Reduced Dose of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide with Tacrolimus for the Prevention of Graft-versus-Host Disease in HLA-Matched Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplants: A Prospective Pilot Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Treatment Protocol and Supportive Care
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Engraftment and Chimerism
3.3. Toxicity and Infectious Complications
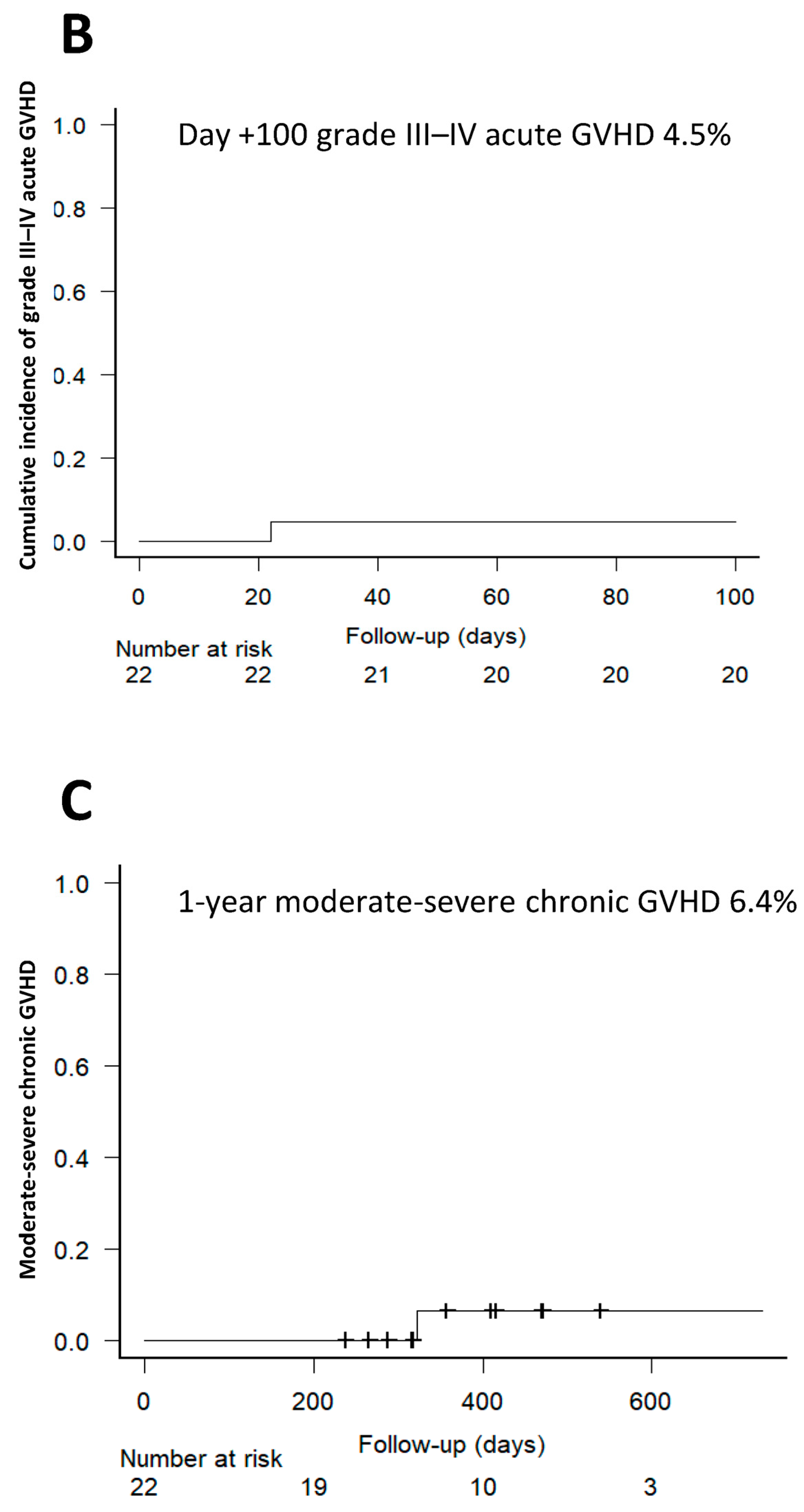
3.4. Incidence of Acute GVHD and Chronic GVHD
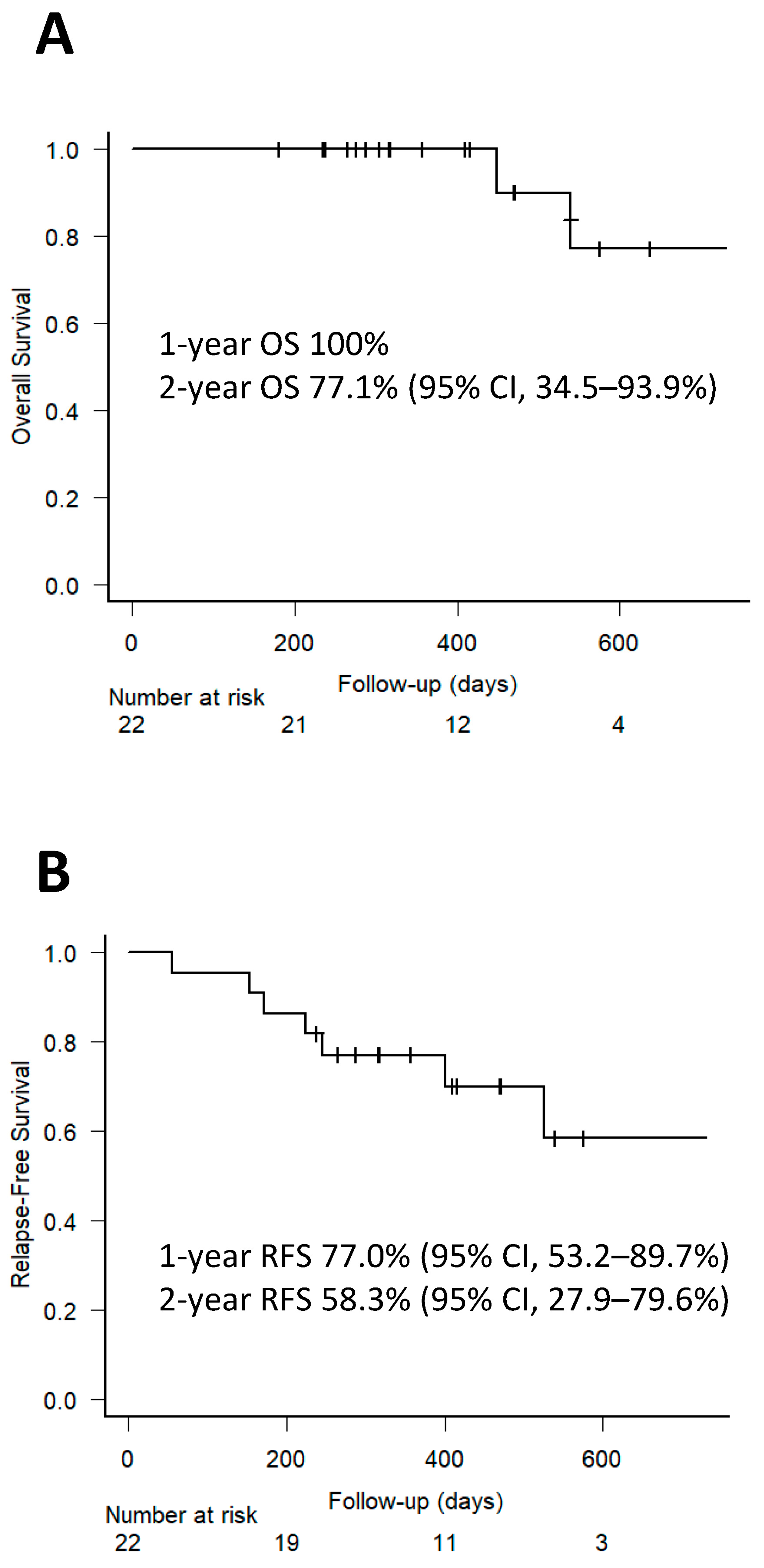
3.5. Disease Relapse and Post-Transplant Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luznik, L.; O’Donnell, P.V.; Symons, H.J.; Chen, A.R.; Leffell, M.S.; Zahurak, M.; Gooley, T.A.; Piantadosi, S.; Kaup, M.; Ambinder, R.F.; et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luznik, L.; O’Donnell, P.V.; Fuchs, E.J. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide for tolerance induction in HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation. Semin. Oncol. 2012, 39, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakry, C.G.; Tsai, H.L.; Bolanos-Meade, J.; Smith, B.D.; Gojo, I.; Kanakry, J.A.; Kasamon, Y.L.; Gladstone, D.E.; Matsui, W.; Borrello, I.; et al. Single-agent GVHD prophylaxis with posttransplantation cyclophosphamide after myeloablative, HLA-matched BMT for AML, ALL, and MDS. Blood 2014, 124, 3817–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, J.; Galimard, J.E.; Labopin, M.; Afanasyev, B.; Sergeevich, M.I.; Angelucci, E.; Kroger, N.; Koc, Y.; Ciceri, F.; Diez-Martin, J.L.; et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide containing regimens after matched sibling, matched unrelated and haploidentical donor transplants in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first complete remission, a comparative study of the ALWP of the EBMT. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, A.; Labopin, M.; Bacigalupo, A.; Afanasyev, B.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Elmaagacli, A.; Itala-Remes, M.; Blaise, D.; Meijer, E.; Koc, Y.; et al. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in HLA matched sibling or matched unrelated donor transplant for patients with acute leukemia, on behalf of ALWP-EBMT. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamae, H.; Fujii, K.; Nanno, S.; Okamura, H.; Nakane, T.; Koh, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakamae, M.; Hirose, A.; Teshima, T.; et al. A prospective observational study of immune reconstitution following transplantation with post-transplant reduced-dose cyclophosphamide from HLA-haploidentical donors. Transpl. Int. 2019, 32, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, S.R.; Abid, M.B.; Auletta, J.J.; Bashey, A.