Underwater Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Diving into the Depths
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles of Underwater Resection Technique
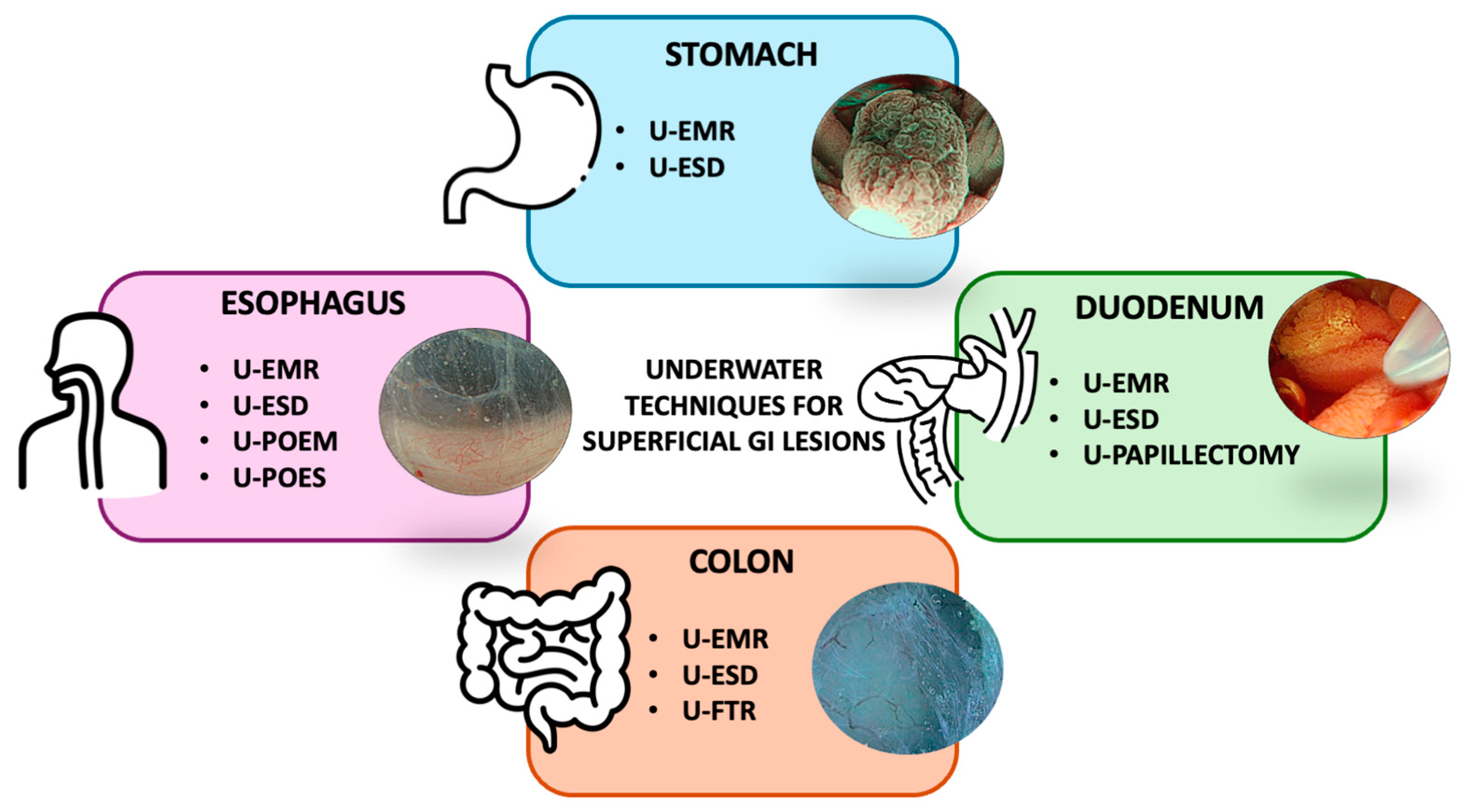
3. Organ-Specific Approaches to Underwater Resection Techniques
3.1. Oesophagus
3.1.1. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Submucosal Dissection
3.1.2. Underwater Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy and Septotomy
3.2. Stomach
3.3. Duodenum
3.3.1. Underwater Resections of Superficial Non-Ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumours
| Author | Design | Year | Country | Technique | Device | ESU Setting | Lesion Size | Lesion/Case Number | Lesion Site | En Bloc/Technical Success | R0 | Recurrence | AEs | Comparative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binmoeller [50] | Prospective | 2013 | USA | U-EMR | Duckbill 15 mm snare | Dry Cut (E 5) | >20 mm | 12 | 2nd duodenum: 12 (100%) | 91.7% * | - | 0% ^ | Bleeding: 3 (25) Other (stricture): 1 (8.3) | - |
| Yamasaki [51] | Prospective | 2018 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10–15 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 3, I4, L 2) | <20 mm | 31 | Bulb 4 (13) 2nd portion 26 (83) 3rd portion 1 (3) | 87% | 61% | 3% | Other (aspiration pneumonia): 1 (3) | - |
| Kiguchi [53] | Retrospective | 2020 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10–20 mm snare | - | <20 mm | 90 (PP) | Proximal: 19 (18%) Distal: 85 (82%) | 87% | 67% | Bleeding: 2 (2) | Conventional EMR: en bloc: 96%, R0: 80% | |
| Iwagami [52] | Retrospective | 2020 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10, 15, 25 mm | Forced pre-coag. (2) Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) | All sizes | 162 | Bulb: 21 (13) 2nd portion: 132 (81) 3rd portion: 9 (6) | 68% | 46% Unclear: 50% | 7/157 underwent follow-up | Bleeding: 3 (1.8) Perforations: 1 (0.6) | - |
| Toya [54] | Retrospective | 2020 | USA | U-EMR | Round stiff snare | Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) Forced coag. (2) | <20 mm | 17 | 2nd portion: 17 (100) | 100% | 88.2% | - | 0 | Conventional EMR: en bloc: 100%, R0: 95.2% |
| Furukawa [6] | Retrospective | 2021 | Japan | U-EMR | Different sizes | Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) | <20 mm | 28 | Bulb: 6 (21.4) 2nd portion: 21 (75.0) 3rd portion: 1 (3.6) | 96.4% | 71.4% | - | 0 | Conventional EMR: en bloc: 72.2%, R0: 50% |
| Yamasaki [7] | Multicentre prospective | 2022 | Japan | U-EMR | 10–20 mm snare | Endocut | <20 mm | 166 | Bulb: 10 (6.0) 2nd portion, preampulla: 71 (42.8) 2nd portion, postampulla: 80 (48.2) 3rd portion: 5 (3.0) | 89.8% | 66.9% | 3.6% | Bleeding: 6 (3.6) | - |
| Miyazaki [57] | Single-centre RCT | 2023 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10–13 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 1) | <12 mm | 64 | Bulb: 7 (10.9) 2nd portion: 57 (89.1) | 92.2% | 70.3% | 0% | Bleeding: 6 (9.4) Other (aspiration pneumonia): 2 (3.1) | CSP: en bloc: 95.4%, R0: 61.5%, recurrence: 1.5% |
| Morais [56] | Retrospective | 2024 | Europe | U-EMR | Braided or monofilament snare | - | 12.0–30.0 mm | 89 | Bulb: 8 (9) 2nd portion: 80 (89.9) 3rd portion: 1 (1.1) | 97.8% | - | 9.7% | Bleeding: 10 (11.2) Perforation: 2 (2.2) | Conventional EMR: technical success: 94.5 |
| Tanaka [55] | Retrospective | 2024 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10–15 mm snare | - | <20 mm | 96 | Bulb: 2 (2) Prox. 2nd portion: 51 (53) Distal 2nd portion: 40 (42) 3rd portion: 3 (3) | 94% | 68% | - | Bleeding: 1 (1.0) | Conventional ERM: en bloc: 91%, R0: 56%. |
| Nagata [60] | Case report | 2018 | Japan | U-ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted hook tip knife | - | 25 mm | 1 | Superior duodenal angle | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | |
| Santos-Antunes [59] | Case report | 2020 | Portugal | U-ESD | - | - | 60 mm | 1 | 2nd portion | 100% | 100% | - | ||
| Granata [61] | Case report | 2014 | Italy | U-papillectomy | - | Dry Cut (E 5) | 20 mm | 1 | Papilla of Vater | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | |
| Yamazaki [62] | Case report | 2020 | Japan | U-papillectomy | Round stiff 15 mm snare | - | - | 1 | Papilla of Vater | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | |
| Mori [63] | Case report | 2020 | Japan | U-papillectomy | - | - | - | 1 | Papilla of Vater | 100% | 100% | - | 0 |
3.3.2. Papilla of Vater: Underwater Papillectomy
3.4. Colon
3.4.1. Underwater EMR for Flat or Sessile Colorectal Lesions
3.4.2. Underwater ESD and Third-Space Technique for Colorectal Lesions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
References
- Ferlitsch, M.; Hassan, C.; Bisschops, R.; Bhandari, P.; Dinis-Ribeiro, M.; Risio, M.; Paspatis, G.A.; Moss, A.; Libânio, D.; Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; et al. Colorectal Polypectomy and Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2024. Endoscopy 2024, 56, 516–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zuo, X.-L. Incidence and Mortality of Post-Polypectomy Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Low-Risk Adenomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Dig. Dis. 2023, 41, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, A.; Shyne, M.; Mandel, J.S.; Snover, D.; Church, T.R. Colonoscopy with Polypectomy Reduces Long-Term Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Both Men and Women: Extended Results From the Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1397–1399.