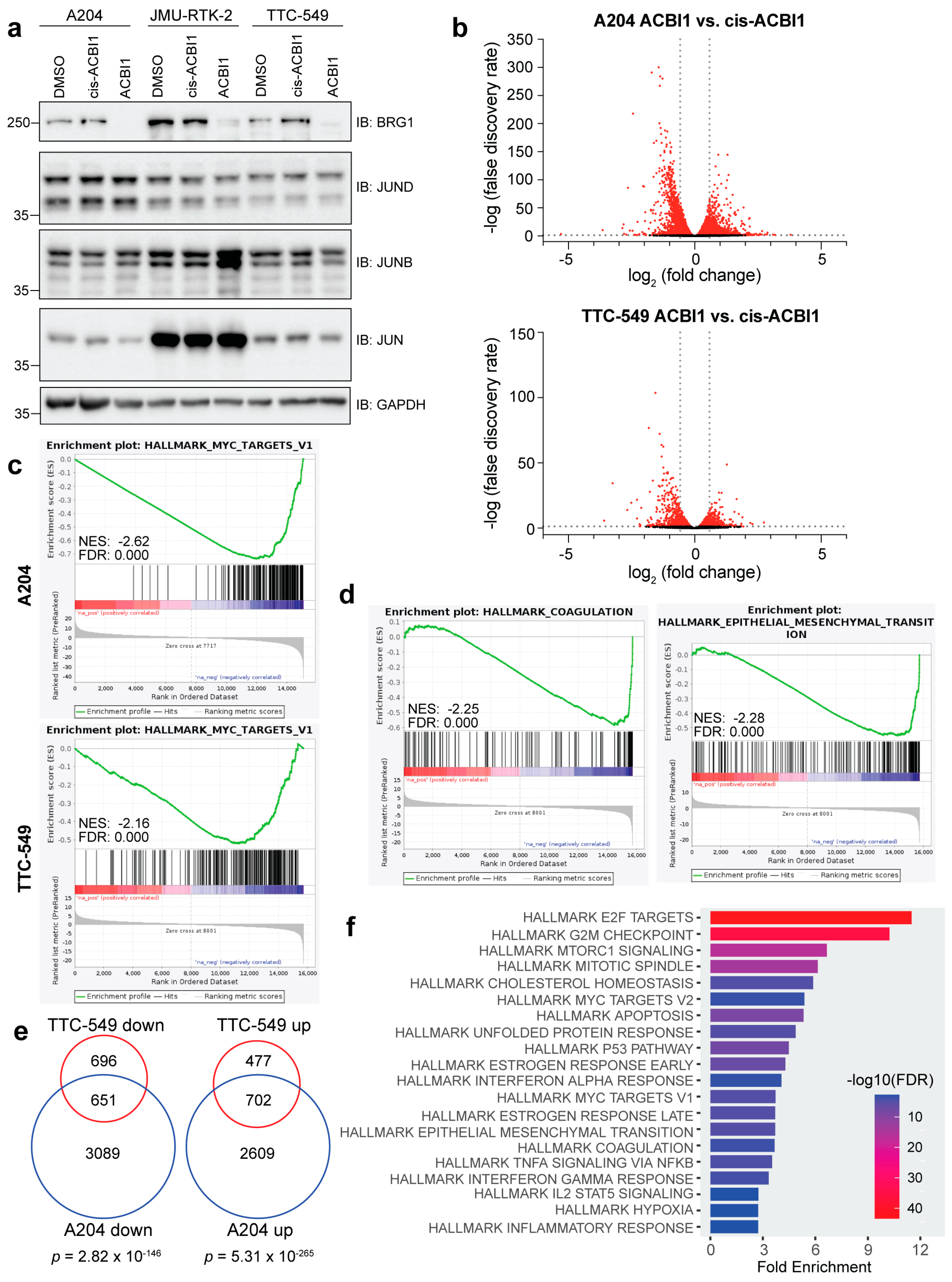
3.1. Acute Depletion of BRG1 Using the ACBI1 Degrader Causes Widespread Gene Expression Changes in Rhabdoid Cell Lines
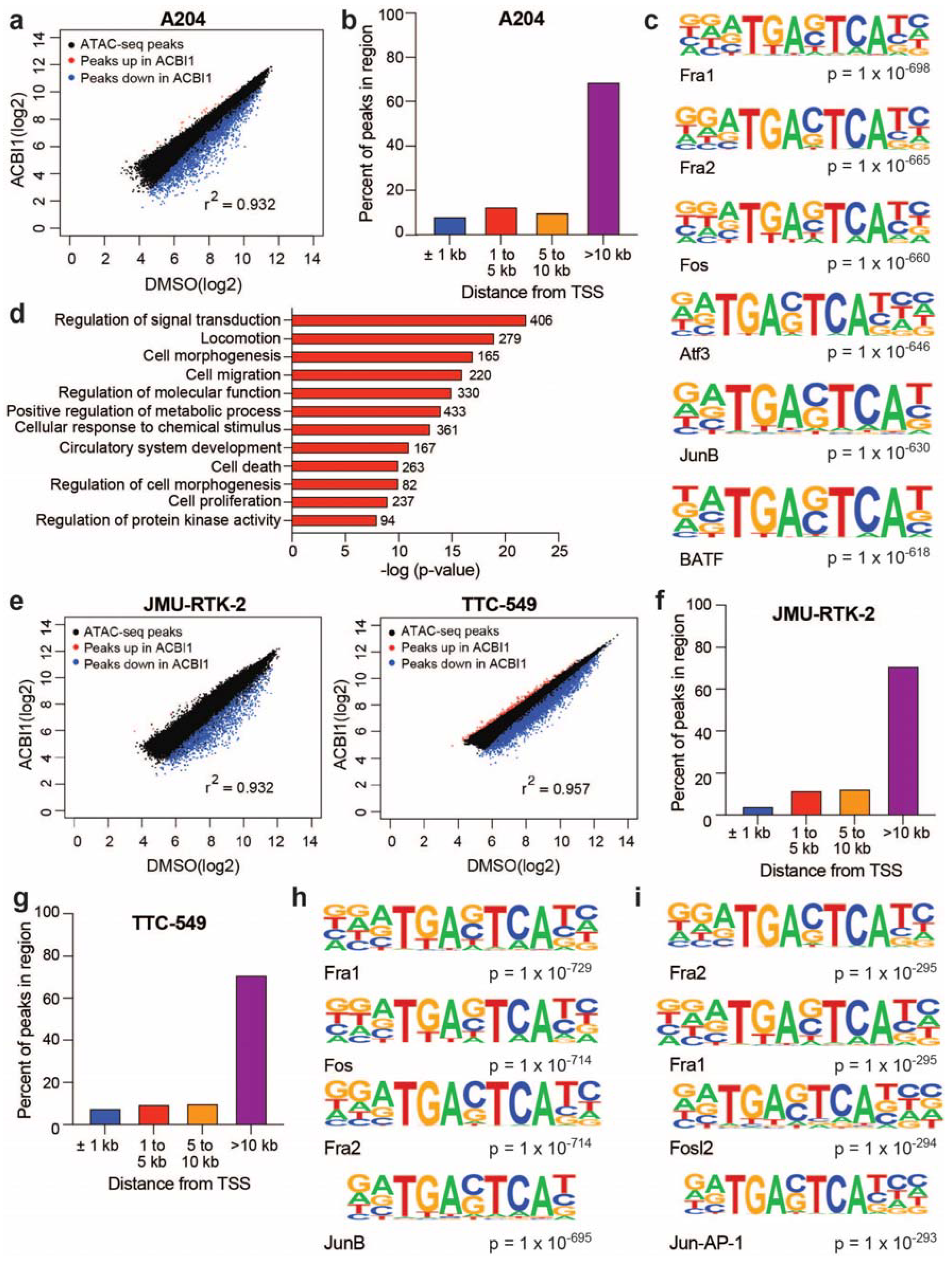
3.2. BRG1-Dependent Accessible Sites Detected across Diverse Rhabdoid Cell Lines Implicate Involvement of the AP-1 Transcription Factor
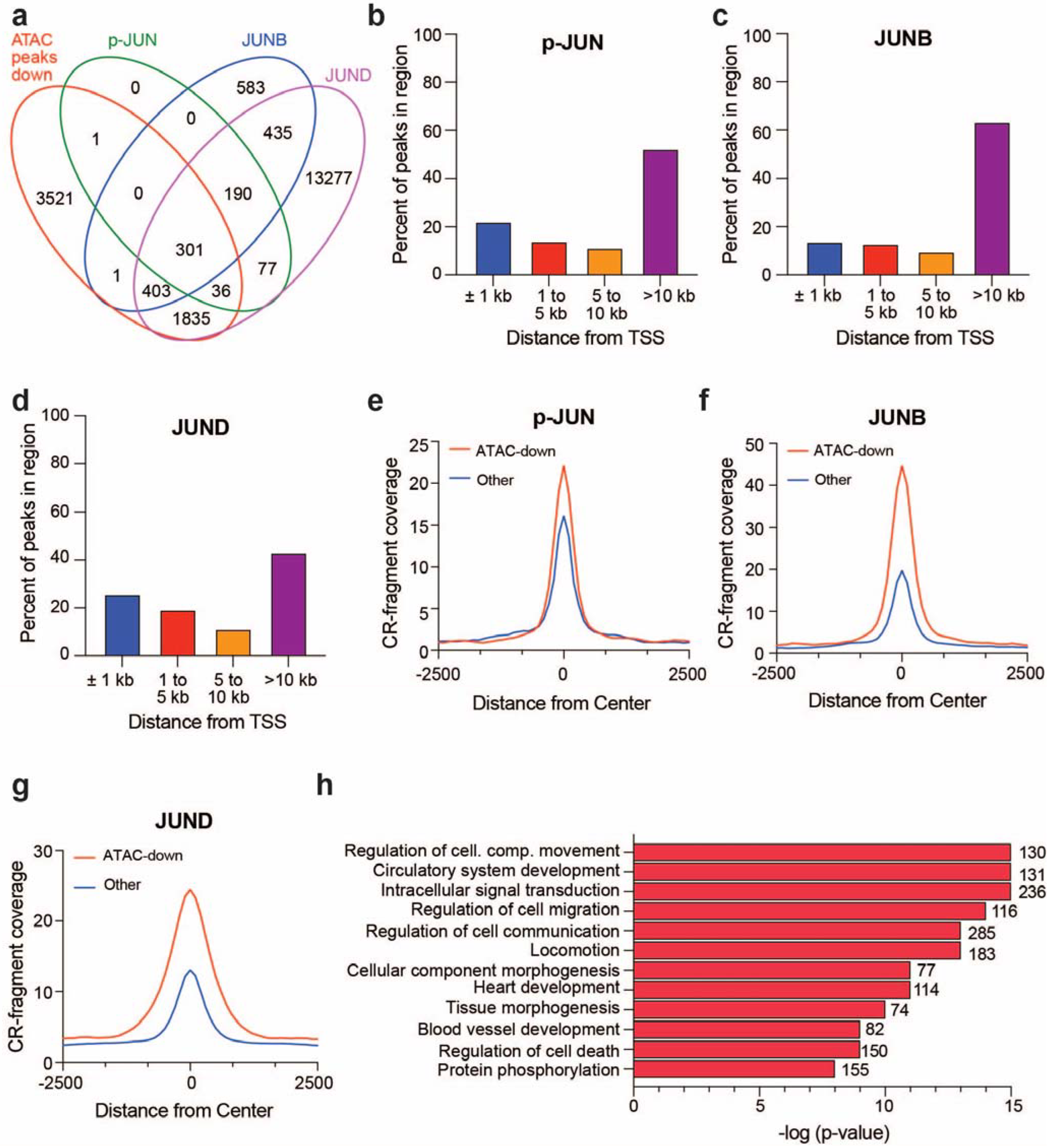
3.3. BRG1-Dependent Accessible Sites Show JUN Family Member Binding
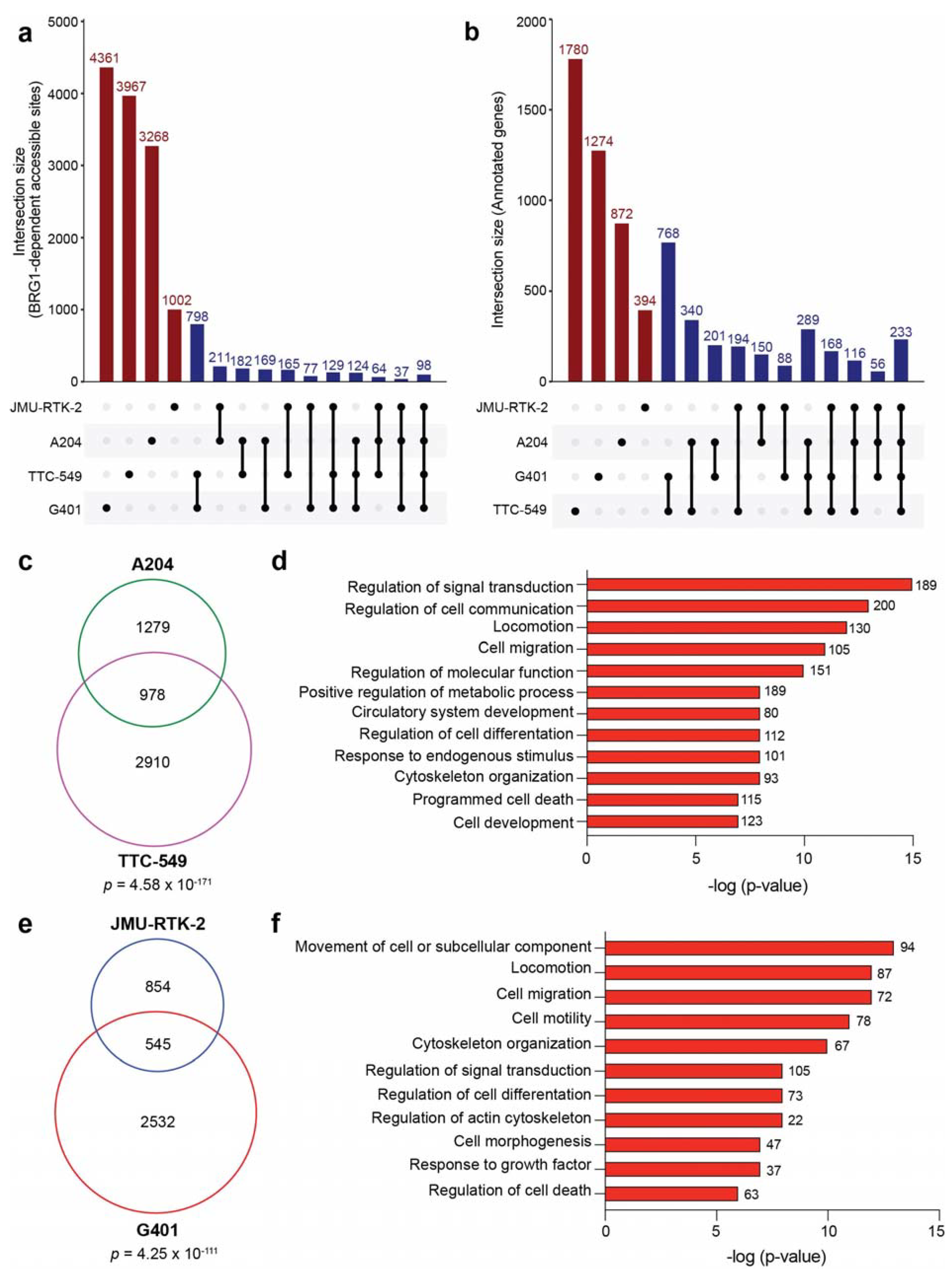
3.4. BRG1-Dependent Accessible Sites Are Context-Dependent
3.5. Accessible Sites Correlate with Enhancer Regions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, C.A.; Tansey, W.P.; Weissmiller, A.M. Emerging Themes in Mechanisms of Tumorigenesis by SWI/SNF Subunit Mutation. Epigenetics Insights 2022, 15, 25168657221115656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashtalir, N.; D’Avino, A.R.; Michel, B.C.; Luo, J.; Pan, J.; Otto, J.E.; Zullow, H.J.; McKenzie, Z.M.; Kubiak, R.L.; St Pierre, R.; et al. Modular Organization and Assembly of SWI/SNF Family Chromatin Remodeling Complexes. Cell 2018, 175, 1272–1288.e1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoch, C.; Hargreaves, D.C.; Hodges, C.; Elias, L.; Ho, L.; Ranish, J.; Crabtree, G.R. Proteomic and bioinformatic analysis of mammalian SWI/SNF complexes identifies extensive roles in human malignancy. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shain, A.H.; Pollack, J.R. The spectrum of SWI/SNF mutations, ubiquitous in human cancers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.W.; Galusha, S.A.; McMenamin, M.E.; Fletcher, C.D.; Orkin, S.H. Haploinsufficiency of Snf5 (integrase interactor 1) predisposes to malignant rhabdoid tumors