Efficacy and Safety of BTKis in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment of the Included Studies
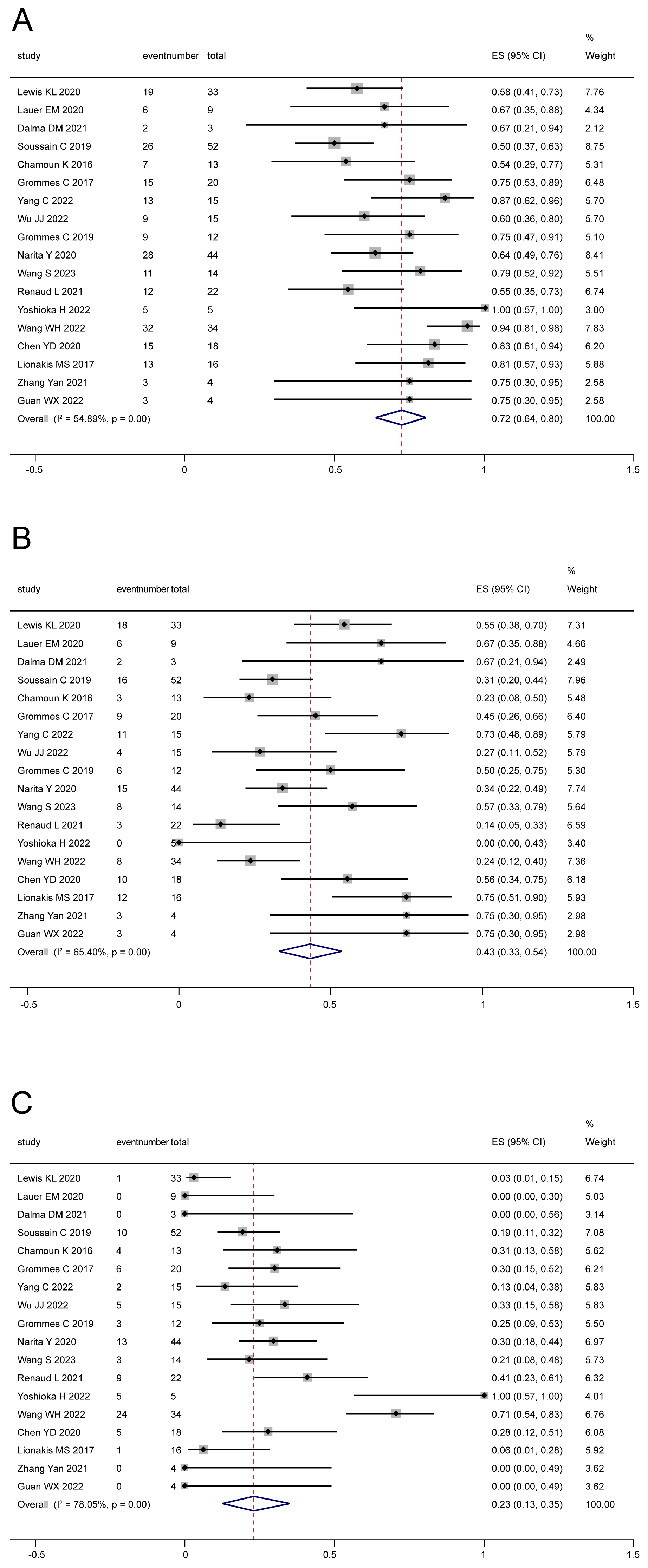
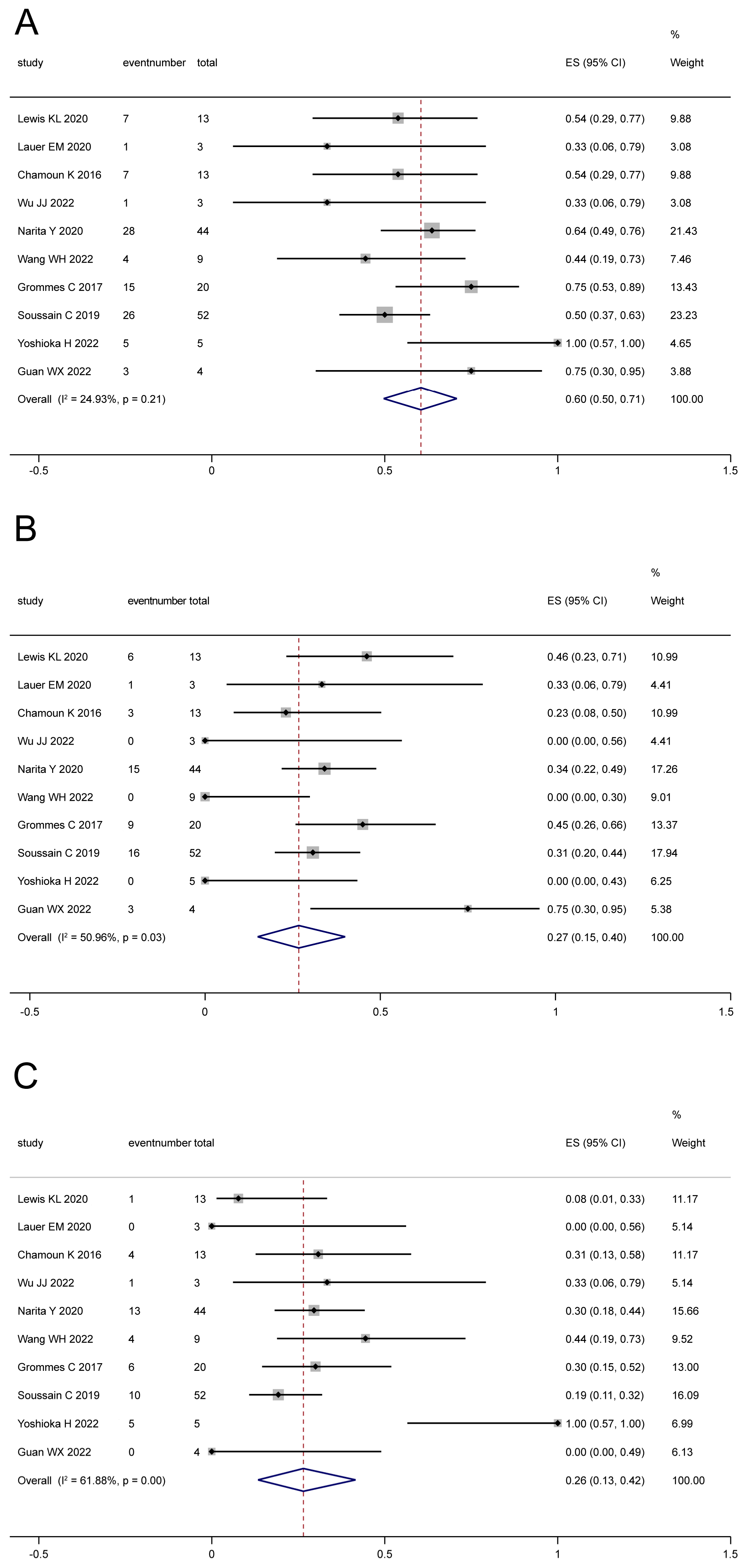
3.3. Efficacy
3.3.1. Tumor Response
3.3.2. Survival
3.4. Adverse Events (AEs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, M.; Engert, A.; Brück, W.; Ferreri, A.J.; Finke, J.; Illerhaus, G.; Klapper, W.; Korfel, A.; Küppers, R.; Maarouf, M.; et al. Modern concepts in the biology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Ding, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Mao, Y.; Chen, T. Current and emerging therapies for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwynarski, K.; Cummin, T.; Osborne, W.; Lewis, J.; Chaganti, S.; Smith, J.; Linton, K.; Greaves, P.; McKay, P.; Fox, C.P.; et al. Management of secondary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang-Xuan, K.; Deckert, M.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Furtner, J.; Gallego Perez-Larraya, J.; Henriksson, R.; Hottinger, A.F.; Kasenda, B.; Lefranc, F.; Lossos, A.; et al. European Association of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guidelines for treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, T.; Tuck, A.; Golestani, F.; Smith, P.; McCulloch, R. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: A practical guide for neurologists. Pract. Neurol. 2023, 23, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, J. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma: A mini-review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1034668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kong, H.; Li, C.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, S.; Lei, T.; Yang, H. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in primary central nervous system lymphoma-evaluation of anti-tumor efficacy and brain distribution. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Witkowska, M.; Smolewski, P. The Role of Bruton’s Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Current Status and Future Directions. Cancers 2022, 14, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, P. Inhibitors targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in cancers: Drug development advances. Leukemia 2021, 35, 312–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Nayak, L.; Tun, H.W.; Batchelor, T.T. Introduction of novel agents in the treatment of primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Geng, D.; Yu, J.T.; Li, Y.; Li, X.Q.; et al. Evidence-based expert consensus on the management of primary central nervous system lymphoma in China. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Cui, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Ibrutinib in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A PRISMA-Compliant Single-Arm Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 707285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, G.; Khurana, M. Ibrutinib in Refractory or Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Present and Future. