Depiction of the Genetic Alterations and Molecular Landscapes of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Quality of Evidence
3. Results
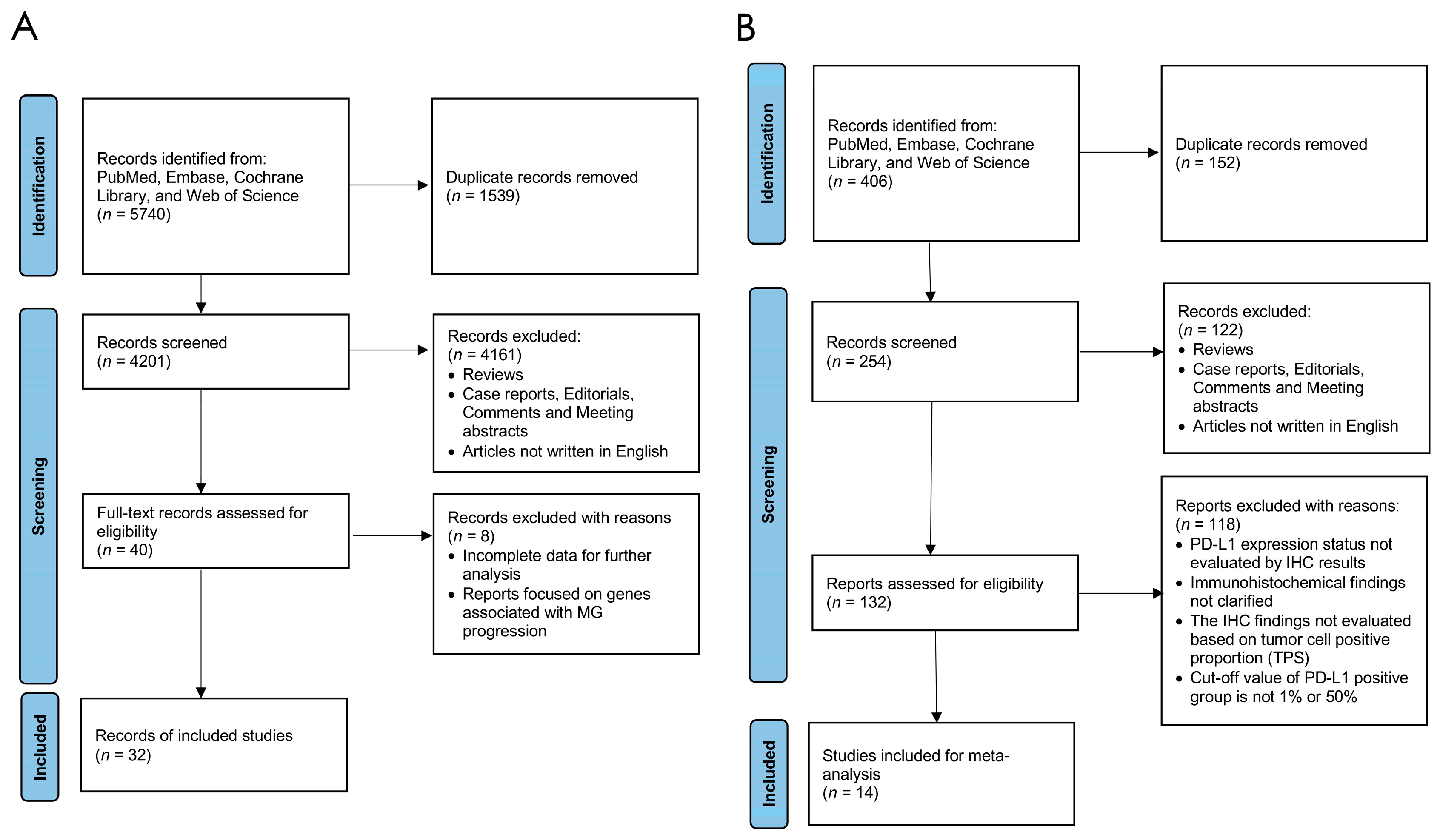
3.1. Literature Selection
3.2. Overall Characteristics
3.2.1. Gene Alteration Cohort
3.2.2. PD-L1 Expression Level Cohort
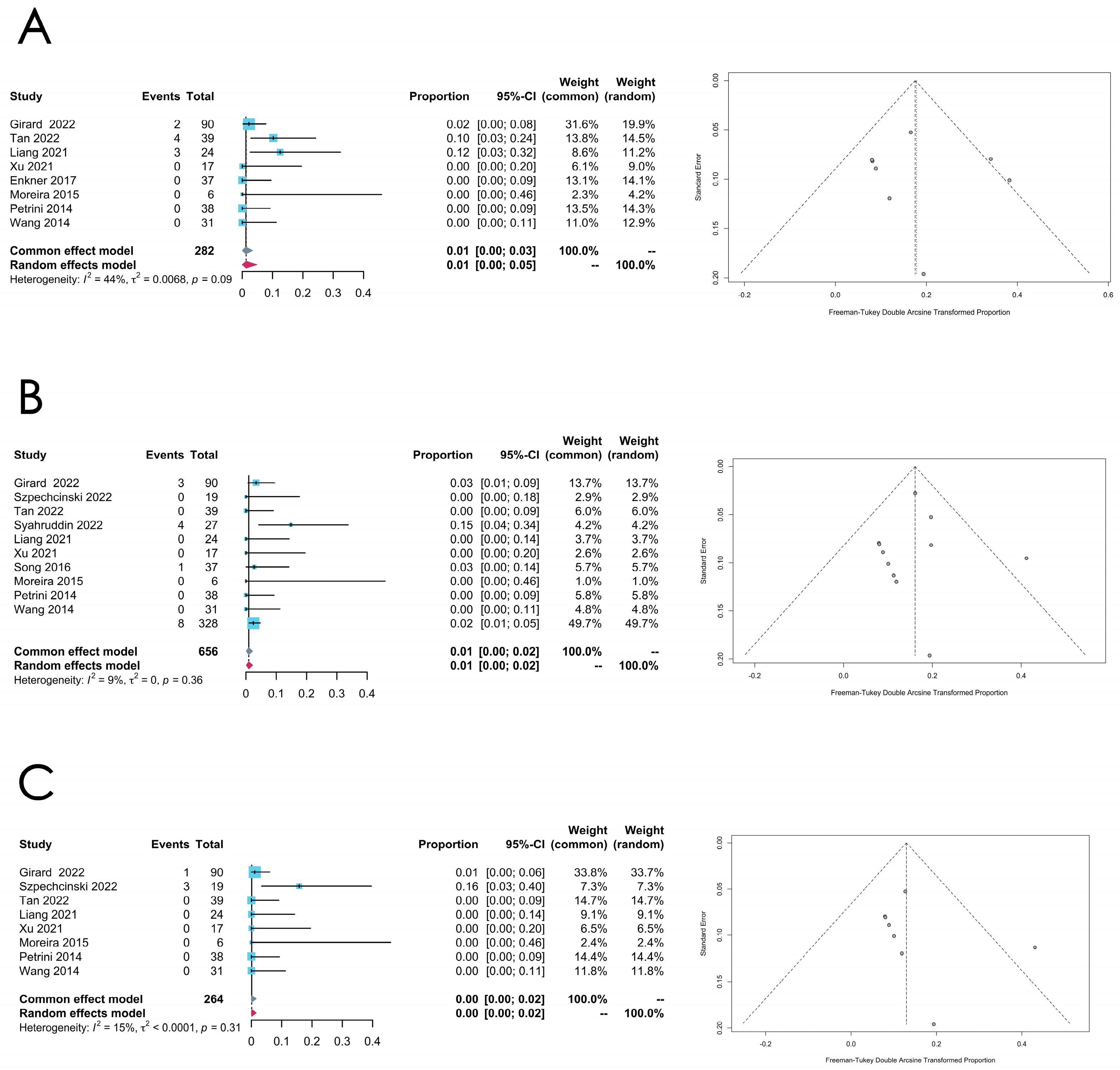
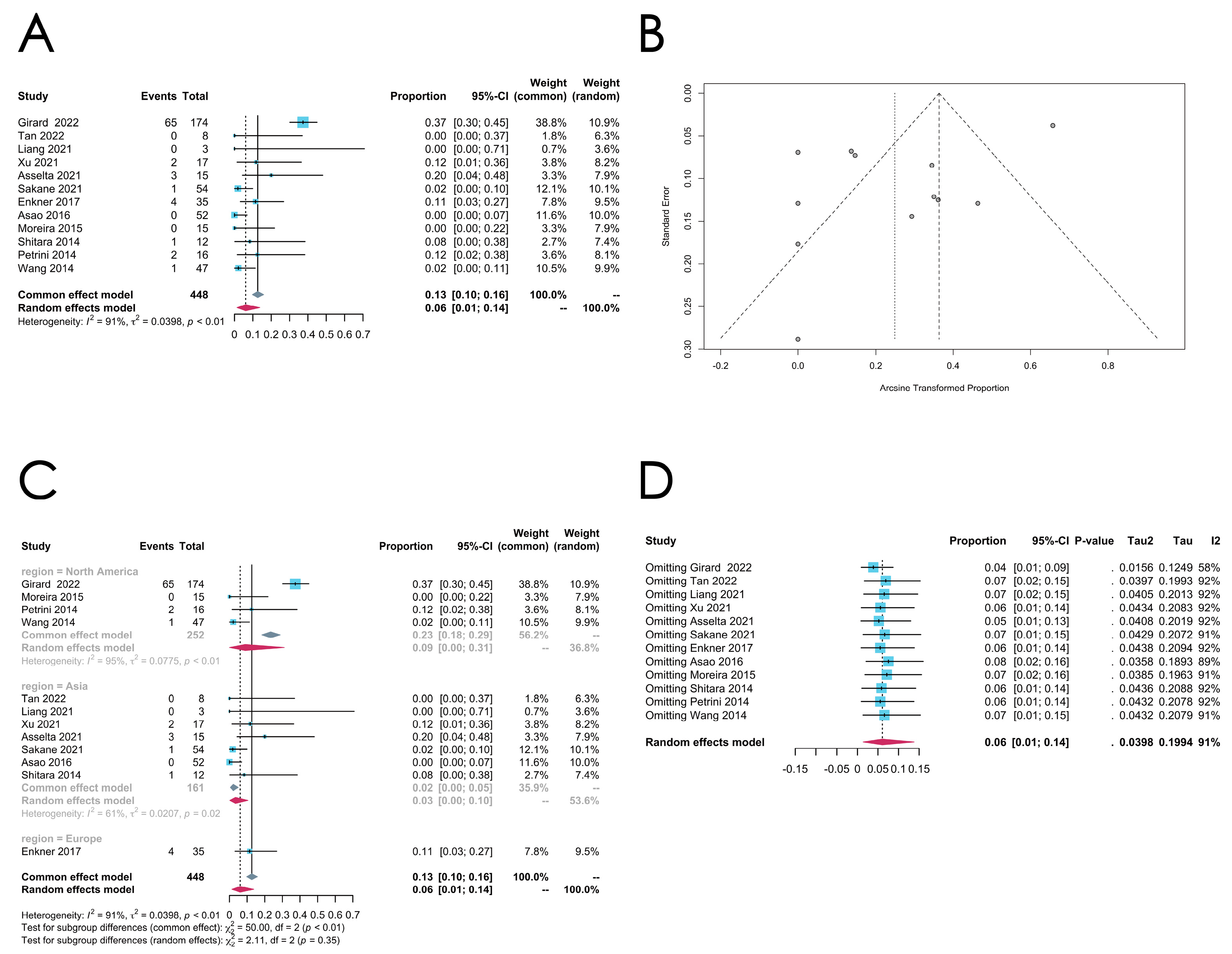
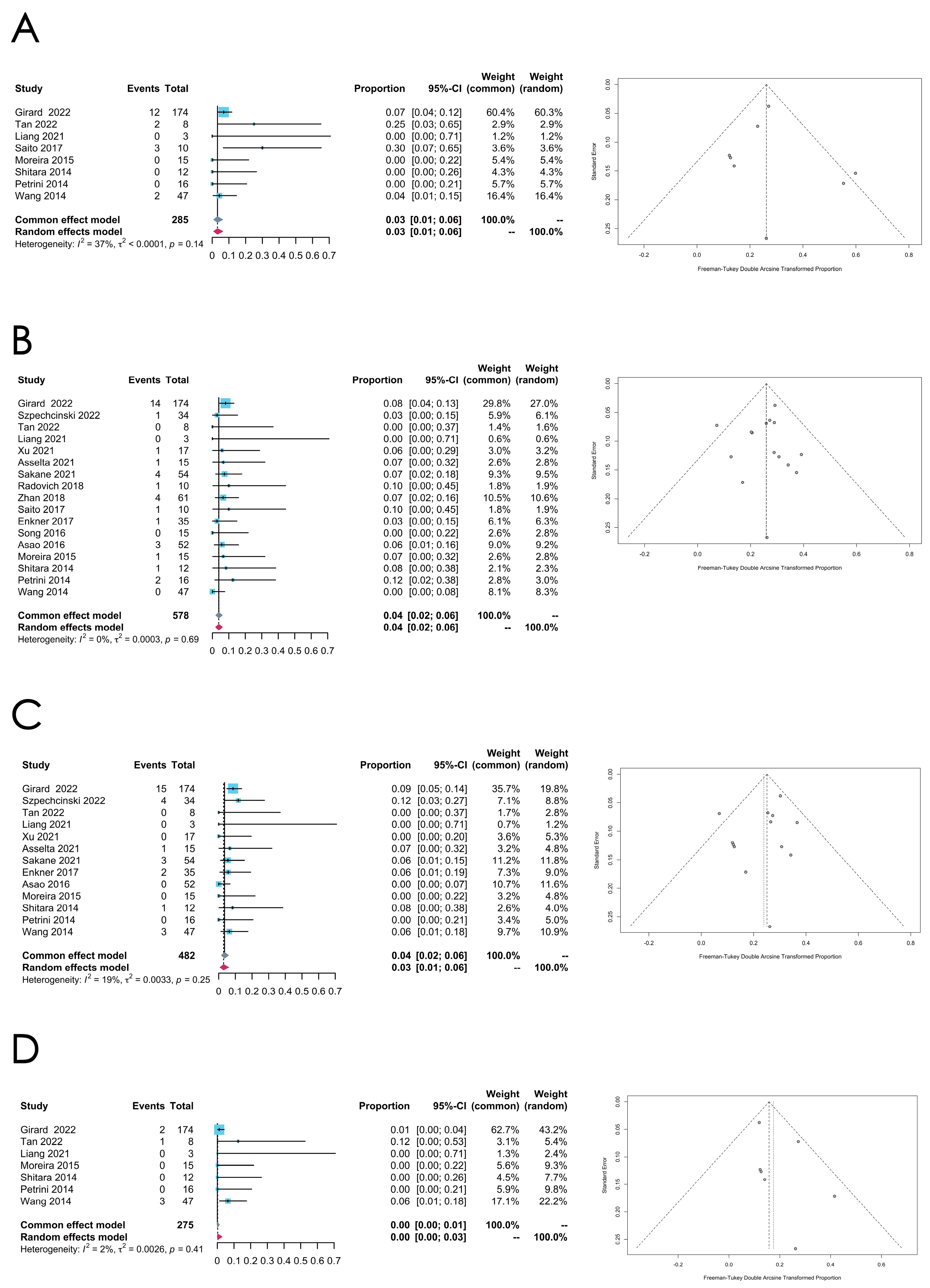
3.3. Meta-Analysis of Gene Mutational Landscape
3.3.1. Overall Mutation Rates
3.3.2. Thymoma
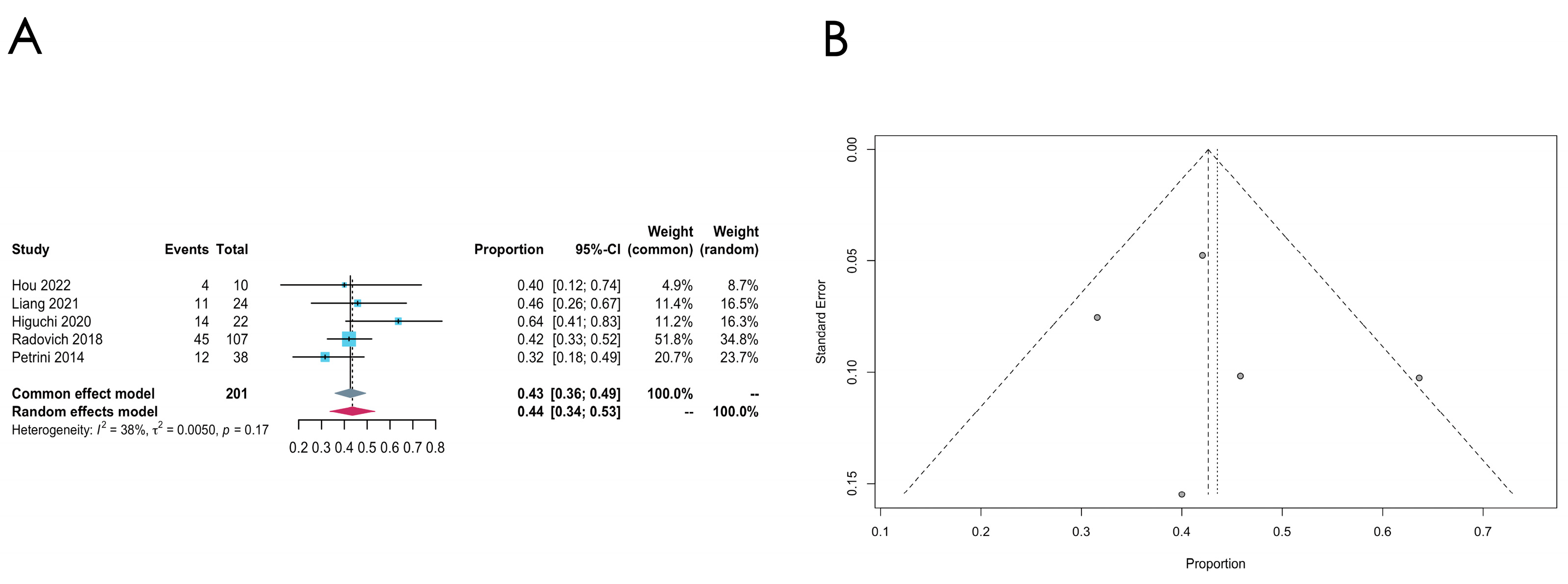
- GTF2I mutation
- TP53 mutation
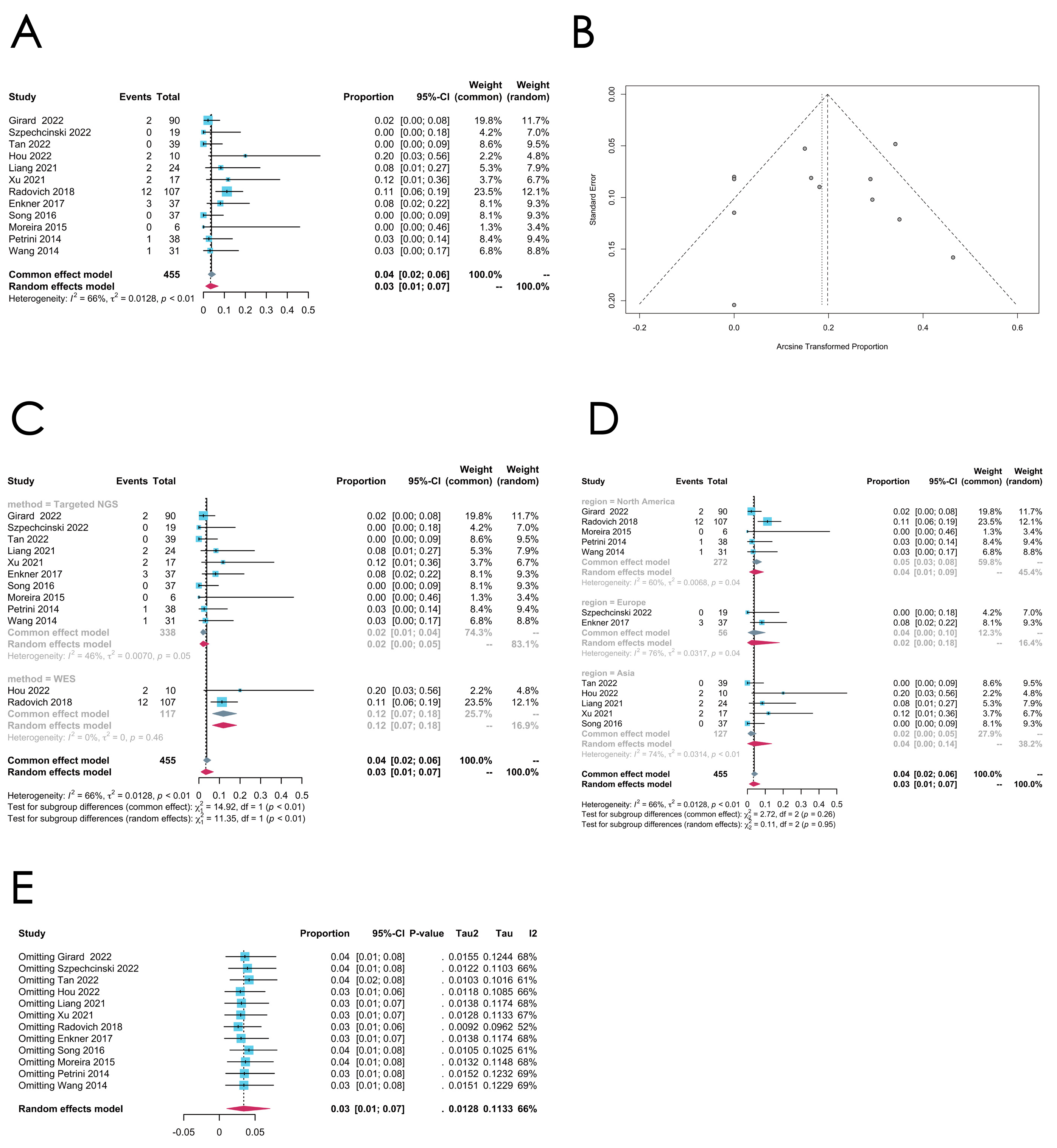
- RAS family gene mutation
3.3.3. Thymic Carcinoma
- TP53 mutation
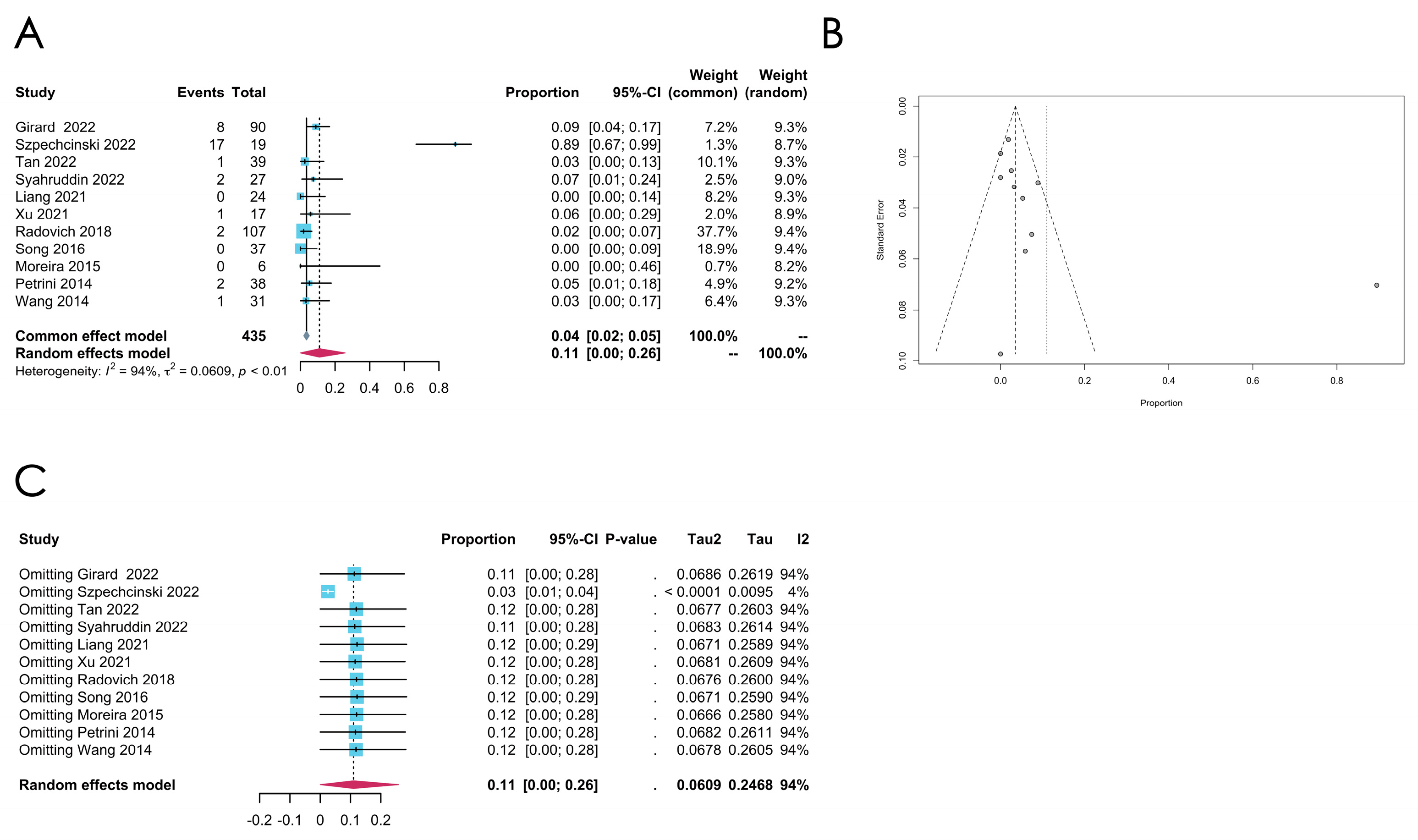
- CDKN2A mutation
- TET2 mutation
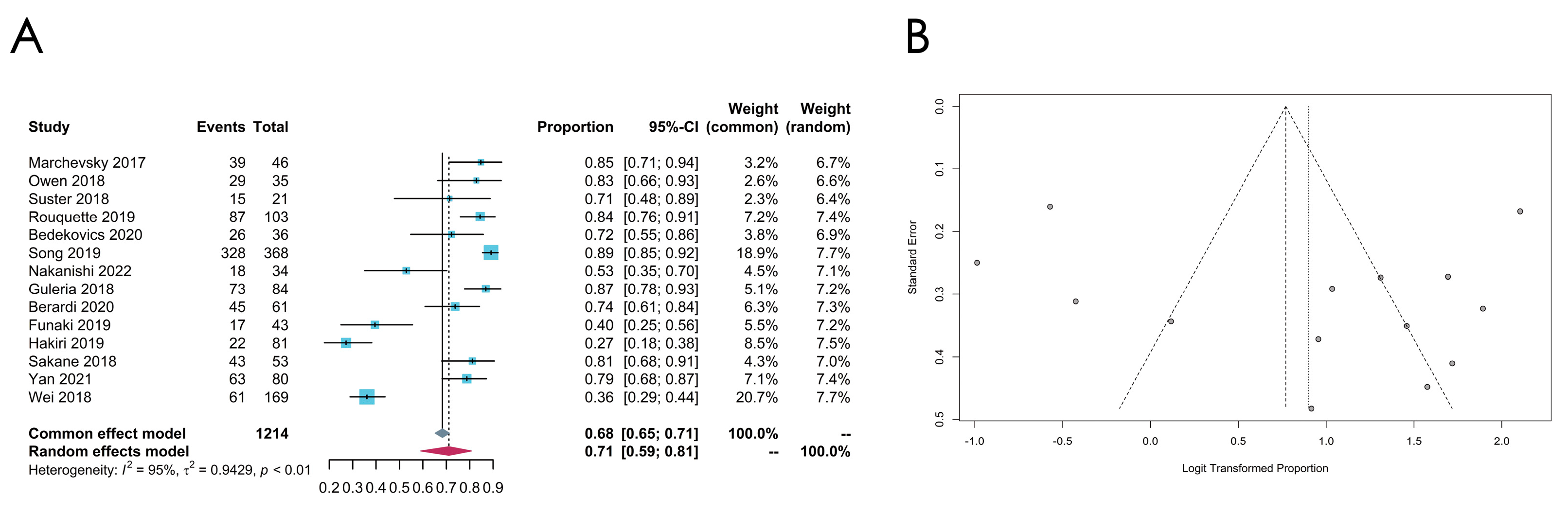
3.4. Meta-Analysis of the PD-L1 Expression Level
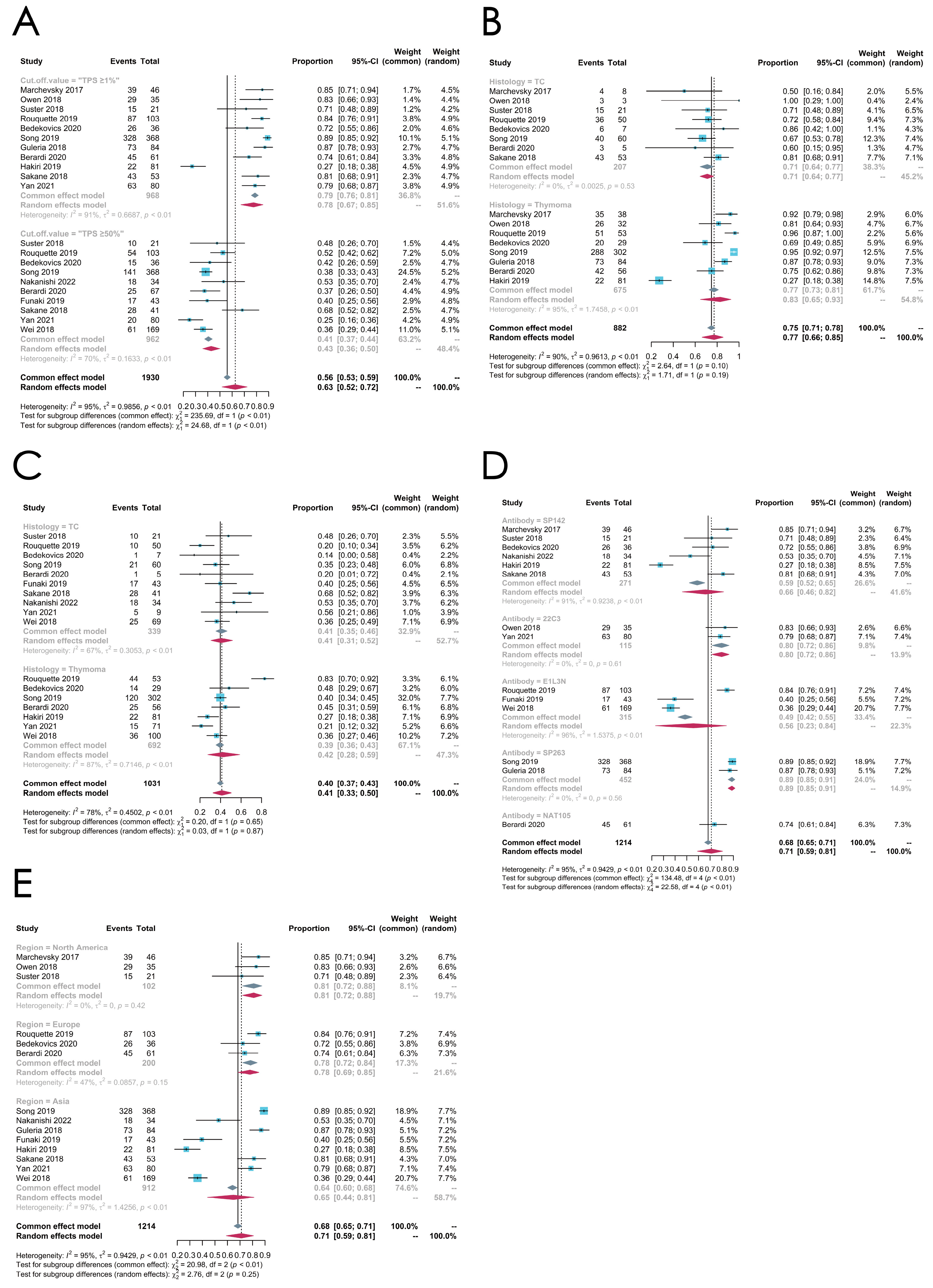
3.4.1. Overall PD-L1 Expression Status
3.4.2. Subgroup Analysis: Cut-Off Value
3.4.3. Subgroup Analysis: Histologic Subtypes
3.4.4. Subgroup Analysis: Antibodies
3.4.5. Subgroup Analysis: Regions
4. Discussion
4.1. Gene Alteration Landscape
4.2. PD-L1 Expression Levels
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Jong, W.K.; Blaauwgeers, J.L.G.; Schaapveld, M.; Timens, W.; Klinkenberg, T.J.; Groen, H.J.M. Thymic Epithelial Tumours: A Population-Based Study of the Incidence, Diagnostic Procedures and Therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1102–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, A.; Chan, J.K.C.; Chalabreysse, L.; Dacic, S.; Detterbeck, F.; French, C.A.; Hornick, J.L.; Inagaki, H.; Jain, D.; Lazar, A.J.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Thymus and Mediastinum: What Is New in Thymic Epithelial, Germ Cell, and Mesenchymal Tumors? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.W.; Cho, J.H.; Ha, J.; Jung, K.-W. Trends in Incidence and Survival of Patients With Thymic Epithelial Tumor in a High-Incidence Asian Country: Analysis of the Korean Central Cancer Registry 1999 to 2017. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkson, C.B.; Vella, E.T.; Ellis, P.M.; Maziak, D.E.; Ung, Y.C.; Yu, E. Surgical, Radiation, and Systemic Treatments of Patients With Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Rajan, A.; Berman, A.; Tomita, Y.; Brzezniak, C.; Lee, M.-J.; Lee, S.; Ling, A.; Spittler, A.J.; Carter, C.A.; et al. Sunitinib in Patients with Chemotherapy-Refractory Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma: An Open-Label Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Satouchi, M.; Itoh, S.; Okuma, Y.; Niho, S.; Mizugaki, H.; Murakami, H.; Fujisaka, Y.; Kozuki, T.; Nakamura, K.; et al. Lenvatinib in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Thymic Carcinoma (REMORA): A Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, H.S.; Ku, B.M.; Choi, Y.-L.; Cristescu, R.; Han, J.; Sun, J.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Patients With Refractory or Relapsed Thymic Epithelial Tumor: An Open-Label Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Auger, H.