Simple Summary
Pathogenic variants in the PALB2 gene significantly increase the risk of developing breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers. However, the prevalence of these mutations in East Asian populations, particularly Koreans, has not been well studied. This research aims to estimate the prevalence of PALB2 variants in these populations by analyzing large-scale genomic databases. Understanding the frequency of PALB2 variants can help in identifying individuals at higher risk for these cancers and guide the development of targeted screening and prevention strategies. The findings from this study provide valuable reference data that can enhance genetic counseling and improve cancer risk management in East Asian populations, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes in these communities.
Abstract
PALB2 is a tumor suppressor gene. Heterozygous germline pathogenic variants of PALB2 significantly increase the lifetime risk of breast cancer and moderately increase the risk of ovarian and pancreatic cancers. This study analyzed the estimated prevalence of PALB2 variants globally, focusing on East Asian and Korean populations, where limited data were previously available. We examined 125,748 exomes from the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD), including 9197 East Asians, and additional data from 5305 individuals in the Korean Variant Archive and 1722 in the Korean Reference Genome Database. All PALB2 variants were interpreted according to guidelines from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Clinical Genome Resource. The global prevalence of PALB2 variants was 0.18%, with the highest prevalence in Finnish populations (0.41%) and the lowest in Ashkenazi Jewish populations (0.04%). East Asians had a prevalence of 0.09%. By combining data from Korean genome databases and gnomAD totaling 8936 individuals, the overall prevalence of PALB2 variants in the Korean population was determined to be 0.13%. This study is the first comprehensive investigation of PALB2 variant prevalence in East Asians and Koreans using gnomAD and Korean genome databases. These findings provide essential reference data for future research and highlight the importance of region-specific genetic studies that will inform genetic counseling and hereditary cancer risk management.
1. Introduction
PALB2 (partner and localizer of BRCA2) is a tumor suppressor gene crucial for repairing DNA double-strand breaks via the homologous recombination pathway [1]. The PALB2 protein interacts with both BRCA1 and BRCA2, forming an essential part of the BRCA complex (BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2-RAD51), which maintains genomic stability. Defects in this pathway are linked to cancer development [2]. Biallelic germline loss-of-function mutations in PALB2 cause Fanconi anemia [3]. In contrast, heterozygous germline pathogenic variants in PALB2 significantly increase the lifetime risk of breast cancer and moderately increase the risks of ovarian and pancreatic cancers [4,5,6].
The prevalence of germline pathogenic variants in PALB2 among breast cancer patients has been reported to range from approximately 0.23–2.65% [7,8]. The estimated lifetime risk of breast cancer for female carriers of PALB2 variants is 53% by age 80 (95% confidence interval, 44–63%) [5]. In control populations, the prevalence of PALB2 variants is reported to be between 0.0% and 0.75% [4,9]. Most studies have been conducted in Western populations, with limited data on East Asians, highlighting the need for further region-specific research.
Although the spectrum of pathogenic PALB2 variants is diverse, studies on patients with breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers have identified the top five most frequently reported pathogenic variants as c.509_510del;p.(Arg170IlefsTer14), c.3113G>A;p.(Trp1038Ter), c.1592del;p.(Leu531CysfsTer30), c.172_175del;p.(Gln60ArgfsTer7), and c.1240C>T;p.(Arg414Ter), which account for 57.3% of all cases [10]. Notably, the c.1592del;p.(Leu531CysfsTer30) variant is recognized as a founder mutation in approximately 1% of Finnish breast cancer patients [8].
According to the latest National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic (Version 3.2024—February 12, 2024) [11], genetic testing for PALB2 variants, along with BRCA1/2, is recommended for patients with suspected hereditary breast, ovarian, or pancreatic cancer. Individuals with pathogenic PALB2 variants are advised to follow breast cancer risk management protocols similar to those for individuals with BRCA1/2 variants. Additionally, carriers of pathogenic PALB2 variants may consider risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy between the ages of 45 and 50 to lower the risk of ovarian cancer.
The gnomAD v2.1.1 database, containing 125,748 exomes with 9197 from East Asian, is a comprehensive global genomic database [12]. Additionally, the Korean Variant Archive (KOVA) provides a reference for genetic variation specific to the Korean population, containing data from 1.896 whole-genome sequencing and 3409 whole exome sequencing [13]. Another major resource, the Korean Reference Genome Database (KRGDB), consists of whole-genome sequencing data from 1722 Koreans [14].
