Comparative Study of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis in Different Hairless Murine Models
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. UV Irradiation
2.3. Clinical Evaluation—Photodocumentation
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Proteasome Activity Assay
2.7. Immunoblot Analysis
2.8. Sebum Levels
2.9. Statistical Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Evaluation
3.1.1. Photodocumentation
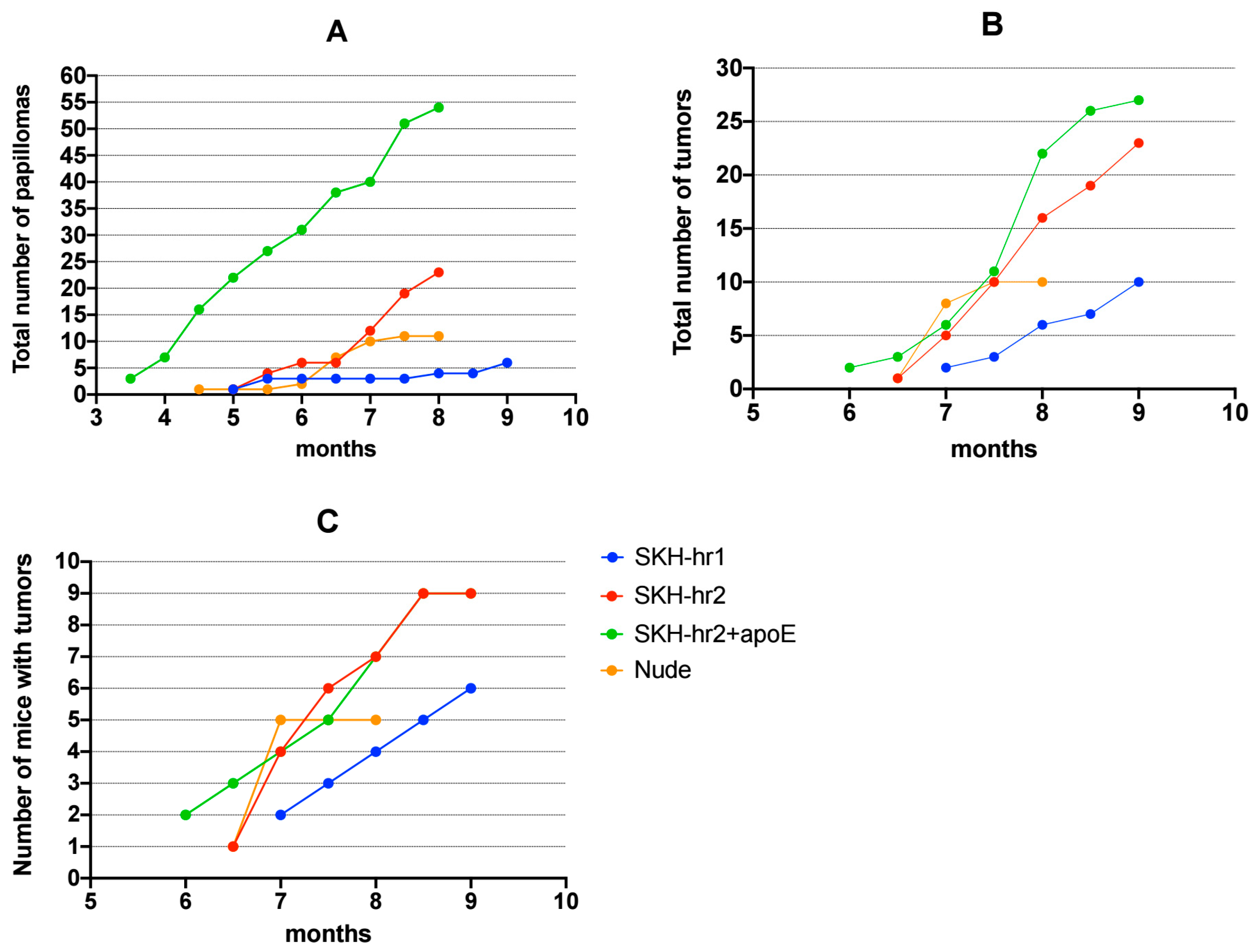
3.1.2. Number of Papillomas and Tumors Formation over Time
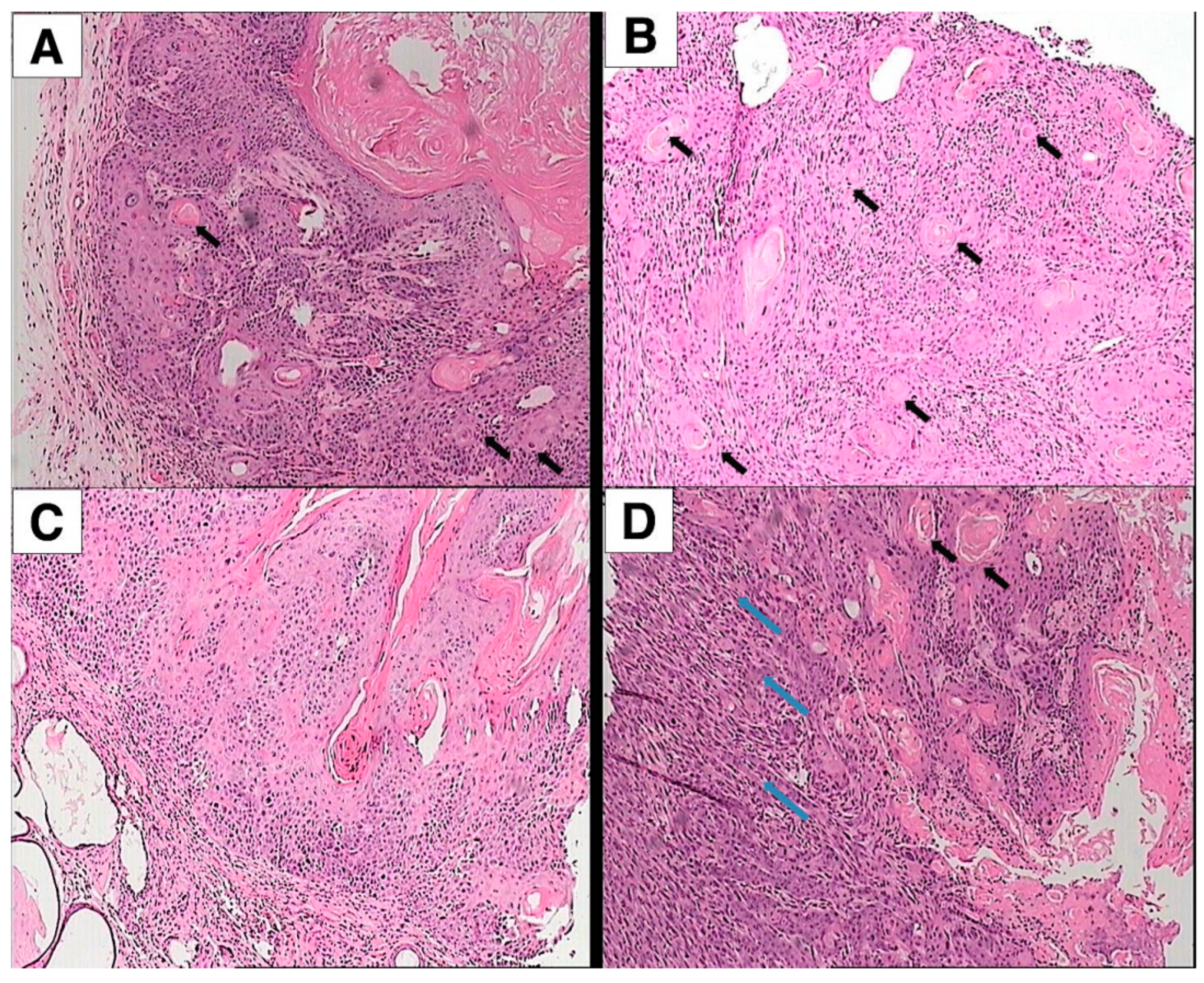
3.2. Histopathological Evaluation
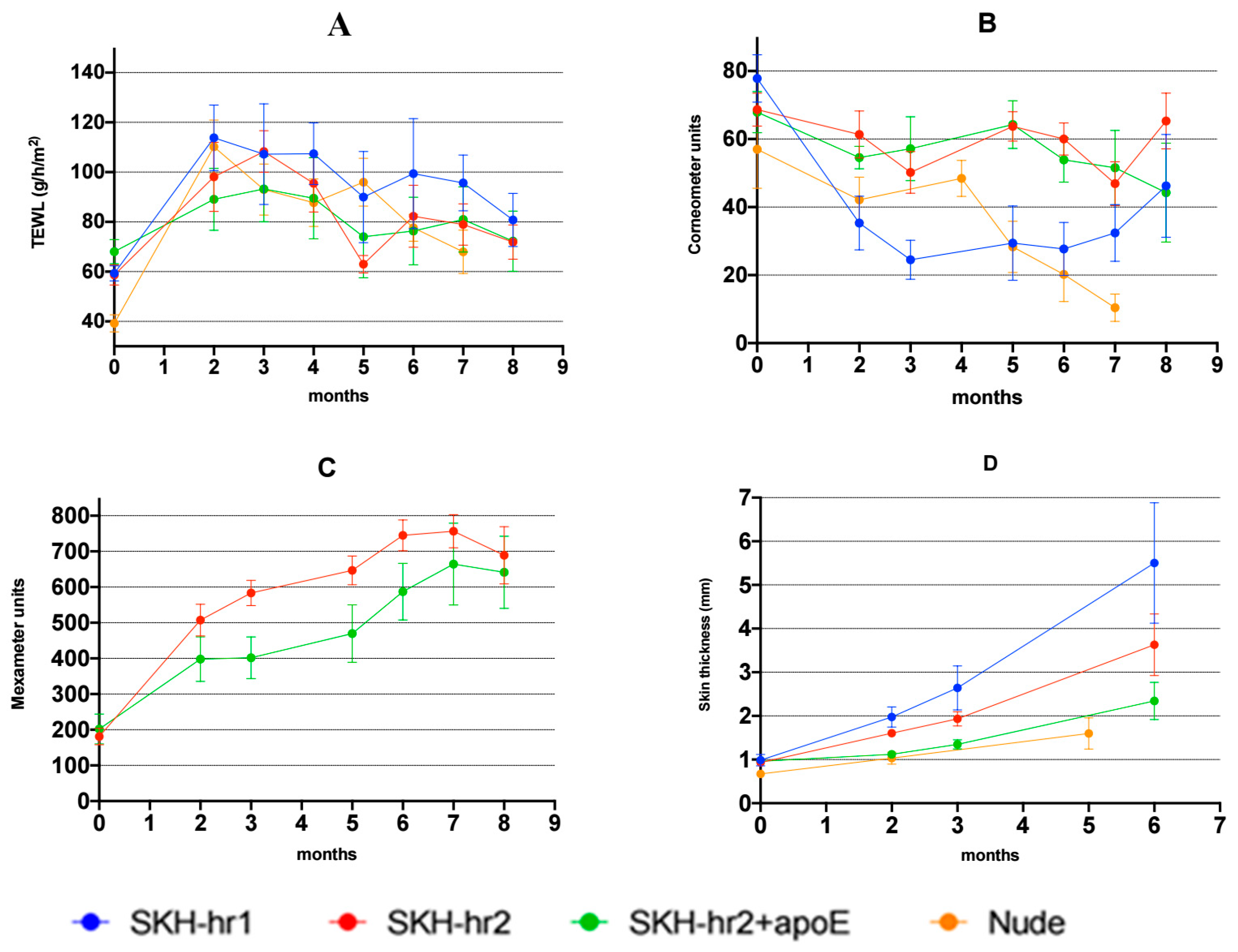
3.3. Biophysical Evaluation
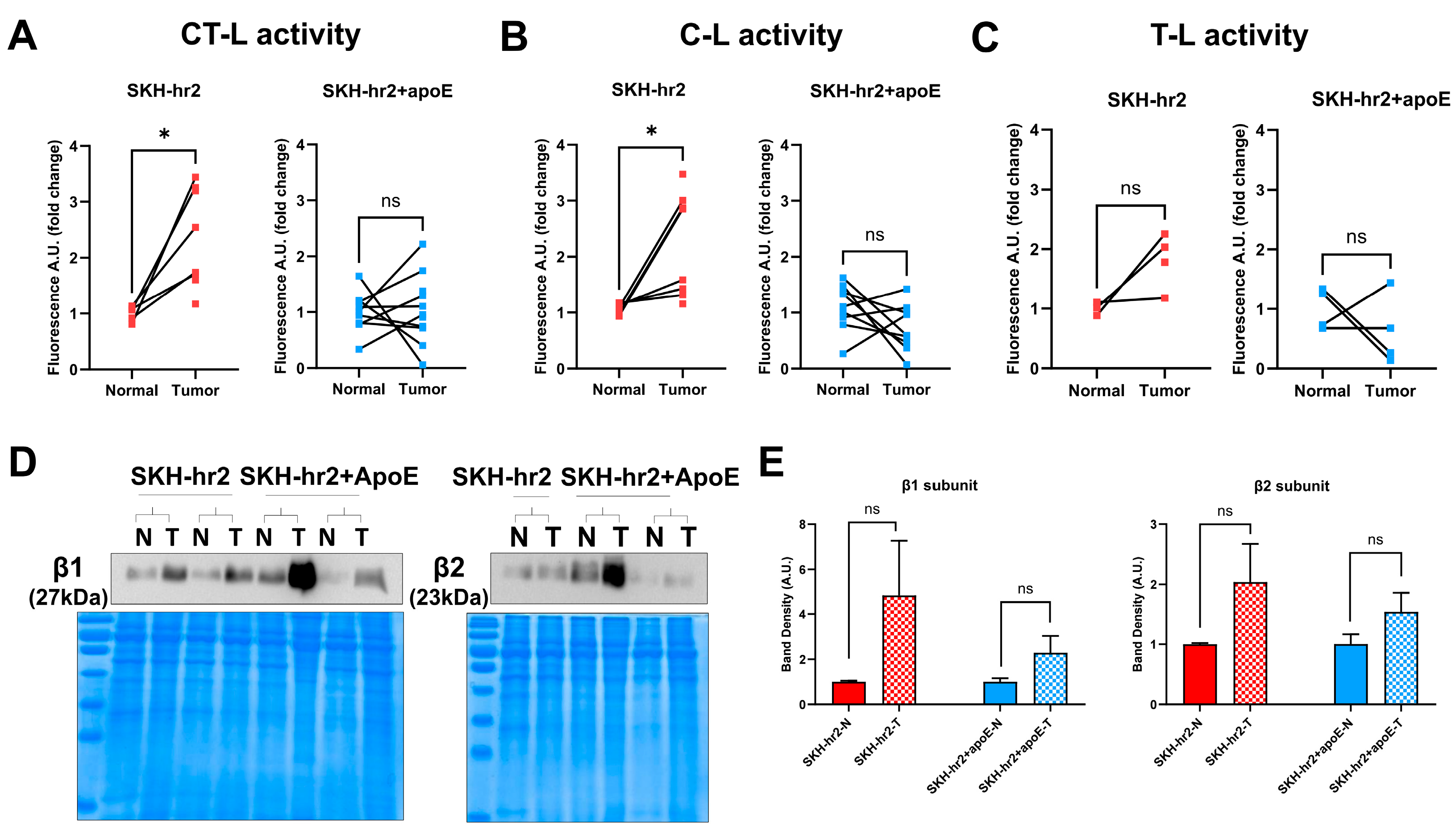
3.4. Proteasome Activities and Expressions
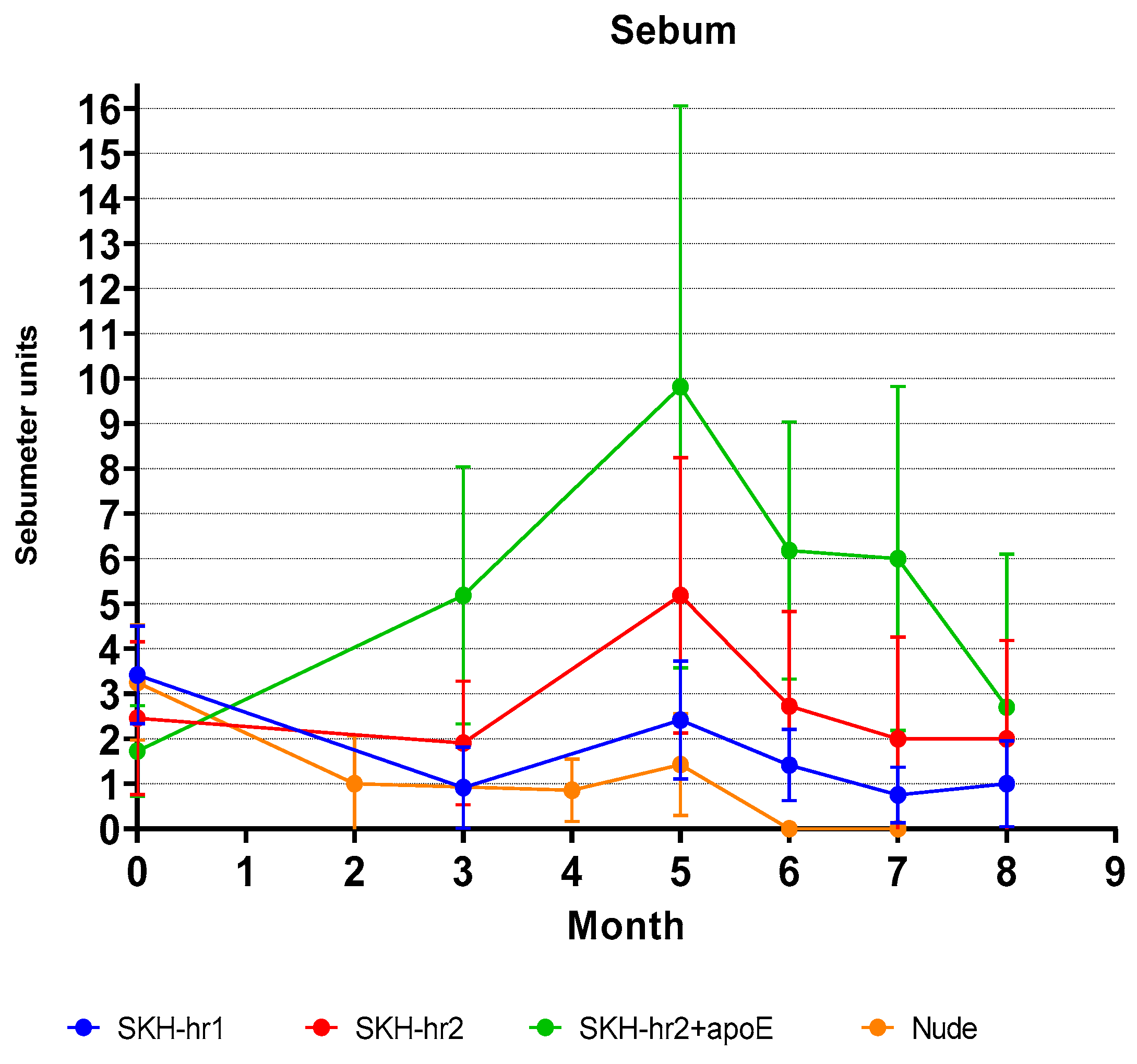
3.5. Sebum Level Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garbe, C.; Forsea, A.M.; Amaral, T.; Arenberger, P.; Autier, P.; Berwick, M.; Boonen, B.; Bylaite, M.; del Marmol, V.; Dreno, B.; et al. Skin cancers are the most frequent cancers in fair-skinned populations, but we can prevent them. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 204, 114074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Kamińska-Winciorek, G.; Lange, D.; Lewandowski, B.; Reich, A.; Sławińska, M.; Pabianek, M.; Szczepaniak, K.; Hankiewicz, A.; Ułańska, M.; et al. The incidence and clinical analysis of non-melanoma skin cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Verdaguer-Faja, J.; Toll, A.; Boada, A.; Guerra-Amor, Á.; Ferrándiz-Pulido, C.; Jaka, A. Management of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Scalp: The Role of Imaging and Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2024, 16, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Howell, J.Y.; Ramsey, M.L. Squamous Cell Skin Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jansen, P.; Lodde, G.C.; Griewank, K.G.; Hadaschik, E.; Roesch, A.; Ugurel, S.; Zimmer, L.; Livingstone, E.; Schadendorf, D. Management