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Thermes, C. Ten Years of Next-Generation Sequencing Technology. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovich, M.; Pickering, C.R.; Felau, I.; Ha, G.; Zhang, H.; Jo, H.; Hoadley, K.A.; Anur, P.; Zhang, J.; McLellan, M.; et al. The Integrated Genomic Landscape of Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The History and Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy: Understanding the Characteristics of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Their Therapeutic Implications. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The Blockade of Immune Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Cheng, B.; Zhong, R.; Li, F.; Xiong, S.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and Tumor Mutation Burden as Pathological Response Biomarkers of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2022, 170, 103582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagir, E.K.; Acikalin, A.; Avci, A.; Gumurdulu, D.; Paydas, S. PD-1 and PD-L1 Expression in Thymic Epithelial Tumours and Non-Neoplastic Thymus. J. Clin. Pathol. 2018, 71, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissferdt, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Kalhor, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Bassett, R.; Wistuba, I.I.; Moran, C.A. Expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in Thymic Epithelial Neoplasms. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, G.; Kim, C.; Thompson, J.; McGuire, C.; Kallakury, B.; Chahine, J.J.; Manning, M.; Mogg, R.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Tan, M.T.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients with Thymic Carcinoma: A Single-Arm, Single-Centre, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.; Zucali, P.A.; Pala, L.; Catania, C.; Bagnardi, V.; Sala, I.; Della Vigna, P.; Perrino, M.; Zagami, P.; Corti, C.; et al. Avelumab plus Axitinib in Unresectable or Metastatic Type B3 Thymomas and Thymic Carcinomas (CAVEATT): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, I.; Meltzer, P.S.; Kim, I.-K.; Lucchi, M.; Park, K.-S.; Fontanini, G.; Gao, J.; Zucali, P.A.; Calabrese, F.; Favaretto, A.; et al. A Specific Missense Mutation in GTF2I Occurs at High Frequency in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Lin, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yu, Z.; Jia, J.; Yu, J.; Zheng, W.; Bai, J.; Chang, L.; et al. Analysis of the Tumor Microenvironment and Mutation Burden Identifies Prognostic Features in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2022, 12, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Cheng, X.; Xu, B.; Zeng, H.; Zou, J.; Su, C.; Chen, Z. Characteristics of Genomic Mutations and Signaling Pathway Alterations in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, N.; Basse, C.; Schrock, A.; Ramkissoon, S.; Killian, K.; Ross, J.S. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of 274 Thymic Epithelial Tumors Unveils Oncogenic Pathways and Predictive Biomarkers. Oncologist 2022, 27, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zu, L.; Yang, L.; Shi, T.; Zhu, S.; Lei, X.; Song, Z.; Chen, J. Frequent Genetic Alterations and Their Clinical Significance in Patients With Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 667148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, M.; Okuda, K.; Suzuki, A.; Tatematsu, T.; Hikosaka, Y.; Moriyama, S.; Sasaki, H.; Fujii, Y.; Yano, M. Genetic Profiling of Thymic Carcinoma Using Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, D. Genomic Characterization of Thymic Epithelial Tumors Reveals Critical Genes Underlying Tumorigenesis and Poor Prognosis. Clin. Genet. 2023, 103, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.L.; Won, H.H.; McMillan, R.; Huang, J.; Riely, G.J.; Ladanyi, M.; Berger, M.F. Massively Parallel Sequencing Identifies Recurrent Mutations in TP53 in Thymic Carcinoma Associated with Poor Prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sunami, K.; Kitahara, S.; Goto, Y.; Kanda, S.; Horinouchi, H.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Ichikawa, H.; et al. Medical Treatment Involving Investigational Drugs and Genetic Profile of Thymic Carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2016, 93, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkner, F.; Pichlhöfer, B.; Zaharie, A.T.; Krunic, M.; Holper, T.M.; Janik, S.; Moser, B.; Schlangen, K.; Neudert, B.; Walter, K.; et al. Molecular Profiling of Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma: Genetic Differences and Potential Novel Therapeutic Targets. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 23, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Hou, Z.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Mutation Analysis of the EGFR Gene and Its Downstream Signaling Pathway in Thymic Carcinoma Patients from a Chinese Han Population. Clin. Respir. J 2018, 12, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselta, R.; Di Tommaso, L.; Perrino, M.; Destro, A.; Giordano, L.; Cardamone, G.; Rubino, L.; Santoro, A.; Duga, S.; Zucali, P.A. Mutation Profile and Immunoscore Signature in Thymic Carcinomas: An Exploratory Study and Review of the Literature. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Masaki, A.; Murase, T.; Okuda, K.; Nakanishi, R.; Inagaki, H. Mutation Profile of Thymic Carcinoma and Thymic Neuroendocrine Tumor by Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 92–99.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Thomas, A.; Lau, C.; Rajan, A.; Zhu, Y.; Killian, J.K.; Petrini, I.; Pham, T.; Morrow, B.; Zhong, X.; et al. Mutations of Epigenetic Regulatory Genes Are Common in Thymic Carcinomas. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Goto, T.; Hirotsu, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Nakagomi, T.; Otake, S.; Amemiya, K.; Oyama, T.; Mochizuki, H.; Omata, M. Primary Driver Mutations in GTF2I Specific to the Development of Thymomas. Cancers 2020, 12, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Rare Frequency of Gene Variation and Survival Analysis in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6337–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Szpechcinski, A.; Szolkowska, M.; Winiarski, S.; Lechowicz, U.; Wisniewski, P.; Knetki-Wroblewska, M. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing of Thymic Epithelial Tumours Revealed Pathogenic Variants in KIT, ERBB2, KRAS, and TP53 in 30% of Thymic Carcinomas. Cancers 2022, 14, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Asao, T.; Honda, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Tsuta, K.; Kono, K.; Watanabe, S.; Ohe, Y.; et al. The Genomic and Epigenomic Landscape in Thymic Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syahruddin, E.; Zaini, J.; Sembiring, R.; Baginta, R.; Fadhillah, M.; Noor, D. TP53 and EGFR Mutational Status in Thymoma: A Genetic Sequencing Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Liu, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, H.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Lin, R.; Wang, T.; et al. Transcriptomic and Mutational Analysis Discovering Distinct Molecular Characteristics Among Chinese Thymic Epithelial Tumor Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 647512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakane, T.; Murase, T.; Okuda, K.; Takino, H.; Masaki, A.; Oda, R.; Watanabe, T.; Kawano, O.; Haneda, H.; Moriyama, S.; et al. A Comparative Study of PD-L1 Immunohistochemical Assays with Four Reliable Antibodies in Thymic Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6993–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiri, S.; Fukui, T.; Mori, S.; Kawaguchi, K.; Nakamura, S.; Ozeki, N.; Kato, T.; Goto, M.; Yatabe, Y.; Yokoi, K. Clinicopathologic Features of Thymoma With the Expression of Programmed Death Ligand 1. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 107, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.; Kim, D.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, C.-M.; Jang, S.J. Clinicopathologic Significance and Immunogenomic Analysis of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) and Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) Expression in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.-F.; Chu, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, S.-H.; Su, W.-C.; Tseng, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Yen, Y.-T. Different Pattern of PD-L1, IDO, and FOXP3 Tregs Expression with Survival in Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2018, 125, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suster, D.; Pihan, G.; Mackinnon, A.C.; Suster, S. Expression of PD-L1/PD-1 in Lymphoepithelioma-like Carcinoma of the Thymus. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.; Chu, B.; Lehman, A.M.; Annamalai, L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shilo, K.; Otterson, G.A. Expression Patterns, Prognostic Value, and Intratumoral Heterogeneity of PD-L1 and PD-1 in Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquette, I.; Taranchon-Clermont, E.; Gilhodes, J.; Bluthgen, M.-V.; Perallon, R.; Chalabreysse, L.; De Muret, A.; Hofman, V.; Marx, A.; Parrens, M.; et al. Immune Biomarkers in Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Expression Patterns, Prognostic Value and Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for PD-L1. Biomark Res. 