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Castillo, P.; Chemaly, R.F.; Chen, M.; Ciurea, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; et al. Posttransplant cyclophosphamide is associated with increased cytomegalovirus infection: A CIBMTR analysis. Blood 2021, 137, 3291–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khimani, F.; Ranspach, P.; Elmariah, H.; Kim, J.; Whiting, J.; Nishihori, T.; Locke, F.L.; Perez Perez, A.; Dean, E.; Mishra, A.; et al. Increased Infections and Delayed CD4(+) T Cell but Faster B Cell Immune Reconstitution after Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide Compared to Conventional GVHD Prophylaxis in Allogeneic Transplantation. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2021, 27, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreira, A.S.; Salas, M.Q.; Remberger, M.; Basso, I.N.; Law, A.D.; Lam, W.; Pasic, I.; Kim, D.; Michelis, F.V.; Viswabandya, A.; et al. Bloodstream Infections and Outcomes Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Single-Center Study. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 50.e1–50.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.Q.; Charry, P.; Puerta-Alcalde, P.; Martinez-Cibrian, N.; Solano, M.T.; Serrahima, A.; Nomdedeu, M.; Cid, J.; Lozano, M.; Chumbinta, M.; et al. Bacterial Bloodstream Infections in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation With Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 850.e1–850.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Valencia, A.I.; Cascos, E.; Carbonell-Ordeig, S.; Charry, P.; Gomez-Hernando, M.; Rodriguez-Lobato, L.G.; Suarez-Lledo, M.; Martinez-Cibrian, N.; Antelo, M.G.; Solano, M.T.; et al. Incidence, risk factors, and impact of early cardiac toxicity after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2018–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulery, R.; Mohty, R.; Labopin, M.; Sestili, S.; Malard, F.; Brissot, E.; Battipaglia, G.; Mediavilla, C.; Banet, A.; Van de Wyngaert, Z.; et al. Early Cardiac Toxicity Associated With Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021, 3, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaphan, E.; Germi, R.; Bailly, S.; Bulabois, C.E.; Carre, M.; Cahn, J.Y.; Thiebaut-Bertrand, A. Risk factors of BK viral hemorrhagic cystitis in allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Doki, N.; Shingai, N.; Yoshioka, K.; Kakihana, K.; Sakamaki, H.; Ohashi, K. The clinical features of fatal cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity in a conditioning regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Aviles, F.