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, R.; Liang, R.; Gao, Y.; Cui, J. Abstract CT132: Orelabrutinib, a potent and selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor with superior safety profile and excellent PK/PD properties. In Proceedings of the AACR Annual Meeting 2020, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, Y.; Nagane, M.; Mishima, K.; Terui, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Yonezawa, H.; Asai, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Sugiyama, K.; Shinojima, N.; et al. Phase I/II study of tirabrutinib, a second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, W. Preliminary Evaluation of Zanubrutinib-Containing Regimens in DLBCL and the Cerebrospinal Fluid Distribution of Zanubrutinib: A 13-Case Series. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, D. S224: Preliminary Results of a Phase II Study of Orelabrutinib in Combination with Anti-Pd-1 Monoclonal Antibody in Refractory or Relapsed Primary Cns Lymphoma. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cui, Y.; Ren, X.; Li, M.; Yu, K.; Shen, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Orelabrutinib Combined with Lenalidomide and Immunochemotherapy for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Retrospective Analysis of Case Series. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 901797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Wang, W.H.; Dong, M.; Ma, S.S.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhu, L.N.; Niu, S.T.; Ding, M.J.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Orelabrutinib-bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based regimens in the treatment of central nervous system lymphoma: A retrospective study. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kwong, J.S.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Sun, F.; Niu, Y.; Du, L. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: A systematic review. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2015, 8, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyaga, V.N.; Arbyn, M.; Aerts, M. Metaprop: A Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch. Public Health 2014, 72, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, H.; Okuda, T.; Nakao, T.; Fujita, M.; Takahashi, J.C. Experience with Tirabrutinib in the Treatment of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma that Is Difficult to Treat with Standard Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 4173–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.L.; Chin, C.K.; Manos, K. Ibrutinib for central nervous system lymphoma: The Australasian Lymphoma Alliance/MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. Br. J. Hematol. 2021, 192, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, E.M.; Waterhouse, M.; Braig, M.; Mutter, J.; Bleul, S.; Duque-Afonso, J.; Duyster, J.; Marks, R.; Reinacher, P.C.; Prinz, M.; et al. Ibrutinib in patients with relapsed/refractory central nervous system lymphoma: A retrospective single-centre analysis. Br. J. Hematol. 