These genomic databases, which encompass diverse ethnic groups, are crucial for estimating the prevalence of PALB2 variants. In our study, we used the 2015 guidelines from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology guidelines (ACMG/AMP guidelines) to analyze PALB2 variants within these databases [15]. Our main objective was to assess the global prevalence of PALB2 variants, with a special focus on East Asian populations that have been underrepresented in previous research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population Database
We obtained PALB2 gene data from gnomAD (v2.1.1), accessible at https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/ (access on 10 October 2021). Our analysis covered 125,748 exomes from diverse populations, including 9197 East Asians, 8.128 African/African-Americans, 17,296 Latino/Admixed Americans, 5.040 Ashkenazi Jewish, 10,824 Finnish, 56,885 non-Finnish Europeans, 15,308 South Asians, and 3070 from other (population not assigned) populations. Within the East Asian cohort, there were 1909 Koreans, 76 Japanese, and 7212 individuals of other East Asian ancestries. We excluded variants marked with “InbreedingCoeff”, “AC0”, or “RF” quality control filters in gnomAD.
For Korean-specific data, we used the KOVA database, which includes information from 5305 Koreans (https://www.kobic.re.kr/kova/, accessed on 6 November 2023), and the KRGDB, which contains whole-genome sequencing data from 1722 Koreans (http://coda.nih.go.kr/coda/KRGDB/index.jsp, accessed on 25 September 2021).
2.2. Classification and Statistical Analysis of PALB2 Variants
All PALB2 variants were interpreted according to the ACMG/AMP guidelines and the Sequence Variant Interpretation guidelines from ClinGen (https://clinicalgenome.org/working-groups/sequence-variant-interpretation/, accessed on 20 March 2024). These guidelines categorize variants into five groups: pathogenic variant (PV), likely pathogenic variant (LPV), variants of uncertain significance, likely benign variant, and benign variant. In silico prediction of variant pathogenicity was performed using REVEL [16] and SpliceAI [17]. The threshold range for REVEL was determined based on the criteria suggested by Pejaver et al. [18], and a SpliceAI Δ score ≥ 0.2 was applied as the threshold for spliceogenicity [19].
We compared all identified PALB2 variants in population databases with previously characterized disease-causing variants from ClinVar and the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD). ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/, accessed on 21 March 2024) is an open-access repository of variant classifications provided by a variety of sources, including clinical laboratories, research institutions, and expert panels. The HGMD professional database (http://www.hgmd.org/, release 2023.04) is a comprehensive collection of germline variants, categorized into six groups. Our primary focus was on disease-causing mutations (DM).
2.3. Prevalence Estimation of PALB2 Variant
The prevalence of PALB2 variant was determined using population databases. For the prevalence analysis, we included variants classified as PV and LPV according to the ACMG/AMP guidelines, PV and LPV interpretations from ClinVar, as well as DM entries from HGMD. To estimate the prevalence of PALB2 variants, we considered the autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. The prevalence was estimated using the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle (1 = p² + 2pq + q²), where p represents the major allele (non-disease) and q represents the minor allele (disease). In the case of autosomal dominant inheritance, carriers are represented by 2pq. We predicted the estimated disease prevalence using 2pq. Statistical analyses were conducted using R version 4.3.2, and 95% confidence intervals were computed for each value. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hanyang University Guri Hospital (approval code is IRB No. HYUH 2021-06-29; granted on 15 July 2021) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
3. Results
We conducted an analysis of 125,748 exomes from the gnomAD database, focusing specifically on 9197 exomes from East Asian populations, with an emphasis on variants within the PALB2 gene. The variants were classified according to ACMG/AMP guidelines and cross-referenced with ClinVar and HGMD, two widely used disease classification databases (Table 1).

Table 1.
Estimated prevalence of PALB2 variants in population database.
According to the ACMG/AMP guidelines, the global prevalence of PALB2 variants was estimated to be 0.18%. The estimated prevalence exhibited significant variation among different populations. Finnish populations had the highest prevalence at 0.41%, while Ashkenazi Jewish populations had the lowest at 0.04%. East Asians showed the second lowest prevalence among the studied groups, at 0.09%. ClinVar data indicated a global prevalence for PALB2 variants of 0.17%. According to HGMD data, the overall prevalence for PALB2 variants was higher, at 0.22%.
