Tumor-Like Lesions in the Craniovertebral Junction: A Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Personal Case Series
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Screening and Data Extraction
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
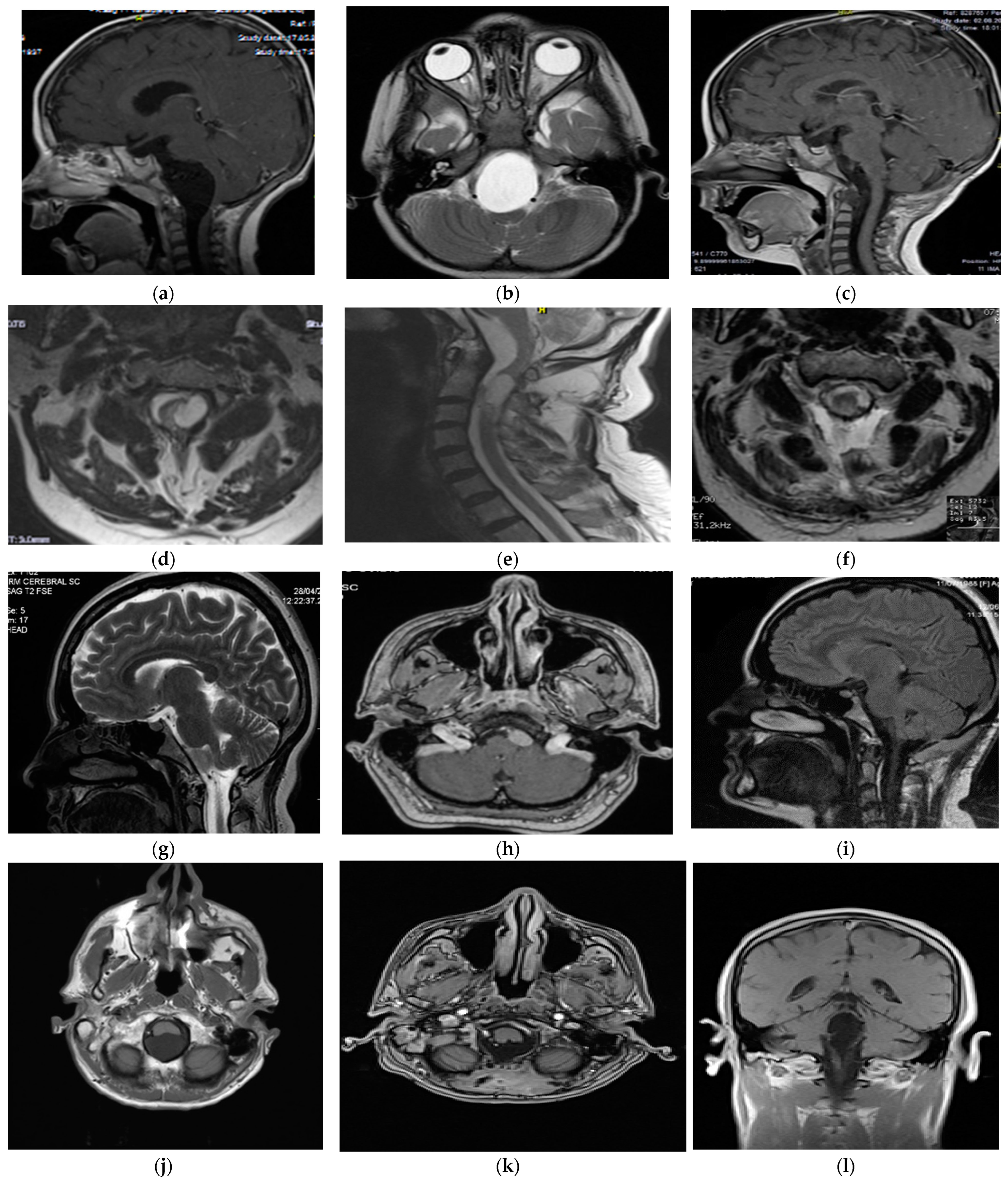
3.1. Personal Case Series (Table 1)
| Case | Age/Sex | Symptoms | Duration | Location | MRI Characteristics | Surgical Approach | Histopathology | Outcome | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30/F | Headache, neck pain, quadriparesis | 2 years | Posterior CVJ, cerebellomedullary cistern to C1 | T1 hyperintensity, T2 hypointensity, no DWI restriction, no enhancement | Craniotomy with C1 laminectomy, posterior midline approach | Neurenteric cyst | No complications, complete excision | 5 years, no recurrence |
| 2 | 3/M | Aseptic meningitis | 1 year | Anterior CVJ, a pontomedullary cistern to C1 | T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity, no DWI restriction, no enhancement | Lateral suboccipital craniotomy with C1 hemilaminectomy, far-lateral approach | Neurenteric cyst | No complications, total excision | 12 years, no recurrence |
| 3 | 73/M | Headache, diplopia, gait disturbances | 15 months | Anterior and lateral CVJ, premedullary cistern to C2 | T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity, no DWI restriction, no enhancement | Lateral suboccipital craniectomy with C1 laminectomy, far-lateral approach | Dermoid cyst | Uneventful, subtotal resection | 8 years, no recurrence |
| 4 | 34/F | Headache | - | Anterior and lateral CVJ, premedullary region | T1 hyperintensity, T2 hypointensity, no enhancement | Lateral suboccipital craniectomy with C1 laminectomy, far-lateral approach | Neurenteric cyst | No complications, total resection | 1 year, no recurrence |
| 5 | 73/M | Headache, gait disturbance, ataxia | 8 months | Posterior and lateral CVJ, cerebellomedullary cistern to C1 | T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity, hyperintensity on DWI, no enhancement | Retromastoid craniotomy, retrosigmoid approach | Epidermoid cyst | No complications, subtotal resection | 3 years, no recurrence |
| 6 | 53/M | Headache, gait disturbance, ataxia, diplopia | 2 years | Posterior CVJ, cerebellomedullary cistern to C1 | T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity, hyperintensity on DWI, no enhancement | Midline suboccipital craniotomy | Epidermoid cyst | No complications, total resection | 6 years, excellent outcome |
| 7 | 22/M | Hydrocephalus, dizziness | 5 days | Posterior CVJ, cerebellomedullary cistern | T1 hypointensity, T2 hyperintensity, hyperintensity on DWI, no enhancement | Posterior midline approach | Epidermoid cyst | Persistent hydrocephalus (VP shunt), good outcome | 5 years, no late complications |
3.2. Search Strategy
3.3. Patient Baseline Characteristics for Tumor-Like Lesions
3.4. The Meta-Analysis of Neurenteric Cyst: Prognostic Factors for Recurrence
3.5. The Meta-Analysis of the Neurenteric Cyst According to the Extent of Resection
3.6. The Meta-Analysis of Neurenteric Cyst According to Different Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Tumor Types and Demographics
4.2. Clinical Implications
4.3. Surgical Outcomes and Recurrence
4.4. Complications and Management
4.5. Meta-Analysis of the Neurenteric Cyst Located at the CVJ