2020, 190, e110–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak-Mihaly, D.; Iluta, S.; Pasca, S.; Jitaru, C.; Roman, A. Ibrutinib Monotherapy as Bridge-to-Transplant for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Oculo-Cerebral Lymphoma. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussain, C.; Choquet, S.; Blonski, M.; Leclercq, D.; Houillier, C.; Rezai, K.; Bijou, F.; Houot, R.; Boyle, E.; Gressin, R.; et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy for relapse or refractory primary CNS lymphoma and primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: Final analysis of the phase II ‘proof-of-concept’ iLOC study by the Lymphoma study association (LYSA) and the French oculo-cerebral lymphoma (LOC) network. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 117, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, K.; Choquet, S.; Boyle, E.; Houillier, C.; Larrieu-Ciron, D.; Al Jijakli, A.; Delrieu, V.; Delwail, V.; Morschhauser, F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory CNS lymphoma: A retrospective case series. Neurology 2017, 88, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Pastore, A.; Palaskas, N.; Tang, S.S.; Campos, C.; Schartz, D.; Codega, P.; Nichol, D.; Clark, O.; Hsieh, W.Y.; et al. Ibrutinib Unmasks Critical Role of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionakis, M.S.; Dunleavy, K.; Roschewski, M.; Widemann, B.C.; Butman, J.A.; Schmitz, R.; Yang, Y.; Cole, D.E.; Melani, C.; Higham, C.S.; et al. Inhibition of B Cell Receptor Signaling by Ibrutinib in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 833–843.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, X.; Ding, T.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, T. The outcome of ibrutinib-based regimens in relapsed/refractory central nervous system lymphoma and the potential impact of genomic variants. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 32, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grommes, C.; Tang, S.S.; Wolfe, J.; Kaley, T.J.; Daras, M.; Pentsova, E.I.; Piotrowski, A.F.; Stone, J.; Lin, A.; Nolan, C.P.; et al. Phase 1b trial of an ibrutinib-based combination therapy in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, L.; Bossard, J.B. Treatment with temozolomide and ibrutinib in recurrent/refractory primary (PCNSL) and secondary CNS lymphoma (SCNSL). Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 107, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Liu, H.; Shen, H. Clinical features and prognostic analysis of 49 cases of newly diagnosed primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Chin. J. Hematol. 2021, 42, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Pang, D.; Guo, H.; Ou, Q. Clinical outcomes of newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma treated with ibrutinib-based combination therapy: A real-world experience of off-label ibrutinib use. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 8676–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Wang, L.; Peng, X. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in vitreoretinal lymphoma: An open-label, prospective, single-center, phase 2 study. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Bai, X. A preliminary study of ibrutinib in combination with chemotherapy for relapsed refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma. Chin. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 36, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M. Therapeutic role and safety analysis of BTK inhibitors in central nervous system lymphoma. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 50, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Cwynarski, K.; Pulczynski, E.; Ponzoni, M.; Deckert, M.; Politi, L.S.; Torri, V.; Fox, C.P.; Rosée, P.L.; Schorb, E.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with methotrexate, cytarabine, thiotepa, and rituximab (MATRix regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma: Results of the first randomisation of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group-32 (IELSG32) phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2016, 3, e217–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusconi, C.; Cheah, C.Y. Ibrutinib improves survival compared with chemotherapy in mantle cell lymphoma with central nervous system relapse. Blood 2022, 140, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambady, P.; Doolittle, N.D.; Fox, C.P. Relapsed and refractory primary CNS lymphoma: Treatment approaches in routine practice. Ann. Lymphoma 2021, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasenda, B.; Ihorst, G.; Schroers, R.; Korfel, A.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.; Egerer, G.; von Baumgarten, L.; Röth, A.; Bloehdorn, J.; Möhle, R.; et al. High-dose chemotherapy with autologous haematopoietic stem cell support for relapsed or refractory primary CNS lymphoma: A prospective multicentre trial by the German Cooperative PCNSL study group. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mappa, S.; Marturano, E.; Licata, G.; Frezzato, M.; Frungillo, N.; Ilariucci, F.; Stelitano, C.; Ferrari, A.; Sorarù, M.; Vianello, F.; et al. Salvage chemoimmunotherapy with rituximab, ifosfamide and etoposide (R-IE regimen) in patients with primary CNS lymphoma relapsed or refractory to high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 31, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, J.; Versmee, L.; Drappatz, J.; Eichler, A.F.; Nayak, L.; Norden, A.; Wong, E.; Pisapia, M.R.; Jones, S.S.; Gordon, A.B.; et al. Pemetrexed in Recurrent or Progressive Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Phase I Multicenter Clinical Trial. Oncologist 2020, 25, 747–e1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
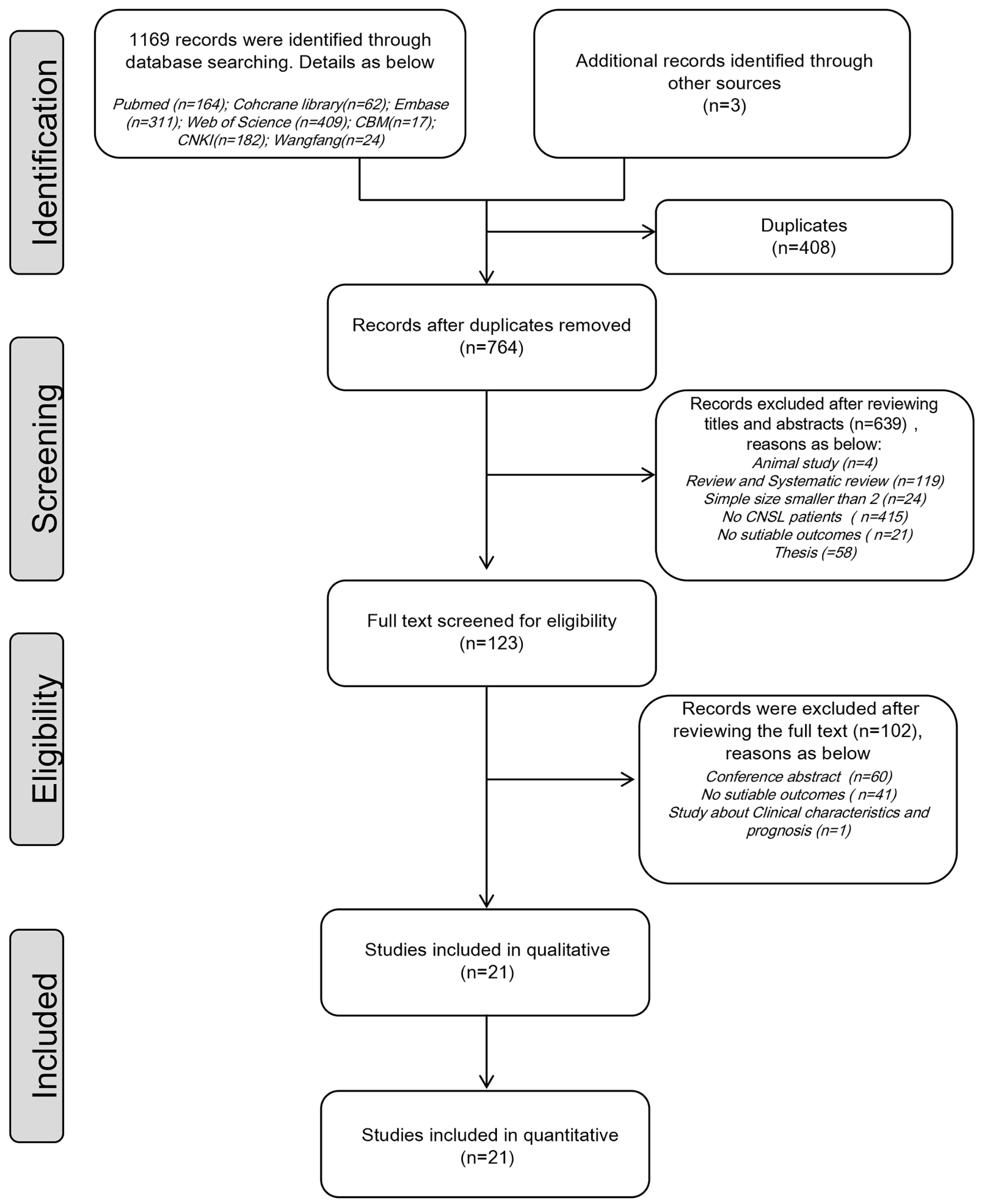


| No. Study | Country | Study Design | No. of Patients | Male/ Female | Median (Range) Age, Years | CNSL Status | Type of CNSL | Intervention | Outcomes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORR (%) | CR (%) | PR (%) | mPFS (Month) | mOS (Month) | ||||||||||
| 1 | Chamoun K 2016 [31] | US | Retrospective case series | 14 | 9/5 | 68 (48–79) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib monotherapy | 50 | 21 | 29 | - | - |