In the gnomAD database, the prevalence of PALB2 variants among Koreans was reported to be 0.10% (Table 2). Additionally, analysis based on the ACMG/AMP guidelines showed a prevalence of PALB2 variants of 0.19% in the KOVA database, which includes data from 5305 individuals. No PALB2 variant was observed in the KRGDB database, which includes 1722 individuals. By combining data from gnomAD, KOVA, and KRGDB, totaling 8936 individuals, the overall prevalence of PALB2 variants in the Korean population was determined to be 0.13%.

Table 2.
Estimated prevalence of PALB2 variants in East Asian and Korean population databases.
The summary in Supplementary Table S1 details the PV and LPV identified in the PALB2 gene, classified according to ACMG/AMP guidelines, within the gnomAD database. Figure 1 provides a schematic representation of these pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants, along with the structural motifs and functional domains of the PALB2 gene. The c.1592del;p.(Leu531CysfsTer30) variant was the most prevalent globally, identified in 46 alleles. This variant was observed across various ethnic groups, with a notable presence in the European (Finnish) population, but was absent in East Asians. The second-most-frequently observed variant, c.2167_2168del;p.(Met723ValfsTer21), was found in 16 alleles, predominantly in individuals of Latino ancestry, but was not observed in East Asians. Further analysis comparing PV/LPV variants in East Asians with those from other ethnic groups showed notable differences. Except for the c.1050_1053del;p.(Thr351ArgfsTer4) variant, the other variants were exclusively found in East Asian populations. Variants classified as PV/LPV in ClinVar and DM variants listed in HGMD are detailed in Table S2 and Table S3, respectively.
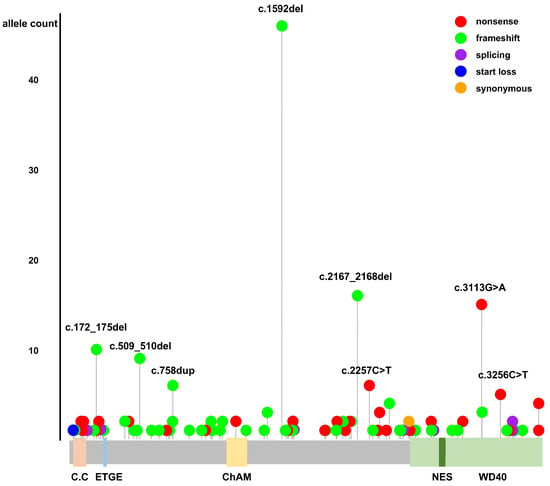
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in the PALB2 gene from gnomAD, and structural motifs and functional domains of PALB2. C.C.: coiled-coil motif; ETGE motif; ChAM: chromatin association motif; WD40: WD40 repeat; NES: nuclear export sequence.
The summary of PV/LPVs found in the Korean database is presented in Table S4. In gnomAD, the variant c.2968G>T;p.(Glu990Ter), which is the most common in East Asians, was not identified in Koreans. Conversely, the c.1048C>T;p.(Gln350Ter) variant was most frequently observed in Koreans. Compared to the total gnomAD population, apart from the c.2167_2168del;p.(Met723ValfsTer21) variant, all variants identified in Koreans were not detected in other ethnic groups
4. Discussion
The findings of this study significantly enhanced our understanding of the prevalence and spectrum of PALB2 pathogenic variants across different populations, with a special focus on East Asians and Koreans. The use of extensive genomic databases, including gnomAD, KOVA, and KRGDB, allowed for a comprehensive analysis, revealing notable differences in variant prevalence among ethnic groups.
Our study determined that the global prevalence of PALB2 pathogenic variants was approximately 0.18%, with significant variation across populations. Finnish populations showed the highest prevalence at 0.41%, while Ashkenazi Jewish populations had the lowest at 0.04%. East Asians exhibited a relatively low prevalence at 0.09%, with Koreans showing a prevalence of 0.13% when data from gnomAD, KOVA, and KRGDB were combined.
Comparing our results with the case-control study reported by Girard et al., which indicated a control PALB2 variant prevalence of 0.75% [9], there is a noticeable difference. However, reassessment of the variants identified in that study using the ACMG/AMP guidelines resulted in a control PALB2 prevalence of 0.25%, which was similar to or slightly higher than the prevalence reported in our study.