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Aymerich, M.; Colomer, D.; Rovira, M.; Martinez, C.; Nadal, E.; Talarn, C.; Carreras, E.; Montserrat, E. Serial quantification of lymphoid and myeloid mixed chimerism using multiplex PCR amplification of short tandem repeat-markers predicts graft rejection and relapse, respectively, after allogeneic transplantation of CD34+ selected cells from peripheral blood. Leukemia 2003, 17, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Harris, A.C.; Young, R.; Devine, S.; Hogan, W.J.; Ayuk, F.; Bunworasate, U.; Chanswangphuwana, C.; Efebera, Y.A.; Holler, E.; Litzow, M.; et al. International, Multicenter Standardization of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease Clinical Data Collection: A Report from the Mount Sinai Acute GVHD International Consortium. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorror, M.L.; Maris, M.B.; Storb, R.; Baron, F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maloney, D.G.; Storer, B. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: A new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005, 106, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Gibson, C.J.; Cutler, C.; Ho, V.T.; Koreth, J.; Alyea, E.P.; Ritz, J.; Sorror, M.L.; Lee, S.J.; Deeg, H.J.; et al. A disease risk index for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2012, 120, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachsmuth, L.P.; Patterson, M.T.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Venzon, D.J.; Gress, R.E.; Kanakry, C.G. Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide prevents graft-versus-host disease by inducing alloreactive T cell dysfunction and suppression. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2357–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmuth, L.P.; Patterson, M.T.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Venzon, D.J.; Kanakry, C.G. Optimized Timing of Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide in MHC-Haploidentical Murine Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamae, H.; Koh, H.; Katayama, T.; Nishimoto, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Nakane, T.; Nakamae, M.; Hirose, A.; Hino, M. HLA haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation using reduced dose of posttransplantation cyclophosphamide for poor-prognosis or refractory leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Exp. Hematol. 