| 2 | Grommes C 2017 [32] | US | Prospective | 20 | 8/12 | 69 (21–85) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Ibrutinib monotherapy | 70 | 45 | 25 | 4.6 | - |
| 3 | Lionakis MS 2017 [33] | US | Retrospective | 18 | 11/70 | 66 (49–87) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib/DA-TEDDi-R combination | 93 | 86 | 7 | 15.3 | NR |
| 4 | Soussain C 2019 [30] | France | Prospective | 52 | 24/28 | 67.5 (47–82) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib monotherapy | 52 | 19 | 33 | 4.8 | 19.2 |
| 5 | Grommes C 2019 [35] | US | Prospective | 15 | 8/7 | 62 (23–74) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Ibrutinib-based combination therapy | 80 | 53 | 27 | 9.2 | NR |
| 6 | Chen F 2020 [38] | China | Retrospective | 11 | 7/4 | 56 (41–68) | Newly diagnosed | Primary | Ibrutinib/MTX combination | 82 | 64 | 18 | 7.4 | NR |
| 7 | Lauer EM 2020 [28] | UK | Retrospective | 9 | NA | 63 (53–82) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Ibrutinib monotherapy or in combination with other regimens | 66 | 66 | 0 | 9.2 | NR |
| 8 | Chen YD 2020 [40] | China | Retrospective | 18 | 10/8 | 58.5 (18–76) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib-based regimen | 83 | 55 | 28 | 6 | 15 |
| 9 | Lewis KL 2020 [27] | Australia | Prospective | 33 | 23/10 | 64 (22–85) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Ibrutinib monotherapy or in combination with other regimens | 58 | 55 | 3 | - | - |
| 10 | Narita Y 2020 [18] | Japan | Prospective | 44 | 24/20 | 60 (29–86) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Tirabrutinib | 64 | 34 | 30 | 2.9 | NR |
| 11 | Dalma DM 2021 [29] | Romania | Retrospective case series | 3 | 1/2 | 60 (53–64) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib monotherapy or in combination with other regimens | 67 | 67 | 0 | - | - |
| 12 | Yu HF 2021 [9] | China | Retrospective | 3 | 1/2 | 76 (45–79) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary | Ibrutinib monotherapy or in combination with other regimens | 100 | 67 | 33 | - | - |
| 13 | Zhang Y 2021 [19] | China | Retrospective case series | 13 | 3/10 | 53 (52–69) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary | Zanubrutinib-based regimens | 88 | 88 | 0 | - | - |
| 14 | Renaud L 2021 [36] | France | Retrospective | 22 | 12/10 | 71 (44–89) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Ibrutinib and temozolomide | 55 | 14 | 41 | 5.3 | 8.9 |
| 15 | Song J 2021 [37] | China | Retrospective | 49 | 32/17 | 63 (33–81) | Newly diagnosed | Primary | ibrutinib or zanubrutinib in combination with other regimens | - | - | - | i: 20 z: 5 | i: 42 z: NR |
| 16 | Yoshioka H 2022 [26] | Japan | Retrospective case series | 5 | 1/4 | 76 (62–77) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Tirabrutinib-based regimens | 100 | 0 | 100 | - | - |
| 17 | Wu JJ 2022 [22] | China | Retrospective | 23 | 15/8 | 55 ± 13.78 (mean) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary/secondary | Orelabrutinib monotherapy or orelabrutinib-based regimens | 68 | 31 | 37 | - | - |