of partial and non-responding cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36 (Suppl. S1), 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Shu, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Feng, X.; Zhao, L. miR-22 promotes immunosuppression via activating JAK/STAT3 signaling in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2023, 44, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suozzi, K.; Turban, J.; Girardi, M. Cutaneous Photoprotection: A Review of the Current Status and Evolving Strategies. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piipponen, M.; Riihilä, P.; Nissinen, L.; Kähäri, V.M. The Role of p53 in Progression of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Premi, S.; Wallisch, S.; Mano, C.M.; Weiner, A.B.; Bacchiocchi, A.; Wakamatsu, K.; Bechara, E.J.; Halaban, R.; Douki, T.; Brash, D.E. Photochemistry. Chemiexcitation of melanin derivatives induces DNA photoproducts long after UV exposure. Science 2015, 347, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, Y.; Ye, X.; Xiong, Z.; Ihsan, A.; Ares, I.; Martínez, M.; Lopez-Torres, B.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Cancer Metabolism: The Role of ROS in DNA Damage and Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2023, 13, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, B.M.; Li, W.Q.; Cho, E.; Curhan, G.C.; Qureshi, A.A. Statin use and risk of skin cancer. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Halimi, H.; Farjadian, S. Cholesterol: An important actor on the cancer immune scene. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1057546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, A.; Jia, Z.; Qiao, C.; Wang, M.; Ding, X. Cholesterol metabolism in drug-resistant cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, T.; Xiao, J. Prognostic role of serum total cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, P.; Xuan, J.