Oligometastatic Urothelial Cancer and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review and an Updated Insight of Current Evidence and Future Directions
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
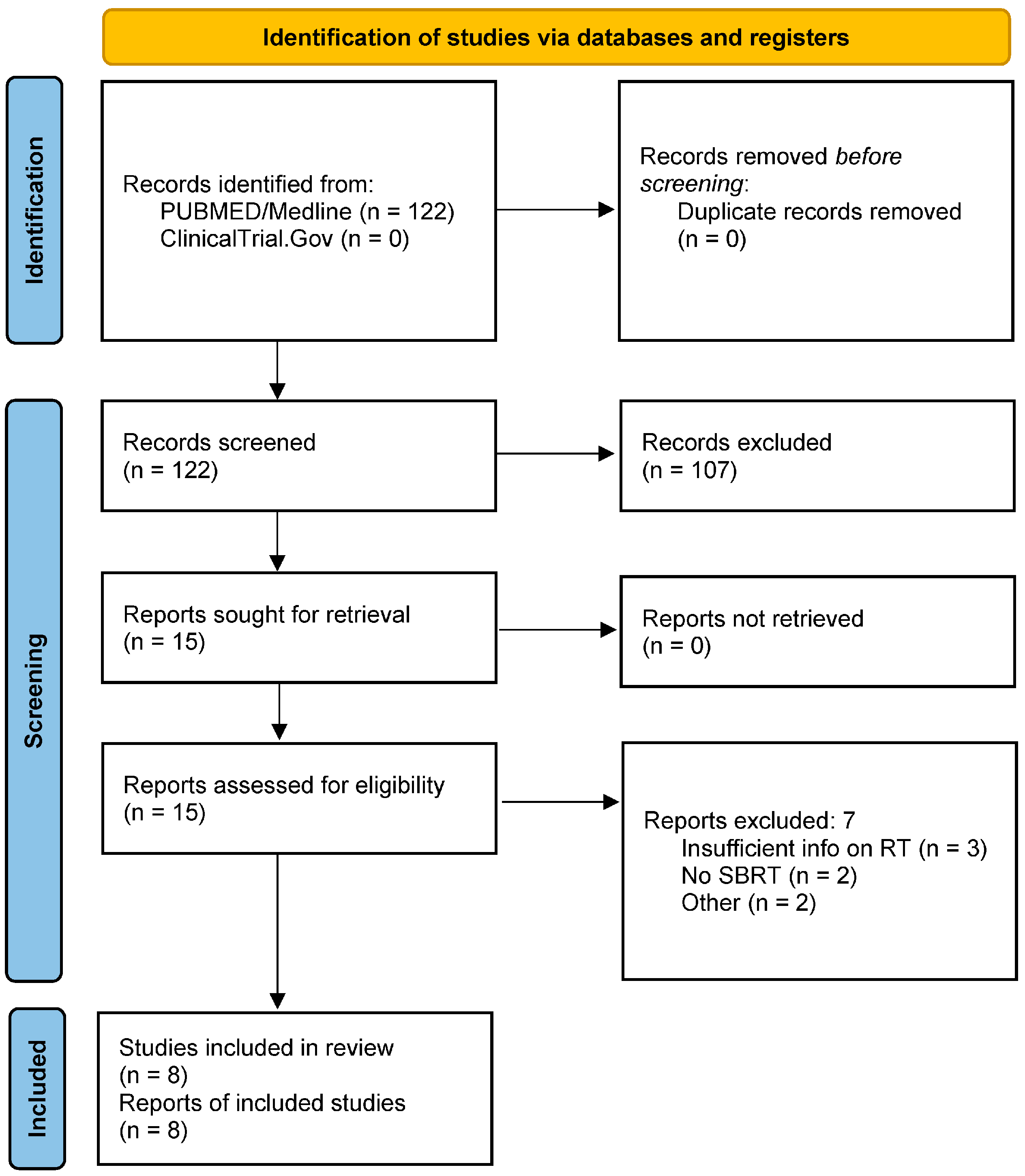
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, A.; Stenzl, A.; Zagouri, F.; Andrikopoulou, A.; Hoskin, P. Defining Oligometastatic Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2023, 55, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, A.; Stenzl, A.; Brown, S.L.; Albiges, L.; Babjuk, M.; Birtle, A.; Briganti, A.; Burger, M.; Choudhury, A.; Colecchia, M.; et al. Definition and Diagnosis of Oligometastatic Bladder Cancer: A Delphi Consensus Study Endorsed by the European Association of Urology, European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology, and European Society of Medical Oncology Genitourinary Faculty. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.A.; Tang, C.; Siva, S.; Berlin, A.; Hannan, R.; Warner, A.; Koontz, B.; De Meeleer, G.; Palma, D.; Ost, P.; et al. Review of Prospective Trials Assessing the Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Metastasis-directed Treatment in Oligometastatic Genitourinary Cancers. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2023, 6, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Valderrama, B.P.; Gupta, S.; Bedke, J.; Kikuchi, E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Iyer, G.; Vulsteke, C.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.J.; et al. Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab in Untreated Advanced Urothelial Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, S.; Choudhury, A.; Hoskin, P.; Song, Y.; Maitre, P. Radiotherapy in metastatic bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y. Introduction and History of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). In Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: Principles and Practices; Nagata, Y., Ed.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kavanagh, B.D.; McGarry, R.C.; Timmerman, R.D. Extracranial radiosurgery (stereotactic body radiation therapy) for oligometastases. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Sowden, A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Brennan, S.E.; Ellis, S.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Ryan, R.; Shepperd, S.; Thomas, J.; et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: Reporting guideline. BMJ 2020, 368, l6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, A.F.; Howard, J.M.; McLaughlin, M.; Meng, X.; Clinton, T.; Sanli, O.; Garant, A.; Bagrodia, A.; Margulis, V.; Lotan, Y.; et al. Metastasis-directed radiation therapy after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 790.e1–790.