Artificial Intelligence-Based Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis Detection in Cervical Cancer †
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
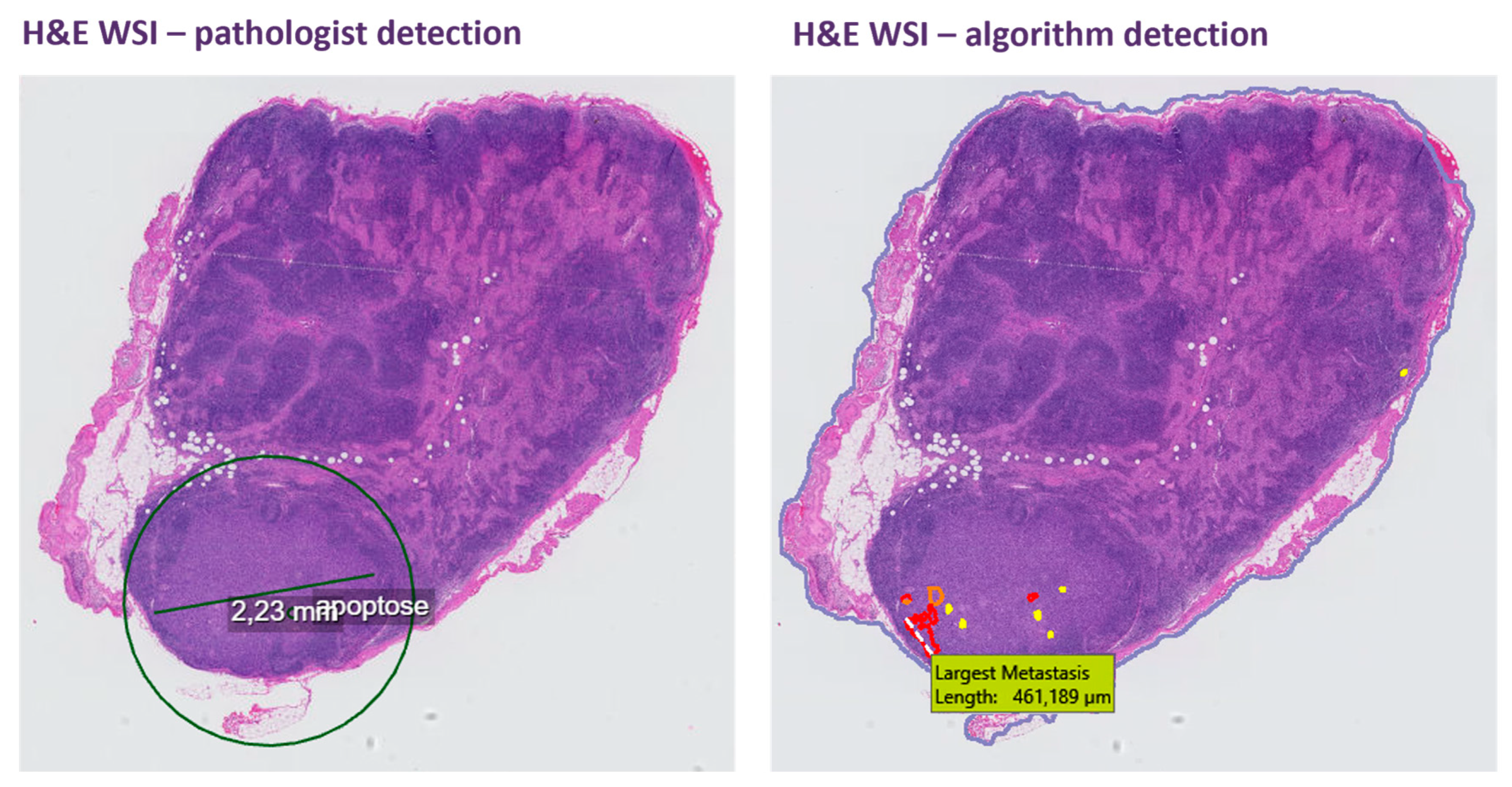
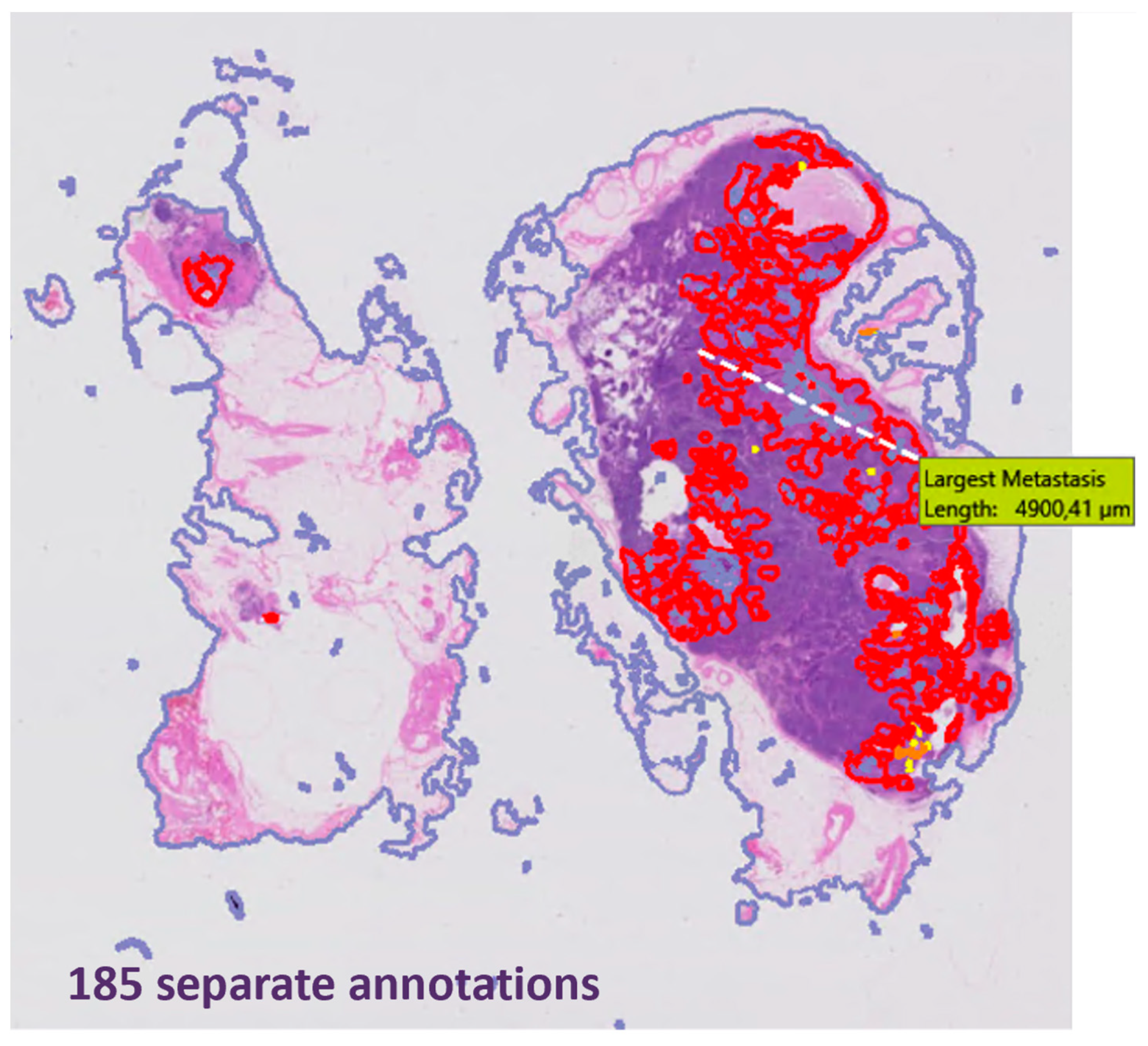
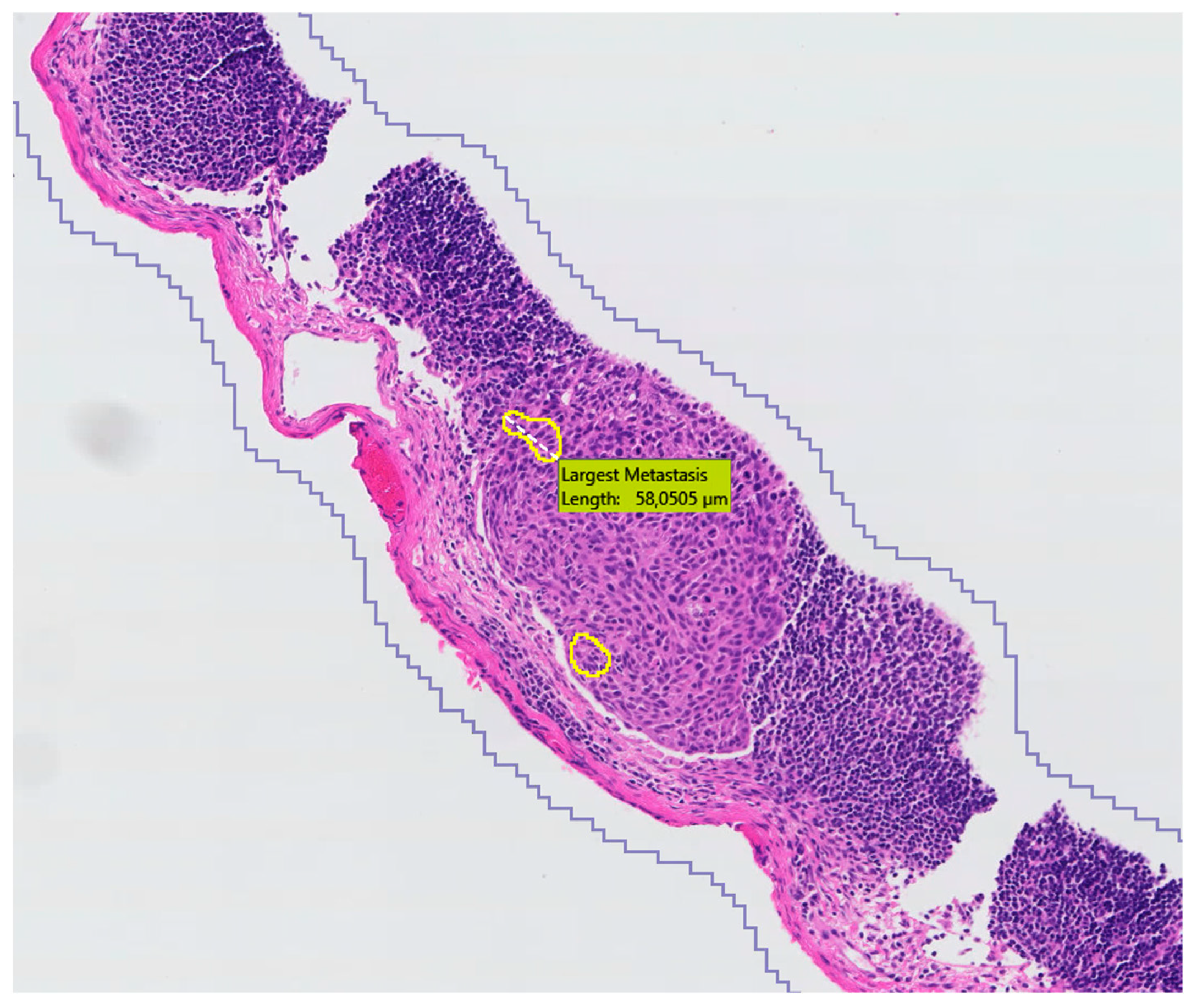
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cibula, D.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Dusek, L.; Zikán, M.; Zaal, A.; Sevcik, L.; Kenter, G.G.; Querleu, D.; Jach, R.; Bats, A.S.; et al. Prognostic significance of low volume sentinel lymph node disease in early-stage cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibula, D.; Raspollini, M.R.; Planchamp, F.; Centeno, C.; Chargari, C.; Felix, A.; Fischerová, D.; Jahnn-Kuch, D.; Joly, F.; Kohler, C.; et al. ESGO/ESTRO/ESP Guidelines for the management of patients with cervical cancer—Update 2023*. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Euscher, E.D.; Malpica, A.; Atkinson, E.N.; Levenback, C.F.; Frumovitz, M.; Deavers, M.T. Ultrastaging improves detection of metastases in sentinel lymph nodes of uterine cervix squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 32, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibula, D.; McCluggage, W.G. Sentinel lymph node (SLN) concept in cervical cancer: Current limitations and unanswered questions. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 152, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibula, D.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Dusek, L.; Slama, J.; Zikán, M.; Zaal, A.; Sevcik, L.; Kenter, G.; Querleu, D.; Jach, R.; et al. Bilateral ultrastaging of sentinel lymph node in cervical cancer: Lowering the false-negative rate and improving the detection of micrometastasis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 127, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundr, P.; Cibula, D.; Němejcová, K.; Tichá, I.; Bártů, M.; Jakša, R. Pathologic Protocols for Sentinel Lymph Nodes Ultrastaging in Cervical Cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 144, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, I.G.T.; Hoogendam, J.P.; Jonges, G.N.; Jürgenliemk-Schulz, I.M.; Braat, A.J.A.T.; van Diest, P.J.; Gerestein, C.G.; Zweemer, R.P. Value of routine cytokeratin immunohistochemistry in detecting low volume disease in cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 165, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G.; Ciompi, F. Deep learning in histopathology: The path to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Veta, M.; Johannes van Diest, P.