The Critical Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multimodal Treatment of Lung Metastasis from Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Endpoints
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Treatment with SBRT
2.4. Statistical Analysis
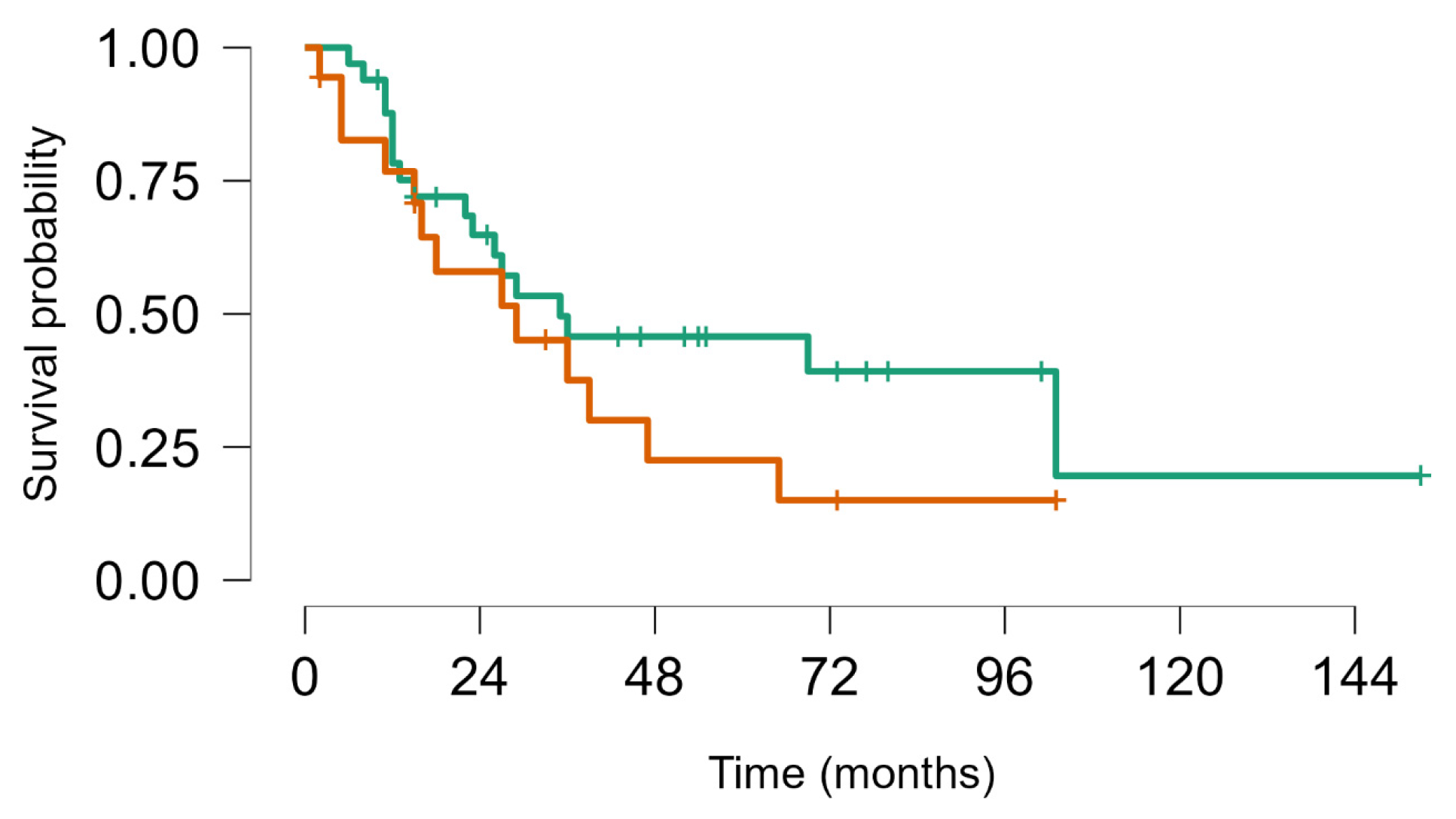
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Response to SBRT
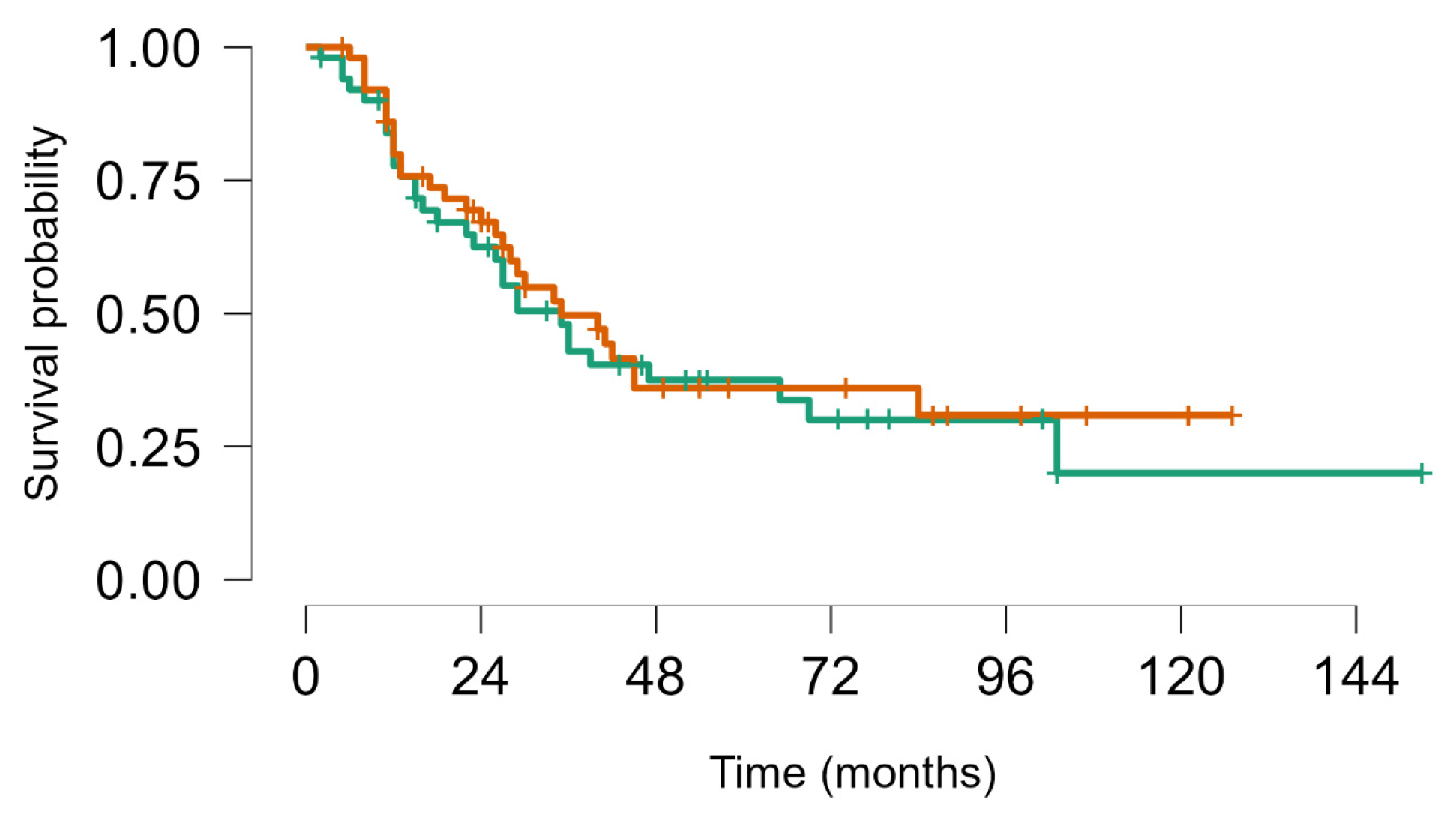
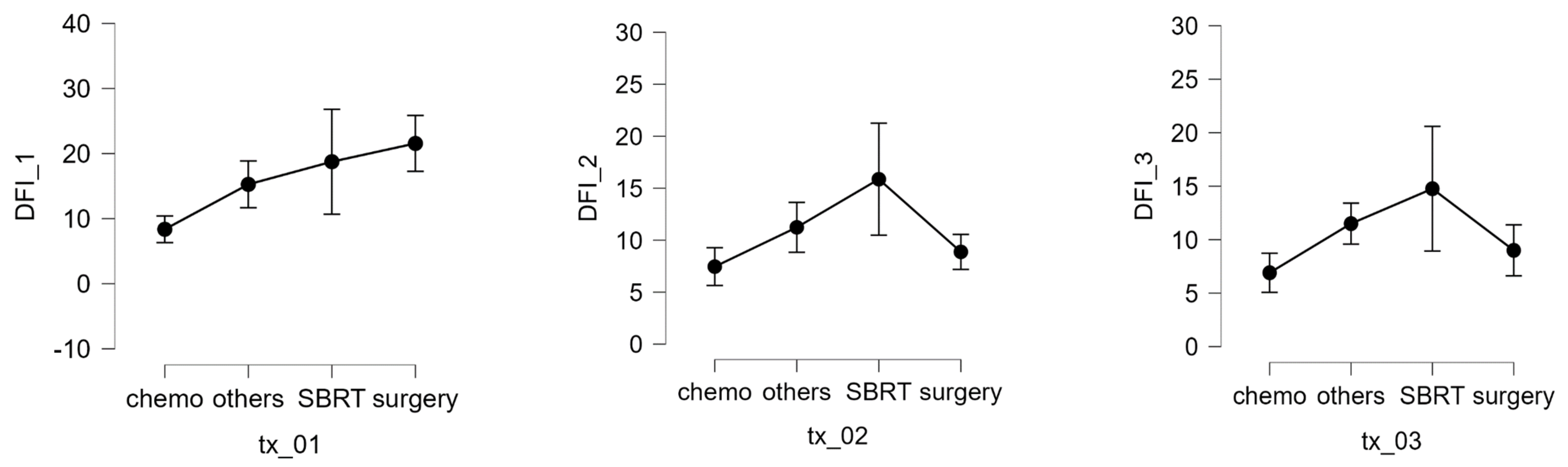
3.3. Analysis of 20 Long-Term Survivors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, S.J.; Frezza, A.M.; Abecassis, N.; Bajpai, J.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Bolle, S.; Bonvalot, S.; et al. Bone sarcomas: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS-ERN PaedCan Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1520–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronchi, A.; Miah, A.B.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Abecassis, N.; Bajpai, J.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Bolle, S.; et al. Soft tissue and visceral sarcomas: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, D.A.; Glenn, J.; Kinsella, T.; Glatstein, E.; Lack, E.E.; Restrepo, C.; White, D.E.; Seipp, C.A.; Wesley, R.; Rosenberg, S.A. Patterns of recurrence in patients with high-grade soft-tissue sarcomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.A.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; Wesley, M.N.; Rosenberg, S.A. Differing determinants of prognosis following resection of pulmonary metastases from osteogenic and soft tissue sarcoma patients. Cancer 1985, 55, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, U.; Palmerini, E.; Porcu, L.; Luksch, R.; Scanagatta, P.; Meazza, C.; Leuzzi, G.; Massimino, M.; Picci, P. Lung metastasectomy for osteosarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults: Proof of permanent cure. Tumori J. 2023, 109, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudgar, N.P.; Brennan, M.F.; Munhoz, R.R.; Bucciarelli, P.R.; Tan, K.S.