| 18 | Yang C 2022 [21] | China | Retrospective | 15 | 5/10 | 62 (33–78) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary | Combination of rituximab, HD-MTX, temozolomide, orelabrutinib, and lenalidomide | 86 | 73 | 13 | 9.8 | NR |
| 19 | Guan WX 2022 [39] | China | Prospective | 10 | 3/7 | 52 (41–74) | Newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory | Primary | BTKi (ibrutinib zanubrutinib or orelabrutinib) monotherapy treatment | 90 | 70 | 20 | - | - |
| 20 | Wang WH 2022 [41] | China | Retrospective | 43 | 22/21 | 53 (52–69) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/Secondary | Ibrutinib-based regimens | 74 | 18 | 56 | - | - |
| 21 | Wang S 2023 [34] | China | Retrospective | 14 | 10/4 | 58 (37–80) | Relapsed/refractory | Primary/Secondary | Ibrutinib-based regimens | 78 | 57 | 21 | 4 | - |
| Studies | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chamoun K 2016 [31] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | NA |
| Grommes C 2017 [32] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Unclear | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Lionakis MS 2017 [33] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Soussain C 2019 [30] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Grommes C 2019 [35] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Chen F 2020 [38] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Lewis KL 2020 [27] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Lauer EM 2020 [28] | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Narita Y 2020 [18] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Chen YD 2020 [40] | Yes | No | Unclear | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Dalma DM 2021 [29] | Yes | No | Unclear | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | NA |
| Renaud L 2021 [36] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Yoshioka H 2021 [26] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | NA |
| Zhang Y 2021 [19] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Yu HF 2021 [9] | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | NA |
| Song J 2021 [37] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Yang C 2022 [21] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Wu JJ 2022 [22] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Guan WX 2022 [39] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Wang WH 2022 [41] | Yes | No | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Wang S 2023 [34] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Unclear | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Study | ORR | CR | PR | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event Number | Total | Effect Size | Lower CI | Upper CI | Event Number | Total | Effect Size | Lower CI | Upper CI | Event Number | Total | Effect Size | Lower CI | Upper CI | |
| Chen F [38] | 9 | 11 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.95 | 7 | 11 | 0.64 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 2 | 11 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.48 |
