SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease—Review and Future Perspectives
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
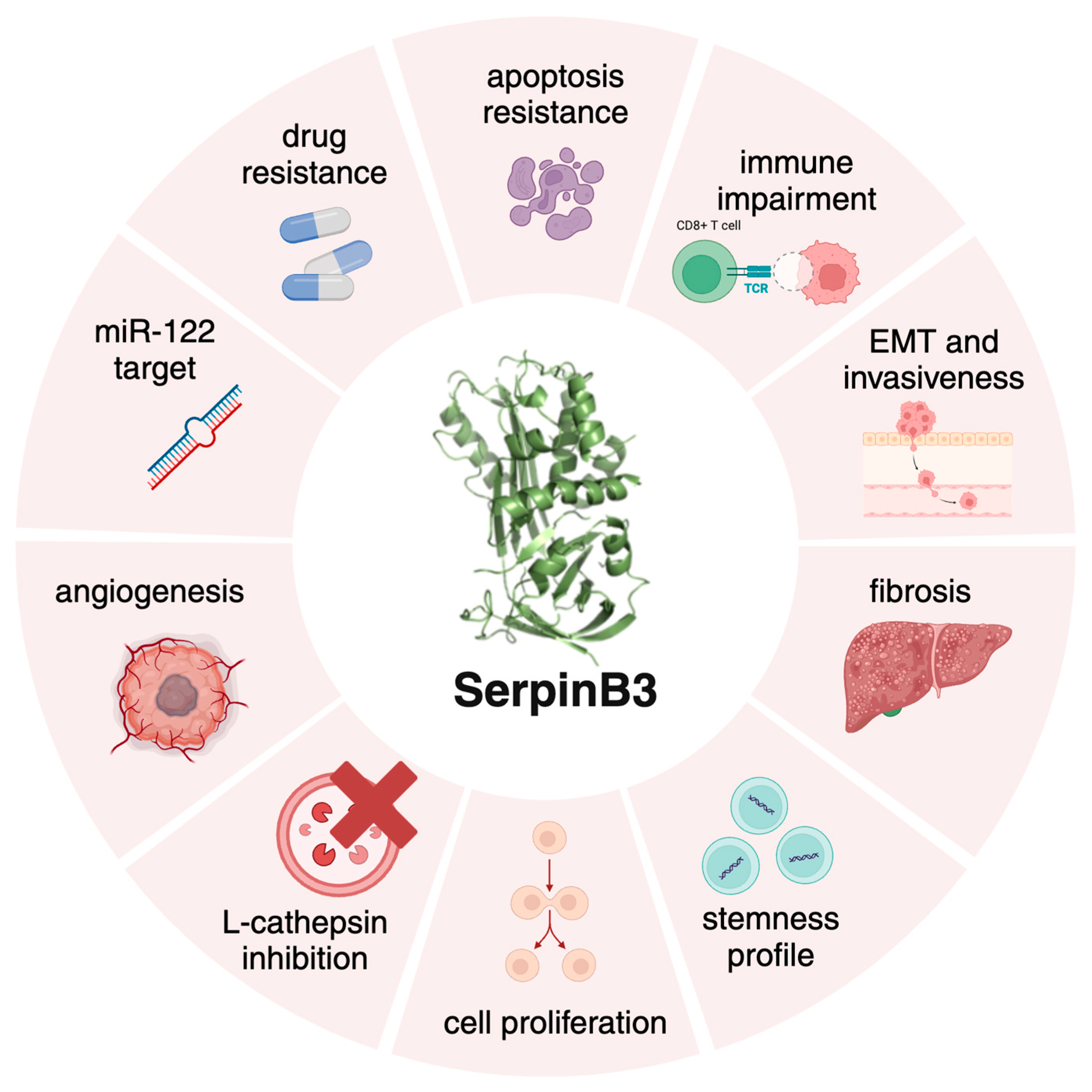
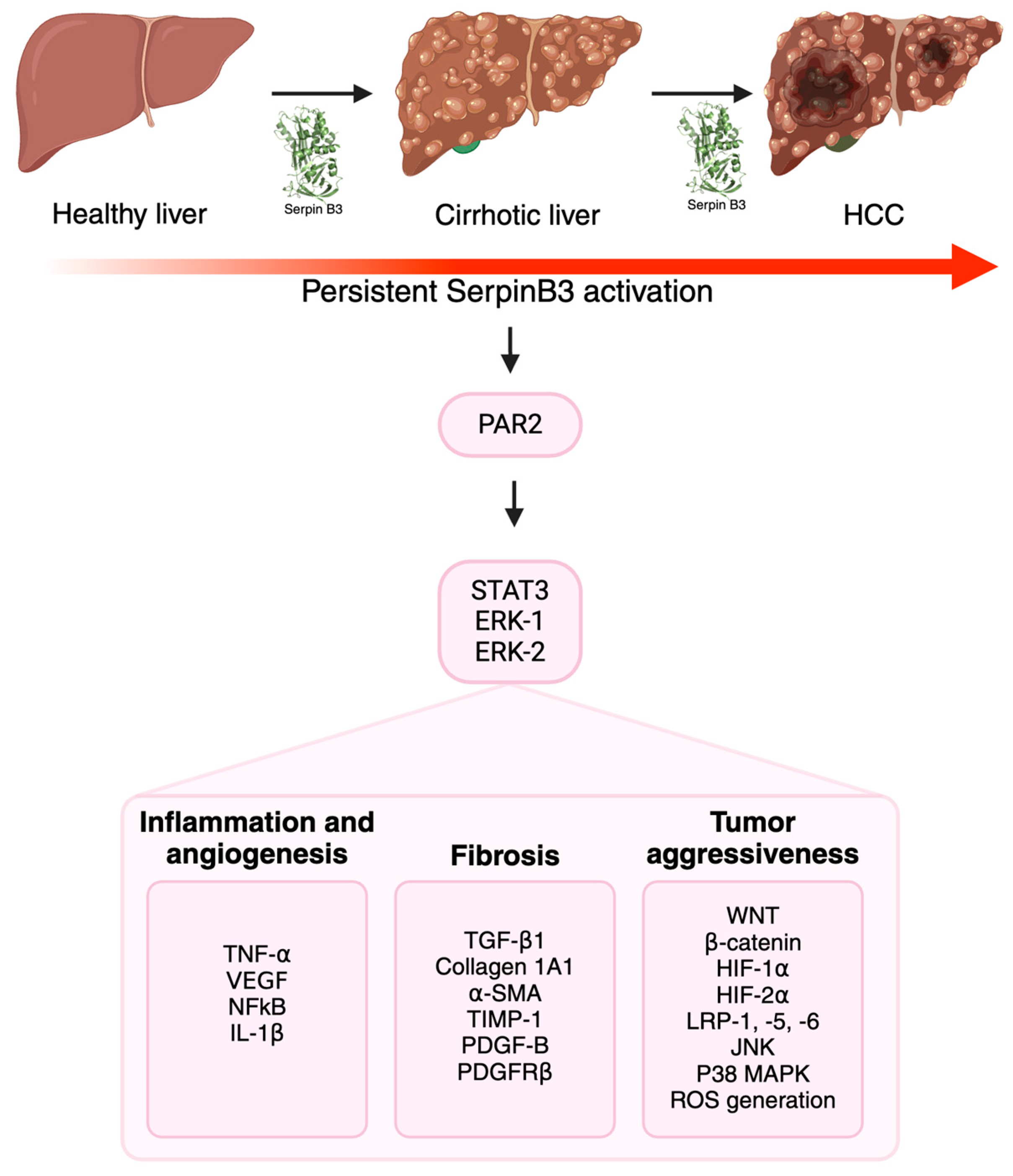
2. SerpinB3 in Fibrosis and Carcinogenesis
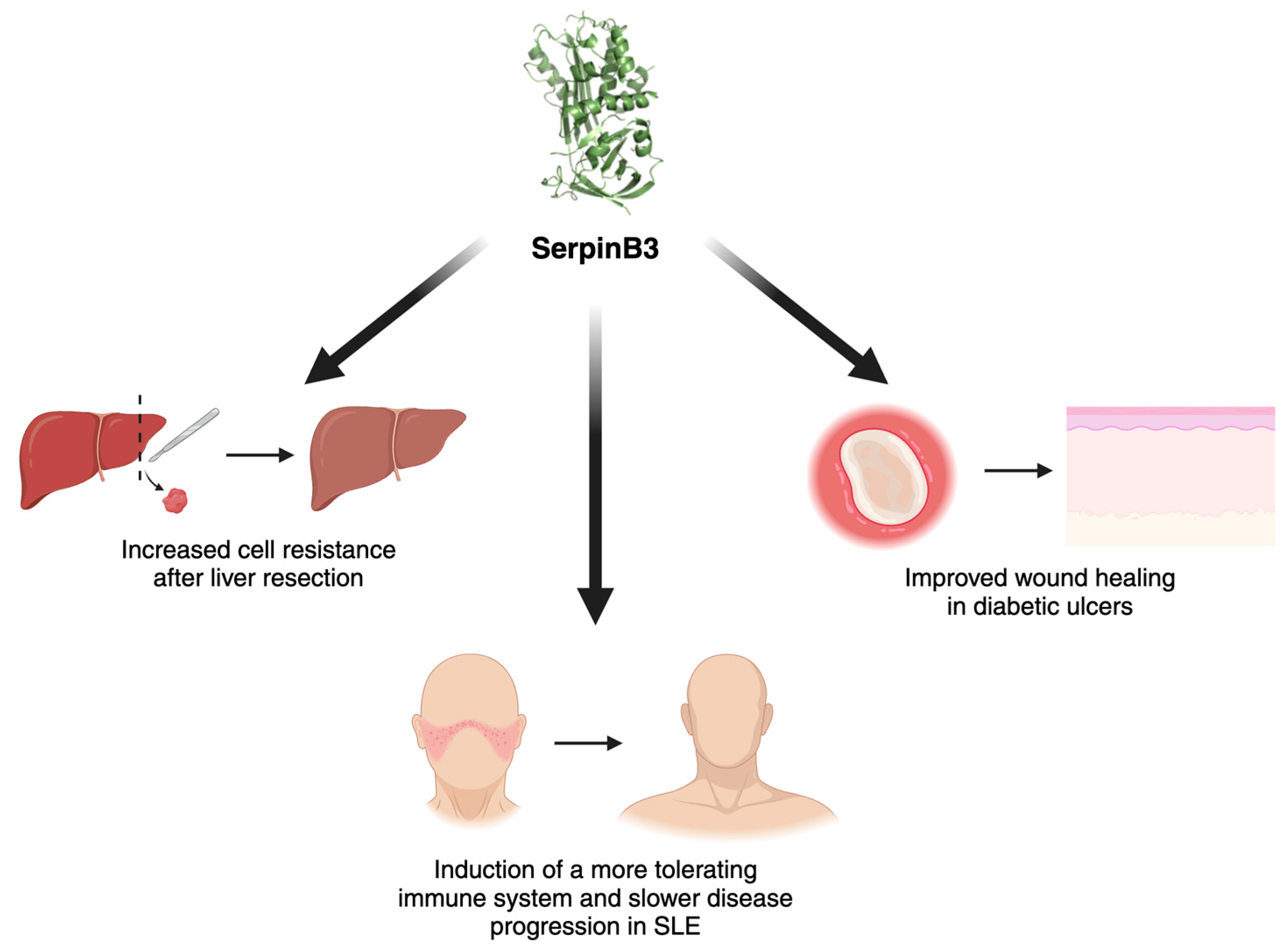
3. SerpinB3 as a Promising Protective Molecule
4. The Future: A Novel Druggable Target for SerpinB3 Inhibition?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heit, C.; Jackson, B.C.; Mcandrews, M.; Wright, M.W.; Thompson, D.C.; Silverman, G.A.; Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Update of the Human and Mouse SERPIN Gene Superfamily. Hum. Genom. 2013, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janciauskiene, S.; Lechowicz, U.; Pelc, M.; Olejnicka, B.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Value of Human Serpin Family Proteins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.R.; Giri, H. Anticoagulant and Signaling Functions of Antithrombin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 3142–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Manithody, C.; Li, J.; Rezaie, A.R. Antithrombin Up-Regulates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signalling during Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janciauskiene, S.M.; Bals, R.; Koczulla, R.; Vogelmeier, C.; Köhnlein, T.; Welte, T. The Discovery of A1-Antitrypsin and Its Role in Health and Disease. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.H.P.; Zhang, Q.; McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M.; Silverman, G.A.; Wong, W.; Rosado, C.J.; Langendorf, C.G.; Pike, R.N.; Bird, P.I.; et al. An Overview of the Serpin Superfamily. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pontisso, P.; Parola, M. SERPINB3 in Fibrogenic Chronic Liver Diseases and Primary Liver Cancers. Explor. Dig. Dis. 2024, 3, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izuhara, K.; Ohta, S.; Kanaji, S.; Shiraishi, H.; Arima, K. Recent Progress in Understanding the Diversity of the Human Ov-Serpin/Clade B Serpin Family. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2541–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Torigoe, T. Radioimmunoassay for Tumor Antigen of Human Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer 1977, 40, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Sheshadri, N.; Zong, W.X. SERPINB3 and B4: From Biochemistry to Biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 62, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, S.; Marques, P.I.; Matthiesen, R.; Seixas, S. Adaptive Evolution and Divergence of SERPINB3: A Young Duplicate in Great Apes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tolomeo, A.M.; Quarta, S.; Biasiolo, A.; Ruvoletto, M.; Pozzobon, M.; De Lazzari, G.; Malvicini, R.; Turato, C.; Arrigoni, G.; Pontisso, P.; et al. Engineered EVs for Oxidative Stress Protection. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidalino, L.; Doria, A.; Quarta, S.; Zen, M.; Gatta, A.; Pontisso, P. SERPINB3, Apoptosis and Autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 9, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciscato, F.; Sciacovelli, M.; Villano, G.; Turato, C.; Bernardi, P.; Rasola, A.; Pontisso, P. SERPINB3 Protects from Oxidative Damage by Chemotherapeutics through Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiratory Complex I. Oncotarget 2013, 5, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numa, F.; Takeda, O.; Nakata, M.; Nawata, S.; Tsunaga, N.; Hirabayashi, K.; Suminami, Y.; Kato, H.; Hamanaka, S. Tumor Necrosis Factor a Stimulates the Production of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen in Normal Squamous Cells. Tumor Biol. 1996, 17, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catanzaro, J.M.; Sheshadri, N.; Zong, W.X. SerpinB3/B4: Mediators of Ras-Driven Inflammation and Oncogenesis. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3155–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Catanzaro, J.M.; Sheshadri, N.; Pan, J.A.; Sun, Y.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Powers, R.S.; Crawford, H.C.; Zong, W.X. Oncogenic Ras Induces Inflammatory Cytokine Production by Upregulating the Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigens SerpinB3/B4. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, S.; Vidalino, L.; Turato, C.; Ruvoletto, M.; Calabrese, F.; Valente, M.; Cannito, S.; Fassina, G.; Parola, M.; Gatta, A.; et al. SERPINB3 Induces Epithelial—Mesenchymal Transition. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, V.; Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Freeman, R.; Yang, J.; Inkman, M.J.; Ghosh, S.; Ruiz, F.; Jayachandran, K.; et al. SCCA1/SERPINB3 Suppresses Antitumor Immunity and Blunts Therapy-Induced T Cell Responses via STAT-Dependent Chemokine Production. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e163841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.; Lunardi, F.; Giacometti, C.; Marulli, G.; Gnoato, M.; Pontisso, P.; Saetta, M.; Valente, M.; Rea, F.; Perissinotto, E.; et al. Overexpression of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Clinicopathological Correlations. Thorax 2008, 63, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease—A Global Public Health Perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of Liver Diseases in the World. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and Regional Mortality from 235 Causes of Death for 20 Age Groups in 1990 and 2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turato, C.; Calabrese, F.; Biasiolo, A.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Tono, N.; Paccagnella, D.; Fassina, G.; Merkel, C.; Harrison, T.J.; et al. SERPINB3 Modulates TGF-Β Expression in Chronic Liver Disease. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.; Villano, G.; Turato, C.; Cannito, S.; Paternostro, C.; Busletta, C.; Biasiolo, A.; Quarta, S.; Morello, E.; Bocca, C.; et al. SerpinB3 Promotes Pro-Fibrogenic Responses in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turato, C.; Biasiolo, A.; Pengo, P.; Frecer, V.; Quarta, S.; Fasolato, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Beneduce, L.; Zuin, J.; Fassina, G.; et al. Increased Antiprotease Activity of the SERPINB3 Polymorphic Variant SCCA-PD. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Turato, C.; Cannito, S.; Quarta, S.; Biasiolo, A.; Ruvoletto, M.; Novo, E.; Marafatto, F.; Guerra, P.; Tonon, M.; et al. The Polymorphic Variant of SerpinB3 (SerpinB3-PD) Is Associated with Faster Cirrhosis Decompensation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turato, C.; Vitale, A.; Fasolato, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Terrin, L.; Quarta, S.; Ramirez Morales, R.; Biasiolo, A.; Zanus, G.; Zali, N.; et al. SERPINB3 Is Associated with TGF-Β1 and Cytoplasmic β-Catenin Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinomas with Poor Prognosis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrin, L.; Agostini, M.; Ruvoletto, M.; Martini, A.; Pucciarelli, S.; Bedin, C.; Nitti, D.; Pontisso, P. SerpinB3 Upregulates the Cyclooxygenase-2/β-Catenin Positive Loop in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debebe, A.; Medina, V.; Chen, C.Y.; Mahajan, I.M.; Jia, C.; Fu, D.; He, L.; Zeng, N.; Stiles, B.W.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Activation and Macrophage Induction during Liver Cancer Development Following Steatosis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6020–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Basler, K. The Many Faces and Functions of B-Catenin. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2714–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turato, C.; Buendia, M.A.; Fabre, M.; Redon, M.J.; Branchereau, S.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Perilongo, G.; Grotzer, M.A.; Gatta, A.; et al. Over-Expression of SERPINB3 in Hepatoblastoma: A Possible Insight into the Genesis of This Tumour? Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarta, S.; Cappon, A.; Turato, C.; Ruvoletto, M.; Cannito, S.; Villano, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Maggi, M.; Protopapa, F.; Bertazza, L.; et al. SerpinB3 Upregulates Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein (LRP) Family Members, Leading to Wnt Signaling Activation and Increased Cell Survival and Invasiveness. Biology 2023, 12, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, B.; Pan, W.; Farr, G.H.; Flynn, C.; Yuan, H.; Takada, S.; Kimelman, D.; Li, L.; et al. Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein-5 Binds to Axin and Regulates the Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. Extracellular Hsp90á and Clusterin Synergistically Promote Breast Cancer Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis via LRP1. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs228213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver Fibrosis: Pathophysiology, Pathogenetic Targets and Clinical Issues. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Szabo, G. Hypoxia and Hypoxia Inducible Factors: Diverse Roles in Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2012, 55, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannito, S.; Paternostro, C.; Busletta, C.; Bocca, C.; Colombatto, S.; Miglietta, A.; Novo, E.; Parola, M. Hypoxia, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Fibrogenesis in Chronic Liver Diseases. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roth, K.J.; Copple, B.L. Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in the Development of Liver Fibrosis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglia, B.; Novo, E.; Protopapa, F.; Maggiora, M.; Bocca, C.; Cannito, S.; Parola, M. Hypoxia, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzner, L.M.W.; Murray, A.J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors as Key Players in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 753268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majmundar, A.J.; Wong, W.J.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and the Response to Hypoxic Stress. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.K.; Tennant, D.A.; Mckeating, J.A. Hypoxia Inducible Factors in Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Understanding and Future Directions. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schito, L.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Master Regulators of Cancer Progression. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Lou, T. Hypoxia Inducible Factors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, S.R. Defining Normoxia, Physoxia and Hypoxia in Tumours—Implications for Treatment Response. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. The Role of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 409272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menrad, H.; Werno, C.; Schmid, T.; Copanaki, E.; Deller, T.; Dehne, N.; Brüne, B. Roles of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) versus HIF-2α in the Survival of Hepatocellular Tumor Spheroids. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Sun, X.P.; Qiao, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, D.; Jin, X.; Dong, X.; Wang, J.J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, X. Downregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2a Improves the Efficacy of Doxorubicin in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, W.M.; Bai, H.; Shi, R.Y.; Nayar, S.K.; Devbhandari, R.P.; He, Y.Z.; Zhu, Q.F.; et al. Hypoxia Inducible Factor 2 Alpha Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth through the Transcription Factor Dimerization Partner 3/E2F Transcription Factor 1-Dependent Apoptotic Pathway. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Zhai, B.; He, C.; Tan, G.; Jiang, X.; Pan, S.; Dong, X.; Wei, Z.; Ma, L.; Qiao, H.; et al. Upregulation of HIF-2α Induced by Sorafenib Contributes to the Resistance by Activating the TGF-α/EGFR Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-L.; Liu, L.-P.; Niu, L.; Sun, Y.-F.; Yang, X.-R.; Fan, J.; Ren, J.-W.; Chen, G.G.; Lai, P.B.S. Downregulation and Pro-Apoptotic Effect of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2 Alpha in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34571–34581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Zhanyu, L.; Gong, Y.; Zou, B.; Liu, X.; Ding, L.; Li, P.; Zhu, Z.; et al. HIF-2a Upregulation Mediated by Hypoxia Promotes NAFLD-HCC Progression by Activating Lipid Synthesis via the PI3K-AKT-MTOR Pathway. Aging 2019, 11, 10839–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontisso, P.; Calabrese, F.; Benvegnù, L.; Lise, M.; Belluco, C.; Ruvoletto, M.G.; De Falco, S.; Marino, M.; Valente, M.; Nitti, D.; et al. Overexpression of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen Variants in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foglia, B.; Sutti, S.; Cannito, S.; Rosso, C.; Maggiora, M.; Autelli, R.; Novo, E.; Bocca, C.; Villano, G.; Ramavath, N.N.