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Bains, M.S.; Bott, M.; Huang, J.; Park, B.J.; et al. Pulmonary metastasectomy with therapeutic intent for soft-tissue sarcoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 154, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardenberg, R.A.; Figueiredo, L.P.; Haddad, F.J.; Gross, J.L.; Younes, R.N. Pulmonary metastasectomy from soft tissue sarcomas. Clinics 2010, 65, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetta, C.; Rocca, M.; Salone, M.; Longhi, A.; Ferrari, C.; Londero, F.; Parise, G.; Parise, O.; Giugliano, A.; Maessen, J.G.; et al. Predictors of lung recurrence and disease-specific mortality after pulmonary metastasectomy for soft tissue sarcoma. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 37, 101532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Demmy, T.L. Pulmonary metastasectomy for soft tissue sarcoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 21, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, G.; Elshafiey, M.; Romeih, M.; Elgammal, A.; Kamel, A.; Salama, A.; Farid, N.; Zaky, I. Prognostic significance of the ratio of surgically resected to radiologically detected lung nodules in patients with metastatic osteosarcoma. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 40, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Malvar, J.; Chi, Y.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Shah, R.; Navid, F.; Stein, J.E.; Mascarenhas, L. Survival outcomes and surgical morbidity based on surgical approach to pulmonary metastasectomy in pediatric, adolescent and young adult patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 20231–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onderdonk, B.E.; Gutiontov, S.I.; Chmura, S.J. The Evolution (and Future) of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Oligometastatic Disease. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North. Am. 2020, 34, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, D.A.; Olson, R.; Harrow, S.; Gaede, S.; Louie, A.V.; Haasbeek, C.; Mulroy, L.; Lock, M.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Yaremko, B.P.