The Multimodality Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
2.1. Clinical Features
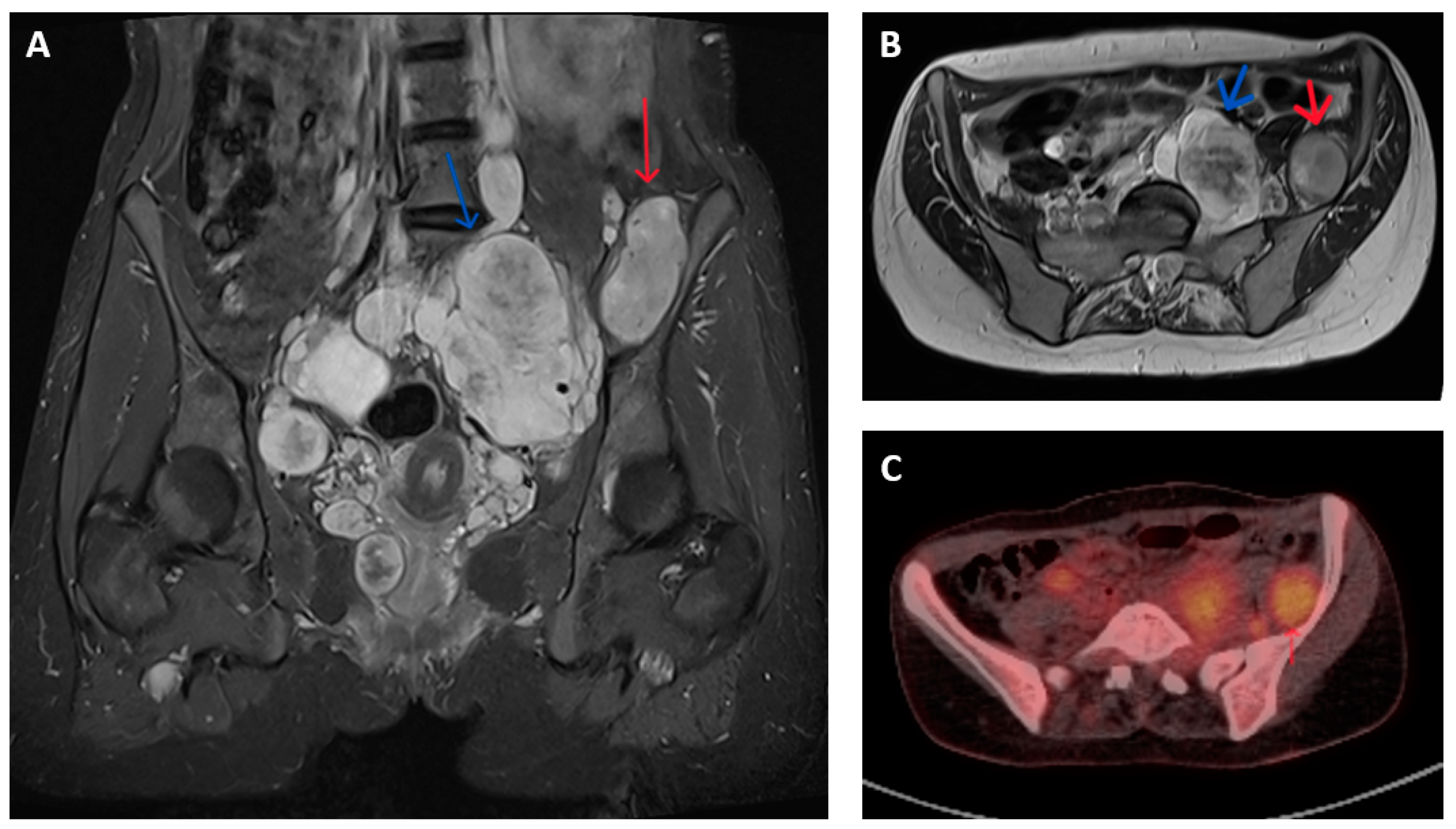
2.2. Imaging Characteristics
2.3. Histology and Molecular Pathology
3. Multimodality Management of MPNSTs
4. Localized MPNST
5. Local Recurrence
6. Inoperable or Metastatic Disease
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amirian, E.S.; Goodman, J.C.; New, P.; Scheurer, M.E. Pediatric and adult malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: An analysis of data from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 116, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Baser, M.E.; McGaughran, J.; Sharif, S.; Howard, E.; Moran, A. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in neurofibromatosis. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 39, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, R.G.; Guha, A. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 15, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutmann, D.H.; Ferner, R.E.; Listernick, R.H.; Korf, B.R.; Wolters, P.L.; Johnson, K.J. Neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, M.; Høland, M.; Ågesen, T.H.; Brekke, H.R.; Liestøl, K.; Hall, K.S.; Mertens, F.; Picci, P.; Smeland, S.; Lothe, R.A. Survival meta-analyses for >1800 malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor patients with and without neurofibromatosis type 1. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.M.; Antonescu, C.R.; Fletcher, C.D.; Kim, A.; Lazar, A.J.; Quezado, M.M.; Reilly, K.M.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Stewart, D.R.; Viskochil, D.; et al. Histopathologic evaluation of atypical neurofibromatous tumors and their transformation into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor in patients with neurofibromatosis 1—A consensus overview. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legius, E.; Messiaen, L.; Wolkenstein, P.; Pancza, P.; Avery, R.A.; Berman, Y.; Blakeley, J.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Cunha, K.S.; Ferner, R.; et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis type 1 and Legius syndrome: An international consensus recommendation. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucky, C.-C.H.; Johnson, K.N.; Gray, R.J.; Pockaj, B.A.; Ocal, I.T.; Rose, P.S.; Wasif, N. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST): The Mayo Clinic experience. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 19, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.D.; Shaigany, K.; Fang, C.H.; Park, R.C.; Baredes, S.; Eloy, J.A. Comparative Analysis of Head and Neck and Non–Head and Neck Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, C.J.; Strauss, D.C.; Bonvalot, S.; Rutkowski, P.; Desai, A.; Gladdy, R.A.; Gonzalez, R.; Gyorki, D.E.; Fairweather, M.; van Houdt, W.J.; et al. Management of Primary Retroperitoneal Sarcoma (RPS) in the Adult: An Updated Consensus Approach from the Transatlantic Australasian RPS Working Group. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 7873–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeyrie-Allanore, L.; Ismaili, N.; Bastuji-Garin, S.; Zeller, J.; Wechsler, J.; Revuz, J.; Wolkenstein, P. Symptoms associated with malignancy of peripheral nerve sheath tumours: A retrospective study of 69 patients with neurofibromatosis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demehri, S.; Belzberg, A.; Blakeley, J.; Fayad, L.M. Conventional and Functional MR Imaging of Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors: Initial Experience. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumine, A.; Kusuzaki, K.; Nakamura, T.; Nakazora, S.; Niimi, R.; Matsubara, T.; Uchida, K.; Murata, T.; Kudawara, I.; Ueda, T.; et al. Differentiation between neurofibromas and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in neurofibromatosis 1 evaluated by MRI. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.; Geitenbeek, R.T.J.; Coert, J.H.; Hanff, D.F.; Graven, L.H.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Verhoef, C.; Taal, W. A Bayesian approach for diagnostic accuracy of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasa, J.; Nishida, Y.; Tsukushi, S.; Shido, Y.; Sugiura, H.; Nakashima, H.; Ishiguro, N. MRI features in the differentiation of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors and neurofibromas. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.N.; Lu, Q.R. Therapeutic Targets for Malignant Peripheral nerve Sheath Tumors. Future Neurol. 