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Weilert, F.; Shah, J.; Bhat, Y.; Kane, S. “Underwater” EMR without Submucosal Injection for Large Sessile Colorectal Polyps (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 75, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Shichijo, S.; Uedo, N.; Ishihara, R. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Colorectal Lesions: Can It Be an “Underwater” Revolution? DEN Open 2022, 2, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, M.; Mitoro, A.; Ozutumi, T.; Fujinaga, Y.; Nakanishi, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Saikawa, S.; Sato, S.; Sawada, Y.; Takaya, H.; et al. Efficacy of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Superficial Non-Ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumor. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Uedo, N.; Akamatsu, T.; Kagawa, T.; Higashi, R.; Dohi, O.; Furukawa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Nonrecurrence Rate of Underwater EMR for ≤20-Mm Nonampullary Duodenal Adenomas: A Multicenter Prospective Study (D-UEMR Study). Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1010–1018.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagl, S.; Ebigbo, A.; Goelder, S.K.; Roemmele, C.; Neuhaus, L.; Weber, T.; Braun, G.; Probst, A.; Schnoy, E.; Kafel, A.J.; et al. Underwater vs Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Large Sessile or Flat Colorectal Polyps: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1460–1474.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, P. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Adenomas and Colorectal Serrated Lesions: A Prospective Clinical Study. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Sánchez, J.; Alvarez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Pellisé, M.; Coto-Ugarte, D.; Uchima, H.; Aranda-Hernández, J.; Santiago García, J.; Marín-Gabriel, J.C.; Riu Pons, F.; Nogales, O.; et al. Underwater versus Conventional EMR of Large Nonpedunculated Colorectal Lesions: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 941–951.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, P.V.; Aihara, H.; Karasik, M.S.; Ngamruengphong, S.; Aadam, A.A.; Othman, M.O.; Sharma, N.; Grimm, I.S.; Rostom, A.; Elmunzer, B.J.; et al. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in North America: A Large Prospective Multicenter Study. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2317–2327.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohata, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sakai, E.; Takeuchi, Y.; Chino, A.; Takamaru, H.; Kodashima, S.; Hotta, K.; Harada, K.; Ikematsu, H.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes After Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Large Colorectal Epithelial Neoplasms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Cohort Trial from Japan. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1423–1434.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, E.; Wong Kee Song, L.M. Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1925–1937.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Barret, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Familiari, P.; Gonzalez, J.-M.; Van Hooft, J.E.; Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; Louis, H.; Martinek, J.; Van Meer, S.; et al. Endoscopic Management of Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders—Part 2: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weusten, B.L.A.M.; Barret, M.; Bredenoord, A.J.; Familiari, P.; Gonzalez, J.-M.; Van Hooft, J.E.; Ishaq, S.; Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; Louis, H.; Van Meer, S.; et al. Endoscopic Management of Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders—Part 1: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 498–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, H.; Dacha, S.; Anand, G.S.; Byrne, K.R.; Chahal, P.; James, T.; Kowalski, T.E.; Repaka, A.; Saadi, M.; Sheth, S.G.; et al. Core Curriculum for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, Q.; Xu, E.-P.; Yao, L.-Q.; Cai, S.-L.; Qi, Z.-P.; Sun, D.; He, D.-L.; Yalikong, A.; Lv, Z.-T.; et al. Prediction of Technically Difficult Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Large Superficial Colorectal Tumors: A Novel Clinical Score Model. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 133–144.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sferrazza, S.; Maida, M.; Calabrese, G.; Facciorusso, A.; Fuccio, L.; Frazzoni, L.; Maselli, R.; Repici, A.; Di Mitri, R.; Santos-Antunes, J. The Derivation and External Validation of a Fibrosis Risk Model for Colorectal Tumours Undergoing Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmoeller, K.F. Underwater EMR without Submucosal Injection: Is Less More? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Y.; Flynn, M.M.; Patrie, J.T.; Cox, D.G.; Bleibel, W.; Mann, J.A.; Sauer, B.G.; Shami, V.M. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Colorectal Neoplasia Is Easily Learned, Efficacious, and Safe. Surg. Endosc. 2014, 28, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, S.; Khan, S.R.; Kumar, A.; Mohan, B.P.; Ramai, D.; Kassab, L.L.; Draganov, P.V.; Othman, M.O.; Kochhar, G.S. Efficacy and Histologic Accuracy of Underwater versus Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Large (>20 Mm) Colorectal Polyps: A Comparative Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 471–482.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Hamerski, C.M.; Shah, J.N.; Bhat, Y.M.; Kane, S.D.; Garcia-Kennedy, R. Attempted Underwater En Bloc Resection for Large (2–4 Cm) Colorectal Laterally Spreading Tumors (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Libânio, D.; Bastiaansen, B.A.J.; Bhandari, P.; Bisschops, R.; Bourke, M.J.; Esposito, G.; Lemmers, A.; Maselli, R.; Messmann, H.; et al. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Superficial Gastrointestinal Lesions: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline—Update 2022. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 591–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.; Rahmi, G.; Perrod, G.; Pioche, M.; Canard, J.-M.; Cesbron-Métivier, E.; Boursier, J.; Samaha, E.; Vienne, A.; Lépilliez, V.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up after Endoscopic Resection for Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Western Study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumbe-Mandengue, P.; Geyl, S.; Guyot, A.; Pioche, M.; Rodrigues, R.; Albouys, J.; Jacques, J. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for a Protruding Lesion in the Esophagus. Endoscopy 2022, 54, E869–E870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, S.; Xu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Mei, Z.; He, S. Precutting and Trimming-Assisted Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Large Early Esophageal Cancer. Endoscopy 2023, 55, E494–E495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, G.P.; Dirks, R.C.; Ansari, M.T.; Clay, J.; Dunst, C.M.; Lundell, L.; Marks, J.M.; Molena, D.; Rooker, C.; Saxena, P.; et al. SAGES Guidelines for the Use of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) for the Treatment of Achalasia. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 1931–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Familiari, P.; Gigante, G.; Marchese, M.; Boskoski, I.; Tringali, A.; Perri, V.; Costamagna, G. Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Esophageal Achalasia: Outcomes of the First 100 Patients With Short-Term Follow-Up. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Bhat, Y.M. Underwater Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallit, R.; Barret, M.; Abouali, E.; Belle, A.; Leandi, C.; Coriat, R.; Chaussade, S. Underwater Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 94–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capogreco, A.; Hassan, C.; De Blasio, F.; Massimi, D.; De Sire, R.; Galtieri, P.A.; Despott, E.J.; Alkandari, A.; Bhandari, P.; Facciorusso, A.; et al. Prophylactic Underwater Vessel Coagulation for Submucosal Endoscopy. Gut 2024, 73, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repici, A.; Spadaccini, M.; Belletrutti, P.J.; Galtieri, P.A.; Fugazza, A.; Anderloni, A.; Carrara, S.; Di Leo, M.; Pellegatta, G.; Cappello, A.; et al. Peroral Endoscopic Septotomy for Short-Septum Zenker’s Diverticulum. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Mondragón, O.V.; Solórzano Pineda, M.O.; Blancas Valencia, J.M. Zenker’s Diverticulum: Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Septum Division (Z-POEM). Dig. Endosc. 2018, 30, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maselli, R.; Alfarone, L.; Massimi, D.; De Sire, R.; Capogreco, A.; Repici, A. Saline-Immersion Peroral Endoscopic Septotomy: A Case Report. VideoGIE 2023, 9, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagami, H.; Kanesaka, T.; Ishihara, R.; Uedo, N. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Remaining Early Gastric Cancer after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Endoscopy 2019, 51, E229–E230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, H.; Kono, Y.; Nakagawa, M. Intramucosal Gastric Cancer on the Prepylorus Completely Resected by Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.K. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Neoplasms in the Pyloric Ring of the Stomach: Four Case Reports. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 3050–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, Y.; Sakae, H.; Okada, H. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Gastric Polyp. Dig. Endosc. 2018, 30, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Uedo, N.; Kawakami, Y.; Hayata, N.; Mita, E. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Gastric Neoplasms. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E1155–E1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, G.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Mita, E. Salvage Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Recurrent Gastric Cancer after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Endoscopy 2022, 54, E792–E793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Wu, S.; Mei, Z.; He, S. Integration of Endoscopic Screening, Magnification, and Resection for Early Gastric Cancer: Advantages of Underwater EMR (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 98, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamoto, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ishiguro, S.; Nakatsuka, S.; Yunokizaki, H.; Ezoe, Y.; Matsuno, K.; Nakahira, H.; Shichijo, S.; Maekawa, A.; et al. Feasibility of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Endoscopic Management of Gastric Neoplasms in Patients with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 6877–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.S. Feasibility and Efficacy of Gastric Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Shichijo, S. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for a Residual Gastric Lesion after Unsuccessful Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in a Patient with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Dig. Endosc. 