4.6. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vhora, R.; Vhora, S.; Katkar, A.; Ghate, P. A case report of craniovertebral junction intradural extramedullary neurenteric cyst. Med. J. Dr. D. Y. Patil. Univ. 2014, 7, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.H.; Traynelis, V.C. Spinal neurenteric cysts in the magnetic resonance imaging era. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 97–105, discussion 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebi, M.; Abumi, K.; Barbieri, A.; Behari, S.; Benzel, E.C.; Bolognese, P.; Burute, N.; Cacciola, F.; Carpentier, A.; Carrau, R.L.; et al. The Craniovertebral Junction: Diagnosis, Pathology, Surgical Techniques; Goel, A., Cacciola, F., Eds.; Georg Thieme KG: Stuttgart, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Hong, J.H.; Han, M.S.; Moon, B.J.; Koo, J.Y.; Lee, J.K. Neurenteric cyst of the craniovertebral junction treated to reduce recurrence using different strategies: Two case reports and a literature review. Medicine 2023, 102, e33844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, R.H.; D’Osvaldo, D.H.; Vilarino, A.; Amante, M.F.; Dillon, H.S. Neurenteric Cyst of the Ventral Craniocervical Junction: Case Report and Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.R.; Panigrahi, M.; Rao, S. Neurenteric cyst at the craniovertebral junction: A report of two cases. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2013, 8, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Lim, J.; Cho, K.G. Anterior Craniocervical Junctional Neurenteric Cyst. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2021, 9, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Couldwell, W.T. Far-lateral transcondylar approach: Surgical technique and its application in neurenteric cysts of the cervicomedullary junction. Report of two cases. Neurosurg. Focus. 2005, 19, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Rahman, A.; Ahmed, N.; Alam, S. Huge Ventral Cervicomedullary Neurenteric Cyst: A Rare Entity with Good Surgical Outcome and Appraisal. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2020, 15, 1016–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.H. Craniovertebral junction neoplasms in the pediatric population. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2008, 24, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.H.; Dlouhy, B.J. Neurenteric cysts at foramen magnum in children: Presentation, imaging characteristics, and surgical management-case series and literature review. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Sharma, B.S.; Khosla, V.K.; Mathuria, S.N.; Pathak, A.; Tewari, M.K. Far lateral approach for foramen magnum lesions. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2000, 40, 48–52, discussion 52–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crockard, H.A.; Sen, C.N. The transoral approach for the management of intradural lesions at the craniovertebral junction: Review of 7 cases. Neurosurgery 1991, 28, 88–97, discussion 97–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kak, V.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Sharma, B.S.; Banerjee, A.K. Craniospinal enterogenous cyst: MR findings. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1990, 14, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisciano, P.; Ferini, G.; Watanabe, G.; Conching, A.; Ogasawara, C.; Scalia, G.; Bin-Alamer, O.; Haider, A.S.; Passanisi, M.; Maugeri, R.; et al. Surgical Management of Craniovertebral Junction Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4842–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorano, E.; Spena, G.; Sovardi, F.; Dehgani-Mobaraki, P.; Pagella, F.; Montalbetti, A.; Peppucci, E.; Grasso, C.; Zoia, C. Extremely Rare Pathologies of the Craniovertebral Junction Region: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. Surgeries 2023, 4, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarelli, M.; Massimi, L.; Kondageski, C.; Di Rocco, C. Intracranial midline dermoid and epidermoid cysts in children. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzagmout, M.; Agharbi, S.; Chakour, K.; Chaoui, M.E. Dermoid cyst of the posterior fossa. Neurosciences 2011, 16, 153–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zarineh, A.; Leon, M.E.; Saad, R.S.; Silverman, J.F. Multiple neuroenteric cysts at cerebello-pontine angle and foramen magnum: A case report and review of the literature. Neuropathology 2009, 29, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Savardekar, A.; Chhabra, R.; Radotra, B.D.; Gupta, S.K. Unusual imaging finding of a “fluid-fluid” level in a neurenteric cyst at anterior margin of the cervico-medullary junction. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 29, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejjani, G.K.; Wright, D.C.; Schessel, D.; Sekhar, L.N. Endodermal cysts of the posterior fossa. Report of three cases and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budke, M.; Luglietto, D.; Vitaliano Muzii, F. Surgical anatomy of a neurenteric cyst anterior to the brainstem. Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery 2020, 21, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Chandramouli, T.C.; Rao, R.M. Ventral foramen magnum neurenteric cyst presenting as acute rapidly progressive quadriparesis and respiratory compromise: A case report and review of literature. Neurol. India 2013, 61, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Nagaishi, M.; Nakae, R.; Takigawa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, K. Intracranial endodermal cyst presenting with nonobstructive hydrocephalus: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e14322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, O.A.G.; Deepak, S.; Salem, O.; Arzoglou, V. The oldest presenting neurenteric cyst of the spinal cord. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 37, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.M.; Mathis, D.A.; Hobbs, J.K.; Timpone, V.M. Intracranial neurenteric cyst mimicking an ependymoma: Imaging features, pathologic correlation and review of literature. Clin. Imaging 2017, 44, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Izumi, H.; Nonaka, S.; Okura, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, M.; Yasumoto, Y.; Ishii, H. Spinal endodermal cyst undergoing malignant transformation and marked elevation of serum carbohydrate 19-9 level. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 37, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmed, I.H.; Boughamoura, M.; Dirks, P.; Kulkarni, A.V.; Rutka, J.T.; Drake, J.M. Neurosurgical management of neurenteric cysts in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2013, 11, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, R.S.; Cinalli, G.; Roujeau, T.; Sainte-Rose, C.; Pierre-Kahn, A.; Zerah, M. Neurenteric cysts in children: 16 consecutive cases and review of the literature. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 103, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, Y.; Nagasaka, T.; Takayasu, M.; Takagi, T.; Hata, N.; Yoshida, J. Recurrence of a neurenteric cyst with malignant transformation in the foramen magnum after total resection. Case report. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Nagatomi, A.; Ochi, M.; Kurisu, K. Intracranial neurenteric cyst with recurrence and extensive craniospinal dissemination. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 347–352, discussion 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, D.A.; Wang, L.; Ji, N.; Zhang, J. Recurrent intracranial neurenteric cyst with malignant transformation: A case report and literature review. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, G.P.; Symon, L.; Kendall, B.; Pires, M. Intracranial neurenteric cysts. Report of two cases. J. Neurosurg. 