2019, 14, FNL7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.A.; Slavc, I.; Theisen, B.E.; Rausch, I.; Weber, M.; Happak, W.; Aszmann, O.; Hojreh, A.; Peyrl, A.; Amann, G.; et al. Monitoring of plexiform neurofibroma in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1 by [18F]FDG-PET imaging. Is it of value in asymptomatic patients? Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzaczy, D.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Azizi, A.A.; Haug, A.R.; Senn, D.; Beitzke, D.; Weber, M.; Traub-Weidinger, T. Does elevated glucose metabolism correlate with higher cell density in Neurofibromatosis type 1 associated peripheral nerve sheath tumors? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertitta, L.; Jannic, A.; Zehou, O.; Bergqvist, C.; Ferkal, S.; Moryousef, S.; Lerman, L.; Mulé, S.; Luciani, A.; Bapst, B.; et al. Whole-Body Positron Emission Tomography with 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose/Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Screening Tool for the Detection of Malignant Transformation in Individuals with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 1754–1761.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurlock, G.; Knight, S.J.L.; Thomas, N.; Kiehl, T.-R.; Guha, A.; Upadhyaya, M. Molecular evolution of a neurofibroma to malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) in an NF1 patient: Correlation between histopathological, clinical and molecular findings. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.S.; Russell, T.A.; Eckardt, M.A.; Motamedi, K.; Seeger, L.L.; Singh, A.S.; Bernthal, N.M.; Kalbasi, A.; Dry, S.M.; Nelson, S.D.; et al. Oncologic Accuracy of Image-guided Percutaneous Core-Needle Biopsy of Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors at a High-volume Sarcoma Center. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmi, M.; Thiesse, P.; Ranchere, D.; Mognetti, T.; Pinson, S.; Renard, C.; Decouvelaere, A.-V.; Blay, J.-Y.; Combemale, P. Diagnostic Accuracy of PET/CT-Guided Percutaneous Biopsies for Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovronsky, D.M.; Oberholtzer, J.C. Pathologic classification of peripheral nerve tumors. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 15, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Pekmezci, M.; Folpe, A.L.; Ersen, A.; Horvai, A.E. Diagnostic utility of SOX10 to distinguish malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor from synovial sarcoma, including intraneural synovial sarcoma. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coindre, J.-M.; Terrier, P.; Guillou, L.; Le Doussal, V.; Sastre, X.; Vilain, M.-O.; Bui, B.N.; Collin, F.; Ranchère, D.; Bonichon, F. Predictive value of grade for metastasis development in the main histologic types of adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer 2001, 91, 1914–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, T.; Perez-Piñera, P.; Díaz-Esnal, B.; Vega, J. S-100 proteins in the human peripheral nervous system. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 60, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Kuroda, M.; Nagasaka, T.; Hara, K.; Takahashi, E.; Hayakawa, S.; Ono, K.; Maeda, N.; Mori, N.; et al. Nestin expression as a new marker in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Pathol. Int. 2007, 57, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottillo, I.; Ahlquist, T.; Brekke, H.; Danielsen, S.A.; Berg, E.v.D.; Mertens, F.; Lothe, R.A.; Dallapiccola, B. Germline and somatic NF1 mutations in sporadic and NF1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours. J. Pathol. 2009, 217, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Roman, R.J.; Burks, S.S.; Debs, L.; Cajigas, I.; Levi, A.D. The Risk of Peripheral Nerve Tumor Biopsy in Suspected Benign Etiologies. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, E326–E332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzar, B.; Shanesmith, R.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Fisher, C.; Calonje, E. Cutaneous epithelioid malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour: A clinicopathological analysis of 11 cases. Histopathology 2016, 68, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Ayyanar, P.; Padhi, S.; Purkait, S.; Muduly, D.K.; Samal, S.C. Epithelioid Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (Epithelioid-MPNST) Presenting as Bleeding Rectal Polyp: A Case Report with Systematic Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2019, 20, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thway, K.; Fisher, C. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: Pathology and genetics. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 18, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Spurlock, G.; Monem, B.; Thomas, N.; Friedrich, R.E.; Kluwe, L.; Mautner, V. Germline and somatic NF1 gene mutations in plexiform neurofibromas. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, E103–E111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Kluwe, L.; Spurlock, G.; Monem, B.; Majounie, E.; Mantripragada, K.; Ruggieri, M.; Chuzhanova, N.; Evans, D.; Ferner, R.; et al. Germline and somatic NF1 gene mutation spectrum in NF1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNSTs). Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Spurlock, G.; Kluwe, L.; Chuzhanova, N.; Bennett, E.; Thomas, N.; Guha, A.; Mautner, V. The spectrum of somatic and germline NF1 mutations in NF1 patients with spinal neurofibromas. Neurogenetics 2009, 10, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.; Tovell, H.; Frayling, I.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Upadhyaya, M. The NF1 somatic mutational landscape in sporadic human cancers. Hum. Genom. 2017, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Verdijk, R.M.; Bakker, M.A.D.; Dubbink, H.J.; Hop, W.C.J.; Dinjens, W.N.M.; Kros, J.M. TP53 mutation analysis of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirbe, A.C.; Dahiya, S.; Miller, C.A.; Li, T.; Fulton, R.S.; Zhang, X.; McDonald, S.; DeSchryver, K.; Duncavage, E.J.; Walrath, J.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals the Order of Genetic Changes during Malignant Transformation and Metastasis in a Single Patient with NF1-plexiform Neurofibroma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4201–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Huson, S.M.; Birch, J.M. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in inherited disease. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2012, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichowski, K.; Shih, T.S.; Schmitt, E.; Santiago, S.; Reilly, K.; McLaughlin, M.E.; Bronson, R.T.; Jacks, T. Mouse models of tumor development in neurofibromatosis type 1. Science 1999, 286, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, G.P.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Ino, Y.; Møller, M.B.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Louis, D.N. Malignant transformation of neurofibromas in neurofibromatosis 1 is associated with CDKN2A/p16 inactivation. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beert, E.; Brems, H.; Daniëls, B.; De Wever, I.; Van Calenbergh, F.; Schoenaers, J.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Gevaert, O.; De Raedt, T.; van den Bruel, A.; et al. Atypical neurofibromas in neurofibromatosis type 1 are premalignant tumors. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2011, 50, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemov, A.; Li, H.; Presley, W.; Wallace, M.R.; Miller, D.T. Genetics of human malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2 (Suppl. S1), i50–i61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemov, A.; Hansen, N.F.; Sindiri, S.; Patidar, R.; Higham, C.S.; Dombi, E.; Miettinen, M.M.; Fetsch, P.; Brems, H.; Chandrasekharappa, S.C.; et al. Low mutation burden and frequent loss of CDKN2A/B and SMARCA2, but not PRC2, define premalignant neurofibromatosis type 1-associated atypical neurofibromas. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Teckie, S.; Wiesner, T.; Ran, L.; Granada, C.N.P.; Lin, M.; Zhu, S.; Cao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Sboner, A.; et al. PRC2 is recurrently inactivated through EED or SUZ12 loss in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Raedt, T.; Beert, E.; Pasmant, E.; Luscan, A.; Brems, H.; Ortonne, N.; Helin, K.; Hornick, J.L.; Mautner, V.; Kehrer-Sawatzki, H.; et al. PRC2 loss amplifies Ras-driven transcription and confers sensitivity to BRD4-based therapies. Nature 2014, 514, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Jones, S.; Sausen, M.; McMahon, K.; Sharma, R.; Wang, Q.; Belzberg, A.J.; Chaichana, K.