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J.; Shan, L.; Du, Q.; Ren, Y.; Ye, J. Cholesterol Enhances Colorectal Cancer Progression via ROS Elevation and MAPK Signaling Pathway Activation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Hughes-Fulford, M. Human prostate cancer cells lack feedback regulation of low-density lipoprotein receptor and its regulator, SREBP2. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumah, E.; Bibee, K. Modelling cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma for laboratory research. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriazi, M.; Alexandratou, E.; Yova, D.; Rallis, M.; Trebst, T. Topical photodynamic therapy of murine non-melanoma skin carcinomas with aluminum phthalocyanine chloride and a diode laser: Pharmacokinetics, tumor response and cosmetic outcomes. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2008, 24, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; Marchalik, R.; Merlino, G.; Michael, H. Mouse models of UV-induced melanoma: Genetics, pathology, and clinical relevance. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nowotarski, S.L.; Feith, D.J.; Shantz, L.M. Skin Carcinogenesis Studies Using Mouse Models with Altered Polyamines. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2015, 8 (Suppl. S1), 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H. Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Szadvari, I.; Krizanova, O.; Babula, P. Athymic nude mice as an experimental model for cancer treatment. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65 (Suppl. S4), S441–S453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalin, J.H.; Eroglu, A.; Liu, H.; Holtzclaw, W.D.; Leigh, I.; Proby, C.M.; Fahey, J.W.; Cole, P.A.