Dysbiosis of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Head-and-Neck Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study Using the Capsule Sponge Device
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Overview
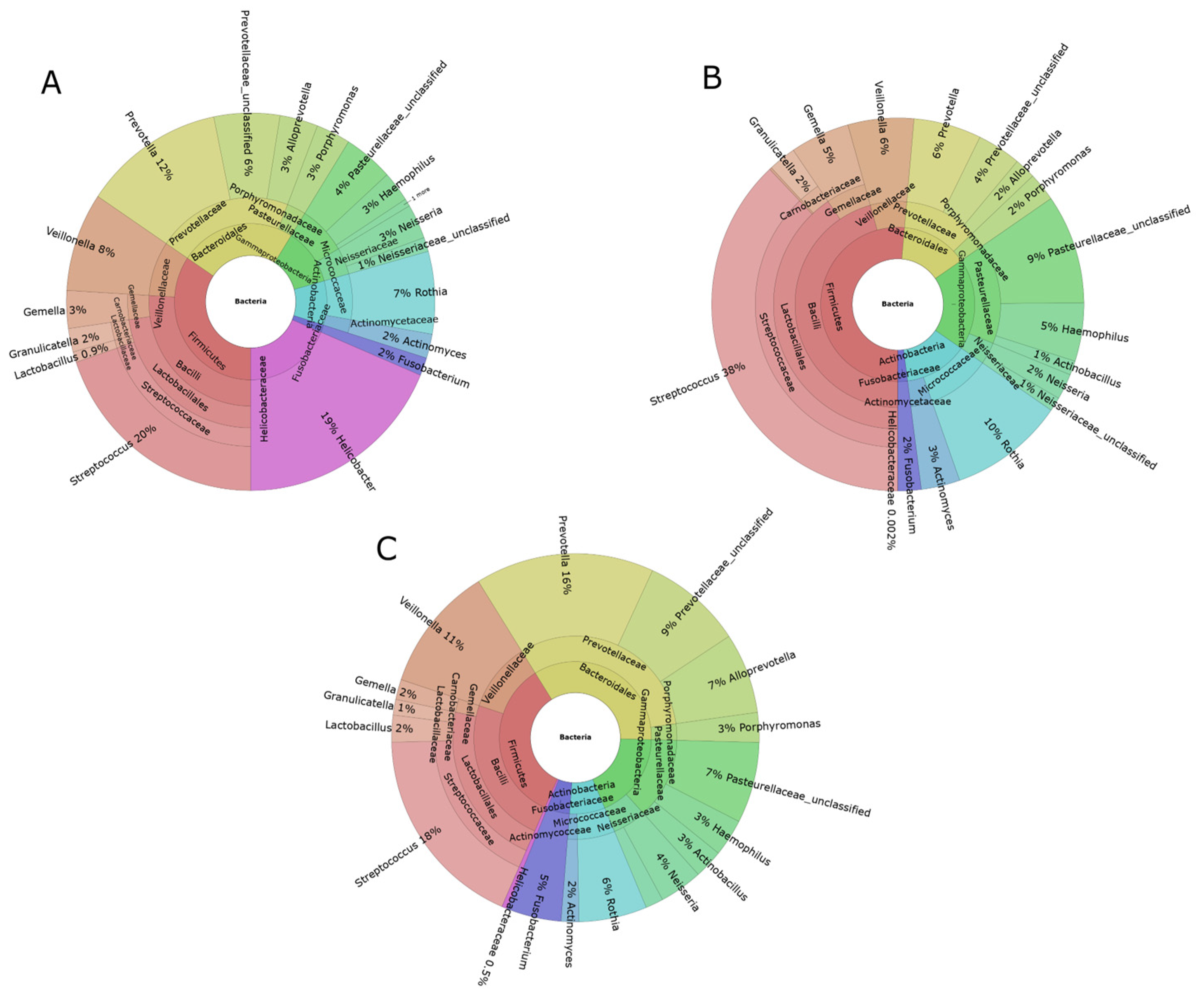
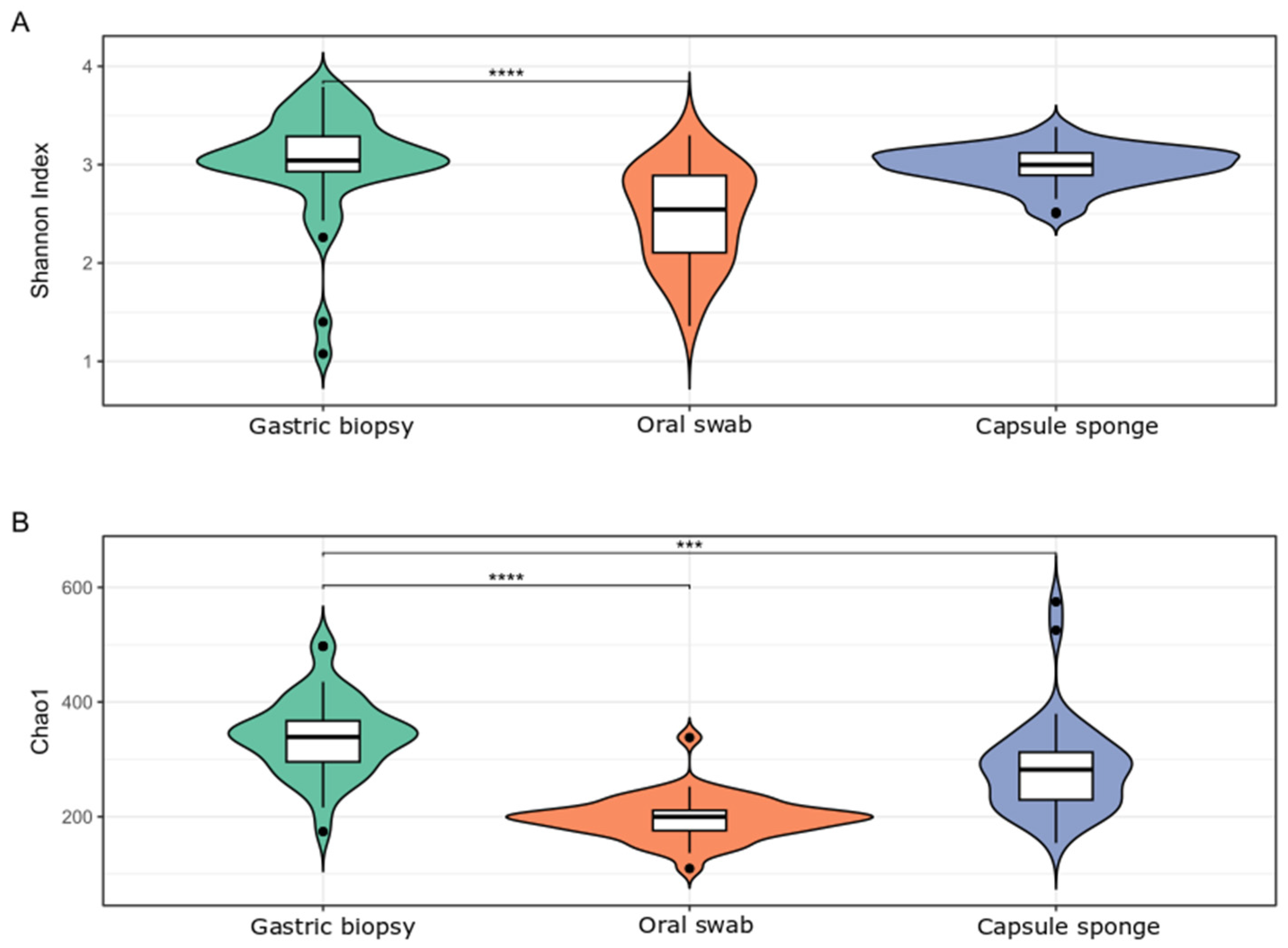
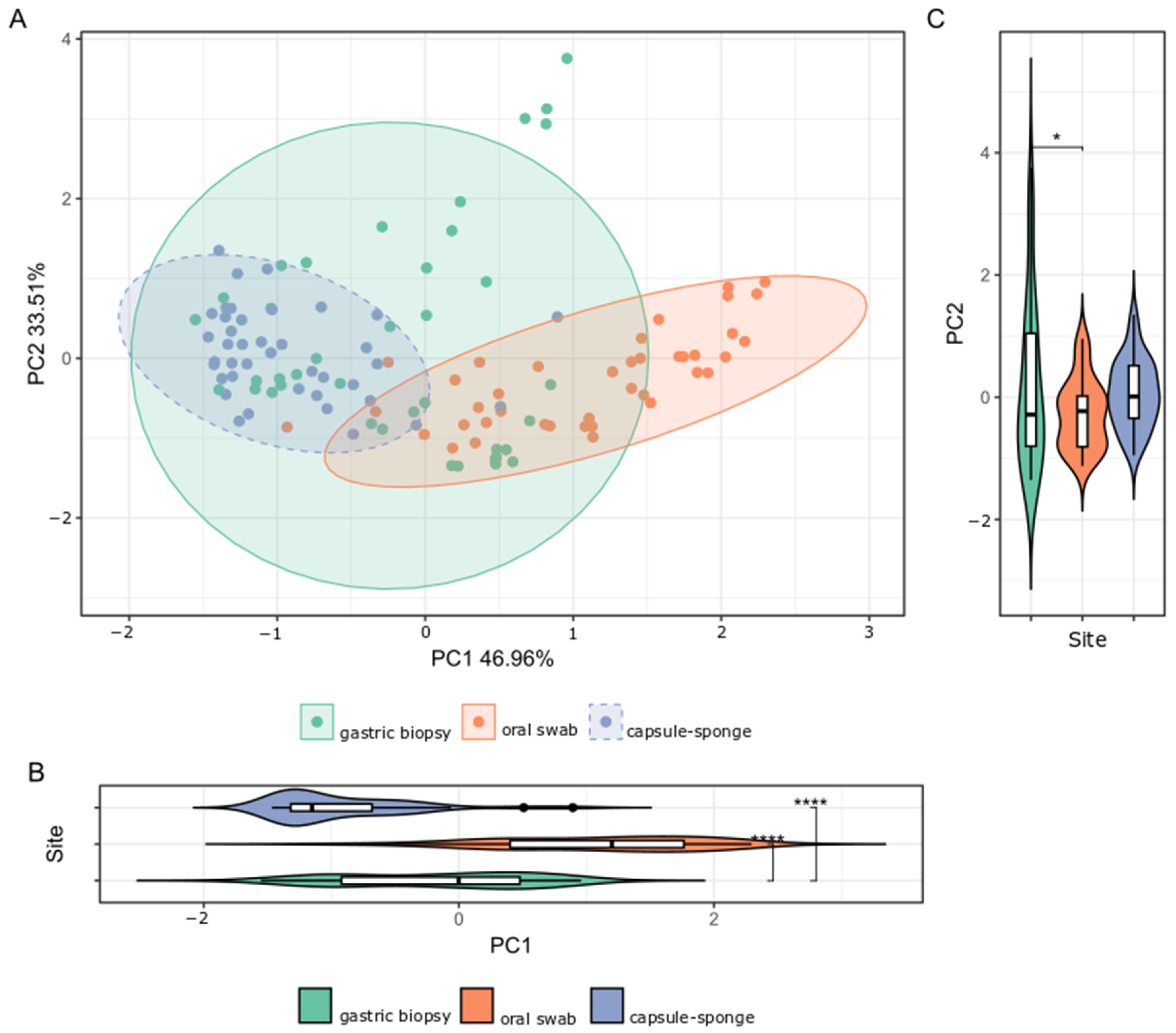
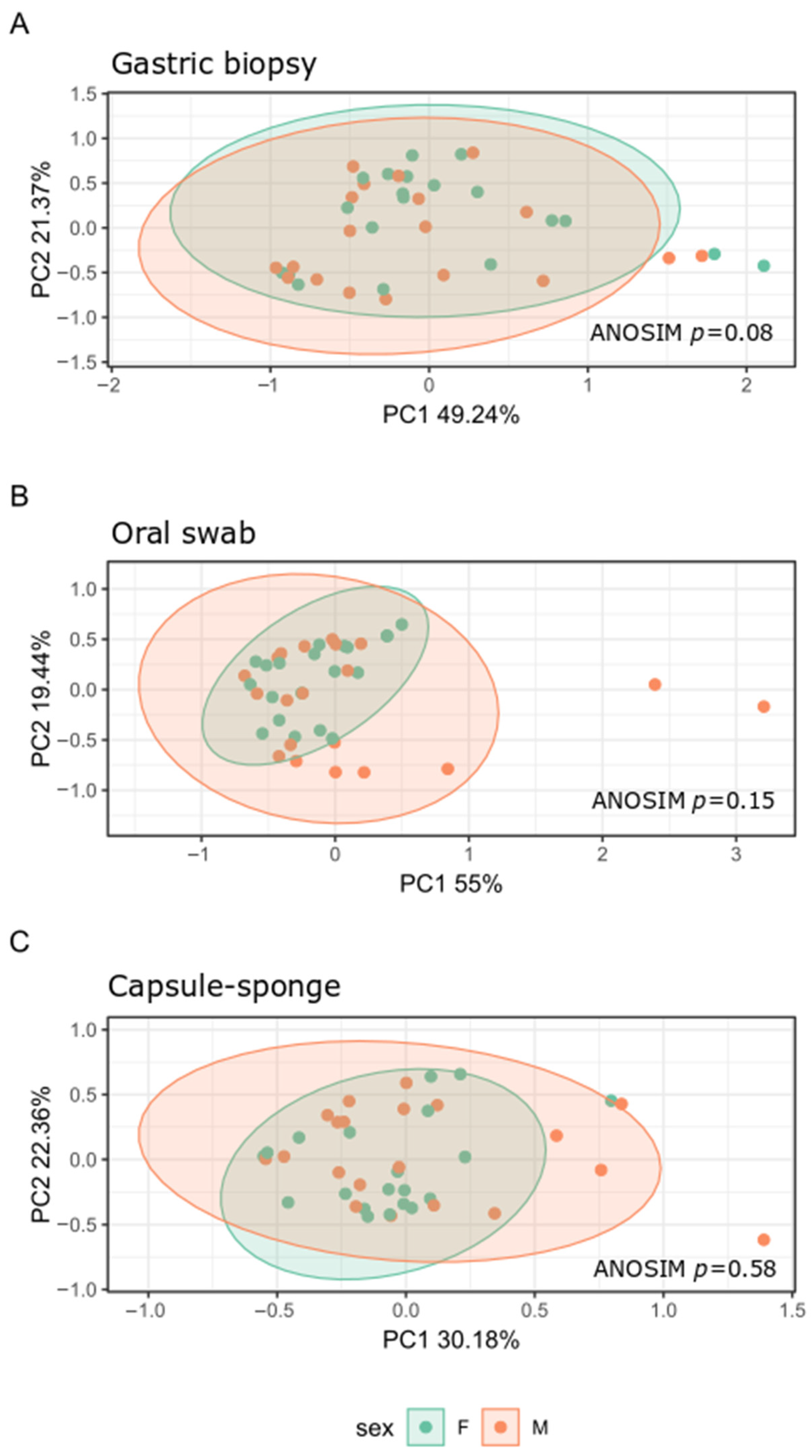
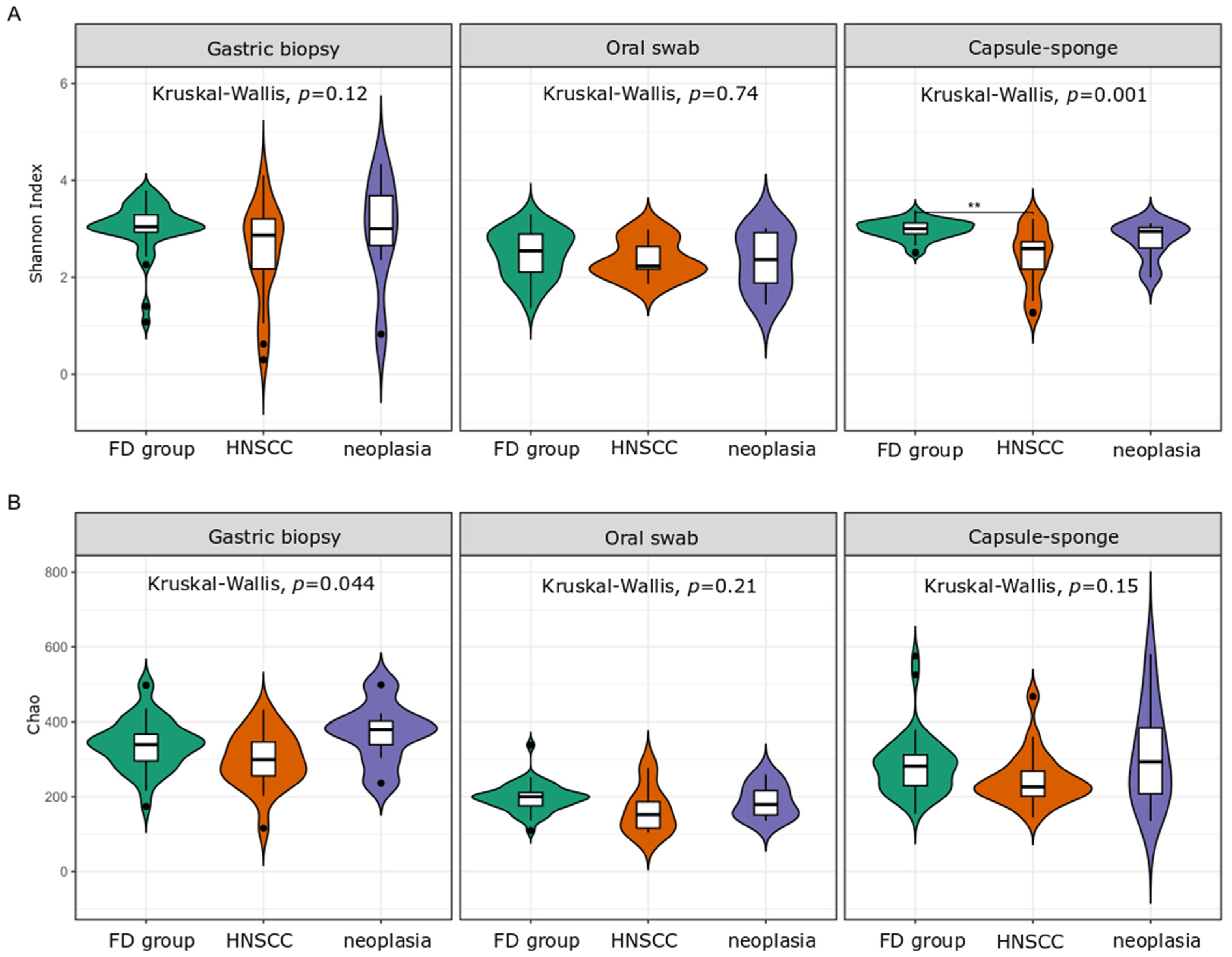
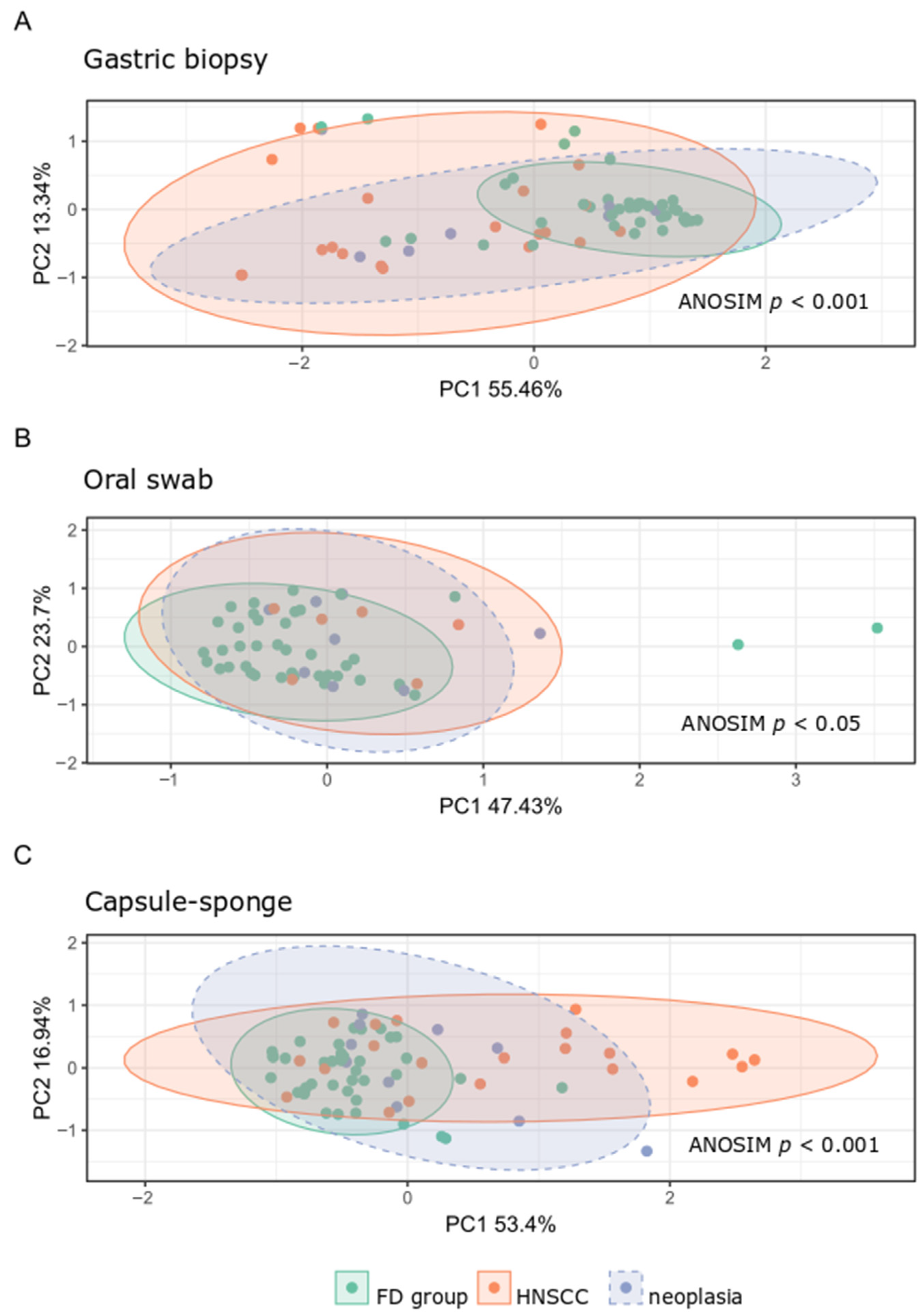
3.2. General Bacterial Populations
3.3. Characterization of Microbiota in the FD Group
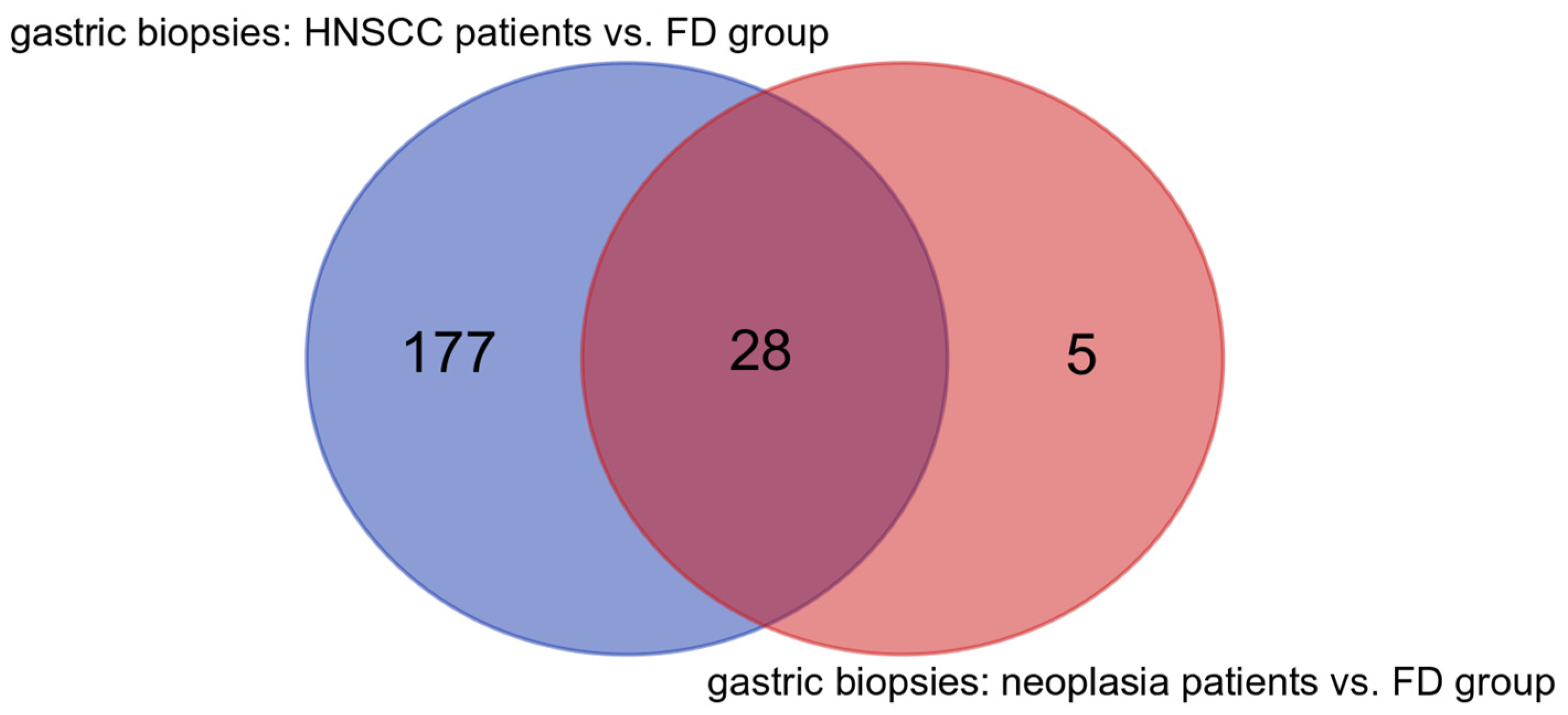
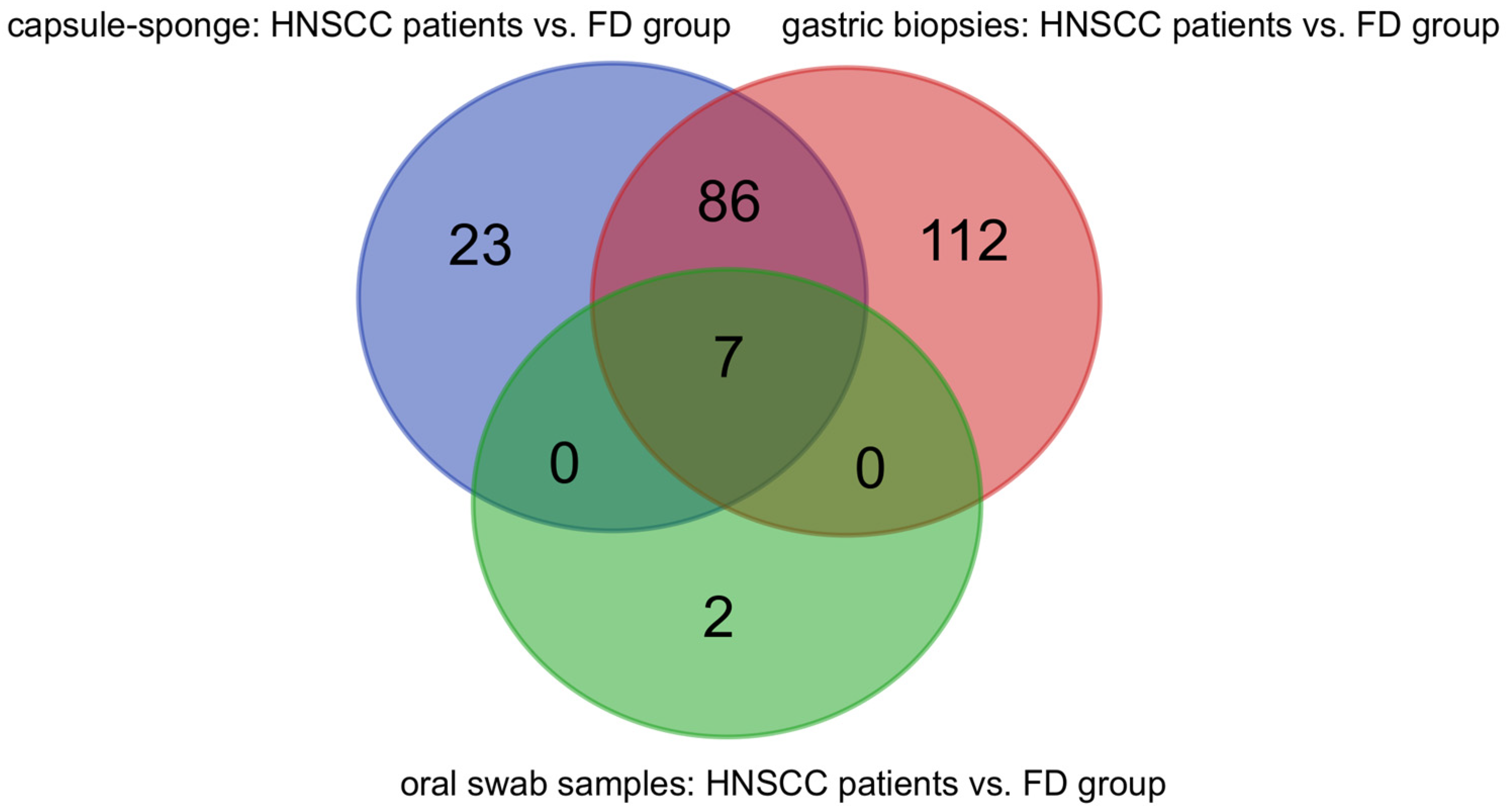
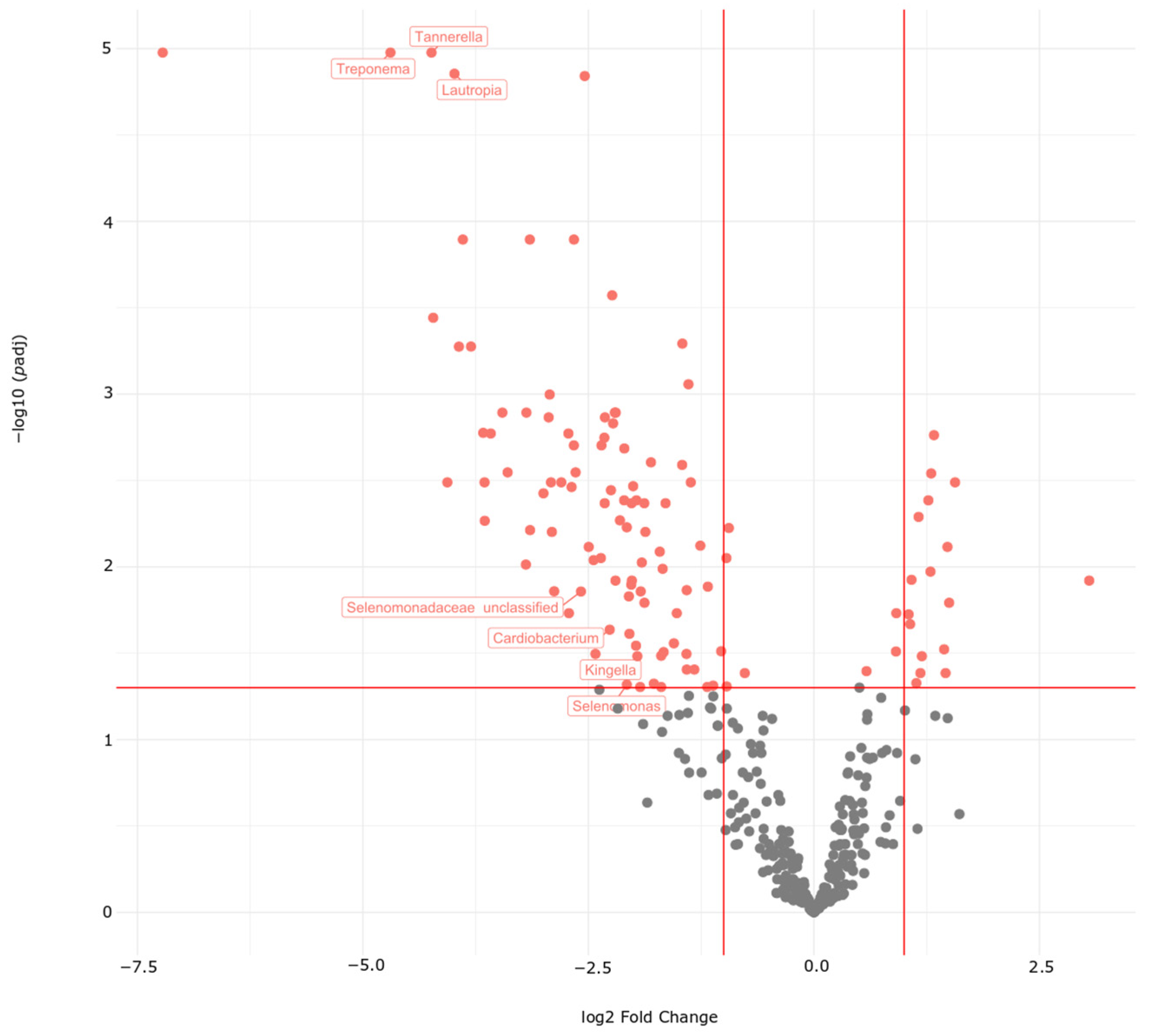
3.4. Microbiota Analysis of the HNSCC Survivors and Esophageal Squamous Intraepithelial Neoplasia Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- She, J.-J.; Liu, W.-X.; Ding, X.-M.; Guo, G.; Han, J.; Shi, F.-Y.; Lau, H.C.-H.; Ding, C.-G.; Xue, W.-J.; Shi, W.; et al. Defining the Biogeographical Map and Potential Bacterial Translocation of Microbiome in Human “Surface Organs”. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, G.; Compare, D.; Rocco, A. A Microbiota-Centric View of Diseases of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G. Advancement of the Relationship between Esophageal Microorganisms and Esophageal Diseases. Gastroenterol. Endosc. 2024, 2, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Gail, M.H.; Shi, J.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Paster, B.J.; Dye, B.A.; Wang, G.-Q.; Wei, W.-Q.; Fan, J.-H.; Qiao, Y.-L.; et al. Association between Upper Digestive Tract Microbiota and Cancer-Predisposing States in the Esophagus and Stomach. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ando, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Maeda, O.; Watanabe, O.; Funasaka, K.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ohmiya, N.; Goto, H. Characterization of Bacterial Biota in the Distal Esophagus of Japanese Patients with Reflux Esophagitis and Barrett’s Esophagus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Abrams, J.A. Emerging Insights into the Esophageal Microbiome. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2018, 16, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Cheng, J.; Duncan, A.E.; Kau, A.L.; Griffin, N.W.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Twins Discordant for Obesity Modulate Metabolism in Mice. Science 2013, 341, 1241214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Haake, S.K.; Mannon, P.; Lemon, K.P.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Huttenhower, C.; Izard, J. Composition of the Adult Digestive Tract Bacterial Microbiome Based on Seven Mouth Surfaces, Tonsils, Throat and Stool Samples. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chen, T.; Izard, J.; Paster, B.J.; Tanner, A.C.R.; Yu, W.-H.; Lakshmanan, A.; Wade, W.G. The Human Oral Microbiome. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5002–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maukonen, J.; Mättö, J.; Suihko, M.-L.; Saarela, M. Intra-Individual Diversity and Similarity of Salivary and Faecal Microbiota. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.F.; Lindberg, M.; Jakobsson, H.; Bäckhed, F.; Nyrén, P.; Engstrand, L. Comparative Analysis of Human Gut Microbiota by Barcoded Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bik, E.M.; Eckburg, P.B.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Purdom, E.A.; Francois, F.; Perez-Perez, G.; Blaser, M.J.; Relman, D.A. Molecular Analysis of the Bacterial Microbiota in the Human Stomach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, A.; Fero, J.; McCoy, C.; Claywell, B.C.; Sanchez, C.A.; Blount, P.L.; Li, X.; Vaughan, T.L.; Matsen, F.A.; Reid, B.J.; et al. Bacterial Composition of the Human Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiome Is Dynamic and Associated with Genomic Instability in a Barrett’s Esophagus Cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Q.; Feng, L.; Cai, X.; Qian, Y.; Xu, L. Esophageal Microflora in Esophageal Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1145791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Nossa, C.W.; Francois, F.; Peek, R.M.; Pei, Z. Inflammation and Intestinal Metaplasia of the Distal Esophagus Are Associated with Alterations in the Microbiome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, K.L.; Siddhi, S.S.; Cleary, S.; Steed, H.; Miller, M.H.; Macfarlane, S.