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, P.; Husain, N.; Shukla, S.; Kumar, S.; Parshad, R.; Jain, D. PD-L1 Immuno-Expression Assay in Thymomas: Study of 84 Cases and Review of Literature. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 34, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchevsky, A.M.; Walts, A.E. PD-L1, PD-1, CD4, and CD8 Expression in Neoplastic and Nonneoplastic Thymus. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 60, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, R.; Goteri, G.; Brunelli, A.; Pagliaretta, S.; Paolucci, V.; Caramanti, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Refai, M.; Pompili, C.; Morgese, F.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of Programmed Cell Death Protein 1/Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Pathway in Thymic Malignancies with Combined Immunohistochemical and Biomolecular Approach. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedekovics, J.; Beke, L.; Mokanszki, A.; Szilagyi, S.; Mehes, G. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2020, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Ozeki, N.; Tateyama, H.; Kadomatsu, Y.; Ueno, H.; Goto, M.; Nakamura, S.; Fukumoto, K.; Chen-Yoshikawa, T.F. Skeletal Muscle and Related Protein Expression as Prognostic Factors in Thymic Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 3245–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Feng, J.; Hong, B.; Qian, Y. The Expression of PD-L1 and B7-H4 in Thymic Epithelial Tumor and Its Relationship With Tumor Immune-Infiltrating Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 662010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, S.; Shintani, Y.; Fukui, E.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kanzaki, R.; Ose, N.; Kanou, T.; Minami, M.; Mori, E.; Okumura, M. The Prognostic Impact of Programmed Cell Death 1 and Its Ligand and the Correlation with Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Thymic Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, R.; Goteri, G.; Pagliaretta, S.; Paolucci, V.; Morgese, F.; Conti, A.; Refai, M.; Pompili, C.; Duranti, C.; Marcantognini, G.; et al. The Role of Angiogenetic Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Thymic Malignancies and Thymic Benign Lesions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 7245–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, A.; Okuma, Y. From Rarity to Reality: Osimertinib’s Promising Horizon in Treating Uncommon EGFR Mutations in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3128–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elm, L.; Levidou, G. The Molecular Landscape of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockhammer, P.; Grant, M.; Wurtz, A.; Foggetti, G.; Expósito, F.; Gu, J.; Zhao, H.; Choi, J.; Chung, S.; Li, F.; et al. Co-Occurring Alterations in Multiple Tumor Suppressor Genes Are Associated With Worse Outcomes in Patients With EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ramesh, A.; Gusev, Y.; Bhuvaneshwar, K.; Giaccone, G. Molecular Predictors of Response to Pembrolizumab in Thymic Carcinoma. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Sasaki, H.; Kawano, O.; Endo, K.; Haneda, H.; Yukiue, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. Expression and Mutation Statuses of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Thymic Epithelial Tumors. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 36, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, K.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Ishii, G.; Goto, K.; Kubota, K.; Ohmatsu, H.; Niho, S.; Nagai, K.; Saijo, N. Mutational Status of EGFR and KIT in Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma. Lung Cancer 2008, 62, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N.; Shen, R.; Guo, T.; Zakowski, M.F.; Heguy, A.; Riely, G.J.; Huang, J.; Lau, C.; Lash, A.E.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Reveals Clinically Relevant Molecular Distinctions between Thymic Carcinomas and Thymomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, L. Inhibitory B7-Family Molecules in the Tumour Microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Rizvi, H.; Bandlamudi, C.; Sauter, J.L.; Travis, W.D.; Rekhtman, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Sawan, P.; Beras, A.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Correlates of PD-L1 Expression in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuya, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Asao, T.; Kitahara, S.; Goto, Y.; Kanda, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nokihara, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Watanabe, S.-I.; et al. Expression of Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) and Its Ligand (PD-L1) in Thymic Epithelial Tumors: Impact on Treatment Efficacy and Alteration in Expression after Chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2016, 99, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | Region | Cohort Size | WHO Histologic Classification | Number of Subjects | Sequencing Method | Gene Panel | Genes Detected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Girard et al., 2022 [22] | US | 264 | Thymoma TC | 174 90 | Targeted NGS | 318 cancer-related genes plus 37 introns from 28 genes frequently rearranged in cancer | CDKN2A, TP53, KIT, RAS, etc. |
| Szpechcinski et al., 2022 [35] | Poland | 53 | Thymoma TC | 19 34 | Targeted NGS | 15 genes implicated in common solid tumors | ERBB2, KIT, KRAS, FOXL2, etc. |
| Tan et al., 2022 [25] | China | 47 | Thymoma TC | 39 8 | Targeted NGS | 315 cancer-related genes | TP53, TET2, ATM, DNMT3A, etc. |
| Syahruddin et al., 2022 [37] | Indonesia | 27 | Thymoma | 27 | PCR | TP53 and EGFR | TP53, EGFR |
| Hou et al., 2022 [20] | China | 15 | Thymoma TC | 10 5 | WES | - | GTF2I, HRAS, NBPF14, etc. |
| Liang et al., 2021 [38] | China | 27 | Thymoma TC | 24 3 | Targeted NGS | a 476-gene panel | ATM, NF1, GTF2I, NRAS, etc. |
| Xu et al., 2021 [23] | China | 34 | Thymoma TC | 17 17 | Targeted NGS | a panel of 56 cancer-related genes | TP53, MTOR, CDKN2A, etc. |
| Asselta et al., 2021 [30] | Italy | 15 | TC | 15 | Targeted NGS | 50 onco- and tumor-suppressor genes | CDKN2A, RAS, FGFR3, etc. |
| Sakane et al., 2021 [31] | Japan | 54 | TC | 54 | Targeted NGS | 50 of the most commonly reported oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes | PDGFRA, KIT, PIK3CA, RAS, etc. |