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; van der Laak, J.; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; Balkenhol, M.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women with Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kohlberger, T.; Norouzi, M.; Dahl, G.E.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Olson, N.; Peng, L.H.; Hipp, J.D.; Stumpe, M.C. Artificial Intelligence-Based Breast Cancer Nodal Metastasis Detection: Insights Into the Black Box for Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.F.; MacDonald, R.; Liu, Y.; Truszkowski, P.; Hipp, J.D.; Gammage, C.; Thng, F.; Peng, L.; Stumpe, M.C. Impact of Deep Learning Assistance on the Histopathologic Review of Lymph Nodes for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, B.; Tahir, M.; Hu, Y.; Kellough, D.; Lujan, G.; Sun, S.; Parwani, A.V.; Li, Z. Artificial Intelligence-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Lymph Node Metastasis on Histologic Slides in a Digital Workflow. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dooijeweert, C.; Flach, R.N.; ter Hoeve, N.D.; Vreuls, C.P.H.; Goldschmeding, R.; Freund, J.E.; Pham, P.; Nguyen, T.Q.; van der Wall, E.; Frederix, G.W.J.; et al. Clinical implementation of artificial-intelligence-assisted detection of breast cancer metastases in sentinel lymph nodes: The CONFIDENT-B single-center, non-randomized clinical trial. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeten, I.G.; Stathonikos, N.; Hoogendam, J.P.; Gerestein, C.G.; Jonges, G.N.; Zweemer, R.P.; Diest, P.J. 232 Sensitivity of a deep learning algorithm for detection of sentinel lymph node metastases in cervical cancer: A proof-of-concept study. In Proceedings of the ESGO 2024 Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 7–10 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stathonikos, N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Spoto, C.P.; Verdaasdonk, M.A.M.; van Diest, P.J. Being fully digital: Perspective of a Dutch academic pathology laboratory. Histopathology 2019, 75, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Sánchez, C.I.; Timofeeva, N.; Hermsen, M.; Nagtegaal, I.; Kovacs, I.