Complex Sleeve Lobectomy Has Lower Postoperative Major Complications Than Pneumonectomy in Patients with Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
- To evaluate and analyze the incidence of the overall complication rate, major complication and mortality by comparing the CSL group with the contemporary PN group;
- To evaluate and analyze the risk factors of major complications as defined as 3b or more in the Clavien–Dindo classification [19].
- The evaluation of overall and disease-free survival between the two groups;
- Analysis of the risk factors of poor overall survival.
2.2. Operative Technique
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Characteristics
3.2. Type of Resections
3.3. Postoperative Results
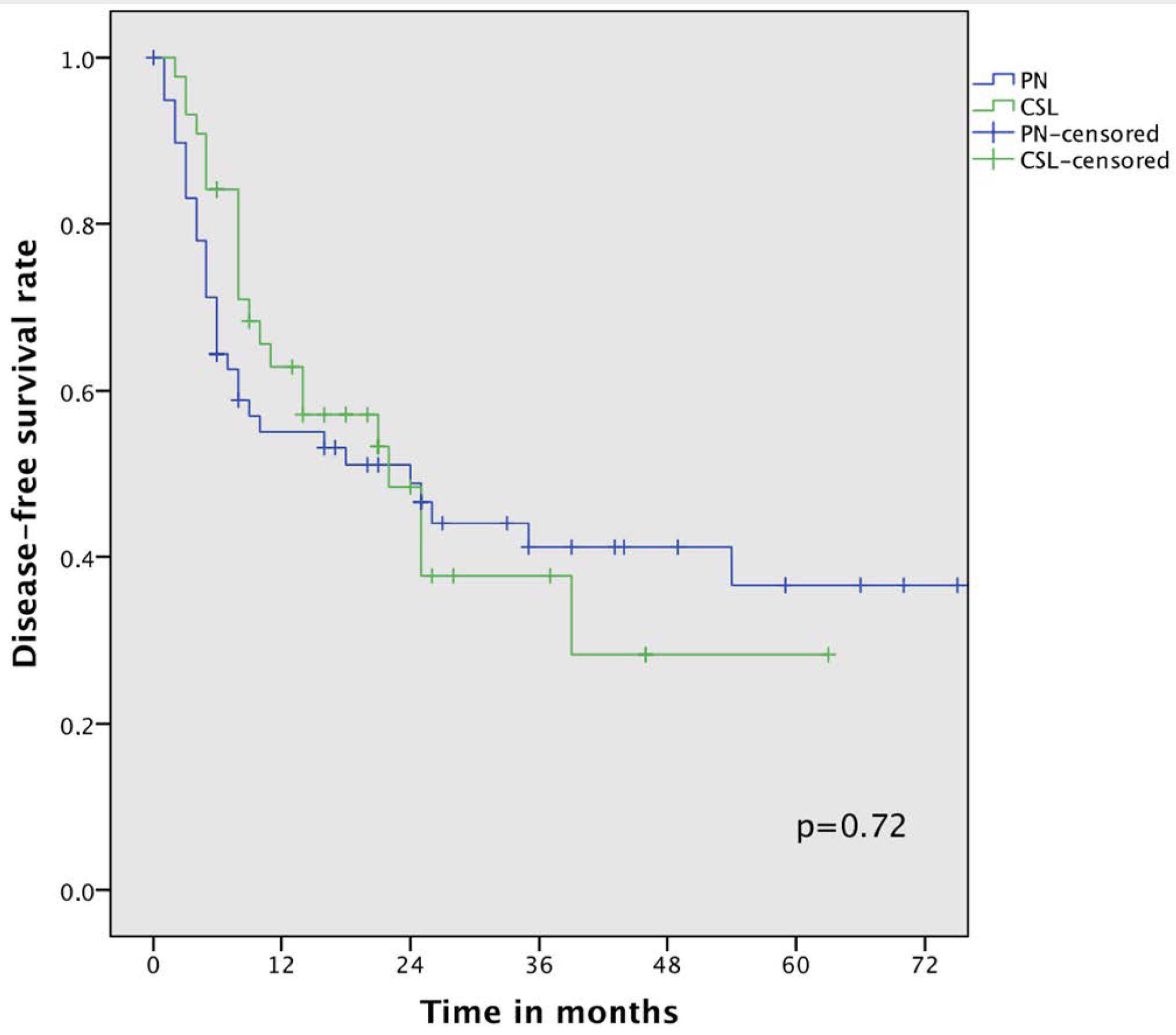
3.4. Oncological Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rea, F.; Marulli, G.; Schiavon, M.; Zuin, A.; Hamad, A.M.; Rizzardi, G.; Perissinotto, E.; Sartori, F. A quarter of a century experience with sleeve lobectomy for non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2008, 34, 488–492; discussion 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patella, M.; Brunelli, A.; Adams, L.; Cafarotti, S.; Costardi, L.; De Leyn, P.; Decaluwé, H.; Franks, K.N.; Fuentes, M.; Jimenez, M.F.; et al. A Risk Model to Predict the Delivery of Adjuvant Chemotherapy Following Lung Resection in Patients with Pathologically Positive Lymph Nodes. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 35, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022. 16 March 2022. Available online: www.nccn.org (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Chen, J.; Soultanis, K.M.; Sun, F.; Gonzalez-Rivas, D.; Duan, L.; Wu, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, G. Outcomes of sleeve lobectomy versus pneumonectomy: A propensity score-matched study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 162, 1619–1628.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhong, Y.; Deng, J.; She, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hu, X.; Xie, D.; Chen, C. Comparison of Bronchial Sleeve Lobectomy with Pulmonary Arterioplasty Versus Pneumonectomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 113, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Yang, H.C.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, K.; Shim, Y.M.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, J. Sleeve lobectomy as an alternative procedure to pneumonectomy for non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès, P.B.; Mordant, P.; Renaud, S.; Brouchet, L.; Thomas, P.A.; Dahan, M.; Bernard, A.; Epithor Project (French Society of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery). Sleeve lobectomy may provide better outcomes than pneumonectomy for non-small cell lung cancer. A decade in a nationwide study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 184–195.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelsattar, Z.M.; Shen, K.R.; Yendamuri, S.; Cassivi, S.; Nichols, F.C., 3rd; Wigle, D.A.; Allen, M.S.; Blackmon, S.H. Outcomes After Sleeve Lung Resections Versus Pneumonectomy in the United States. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 1656–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.; Chriqui, L.E.; Décaluwé, H.; Aigner, C.; Rényi-Vámos, F.; Opitz, I.; Furák, J.; Szanto, Z.; Brunelli, A.; Falcoz, P.E. Sleeve lobectomy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A report from the European Society of Thoracic Surgery database 2021. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Caro, A.; Garcia, S.; Reguart, N.; Cladellas, E.; Arguis, P.; Sanchez, M.; Gimferrer, J.M. Determining the appropriate sleeve lobectomy versus pneumonectomy ratio in central non-small cell lung cancer patients: An audit of an aggressive policy of pneumonectomy avoidance. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2011, 39, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Dong, A.; Fan, J.; Cheng, H. Does sleeve lobectomy concomitant with or without pulmonary artery reconstruction (double sleeve) have favorable results for non-small cell lung cancer compared with pneumonectomy? A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2007, 32, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Tsubota, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Satake, S.; Yamagishi, H. Extended sleeve lobectomy for lung cancer: The avoidance of pneumonectomy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1999, 118, 710–713; discussion 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voltolini, L.; Gonfiotti, A.; Viggiano, D.; Borgianni, S.; Farronato, A.; Bongiolatti, S. Extended sleeve-lobectomy for centrally located locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer is a feasible approach to avoid pneumonectomy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 4090–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthet, J.P.; Paradela, M.; Jimenez, M.J.; Molins, L.; Gómez-Caro, A. Extended sleeve lobectomy: One more step toward avoiding pneumonectomy in centrally located lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chida, M.; Minowa, M.; Miyoshi, S.; Kondo, T. Extended sleeve lobectomy for locally advanced lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2009, 87, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, T.H.; Cho, J.H.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Zo, J.I.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, J. Extended sleeve lobectomy for centrally located non-small-cell lung cancer: A 20-year single-centre experience. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 54, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Fukui, M.; Takamochi, K.; Oh, S.; Suzuki, K. Surgical Outcome After Extended Sleeve Lobectomy in Centrally Located Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 114, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inci, I.; Benker, M.; Çitak, N.; Schneiter, D.; Caviezel, C.; Hillinger, S.; Opitz, I.; Weder, W. Complex sleeve lobectomy has the same surgical outcome when compared with conventional lobectomy in pa-tients with lung cancer. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 57, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiolatti, S.; Mazzoni, F.; Gonfiotti, A.; Salvicchi, A.; Viggiano, D.; Ferrari, K.; Scotti, V.; Voltolini, L. Impact of Persistent N2 Disease and Lymph Node Ratio on Oncological Outcomes after Multimodal Treatment in Pre-Operative Histologically Proven N2 Disease Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Oncol. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunswicker, A.; Taylor, M.; Grant, S.W.; Abah, U.; Smith, M.; Shackcloth, M.; Granato, F.; Shah, R.; Rammohan, K.; North West Thoracic Surgery Collaborative (NWTSC). Pneumonectomy for primary lung cancer: Contemporary outcomes, risk factors and model validation. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 34, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Xia, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Inci, I.; Davoli, F.; Waseda, R.; Filosso, P.L.; White, A. Sleeve lobectomy compared with pneumonectomy for operable centrally located non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magouliotis, D.E.; Zotos, P.A.; Karamolegkou, A.P.; Tatsios, E.; Spiliopoulos, K.; Athanasiou, T. Long-Term Survival after Extended Sleeve Lobectomy (ESL) for Central Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Meta-Analysis with Reconstructed Time-to-Event Data. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Mei, J.; Liu, C.; Guo, C.; Gonzalez, M.; Bölükbas, S.; Voltolini, L.; Pu, Q.; Liu, L. Risk factors and outcomes of bronchopleural fistula after bronchoplasty in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective multivariate analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, G.E.; Abdurahman, A.; Yi, Q.L.; Johnston, M.; Waddell, T.K.; Pierre, A.; Keshavjee, S.; Ginsberg, R. Risk of a right pneumonectomy: Role of bronchopleural fistula. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, J.; Loberg, A.; Dunning, J.; Dark, J. Is a sleeve lobectomy significantly better than a pneumonectomy? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 11, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, L.J.; Jordan, S.; Demmy, T.; Dexter, E.; Hennon, M.; Nwogu, C.; Yendamuri, S.; Picone, A. Analyzing the impact of minimally invasive surgical approaches on post-operative outcomes of pneumonectomy and sleeve lobectomy patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Imai, K.; Takashima, S.; Kurihara, N.; Kuriyama, S.; Iwai, H.; Tozawa, K.; Saito, H.; Nomura, K.; Minamiya, Y. Outcomes and pulmonary function after sleeve lobectomy compared with pneumonectomy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, S.; You, X.; Aramini, B.; Shabaturov, L.; Jiang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, J. Extended Sleeve Lobectomy is an Alternative for Centrally Located Lung Cancer with Superior Short- and Long-term Outcomes. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e621–e628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | PN (n = 60) | CSL (n = 44) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex male | 40 (66.7%) | 31 (70.5%) | 0.68 |
