Comprehensive Landscape of BRAF Variant Classes, Clonalities, and Co-Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Using ctDNA Profiling
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
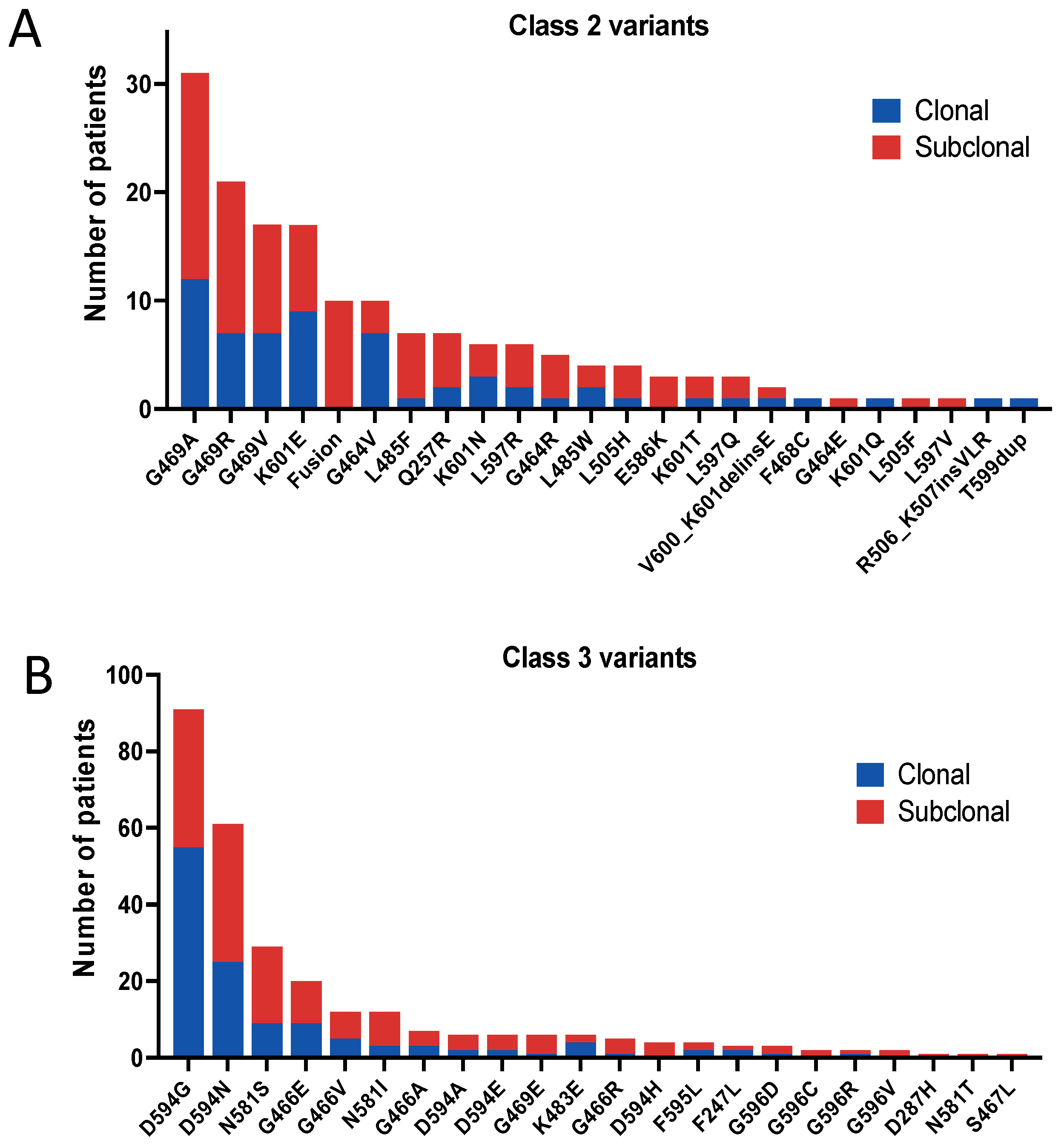
3.2. Distribution of BRAF Variant Classes
3.3. Clonality of BRAF Variant Classes
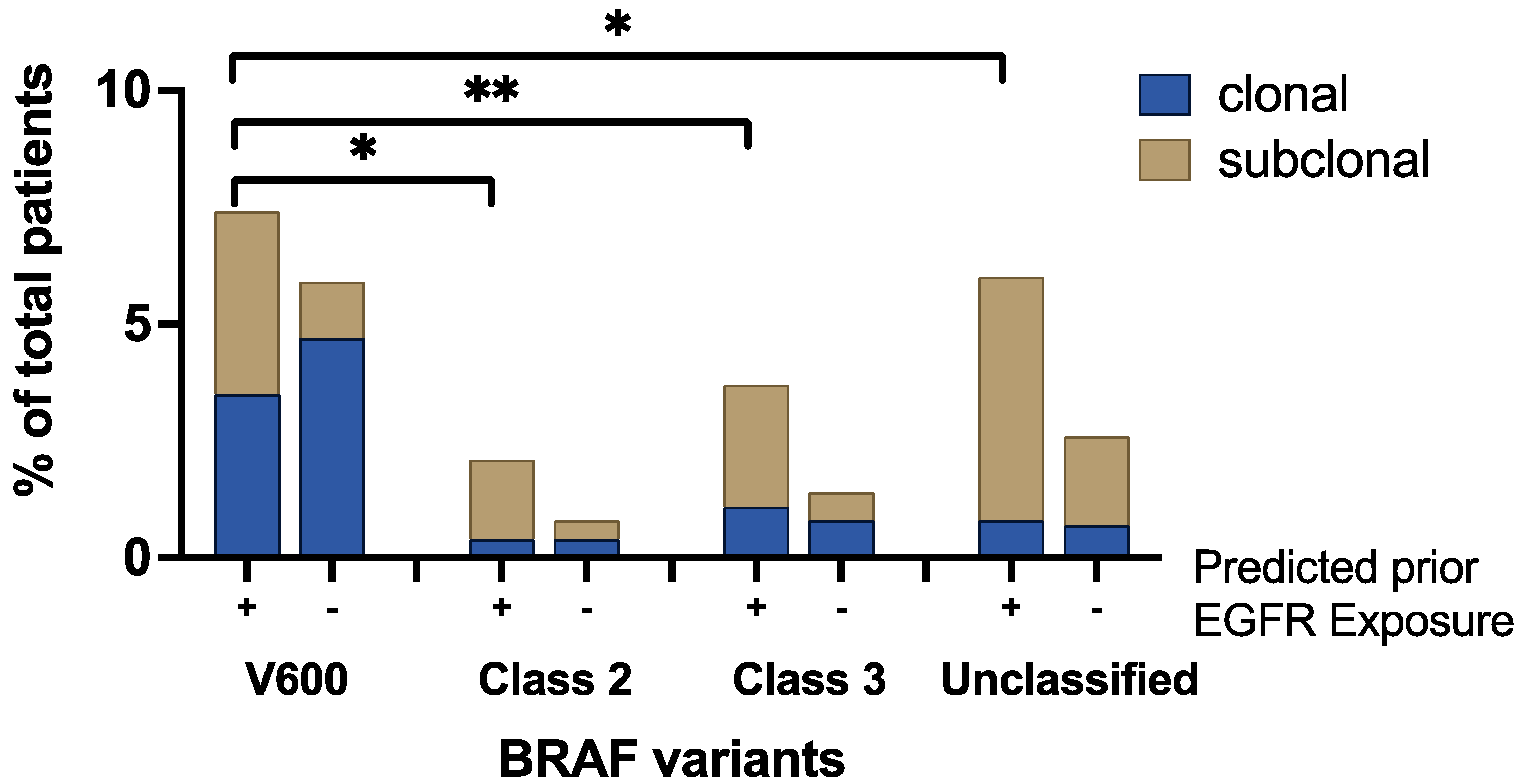
3.4. Clonality and Anti-EGFR Exposure Score
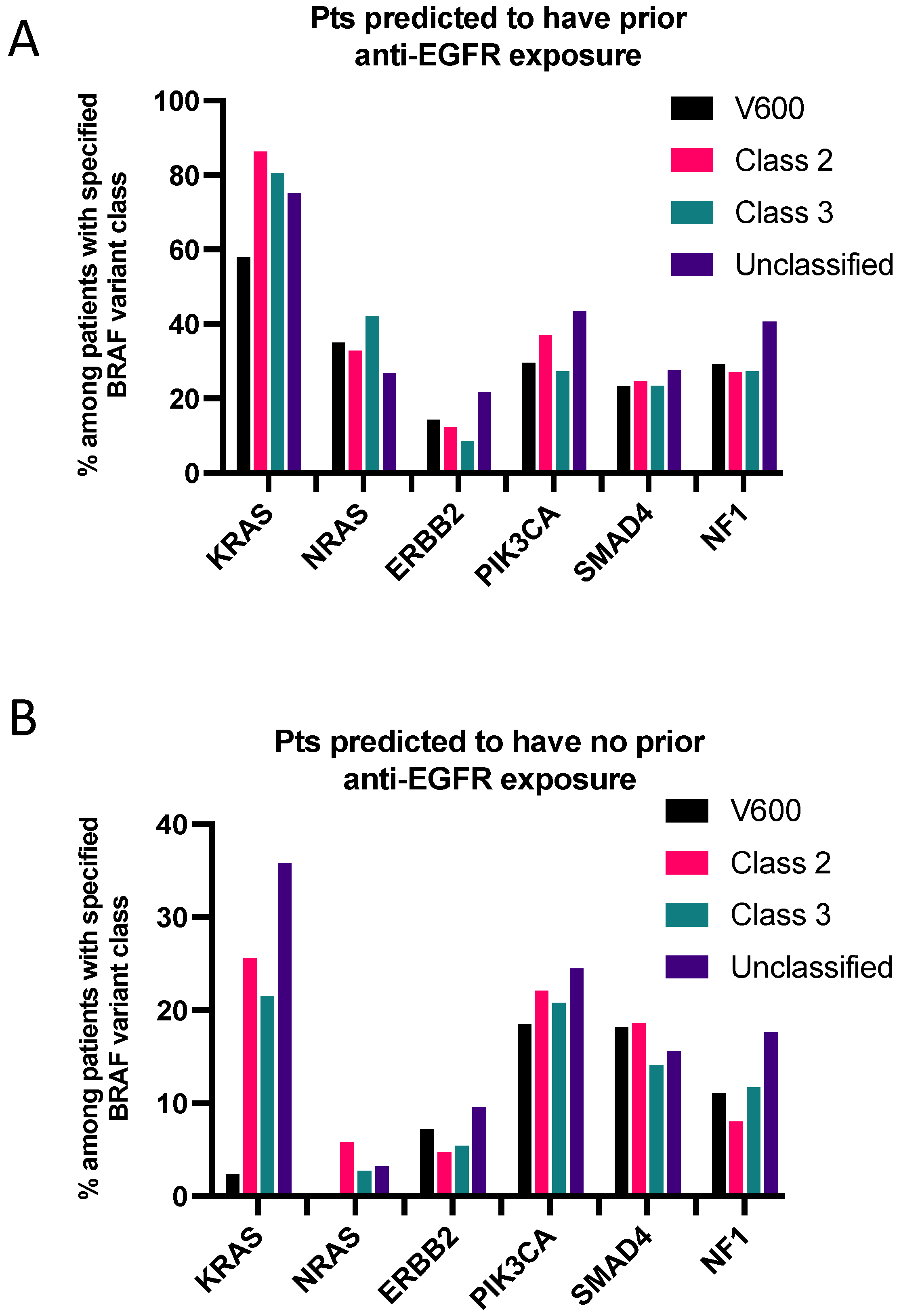
3.5. Co-Mutations Analysis
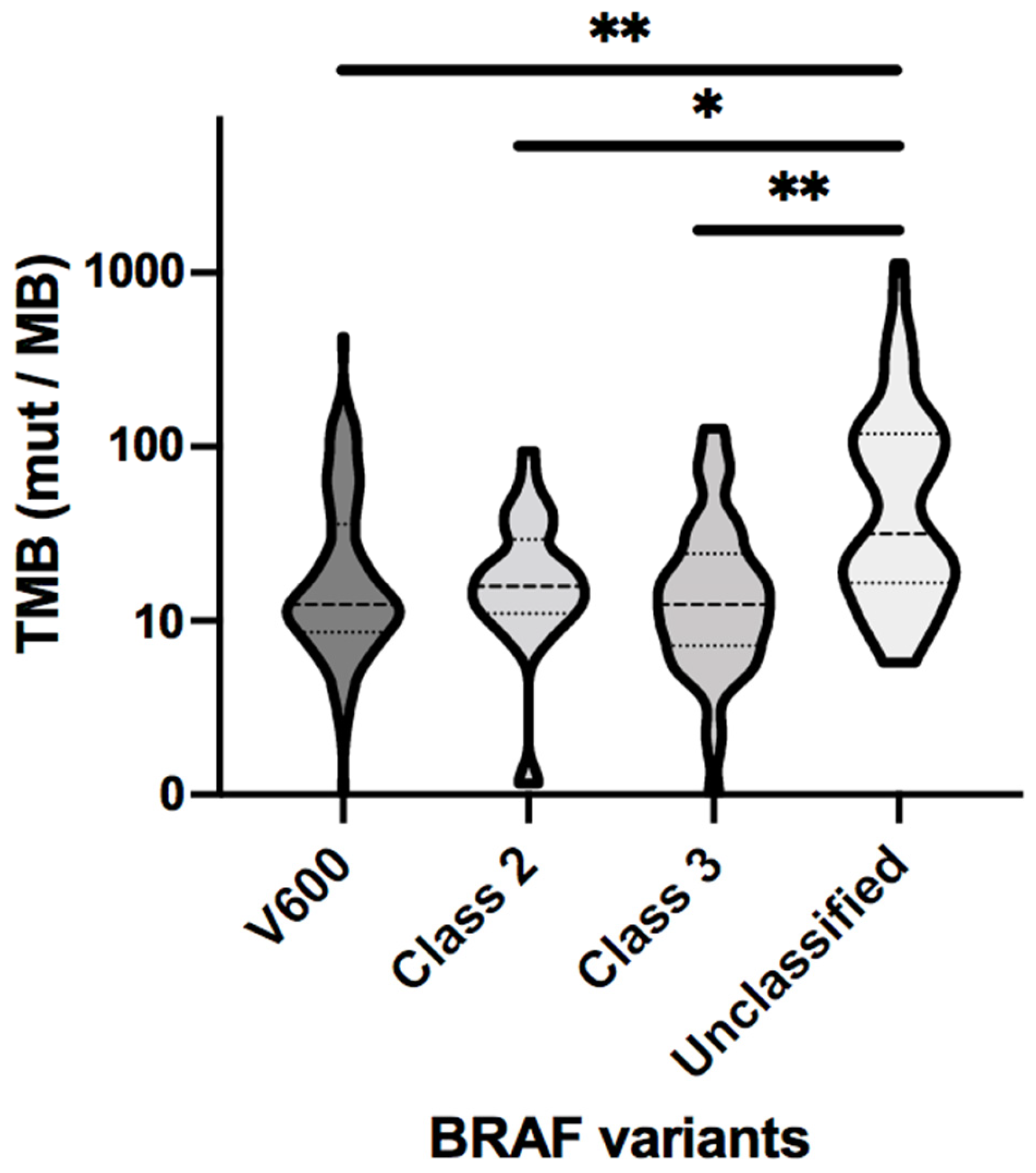
3.6. Clinical Cohort Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aguilar, E.A.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Kim, T.W.; Van Cutsem, E.; Geva, R.; Jäger, D.; Hara, H.; Burge, M.; O’Neil, B.; Kavan, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Phase II open-label study of pembrolizumab in treatment-refractory, microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: KEYNOTE-164. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, T.; Shiu, K.K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in microsatellite-instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, H.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Luisa Limon, M.; Wong, K.Y.; Hendlisz, A.; Aglietta, M.; García-Alfonso, P.; Neyns, B.; Luppi, G.; Cardin, D.B.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab for microsatelliteinstability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: The phase II CheckMate 142 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.X.; Jonker, D.J.; Loree, J.M.; Kennecke, H.F.; Berry, S.R.; Couture, F.; Ahmad, C.E.; Goffin, J.R.; Kavan, P.; Harb, M.; et al. Effect of combined immune checkpoint inhibition vs best supportive care alone in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: The Canadian Cancer Trials Group CO.26 Study. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, C.; Kim, T.W.; Bendell, J.; Argilés, G.