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastatic Cancers: Long-Term Results of the SABR-COMET Phase II Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2830–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Londero, F.; Grossi, W.; Morelli, A.; Parise, O.; Masullo, G.; Tetta, C.; Livi, U.; Maessen, J.G.; Gelsomino, S. Surgery versus stereotactic radiotherapy for treatment of pulmonary metastases. A systematic review of literature. Future Sci. OA 2020, 6, FSO471. [Google Scholar]
- Frakulli, R.; Salvi, F.; Balestrini, D.; Parisi, A.; Palombarini, M.; Cammelli, S.; Rocca, M.; Salone, M.; Longhi, A.; Ferrari, S.; et al. Stereotactic Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Lung Metastases from Bone and Soft-tissue Sarcomas. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 5581–5586. [Google Scholar]
- Navarria, P.; Ascolese, A.M.; Cozzi, L.; Tomatis, S.; D’Agostino, G.R.; De Rose, F.; De Sanctis, R.; Marrari, A.; Santoro, A.; Fogliata, A.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases from soft tissue sarcoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarria, P.; Baldaccini, D.; Clerici, E.; Marini, B.; Cozzi, L.; Franceschini, D.; Bertuzzi, A.F.; Quagliuolo, V.; Torri, V.; Colombo, P.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Lung Metastases From Sarcoma in Oligometastatic Patients: A Phase 2 Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 114, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetta, C.; Londero, F.; Micali, L.R.; Parise, G.; Algargoush, A.T.; Algargoosh, M.; Albisinni, U.; Maessen, J.G.; Gelsomino, S. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Versus Metastasectomy in Patients With Pulmonary Metastases From Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, J.; Ford, R.; Sargent, D.; Schwartz, L.H.; Rubinstein, L.; Lacombe, D.; Eisenhauer, E.; Verweij, J.; Therasse, P.; RECIST Working Party. Individual patient data analysis to assess modifications to the RECIST criteria. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_5.0/CTCAE_v5.0_2017-11-27.xlsx (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Lagerwaard, F.J.