| Age | 66.6 ± 8.01 | 67.6 ± 6.73 | 0.53 |
| BMI | 25.8 ± 4.6 | 24.1 ± 3.8 | 0.06 |
| PS | 0.8 | ||
| 0 | 16 (26.7%) | 13 (29.5%) | |
| 1 | 33 (55%) | 25 (56.8%) | |
| 2 | 11 (18.3%) | 6 (13.6%) | |
| mCCI | 0.65 | ||
| 0 | 13 (21.7%) | 9 (20.5%) | |
| 1 | 12 (20%) | 11 (25%) | |
| 2 | 15 (25%) | 15 (34.1%) | |
| 3 | 10 (16.7%) | 3 (6.8%) | |
| >4 | 10 (16.7%) | 6 (13.7%) | |
| ASA | 0.42 | ||
| 1 | 13 (21.7%) | 11 (25%) | |
| 2 | 22 (36.7%) | 19 (43.2%) | |
| 3 | 25 (41.7%) | 13 (29.5%) | |
| 4 | 0 | 1 (2.2%) | |
| FEV1% | 81.7 ± 16 | 82.2 ± 20.4 | 0.9 |
| FVC% | 95.3 ± 18.7 | 99.9 ± 24 | 0.33 |
| DLCO% | 68.5 ± 17.9 | 66.7 ± 15.5 | 0.63 |
| cSTAGE | 0.64 | ||
| IA | 3 (5%) | 1 (2.3%) | |
| IB | 1 (1.7%) | 0 | |
| IIA | 2 (3.3%) | 2 (4.5%) | |
| IIB | 15 (25%) | 13 (29.5%) | |
| IIIA | 33 (55%) | 22 (50%) | |
| IIIB | 4 (6.7%) | 6 (13.6%) | |
| IIIC | 1 (1.7%) | 0 | |
| IV | 1 (1.7%) | 0 | |
| NAC | 21 (35%) | 14 (31.8%) | 0.73 |
| NACRT | 0 | 2 (4.9%) | 0.34 |
| Variable | PN (n = 60) | CSL (n = 44) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type of procedure | Right 23 (38.3%) Left 37 (61.7%) | ESL type A 15 (34.1%) | |
| ESL type B 2 (4.5%) | |||
| ESL type C 17 (38.6%) | |||
| ESL type D 3 (6.8%) | |||
| ESL not classified (E) 1 (2.3%) | |||
| Double sleeve 6 (13.5%) | |||
| Bronchial flap coverage | 33 (55%) | 5 (11.4%) | <0.01 |
| Variables | PN (n = 60) | CSL (n = 44) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathology | 0.14 | ||
| ADC | 29 (48.3%) | 15 (34.1%) | |
| SCC | 31 (51.7%) | 29 (65.9%) | |
| pSTAGE | 0.71 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 (2.3%) | |
| IA | 3 (5%) | 3 (6.8%) | |
| IB | 4 (6.7%) | 1 (2.3%) | |
| IIA | 4 (6.7%) | 3 (6.8%) | |
| IIB | 11 (18.3%) | 11 (25%) | |
| IIIA | 21 (35%) | 16 (36.4%) | |
| IIIB | 17 (28.3%) | 9 (20.5%) | |
| pN0 | 20 (33.3%) | 13 (29.5%) | 0.78 |
| pN1 | 18 (30%) | 16 (36.4%) | |
| pN2 | 22 (36.7%) | 15 (34.1%) | |
| pR0 | 53 (88.3%) | 39 (88.6%) | 0.96 |
| Tumor diameter cm | 5.74 ± 2.76 | 5.14 ± 2.85 | 0.3 |
| HS | 10.68 ± 7.1 | 12.7 ± 8.93 | 0.18 |
| Patients with at least one complication | 36 (60%) | 24 (54.5%) | 0.57 |
| Clavien–Dindo classification | <0.01 | ||
| 1 | 2 (3.3%) | 1 (2.3%) | |
| 2 | 21 (35%) | 8 (18.2%) | |
| 3a | 0 | 11 (25%) | |
| 3b | 3 (5%) | 1 (2.3%) | |
| 4a | 6 (10%) | 2 (4.5%) | |
| 4b | 1 (1.7%) | 0 | |
| 5 | 3 (5%) | 0 | |
| Major complications (>3b) | 13 (21.7%) | 3 (6.8%) | 0.038 |
| Bronchial dehiscence | 4 (6.7%) | 2 (4.5%) | 0.64 |
| Postoperative mortality | 3 (5%) | 0 | 0.13 |
| Recurrence | 26 (43.3%) | 20 (45.5%) | 0.83 |
| Pattern of recurrence | 0.1 | ||
| No recurrence | 34 (56.7%) | 24 (54.5%) | |
| Local | 1 (1.7%) | 6 (13.6%) | |
| Regional | 3 (5%) | 2 (4.5%) | |
| Distant | 22 (36.7%) | 12 (27.3%) | |
| ACHT | 27 (45.8%) | 19 (43.2%) | 0.79 |
| ART | 6 (10.9%) | 2 (7.1%) | 0.58 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | CI95% | p | OR | CI95% | p |
| Sex male | 1.85 | 0.62–5.5 | 0.26 | |||
| Age > 70 | 2.16 | 0.68–6.87 | 0.18 | 3.31 | 0.86–12.7 | 0.081 |