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Falcone, A.; Fakih, M.; Kozloff, M.; Segal, N.H.; et al. Atezolizumab with or without cobimetinib versus regorafenib in previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (IMblaze370): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overman, M.J.; McDermott, R.; Leach, J.L.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.J.; Morse, M.A.; Desai, J.; Hill, A.; Axelson, M.; Moss, R.A.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Lonardi, S.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Lenz, H.J.; Gelsomino, F.; Aglietta, M.; Morse, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; McDermott, R.; Hill, A.; et al. Durable Clinical Benefit With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in DNA Mismatch Repair-Deficient/Microsatellite Instability-High Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Xiao, B.Y.; Tang, J.H.; Li, D.D.; Wang, F.; Ding, Y.; Han, K.; Kong, L.H.; Ling, Y.H.; Mei, W.J.; et al. Efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors for colorectal cancer and polyps in Lynch syndrome patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 192, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sandhu, J.; Ouyang, C.; Ye, J.; Lee, P.P.; Fakih, M. Clinical response to immunotherapy targeting programmed cell death receptor 1/programmed cell death ligand 1 in patients with treatment-resistant microsatellite stable colorectal cancer with and without liver metastases. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2118416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF Gene in Human Cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fouchardière, C.; Cohen, R.; Malka, D.; Guimbaud, R.; Bourien, H.; Lièvre, A.; Cacheux, W.; Artru, P.; François, E.; Gilabert, M.; et al. Characteristics of BRAFV600E Mutant, Deficient Mismatch Repair/Proficient Mismatch Repair, Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Series of 287 Patients. Oncologist 2019, 24, e1331–e1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarpia, L.; Lippman, S.M.; El-Naggar, A.K. Targeting the MAPK-RAS-RAF Signaling Pathway in Cancer Therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, S.A.; Beare, D.; Boutselakis, H.; Bamford, S.; Bindal, N.; Tate, J.