In this study, the variants among the PV/LPVs of the PALB2 gene in the gnomAD database were found in the following order: c.1592del;p.(Leu531CysfsTer30), c.2167_2168del;p.(Met723ValfsTer21), c.3113G>A;p.(Trp1038Ter), c.172_175del;p.(Gln60ArgfsTer7), and c.509_510del;p.(Arg170IlefsTer14). These results are consistent with a previous large-scale systematic review of breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancers [10], which reported the same top-five PALB2 variants, with the exception of c.2167_2168del;p.(Met723ValfsTer21). This suggests that genomic database studies can reliably predict prevalent variants in real patients, providing valuable insights for genetic counseling and risk assessment. However, among the 10 PALB2 variants found in the Korean genomic database, c.1048C>T;p.(Gln350Ter) and c.3267_3268del;p.(Phe1090SerfsTer6) were consistent with two Korean breast cancer patients among Korean breast, ovarian, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients [20,21,22,23,24]. This suggests some uncertainty due to the small number of patients in certain ethnic groups and highlights the need for further studies.
To further investigate the variant spectrum, we compared the 10 variants identified in the Korean database with large-scale databases from China (15,068 genomes) and Japan (59,940 genomes) [25,26,27]. Of the 10 variants, only 2 (c.2167_2168del and c.2834+2T>C) were found in the Japanese population, and none were identified in the Chinese population. The variant spectrum found in the Korean population is distinct, not only when compared to other ethnic groups but also within East Asia itself.
The ACMG has updated its guidelines to include PALB2, along with BRCA1/2, in the ACMG SF v3.2 list for reporting secondary findings from clinical exome and genome sequencing [28]. Additionally, population-based BRCA1/BRCA2/RAD51C/RAD51D/BRIP1/PALB2 testing has been found to be more cost-effective than strategies based on clinical criteria or family history based BRCA1/BRCA2/RAD51C/RAD51D/BRIP1/PALB2 testing [29]. It is crucial to evaluate PALB2 variants during genetic testing, particularly for individuals of European (Finnish) descent, who had the highest carrier frequency in this study. Research indicates that individuals with pathogenic PALB2 variants have a lifetime breast cancer risk of up to 53% by age 80 [5]. Therefore, implementing a comprehensive surveillance plan, including regular breast cancer screening and considering risk reduction strategies such as prophylactic surgery, is essential [11].
According to data retrieved from the Korea Statistical Information Service (http://kosis.kr/, accessed 3 June 2024), the total population of South Korea as of 2024 is 51.8 million. In this study, among 8936 individuals from the genomic database, the prevalence of PALB2 PV/LPV was 0.13%. Given this prevalence, it is estimated that approximately 67,000 individuals in Korea carry PALB2 PV/LPV variants. According to a Korean BRCA1/2 negative breast cancer cohort study, it was confirmed that 2.43% (17/700) of BRCA1/2 negative breast cancers were caused by PALB2 variants [23]. In addition, PALB2 variants were identified in one case each in Korean ovarian cancer and pancreatic cancer cohorts [22,24]. However, genetic counseling for patients with PALB2 variants and their families remains insufficient in Korea. Since PALB2 variants are inherited in an autosomal dominant, there is a 50% chance that other family members may carry the same variant. Therefore, appropriate prevention and treatment strategies for PALB2 related cancer will also be needed in Koreans.
This study has several limitations. First, large deletions or insertions (defined as those over 50 base pairs and often spanning multiple exons) within the PALB2 gene were not included in the analysis, which could result in an underestimation of the actual prevalence of PALB2 variants. Previous studies have reported the presence of PALB2 deletions or insertions including Koreans [6,23,30], but such variants were not detectable in our current dataset. Second, the prevalence estimates were derived solely from genes registered in genomic databases, which introduces potential inaccuracies. This approach does not incorporate detailed clinical information from patients, and as additional evidence becomes available, some variants currently classified as variants of uncertain significance (VUS) may be reclassified as PV/LPV, while conversely, PV/LPV may be reclassified as VUS. Moreover, since the penetrance of PALB2 is not 100%, the actual number of patients expressing the phenotype may be lower than the predicted prevalence. This discrepancy underscores the importance of integrating comprehensive clinical data with genomic information to improve the accuracy of prevalence estimates and variant interpretation.