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Bult, P.; van Ginneken, B.; van der Laak, J. Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, P.; Baguer, D.O.; Duschner, N.; Arrastia, J.L.; Schmidt, M.; Landsberg, J.; Wenzel, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Hadaschik, E.; Maass, P.; et al. Deep learning detection of melanoma metastases in lymph nodes. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 188, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, Z.; Jia, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Q.; Li, J.; Dai, H.; et al. Automatic detection of squamous cell carcinoma metastasis in esophageal lymph nodes using semantic segmentation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, G.; Liu, C.; Huang, D.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y. Diagnosis of lymph node metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using deep learning. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.H.; Gilbertson, J.R.; Hanna, M.G.; Olson, N.H.; Seheult, J.N.; Sorace, J.M.; Stram, M.N. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 1228–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Kim, S.; Cho, C.E.; Song, I.H.; Lee, H.J.; Ahn, S.; Park, S.Y.; Gong, G.; Kim, N. Effectiveness of transfer learning for enhancing tumor classification with a convolutional neural network on frozen sections. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Song, I.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Yang, D.H.; Kim, N.; Shin, D.; Yoo, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, D.; et al. Challenge for Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithm for Metastases Classification in Sentinel Lymph Nodes on Frozen Tissue Section Digital Slides in Women with Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 52, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. Emerging role of deep learning-based artificial intelligence in tumor pathology. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flach, R.N.; Stathonikos, N.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ter Hoeve, N.D.; van Diest, P.J.; van Dooijeweert, C. CONFIDENT-trial protocol: A pragmatic template for clinical implementation of artificial intelligence assistance in pathology. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e067437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients (n = 21) | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 42 (23–63) | |