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Investigation into the use of histone deacetylase inhibitor MS-275 as a topical agent for the prevention and treatment of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in an SKH-1 hairless mouse model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Husain, Z.; Pathak, M.A.; Flotte, T.; Wick, M.M. Role of ultraviolet radiation in the induction of melanocytic tumors in hairless mice following 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene application and ultraviolet irradiation. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4964–4970, Erratum in Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karamani, C.; Antoniadou, I.T.; Dimou, A.; Andreou, E.; Kostakis, G.; Sideri, A.; Vitsos, A.; Gkavanozi, A.; Sfiniadakis, I.; Skaltsa, H.; et al. Optimization of psoriasis mouse models. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2021, 108, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemlewska, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Mokrzyńska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Szczepanek, D.; Sowa, I.; Wójciak, M. Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory and Antibacterial Properties of Raphanus sativus L. Leaf and Root Kombucha-Fermented Extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gidado, I.M.; Nwokoye, I.I.; Triantis, I.F.; Qassem, M.; Kyriacou, P.A. Multi-Modal Spectroscopic Assessment of Skin Hydration. Sensors 2024, 24, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, E.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Baek, J.H.; Boo, Y.C. Skin Color Analysis of Various Body Parts (Forearm, Upper Arm, Elbow, Knee, and Shin) and Changes with Age in 53 Korean Women, Considering Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vasilopoulou, M.A.; Gioran, A.; Theodoropoulou, M.; Koutsaviti, A.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E.; Chondrogianni, N. Healthspan improvement and anti-aggregation effects induced by a marine-derived structural proteasome activator. Redox Biol. 2022, 56, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Graça, A.; Martins, A.M.; Pinto, P.