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboudaram, A.; Chaltiel, L.; Pouessel, D.; Graff-Cailleaud, P.; Benziane-Ouaritini, N.; Sargos, P.; Schick, U.; Crehange, G.; Cohen-Jonathan Moyal, E.; Chevreau, C.; et al. Consolidative Radiotherapy for Metastatic Urothelial Bladder Cancer Patients with No Progression and with No More than Five Residual Metastatic Lesions Following First-Line Systemic Therapy: A Retrospective Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augugliaro, M.; Marvaso, G.; Ciardo, D.; Zerini, D.; Riva, G.; Rondi, E.; Vigorito, S.; Comi, S.; De Cobelli, O.; Orecchia, R.; et al. Recurrent oligometastatic transitional cell bladder carcinoma: Is there room for radiotherapy? Neoplasma 2019, 66, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francolini, G.; Desideri, I.; Detti, B.; Di Cataldo, V.; Masi, L.; Caramia, G.; Visani, L.; Terziani, F.; Muntoni, C.; Lo Russo, M.; et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy in oligoprogressive and oligorecurrent urothelial cancer patients: A retrospective experience. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2019, 19, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzese, C.; Francolini, G.; Nicosia, L.; Alongi, F.; Livi, L.; Scorsetti, M. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in the Management of Oligometastatic and Oligoprogressive Bladder Cancer and Other Urothelial Malignancies. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundahl, N.; Vandekerkhove, G.; Decaestecker, K.; Meireson, A.; De Visschere, P.; Fonteyne, V.; De Maeseneer, D.; Reynders, D.; Goetghebeur, E.; Van Dorpe, J.; et al. Randomized Phase 1 Trial of Pembrolizumab with Sequential Versus Concomitant Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaas, M.; Sundahl, N.; Kruse, V.; Rottey, S.; De Maeseneer, D.; Duprez, F.; Lievens, Y.; Surmont, V.; Brochez, L.; Reynders, D.; et al. Checkpoint Inhibitors in Combination with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: The CHEERS Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; D’Abbiero, N.; Baldari, G.; Andreani, S.; Ruffini, L.; Viansone, A.A.; Buti, S. Radiotherapy for the treatment of distant nodes metastases from oligometastatic urothelial cancer: A retrospective case series. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 25, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, A.; Ost, P.; Sundahl, N. Is There a Benefit of Combining Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy in Bladder Cancer? Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Del-Alba, A.; Conde-Moreno, A.J.; Garcia Vicente, A.M.; Gonzalez-Peramato, P.; Linares-Espinos, E.; Climent, M.A.; The Sogug Multidisciplinary Working, G. Management of Patients with Metastatic Bladder Cancer in the Real-World Setting from the Multidisciplinary Team: Current Opinion of the SOGUG Multidisciplinary Working Group. Cancers 2022, 14, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Bellmunt, J.; Comperat, E.; De Santis, M.; Huddart, R.; Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Valderrama, B.P.; Ravaud, A.; Shariat, S.F.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline interim update on first-line therapy in advanced urothelial carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Carrión, A.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.M.