| Histologic subtype | ||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 15 | 71.4 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 5 | 23.8 |
| Clear cell carcinoma | 1 | 4.8 |
| Histologic grade | ||
| Grade I | 1 | 4.8 |
| Grade II | 8 | 38.1 |
| Grade III | 11 | 52.4 |
| Grade not applicable * | 1 | 4.8 |
| Metastasis | ||
| Macrometastasis | 10 | 47.6 |
| Micrometastasis | 11 | 52.4 |
| Frozen section performed | 19 | 90.5 |
| Number of SLNs removed, median (range) | 2 (1–4) | |
| Number of H&E slides per patient **, median (range) | 18 (6–52) | |
| Number of annotations per patient **, median (range) | 128 (32–2093) | |
| Number of annotations without frozen sections, median (range) | 81 (10–464) | |
| Yellow annotations | 39 (7–165) | |
| Orange annotations | 11 (2–63) | |
| Red annotations | 10 (1–402) |
| Sentinel Lymph Nodes (n = 47) | |
|---|---|
| Negative * | 20 |
| Positive | 27 |
| Macrometastasis | 13 |
| Detected with H&E ** | 13 |
| Detected with algorithm | 13 |
| Micrometastasis | 14 |
| Detected with H&E ** | 12 |
| Detected with IHC only | 2 |
| Detected with algorithm | 12 |
| Case | Cancer Type | Metastasis Size | SLN Count | FS Performed | Number of Positive SLNs | Outcome of the Algorithm (Based on HE) | Visiopharm Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 2 | TP/NA | 1—detected in HE+FS slides; 2—tumor cells only visible in IHC slide (deeper levels), not in H&E |
| 2 | Clear cell | Macro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in FS slides * |
| 3 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E (not present in FS) |
| 4 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E (not present in FS) |
| 5 | Adeno | Macro | 4 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 6 | Adeno | Macro | 2 | Yes | 2 | TP | Both detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 7 | Squamous | Micro | 3 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides (not present in FS) |
| 8 | Squamous | Macro | 2 | Yes | 2 | TP | Both detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 9 | Adeno | Macro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 10 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 11 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides (not present in FS) |
| 12 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides (not present in FS) |