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. Combining protection with skin health: In vivo studies of an innovative gelatin/tannic acid-based hydrogel patch to prevent PPE-related skin lesions. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Jamovi Project. Jamovi. (Version 2.3) [Computer Software]. 2022. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Catalgol, B.; Ziaja, I.; Breusing, N.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Alpertunga, B.; Schroeder, P.; Chondrogianni, N.; Gonos, E.S.; Petropoulos, I.; et al. The proteasome is an integral part of solar ultraviolet a radiation-induced gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30076–30086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McHugh, A.; Fernandes, K.; South, A.P.; Mellerio, J.E.; Salas-Alanís, J.C.; Proby, C.M.; Leigh, I.M.; Saville, M.K. Preclinical comparison of proteasome and ubiquitin E1 enzyme inhibitors in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: The identification of mechanisms of differential sensitivity. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20265–20281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Nowowiejska, J.; Baran, A.; Flisiak, I. Lipid Alterations and Metabolism Disturbances in Selected Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zamudio Díaz, D.F.; Busch, L.; Kröger, M.; Klein, A.L.; Lohan, S.B.; Mewes, K.R.; Vierkotten, L.; Witzel, C.; Rohn, S.; Meinke, M.C. Significance of melanin distribution in the epidermis for the protective effect against UV light. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hart, P.H.