Subxiphoid Single-Port Robotic Thymectomy Using the Single-Port Robotic System versus VATS: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective, and Propensity Score-Matched Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Creation of the Subxiphoid Tunnel
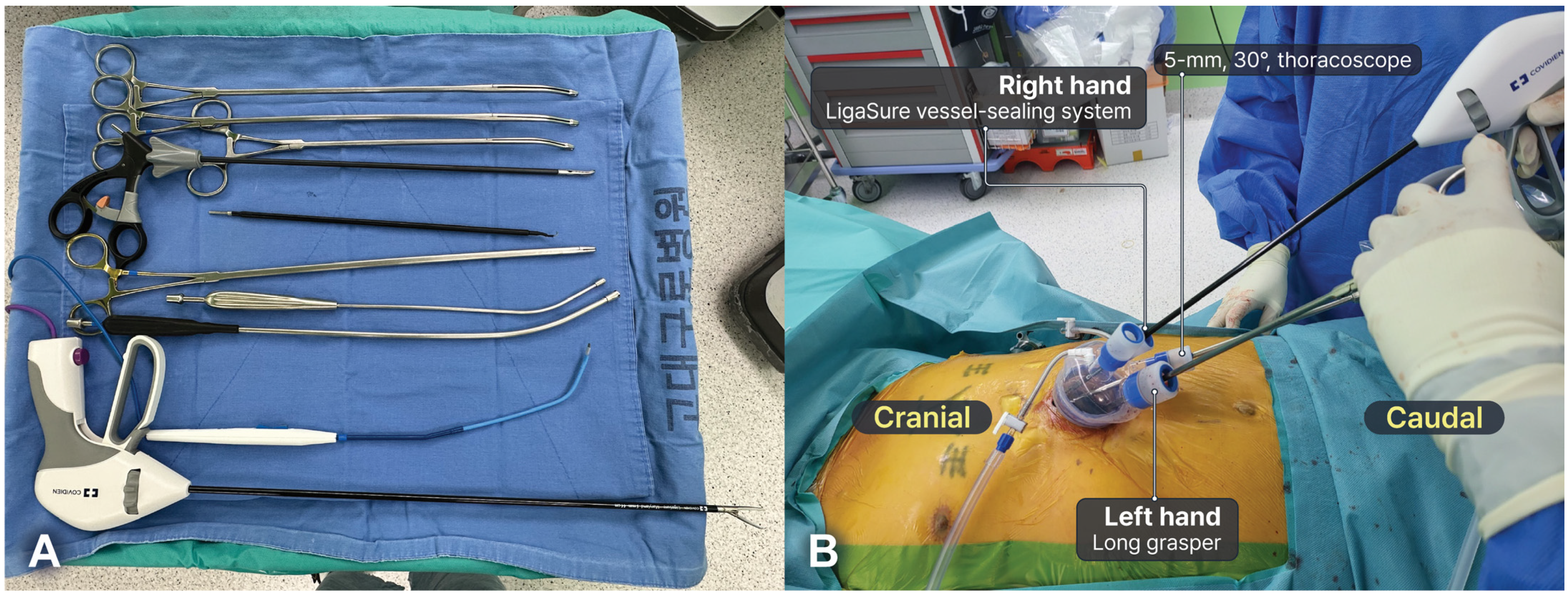
2.3. Surgical Technique: Subxiphoid SRATS Thymectomy
2.4. Surgical Technique: Subxiphoid SVATS Thymectomy
2.5. Conversion to Sternotomy or Multi-Port Surgery
2.6. Postoperative Management
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethical Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duwe, B.V.; Sterman, D.H.; Musani, A.I. Tumors of the mediastinum. Chest 2005, 128, 2893–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Chan, J.K.; Yin, C.H.; Lee, C.C.; Chern, C.U.; Liao, C.I. Trends in the incidence of thymoma, thymic carcinoma, and thymic neuroendocrine tumor in the United States. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0227197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, K. Therapy for thymic epithelial tumors. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 62, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedant, A.J.; Handorf, E.A.; Su, S.; Scott, W.J. Minimally invasive versus open thymectomy for thymic malignancies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Huang, Y. Thoracoscopic thymectomy versus open thymectomy for the treatment of thymoma: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.Y.; Wang, W. Robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery vs. sternotomy for thymectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1048547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, G. Robotic surgery for the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.J.; Kang, C.H. Robotic thymectomy for advanced thymic epithelial tumor: Indications and technical aspects. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückert, J.C.; Swierzy, M.; Ismail, M. Comparison of robotic and nonrobotic thoracoscopic thymectomy: A cohort study. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, I.; Hashizume, M.; Shimada, M.; Tomikawa, M.; Tomiyasu, M.; Suemitsu, R.; Sugimachi, K. Thoracoscopic thymomectomy with the da Vinci computer-enhanced surgical system. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2001, 122, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chendaer, N.; Jiang, N.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C. A propensity score-matching analysis: Robotic thymectomy through the subxiphoid has advantages over video-assisted thymectomy surgery. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2023, 33, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Na, K.J.; Kang, C.H.; Park, S.; Park, I.K.; Kim, Y.T. Robotic subxiphoid thymectomy versus lateral thymectomy: A propensity score-matched comparison. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62, ezac288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Kaneda, S.; Hachimaru, A.; Tochii, D.; Maeda, R.; Tochii, S.; Takagi, Y. Thymectomy via a subxiphoid approach: Single-port and robot-assisted. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, S265–S271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Biportal robotic surgery for anterior mediastinal mass. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 12, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Han, K.N.; Hong, J.I.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, D.J.; Choi, Y.H. Subxiphoid approach for robotic single-site-assisted thymectomy. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 58, i34–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Stein, H.; Heo, S.Y.; Kim, H.K. Initial experience with and surgical outcomes of da Vinci single-port system in general thoracic surgery. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, T.H.; Kim, H.K. Robotic thoracic surgery using the single-port robotic system: Initial experience with more than 100 cases. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenfant, L.; Kim, S.; Aminsharifi, A.; Sawczyn, G.; Kaouk, J. Floating docking technique: A simple modification to improve the working space of the instruments during single-port robotic surgery. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T. Single-port thymectomy using a subxiphoid approach-surgical technique. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowse, P.G.; Roden, A.C.; Corl, F.M.; Allen, M.S.; Cassivi, S.D.; Nichols, F.C.; Shen, K.R.; Wigle, D.A.; Blackmon, S.H. Minimally invasive thymectomy: The Mayo Clinic experience. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 4, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, M.K.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Rahouma, M.; Lee, B.; Harrison, S.; Stiles, B.M.; Abdelrahman, A.M.; Altorki, N.K.; Port, J.L. National trends and perioperative outcomes of robotic resection of thymic tumours in the United States: A propensity matching comparison with open and video-assisted thoracoscopic approaches†. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 56, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şehitogullari, A.; Nasır, A.; Anbar, R.; Erdem, K.; Bilgin, C. Comparison of perioperative outcomes of videothoracoscopy and robotic surgical techniques in thymoma. Asian J. Surg. 2020, 43, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Hurd, J.; Shah, S.A.; Liou, D.; Wang, H.; Backhus, L.M.; Lui, N.S.; D'Amico, T.A.; Shrager, J.B.; Berry, M.F. A national analysis of open versus minimally invasive thymectomy for stage I to III thymoma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 160, 555–567.e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Zuo, C.J.; Sun, T.Y.; Jiang, B. Robot versus video-assisted thoracoscopic thymectomy for large thymic epithelial tumors: A propensity-matched analysis. BMC Surg. 2023, 23, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Han, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Niu, Z.; et al. Robotic-assisted Versus Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Lobectomy: Short-term Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial (RVlob Trial). Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, G.; Abbas, A.E.; Muriana, P.; Lembo, R.; Bottoni, E.; Perroni, G.; Testori, A.; Dieci, E.; Bakhos, C.T.; Car, S.; et al. Perioperative Outcome of Robotic Approach Versus Manual Videothoracoscopic Major Resection in Patients Affected by Early Lung Cancer: Results of a Randomized Multicentric Study (ROMAN Study). Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 726408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, R.M.; Araujo, P.; Lauricella, L.L.; Campos, J.R.M.; Trindade, J.R.M.; Pêgo-Fernandes, P.M. A Brazilian randomized study: Robotic-Assisted vs. Video-assisted lung lobectomy Outcomes (BRAVO trial). J. Bras. Pneumol. 2022, 48, e20210464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qsous, G.; Downes, A.; Carroll, B.; Rowe, S.; Manoj, S.; McFadyen, R.; Korelidis, G.; Tolan, M.; Healy, D.G. A Comparison of the Differences in Postoperative Chronic Pain Between Video-Assisted and Robotic-Assisted Approaches in Thoracic Surgery. Cureus 2022, 14, e31688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Huang, J.; Jiang, G. Unilateral video-assisted thoracoscopic extended thymectomy offers long-term outcomes equivalent to that of the bilateral approach in the treatment of non-thymomatous myasthenia gravis. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 21, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Wang, K.M.; Lin, C.H.; Lin, S.H.; Lin, W.C. Thoracoscopic surgery via a single-incision subxiphoid approach is associated with less postoperative pain than single-incision transthoracic or three-incision transthoracic approaches for spontaneous pneumothorax. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, S272–S278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Paiva, A.; Pinto, C.; Fernandes, P.; Pinho, P. A subxiphoid uniportal approach for a surgical biopsy. Multimed. Man. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Ashikari, S.; Tochii, S.; Sugimura, H.; Hattori, Y. Single-incision subxiphoid approach for bilateral metastasectomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Rivas, D.; Lirio, F.; Sesma, J.; Abu Akar, F. Subxiphoid complex uniportal video-assisted major pulmonary resections. J. Vis. Surg. 2017, 3, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qi, G.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X. Meta-analysis of subxiphoid approach versus lateral approach for thoracoscopic Thymectomy. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Dai, Q.; Xu, D. The early perioperative outcomes of subxiphoid approach versus lateral intercostal approach thoracoscopic thymectomy for thymic tumors: A meta-analysis. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2022, 32, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Xin, N.; Wei, R.; Huang, K. Effect evaluation of subxiphoid and intercostal thymectomy: A meta-analysis and Ssstematic review. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 925003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouarab, A.A.; Rahouma, M.; Kamel, M.; Ghaly, G.; Mohamed, A. Single versus multi-incisional video-assisted thoracic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. A 2018, 28, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magouliotis, D.E.; Fergadi, M.P.; Spiliopoulos, K.; Athanassiadi, K. Uniportal versus multiportal video-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy for lung cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Lung 2021, 199, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Uniportal versus multiportal video-assisted thoracoscopic anatomical resection for NSCLC: A meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 15, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Sugimura, H.; Tochii, D.; Kihara, M.; Hattori, Y. Single-port thymectomy through an infrasternal approach. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 93, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | SRATS (n = 85) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value | SRATS (n = 25) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value |
| Age (years) | 53.38 ± 12.98 | 57.6 ± 13.93 | 0.520 | 57.72 ± 13.69 | 57.6 ± 13.93 | 0.844 |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 33 (39%) | 13 (52%) | 0.240 | 13 (52%) | 13 (52%) | 1.000 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.99 ± 3.90 | 24.79 ± 3.40 | 0.963 | 24.99 ± 2.81 | 24.79 ± 3.40 | 0.820 |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | ||||||
| Hypertension | 21 (25%) | 10 (40%) | 0.135 | 7 (28%) | 10 (40%) | 0.551 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 (14%) | 6 (24%) | 0.236 | 5 (20%) | 6 (24%) | 1.000 |
| COPD | 5 (6%) | 1 (4%) | 1.000 | 3 (12%) | 1 (4%) | 0.609 |
| Myasthenia gravis | 7 (8%) | 3 (12%) | 0.692 | 3 (12%) | 3 (12%) | 1.000 |
| ASA score | 2.32 ± 0.71 | 2.36 ± 0.70 | 0.749 | 2.28 ± 0.79 | 2.36 ± 0.70 | 0.835 |
| Mass size (cm) | 3.29 ± 1.61 | 3.84 ± 2.01 | 0.216 | 3.68 ± 1.87 | 3.84 ± 2.01 | 0.773 |
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRATS (n = 85) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value | SRATS (n = 25) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value | |
| Completeness of resection (R0) | 85 (100%) | 25 (100%) | 1.000 | 25 (100%) | 25 (100%) | 1.000 |
| Extent of resection, n (%) | 0.076 | 0.235 | ||||
| Extended thymectomy | 83 (98%) | 22 (88%) | 25 (100%) | 22 (88%) | ||
| Partial thymectomy | 2 (2%) | 3 (12%) | 0 | 3 (12%) | ||
| Resected adjacent structures, n (%) | ||||||
| Lung | 1 (1%) | 2 (8%) | 0.129 | 1 (4%) | 2 (8%) | 1.000 |
| Innominate vein | 2 (2%) | 0 | 1.000 | 0 | 0 | |