| Wu JJ [22] | 4 | 4 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 2 | 4 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 2 | 4 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.85 |
| Guan WX [39] | 6 | 6 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 1.00 | 4 | 6 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 2 | 6 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.70 |
| Zhang Y [19] | 4 | 4 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 4 | 4 | 1.00 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 0 | 4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.49 |
| Yu HF [9] | 2 | 2 | 1.00 | 0.34 | 1.00 | 1 | 2 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.91 | 1 | 2 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.91 |
| Lionakis MS [33] | 5 | 5 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 | 5 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 5 | 5 | 1.00 | 0.57 | 1.00 |
| Grommes C [35] | 3 | 3 | 1.00 | 0.44 | 1.00 | 1 | 3 | 0.53 | 0.23 | 0.82 | 2 | 3 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.76 |
| Adverse Event in Detail | All Types of BTKis (95% CI) | I2 | Ibrutinib (95% CI) | I2 | Second-Generation BTKis (95% CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.09 (0.02, 0.18) | 55.82% | 0.13 (0.07, 0.21) | 0.00% | 0.04 (0.00, 0.19) | 68.06% |
| Neutropenia | 0.12 (0.04, 0.22) | 67.96% | 0.12 (0.03, 0.26) | 68.64% | 0.11 (0.00, 0.34) | 77.83% |
| Anemia | 0.12 (0.05, 0.20) | 0.00% | 0.12 (0.05, 0.20) | 0.00% | NA | |
| Leukopenia | 0.10 (0.02, 0.20) | 74.96% | 0.10 (0.01, 0.25) | 78.61% | 0.09 (0.00, 0.30) | 76.17% |
| Lymphopenia | 0.19 (0.00, 0.56) | 92.37% | 0.19 (0.00, 0.56) | 92.37% | NA | |
| Febrile neutropenia | 0.04 (0.00, 0.19) | 53.85% | 0.04 (0.00, 0.19) | 53.85% | NA | |
| Aspergillosis | 0.03 (0.00, 0.8) | 0.00% | 0.03 (0.00, 0.8) | 0.00% | NA | |
| Infection | 0.12 (0.04, 0.22) | 72.33% | 0.14 (0.05, 0.27) | 75.07% | 0.03 (0.00, 0.10) | 0.00% |
| Bleeding | 0.02 (0.00, 0.06) | 0.00% | 0.02 (0.00, 0.06) | 0.00% | 0.02 (0.00, 0.14) | 0.00% |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.01 (0.00, 0.04) | 0.00% | 0.01 (0.00, 0.04) | 0.00% | NA | |
| Transaminase increase | 0.05 (0.00, 0.14) | 66.13% | 0.13 (0.01, 0.31) | 75.96% | 0.01 (0.0, 0.06) | 0.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, D.; Ji, C. Efficacy and Safety of BTKis in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050860
Zhang Y, Ye J, Chen H, Zhou D, Ji C. Efficacy and Safety of BTKis in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050860
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yan, Jingjing Ye, Hao Chen, Daobin Zhou, and Chunyan Ji. 2024. "Efficacy and Safety of BTKis in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 5: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050860
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ye, J., Chen, H., Zhou, D., & Ji, C. (2024). Efficacy and Safety of BTKis in Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(5), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050860