| Yang et al., 2021 [21] | China | 15 | Thymoma TC | 6 9 | WES | - | ZNF429, ZNF208, ERBB4, etc. |
| Higuchi et al., 2020 [33] | Japan | 22 | Thymoma | 22 | Targeted sequencing | GTF2I | GTF2I |
| Radovich et al., 2018 [10] | US | 117 | Thymoma TC | 107 10 | WES | - | GTF2I, RAS, TP53 |
| Zhan et al., 2018 [29] | China | 61 | TC | 61 | PCR and direct sequencing | EGFR pathway genes | EGFR, PI3KCA, BRAF, etc. |
| Saito et al., 2017 [36] | Japan | 10 | TC | 10 | WES | - | TP53, RAS, CYLD, SETD2, etc. |
| Enkner et al., 2017 [28] | Austria | 72 | Thymoma TC | 37 35 | Targeted NGS | 50 onco- and tumor-suppressor genes | RAS, SMARCB1, CDKN2A, FGFR3, etc. |
| Song et al., 2016 [34] | China | 52 | Thymoma TC | 37 15 | Targeted NGS | a panel of 22 genes | EGFR, PIK3CA, etc. |
| Asao et al., 2016 [27] | Japan | 52 | TC | 52 | Targeted NGS | 50 cancer-related genes | TP53, FBXW7, etc. |
| Moreira et al., 2015 [26] | US | 21 | Thymoma TC | 6 15 | Targeted NGS | 275 commonly implicated oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and members of pathways considered actionable by targeted therapies | BCOR, MLL3, RAS, KDM6A, etc. |
| Shitara et al., 2014 [24] | Japan | 12 | TC | 12 | Targeted NGS | 409 tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes | NF1, KIT, CDKN2A, TET1, TP53, etc. |
| Petrini et al., 2014 [19] | US | 54 | Thymoma TC | 38 16 | WES and Targeted NGS | 197-gene assay | GTF2I, TP53, CDKN2A, etc. |
| Wang et al., 2014 [32] | US | 78 | Thymoma TC | 31 47 | Targeted NGS | 197 cancer-related genes | DCC, RAS, SETD2, BAP1, etc. |
| Study | Region | Cohort Size | WHO Histologic Classification | Cut-Off Value for Positive | Sample Source | Treatment | Antibody for IHC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marchevsky et al., 2017 [47] | US | 46 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% | Surgical resection | NA | SP142 |
| Owen et al., 2018 [44] | US | 35 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% | Surgical resection | NA | 22C3 |
| Suster et al., 2018 [43] | US | 21 | TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection | NA | SP142 |
| Rouquette et al., 2019 [45] | France | 103 | B3, TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection and biopsy | NA | E1L3N, 22C3, SP142, SP263 |
| Bedekovics et al., 2020 [49] | Hungary | 36 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection | preoperative radio-based/cisplatin-based chemotherapy | SP142 |
| Song et al., 2019 [41] | South Korea | 368 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection | neoadjuvant and/or postoperative adjuvant radiation or chemotherapy | SP263 |
| Nakanishi et al., 2022 [50] | Japan | 34 | TC | 50% | Surgical resection | NA | SP142 |
| Guleria et al., 2018 [46] | India | 84 | A, AB, B1-3 | 1% | Surgical resection and biopsy | NA | SP263 |
| Berardi et al., 2020 [48] | Italy | 61 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection and biopsy | NA | NAT105 |
| Funaki et al., 2019 [52] | Japan | 43 | TC | 50% | Surgical resection | preoperative radio-based/cisplatin-based chemotherapy | E1L3N |