| PN | 3.78 | 1.006–14.2 | 0.049 | 4.21 | 0.93–19.03 | 0.073 |
| ECOG PS > 2 | 2.87 | 0.85–9.75 | 0.089 | 2.07 | 0.32–13.2 | 0.44 |
| mCCI > 3 | 2.33 | 0.77–7 | 0.13 | 1.59 | 0.29–8.51 | 0.58 |
| FEV1% < 60 | 1.42 | 0.16–12.5 | 0.75 | |||
| DLCO% < 60 | 1.76 | 0.5–6.19 | 0.37 | |||
| NAC | 1.63 | 0.48-5.48 | 0.42 | |||
| Clinical stage | 0.14 | |||||
| I–II | ref | |||||
| III–IV | 2.25 | 0.76–6.61 | 0.14 | 2.75 | 0.7–10.7 | |
| Right side | 3.85 | 1.22–12.07 | 0.021 | 5.75 | 1.43–23.1 | 0.014 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR | CI95% | p | HR | CI95% | p |
| Sex male | 1.21 | 0.66–2.19 | 0.52 | |||
| Age > 70 | 1.65 | 0.88–3.06 | 0.11 | 1.71 | 0.72–4.06 | 0.22 |
| PN | 0.97 | 0.53–1.76 | 0.92 | |||
| CLS | ref | |||||
| ECOG PS > 2 | 2.23 | 0.87–5.6 | 0.09 | 1.78 | 0.6–5.25 | 0.29 |
| R1 | 1.41 | 0.78–2.53 | 0.25 | |||
| Stage III–IV | 1.49 | 0.8–2.77 | 0.2 | |||
| Recurrence | 5.47 | 2.7–11 | <0.01 | 6.88 | 2.5–18.9 | <0.01 |
| Pathology | ||||||
| SCC | Ref | |||||
| ADC | 1.06 | 0.59–1.91 | 0.82 | |||
| ACHT | 0.82 | 0.45–1.48 | 0.52 | |||
| ART | 3.19 | 1.27–8.01 | 0.014 | 2.53 | 0.88–7.25 | 0.084 |
| Pneumonectomy | |
| PROS | CONS |
| Technically easier | Higher mortality |
| Lower local recurrence | Higher major complication rate |
| Complex management of complications | |
| No survival advantage | |
| Theoretically worse QoL, worse compliance with other oncological treatments | |
| Complex sleeve lobectomy | |
| Parenchymal preservation, theoretically more functional conservation | More technically demanding procedure |
| Lower incidence of major complications | Higher local recurrence rate |
| Low mortality | |
| Resection also feasible in compromised patients | |
| Easier management of complications | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voltolini, L.; Viggiano, D.; Gonfiotti, A.; Borgianni, S.; Mugnaini, G.; Salvicchi, A.; Bongiolatti, S. Complex Sleeve Lobectomy Has Lower Postoperative Major Complications Than Pneumonectomy in Patients with Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020261
Voltolini L, Viggiano D, Gonfiotti A, Borgianni S, Mugnaini G, Salvicchi A, Bongiolatti S. Complex Sleeve Lobectomy Has Lower Postoperative Major Complications Than Pneumonectomy in Patients with Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020261
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoltolini, Luca, Domenico Viggiano, Alessandro Gonfiotti, Sara Borgianni, Giovanni Mugnaini, Alberto Salvicchi, and Stefano Bongiolatti. 2024. "Complex Sleeve Lobectomy Has Lower Postoperative Major Complications Than Pneumonectomy in Patients with Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 2: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020261
APA StyleVoltolini, L., Viggiano, D., Gonfiotti, A., Borgianni, S., Mugnaini, G., Salvicchi, A., & Bongiolatti, S. (2024). Complex Sleeve Lobectomy Has Lower Postoperative Major Complications Than Pneumonectomy in Patients with Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 16(2), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020261