2024, 36, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Kato, M.; Kanai, T.; Yahagi, N. A Successful Case of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Using the Water Pressure Method for Early Gastric Cancer with Severe Fibrosis. VideoGIE 2022, 7, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, T.; Tashima, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Mashimo, Y.; Itoi, T.; Ryozawa, S. Successful Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection with Gel Immersion for Early Gastric Cancer in an Upside-down Stomach. Endoscopy 2024, 56, E258–E259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S.; Sakai, Y.; Kasanuki, J.; Kondo, F.; Ooka, Y.; Kato, K.; Arai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Matsumura, T.; Bekku, D.; et al. Indications for the Use of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Gastric Cancer in Japan: A Comparative Study with Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbiervliet, G.; Moss, A.; Arvanitakis, M.; Arnelo, U.; Beyna, T.; Busch, O.; Deprez, P.H.; Kunovsky, L.; Larghi, A.; Manes, G.; et al. Endoscopic Management of Superficial Nonampullary Duodenal Tumors: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Kanai, T.; Yahagi, N. Endoscopic Resection of Superficial Non-ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumor. DEN Open 2022, 2, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Shah, J.N.; Bhat, Y.M.; Kane, S.D. “Underwater” EMR of Sporadic Laterally Spreading Nonampullary Duodenal Adenomas (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2013, 78, 496–502.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Uedo, N.; Takeuchi, Y.; Higashino, K.; Hanaoka, N.; Akasaka, T.; Kato, M.; Hamada, K.; Tonai, Y.; Matsuura, N.; et al. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Superficial Nonampullary Duodenal Adenomas. Endoscopy 2017, 50, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagami, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Ohmori, M.; Matsuno, K.; Inoue, S.; Iwatsubo, T.; Nakahira, H.; Matsuura, N.; et al. Feasibility of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Management of Residues for Superficial Non-ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Neoplasms. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiguchi, Y.; Kato, M.; Nakayama, A.; Sasaki, M.; Mizutani, M.; Tsutsumi, K.; Akimoto, T.; Takatori, Y.; Mutaguchi, M.; Takabayashi, K.; et al. Feasibility Study Comparing Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Superficial Non-ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumor < 20 Mm. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toya, Y.; Endo, M.; Yamazato, M.; Yamada, S.; Kumei, T.; Hirai, M.; Eizuka, M.; Morishita, T.; Akasaka, R.; Yanai, S.; et al. Resectability of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Duodenal Tumor: A Single-center, Retrospective Pilot Study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 3191–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Urabe, Y.; Takemoto, H.; Ishibashi, K.; Konishi, H.; Matsubara, Y.; Takehara, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Tanino, F.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Can Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Be an Alternative to Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Superficial Non-ampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumors? DEN Open 2024, 4, e312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, R.; Amorim, J.; Medas, R.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Santos-Antunes, J.; Legros, R.; Albouys, J.; Moll, F.; Marques, M.; Vilas-Boas, F.; et al. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Vs Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Superficial Nonampullary Duodenal Epithelial Tumors in the Western Setting. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, S1542356524004853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Nakayama, A.; Sasaki, M.; Minezaki, D.; Morioka, K.; Iwata, K.; Masunaga, T.; Kubosawa, Y.; Mizutani, M.; Hayashi, Y.; et al. Resectability of Small Duodenal Tumors: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Cold Snare Polypectomy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M. Usefulness of Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Saline Solution with a Monopolar Knife for Colorectal Tumors (with Videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Antunes, J.; Morais, R.; Marques, M.; Macedo, G. Underwater Duodenal ESD of a Large Adenoma Using the Pocket-Creation Method. GE-Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 28, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M. Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Saline Solution Using a Bent-Type Knife for Duodenal Tumor. VideoGIE 2018, 3, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, A.; Curcio, G.; Ligresti, D.; Barresi, L.; Ilaria, T.; Liotta, R.; Traina, M. Endoscopic Ampullectomy: To Inject or Not to Inject? The Underwater Technique. Endoscopy 2014, 46, E478–E479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, T.; Uchida, D.; Yamasaki, Y.; Tomoda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kato, H.; Okada, H. Underwater Endoscopic Papillectomy Using Double-Balloon Endoscopy. Endoscopy 2020, 52, E55–E56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Kurita, A.; Yazumi, S. Underwater Endoscopic Papillectomy for Residual Tumor after Endoscopic Papillectomy: First Report. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 32, e162–e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Hamerski, C.M.; Shah, J.N.; Bhat, Y.M.; Kane, S.D. Underwater EMR of Adenomas of the Appendiceal Orifice (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uedo, N.; Nemeth, A.; Johansson, G.; Toth, E.; Thorlacius, H. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Large Colorectal Lesions. Endoscopy 2014, 47, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Radaelli, F.; Spinzi, G. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: The Third Way for En Bloc Resection of Colonic Lesions? United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siau, K.; Ishaq, S.; Cadoni, S.; Kuwai, T.; Yusuf, A.; Suzuki, N. Feasibility and Outcomes of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for ≥ 10 Mm Colorectal Polyps. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Sakai, H.; Ogawa, T.; Sakiyama, N.; Ueda, Y.; Shirakawa, A.; Okada, Y.; Sanada, K.; Nakase, K.; Mandai, K.; et al. Feasibility of Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Colorectal Lesions: A Single Center Study in Japan. Gastroenterol. Res. 2018, 11, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, D.M.; Brito, H.P.; Chaves, L.T.; Rodrigues, R.A.; Sugai, B.M. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Serrated Adenomas. Clinics 2018, 73, e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashina, T.; Uedo, N.; Akasaka, T.; Iwatsubo, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Akamatsu, T.; Kawamura, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fujii, S.; Kusaka, T.; et al. Comparison of Underwater vs Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Intermediate-Size Colorectal Polyps. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 451–461.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.-C.; Uedo, N.; Hsieh, P.-H. Comparison of Underwater and Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Removing Sessile Colorectal Polyps: A Propensity-Score Matched Cohort Study. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 07, E1528–E1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Cui, H.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Tong, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L. Underwater versus Conventional Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Small Size Non-Pedunculated Colorectal Polyps: A Randomized Controlled Trial: (UEMR vs. CEMR for Small Size Non-Pedunculated Colorectal Polyps). BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, A.W.; Leung, J.W.; Wilson, M.D.; Leung, F.W. Underwater versus Conventional Endoscopic Resection of Nondiminutive Nonpedunculated Colorectal Lesions: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 643–654.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, R.L.; Percy, D.B. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection without Submucosal Injection (UEMR) for Large Colorectal Polyps: A Community-Based Series. Am. J. Surg. 2020, 220, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Shichijo, S.; Kanesaka, T.; Maekawa, A.; Higashino, K.; Uedo, N.; Ishihara, R.; Takeuchi, Y. Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection versus Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for 20–30 Mm Colorectal Polyps. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagami, H.; Akamatsu, T.; Ogino, S.; Morimura, H.; Shimoyama, M.; Terashita, T.; Nakano, S.; Wakita, M.; Edagawa, T.; Konishi, T.; et al. Longly-Attached Cap Can Contribute to En Bloc Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of 20–30 Mm Colorectal Intramucosal Lesions. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E1562–E1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, M.; Shinozaki, S.; Nomura, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Kitamura, M.; Fukuda, H.; Arita, M.; Takezawa, T.; Sunada, K.; et al. Feasibility of Progressive Polyp Contraction with Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in ≥20 Mm Superficial Colorectal Lesions. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E1577–E1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchima, H.; Calm, A.; Muñoz-González, R.; Caballero, N.; Rosinach, M.; Marín, I.; Colán-Hernández, J.; Iborra, I.; Castillo-Regalado, E.; Temiño, R.; et al. Underwater Cap-Suction Pseudopolyp Formation for Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: A Simple Technique for Treating Flat, Appendiceal Orifice or Ileocecal Valve Colorectal Lesions. Endoscopy 2023, 55, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, S.-Y.; You, H.-S.; Jung, Y.-W.; Joo, Y.-E.; Myung, D.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, N.I.; Kim, S.-J.; Ju, J.K. Modified Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Intermediate-Sized Sessile Colorectal Polyps. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1200145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, K.; Matsumura, T.; Matsusaka, K.; Inaba, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Akizue, N.; Kaneko, T.; Ota, M.; Ohta, Y.; Taida, T.; et al. Outcomes for Underwater Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of 21–30-Mm Colorectal Polyps: A Feasible Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 3963–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizawa, H.; Hotta, K.; Imai, K.; Ito, S.; Kishida, Y.; Takada, K.; Okumura, T.; Kawata, N.; Yoshida, M.; Maeda, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Gel Immersion Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Non-Pedunculated Colorectal Polyps. Life 2023, 13, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, L.; Martins, B.; Andrade De Paulo, G.; Kawaguti, F.S.; Baba, E.R.; Uemura, R.S.; Gusmon, C.C.; Geiger, S.N.; Moura, R.N.; Pennacchi, C.; et al. Underwater versus Conventional EMR for Nonpedunculated Colorectal Lesions: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, S.; Akasaka, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Tsujii, Y.; Nagai, K.; Higashino, K.; Ishihara, R.; Iijima, H.; Takehara, T. “Underwater” Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Novel Method for Resection in Saline with a Bipolar Needle Knife for Colorectal Epithelial Neoplasia. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 5031–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecinato, P.; Lucarini, M.; Campanale, C.; Azzolini, F.; Bassi, F.; Sassatelli, R. Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection and Hybrid Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection as Rescue Therapy in Difficult Colorectal Cases. Endosc. Int. Open 2022, 10, E1225–E1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Fukuzawa, M.; Aikawa, H.; Nemoto, D.; Muramatsu, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Uchida, K.; Madarame, A.; Morise, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Colorectal Tumors Decreases the Incidence of Post-electrocoagulation Syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, K.; Takada, K.; Hotta, K.; Imai, K.; Ito, S.; Kishida, Y.; Ono, H. Underwater Endoscopic Full-Thickness Resection with Snare as a Salvage Technique for Residual Colon Lesion. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 2117–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoni, S.; Liggi, M.; Gallittu, P.; Mura, D.; Fuccio, L.; Koo, M.; Ishaq, S. Underwater Endoscopic Colorectal Polyp Resection: Feasibility in Everyday Clinical Practice. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despott, E.J.; Murino, A. Saline-Immersion Therapeutic Endoscopy (SITE): An Evolution of Underwater Endoscopic Lesion Resection. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Straus Takahashi, M.; Eyileten Postula, C.; Buccino, V.R.; Muscatiello, N. Efficacy of Hemostatic Powders in Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Iwagami, H.; Nakahira, H.; Matsuura, N.; Shichijo, S.; Maekawa, A.; Kanesaka, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Higashino, K.; et al. Propensity Score-matched Analysis of Endoscopic Resection for Recurrent Colorectal Neoplasms: A Pilot Study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2568–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaji, S.; Morita, Y.; Kudo, T.; Yamada, K.; Kato, T.; Sakai, A.; Takao, T.; Sawada, R.; Harada, H.; Urakawa, N.; et al. Laparoscopic Endoscopic Cooperative Surgery Using Open-Window Suturing Technique for Treating Non-Ampullary Superficial Duodenal Neoplasms Located on the Pancreatic Side. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 2266–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, H.; Nakahara, R.; Murakami, D.; Suehiro, S.; Ujihara, T.; Sagami, R.; Katsuyama, Y.; Hayasaka, K.; Amano, Y. Saline-Pocket Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Superficial Colorectal Neoplasms: A Randomized Controlled Trial (with Video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 90, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libânio, D.; Pimentel-Nunes, P.; Bastiaansen, B.; Bisschops, R.; Bourke, M.J.; Deprez, P.H.; Esposito, G.; Lemmers, A.; Leclercq, P.; Maselli, R.; et al. Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Techniques and Technology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical Review. Endoscopy 2023, 55, 361–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Masunaga, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Nakajima, K.; Yahagi, N.; Kato, M. Automatic Water Irrigation Synchronized with the Electrosurgical Unit: Bubble-Free Underwater Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection. Endoscopy 2024, 56, E468–E469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yabuuchi, Y.; Shigeta, K.; Yoshida, M.; Nagao, S.; Noguchi, A.; Morita, Y.; Shintani, S.; Inatomi, O.; et al. Gel Immersion Endoscopic Mucosal Resection for Early Gastric Neoplasms: A Multicenter Case Series Study. Endosc. Int. Open 2024, 12, E435–E439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author | Design | Year | Country | Technique | Device | ESU Setting | Lesion Size/Disease | Lesion/Case Number | Lesion Site | En Bloc/Technical Success | R0 | Recurrence | AEs | Comparative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doumbe-Mandengue [25] | Case report | 2022 | France | U-EMR | 15 mm snare | - | 20 mm | 1 | GEJ | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Deng [26] | Case report | 2023 | China | U-Hybrid ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted knife Round 30 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) Swift coag. (3) | 40 mm | 1 | Oesophagus | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Binmoeller [29] | Case report | 2016 | USA | U-POEM | Waterjet system-assisted knife | - | Type II achalasia | 2 | Oesophagus | 100% | - | - | 0 | - |
| Hallit [30] | Case report | 2020 | France | U-POEM | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | Tunnel and myotomy: spray coag. (4) endocut (E 1/3–3) | Type II achalasia | 3 | Oesophagus | 100% | - | - | 1 (minimal pneumomediastinum) | - |
| Capogreco [31] | Case series | 2024 | Italy | PUC-POEM | Waterjet system-assisted knife | Swift coag. (3) | - | 21 | Oesophagus | - | - | - | 0 | |
| Maselli [34] | Case report | 2024 | Italy | U-POES | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | - | Short–septum (20 mm) Zenker diverticulum | 1 | Proximal oesophagus | 100% | - | - | 0 | - |