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.; Dawson, E.; Ponting, L.; et al. COSMIC: Somatic Cancer Genetics at High-Resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D777–D783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Yaeger, R.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.S.; Tao, A.; Torres, N.M.; Chang, M.T.; Drosten, M.; Zhao, H.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Tumours with Class 3 BRAF Mutants Are Sensitive to the Inhibition of Activated RAS. Nature 2017, 548, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.C.; Renfro, L.A.; Al-Shamsi, H.O.; Schrock, A.B.; Rankin, A.; Zhang, B.Y.; Kasi, P.M.; Voss, J.S.; Leal, A.D.; Sun, J.; et al. Non-V600 BRAF Mutations Define a Clinically Distinct Molecular Subtype of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremolini, C.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Amatu, A.; Antoniotti, C.; Moretto, R.; Berenato, R.; Perrone, F.; Tamborini, E.; Aprile, G.; Lonardi, S.; et al. BRAF Codons 594 and 596 Mutations Identify a New Molecular Subtype of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer at Favorable Prognosis. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Z.; Shen, L.; Wang, X. Real-world treatment and outcomes of patients with metastatic BRAF mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 10473–10484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicolantonio, F.; Martini, M.; Molinari, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Arena, S.; Saletti, P.; De Dosso, S.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Frattini, M.; Siena, S.; et al. Wild-Type BRAF Is Required for Response to Panitumumab or Cetuximab in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5705–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.; Loree, J.M.; Jacome, A.A.; Mendis, S.; Syed, M.; Morris Ii, V.K.; Parseghian, C.M.; Dasari, A.; Pant, S.; Raymond, V.M.; et al. Atypical, Non-V600 BRAF Mutations as a Potential Mechanism of Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachou, M.S.; Mauri, D.; Zarkavelis, G.; Ntellas, P.; Tagkas, C.; Gkoura, S.; Pentheroudakis, G. Plasma ctDNA RAS status selects patients for anti-EGFR treatment rechallenge in metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Exp. Oncol. 2021, 43, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jones, J.C.; Kipp, B.R.; Grothey, A. Activity of EGFR Antibody in Non-V600 BRAF Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeger, R.; Kotani, D.; Mondaca, S.; Parikh, A.R.; Bando, H.; Van Seventer, E.E.; Taniguchi, H.; Zhao, H.; Thant, C.N.; de Stanchina, E.; et al. Response to Anti-EGFR Therapy in Patients with BRAF Non-V600-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7089–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E–Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.H.; et al. Association of Tumour Mutational Burden with Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumours Treated with Pembrolizumab: Prospective Biomarker Analysis of the Multicohort, Open-Label, Phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, F.; Song, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Lui, S.; Wu, M. Tumor Mutational Burden Predicting the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 751407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.T.C.; Garnett, M.J.; Roe, S.M.; Lee, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Good, V.M.; Jones, C.M.; Marshall, C.J.; Springer, C.J.; Barford, D.; et al. Mechanism of Activation of the RAF-ERK Signaling Pathway by Oncogenic Mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004, 116, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoulia, Z.; Gavathiotis, E.; Poulikakos, P.I. New Perspectives for Targeting RAF Kinase in Human Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Su, W.; Yaeger, R.; Tao, J.; Na, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Rymar, A.; Tao, A.; et al. RAF Inhibitor PLX8394 Selectively Disrupts BRAF Dimers and RAS-Independent BRAF-Mutant-Driven Signaling. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| BRAF Variants | 14,742 mCRC Patients, 1733 Patients with BRAF Variants 1905 Total Variants, 431 Unique Variants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V600 | Class II | Class III | Unclassified | |
| Pts (% of BRAF pts, % of total CRC pts) | 926 (53.4%, 6.3%) | 159 (9.1%, 1.1%) | 277 (16.0%, 1.9%) | 475 (27.4%, 3.2%) |
| Variants (% of total variants) | 926 (48.6%) | 163 (8.6%) | 284 (14.9%) | 532 (27.9%) |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 408 (44.1%) | 94 (59.1%) | 165 (60.0%) | 267 (56.2%) |
| Female | 518 (55.9%) | 65 (40.9%) | 112 (40.4%) | 208 (43.8%) |
| Age, years, median (range) | 65 (16–98) | 61 (28–95) | 59 (28–94) | 61 (14–95) |
| ≥65 | 472 (51.0%) | 59 (37.1%) | 113 (40.8%) | 190 (40.0%) |
| <65 | 451 (48.7%) | 100 (62.9%) | 163 (58.8%) | 284 (59.8%) |
| NA | 3 (0.3%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.4%) | 1 (0.2%) |
| % of Total BRAF Variants (% of the Class) | Clonal Variant | Subclonal Variant |
|---|---|---|
| V600 | 34.3% (70.7%) | 14.2% (29.3%) |
| Class II | 3.2% (37.4%) | 5.4% (62.6%) |
| Class III | 6.6% (44.0%) | 8.3% (56.0%) |
| Unclassified | 5.9% (21.2%) | 22% (78.8%) |
| Clonal Median VAF (Range) | Subclonal Median VAF (Range) | |
|---|---|---|
| V600 | 6.3% (0.03–94.9%) | 0.2% (0.01–36.0%) |
| Class II | 7.4% (0.05–75.5%) | 0.2% (0.03–14.7%) |
| Class III | 8.1% (0.05–55.7%) | 0.2% (0.01–27.6%) |
| Unclassified | 2.7% (0.10–55.1%) | 0.3% (0.04–31.6%) |