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Smit, E.F.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S. Outcomes of risk-adapted fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossa, S.D.; Loge, J.H.; Dahl, A.A. Long-term survivorship after cancer: How far have we come? Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19 (Suppl. 5), v25–v29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, A.D.; Haupt, E.E.; Chan, C.M.; Spiguel, A.R.; Scarborough, M.T.; Zlotecki, R.A.; Gibbs, P.C. Treatment of Sarcoma Lung Metastases with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Sarcoma 2018, 2018, 9132359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeland, S.; Bielack, S.S.; Whelan, J.; Bernstein, M.; Hogendoorn, P.; Krailo, M.D.; Gorlick, R.; Janeway, K.A.; Ingleby, F.C.; Anninga, J.; et al. Survival prognosis with osteosarcoma: Outcomes in more than 2000 patients in the EURAMOS-1 (European American Osteosrcoma Study) cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 109, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Han, I.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, H.S.; Park, J.W.; Kim, H.S. Postmetastasis survival in high-grade extremity osteosarcoma: A retrospective analysis of prognostic factors in 126 patients. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Luksch, R.; Hall, K.S.; Fagioli, F.; Prete, A.; Tamburini, A.; Tienghi, A.; DiGirolamo, S.; Paioli, A.; Abate, M.E.; et al. Post-relapse survival in patients with Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Billups, C.A.; Kun, L.E.; Rao, B.N.; Pratt, C.B.; Merchant, T.E.; Santana, V.M.; Pappo, A.S. Survival after recurrence of Ewing Tumors. Cancer 2002, 94, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, S.E.; Wozniak, A.W.; Billups, C.A.; Wu, J.; McPherson, V.; Neel, M.D.; Rao, B.N.; Daw, N.C. Survival of pediatric patients after relapsed osteosarcoma: The St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital experience. Cancer 2013, 119, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonnaux, M.; Brahmi, M.; Schiffler, C.; Meeus, P.; Sunyach, M.; Bouhamama, A.; Karanian, M.; Tirode, F.; Pissaloux, D.; Vaz, G.; et al. Very long-term survivors among patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebow, E.S.; Lobaugh, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Dickson, M.A.; Rosenbaum, E.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Nacev, B.A.; Shepherd, A.F.; Shaverdian, N.; Wolden, S.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for sarcoma pulmonary metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 187, 109824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkin, P.M.; Gore, E.; Charlson, J.; Neilson, J.C.; Johnstone, C.; King, D.M.; Hackbarth, D.A.; Wooldridge, A.; Mannem, R.; Bedi, M. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for metastatic sarcoma to the lung: Adding to the arsenal of local therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, B.C.; Bernstein, K.A.; DeLaney, T.F.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Kolker, J.D.; Choy, E.; Levin, W.P.; Weber, K.L.; Muniappan, A.; Berman, A.T.; et al. Multi-institutional analysis of stereotactic body radiotherapy for sarcoma pulmonary metastases: High rates of local control with favorable toxicity. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 122, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Hahn, S.M.; Stetson, R.L.; Friedberg, J.S.; Pechet, T.T.; Sher, D.J. Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic body radiation therapy versus surgical resection for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2013, 119, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Jin, C.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Cost-effectiveness of stereotactic body radiotherapy in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review. Expert. Rev. Pharmacoeconomics Outcomes Res. 2022, 22, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancia, A.; Ingrosso, G.; Carosi, A.; Bottero, M.; Cancelli, A.; Turturici, I.; Ponti, E.; Santoni, R. Oligometastatic cancer in elderly patients: The “blitzkrieg” radiotherapy approach: SBRT in oligometastatic elderly patients. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | Median | 40 (11–81) year |