in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13796–13800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.W.; Leroux, M.M.; Fleming, M.D.; Orkin, S.H. Highly penetrant, rapid tumorigenesis through conditional inversion of the tumor suppressor gene Snf5. Cancer Cell 2002, 2, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.F.; Cohn, S.; Christie, A.; McKenzie, T.; Wolff, N.; Do, Q.N.; Madhuranthakam, A.J.; Pedrosa, I.; Wang, T.; Dey, A.; et al. Modeling Renal Cell Carcinoma in Mice: Bap1 and Pbrm1 Inactivation Drive Tumor Grade. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Alver, B.H.; San Roman, A.K.; Wilson, B.G.; Wang, X.; Agoston, A.T.; Park, P.J.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Roberts, C.W. ARID1A loss impairs enhancer-mediated gene regulation and drives colon cancer in mice. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, D.A.; Beckwith, J.B.; Mierau, G.W.; Luckey, D.W. Rhabdoid tumor of kidney. A report of 111 cases from the National Wilms’ Tumor Study Pathology Center. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1989, 13, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhwald, M.C.; Biegel, J.A.; Bourdeaut, F.; Roberts, C.W.; Chi, S.N. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors-current concepts, advances in biology, and potential future therapies. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lee, R.S.; Alver, B.H.; Haswell, J.R.; Wang, S.; Mieczkowski, J.; Drier, Y.; Gillespie, S.M.; Archer, T.C.; Wu, J.N.; et al. SMARCB1-mediated SWI/SNF complex function is essential for enhancer regulation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Troisi, E.C.; Howard, T.P.; Haswell, J.R.; Wolf, B.K.; Hawk, W.H.; Ramos, P.; Oberlick, E.M.; Tzvetkov, E.P.; et