| V600 | Class II | Class III | Unclassified | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR exposure | ||||
| clonal | 3.5% | 0.4% | 1.1% | 0.8% |
| subclonal | 3.9% | 1.7% | 2.6% | 5.2% |
| no EGFR exposure | ||||
| clonal | 4.7% | 0.4% | 0.8% | 0.7% |
| subclonal | 1.2% | 0.4% | 0.6% | 1.9% |
| Number of Samples | TMB Median (mut/MB) | |
|---|---|---|
| V600 | 120 | 12.44 |
| Class II | 36 | 15.79 |
| Class III | 45 | 12.44 |
| Unclassified | 57 | 31.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, B.; Morris, V.; Wang, X.; Dasari, A.; Raghav, K.; Shen, J.P.; Lee, M.S.; Huey, R.; Parseghian, C.; Willis, J.; et al. Comprehensive Landscape of BRAF Variant Classes, Clonalities, and Co-Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Using ctDNA Profiling. Cancers 2024, 16, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040737
Johnson B, Morris V, Wang X, Dasari A, Raghav K, Shen JP, Lee MS, Huey R, Parseghian C, Willis J, et al. Comprehensive Landscape of BRAF Variant Classes, Clonalities, and Co-Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Using ctDNA Profiling. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040737
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Benny, Van Morris, Xuemei Wang, Arvind Dasari, Kanwal Raghav, John Paul Shen, Michael S. Lee, Ryan Huey, Christine Parseghian, Jason Willis, and et al. 2024. "Comprehensive Landscape of BRAF Variant Classes, Clonalities, and Co-Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Using ctDNA Profiling" Cancers 16, no. 4: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040737
APA StyleJohnson, B., Morris, V., Wang, X., Dasari, A., Raghav, K., Shen, J. P., Lee, M. S., Huey, R., Parseghian, C., Willis, J., Wolff, R., Drusbosky, L. M., Overman, M. J., & Kopetz, S. (2024). Comprehensive Landscape of BRAF Variant Classes, Clonalities, and Co-Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Using ctDNA Profiling. Cancers, 16(4), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040737