| Hakiri et al., 2019 [40] | Japan | 81 | A, AB, B1-3 | 1% | Surgical resection | NA | SP142 |
| Sakane et al., 2018 [39] | Japan | 53 | TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection and biopsy | chemotherapy/radiotherapy | SP142, SP263, 22C3, 28-8 |
| Yan et al., 2021 [51] | China | 80 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 1% and 50% | Surgical resection | NA | 22C3 |
| Wei et al., 2018 [42] | China | 169 | A, AB, B1-3, TC | 50% | Surgical resection and biopsy | preoperative radio-based/cisplatin-based chemotherapy | E1L3N |
| Subtype | Gene | Number of Included Studies | Pooled Estimated Rate (95% Confidence Interval) | I2 | p-Value | Model | Transformation Method | Egger’s Test (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymoma | GTF2I | 5 | 0.4263 [0.3590;0.4936] | 38% | 0.1657 | Common effect model | Untransformed | 0.6476 |
| TP53 | 11 | 0.1101 [0.0000; 0.2586] | 94% | <0.0001 | Random effect model | Untransformed | 0.1139 | |
| RAS | 12 | 0.0341 [0.0104; 0.0710] | 66% | 0.0007 | Random effect model | Arcsine | 0.6011 | |
| ATM | 8 | 0.0121 [0.0003; 0.0342] | 44% | 0.0855 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.8333 | |
| EGFR | 10 | 0.0093 [0.0014; 0.0218] | 9% | 0.3584 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.8802 | |
| KIT | 8 | 0.0011 [0.0000; 0.0157] | 15% | 0.3111 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.4357 | |
| Thymic Carcinoma | TP53 | 16 | 0.1797 [0.0732; 0.3203] | 91% | <0.0001 | Random effect model | Arcsine | 0.4031 |
| CDKN2A | 12 | 0.0608 [0.0139; 0.1378] | 91% | <0.0001 | Random effect model | Arcsine | 0.0654 | |
| TET2 | 8 | 0.0318 [0.0087; 0.0639] | 37% | 0.1363 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.7948 | |
| RAS | 17 | 0.0389 [0.0201; 0.0616] | 0% | 0.6887 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.9315 | |
| KIT | 13 | 0.0352 [0.0164; 0.0586] | 19% | 0.2496 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.3152 | |
| DNMT3A | 7 | 0.0001 [0.0000; 0.0127] | 2% | 0.4103 | Common effect model | Freeman–Tukey double arcsine | 0.2678 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Feng, X.; Liang, Z.; Jin, R.; Li, X. Depiction of the Genetic Alterations and Molecular Landscapes of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172966
Wang X, Jin H, Feng X, Liang Z, Jin R, Li X. Depiction of the Genetic Alterations and Molecular Landscapes of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(17):2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172966
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Hongming Jin, Xiaotong Feng, Zhijian Liang, Ruoyi Jin, and Xiao Li. 2024. "Depiction of the Genetic Alterations and Molecular Landscapes of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 17: 2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172966
APA StyleWang, X., Jin, H., Feng, X., Liang, Z., Jin, R., & Li, X. (2024). Depiction of the Genetic Alterations and Molecular Landscapes of Thymic Epithelial Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(17), 2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172966






