Recent Advances in the Molecular Biology of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: How to Define Prognosis and Guide Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. How to Define Prognosis
2.1. TP53 Aberrations
2.2. IGVH Mutational Status
2.3. Emerging Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers
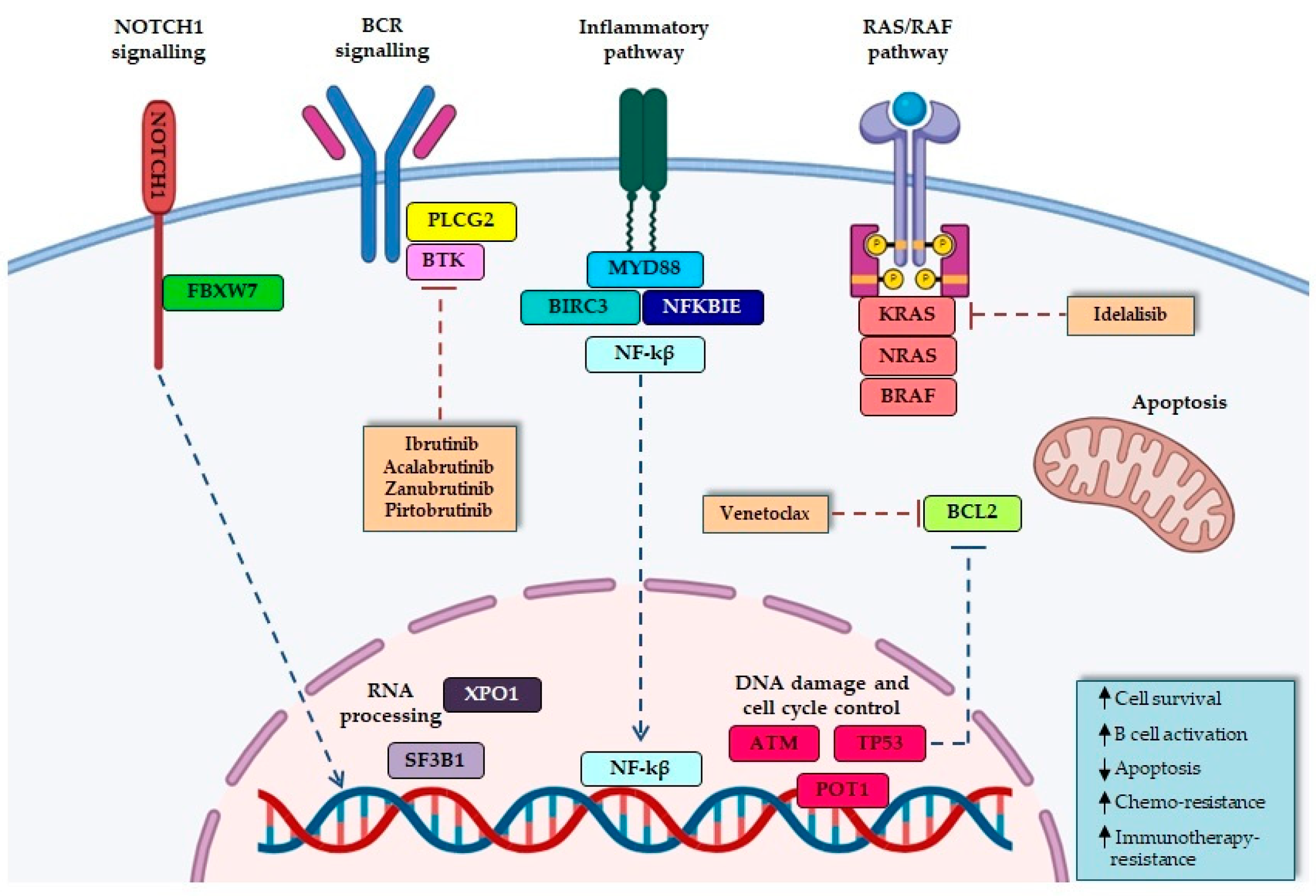
2.3.1. Microenvironment-Dependent Signaling through NOTCH
NOTCH1
FBXW7
2.3.2. RNA Processing
SF3B1
XPO1
2.3.3. DNA Damage and Cell Cycle Control
ATM
POT1
2.3.4. NF-κB Signaling Pathways
BIRC3
NFKBIE
2.3.5. Inflammatory Receptors
MYD88
2.3.6. MAPK–Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase
RAS/RAF Genes
3. How to Guide Treatment Choice in First-Line Therapy
3.1. The Role of TP53 Mutations and/or del(17p) in the Choice of First-Line Therapy
3.2. The Role of IGVH Mutational Status in the Choice of First-Line Therapy
4. How to Guide Treatment Choice in Relapsed/Refractory Disease
4.1. The Role of TP53 Mutations and/or del(17p) in the Choice of Second-Line Therapy
4.2. The Role of Prior Lines of Therapy
4.3. Mechanisms of Resistance to Target Therapy and New Drugs
5. The Emerging Role of MRD: Are We Ready for Clinical Use?
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shadman, M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajüter, H.; Wellmann, I.; Khil, L.; Jöckel, K.H.; Zhang, C.; Fink, A.M.; Hallek, M.; Stang, A. Survival of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia before and after the introduction of chemoimmunotherapy in Germany. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Straten, L.; Levin, M.D.; Visser, O.; Posthuma, E.F.M.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Kater, A.P.; Dinmohamed, A.G. Survival continues to increase in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A population-based analysis among 20 468 patients diagnosed in the Netherlands between 1989 and 2016. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; de Oliveira Araujo, I.B.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. Correction: “The 5th edition of The World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms” Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1720–1748. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swedlow, S.H.; Anderson, S.H.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, F.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253, Erratum in Blood 2023, 141, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, G.E.; Rawstron, A.C.; Ghia, P.; Hillmen, P.; Houlston, R.S.; Kay, N.; Schleinitz, T.A.; Caporaso, N.; Consortium, I.F.C. Diagnostic criteria for monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 130, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Cramer, P.; Fürstenau, M.; Al-Sawaf, O.; von Tresckow, J.; Fink, A.M.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Vehling-Kaiser, U.; et al. The CLL12 trial: Ibrutinib vs placebo in treatment-naïve, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2022, 139, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, D.A.; Tausch, E.; Taylor-Weiner, A.N.; Stewart, C.; Reiter, J.G.; Bahlo, J.; Kluth, S.; Bozic, I.; Lawrence, M.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 2015, 526, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Beà, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Gutiérrez-Abril, J.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Pérez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International CLL-IPI Working Group. An international prognostic index for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL-IPI): A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Giza, A.; Robrecht, S.; Cramer, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Fink, A.M.; Fürstenau, M.; Kutsch, N.; Simon, F.; et al. Reassessing the chronic lymphocytic leukemia International Prognostic Index in the era of targeted therapies. Blood 2024, 143, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braish, J.; Cerchione, C.; Ferrajoli, A. An overview of prognostic markers in patients with CLL. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1371057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcikova, J.; Pavlova, S.; Baliakas, P.; Chatzikonstantinou, T.; Tausch, E.; Catherwood, M.; Rossi, D.; Soussi, T.; Tichy, B.; Kater, A.P.; et al. ERIC recommendations for TP53 mutation analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia-2024 update. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Cymbalista, F.; Ghia, P.; Jäger, U.; Pospisilova, S.; Rosenquist, R.; Schuh, A.; Stilgenbauer, S. aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An overview of the clinical implications of improved diagnostics. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, P.; Onyszczuk, J.; Szymczyk, A.; Podhorecka, M. Therapeutic Options for Patients with TP53 Deficient Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Narrative Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1459–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcikova, J.; Pavlova, S.; Kunt Vonkova, B.; Radova, L.; Plevova, K.; Kotaskova, J.; Pal, K.; Dvorackova, B.; Zenatova, M.; Hynst, J.; et al. Low-burden TP53 mutations in CLL: Clinical impact and clonal evolution within the context of different treatment options. Blood 2021, 138, 2670–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomben, R.; Rossi, F.M.; Vit, F.; Bittolo, T.; D’Agaro, T.; Zucchetto, A.; Tissino, E.; Pozzo, F.; Vendramini, E.; Degan, M.; et al. Mutations with Low Variant Allele Frequency Predict Short Survival in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Khiabanian, H.; Spina, V.; Ciardullo, C.; Bruscaggin, A.; Famà, R.; Rasi, S.; Monti, S.; Deambrogi, C.; De Paoli, L.; et al. Clinical impact of small TP53 mutated subclones in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussi, T.; Baliakas, P. Landscape of TP53 Alterations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 808886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, S.J.; Clifford, R.; Parker, H.; Antoniou, P.; Stec-Dziedzic, E.; Larrayoz, M.; Davis, Z.; Kadalyayil, L.; Colins, A.; Robbe, P.; et al. Clinical significance of TP53, BIRC3, ATM and MAPK-ERK genes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Data from the randomised UK LRF CLL4 trial. Leukemia 2020, 34, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcikova, J.; Stano-Kozubik, K.; Tichy, B.; Kantorova, B.; Pavlova, S.; Tom, N.; Radova, L.; Smardova, J.; Pardy, F.; Doubek, M.; et al. Detailed analysis of therapy-driven clonal evolution of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Carretero, C.; González-Gascón-Y-Marín, I.; Rodríguez-Vicente, A.E.; Quijada-Álamo, M.; Hernández-Rivas, J.; Hernández-Sánchez, M.; Hernández-Rivas, J.M. The Evolving Landscape of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia on Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agathangelidis, A.; Chatzidimitriou, A.; Chatzikonstantinou, T.; Tresoldi, C.; Davis, Z.; Giudicelli, V.; Kossida, S.; Belessi, C.; Rosenquist, R.; Ghia, P.; et al. Immunoglobulin gene sequence analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The 2022 update of the recommendations by ERIC, the European Research Initiative on CLL. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Nadeu, F.; Colomer, D.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From molecular pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammal, S.; Semaan, W.; Aprahamian, N.; Moussallem, R.; Chebly, A. Spotlight on borderline-IGHV mutational status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1430225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angotzi, F.; Cellini, A.; Ruocco, V.; Cavarretta, C.A.; Zatta, I.; Serafin, A.; Pravato, S.; Pagnin, E.; Bonaldi, L.; Frezzato, F.; et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) with Borderline Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Mutational Status, a Rare Subgroup of CLL with Variable Disease Course. Cancers 2024, 16, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.; Agathangelidis, A.; Schneider, C.; Bahlo, J.; Robrecht, S.; Tausch, E.; Bloehdorn, J.; Hoechstetter, M.; Fischer, K.; Eichhorst, B.; et al. Prognostic impact of prevalent chronic lymphocytic leukemia stereotyped subsets: Analysis within prospective clinical trials of the German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG). Haematologica 2020, 105, 2598–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatopoulos, B.; Timbs, A.; Bruce, D.; Smith, T.; Clifford, R.; Robbe, P.; Burns, A.; Vavoulis, D.V.; Lopez, L.; Antoniou, P.; et al. Targeted deep sequencing reveals clinically relevant subclonal IgHV rearrangements in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wang, Y.L. Prognostic and Predictive Molecular Biomarkers in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelloul, F.Z.; Yang, R.K.; Wang, P.; Garces, S.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Ok, C.Y.; Loghavi, S.; Routbort, M.J.; Zuo, Z.; Yin, C.C.; et al. Non-coding NOTCH1 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia negatively impact prognosis. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E100–E102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Fabbri, G.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Forconi, F.; Marasca, R.; Laurenti, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, L.; Cerretani, E.; Vento, F.; Montanaro, A.; Moron Dalla Tor, L.; Simoncini, E.; Giaimo, M.; Gherli, A.; Zamponi, R.; Tartaglione, I.; et al. CAD204520 Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Schnaiter, A.; Paschka, P.; Zenz, T.; Rossi, M.; Döhner, K.; Bühler, A.; Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Kneba, M.; et al. Gene mutations and treatment outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from the CLL8 trial. Blood 2014, 123, 3247–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, F.; Delgado, J.; Royo, C.; Baumann, T.; Stankovic, T.; Pinyol, M.; Jares, P.; Navarro, A.; Martín-García, D.; Beà, S.; et al. Clinical impact of clonal and subclonal TP53, SF3B1, BIRC3, NOTCH1, and ATM mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, V.; Close, W.; Kugler, S.J.; Reichenzeller, M.; Yosifov, D.Y.; Bloehdorn, J.; Pan, L.; Tausch, E.; Westhoff, M.A.; Döhner, H.; et al. FBXW7 mutations reduce binding of NOTCH1, leading to cleaved NOTCH1 accumulation and target gene activation in CLL. Blood 2019, 133, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D. FBXW7 is a biologically validated cancer driver gene for CLL. Blood 2019, 133, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, L.; Thorvaldsdottir, B.; Sutton, L.A.; Karakatsoulis, G.; Meggendorfer, M.; Parker, H.; Nadeu, F.; Brieghel, C.; Laidou, S.; Moia, R.; et al. Different prognostic impact of recurrent gene mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia depending on IGHV gene somatic hypermutation status: A study by ERIC in HARMONY. Leukemia 2023, 37, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Gambe, R.G.; Sun, J.; Martinez, A.Z.; Cartun, Z.J.; Regis, F.F.D.; Wan, Y.; Fan, J.; Brooks, A.N.; Herman, S.E.M.; et al. A Murine Model of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Based on B Cell-Restricted Expression of Sf3b1 Mutation and Atm Deletion. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 283–296.e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Dalla-Favera, R. The molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, J.S.; Hing, Z.A.; Harrington, B.; Baumhardt, J.; Ozer, H.G.; Lehman, A.; Giacopelli, B.; Beaver, L.; Williams, K.; Skinner, J.N.; et al. Recurrent XPO1 mutations alter pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austen, B.; Powell, J.E.; Alvi, A.; Edwards, I.; Hooper, L.; Starczynski, J.; Taylor, A.M.; Fegan, C.; Moss, P.; Stankovic, T. Mutations in the ATM gene lead to impaired overall and treatment-free survival that is independent of IGVH mutation status in patients with B-CLL. Blood 2005, 106, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crassini, K.; Stevenson, W.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Best, O.G. Molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampson, B.L.; Gupta, A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Mashima, K.; Petráčková, A.; Wang, Z.; Wojciechowska, N.; Shaughnessy, C.J.; Baker, P.O.; Fernandes, S.M.; et al. Rare Germline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, A.J.; Quesada, V.; Foronda, M.; Conde, L.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Villamor, N.; Rodríguez, D.; Kwarciak, A.; Garabaya, C.; Gallardo, M.; et al. POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasi, S.; Khiabanian, H.; Ciardullo, C.; Terzi-di-Bergamo, L.; Monti, S.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; Deambrogi, C.; Martuscelli, L.; et al. Clinical impact of small subclones harboring NOTCH1, SF3B1 or BIRC3 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2016, 101, e135–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonato, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Bomben, R.; Canarutto, G.; Felician, G.; Martines, C.; Zucchetto, A.; Pozzo, F.; Vujovikj, M.; Polesel, J.; et al. NFKBIE mutations are selected by the tumor microenvironment and contribute to immune escape in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Valle, V.; Roos-Weil, D.; Scourzic, L.; Mouly, E.; Aid, Z.; Darwiche, W.; Lecluse, Y.; Damm, F.; Mémet, S.; Mercher, T.; et al. Nfkbie-deficiency leads to increased susceptibility to develop B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in aged mice. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, W.; Lin, P.; Strati, P.; Patel, K.P.; Routbort, M.J.; Hu, S.; Wei, P.; Khoury, J.D.; You, M.J.; Loghavi, S.; et al. Clinicopathological characterization of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with MYD88 mutations: L265P and non-L265P mutations are associated with different features. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Trillos, A.; Navarro, A.; Aymerich, M.; Delgado, J.; López-Guillermo, A.; Campo, E.; Villamor, N. Clinical impact of MYD88 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 1611–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez, N.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Montraveta, A.; Lopez-Guerra, M.; Rosich, L.; Nadeu, F.; Valero, J.G.; Aymerich, M.; Magnano, L.; Rozman, M.; et al. Mutations in the RAS-BRAF-MAPK-ERK pathway define a specific subgroup of patients with adverse clinical features and provide new therapeutic options in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2019, 104, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeksma, A.C.; Taylor, J.; Wu, B.; Gardner, J.R.; He, J.; Nahas, M.; Gonen, M.; Alemayehu, W.G.; Te Raa, D.; Walther, T.; et al. Clonal diversity predicts adverse outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Ghia, P.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Devereux, S.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of first-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with CLL/SLL: 5 years of follow-up from the phase 3 RESONATE-2 study. Leukemia 2020, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Booth, A.M.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; Barr, P.M.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Regimens versus Chemoimmunotherapy in Older Patients with Untreated CLL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Perez Burbano, G.; Ruppert, A.S.; Miller, C.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Wall, A.; Ding, W.; Bartlett, N.L.; Brander, D.M.; et al. Follow-up from the A041202 study shows continued efficacy of ibrutinib regimens for older adults with CLL. Blood 2024, 143, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Novak, J.; Strugov, V.; Gill, D.; et al. First-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Kay, N.E.; Hanson, C.A.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Ibrutinib-Rituximab or Chemoimmunotherapy for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Brown, J.R.; Kahl, B.S.; Ghia, P.; Giannopoulos, K.; Jurczak, W.; Šimkovič, M.; Shadman, M.; Österborg, A.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib versus bendamustine and rituximab in untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SEQUOIA): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Al-Sawaf, O.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Tandon, M.; Dixon, M.; Robrecht, S.; Warburton, S.; Humphrey, K.; Samoylova, O.; et al. Venetoclax and Obinutuzumab in Patients with CLL and Coexisting Conditions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Jin, H.Y.; Robrecht, S.; Choi, Y.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kotak, A.; Chang, Y.M.; Fink, A.M.; Tausch, E.; et al. Transcriptomic profiles and 5-year results from the randomized CLL14 study of venetoclax plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorst, B.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Fürstenau, M.; von Tresckow, J.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Gregor, M.; Juliusson, G.; Thornton, P.; et al. First-Line Venetoclax Combinations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, M.; Kater, A.P.; Robrecht, S.; von Tresckow, J.; Zhang, C.; Gregor, M.; Thornton, P.; Staber, P.B.; Tadmor, T.; Lindström, V.; et al. First-line venetoclax combinations versus chemoimmunotherapy in fit patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (GAIA/CLL13): 4-year follow-up from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 744–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Owen, C.; Moreno, C.; Follows, G.; Munir, T.; Levin, M.D.; Benjamini, O.; Janssens, A.; Osterborg, A.; Robak, T.; et al. Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib-Venetoclax in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Comorbidities. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Kipps, T.J.; Jacobs, R.; Opat, S.; Barr, P.M.; Tedeschi, A.; Trentin, L.; Bannerji, R.; et al. Fixed-duration ibrutinib plus venetoclax for first-line treatment of CLL: Primary analysis of the CAPTIVATE FD cohort. Blood 2022, 139, 3278–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, C.U.; Munir, T.; Moreno, C.; Owen, C.; Follows, G.A.; Benjamini, O.; Janssens, A.; Levin, M.D.; Robak, T.; Simkovic, M.; et al. Fixed-duration ibrutinib-venetoclax versus chlorambucil-obinutuzumab in previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (GLOW): 4-year follow-up from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Allan, J.; Siddiqi, T.; Wierda, W.G.; Tam, C.; Moreno, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Szafer-Glusman, E.; Zhou, C.; Abbazio, C.; et al. P617: Fixed-duration (fd) ibrutinib + venetoclax for first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (cll)/small lymphocytic lymphoma (sll): 4-y follow-up from fd cohort of phase 2 captivate study. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e2822842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Hallek, M.; Jerkeman, M.; Buske, C.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline interim update on new targeted therapies in the first line and at relapse of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Busch, R.; Denzel, T.; Häbe, S.; Winkler, D.; Bühler, A.; Edelmann, J.; Bergmann, M.; Hopfinger, G.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4473–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Tian, X.; Wiestner, A. Ibrutinib for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivina, M.; Kim, E.; Wierda, W.G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Jain, N.; Thompson, P.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.; Burger, J.A. Ibrutinib induces durable remissions in treatment-naïve patients with CLL and 17p deletion and/or TP53 mutations. Blood 2021, 138, 2589–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, J.N.; Shanafelt, T.; Wiestner, A.; Moreno, C.; O’Brien, S.M.; Li, J.; Krigsfeld, G.; Dean, J.P.; Ahn, I.E. Long-term efficacy of first-line ibrutinib treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukaemia in patients with TP53 aberrations: A pooled analysis from four clinical trials. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Robak, T.; Ghia, P.; Kahl, B.S.; Walker, P.; Janowski, W.; Simpson, D.; Shadman, M.; Ganly, P.S.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib monotherapy for patients with treatment naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia and 17p deletion. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2354–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.N.; Flinn, I.W.; Siddiqi, T.; Ghia, P.; Tam, C.S.; Kipps, T.J.; Barr, P.M.; Elinder Camburn, A.; Tedeschi, A.; Badoux, X.C.; et al. Outcomes in Patients with High-Risk Features after Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax: Phase II CAPTIVATE Study in First-Line Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2593–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Wierda, W.G.; Barr, P.M.; Kipps, T.J.; Siddiqi, T.; Allan, J.N.; Hunter, Z.; Zhou, C.; Szoke, A.; Dean, J.P.; et al. Relapse after First-Line Fixed Duration Ibrutinib + Venetoclax: High Response Rates to Ibrutinib Retreatment and Absence of BTK Mutations in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL) with up to 5 Years of Follow-up in the Phase 2 Captivate Study. Blood 2023, 142, 633. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, P.A.; Bazinet, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Tam, C.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Saha, S.; Peterson, C.B.; Plunkett, W.; Keating, M.J. Sustained remissions in CLL after frontline FCR treatment with very-long-term follow-up. Blood 2023, 142, 1784–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Hanson, C.A.; Paietta, E.M.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Long-term outcomes for ibrutinib-rituximab and chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: Updated results of the E1912 trial. Blood 2022, 140, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Pitchford, A.; Bloor, A.; Broom, A.; Young, M.; Kennedy, B.; Walewska, R.; Furtado, M.; Preston, G.; Neilson, J.R.; et al. Ibrutinib and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (FLAIR): Interim analysis of a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, T.; Cairns, D.A.; Bloor, A.; Allsup, D.; Cwynarski, K.; Pettitt, A.; Paneesha, S.; Fox, C.P.; Eyre, T.A.; Forconi, F.; et al. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Therapy Guided by Measurable Residual Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierda, W.G.