al. BRD9 defines a SWI/SNF sub-complex and constitutes a specific vulnerability in malignant rhabdoid tumors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, R.T.; Pulice, J.L.; Valencia, A.M.; McBride, M.J.; McKenzie, Z.M.; Gillespie, M.A.; Ku, W.L.; Teng, M.; Cui, K.; Williams, R.T.; et al. SMARCB1 is required for widespread BAF complex-mediated activation of enhancers and bivalent promoters. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, B.C.; D’Avino, A.R.; Cassel, S.H.; Mashtalir, N.; McKenzie, Z.M.; McBride, M.J.; Valencia, A.M.; Zhou, Q.; Bocker, M.; Soares, L.M.M.; et al. A non-canonical SWI/SNF complex is a synthetic lethal target in cancers driven by BAF complex perturbation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, T.W.R.; Porter, D.K.; Amaral, M.L.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Benner, C.; Hargreaves, D.C. Chromatin accessibility underlies synthetic lethality of SWI/SNF subunits in ARID1A-mutant cancers. eLife 2017, 6, e30506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alver, B.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lu, P.; Wang, X.; Manchester, H.E.; Wang, W.; Haswell, J.R.; Park, P.J.; Roberts, C.W. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex is required for maintenance of lineage specific enhancers. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.S.; Stewart, C.; Carter, S.L.; Ambrogio, L.; Cibulskis, K.; Sougnez, C.; Lawrence, M.S.; Auclair, D.; Mora, J.; Golub, T.R.; et al. A remarkably simple genome underlies highly malignant pediatric rhabdoid cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2983–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, K.C.; Maxwell, J.N.; Wang, J.; Jones, C.A.; Csaki, G.T.; Florian, A.C.; Romer, A.S.; Bryant, D.L.; Farone, A.L.; Liu, Q.; et