| Author | Design | Year | Country | Technique | Device | ESU Setting | Lesion Size | Lesion Number | Lesion Site | En Bloc | R0 | Recurrence | AEs | Comparative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kono [38] | Case report | 2018 | Japan | U-EMR | - | - | Pedunculated lesion | 1 | Corpus | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Iwagami [35] | Case report | 2019 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 25 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 3) Forced coag. (E 2) | 15 mm | 1 | Pylorus | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Uemura [36] | Case report | 2019 | Japan | U-EMR | 30 mm snare | - | Pedunculated lesion | 1 | Pylorus | 100% | 100% | 0 | 0 | - |
| Kim [37] | Case series | 2020 | Republic of Korea | U-EMR | Crescent-type snare | Endocut Q (E 2, I 5, L 3) | <15 mm | 4 | Pylorus | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Yamamoto [39] | Retrospective | 2022 | Japan | U-EMR | 10–33 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 3) Forced coag. (2) | 10 mm (2–50) | 36 | Upper: 11 (30.6) Middle: 16 (44.4) Lower: 5 (13.9) | 100% | 72.4% | 0 | 0 | - |
| Tanabe [40] | Case report | 2022 | Japan | U-EMR | 10 mm snare | Endocut Q | 5 mm scar | 1 | Antrum | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Deng [41] | Case report | 2023 | China | U-EMR | - | Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) | 10 mm | 1 | Antrum | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | |
| Shimamoto [42] | Retrospective | 2023 | Japan | U-EMR | Round stiff 10–20 mm snare | Endocut Q (E 3, I 4, L 2) Soft coag. (4) | <20 mm | 25 | - | 88% | 56% | 0 | 0 | Conventional-EMR: en bloc: 92%, R0 75%, recurrence: 16.7%. |
| Kim [43] | Retrospective | 2024 | Republic of Korea | U-EMR | Hexagonal 15–20 mm snare | Endocut Q (level 2, L 3) | 10.1 ± 2.8 | 76 | Cardias: 4 (5.3) Body: 15 (19.7) Antrum: 46 (60.5) Pylorus: 11 (14.5) | 100% | 93.4% | 2.6% | Bleeding: 28 (36.8) Other: 5 (6.6) | Rescue ESD: en bloc: 100%, R0: 100%, recurrence: 0 |
| Okubo [44] | Case report | 2024 | Japan | U-EMR | - | - | 25 mm | 1 | Fundus | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Miyazaki [45] | Case report | 2022 | Japan | U-ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | Dry cut (E 2.5); Swift coag. (E 3.5) | 15 mm | 1 | Lesser curvature | 100% | 100% | - | 0 | - |
| Muramatsu [46] | Case report | 2024 | Japan | U-ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | - | 10 mm | 1 | Upside-down stomach | 100% | 100% | 0 | 0 |
| Author | Design | Year | Country | Technique | Device | ESU Setting | Lesion Size | Lesion Number | Lesion Site | En Bloc | R0 | Recurrence | AEs | Comparative |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binmoller [22] | Prospective | 2015 | USA | U-EMR | Stiff braided 33 mm snare | Autocut (E 5) | >20 mm | 50 | Right C: 38 (76) Left C: 12 (24) R: 3 (6) | 55% | 46% | 5% | Bleeding: 1 (2%) | - |
| Uedo [65] | Retrospective | 2015 | Sweden | U-EMR | Stiff rounded 33 mm snares | Endocut (E 2) Forced coag. (2) | >15 mm | 11 | C: 7 (63.6) AC: 1 (9.1) TC: 2 (18.2) R: 1 (9.1) | 55.5% | 64% | - | 0 | - |
| Binmoeller [64] | Prospective | 2016 | USA | U-EMR | 15–25 stiff snares | Dry cut (E 5) | 15 (8–50) | 27 | Appendiceal orifice | 59% | - | 2/21 underwent follow-up | Post-polypectomy coagulation syndrome: 2 (7%) | - |
| Amato [66] | Prospective | 2016 | Italy | U-EMR | 15–32 mm stiff rounded snares | Endocut (E 3) | >10 mm | 25 | Right C: 18 (72%) Left C: 4 (16) R: 3 (12) | 76% | 76% | - | 0 | - |
| Cadoni [67] | Retrospective | 2018 | Italy | U-EMR | Polyfilament duckbill or oval snares Monofilament snares | Dry cut (E 5) or endocut Q (E 3) Forced coag. (E 3) | Any size 108 (55.4) flat or sessile lesions 87 (44.6) pedunculated lesions | 195 | Right C: 38 (19.5) TC: 29 (14.9) Left C or R: 128 (65.6) | 87.7% | 97.6%, just for sessile or flat lesions | - | Bleeding: 16 (8.2%) | 6–9 mm: CSP >10 mm: conventional EMR En bloc: 84.4%, R0: 100% |
| Kawamura [68] | Retrospective | 2018 | Japan | U-EMR | 10, 13 or 33 mm rotatable snares | Pulse-cut slow (20 W) Forced coag. (2) | Any size | 64 | C: 9 (14) AC: 12 (19) TC: 12 (19) DC: 7 (11) SC: 17 (27) R: 7 (11) | 81% | 54% | Bleeding: 3 (5) Perforation: 1 (2%) | - | |
| Siau [67] | Single-centre RCT | 2018 | UK | U-EMR | 25 mm snare, other types | Left colon: 30 W E 2 Right colon: 20 W E 2 | >10 mm | 97 | C: 13 (13.4) AC: 7 (7.2) TC: 12 (12.4) DC: 1 (1.0) SC: 24 (24.7) R: 40 (41.2) | 82.9% | - | 8/59 underwent follow-up | 4 (4.1) | - |
| Chaves [69] | Retrospective | 2018 | Brazil | U-EMR | 15–25 mm multifilament snare | Endocut (E 3, I 6, L 1) | >10 mm | 16 | C: 1 (6.3) AC: 10 (62.4) TC: 4 (25) DC: 1 (6.3) | 8 (50.0%) | - | - | 0 | - |
| Yamashina [70] | Multicentre RCT | 2019 | Japan | U-EMR | - | Endocut or pulse-cut mode | 10–20 mm | 108 | C: 16 (15) AC: 21 (19) TC: 29 (27) DC: 11 (10) SC: 23 (21) R: 8 (7.4) | 89% | 69% | Bleeding: 3 (2.8) | Conventional EMR (en bloc: 75%, R0: 50%) | |
| Chien [71] | Retrospective | 2019 | Taiwan | U-EMR | - | - | >10 | 121 | Right C: 94 (52.5) Left C: 77 (43.0) | 141 (82.5) | - | - | Bleeding: 11 (6.5) Perforation: 4 (2.4) | Conventional EMR (en bloc: 87.6%) |
| Zhang [72] | Multicentre RCT | 2020 | China | U-EMR | Round snare | Endo cut Q (E 4, I 6, L 1) Forced coag. (E 2) | 4–9 mm | 71 | AC: 13 (18.3) TC: 21 (29.6) (29.6) DC: 6 (8.4) SC: 22 (31.0) R: 9 (12.7) | 94.4% | - | - | Bleeding: 1 (1.5) | CSP En bloc: 91.5% |
| Yen [73] | Single-centre RCT | 2020 | USA | U-EMR | 6–9 mm: 9 mm dedicated cold snare >10 mm: 15 mm firm monofilament hot snare | Endocut Q, (E 3, I 3, L 1) | 6–20 mm >20 mm | 248 | C: 25 (10.1) AC: 67 (27.0) TC: 110 (44.4) DC: 15 (6.1) SC: 21 (8.5) R: 10 (4.0) | Overall: 89.9% 6–9 mm: 97.2% 10–19 mm: 84.6% >20 mm: 25% | - | - | Bleeding: 10 (4.0) | 6–9 mm: CSP >10 mm: conventional EMR Overall R0: 90.2% |