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Swift, G.J.; Jaksic, A.; Noonan, F.P.; Finlay-Jones, J.J. Dermal mast cells determine susceptibility to ultraviolet B-induced systemic suppression of contact hypersensitivity responses in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Takeuchi, S.; Zhang, W.; Wakamatsu, K.; Ito, S.; Hearing, V.J.; Kraemer, K.H.; Brash, D.E. Melanin acts as a potent UVB photosensitizer to cause an atypical mode of cell death in murine skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15076–15081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jayakar, S.K.; Loudig, O.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; Kim, R.S.; Ow, T.J.; Ustun, B.; Harris, T.M.; Prystowsky, M.B.; Childs, G.; Segall, J.E.; et al. Apolipoprotein E Promotes Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Chen, H. Apolipoproteins: New players in cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1051280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pecorelli, A.; Woodby, B.; Prieux, R.; Valacchi, G. Involvement of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in pollution-induced skin damage. Biofactors 2019, 45, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovčević, A.; Žarković, K.; Jakovčević, D.; Rakušić, Z.; Prgomet, D.; Waeg, G.; Šunjić, S.B.; Žarković, N. The Appearance of 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal (HNE) in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oropharynx. Molecules 2020, 25, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zadlo, A.; Pilat, A.; Sarna, M.; Pawlak, A.; Sarna, T. Redox Active Transition Metal ions Make Melanin Susceptible to Chemical Degradation Induced by Organic Peroxide. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 75, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reelfs, O.; Tyrrell, R.M.; Pourzand, C. Ultraviolet a radiation-induced immediate iron release is a key modulator of the activation of NF-kappaB in human skin fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 95% Confidence Interval | Shapiro–Wilk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Model | Mean | Lower | Upper | SD | W | p | |