1991, 75, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, G.L.; Borkar, S.A.; Subbarao, K.C.; Sharma, M.C.; Mahapatra, A.K. Neurenteric cyst of the ventral cervicomedullary region. J. Pediatr. Neurosci. 2012, 7, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuse, T.; Yamada, K.; Kamiya, K.; Inagaki, H. Neurenteric cyst at the craniovertebral junction: Report of two cases. Surg. Neurol. 1998, 50, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koksel, T.; Revesz, T.; Crockard, H.A. Craniospinal neurenteric cyst. Br. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 4, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, A.; Miyake, H.; Tsuji, M.; Ukita, T.; Ito, S.; Matsuda, N.; Ohmura, T. Neurenteric cyst of the lower clivus. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, E224–E225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes, A.H.; Ryken, T.C. Craniocervical intradural neurenteric cysts. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 1995, 22, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Marx, S.; Zhang, C.; Cao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, D. Intramedullary bronchogenic cyst in the foramen magnum region accompanied with syringomyelia: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2019, 98, e14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeb, Z.L.; Maroon, J.C. Diagnosis of craniocervical dermoid by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: A case report. J. Comput. Tomogr. 1985, 9, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareff, J.A.; Hoil Parra, J.A. Intradural neurenteric cyst at the craniovertebral junction. Childs Nerv. Syst. 1995, 11, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, J.; Reul, J.; Mayfrank, L.; Ramaekers, V.; Thron, A. Duplication of a vertebral artery associated with epidermoid cyst of the posterior fossa. Eur. Radiol. 1997, 7, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekmann-Guiroy, B.; Huang, P.S. Klippel-Feil syndrome in association with a craniocervical dermoid cyst presenting as aseptic meningitis in an adult: Case report. Neurosurgery 1989, 25, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.G.; Babu, R.; Kranz, P.G.; McLendon, R.E.; Adamson, C. Intraaxial dermoid cyst of the medulla. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Geng, S.M.; Liu, P.N.; Lv, G. Association of Craniovertebral Junction Anomalies, Klippel-Feil Syndrome, Ruptured Dermoid Cyst and Mirror Movement in One Patient: A Unique Case and Literature Review. Turk. Neurosurg. 2016, 26, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, Y.; Nejat, F.; Khashab, M.E.; Ashrafi, M.R. Mirror movement associated with neural tube defects. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, B.S.; Duvall, E.R.; el Gammal, T.; Garcia, J.H.; Gupta, K.L.; Kapila, A. Neuroimaging features of neurenteric cysts: Analysis of nine cases and review of the literature. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1993, 14, 735–746. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, P.S.; Gupta, A.; Mishra, N.K.; Mehta, V.S. Association of craniovertebral and upper cervical anomalies with dermoid and epidermoid cysts: Report of four cases. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, E1155, discussion E1155. [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima, K.; Kohno, M.; Izawa, H.; Tanaka, Y. Partial Transcondylar Approach for Ventral Foramen Magnum Neurenteric Cyst: 2-Dimensional Operative Video. Oper. Neurosurg. 