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Kipps, T.J.; Opat, S.; Tedeschi, A.; Badoux, X.C.; Kuss, B.J.; Jackson, S.; Moreno, C.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Venetoclax for First-Line Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Primary Analysis Results From the Minimal Residual Disease Cohort of the Randomized Phase II CAPTIVATE Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3853–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odetola, O.; Ma, S. Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2023, 18, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Biology and Treatment of Richter Transformation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.F.; D’Rozario, J.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; de la Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Enduring undetectable MRD and updated outcomes in relapsed/refractory CLL after fixed-duration venetoclax-rituximab. Blood 2022, 140, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.; Harrup, R.; Kipps, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; De La Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. S201 final 7-year follow up and retreatment substudy analysis of murano: Venetoclaxrituximab (venr)-treated patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (R/R CLL). HemaSphere 2023, 7, e492813f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Ghia, P.; Kater, A.P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Furman, R.R.; O’Brien, S.; Yenerel, M.N.; Illés, A.; Kay, N.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results of the First Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A.; Thompson, P.A.; Allan, J.N.; Coleman, M.; Sharman, J.P.; Cheson, B.D.; Jones, D.; Izumi, R.; Frigault, M.M.; Quah, C.; et al. Phase II study of acalabrutinib in ibrutinib-intolerant patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; Jurczak, W.; Kaźmierczak, M.; Lamanna, N.; O’Brien, S.M.; Tam, C.S.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, K.; et al. Zanubrutinib or Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Coutre, S.E.; Mato, A.R.; Hillmen, P.; Tam, C.; Österborg, A.; Siddiqi, T.; Thirman, M.J.; Furman, R.R.; et al. Ibrutinib for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with 17p deletion (RESONATE-17): A phase 2, open-label, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Pluta, A.; Wach, M.; Lysak, D.; Šimkovič, M.; Kriachok, I.; Illés, Á.; de la Serna, J.; Dolan, S.; Campbell, P.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Investigator’s Choice in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Final ASCEND Trial Results. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Tausch, E.; Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Eichhorst, B.; Hallek, M.; Hillmen, P.; Schneider, C.; Schetelig, J.; Böttcher, S.; et al. Six-year follow-up and subgroup analyses of a phase 2 trial of venetoclax for del(17p) chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, N.V.; Gill, S.; Hexner, E.O.; Schuster, S.; Nasta, S.; Loren, A.; Svoboda, J.; Stadtmauer, E.; Landsburg, D.J.; Mato, A.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes From a Randomized Dose Optimization Study of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T Cells in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Lacey, S.F.; Orlando, E.J.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Gohil, M.; Lundh, S.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Wang, Y.; O’Connor, R.S.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Determinants of response and resistance to CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Owen, C.; Robak, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Burger, J.A.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Dearden, C.; Grosicki, S.; et al. Up to 8-year follow-up from RESONATE-2: First-line ibrutinib treatment for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhoda, S.; Vistarop, A.; Wang, Y.L. Resistance to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Ruppert, A.S.; Guinn, D.; Lehman, A.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, A.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Coleman, J.; Jones, D.; et al. BTKC481S-Mediated Resistance to Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinquenel, A.; Fornecker, L.M.; Letestu, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Fleury, C.; Lazarian, G.; Dilhuydy, M.S.; Nollet, D.; Guieze, R.; Feugier, P.; et al. Prevalence of. Blood 2019, 134, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama, T.G.; Kyung, D.; O’Brien, S. Mechanisms of ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and alternative treatment strategies. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlarikova, L.; Petrackova, A.; Papajik, T.; Turcsanyi, P.; Kriegova, E. Resistance-Associated Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients Treated With Novel Agents. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Galanina, N.; Guo, A.; Lee, J.; Kadri, S.; Van Slambrouck, C.; Long, B.; Wang, W.; Ming, M.; Furtado, L.V.; et al. Identification of a structurally novel BTK mutation that drives ibrutinib resistance in CLL. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68833–68841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, S.; Sutton, L.A.; Ljungström, V.; Capasso, A.; Pandzic, T.; Weström, S.; Foroughi-Asl, H.; Skaftason, A.; Gellerbring, A.; Lyander, A.; et al. BTK and PLCG2 remain unmutated in one-third of patients with CLL relapsing on ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2794–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalsa, J.K.; Cha, J.; Utro, F.; Naeem, A.; Murali, I.; Kuang, Y.; Vasquez, K.; Li, L.; Tyekucheva, S.; Fernandes, S.M.; et al. Genetic events associated with venetoclax resistance in CLL identified by whole-exome sequencing of patient samples. Blood 2023, 142, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Croner, L.J.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Badoux, X.C.; Eckert, K.; Cheung, L.W.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Dean, J.P.; et al. Absence of BTK, BCL2, and PLCG2 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Relapsing after First-Line Treatment with Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.; Stephens, D.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Bhat, S.; Savage, R.E.; Chai, F.; Eathiraj, S.; Granlund, L.; Szuszkiewicz, L.A.; Schwartz, B.; et al. Final Results of Phase 1, Dose Escalation Study Evaluating ARQ 531 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoid Malignancies. Blood 2019, 134, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Mi, X.; Thompson, M.C.; Montoya, S.; Notti, R.Q.; Afaghani, J.; Durham, B.H.; Penson, A.; Witkowski, M.T.; Lu, S.X.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Noncovalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, A.; Valeryevich, D.A.; Patel, M.R.; Tees, M.T.; Flinn, I.W.; Ai, W.Z.; Patel, K.; Wang, M.; O’Brien, S.M.; Nandakumar, S.; et al. A first-in-human phase 1 trial of NX-2127, a first-in-class oral BTK degrader with IMiD-like activity, in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Rawstron, A.C.; Brock, K.; Muñoz-Vicente, S.; Yates, F.J.; Bishop, R.; Boucher, R.; MacDonald, D.; Fegan, C.; McCaig, A.; et al. Ibrutinib Plus Venetoclax in Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: The CLARITY Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2722–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Awan, F.T.; Heerema, N.A.; Hoffman, C.; Lozanski, G.; Maddocks, K.J.; Moran, M.E.; Reid, M.A.; et al. Phase 1b study of obinutuzumab, ibrutinib, and venetoclax in relapsed and refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 1568–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Rawstron, A.; Cymbalista, F.; Badoux, X.; Rossi, D.; Brown, J.R.; Egle, A.; Abello, V.; Cervera Ceballos, E.; Herishanu, Y.; et al. Measurable residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Expert review and consensus recommendations. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3059–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Böttcher, S.; Letestu, R.; Villamor, N.; Fazi, C.; Kartsios, H.; de Tute, R.M.; Shingles, J.; Ritgen, M.; Moreno, C.; et al. Improving efficiency and sensitivity: European Research Initiative in CLL (ERIC) update on the international harmonised approach for flow cytometric residual disease monitoring in CLL. Leukemia 2013, 27, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Fischer, K.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Busch, R.M.; Fingerle-Rowson, G.; Fink, A.M.; Bühler, A.; Zenz, T.; Wenger, M.K.; et al. Minimal residual disease quantification is an independent predictor of progression-free and overall survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A multivariate analysis from the randomized GCLLSG CLL8 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D. Benefit with MRD-guided treatment in CLL. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Lopez, C.A.; Barrientos, J.C. MRD-directed therapy in CLL: Ready for prime time? Hematology Am Soc Hematol. Educ Program. 2023, 2023, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeu, F.; Clot, G.; Delgado, J.; Martín-García, D.; Baumann, T.; Salaverria, I.; Beà, S.; Pinyol, M.; Jares, P.; Navarro, A.; et al. Clinical impact of the subclonal architecture and mutational complexity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Goradia, H.; Martinez-Calle, N.; Patten, P.; Munir, T. The evolving use of measurable residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia clinical trials. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1130617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benintende, G.; Pozzo, F.; Innocenti, I.; Autore, F.; Fresa, A.; D’Arena, G.; Gattei, V.; Lurenti, L. Measurable residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Detection Method * | Clinical Significance in Prognosis |
|---|---|---|
| Unmutated IGHV | Sanger, NGS | Shorter TTFT and poorer response to CIT Mandatory in pre-treatment evaluation (stable status during disease course) |
| Del(17p)/TP53 mutation | FISH + Sanger, NGS | Resistance to CIT and rapid disease progression Mandatory in pre-treatment evaluation |
| Complex Karyotype | Conventional Karyotyping | Unfavorable outcome after CIT, independently of TP53 alterations; Controversial role after novel targeted agents |
| NOTCH1 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Worse outcome and poor response to rituximab treatment |
| FBXW7 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Poorer PFS and OS in patients with early-stage disease |
| SF3B1 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Poor prognosis |
| XPO1 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Inferior PFS and OS. Independent prognostic variables |
| Del(11q)/ATM mutation | FISH + Sanger, NGS | Shorter TTFT but better response to BTK inhibitors in the presence of del(11q) Germline mutations could be detected |
| POT1 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Poor OS Germline mutations could be detected |
| BIRC3 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Unfavorable prognosis, but not confirmed across literature; probable predictive role |
| NFKBIE mutation | Sanger, NGS | Reduced response to ibrutinib treatment |
| MYD88 mutation | Sanger, NGS | Good prognosis |
| RAS/RAF mutation | Sanger, NGS | BRAF: adverse OS NRAS/KRAS: no adverse OS |
| Trial | Arms | Phase | Total Participants | MRD As a Primary Outcome | MRD as a Secondary Outcome | MRD Stopping Rules | MRD Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MURANO | BR vs. VR | 3 | 389 | No | YES | No | FC, ASO |
| CLARITY | IV single arm | 2 | 54 | YES | No | YES | FC |
| CLL14 | ClbO vs. VO | 3 | 432 | No | YES | No | FC, ASO, NGS |
| CAPTIVATE MRD | IV then I or placebo if U-MRD4 | 2 | 54 | No | YES for the IV vs. placebo | No | FC |
| CAPTIVATE FD | IV | 2 | 159 | No | YES | No | FC |
| GLOW | IV vs. ClbO | 3 | 211 | No | YES | No | NGS, FC |
| FLAIR | FCR, IR, I, IV | 3 | 771 | YES for IV vs. 1 or 1R | YES for FCR vs. IR | YES for the I arms | FC |
| CLL13 | CIT vs. VR vs. VO vs. VIO | 3 | 926 | YES | No | No | FC |
| GALACTIC | O consolidation | 2 | 48 | YES | No | No | FC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arcari, A.; Morello, L.; Borotti, E.; Ronda, E.; Rossi, A.; Vallisa, D. Recent Advances in the Molecular Biology of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: How to Define Prognosis and Guide Treatment. Cancers 2024, 16, 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203483
Arcari A, Morello L, Borotti E, Ronda E, Rossi A, Vallisa D. Recent Advances in the Molecular Biology of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: How to Define Prognosis and Guide Treatment. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203483
Chicago/Turabian StyleArcari, Annalisa, Lucia Morello, Elena Borotti, Elena Ronda, Angela Rossi, and Daniele Vallisa. 2024. "Recent Advances in the Molecular Biology of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: How to Define Prognosis and Guide Treatment" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203483
APA StyleArcari, A., Morello, L., Borotti, E., Ronda, E., Rossi, A., & Vallisa, D. (2024). Recent Advances in the Molecular Biology of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: How to Define Prognosis and Guide Treatment. Cancers, 16(20), 3483. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203483