| 13 | Squamous | Macro + micro | 2 | Yes | 2 | TP | 1—detected in H&E + FS slides (micro); 2—detected in H&E + FS slides (macro) |
| 14 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides |
| 15 | Adeno | Micro | 2 | Yes | 2 | TP | 1—detected in H&E slides (not present in FS); 2—detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 16 | Squamous | Macro | 3 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides (not present in FS) ** |
| 17 | Adeno | Macro | 4 | Yes | 2 | TP | 1—detected in H&E slides (not present in FS); 2—detected in H&E + FS slides |
| 18 | Squamous | Macro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides, missed in FS slides |
| 19 | Squamous | Macro | 2 | No | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E slides |
| 20 | Squamous | Micro | 1 | No | 1 | NA | Tumor cells only visible in IHC slides (deeper levels), not in H&E |
| 21 | Squamous | Micro | 2 | Yes | 1 | TP | Detected in H&E + FS slides |
| TOTAL | 47 | 19 | 27 | 25 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baeten, I.G.T.; Hoogendam, J.P.; Stathonikos, N.; Gerestein, C.G.; Jonges, G.N.; van Diest, P.J.; Zweemer, R.P. Artificial Intelligence-Based Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis Detection in Cervical Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213619
Baeten IGT, Hoogendam JP, Stathonikos N, Gerestein CG, Jonges GN, van Diest PJ, Zweemer RP. Artificial Intelligence-Based Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis Detection in Cervical Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(21):3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213619
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaeten, Ilse G. T., Jacob P. Hoogendam, Nikolas Stathonikos, Cornelis G. Gerestein, Geertruida N. Jonges, Paul J. van Diest, and Ronald P. Zweemer. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis Detection in Cervical Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 21: 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213619
APA StyleBaeten, I. G. T., Hoogendam, J. P., Stathonikos, N., Gerestein, C. G., Jonges, G. N., van Diest, P. J., & Zweemer, R. P. (2024). Artificial Intelligence-Based Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis Detection in Cervical Cancer. Cancers, 16(21), 3619. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213619