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Dillon, J.F. Oesophageal Bacterial Biofilm Changes in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease, Barrett’s and Oesophageal Carcinoma: Association or Causality? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Benno, Y. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Human Gut Microbiota Using 16S rDNA Clone Libraries and Strictly Anaerobic Culture-Based Methods. Microbiol. Immunol. 2002, 46, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Vogtmann, E.; Liu, A.; Qin, J.; Chen, W.; Abnet, C.C.; Wei, W. Microbial Characterization of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Gastric Cardia Adenocarcinoma from a High-Risk Region of China. Cancer 2019, 125, 3993–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, I.; Konikoff, F.M.; Oppenheim, M.; Gophna, U.; Half, E.E. Gastric Microbiota Is Altered in Oesophagitis and Barrett’s Oesophagus and Further Modified by Proton Pump Inhibitors. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.H.; Yaghoobi, M. The Esophageal and Gastric Microbiome in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minalyan, A.; Gabrielyan, L.; Scott, D.; Jacobs, J.; Pisegna, J.R. The Gastric and Intestinal Microbiome: Role of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, J.; Kulecka, M.; Zawada, I.; Żeber-Lubecka, N.; Paziewska, A.; Graca-Pakulska, K.; Dąbkowski, K.; Skubisz, K.; Cybula, P.; Ambrożkiewicz, F.; et al. The Gastric Microbiota in Patients with Crohn’s Disease; a Preliminary Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Januszewicz, W.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Early Detection and Therapeutics. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, Y.; Etemadi, A.; Abnet, C.C. Microbiome and Cancers of the Esophagus: A Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Lee, S.K. Exploring Esophageal Microbiomes in Esophageal Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 26, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillon, S.A.; Harris, J.K.; Wagner, B.D.; Kelly, C.J.; Stevens, M.J.; Moore, W.; Fang, R.; Schroeder, S.; Masterson, J.C.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Novel Device to Sample the Esophageal Microbiome—The Esophageal String Test. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.R.F.; Walker, A.W.; O’Donovan, M.; Parkhill, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C. A Non-Endoscopic Device to Sample the Oesophageal Microbiota: A Case-Control Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.; Zavala, S.R. Functional Dyspepsia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini, V. Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Beyond Rome IV. Dig. Dis. Basel Switz. 2017, 35 (Suppl. S1), 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.L.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeber-Lubecka, N.; Kulecka, M.; Lindner, B.; Krynicki, R.; Paziewska, A.; Nowakowski, A.; Bidzinski, M.; Ostrowski, J. Increased Diversity of a Cervical Microbiome Associates with Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1005537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard Tools—By Broad Institute. Available online: https://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; He, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. LinDA: Linear Models for Differential Abundance Analysis of Microbiome Compositional Data. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a Package of R Functions for Community Ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, T.; Xia, C.; Zou, X.; Chen, W. Esophageal Cancer Statistics in China, 2011: Estimates Based on 177 Cancer Registries. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitaloni, M.; Caccialanza, R.; Ravasco, P.; Carrato, A.; Kapala, A.; de van der Schueren, M.; Constantinides, D.; Backman, E.; Chuter, D.; Santangelo, C.; et al. The Impact of Nutrition on the Lives of Patients with Digestive Cancers: A Position Paper. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 7991–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. The Relationship between Nutrition and the Immune System. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1082500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaber-Ciopinska, A.; Kiprian, D.; Wieszczy, P.; Bielasik, A.; Bugajski, M.; Januszewicz, W.; Jarzabski, A.; Niemiec, M.; Mroz, A.; Kawecki, A.; et al. Narrow Band Imaging versus Lugol Chromoendoscopy in Screening for Esophageal Squamous Neoplasia: A Randomized Trial. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2023, 133, 16462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susetyowati, S.; Kurniasari, F.N.; Sholikhati, A.S.; Hardianti, M.; Ekaputra, E. Assessment of Nutritional Status in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Before Radiotherapy: A Single-Center, Cross-Sectional Study. Medeni. Med. J. 2024, 39, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnano, M.; Mola, P.; Machetta, G.; Maffeis, P.; Forestiero, I.; Cavagna, R.; Artino, E.; Boffano, P. The Nutritional Assessment of Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 272, 3793–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Gut Microbiota and Human Health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciernikova, S.; Sevcikova, A.; Stevurkova, V.; Mego, M. Diet-Driven Microbiome Changes and Physical Activity in Cancer Patients. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1285516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y. Nutrition Intervention and Microbiome Modulation in the Management of Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, W. How and Why Men and Women Differ in Their Microbiomes: Medical Ecology and Network Analyses of the Microgenderome. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1902054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tong, X.; Jie, Z.; Zhu, J.; Tian, L.; Sun, Q.; Ju, Y.; Zou, L.; Lu, H.; Qiu, X.; et al. Sex Differences in the Oral Microbiome, Host Traits, and Their Causal Relationships. iScience 2023, 26, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivetta, G.; Dottori, L.; Fontana, F.; Cingolani, S.; Ligato, I.; Dilaghi, E.; Milani, C.; Ventura, M.; Borro, M.; Esposito, G.; et al. Gastric Microbiota Gender Differences in Subjects with Healthy Stomachs and Autoimmune Atrophic Gastritis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: Sources, Methods and Major Patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.A.; Wu, J.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Purdue, M.P.; Freedman, N.D.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. Oral Microbiome Composition Reflects Prospective Risk for Esophageal Cancers. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6777–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, J.T.; DeClercq, V.; Van Limbergen, J.; Langille, M.G.I. Assessing the Variation within the Oral Microbiome of Healthy Adults. mSphere 2020, 5, e00451-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Dong, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Yu, A.; Chen, W.; Wei, W. Composition and Consistence of the Bacterial Microbiome in Upper, Middle and Lower Esophagus before and after Lugol’s Iodine Staining in the Esophagus Cancer Screening. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, E.J.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A. Potential Role of the Microbiome in Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Z.; Bini, E.J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Francois, F.; Blaser, M.J. Bacterial Biota in the Human Distal Esophagus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4250–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Yin, J.; Zhao, J.; Ma, S.-R.; Wang, H.-R.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Wei, W.-Q. Microbial Similarity and Preference for Specific Sites in Healthy Oral Cavity and Esophagus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liatsos, C.