Despite these limitations, this study effectively estimated the prevalence of PALB2 variants across various ethnic groups. Notably, this is the most extensive study conducted on East Asians, particularly Koreans, to analyze the PALB2 gene. Consequently, this research provides a more accurate prediction of carrier frequency and incidence among both East Asians and Koreans. Given the recent advancements in surveillance and treatment options for PALB2-associated cancers, identifying carriers of PALB2 variants is essential for effective management and intervention.
5. Conclusions
This study is the first comprehensive investigation of PALB2 variant prevalence in East Asians and Koreans using gnomAD and the Korean genome database. We found that East Asians have the second-lowest prevalence of PALB2 variants among various ethnic groups, with significant differences in variant distributions compared to other populations. These findings provide essential reference data for future research and highlight the importance of region-specific genetic studies in enhancing genetic counseling and managing hereditary cancer risks.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers16193318/s1, Table S1: Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants classified according to the 2015 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and Association for Molecular Pathology guidelines in gnomAD; Table S2: Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in ClinVar from gnomAD; Table S3: Disease-causing mutations in the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) from gnomAD; Table S4: Pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in Korean databases classified according to the ACMG/AMP guidelines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-S.K. and S.-Y.K.; methodology, T.L.; formal analysis, J.E.P., M.-C.K., E.H.C., M.-A.J., D.W. and B.P.; resources, T.L., E.H.C., and C.-S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, J.E.P.; writing—review and editing, C.-S.K. and S.-Y.K.; visualization, J.E.P.; supervision, C.-S.K. and S.-Y.K.; project administration, S.-Y.K.; funding acquisition, J.E.P. and S.-Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF2021R1I1A1A01049183) and by a grant of the Korean Cancer Survivors Healthcare R&D Project through the National Cancer Center, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (RS-2023-CC139201).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Hanyang University Guri Hospital (approval code is IRB No. HYUH 2021-06-29; granted on 15 July 2021) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to those responsible for creating and maintaining gnomAD, ClinVar, and HGMD databases.
Conflicts of Interest
Author T.L. and C.-S.K. were employed by the company GC Genome and have no conflict of interest. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Xia, B.; Sheng, Q.; Nakanishi, K.; Ohashi, A.; Wu, J.; Christ, N.; Liu, X.; Jasin, M.; Couch, F.J.; Livingston, D.M. Control of BRCA2 cellular and clinical functions by a nuclear partner, PALB2. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, L.; Cai, H.; Xia, B.; Yu, X. PALB2 links BRCA1 and BRCA2 in the DNA-damage response. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischkowitz, M.; Xia, B. PALB2/FANCN: Recombining cancer and Fanconi anemia. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7353–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, N.; Seal, S.; Thompson, D.; Kelly, P.; Renwick, A.; Elliott, A.; Reid, S.; Spanova, K.; Barfoot, R.; Chagtai, T.; et al. PALB2, which encodes a BRCA2-interacting protein, is a breast cancer susceptibility gene. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Leslie, G.; Doroszuk, A.; Schneider, S.; Allen, J.; Decker, B.; Dunning, A.M.; Redman, J.; Scarth, J.; Plaskocinska, I.; et al. Cancer Risks Associated With Germline PALB2 Pathogenic Variants: An International Study of 524 Families. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.C.; Casadei, S.; Heikkinen, T.; Barrowdale, D.; Pylkäs, K.; Roberts, J.; Lee, A.; Subramanian, D.; De Leeneer, K.; Fostira, F.; et al. Breast-cancer risk in families with mutations in PALB2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southey, M.C.; Goldgar, D.E.; Winqvist, R.; Pylkäs, K.; Couch, F.; Tischkowitz, M.; Foulkes, W.D.; Dennis, J.; Michailidou, K.; van Rensburg, E.J.; et al. PALB2, CHEK2 and ATM rare variants and cancer risk: Data from COGS. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkko, H.; Xia, B.; Nikkilä, J.; Schleutker, J.; Syrjäkoski, K.; Mannermaa, A.; Kallioniemi, A.; Pylkäs, K.; Karppinen, S.M.; Rapakko, K.; et al. A recurrent mutation in PALB2 in Finnish cancer families. Nature 2007, 446, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, E.; Eon-Marchais, S.; Olaso, R.; Renault, A.L.; Damiola, F.; Dondon, M.G.; Barjhoux, L.; Goidin, D.; Meyer, V.; Le Gal, D.; et al. Familial breast cancer and DNA repair genes: Insights into known and novel susceptibility genes from the GENESIS study, and implications for multigene panel testing. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1962–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.; Bellis, S.; Koller, T.; Tischkowitz, M.; Liau, S.S. A systematic review of predicted pathogenic PALB2 variants: An analysis of mutational overlap between epithelial cancers. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic (Version 3.2024). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/genetics_bop.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2024).