2019, 16, E81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, G.; Krauss, J.; Collmann, H.; Schrod, L.; Sorensen, N. Recurrent bacterial meningitis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1996, 155, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, R.L.; Schwartz, M.L.; Lewis, A.J. Neurenteric cyst located dorsal to the cervical spine: Case report. Neurosurgery 1991, 28, 583–587, discussion 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzumdar, D.; Goel, A. Posterior cranial fossa dermoid in association with craniovertebral and cervical spinal anomaly: Report of two cases. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2001, 35, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, F.G.; Aksoy, O.G.; Gomori, J.M. Klippel-Feil syndrome in association with posterior fossa suboccipital dermoid cyst. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, N.; Weil, A.G.; Demers, J.; Shedid, D. Klippel-Feil syndrome associated with a craniocervico-thoracic dermoid cyst. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S61–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelper, R.L.; Kagan-Hallet, K.S.; Huntington, H.W. Brainstem subarachnoid respiratory epithelial cysts: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Hum. Pathol. 1986, 17, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, J.; Bizik, I.; Surkala, J.; Steno, J.; Steno, A. Neurenteric cysts, incidence and surgical treatment. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2019, 120, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias, J.; Carrasco; De la Fuente, P.; Galbarriatu, L.; Paternain, C.; Ruiz de Gopegui, E.; Zaldumbide, L.; Pomposo, I. Neurenteric CYST of the craniocervical junction. Case report. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2021, 23, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulqader, S.B.; Elahi, B.N.; Alshoumer, A.; Alzhrani, G. Neurenteric cyst of the dorsal craniocervical junction in an adult: A case report and operative video. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2022, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Oketani, H.; Mizoguchi, M.; Hata, N.; Suzuki, S.O.; Iihara, K. A Dorsally Located Endodermal Cyst in the Foramen Magnum Mimicking an Arachnoid Cyst: A Case Report. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2020, 55, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, G.; Chen, G.; Guo, H.; Li, M.; Liang, J.; Bao, Y. Single-Center Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Experience of Foramen Magnum Neurenteric Cyst: Report of 6 Cases and Brief Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e608–e616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagnik, K.J.; Vakharia, K.; Vaubel, R.A.; Vizcaino, M.A.; Benson, J.C.; Daniels, D.J.; Link, M.J.; Van Gompel, J.J. Surgical Experience and Management of Intracranial Neurenteric Cysts: Single-Center Experience and Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2023, 84, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, G.L.; Sharma, B.S.; Mahapatra, A.K. Ventral foramen magnum neurenteric cysts: A case series and review of literature. Neurosurg. Rev. 2016, 39, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lai, R.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Case Report Series and Review of Rare Intradural Extramedullary Neoplasms-Bronchiogenic Cysts. Medicine 2015, 94, e2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, P.M.R.; Zaazoue, M.A.; Francois, R.; Dupervil, D.G.; Berkowitz, A.L.; Alexandrescu, S.; Proctor, M.R. Neurenteric cyst at the dorsal craniocervical junction in a child: Case report. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 48, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, M.M.; Bouros, D.; Klimko, A.; Florian, I.A.; Florian, I.S. Intracranial epidermoid cysts: Benign entities with malignant behavior: Experience with 36 cases. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Devi, B.I.; Bhat, D.I.; Somanna, S. Unusual complications of a benign tumour—Our experience with midline posterior fossa epidermoids. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 27, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, D.R.; Burokas, L.; Brown, H.G.; Hahn, Y.S.; Nikas, D. Management of an unusual, recurrent neurenteric cyst in an infant: Case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, M.T.; Osborn, A.G.; Chin, S.S.; Smirniotopoulos, J.G. Intracranial neurenteric cysts: Imaging and pathology spectrum. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozalp, H.; Hamzaoglu, V.; Karatas, D.; Dagtekin, A.; Yildiz, M.; Avci, E. Rare Cause of Acute Tetraplegia and Respiratory Arrest: Cervicomedullary Neuroenteric Cyst in a Child: Case Report. NMC Case Rep. J. 2019, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Jia, G.; Zhang, L.; Hao, S.; Geng, S. Diagnosis and management of adult intracranial neurenteric cysts. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 44–52, discussion 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, S.D.; Ali, S.; Burmaka, P.; Fercho, J.; Szmuda, T.; Abuhaimed, A.; Alotaibi, Y.; Sloniewski, P.; Krakowiak, M. Predictors for complete surgical resection of posterior fossa neurenteric cysts: A case report and meta-analysis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter (Nr., %)/Group | Total | Neurenteric | Dermoid | Epidermoid | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histopathology | 170 (100%) | 138 (81.2%) | 19 (11.2%) | 13 (7.6%) | - |
| Sex (male) | 83 (48.8%) | 66 (47.8%) | 12 (63.2%) | 5 (38.3%) | 0.348 * |
| Age (median (IQR)) | 27 (15–42) | 30 (16–41.25) | 16 (7–31) | 27 (16.5–57) | 0.182 ** |
| Signs and symptoms (Nr., %) | |||||
| Headache (N = 167) | 95 (56.9%) | 79 (58.5%) | 7 (36.8%) | 9 (69.2%) | 0.141 * |
| Neck pain (N = 168) | 59 (35.1%) | 52 (38.2%) | 5 (26.3%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0.198 * |
| Head and neck movement Limitation (N = 168) | 29 (17.3%) | 19 (14%) | 7 (36.8%) | 3 (23.1%) | 0.032 * |
| Nausea and vomiting (N = 168) | 26 (15.5%) | 19 (14%) | 4 (21.1%) | 3 (23.1%) | 0.461 * |
| Paresis (N = 168) | |||||
| Absent | 119 (70.8%) | 93 (68.4%) | 16 (84.2%) | 10 (76.9%) | 0.590 * |
| Monoparesis | 4 (2.4%) | 4 (2.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Hemiparesis | 9 (5.4%) | 9 (6.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Quadriparesis | 26 (15.5%) | 22 (16.2%) | 1 (5.3%) | 3 (23.1%) | |
| Bibrachial paresis | 4 (2.4%) | 2 (1.5%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Paraparesis | 2 (1.2%) | 2 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Other pyramidal signs | 4 (2.4%) | 4 (2.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| 6,7,8th nerve paresis (N = 168) | 19 (11.3%) | 14 (10.3%) | 2 (10.5%) | 3 (23.1%) | 0.329 * |
| Lower cranial nerve paresis (N = 167) | 29 (17.4%) | 25 (18.5%) | 3 (15.8%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.741 * |
| Cerebellar signs (N = 167) | 33 (19.8%) | 19 (14.1%) | 6 (31.6%) | 8 (61.5%) | <0.001 * |
| Sensory abnormalities (N = 168) | 29 (17.3%) | 24 (17.6%) | 5 (26.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0.135 * |
| Cardio-respiratory events (N = 167) | 6 (3.6%) | 6 (4.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1.000 * |
| Bladder and bowel involvement (N = 168) | 4 (2.4%) | 3 (2.2%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0.574 * |
| Meningitis (N = 168) | 22 (13.1%) | 15 (11%) | 6 (31.6%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.049 * |
| Symptomatic hydrocephalus (N = 168) | 12 (7.1%) | 7 (5.1%) | 2 (10.5%) | 3 (23.1%) | 0.030 * |
| Nystagmus (N = 168) | 9 (5.4%) | 7 (5.1%) | 1 (5.3%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.811 * |