| Number of papillomas | Skh-hr1 | 0.175 | 0.106 | 0.244 | 0.382 | 0.46 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2 | 1.042 | 0.7955 | 1.288 | 1.362 | 0.736 | <0.001 | |
| Nude | 0.698 | 0.4697 | 0.926 | 1.064 | 0.663 | <0.001 | |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE | 3.233 | 2.3882 | 4.078 | 4.676 | 0.699 | <0.001 | |
| Number of tumors | Skh-hr1 | 0.183 | 0.0572 | 0.309 | 0.698 | 0.288 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2 | 0.65 | 0.4882 | 0.812 | 0.895 | 0.722 | <0.001 | |
| Nude | 0.593 | 0.4273 | 0.759 | 0.773 | 0.711 | <0.001 | |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE | 0.85 | 0.637 | 1.063 | 1.179 | 0.732 | <0.001 | |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Model | ||||
| Skh-hr2 vs. Skh-hr1 | 1.812 | 0.3512 | 5.1594 | <0.001 |
| Nude vs. Skh-hr1 | 1.571 | 0.3795 | 4.1383 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE vs. Skh-hr1 | 2.701 | 0.3684 | 7.331 | <0.001 |
| Non-irradiated vs. Skh-hr1 | −18.003 | 866.143 | −0.021 | 0.983 |
| 95% Exp(B) Confidence Interval | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Estimate | SE | Odds Ratios | Lower | Upper | z | p |
| Skh-hr2 vs. Skh-hr1 | 1.78 | 0.236 | 5.9524 | 3.84 | 9.72 | 7.5637 | <0.001 |
| Nude vs. Skh-hr1 | 1.38 | 0.254 | 3.9867 | 2.47 | 6.7 | 5.4545 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE vs. Skh-hr1 | 2.92 | 0.224 | 18.4762 | 12.23 | 29.57 | 13.0174 | <0.001 |
| Non-irradiated vs. Skh-hr1 | −16.56 | 521.937 | 6.43 × 10−8 | 0 | 0 | −0.0317 | 0.975 |
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Animal Model | ||||
| Skh-hr2 vs. Skh-hr1 | 4.51 | 0.649 | 6.9547 | <0.001 |
| Nude vs. Skh-hr1 | 5.8 | 0.773 | 7.4958 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE vs. Skh-hr1 | 5.06 | 0.685 | 7.3883 | <0.001 |
| Non-irradiated vs. Skh-hr1 | −18.2 | 1192.95 | −0.0153 | 0.988 |