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Kyriakos, N.; Galanopoulos, M.; Doulberis, M.; Giakoumis, M.; Petridou, E.; Mavrogiannis, C.; Rokkas, T.; Kountouras, J. Helicobacter Pylori, Gastric Microbiota and Gastric Cancer Relationship: Unrolling the Tangle. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, R.; Hou, G.; Ming, W.; Fan, T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Lu, Z.; et al. Characterization of the Esophageal Microbiota and Prediction of the Metabolic Pathways Involved in Esophageal Cancer. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Malekzadeh, R.; Ploner, A.; Shakeri, R.; Sotoudeh, M.; Fahimi, S.; Nasseri-Moghaddam, S.; Kamangar, F.; Abnet, C.C.; Winckler, B.; et al. Variations of Gastric Corpus Microbiota Are Associated with Early Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Dysplasia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; He, F.; Liu, S.; Yan, S.; Huang, L.; Lu, W.; et al. Streptococcus and Prevotella Are Associated with the Prognosis of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, C.-H.; Jia, M.; Xing, X.; Gao, L.; Tsai, H.-T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; et al. Tumor-Associated Microbiota in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Liang, S.; Shan, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; et al. Presence of Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Esophagus and Its Association with the Clinicopathological Characteristics and Survival in Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2016, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Winckler, B.; Lu, M.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Oral Microbiota and Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | FD Patients | HNSCC Survivors | Esophageal Squamous Intraepithelial Neoplasia |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases | 40 | 21 | 11 |
| Age: mean (±SD) years | 59.2 (±13.9) | 66.6 (±10.9) | 66.0 (±10.3) |
| Sex: male; n (%) | 20 (50%) | 20 (95.2%) | 5 (45.5%) |
| BMI: median cm/m2 (IQR) | 26.2 (24.6–28.3) | 26.5 (25.7–27.9) | 23.4 (21.5–26.4) |