| Mirror movement (N = 168) | 2 (1.2%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (10.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0.018 * |
| Onset of symptoms (N = 144) | |||||
| Insidious | 126 (87.5%) | 104 (86.7%) | 12 (100%) | 10 (83.3%) | 0.468 * |
| Suddenly | 18 (12.5%) | 16 (83.3%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (16.7%) | |
| Symptoms duration (N = 125) (median (IQR)) (months) | 5 (1.25–12) | 4 (1–12) | 6 (2–24) | 10 (2.25–24) | 0.315 ** |
| Location of tumor (N = 168) | |||||
| Anterior CVJ | 60 (35.7%) | 56 (41.2%) | 1 (5.3%) | 3 (23.1%) | <0.001 * |
| Anterior and lateral CVJ | 61 (36.3%) | 57 (41.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 1 (7.7%) | |
| Posterior CVJ | 33 (19.6%) | 12 (8.8%) | 14 (73.7%) | 7 (53.8%) | |
| Posterior and lateral CVJ | 10 (6%) | 7 (5.1%) | 1 (5.3%) | 2 (15.4%) | |
| Lateral CVJ | 4 (2.4%) | 4 (2.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Cistern location (N = 167) | |||||
| Premedullary cistern | 25 (15%) | 23 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (15.4%) | <0.001 * |
| Premedullary cistern down to the spinal canal | 43 (25.7%) | 40 (29.6%) | 3 (15.8%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Cerebellomedullary cistern | 23 (13.8%) | 7 (5.2%) | 13 (68.4%) | 3 (23.1%) | |
| Cerebellomedullary cistern down to the spinal canal | 18 (10.8%) | 11 (8.1%) | 2 (10.5%) | 5 (38.5%) | |
| Pontomedullary cistern | 21 (12.6%) | 20 (14.8%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.7%) | |
| Pontomedullary cistern down to the spinal canal | 18 (10.8%) | 17 (12.6%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.7%) | |
| Subarachnoid space at the level of upper cervical canal | 17 (10.2%) | 16 (11.9%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (7.7%) | |
| Intramedullary | 2 (1.2%) | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (5.3%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Cyst volume (Median (IQR)) (N = 40) | 14.86 (6.26–40.16) | 13.87 (6.43–30) | 8 (6.89–37.6) | 54.9 (28.08–84.38) | 0.254 ** |
| MRI aspect (N = 129) | |||||
| Homogeneous | 92 (71.3%) | 74 (71.8%) | 10 (66.7%) | 8 (72.7%) | 0.934 * |
| Heterogeneous | 37 (28.7%) | 29 (28.2%) | 5 (33.3%) | 3 (27.3%) | |
| T1 aspect (N = 140) | |||||
| Hyposignal | 54 (38.6%) | 39 (34.2%) | 8 (57.1%) | 7 (58.3%) | 0.090 * |
| Isosignal | 19 (13.6%) | 18 (15.6%) | 1 (7.1%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Hypersignal | 53 (37.9%) | 46 (40.4%) | 2 (14.3%) | 5 (41.7%) | |
| Mixed | 14 (10%) | 11 (9.6%) | 3 (21.4%) | 0 (0%) | |
| T2 aspect (N = 130) | |||||
| Hyposignal | 23 (17.7%) | 16 (14.8%) | 2 (20%) | 5 (41.7%) | 0.320 * |
| Isosignal | 9 (6.9%) | 8 (7.4%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (8.3%) | |
| Hypersignal | 89 (69.5%) | 76 (70.4%) | 7 (70%) | 6 (50%) | |
| Mixed | 9 (6.9%) | 8 (7.4%) | 1 (10%) | 0 (0%) | |
| DWI (N = 36) | |||||
| No restriction | 30 (83.3%) | 23 (88.5%) | 1 (33.3%) | 6 (85.7%) | 0.020 * |
| Mild restriction | 3 (8.3%) | 3 (11.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Hyperintense | 3 (8.3%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (66.7%) | 1 (14.3%) | |
| Enhancement (N = 108) | |||||
| Absent | 74 (68.5%) | 61 (66.3%) | 5 (83.3%) | 8 (20%) | 0.895 * |
| Rim enhancement | 28 (25.9%) | 25 (27.2%) | 1 (16.7%) | 2 (20%) | |
| Homogenous | 4 (3.7%) | 4 (4.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Other (irregular/linear) | 2 (1.9%) | 2 (2.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Position (N = 60) | |||||
| Lateral | 23 (38.3%) | 21 (40.4%) | 1 (33.3%) | 1 (20%) | 0.058 * |