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Deletion of HIF2α Prevents NASH-Related Liver Carcinogenesis by Decreasing Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 459–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turato, C.; Cannito, S.; Simonato, D.; Villano, G.; Morello, E.; Terrin, L.; Quarta, S.; Biasiolo, A.; Ruvoletto, M.; Martini, A.; et al. SerpinB3 and Yap Interplay Increases Myc Oncogenic Activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannito, S.; Foglia, B.; Villano, G.; Turato, C.; Delgado, T.C.; Morello, E.; Pin, F.; Novo, E.; Napione, L.; Quarta, S.; et al. Serpin B3 Differently Up-Regulates Hypoxia Inducible Factors -1α and -2α in Hepatocellula Arcinoma: Mechanisms Revealing Novel Potential Therapeutic Targets. Cancers 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, E.; Cappon, A.; Villano, G.; Quarta, S.; Cannito, S.; Bocca, C.; Turato, C.; Guido, M.; Maggiora, M.; Protopapa, F.; et al. SerpinB3 as a Pro-Inflammatory Mediator in the Progression of Experimental Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 910526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Kuang, H.; Ansari, S.; Liu, T.; Gong, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Landscape of Intercellular Crosstalk in Healthy and NASH Liver Revealed by Single-Cell Secretome Gene Analysis. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 644–660.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, E.B.; Rha, J.; Selak, M.A.; Unger, T.L.; Keith, B.; Liu, Q.; Haase, V.H. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 2 Regulates Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, A.; Taylor, M.; Xue, X.; Matsubara, T.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Shah, Y.M. Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factor 2α Promotes Steatohepatitis through Augmenting Lipid Accumulation, Inflammation, and Fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, E.; Sutti, S.; Foglia, B.; Novo, E.; Cannito, S.; Bocca, C.; Rajsky, M.; Bruzzì, S.; Abate, M.L.; Rosso, C.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible Factor 2α Drives Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Progression by Triggering Hepatocyte Release of Histidine-rich Glycoprotein. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2196–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.A.; Friedman, S.L. Inflammatory and Fibrotic Mechanisms in NAFLD—Implications for New Treatment Strategies. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Shubrook, J.H.; Younossi, Z.; Natarajan, Y.; Bugianesi, E.; Rinella, M.E.; Harrison, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.; Pfotenhauer, K.; Klein, S.; et al. Preparing for the NASH Epidemic: A Call to Action. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1030–1042.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nagaya, T.; Torigoe, T. Heterogeneity of a Tumor Antigen TA-4 of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Relation to Its Appearance in the Circulation. Gan 1984, 75, 433–435. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilakopoulos, T.; Troupis, T.; Sotiropoulou, C.; Zacharatos, P.; Katsaounou, P.; Parthenis, D.; Noussia, O.; Troupis, G.; Papiris, S.; Kittas, C.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2001, 32, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, J.; Hedström, J.; Grénman, R.; Leivo, I.; Finne, P.; Palotie, A.; Orpana, A. Relative Levels of SCCA2 and SCCA1 MRNA in Primary Tumors Predicts Recurrent Disease in Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 95, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie-Duguid, E.S.R.; Sweeney, K.; Stewart, K.N.; Miller, I.D.; Smyth, E.; Heys, S.D. SerpinB3, a New Prognostic Tool in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovina, S.; Wang, S.; Henke, L.E.; Luke, C.J.; Pak, S.C.; Dewees, T.; Pfeifer, J.D.; Schwarz, J.K.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Serum Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen as an Early Indicator of Response during Therapy of Cervical Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turato, C.; Scarpa, M.; Kotsafti, A.; Cappon, A.; Quarta, S.; Biasiolo, A.; Cavallin, F.; Trevellin, E.; Guzzardo, V.; Fassan, M.; et al. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen 1 Is Associated to Poor Prognosis in Esophageal Cancer through Immune Surveillance Impairment and Reduced Chemosensitivity. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, A.; Prasai, K.; Zemla, T.J.; Ahmed, F.Y.; Elnagar, M.B.; Giama, N.H.; Guzzardo, V.; Biasiolo, A.; Fassan, M.; Yin, J.; et al. SerpinB3/4 Expression Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guido, M.; Roskams, T.; Pontisso, P.; Fassan, M.; Thung, S.N.; Giacomelli, L.; Sergio, A.; Farinati, F.; Cillo, U.; Rugge, M. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen in Human Liver Carcinogenesis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2008, 61, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasiolo, A.; Chemello, L.; Quarta, S.; Cavalletto, L.; Bortolotti, F.; Caberlotto, C.; Beneduce, L.; Bernardinello, E.; Tono, N.; Fassina, G.; et al. Monitoring SCCA-IgM Complexes in Serum Predicts Liver Disease Progression in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis. J. Viral Hepat. 2008, 15, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneduce, L.; Castaldi, F.; Marino, M.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Benvegnù, L.; Calabrese, F.; Gatta, A.; Pontisso, P.; Fassina, G. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen-Immunoglobulin M Complexes as Novel Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, E.; Pan, J.-A.; Zong, W.-X. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen 1 Promotes Caspase-8-Mediated Apoptosis in Response to Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress While Inhibiting Necrosis Induced by Lysosomal Injury. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 2902–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshadri, N.; Catanzaro, J.M.; Bott, A.J.; Sun, Y.; Ullman, E.; Chen, E.I.; Pan, J.A.; Wu, S.; Crawford, H.C.; Zhang, J.; et al. SCCA1/SERPINB3 Promotes Oncogenesis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the Unfolded Protein Response and IL6 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6318–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminami, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Vujanovic, N.L.; Hirabayashi, K.; Kato, H.; Whiteside, T.L. Inhibition of Apoptosis in Human Tumour Cells by the Tumour-Associated Serpin, SCC Antigen-1. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, C.; Nakanishi, J.; Kadoya, K.; Hibino, T. Serpin Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen Inhibits UV-Induced Apoptosis via Suppression of c-JUN NH2-Terminal Kinase. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, A.; Suminami, Y.; Hirakawa, H.; Nawata, S.; Numa, F.; Kato, H. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen Suppresses Radiation-Induced Cell Death. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, G.; Turato, C.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Ciscato, F.; Terrin, L.; Semeraro, R.; Paternostro, C.; Parola, M.; Alvaro, D.; et al. Hepatic Progenitor Cells Express SerpinB3. BMC Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turato, C.; Fornari, F.; Pollutri, D.; Fassan, M.; Quarta, S.; Villano, G.; Ruvoletto, M.; Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L.; Pontisso, P. MiR-122 Targets SerpinB3 and Is Involved in Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakral, S.; Ghoshal, K. MiR-122 Is a Unique Molecule with Great Potential in Diagnosis, Prognosis of Liver Disease, and Therapy Both as MiRNA Mimic and Antimir. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, M.; Spasic, M.V.; Altamura, S.; Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Kiss, J.; Stolte, J.; Sparla, R.; D’Alessandro, L.A.; Klingmüller, U.; et al. The Liver-Specific MicroRNA MiR-122 Controls Systemic Iron Homeostasis in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, S.; Tan, X.; Monga, S.P.S. β-Catenin and Met Deregulation in Childhood Hepatoblastomas. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2005, 8, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairo, S.; Armengol, C.; De Reyniès, A.; Wei, Y.; Thomas, E.; Renard, C.A.; Goga, A.; Balakrishnan, A.; Semeraro, M.; Gresh, L.; et al. Hepatic Stem-like Phenotype and Interplay of Wnt/β-Catenin and Myc Signaling in Aggressive Childhood Liver Cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A. The Emerging Family of Hepatoblastoma Tumours: From Ontogenesis to Oncogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, J.U.; Raggi, C.; Andersen, J.B.; Seo, D.; Avital, I.; Geller, D.; Lee, Y.H.; Kitade, M.; Holczbauer, A.; Gillen, M.C.; et al. Human Hepatic Cancer Stem Cells Are Characterized by Common Stemness Traits and Diverse Oncogenic Pathways. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Honda, M.; Nakamoto, Y.; Baba, M.; Nio, K.; Hara, Y.; Zeng, S.S.; Hayashi, T.; Kondo, M.; Takatori, H.; et al. Discrete Nature of EpCAM+ and CD90+ Cancer Stem Cells in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correnti, M.; Cappon, A.; Pastore, M.; Piombanti, B.; Lori, G.; Oliveira, D.V.P.N.; Munoz-Garrido, P.; Lewinska, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Coulouarn, C.; et al. The Protease-Inhibitor SerpinB3 as a Critical Modulator of the Stem-like Subset in Human Cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, C.; Invernizzi, P.; Andersen, J.B. Impact of Microenvironment and Stem-like Plasticity in Cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular Networks and Biological Concepts. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, C.; Correnti, M.; Sica, A.; Andersen, J.B.; Cardinale, V.; Alvaro, D.; Chiorino, G.; Forti, E.; Glaser, S.; Alpini, G.; et al. Cholangiocarcinoma Stem-like Subset Shapes Tumor-Initiating Niche by Educating Associated Macrophages. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, J.B.; Spee, B.; Blechacz, B.R.; Avital, I.; Komuta, M.; Barbour, A.; Conner, E.A.; Gillen, M.C.; Roskams, T.; Roberts, L.R.; et al. Genomic and Genetic Characterization of Cholangiocarcinoma Identifies Therapeutic Targets for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1021–1031.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Arai, Y.; Totoki, Y.; Shirota, T.; Elzawahry, A.; Kato, M.; Hama, N.; Hosoda, F.; Urushidate, T.; Ohashi, S.; et al. Genomic Spectra of Biliary Tract Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gringeri, E.; Biasiolo, A.; Di Giunta, M.; Mescoli, C.; Guzzardo, V.; Sartori, A.; Cirillo, G.; Nieddu, E.; D’Amico, F.E.; Pontisso, P.; et al. Bile Detection of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen (SCCA) in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2023, 55, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Luke, C.J.; Pak, S.C.; Shi, V.; Chen, L.; Moore, J.; Andress, A.P.; Jayachandran, K.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. SERPINB3 (SCCA1) Inhibits Cathepsin L and Lysoptosis, Protecting Cervical Cancer Cells from Chemoradiation. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.B. Review of STAT3 (Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription) in Head and Neck Cancer. Oral. Oncol. 2015, 51, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, S.; Ushijima, K.; Kawano, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Terada, A.; Fujiyoshi, N.; Nishio, S.; Tsuda, N.; Ijichi, M.; Kakuma, T.; et al. Expression of Activated Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Cervical Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Lu, S. A Meta-Analysis of STAT3 and Phospho-STAT3 Expression and Survival of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 40, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Pal, S.K.; Reckamp, K.; Figlin, R.A.; Yu, H. STAT3: A Target to Enhance Antitumor Immune Response. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 344, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, L.L.; Yu, G.T.; Wu, L.; Mao, L.; Deng, W.W.; Liu, J.F.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.F.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.J. STAT3 Induces Immunosuppression by Upregulating PD-1/PD-L1 in HNSCC. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Niu, G.; Kortylewski, M.; Burdelya, L.; Shain, K.; Zhang, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Gabrilovich, D.; Heller, R.; Coppola, D.; et al. Regulation of the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses by Stat-3 Signaling in Tumor Cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, W.; Ahn, S.E.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, M.K.; Chung, H.H.; Song, Y.S.; et al. SERPINB3 in the Chicken Model of Ovarian Cancer: A Prognostic Factor for Platinum Resistance and Survival in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ohara, Y.; Tang, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Dorsey, T.H.; Cawley, H.; Moreno, P.; Chari, R.; Guest, M.R.; Azizian, A.; et al. SERPINB3-MYC Axis Induces the Basal-like/Squamous Subtype and Enhances Disease Progression in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.R.; Liu, C.J.; Hu, H.; Yang, M.; Guo, A.Y. Biological Pathway-Derived TMB Robustly Predicts the Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cells 2022, 11, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadini, G.P.; Albiero, M.; Millioni, R.; Poncina, N.; Rigato, M.; Scotton, R.; Boscari, F.; Brocco, E.; Arrigoni, G.; Villano, G.; et al. The Molecular Signature of Impaired Diabetic Wound Healing Identifies SerpinB3 as a Healing Biomarker. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1947–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Deng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. An Update on Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosing Diabetic Foot Ulcer at Early Stage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiero, M.; Fullin, A.; Villano, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Quarta, S.; Bernardotto, S.; Turato, C.; Ruvoletto, M.; Fadini, G.P.; Pontisso, P.; et al. Semisolid Wet Sol–Gel Silica/Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose Formulation for Slow Release of Serpin B3 Promotes Wound Healing In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, M.; Luisetto, R.; Ghirardello, A.; Cavicchioli, L.; Codolo, G.; Biasiolo, A.; Maggioni, G.; Saccon, F.; Beggio, M.; Cappon, A.; et al. SERPINB3 Delays Glomerulonephritis and Attenuates the Lupus-like Disease in Lupus Murine Models by Inducing a More Tolerogenic Immune Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, G.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.G.; Turato, C.; Vidalino, L.; Biasiolo, A.; Tono, N.; Lunardi, F.; Calabrese, F.; Dall’Olmo, L.; et al. Role of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Antigen-1 on Liver Cells after Partial Hepatectomy in Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 25, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gringeri, E.; Villano, G.; Brocco, S.; Polacco, M.; Calabrese, F.; Sacerdoti, D.; Cillo, U.; Pontisso, P. SerpinB3 as Hepatic Marker of Post-Resective Shear Stress. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, R.Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Feng, D.; Wen, Y.; Xia, Y.; Colgan, S.P.; Eltzschig, H.K.; Ju, C. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Reprograms Liver Macrophages to Protect Against Acute Liver Injury Through the Production of Interleukin-6. Hepatology 2020, 71, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, R. Liver Regeneration: From Myth to Mechanism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannito, S.; Turato, C.; Paternostro, C.; Biasiolo, A.; Colombatto, S.; Cambieri, I.; Quarta, S.; Novo, E.; Morello, E.; Villano, G.; et al. Hypoxia Up-Regulates SERPINB3 through HIF-2α in Human Liver Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2014, 6, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akerman, P.; Cote, P.; Yang, I.; McCLAIN, C.; Nelson, S.; Bagby, G.J.; Mae Diehl, A.; Qi Yang, S.; Mc-Clain, C. Antibodies to Tumor Necrosis Factor-a Inhibit Liver Regeneration after Partial Hepatectomy. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 1992, 263, G579–G585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of Interleukin (IL)-6-Type Cytokine Signalling and Its Regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressman, D.E.; Greenbaum, L.E.; DeAngelis, R.A.; Ciliberto, G.; Furth, E.E.; Poli, V.; Taub, R. Liver Failure and Defective Hepatocyte in Lnterleukin-6-Deficient Mice; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; Volume 245. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.T.; Darnell, J.E. Serpin B3/B4, Activated by STAT3, Promote Survival of Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanke, T.; Takizawa, T.; Kabeya, M.; Kawabata, A. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Proteinase-Activated Receptors (PARs): PAR-2 as a Potential Therapeutic Target. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 97, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaj, P.; Olejar, T.; Matej, R. PAR2: The Cornerstone of Pancreatic Diseases. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, R.; Shearer, A.M.; Fletcher, E.K.; Nguyen, N.; Guha, S.; Cox, D.H.; Abdelmalek, M.; Wang, Y.; Baleja, J.D.; Covic, L.; et al. PAR2 Controls Cholesterol Homeostasis and Lipid Metabolism in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Fletcher, E.K.; Rana, R.; Michael, E.S.; Nguyen, N.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. PAR2 Promotes Impaired Glucose Uptake and Insulin Resistance in NAFLD through GLUT2 and Akt Interference. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1778–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.M.; Rana, R.; Austin, K.; Baleja, J.D.; Nguyen, N.; Bohm, A.