| Sex | Male | 71 |
| Female | 31 | |
| Histotype | Bone Sarcoma | 51 |
| Soft Tissue Sarcoma | 51 | |
| Stage at Dx | Localized | 76 |
| Metastatic | 26 | |
| Patients with lung metastatic nodules at 1st relapse | 1–3 | 66 |
| 4–9 | 21 | |
| ≥10 | 15 | |
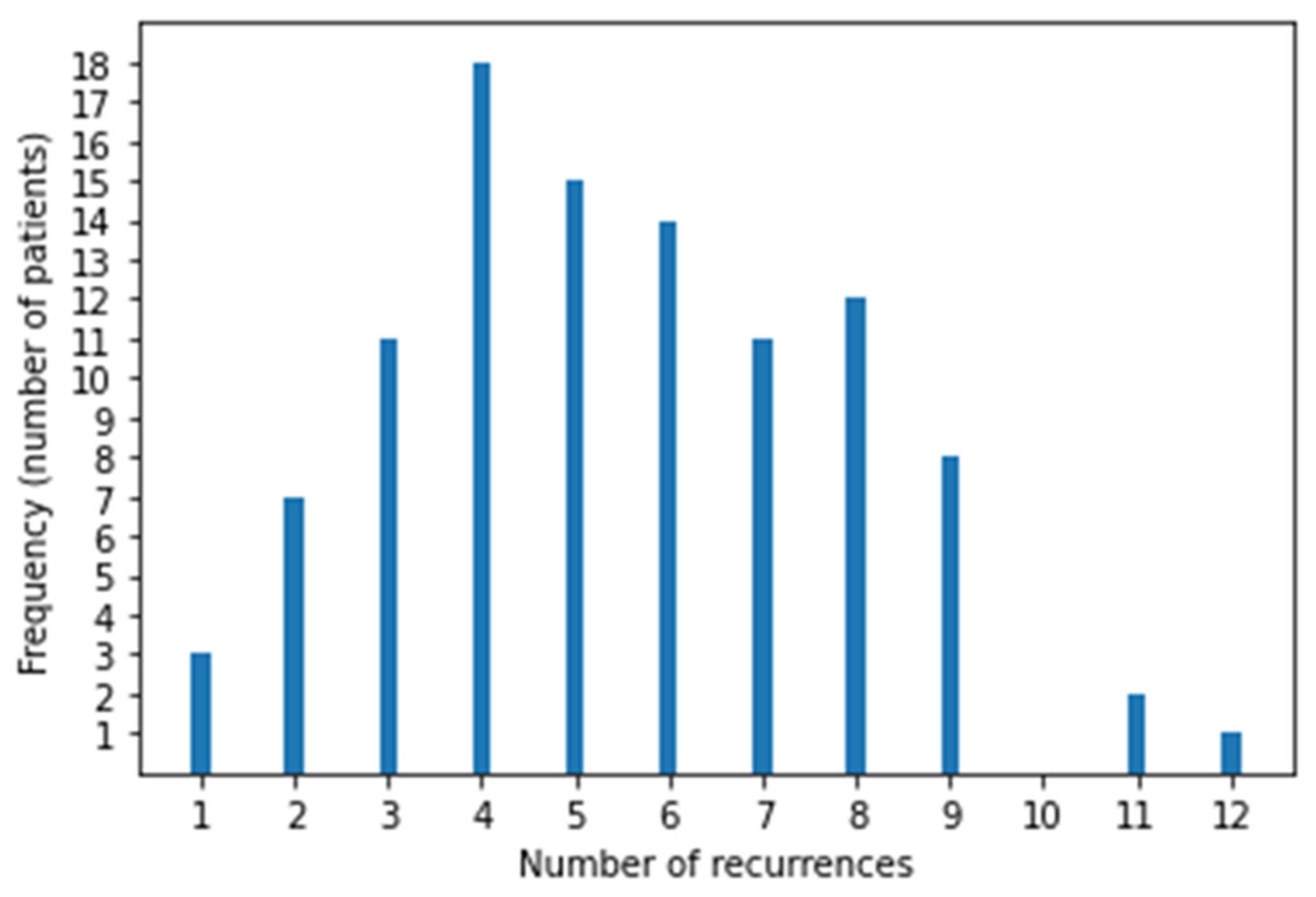
| Recurrences per patient, n | Median (range) | 4 (1–12) |
| Pre-SBRT chemo, n patients | 75 | |
| Pre-SBRT surgery, n patients | 52 | |
| N irradiated nodules | 276 | |
| Median Nodule diameter | 10 (IQR 6.7–15.2) mm | |
| Median dose Gy | 48 (40–54) | |
| Number of SBRT course for each patient | Median | 2 (1–11) |
| RECIST Response, % | CR | 61.3% |
| PR | 6.6% | |
| SD | 8.8% | |
| PD | 22% | |
| NE | 1.1% | |
| Local control rate after 1st SBRT | 12 months | 86% |
| 24 months | 78% | |
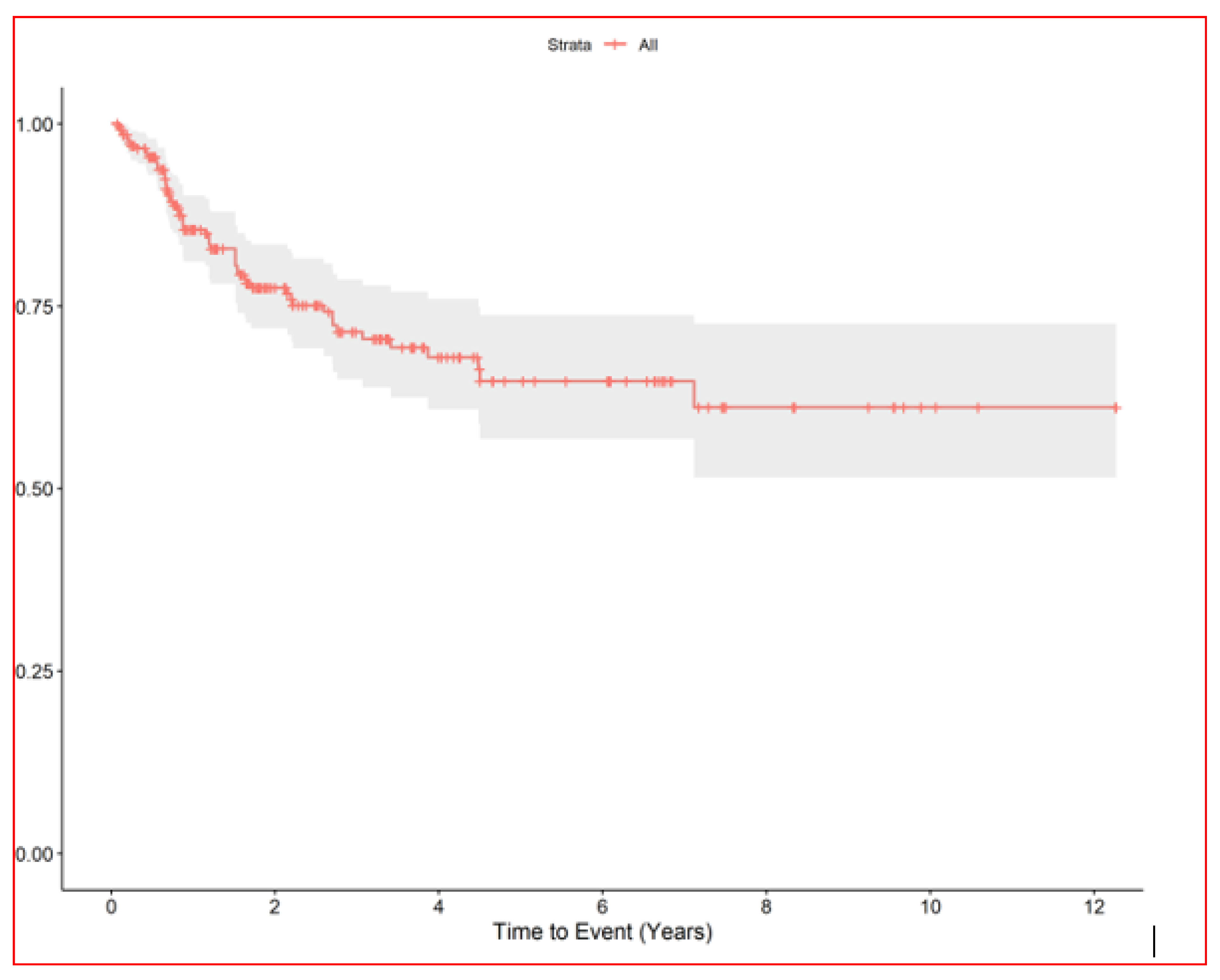
| Survival from 1st SBRT | Median OS | 2.9 (95% CI, 2.2–3.8) |
| 5-year OS | 37% (95% CI, 27–48) | |
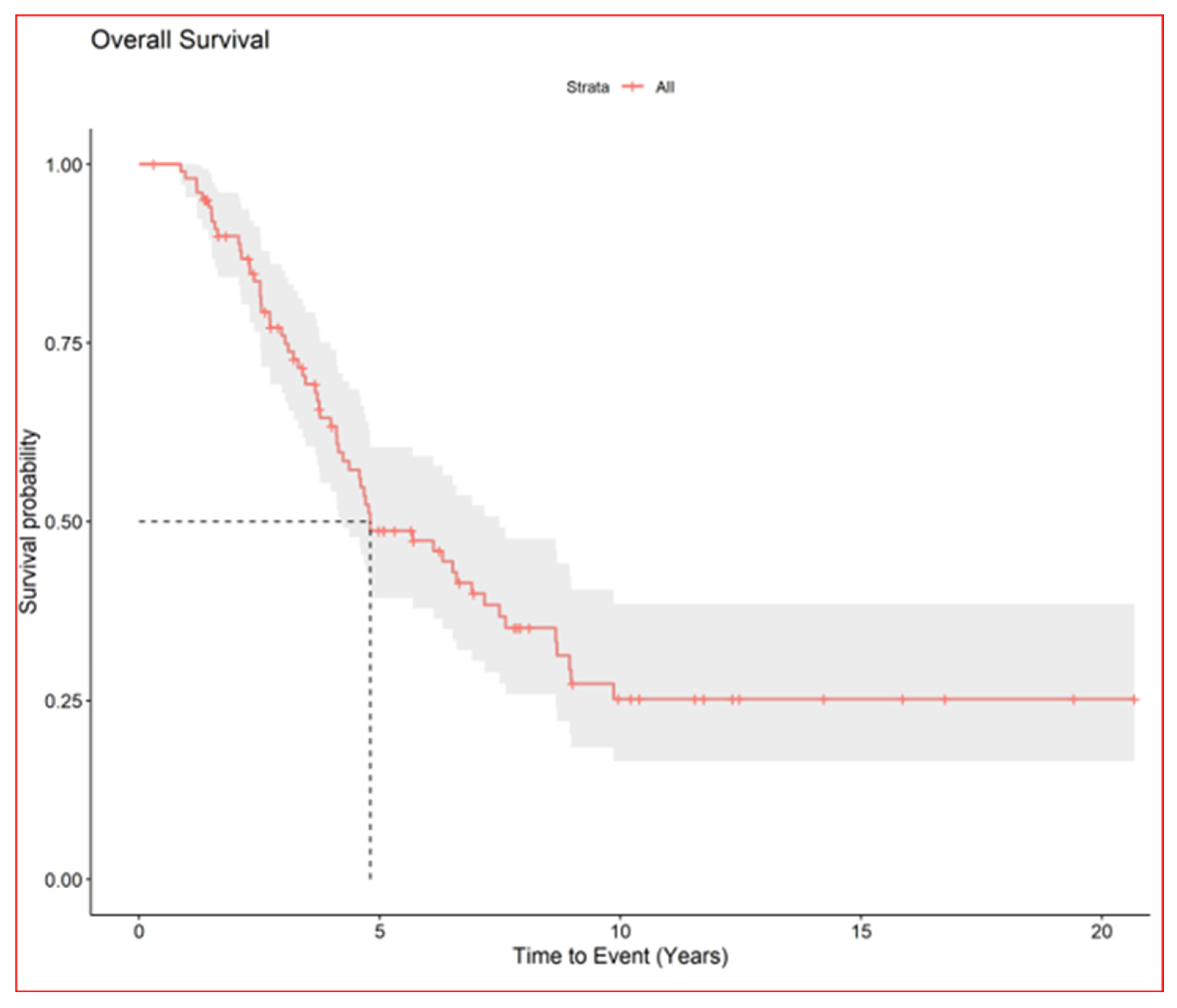
| Survival from 1st metastases | Median | 4.8 years (95% CI, 4.1–7.5) |
| 5-year | 49% (95% CI, 39–60) |
| Histotypes | N |
|---|---|
| Bone Sarcoma, total | 51 |
| Osteosarcoma | 21 |
| Ewing Sarcoma | 18 |
| Chondrosarcoma | 5 |
| Undifferentiated Sarcoma | 3 |
| Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma | 1 |
| Giant Cell Tumor | 1 |
| Leiomyosarcoma of bone | 1 |
| Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma of bone | 1 |
| Soft Tissue Sarcoma, total | 51 |
| Undifferentiated Sarcoma | 14 |
| Synovial Sarcoma | 7 |
| Extra-skeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma | 5 |
| Leiomyosarcoma | 5 |
| Liposarcoma | 5 |
| Extra-skeletal Osteosarcoma | 4 |
| MPNST | 4 |
| Myxofibrosarcoma | 2 |
| Triton Tumor | 2 |
| ASPS | 1 |
| Malignant Myoepithelioma | 1 |
| Solitary Malignant Fibrous Tumor | 1 |
| Relapse No. | N pt | Surgery | CT | SBRT | SBRT Combo | Other Tx/WS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 102 | 34 | 30 | 8 | 11 | 19 |