| Prone | 21 (35%) | 20 (38.5%) | 1 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Supine | 3 (5%) | 3 (5.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Sitting | 13 (21.7%) | 8 (15.4%) | 1 (33.3%) | 4 (80%) | |
| Craniotomy approach (N = 135) | |||||
| Far-lateral | 34 (25.2%) | 31 (29%) | 2 (11.1%) | 1 (10%) | 0.002 * |
| Far-lateral transcondylar | 23 (17%) | 22 (20.6%) | 1 (5.6%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Posterior midline | 51 (37.8%) | 30 (28%) | 15 (83.3%) | 6 (60%) | |
| Retrosigmoid | 23 (17%) | 20 (18.7%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (30%) | |
| Transoral | 4 (3%) | 4 (3.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Adhesion to surrounding brain (N = 123) | 87 (70.7%) | 72 (70.6%) | 9 (69.2%) | 6 (75%) | 1.000 * |
| Extent of resection (N = 157) | |||||
| Total | 100 (63.7%) | 85 (65.9%) | 9 (52.9%) | 6 (54.5%) | 0.452 * |
| Near-total | 17 (10.8%) | 14 (10.9%) | 1 (5.9%) | 2 (18.2%) | |
| Subtotal | 40 (25.5%) | 30 (23.3%) | 7 (41.2%) | 3 (27.3%) | |
| Postoperative meningitis | 10 (5.9%) | 10 (7.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0.556 * |
| Complications (N = 151) | 41 (27.2%) | 35 (28%) | 5 (31.3%) | 1 (10%) | 0.443 * |
| Postoperative CT/MRI (N = 109) | |||||
| No evidence of recurrence | 96 (88.1%) | 82 (86.3%) | 8 (100%) | 6 (100%) | 0.653 * |
| Residual lesion | 13 (11.9%) | 13 (13.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Follow-up period (Median (IQR)) (N = 125) | 22 (6–40.5) | 14 (6–36) | 32 (8.5–81) | 24 (4.5–60) | 0.313 ** |
| Associated anomalies (N = 165) | 29 (17.6%) | 12 (9%) | 15 (78.9%) | 2 (16.7%) | <0.001 * |
| Outcome (N = 149) | |||||
| Excellent | 112 (75.2%) | 92 (75.4%) | 12 (75%) | 8 (72.7%) | 0.836 * |
| Good | 29 (19.5%) | 22 (18%) | 4 (25%) | 3 (27.3%) | |
| Poor | 1 (0.7%) | 1 (0.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Dead | 7 (4.7%) | 7 (5.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Recurrence (N = 125) | 15 (12%) | 13(12.4%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1.000 * |
| CSF diversion (N = 153) | 24 (15.7%) | 19 (14.6%) | 3 (27.3%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0.462 * |
| Instrumentation (N = 161) | 8 (5%) | 5 (3.8%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (7.7%) | 0.221 * |
| Parameter | Univariable | Multivariable * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% C.I.) | p | OR (95% C.I.) | P | |
| Symptomatic hydrocephalus | 8.80 (1.56–49.57) | 0.014 | 0.49 (0.00–131,333.92) | 0.490 |
| T1-hyposignal | 4.26 (1.13–15.96) | 0.031 | 5.87 (0.35–97.83) | 0.217 |
| Rim enhancement | 9.66 (2.11–44.15) | 0.003 | 14.13 (1.035–193.03) | 0.047 |
| Subtotal resection | 9.53 (2.62–34.65) | 0.001 | 2.28 (0.15–32.93) | 0.545 |
| Poor outcome | 43 (7.09–260.56) | <0.001 | 139.07 (3.76–5139.77) | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pop, M.M.; Bouros, D.; Klimko, A.; Pop, L.A.; Topal, P.; Topal, A.; Florian, I.S. Tumor-Like Lesions in the Craniovertebral Junction: A Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162788
Pop MM, Bouros D, Klimko A, Pop LA, Topal P, Topal A, Florian IS. Tumor-Like Lesions in the Craniovertebral Junction: A Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162788
Chicago/Turabian StylePop, Maria Mihaela, Dragos Bouros, Artsiom Klimko, Laura Ancuta Pop, Paula Topal, Anil Topal, and Ioan Stefan Florian. 2024. "Tumor-Like Lesions in the Craniovertebral Junction: A Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162788
APA StylePop, M. M., Bouros, D., Klimko, A., Pop, L. A., Topal, P., Topal, A., & Florian, I. S. (2024). Tumor-Like Lesions in the Craniovertebral Junction: A Case Series, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(16), 2788. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162788