| Phrenic nerve | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0.227 | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1.000 |
| Pericardium | 1 (1%) | 1 (4%) | 0.405 | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | 1.000 |
| Anesthesia time (min) | 225.88 ± 79.46 | 214.40 ± 71.59 | 0.724 | 236.00 ± 96.41 | 214.40 ± 71.59 | 0.640 |
| Total operative time (min) | 154.46 ± 74.06 | 146.76 ± 67.07 | 0.674 | 159.72 ± 86.54 | 146.76 ± 67.07 | 0.641 |
| Conversion, n (%) | ||||||
| To median sternotomy | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0.227 | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1.000 |
| To multi-port surgery | 2 (2%) | 5 (20%) | 0.006 | 0 | 5 (20%) | 0.050 |
| Transfusion, n (%) | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0.227 | 0 | 1 (4%) | 1.000 |
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRATS (n = 85) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value | SRATS (n = 25) | SVATS (n = 25) | p-Value | |
| Chest tube drainage duration (days) | 1.40 ± 0.94 | 2.00 ± 1.29 | 0.001 | 1.32 ± 0.75 | 2.00 ± 1.29 | 0.003 |
| Postoperative hospital stays (days) | 2.87 ± 1.26 | 5.08 ± 5.20 | 0.007 | 2.52 ± 1.00 | 5.08 ± 5.20 | 0.003 |
| Postoperative complications (Clavien–Dindo), n (%) | 0.104 | 0.414 | ||||
| None | 80 (94%) | 21 (84%) | 24 (96%) | 21 (84%) | ||
| I | 2 (2%) | 2 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 2 (8%) | ||
| II | 1 (1%) | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (4%) | ||
| IIIa | 2 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| IIIa/IV | 0 | 1 (4%) | 0 | 1 (4%) | ||
| Pathological diagnosis, n (%) | 0.882 | 0.932 | ||||
| Thymoma | 36 (42%) | 10 (40%) | 11 (44%) | 10 (40%) | ||
| Thymic carcinoma | 7 (8%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | 1 (4%) | ||
| Benign cystic lesions | 32 (38%) | 10 (40%) | 8 (32%) | 10 (40%) | ||
| Other | 10 (12%) | 4 (16%) | 5 (20%) | 4 (16%) | ||
| WHO classification, n (%) | 0.551 | 0.812 | ||||
| A | 8 (19%) | 1 (9%) | 3 (25%) | 1 (9%) | ||
| AB | 14 (32%) | 2 (18%) | 4 (33%) | 2 (18%) | ||
| B1 | 5 (12%) | 3(27%) | 2 (17%) | 3 (27%) | ||
| B2 | 5 (12%) | 3 (27%) | 1 (8%) | 3 (27%) | ||
| B3 | 4 (9%) | 1(9%) | 1 (8%) | 1 (9%) | ||
| C | 7 (16%) | 1(9%) | 1 (8%) | 1 (9%) | ||
| T stage, n (%) | 0.558 | 1.000 | ||||
| T1a | 35 (81%) | 10 (91%) | 10 (83%) | 10 (91%) | ||
| T1b | 2 (5%) | 1 (9%) | 1 (8%) | 1 (9%) | ||
| T2 | 5 (12%) | 0 | 1 (8%) | 0 | ||
| T3 | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Park, T.H.; Gu, B.M.; Jung, Y.; Yi, E.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Chung, J.h.; Kim, H.K. Subxiphoid Single-Port Robotic Thymectomy Using the Single-Port Robotic System versus VATS: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective, and Propensity Score-Matched Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162856
Lee JH, Hwang J, Park TH, Gu BM, Jung Y, Yi E, Lee S, Hwang SY, Chung Jh, Kim HK. Subxiphoid Single-Port Robotic Thymectomy Using the Single-Port Robotic System versus VATS: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective, and Propensity Score-Matched Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162856
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jun Hee, Jinwook Hwang, Tae Hyun Park, Byung Mo Gu, Younggi Jung, Eunjue Yi, Sungho Lee, Soon Young Hwang, Jae ho Chung, and Hyun Koo Kim. 2024. "Subxiphoid Single-Port Robotic Thymectomy Using the Single-Port Robotic System versus VATS: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective, and Propensity Score-Matched Study" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162856
APA StyleLee, J. H., Hwang, J., Park, T. H., Gu, B. M., Jung, Y., Yi, E., Lee, S., Hwang, S. Y., Chung, J. h., & Kim, H. K. (2024). Subxiphoid Single-Port Robotic Thymectomy Using the Single-Port Robotic System versus VATS: A Multi-Institutional, Retrospective, and Propensity Score-Matched Study. Cancers, 16(16), 2856. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162856