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Jeon, S.; Lee, J.; Jang, I.; Yang, J.O.; Park, S.; Lee, B.; Choi, J.; Choi, B.O.; et al. A database of 5305 healthy Korean individuals reveals genetic and clinical implications for an East Asian population. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.S.; Hong, K.W.; Jo, H.Y.; Choi, J.; Ban, H.J.; Cho, S.B.; Chung, M. KRGDB: The large-scale variant database of 1722 Koreans based on whole genome sequencing. Database 2020, 2020, baz146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Byrne, A.B.; Feng, B.J.; Pagel, K.A.; Mooney, S.D.; Karchin, R.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.; Harrison, S.M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Greenblatt, M.S.; et al. Calibration of computational tools for missense variant pathogenicity classification and ClinGen recommendations for PP3/BP4 criteria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.C.; Hoya, M.; Wiggins, G.A.R.; Lindy, A.; Vincent, L.M.; Parsons, M.T.; Canson, D.M.; Bis-Brewer, D.; Cass, A.; Tchourbanov, A.; et al. Using the ACMG/AMP framework to capture evidence related to predicted and observed impact on splicing: Recommendations from the ClinGen SVI Splicing Subgroup. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 110, 1046–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, D.Y.; Choi, D.H.; Oh, M.; Shin, I.; Park, W.; Huh, S.J.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.W. Frequency of pathogenic germline mutation in CHEK2, PALB2, MRE11, and RAD50 in patients at high risk for hereditary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 161, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, S.T.; Nam, E.J.; Han, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.I.; Park, H.S. Variants of cancer susceptibility genes in Korean BRCA1/2 mutation-negative patients with high risk for hereditary breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, G.D.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.N.; Chae, H.; Han, E.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M. Clinical Validity of Next-Generation Sequencing Multi-Gene Panel Testing for Detecting Pathogenic Variants in Patients With Hereditary Breast-Ovarian Cancer Syndrome. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Shin, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.T.; Nam, E.J.; Han, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.I.; Park, H.S. Implication and Influence of Multigene Panel Testing with Genetic Counseling in Korean Patients with BRCA1/2 Mutation-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.H.; Park, S.; Chun, J.W.; Cho, E.; Choi, J.; Lee, D.E.; Shim, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, S.S.; Park, S.J.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Germline Pathogenic Variants in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, M.; Feng, Z.; Sun, X.; Lu, J.; Xu, Y.; Du, P.; Wang, T.; Hu, R.; et al. The ChinaMAP analytics of deep whole genome sequences in 10,588 individuals. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.W.; Liu, K.Q.; Wang, P.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Chen, J.Y.; Xu, X.J.; Xu, J.J.; Qiu, M.C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Cohort profile: The Westlake BioBank for Chinese (WBBC) pilot project. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadaka, S.; Kawashima, J.; Hishinuma, E.; Saito, S.; Okamura, Y.; Otsuki, A.; Kojima, K.; Komaki, S.; Aoki, Y.; Kanno, T.; et al. jMorp: Japanese Multi-Omics Reference Panel update report 2023. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, D622–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.T.; Lee, K.; Abul-Husn, N.S.; Amendola, L.M.; Brothers, K.; Chung, W.K.; Gollob, M.H.; Gordon, A.S.; Harrison, S.M.; Hershberger, R.E.; et al. ACMG SF v3.2 list for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing: A policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2023, 25, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, R.; Patel, S.; Gordeev, V.S.; Antoniou, A.C.; Smith, S.; Lee, A.; Hopper, J.L.; MacInnis, R.J.; Turnbull, C.; Ramus, S.J.; et al. Cost-effectiveness of Population-Based BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51C, RAD51D, BRIP1, PALB2 Mutation Testing in Unselected General Population Women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janatova, M.; Kleibl, Z.; Stribrna, J.; Panczak, A.; Vesela, K.; Zimovjanova, M.; Kleiblova, P.; Dundr, P.; Soukupova, J.; Pohlreich, P. The PALB2 gene is a strong candidate for clinical testing in BRCA1- and BRCA2-negative hereditary breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).