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Targeting Liver Fibrosis with a Cell-Penetrating Protease-Activated Receptor-2 (PAR2) Pepducin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23188–23198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F.; Yao, Y.; Lai, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, X. Tryptase Promotes the Profibrotic Phenotype Transfer of Atrial Fibroblasts by PAR2 and PPARγ Pathway. Arch. Med. Res. 2018, 49, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, I.; Hess, S.; Schulz, H.; Eckl, R.; Busch, G.; Montens, H.P.; Brandl, R.; Seidl, S.; Schömig, A.; Ott, I. Membrane-Type Serine Protease-1/Matriptase Induces Interleukin-6 and -8 in Endothelial Cells by Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor-2: Potential Implications in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camerer, E.; Huang, W.; Coughlin, S.R.; Majerus, P.W. Tissue Factor-and Factor X-Dependent Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor 2 by Factor VIIa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5255–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, B.P.; Kopec, A.K.; Joshi, N.; Cline, H.; Brown, J.A.; Bishop, S.C.; Kassel, K.M.; Rockwell, C.; Mackman, N.; Luyendyk, J.P. Hepatocyte Tissue Factor Activates the Coagulation Cascade in Mice. Blood 2013, 121, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Chung, H.Y. Protease-Activated Receptor 2 Induces ROS-Mediated Inflammation through Akt-Mediated NF-ΚB and FoxO6 Modulation during Skin Photoaging. Redox Biol. 2021, 44, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.A.; Cunningham, M.R.; Bushell, T.; Plevin, R. The Development of Proteinase-Activated Receptor-2 Modulators and the Challenges Involved. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2525–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villano, G.; Novo, E.; Turato, C.; Quarta, S.; Ruvoletto, M.; Biasiolo, A.; Protopapa, F.; Chinellato, M.; Martini, A.; Trevellin, E.; et al. The Protease Activated Receptor 2—CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Beta—SerpinB3 Axis Inhibition as a Novel Strategy for the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Metab. 2024, 81, 101889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clade Name | Localization | Protein Name |
|---|---|---|
| A | Extracellular | α1 antitrypsin, antitrypsin-related protein, α1 anti-chymotrypsin, kallistatin, protein C inhibitor, centerin, protein Z-dependent proteinase inhibitor, SerpinA11 antiprotease-like, vaspin, SerpinA13, corticosteroid-binding globulin, thyroxine-binding globulin, angiotensinogen |
| B | Intracellular | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor, plasminogen activator inhibitor-2, squamous cell carcinoma antigen-1, squamous cell carcinoma antigen-2, S proteinase inhibitor, megsin, cytoplasmic antiproteinase 8, cytoplasmic antiproteinase 9, bomapin, epipin, yukopin, headpin, maspin |
| C | Extracellular | Antithrombin |
| D | Extracellular | Heparin cofactor II |
| E | Extracellular | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, protease nexin I, serpin family E member 3 |
| F | Extracellular | Alpha-2 antiplasmin, pigment epithelium-derived factor |
| G | Extracellular | C1 esterase inhibitor, C1 inhibitor |
| H | Intracellular | Heparin cofactor II |
| I | Extracellular | Neuroserpin, myoepithelium-derived serine proteinase inhibitor (PI14) pancipin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cagnin, S.; Pontisso, P.; Martini, A. SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease—Review and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2024, 16, 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142579
Cagnin S, Pontisso P, Martini A. SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease—Review and Future Perspectives. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142579
Chicago/Turabian StyleCagnin, Silvia, Patrizia Pontisso, and Andrea Martini. 2024. "SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease—Review and Future Perspectives" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142579
APA StyleCagnin, S., Pontisso, P., & Martini, A. (2024). SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease—Review and Future Perspectives. Cancers, 16(14), 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142579