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Fietkau, R.; Gakis, G.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Lorch, A.; et al. EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Available online: https://d56bochluxqnz.cloudfront.net/documents/full-guideline/EAU-Guidelines-on-Muscle-Invasive-and-Metastatic-Bladder-Cancer-2024.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Powles, T.; Assaf, Z.J.; Degaonkar, V.; Grivas, P.; Hussain, M.; Oudard, S.; Gschwend, J.E.; Albers, P.; Castellano, D.; Nishiyama, H.; et al. Updated Overall Survival by Circulating Tumor DNA Status from the Phase 3 IMvigor010 Trial: Adjuvant Atezolizumab Versus Observation in Muscle-invasive Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldan, J.D.; Schroeder, J.A.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Rathmell, W.K.; Milowsky, M.I.; Solnes, L.B.; Nimmagadda, S.; Gorin, M.A.; Khandani, A.H.; Rowe, S.P. PET/Computed Tomography Transformation of Oncology: Kidney and Urinary Tract Cancers. PET Clin. 2024, 19, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author, Year | Study Type | Population | Metastatic Setting | Sample Size | Intervention (Nr. of Patients) | BED10 Median, Gy (Range) | Comparison (Nr. of Patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 (Patient sample N ≥ 15) | |||||||
| Franzese, 2020 [17] | Retrospective, multicentric | omUC: ≤5 metastases | Synchronous 5%/ Metachronous 95% | 61 | SBRT +/− systemic treatment | 78 Gy (37.5–151 Gy) | N/A |
| Aboudaram, 2023 [14] | Retrospective, multicentric | omUC: ≤5 metastases after 1st line CT | Synchronous/ Metachronous | 91 | 1st line CT + RT (n = 51): -70% RT on bladder -SBRT (38 pts on 53 lesions) | 62 Gy ** | CT only (40) |
| Francolini, 2019 [16] | Retrospective, single-institution | omUC: ≤3 metastases | Metachronous | 19 | SBRT 60–18 Gy/8–1 fx +/− unspecified systemic treatment * | 48 Gy (37.5–105 Gy) | N/A |
| Miranda, 2021 [13] | Retrospective, Single institution | omUC: ≤5 lesions at the time or after cystectomy | Synchronous 6%/ Metachronous 94% | 52 | MDT SBRT: 16 pts Palliative RT 60%/ consolidative RT 40% | N/A SBRT = >6 Gy/fr, 5 or less fractions | N/A |
| Spaas, 2023 [19] | Phase II trial, randomized multicentric, | Limited metastatic HNSCC, NSCLC melanoma, RCC, UC | Synchronous/ Metachronous | 96 (UC:32 *) | SBRT 24 Gy/3 fx to 1–3 metastases and concurrent I.O. 2nd–3rd cycle (16 pts) | 43.2 Gy | Standard of care: I.O. monotherapy (16 patients) |
| Sundhal, 2019 [18] | Phase I Trial | Metastatic UC with no brain involvement | N/A | 18 * | SBRT 24 Gy/3 fx to 1 lesion concurrent to 2nd–3rd cycle I.O. | 43.2 Gy | SBRT 24 Gy/3 fx to 1 lesion prior to 1st cycle I.O. |
| Group 2 (Patient sample N < 15) | |||||||
| Augugliaro, 2018 [15] | Retrospective single-institution | omUC: ≤5 metastases (node, bone, or lung) | N/A | 13 | SBRT 36–20 Gy/5 fx (3–10 fx) | 35.7 Gy (28–60 Gy) | N/A |
| Leonetti, 2018 [20] | Retrospective single-institution | omUC: ≤3 metastases | Synchronous 14%/ Metachronous 86% | 7 | SBRT 40–25 Gy/5 fx +/− systemic treatment (CBCDA or CDDP/Gem) | 48 Gy (37.5–72 Gy) | N/A |