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. Somatic mutations of SUZ12 in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.G. Vemurafenib Treatment of BRAF V600E-Mutated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2013, 11, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, E.Y.; Wakeman, K.M.; Wu, Y.; Gross, J.M.; Chen, E.Y.; Ricciotti, R.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Mantilla, J.G. Prevalence and detection of actionable BRAF V600 and NRAS Q61 mutations in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor by droplet digital PCR. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 129, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery, A.; Clayburgh, D. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: Analysis of the national cancer database. Oral. Oncol. 2019, 98, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gachiani, J.; Kim, D.; Nelson, A.; Kline, D. Surgical management of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neurosurg. Focus. 2007, 22, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baehring, J.M.; Betensky, R.A.; Batchelor, T.T. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: The clinical spectrum and outcome of treatment. Neurology 2003, 61, 696–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tang, X.; Liang, H.; Yang, R.; Yan, T.; Guo, W. Prognosis and risk factors for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Casanova, M.; Bisogno, G.; Mattke, A.; Meazza, C.; Gandola, L.; Sotti, G.; Cecchetto, G.; Harms, D.; Koscielniak, E.; et al. Clear cell sarcoma of tendons and aponeuroses in pediatric patients: A report from the Italian and German Soft Tissue Sarcoma Cooperative Group. Cancer 2002, 94, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagars, G.K.; Ballo, M.T.; Pisters, P.W.T.; Pollock, R.E.; Patel, S.R.; Benjamin, R.S. Surgical margins and reresection in the management of patients with soft tissue sarcoma using conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer 2003, 97, 2544–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggermont, A.A.; Koops, H.S.H.; Klausner, J.J.; Kroon, B.B.; Schlag, P.M.; Liénard, D.; Van Geel, A.A.; Hoekstra, H.H.; Meller, I.I.; Nieweg, O.O.; et al. Isolated limb perfusion with tumor necrosis factor and melphalan for limb salvage in 186 patients with locally advanced soft tissue extremity sarcomas: The cumulative multicenter European experience. Ann. Surg. 1996, 224, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ginkel, R.J.; Thijssens, K.M.J.; Pras, E.; van der Graaf, W.T.A.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Hoekstra, H.J. Isolated limb perfusion with tumor necrosis factor alpha and melphalan for locally advanced soft tissue sarcoma: Three time periods at risk for amputation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvalot, S.; Laplanche, A.; Lejeune, F.; Stoeckle, E.; Le Péchoux, C.; Vanel, D.; Terrier, P.; Lumbroso, J.; Ricard, M.; Antoni, G.; et al. Limb salvage with isolated perfusion for soft tissue sarcoma: Could less TNF-alpha be better? Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelov, L.; Davis, A.; O’Sullivan, B.; Bell, R.; Guha, A. Neurogenic Sarcomas: Experience at the University of Toronto. Neurosurgery 1998, 43, 56–64, discussion 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.K.; Hahn, S.M.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.K.; Shin, K.; Suh, C.O.; Lyu, C.J.; Han, J.W. Outcomes of Treatment for Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors: Different Clinical Features Associated with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, G.P.; Spiliopoulos, K.; Plotkin, S.R.; Hornicek, F.J.; Harmon, D.C.; Delaney, T.F.; Williams, Z. Role of resection of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.; Dullaart, M.J.; van de Sande, M.A.; van Houdt, W.J.; Schellekens, P.P.; Coert, J.H. Resuscitating extremities after soft tissue sarcoma resections: Are functional reconstructions an overlooked option in limb salvage? A systematic review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundinger, G.S.; Prucz, R.B.; Frassica, F.J.; Deune, E.G. Concomitant Upper Extremity Soft Tissue Sarcoma Limb-Sparing Resection and Functional Reconstruction: Assessment of Outcomes and Costs of Surgery. HAND 2014, 9, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.; Dullaart, M.J.; Verhoef, C.; Coert, J.H. A systematic review of functional outcomes after nerve reconstruction in extremity soft tissue sarcomas: A need for general implementation in the armamentarium. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, K.; Ihara, K.; Doi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Iwanaga, R.; Hashimoto, T.; Taguchi, T. Functional neuro-vascularized muscle transfer for oncological reconstruction of extremity sarcoma. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 21, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Wang, H.; Jacobson, A.; Lietz, A.P.; Choy, E.; Raskin, K.A.; Schwab, J.H.; Deshpande, V.; Nielsen, G.P.; DeLaney, T.F.; et al. Radiation-induced and neurofibromatosis-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) have worse outcomes than sporadic MPNST. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.; Coert, J.H.; Flucke, U.E.; Slooff, W.-B.M.; Ho, V.K.; van der Graaf, W.T.; van Dalen, T.; van de Sande, M.A.; van Houdt, W.J.; Grünhagen, D.J.; et al. A nationwide cohort study on treatment and survival in patients with malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 124, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, T.; Le Cesne, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Italiano, A.; Decanter, G.; Bompas, E.; Isambert, N.; Thariat, J.; Linassier, C.; Bertucci, F.; et al. Management and prognosis of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: The experience of the French Sarcoma Group (GSF-GETO). Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 56, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanniec, K.J.; Velazco, C.S.; Bryant, L.A.; Zhang, N.; Casey, W.J., III; Mahabir, R.C.; Rebecca, A.M. Immediate versus Delayed Sarcoma Reconstruction: Impact on Outcomes. Sarcoma 2016, 2016, 7972318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marré, D.; Buendía, J.; Hontanilla, B. Complications Following Reconstruction of Soft-Tissue Sarcoma. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2012, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, G.P.; Schusterman, M.A.; Pollock, R.E.; Kroll, S.S.; Miller, M.J.; Baldwin, B.J.; Romsdahl, M.M.; Janjan, N.A. Immediate versus delayed free-tissue transfer salvage of the lower extremity in soft tissue sarcoma patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 1994, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, L.; Terezakis, S.; Blakeley, J.; Slobogean, B.; Kleinberg, L. Long-Term Outcomes of Radiation Therapy (RT) in the Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST) in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, e474–e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.; Gillespie, A.; Tsokos, M.; Ondos, J.; Dombi, E.; Camphausen, K.; Widemann, B.C.; Kaushal, A. Radiation therapy in management of sporadic and neurofibromatosis type 1-associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, A.J.; Zagars, G.K.; Torres, K.E.; Bird, J.E.; Feig, B.W.; Guadagnolo, B.A. Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors: A Single Institution’s Experience Using Combined Surgery and Radiation Therapy. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Eisenberg, B.L.; Kane, J.M.; Li, X.A.; Lucas, D.; Petersen, I.A.; DeLaney, T.F.; Freeman, C.R.; Finkelstein, S.E.; et al. Significant Reduction of Late Toxicities in Patients With Extremity Sarcoma Treated With Image-Guided Radiation Therapy to a Reduced Target Volume: Results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group RTOG-0630 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.W.; Hirose, T.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Schild, S.E.; Gunderson, L.L. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: Analysis of treatment outcome. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1998, 42, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisters, P.W.; Harrison, L.B.; Leung, D.H.; Woodruff, J.M.; Casper, E.S.; Brennan, M.F. Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in soft tissue sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, M.; Ferrari, A.; Mattke, A.; Zanetti, I.; Casanova, M.; Bisogno, G.; Cecchetto, G.; Alaggio, R.; De Sio, L.; Koscielniak, E.; et al. Pediatric malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor: The Italian and German soft tissue sarcoma cooperative group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8422–8430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Miceli, R.; Rey, A.; Oberlin, O.; Orbach, D.; Brennan, B.; Mariani, L.; Carli, M.; Bisogno, G.; Cecchetto, G.; et al. Non-metastatic unresected paediatric non-rhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue sarcomas: Results of a pooled analysis from United States and European groups. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroep, J.R.; Ouali, M.; Gelderblom, H.; Le Cesne, A.; Dekker, T.J.A.; Van Glabbeke, M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; Hohenberger, P. First-line chemotherapy for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) versus other histological soft tissue sarcoma subtypes and as a prognostic factor for MPNST: An EORTC soft tissue and bone sarcoma group study. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunello, A.; Rizzato, M.D.; Rastrelli, M.; Roma, A.; Maruzzo, M.; Basso, U.; Fiduccia, P.; Buzzaccarini, M.S.; Scarzello, G.; Rossi, C.R.; et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for soft tissue sarcomas: A 10-year mono-institutional experience. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spunt, S.L.; Million, L.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Anderson, J.; Tian, J.; Hibbitts, E.; Coffin, C.; McCarville, M.B.; Randall, R.L.; Parham, D.M.; et al. A risk-based treatment strategy for non-rhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcomas in patients younger than 30 years (ARST0332): A Children’s Oncology Group prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Noesel, M.M.; Orbach, D.; Brennan, B.; Kelsey, A.; Zanetti, I.; de Salvo, G.L.; Gaze, M.N.; Craigie, R.J.; McHugh, K.; Francotte, N.; et al. Outcome and prognostic factors in pediatric malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: An analysis of the European Pediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Group (EpSSG) NRSTS-2005 prospective study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervaiz, N.; Colterjohn, N.; Farrokhyar, F.; Tozer, R.; Figueredo, A.; Ghert, M. A systematic meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2008, 113, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, C.S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Dombi, E.; Perry, A.; Helman, L.J.; Schuetze, S.M.; Ludwig, J.A.; Staddon, A.; Milhem, M.M.; Rushing, D.; et al. SARC006: Phase II Trial of Chemotherapy in Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Associated Chemotherapy-Naive Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Sarcoma 2017, 2017, 8685638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansma, C.Y.M.N.; Acem, I.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Verhoef, C.; Martin, E.; Collaborators, M.; Coert, J.H.; Flucke, U.E.; Slooff, W.-B.M.; van Dalen, T.; et al. Local recurrence in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours: Multicentre cohort study. BJS Open 2024, 8, zrae024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Bowers, N.L.; Bulman, M.; Gokhale, C.; Wallace, A.J.; King, A.T.; Lloyd, S.K.; Rutherford, S.A.; Hammerbeck-Ward, C.L.; Freeman, S.R.; et al. Revisiting neurofibromatosis type 2 diagnostic criteria to exclude LZTR1-related schwannomatosis. Neurology 2017, 88, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Setsu, N.; Kohashi, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishii, T.; Iida, K.I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hakozaki, M.; Aoki, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways and Antitumor Effect of mTOR Inhibitor in NF1-Related and Sporadic Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirbe, A.C.; Cosper, P.F.; Dahiya, S.; Van Tine, B.A. Neoadjuvant Ifosfamide and Epirubicin in the Treatment of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Sarcoma 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, R.H.; Edmonson, J.; Ryan, L.; Pelletier, L. Efficacy of ifosfamide in combination with doxorubicin for the treatment of metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993, 31 (Suppl. S2), S238–S240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Meng, X.; Shi, B.; Shi, J.; Qin, Z.; Wei, P. A retroperitoneal NF1-independent malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor with elevated serum CA125: Case report and discussion. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 109, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahrmann, E.P.; Watson, A.L.; Keng, V.W.; Choi, K.; Moriarity, B.S.; Beckmann, D.A.; Wolf, N.K.; Sarver, A.; Collins, M.H.; Moertel, C.L.; et al. Forward genetic screen for malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor formation identifies new genes and pathways driving tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widemann, B.C.; Lu, Y.; Reinke, D.; Okuno, S.H.; Meyer, C.F.; Cote, G.M.; Chugh, R.; Milhem, M.; Hirbe, A.C.; Kim, A.; et al. Targeting Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) Related Refractory Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST) in a Phase II Study of Everolimus in Combination with Bevacizumab (SARC016). Sarcoma 2019, 2019, 7656747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farschtschi, S.; Kluwe, L.; Park, S.-J.; Oh, S.-J.; Mah, N.; Mautner, V.-F.; Kurtz, A. Upregulated immuno-modulator PD-L1 in malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors provides a potential biomarker and a therapeutic target. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, A.; Kang, S.P.; Rasco, D.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Elassaiss-Schaap, J.; Beeram, M.; Drengler, R.; Chen, C.; Smith, L.; Espino, G.; et al. Phase I Study of Pembrolizumab (MK-3475; Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibody) in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4286–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.N.; Hutzen, B.; Cripe, T.P. The quest for effective immunotherapies against malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: Is there hope? Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2023, 30, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Mahoney, M.R.; Van Tine, B.A.; Atkins, J.; Milhem, M.M.; Jahagirdar, B.N.; Antonescu, C.R.; Horvath, E.; Tap, W.D.; Schwartz, G.K.; et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab treatment for metastatic sarcoma (Alliance A091401): Two open-label, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Borcherding, D.C.; Amin, N.V.; He, K.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, Y.; Dehner, C.; Bhatia, H.; Gothra, A.; Daud, L.; Ruminski, P.; et al. MEK Inhibition Synergizes with TYK2 Inhibitors in NF1-Associated Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1592–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Porter, D.E.; Prasad, V.; Foster, L.; Dall, G.F.; Birch, R.; Grimer, R.J. Survival in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours: A Comparison between Sporadic and Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Tumours. Sarcoma 2009, 2009, 756395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, T.; Plante, C.; Brosseau, J.-P. Toward Understanding the Mechanisms of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trial ID | Design and Population | Agent | Molecular Targets | Trial Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04872543 | Phase II; PRC2 loss MPNST | Cedazuridine + Decitabine | PCR2 mutation | Active, recruiting |
| NCT02584647 | Phase II; any MPNST | Pexidartinib + Sirolimus | Multi-kinase inhibitor mTOR inhibitor | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02700230 | Phase I; any MPNST | MV-NIS | Oncolytic virus targeting NF1 tumour cells | Active, recruiting |
| NCT04917042 | Phase II; any MPNST | Tazemetostat | EZH2 inhibitor | Active, recruiting |
| NCT04465643 | Phase I; neoadjuvant pre-malignant/malignant MPNST | Nivolumab + Ipilimumab | Anti-PD1 + Anti-CTLA4 immune checkpoint inhibitors | Active, recruiting |
| NCT05253131 | Phase II; any MPNST | Selumetinib + BI + Durvalumab | MAPK/MEK inhibitor + Bromodomain inhibitor + anti-PD-L1 inhibitor | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT03611868 | Phase IB/II; any ≥12 years old MPNST | Alrizomadlin + Pembrolizumab | MDM2 inhibitor + anti-PD1 inhibitor | Active, recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seres, R.; Hameed, H.; McCabe, M.G.; Russell, D.; Lee, A.T.J. The Multimodality Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. Cancers 2024, 16, 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193266
Seres R, Hameed H, McCabe MG, Russell D, Lee ATJ. The Multimodality Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193266
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeres, Remus, Hassan Hameed, Martin G. McCabe, David Russell, and Alexander T. J. Lee. 2024. "The Multimodality Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193266
APA StyleSeres, R., Hameed, H., McCabe, M. G., Russell, D., & Lee, A. T. J. (2024). The Multimodality Management of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. Cancers, 16(19), 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193266