| 95% Exp(B) Confidence Interval | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Estimate | SE | Odds Ratios | Lower | Upper | z | p |
| Skh-hr2 vs. Skh-hr1 | 0.467 | 0.1047 | 1.595 | 1.299 | 1.96 | 4.46 | <0.001 |
| Nude vs. Skh-hr1 | 0.41 | 0.1146 | 1.506 | 1.203 | 1.89 | 3.57 | <0.001 |
| Skh-hr2+ApoE vs. Skh-hr1 | 0.667 | 0.1047 | 1.948 | 1.586 | 2.39 | 6.36 | <0.001 |
| Non-irradiated vs. Skh-hr1 | −0.183 | 0.1047 | 0.832 | 0.678 | 1.02 | −1.75 | 0.081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gkikas, G.; Katsiris, D.; Vitsos, A.; Gioran, A.; Ieronymaki, D.; Kostaki, M.; Ladopoulos, G.; Ioannidou, V.; Theodoraki, E.; Chondrogianni, N.; et al. Comparative Study of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis in Different Hairless Murine Models. Cancers 2024, 16, 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203546
Gkikas G, Katsiris D, Vitsos A, Gioran A, Ieronymaki D, Kostaki M, Ladopoulos G, Ioannidou V, Theodoraki E, Chondrogianni N, et al. Comparative Study of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis in Different Hairless Murine Models. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203546
Chicago/Turabian StyleGkikas, Georgios, Dimitrios Katsiris, Andreas Vitsos, Anna Gioran, Dimitra Ieronymaki, Maria Kostaki, Georgios Ladopoulos, Vaya Ioannidou, Elisavet Theodoraki, Niki Chondrogianni, and et al. 2024. "Comparative Study of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis in Different Hairless Murine Models" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203546
APA StyleGkikas, G., Katsiris, D., Vitsos, A., Gioran, A., Ieronymaki, D., Kostaki, M., Ladopoulos, G., Ioannidou, V., Theodoraki, E., Chondrogianni, N., Sfiniadakis, I., Papaioannou, G. T., & Rallis, M. C. (2024). Comparative Study of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinogenesis in Different Hairless Murine Models. Cancers, 16(20), 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203546