| 2nd | 99 | 16 | 35 | 15 | 19 | 14 |
| 3rd | 92 | 12 | 37 | 22 | 17 | 4 |
| 4th | 77 | 9 | 30 | 15 | 12 | 11 |
| 5th | 61 | 5 | 24 | 13 | 13 | 6 |
| 6th | 44 | 2 | 22 | 8 | 3 | 9 |
| 7th | 33 | 2 | 18 | 3 | 3 | 7 |
| 8th | 21 | 0 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 3 |
| 9th | 10 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 |
| 10th | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 11th | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| 12th | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Age | Histo | Stage at Dx | N LM | Relapse n 1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | RR7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | PRDFS ms | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | STS | Local | A | S | SBRT | S | 51 | NED | |||||||||
| 34 | BS | Local | A | S | CT+S | SBRT | CT | SBRT | SBRT | SBRT | 120 | NED | |||||
| 27 | BS | Local | C | S | SBRT | 136 | NED | ||||||||||
| 40 | STS | Metastatic | A | CT | CT +S+SBRT | 38 | NED | ||||||||||
| 68 | STS | Metastatic | A | CT | S x RL + SBRT | SBRT | 44 | NED | |||||||||
| 53 | STS | Local | A | S | SBRT | 240 | NED | ||||||||||
| 47 | BS | Local | A | S | S | S | S | CT + SBRT | S | S | SBRT | SBRT | SBRT | SBRT | SBRT | 205 | NED |
| 58 | STS | Local | A | Ct | CT | CT | SBRT | 100 | NED | ||||||||
| 35 | BS | Local | A | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | SBRT | SBRT | 191 | NED | |||
| 62 | STS | Local | A | Ct | CT | CT+S | S | SBRT | 134 | NED | |||||||
| 59 | STS | Local | A | Sbrt | 88 | NED | |||||||||||
| 15 | BS | Local | A | S | CT+SBRT | S | 92 | NED | |||||||||
| 61 | STS | Local | A | S | S | S | S | SBRT | 272 | NED | |||||||
| 48 | STS | Metastatic | A | CT+S | SBRT | SBRT | 139 | NED | |||||||||
| 18 | STS | Local | B | CT+SBRT | S | S | S | 50 | NED | ||||||||
| 21 | BS | Metastatic | B | CT+S+SBRT | 60 | NED | |||||||||||
| 18 | BS | Local | A | CT | CT | SBRT | 100 | NED | |||||||||
| 17 | BS | Local | C | S | CT | CT | S+SBRT | 70 | NED | ||||||||
| 70 | STS | Local | A | CT+SBRT | 116 | NED | |||||||||||