al. The SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1 facilitates multiple pro-tumorigenic gene expression programs in SMARCB1-deficient cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, N.; Orkin, S.H.; Yuan, G.C. CUT&RUNTools: A flexible pipeline for CUT&RUN processing and footprint analysis. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, R.; Brown, G. DiffBind: Differential Binding Analysis of ChIP-Seq Peak Data. Bioconductor. 2011. Available online: http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DiffBind.html (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, B.K.; Zhao, Y.; McCray, A.; Hawk, W.H.; Deary, L.T.; Sugiarto, N.W.; LaCroix, I.S.; Gerber, S.A.; Cheng, C.; Wang, X. Cooperation of chromatin remodeling SWI/SNF complex and pioneer factor AP-1 shapes 3D enhancer landscapes. Nat Struct Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Liu, T.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.S. Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, K.W.; Tooke, L.S.; Wainwright, L.M.; Judkins, A.R.; Biegel, J.A. Spectrum of SMARCB1/INI1 mutations in familial and sporadic rhabdoid tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnaby, W.; Koegl, M.; Roy, M.J.; Whitworth, C.; Diers, E.; Trainor, N.; Zollman, D.; Steurer, S.; Karolyi-Oezguer, J.; Riedmueller, C.; et al. BAF complex vulnerabilities in cancer demonstrated via structure-based PROTAC design. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmiller, A.M.; Wang, J.; Lorey, S.L.; Howard, G.C.; Martinez, E.; Liu, Q.; Tansey, W.P. Inhibition of MYC by the SMARCB1 tumor suppressor. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodley, C.M.; Romer, A.S.; Wang, J.; Guarnaccia, A.D.; Elion, D.L.; Maxwell, J.N.; Guerrazzi, K.; McCann, T.S.; Popay, T.M.; Matlock, B.K.; et al. Multiple interactions of the oncoprotein transcription factor MYC with the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeler. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3593–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 172, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierbuchen, T.; Ling, E.; Cowley, C.J.; Couch, C.H.; Wang, X.; Harmin, D.A.; Roberts, C.W.M.; Greenberg, M.E. AP-1 Transcription Factors and the BAF Complex Mediate Signal-Dependent Enhancer Selection. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 1067.e1012–1082.e1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-Andre, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loven, J.; Hoke, H.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Lau, A.; Orlando, D.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013, 153, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Ding, Y.; Wild, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Small molecule inhibitors targeting activator protein 1 (AP-1). J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6930–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N.; Strobelt, H.; Vuillemot, R.; Pfister, H. UpSet: Visualization of Intersecting Sets. IEEE Trans Vis. Comput. Graph. 2014, 20, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sansam, C.G.; Thom, C.S.; Metzger, D.; Evans, J.A.; Nguyen, P.T.; Roberts, C.W. Oncogenesis caused by loss of the SNF5 tumor suppressor is dependent on activity of BRG1, the ATPase