| Barclay [74] | Retrospective | 2020 | USA | U-EMR | Stiff rounded 25–33 mm snares | Endocut Q (E 2, I 4, L 1) | >20 mm | 264 | C: 87 (33) AC: 64 (24) TC: 41 816) DC: 16 (6) R: 24 (9) | 28% | - | 10/174 underwent follow-up | Bleeding: 43 (16.3) | - |
| Nagl [8] | Single-centre RCT | 2021 | Germany | U-EMR | 15–25 mm snares | Endocut Q (E 2) Forced coag. | 20–40 mm | 81 | C: 20 (24.7) AC: 28 (34.6) TC: 7 (8.6) DC: 5 (6.2) SC:6 (7.4) R:0 | 33.3% | 32.1% | 15.1% | Bleeding: 19 (23.5%) intra, 1 (1.2) post-procedural | Conventional EMR (en bloc: 18.4%, R0 15.8%, recurrence 24.6%) |
| Inoue [75] | Retrospective | 2021 | Japan | U-EMR | 15–30 mm snare | - | 20–30 mm | 125 | Right C: 99 (79.2) Left C: 23 (18.4%) Rectum: 3 (2.4%) | 61% | 45% | 2/97 underwent follow-up | Bleeding: 5 (4%) Perforation: 1 (0.8) | ESD (en bloc: 99%, R0: 86%, recurrence: 0) |
| Nogueira [9] | Prospective | 2021 | Brazil | U-EMR | Stiff rounded snares | Endocut (E 4) | >5 mm | 51 | Right C: 38 (74.5) Left C: 10 (19.6) R: 3 (5.8) | 52.9% | - | - | Bleeding: 6 (11.8) | - |
| Iwagami [76] | Retrospective | 2022 | Japan | U-EMR | Stiff rounded 10–25 mm snares | Endocut Q (E3/2) Forced coag. (3/4.5) | >20 mm | 52 | AC: 28 (54) TC: 12 (23) DC: 3 (6) SC: 5 (9) R:4 (8) | 75% | 73% | - | Bleeding: 1 (1.9) Perforation: 1 (1.9) | - |
| Okada § [77] | Retrospective | 2022 | Japan | U-EMR | Rounded 15-mm snare | Pure-cut | >20 mm | 11 | Right C: 10 (91%) Left C: 1 (9%) | 91% | 91% | - | 0 | - |
| Uchima [78] | Retrospective | 2023 | Spain | U-EMR Cap suction | Stiff rounded 10–25 mm snares | Endocut Q (E 2) Pulse-cut slow (E 2) | 20 mm (15–30) | 83 | Appendiceal orifice: 11 (13.3) Ileo-caecal valve: 8 (9.6) C: 17 (20.5) AC: 10 (12) TC: 25 (30.1) DC: 2 (2.4) SC: 8 (8.6) R: 2 (2.4) | 54.2% | - | - | Bleeding: 9 (10.8) | - |
| Kim [79] | Single-centre prospective | 2023 | Republic of Korea | U-EMR | Hexagonal snare | Endocut Q (E 1, I 3, L 3) | 10–20 mm | 47 | C: 10 (21.3) AC: 10 (21.3) TC: 12 (25.5) DC: 6 (12.8) SC: 7 (14.9) R: (4.3) | 97.9% | 80.9% | - | Bleeding: 6 (12.8) | - |
| Okimoto [80] | Single-centre RCT | 2023 | Japan | U-EMR | Rounded snare | - | 21–30 mm | 11 | C: 3 (27) AC: 2 (18) TC: 2 (18) DC: 0 SC: 3 (27) R: 1 (9.1) | 82% | 36% | 1/8 underwent follow-up | 0 | ESD (en bloc: 100%, R0: 100%, recurrence: 0/10) |
| Ashizawa ^ [81] | Retrospective | 2023 | Japan | U-EMR | Stiff rounded 10–25 mm snares | Endocut Q (E 3, I 2, L 2) | >10 mm | 25 | C: 6 (24) AC: 8 (32) TC: 4 (16) DC: 3 (12) SC: 4 (16) R: 0 | 80% | 72% | - | 0 | - |
| Rodríguez Sánchez [10] | Multicentre RCT | 2023 | Spain | U-EMR | Wide range of snare types, endoscopist’s discretion | Endocut Q (E 2, I 6, L 1) | >10 mm | 149 | Right C: 71 (47.7) Left C: 78 (52.3) | 31.5% | 27.5% | 9.5% | Bleeding: 31 (20.8) Perforations: 4 (2.7) Others: 7 (4.7) | Conventional EMR: en bloc: 28.4%, R0: 24.1%, recurrence: 11.7% |
| Lenz [82] | Multicentre RCT | 2023 | Brazil | U-EMR | Stiff rounded 13–25 mm snares | Endocut Q (E 3, I 6, L 1) | 10–40 mm | 61 | Right C: 41 (67.2) Left C: 20 (32.8) | 60.7% | - | 2% | 2 (3.3%) | Conventional EMR: en bloc: 54.2%, recurrence: 8 (15%) |
| Nagata [58] | Retrospective | 2017 | Japan | U-ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | Endocut I Swift coag. (3) | 22.5 (17.8–25.3) | 26 | C: 5 (19.2) AC: 4 (15.4) TC: 7 (26.9) DC: 0 (0) SC: 4 (15.4) R: 6 (23.1) | 100% | - | - | 1 (83.8) | - |
| Yoshii [83] | Retrospective | 2018 | Japan | U-ESD | Bipolar needle knife with water-jet function | Endocut I (E 3, I 3, L 3) Swift-coag. (2) Dry-cut (3) | >20 mm | 40 | C: 4 (10) AC: 7 (17.5) TC: 9 (22.5) DC: 4 (10) SC: 7 (17.5) R: 9 (22.5) | 100% | 87.5% ° | - | 0 | - |
| Cecinato [84] | Retrospective | 2022 | Italy | U-ESD | Waterjet system-assisted or not assisted knife | Endocut Q (E 3) Swift coag. (3) Spray coag. (4) | 44.5 (±17.8) | 22 | Right C: 10 (45.5) Left C: 5 (22.7) R: 7 (31.8) | 100% | 100% ° | 0% | Other: 1 (5%) | Hybrid ESD: en bloc: 59.5%, R0:54.5%, recurrence: 2.7% |
| Koyama [85] | Retrospective | 2023 | Japan | U-ESD | Waterjet-not-assisted knife | Endocut I (E 2, I 2, L 2) Swift coag. (3) Forced coag. (3) | 22 (18–27) | 80 | Right C: 54 (68) Left C: 20 (25) Rectum: 6 (7) | 98.7% | 98.7 ° | - | 2 (2.5%) | Conventional-ESD: en bloc: 99.2, R0: 94.4% |
| Shigeta [86] | Case report | 2023 | Japan | U-EFTR | Full thickness resection device system | - | - | 1 | AC: 1 | 100% | 100% | - | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sferrazza, S.; Calabrese, G.; Maselli, R.; Morais, R.; Facciorusso, A.; Mavrogenis, G.; Di Mitri, R.; Repici, A.; Maida, M. Underwater Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Diving into the Depths. Cancers 2024, 16, 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203535
Sferrazza S, Calabrese G, Maselli R, Morais R, Facciorusso A, Mavrogenis G, Di Mitri R, Repici A, Maida M. Underwater Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Diving into the Depths. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203535
Chicago/Turabian StyleSferrazza, Sandro, Giulio Calabrese, Roberta Maselli, Rui Morais, Antonio Facciorusso, Georgios Mavrogenis, Roberto Di Mitri, Alessandro Repici, and Marcello Maida. 2024. "Underwater Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Diving into the Depths" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203535
APA StyleSferrazza, S., Calabrese, G., Maselli, R., Morais, R., Facciorusso, A., Mavrogenis, G., Di Mitri, R., Repici, A., & Maida, M. (2024). Underwater Techniques in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Diving into the Depths. Cancers, 16(20), 3535. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203535