| Smoking: active and former; n (%) | 17 (42.5%) | 18 (85.7%) | 7 (63.6%) |
| Tumor location: n (%) | N/A | Primary tumor site Oral cavity: 3 (14.3%) Oropharynx: 8 (38.1%) Larynx: 10 (47.6%) | Esophagus Proximal: 3 (27.3%) Middle: 5 (45.4%) Distal: 3 (27.3%) |
| Histopathology: n (%) | N/A | Squamous cell carcinoma: 21 (100%) | HG-IEN: 3 (27.3%) pT1a ESCC: 2 (18.2%) pT1b ESCC: 5 (45.5%) T2 ESCC: 1 (9.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeber-Lubecka, N.; Kulecka, M.; Dabrowska, M.; Kluska, A.; Piątkowska, M.; Turkot, M.H.; Pilonis, N.D.; Yusuf, A.; Nowicki-Osuch, K.; Mikula, M.; et al. Dysbiosis of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Head-and-Neck Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study Using the Capsule Sponge Device. Cancers 2024, 16, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203528
Zeber-Lubecka N, Kulecka M, Dabrowska M, Kluska A, Piątkowska M, Turkot MH, Pilonis ND, Yusuf A, Nowicki-Osuch K, Mikula M, et al. Dysbiosis of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Head-and-Neck Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study Using the Capsule Sponge Device. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203528
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeber-Lubecka, Natalia, Maria Kulecka, Michalina Dabrowska, Anna Kluska, Magdalena Piątkowska, Maryla Helena Turkot, Nastazja Dagny Pilonis, Aisha Yusuf, Karol Nowicki-Osuch, Michal Mikula, and et al. 2024. "Dysbiosis of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Head-and-Neck Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study Using the Capsule Sponge Device" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203528
APA StyleZeber-Lubecka, N., Kulecka, M., Dabrowska, M., Kluska, A., Piątkowska, M., Turkot, M. H., Pilonis, N. D., Yusuf, A., Nowicki-Osuch, K., Mikula, M., & Ostrowski, J. (2024). Dysbiosis of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract in Head-and-Neck Cancer Survivors: A Pilot Study Using the Capsule Sponge Device. Cancers, 16(20), 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203528