of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8094–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Daniel, P.; Bradshaw, G.; Shi, H.; Loi, M.; Chew, N.; Parackal, S.; Tsui, V.; Liang, Y.; Koptyra, M.; et al. Generation and multi-dimensional profiling of a childhood cancer cell line atlas defines new therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 660.e667–677.e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Yang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y. Super-enhancer function and its application in cancer targeted therapy. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, C.A.; Wang, J.; Evans, J.R.; Sisk, H.R.; Womack, C.B.; Liu, Q.; Tansey, W.P.; Weissmiller, A.M. Super-Enhancer Dysregulation in Rhabdoid Tumor Cells Is Regulated by the SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1. Cancers 2024, 16, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050916
Jones CA, Wang J, Evans JR, Sisk HR, Womack CB, Liu Q, Tansey WP, Weissmiller AM. Super-Enhancer Dysregulation in Rhabdoid Tumor Cells Is Regulated by the SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050916
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Cheyenne A., Jing Wang, James R. Evans, Hannah R. Sisk, Carl B. Womack, Qi Liu, William P. Tansey, and April M. Weissmiller. 2024. "Super-Enhancer Dysregulation in Rhabdoid Tumor Cells Is Regulated by the SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1" Cancers 16, no. 5: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050916
APA StyleJones, C. A., Wang, J., Evans, J. R., Sisk, H. R., Womack, C. B., Liu, Q., Tansey, W. P., & Weissmiller, A. M. (2024). Super-Enhancer Dysregulation in Rhabdoid Tumor Cells Is Regulated by the SWI/SNF ATPase BRG1. Cancers, 16(5), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050916