| 34 | BS | Local | A | CT+S | CT+S+SBRT | 94 | NED |
| Author (Year) Ref. | No. Patients | Local Control | FU, Median | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lindsay (2018) [22] | 44 | 1-year, 95% | 14 months | 50% (5 years) |
| Baumann (2020) [31] | 44 | 1-year, 96% | 16 months | 43% (2 years) |
| Navarria (2015) [15] | 28 | 5-year, 96% | 65 months | 60% (5 years) |
| Gutik (2023) [30] | 18 | 2-year, 96% | NR | 74% (2 years) |
| Lebow(2023) [29] | 66 | 2 years 92% | 36 months | 49% (2 years) |
| Longhi * present | 102 | 1-year, 86% | 56 months | 49% (5 years) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longhi, A.; Marrari, A.; Tetta, C.; Parmeggiani, A.; Parise, O.; Ferrari, C.; Salvi, F.; Frezza, G. The Critical Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multimodal Treatment of Lung Metastasis from Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cancers 2024, 16, 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213593
Longhi A, Marrari A, Tetta C, Parmeggiani A, Parise O, Ferrari C, Salvi F, Frezza G. The Critical Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multimodal Treatment of Lung Metastasis from Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cancers. 2024; 16(21):3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213593
Chicago/Turabian StyleLonghi, Alessandra, Andrea Marrari, Cecilia Tetta, Anna Parmeggiani, Orlando Parise, Cristina Ferrari, Fabrizio Salvi, and Giovanni Frezza. 2024. "The Critical Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multimodal Treatment of Lung Metastasis from Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas" Cancers 16, no. 21: 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213593
APA StyleLonghi, A., Marrari, A., Tetta, C., Parmeggiani, A., Parise, O., Ferrari, C., Salvi, F., & Frezza, G. (2024). The Critical Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Multimodal Treatment of Lung Metastasis from Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cancers, 16(21), 3593. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16213593