| Author, Year [Ref.] | Median FU Time, Range (Months) | Outcomes and Side Effects | Main Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local Control | Median PFS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | Toxicity (CTCAE v5.0) | |||
| Group 1 (Patient sample N > 15) | ||||||
| Franzese, 2020 [17] | 17.2 (3–91) | 1y-LC: 92%, 2y-LC: 88% | 10 1yPFS = 47% 2yPFS = 38% | 25.6 1yOS = 78.9% 2yOS = 50.7% | Acute/late: G > 3: 0/0 | 2yFFIT: 40% |
| Aboudaram, 2023 [14] | 85.9 (36–101) | N/A | 14.8 [I] vs. 9.7 [C] p = 0.08 | 29.7 [I] vs. 19.7 [C] p = 0.074 | Acute/late: G > 3: 0/0 | Whole population: OS: 21.7 M PFS: 11.1 M |
| Francolini, 2019 [16] | 11.5 (1–44) | 1y-LC: 68% | 5.6 | 13.8 | Acute/lateG > 3: 0/0 | ORR:40% |
| Miranda, 2021 [13] | 26.6 (18.1–39.5) | 1yLC = 72% | 8 Rates(%): 2yPFS = 19 | 51 Rates(%): 2yOS = 60 | Acute/late: G ≥ 3: 4% | |
| Spaas, 2023 [19] | 12.5 (0.7–46.2) | 1yLC = 76% § iCR = 16% § | 4.4 [I] vs. 2.8 [C] p = 0.82 § | 14.3 [I] vs. 11 [C] p = 0.47 § | G ≥ 3:18% no difference between arms | Absolute lymphocyte count changes: 3.0%[C] vs. −13.6%[I] p = 0.006 |
| Sundhal, 2019 [18] | 9 (4–14) | LCR: CR: <30% [C] vs. 50% [I] | 3.5 [I] vs. 3.3 [C] p = N/A | 12.1 [C] vs. 3.5 [I] p = N/A | Arm I = G1–2 vs. Arm C = G1 Overall G > 3 = 0 | ORR = 0[C] vs. 44%[I] 3PR, 1CR SD 50% in both arms |
| Group 2 (Patient sample N < 15) | ||||||
| Augugliaro, 2018 [15] | 25 (3–43) | 4 months LC: 57% (PR,CR,SD) | 4.2 | N/A | G > 2 = 0 | Local failure 9 pts: 6 pts in field + distant PD |
| Leonetti, 2018 [20] | Unclear (5–16) | 1yLC: 100% (PR,CR,SD) | 2.9 | 14 | G > 1 = 0 | LPFI > with 40 Gy/5 fx than with 25 Gy/5 fx |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angrisani, A.; Bosetti, D.G.; Vogl, U.M.; Castronovo, F.M.; Zilli, T. Oligometastatic Urothelial Cancer and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review and an Updated Insight of Current Evidence and Future Directions. Cancers 2024, 16, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183201
Angrisani A, Bosetti DG, Vogl UM, Castronovo FM, Zilli T. Oligometastatic Urothelial Cancer and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review and an Updated Insight of Current Evidence and Future Directions. Cancers. 2024; 16(18):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183201
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngrisani, Antonio, Davide Giovanni Bosetti, Ursula Maria Vogl, Francesco Mosè Castronovo, and Thomas Zilli. 2024. "Oligometastatic Urothelial Cancer and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review and an Updated Insight of Current Evidence and Future Directions" Cancers 16, no. 18: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183201
APA StyleAngrisani, A., Bosetti, D. G., Vogl, U. M., Castronovo, F. M., & Zilli, T. (2024). Oligometastatic Urothelial Cancer and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Systematic Review and an Updated Insight of Current Evidence and Future Directions. Cancers, 16(18), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183201