2015, 43, 921–929.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulery, R.; Goudet, C.; Mannina, D.; Bianchessi, A.; Granata, A.; Harbi, S.; Maisano, V.; Chabannon, C.; Malard, F.; Brissot, E.; et al. Reduced post-transplant cyclophosphamide doses in haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation for elderly patients with hematological malignancies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023, 58, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Xu, L.P.; Bian, Z.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Yan, C.H.; Liu, K.Y.; Huang, X.J. Low-dose post-transplant cyclophosphamide can mitigate GVHD and enhance the G-CSF/ATG induced GVHD protective activity and improve haploidentical transplant outcomes. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1356152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, J.; Kamimura, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Ota, S.; Eto, T.; Kuroha, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kumagai, H.; Matsuo, K.; Akashi, K.; et al. Reduced dose of posttransplant cyclophosphamide in HLA-haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Cai, Y.; Wan, L.; Huang, C.; Qiu, H.; Tong, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, K.; Ding, X.; et al. Low-dose antithymocyte globulin plus low-dose posttransplant cyclophosphamide combined with cyclosporine and mycophenolate mofetil for prevention of graft-versus-host disease after HLA-matched unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Li, Z.; Gui, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhao, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Low-dose post-transplant cyclophosphamide with low-dose antithymocyte globulin for prevention of graft-versus-host disease in first complete remission undergoing 10/10 HLA-matched unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell transplants: A multicentre, randomized controlled trial. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022, 57, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltermann, Y.; Heim, D.; Medinger, M.; Baldomero, H.; Halter, J.P.; Gerull, S.; Arranto, C.; Passweg, J.R.; Kleber, M. Reduced dose of post-transplantation cyclophosphamide compared to ATG for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in recipients of mismatched unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation: A single-center study. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gui, R.; Zu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Zhan, X.; Fu, Y.; et al. Reduced-dose post-transplant cyclophosphamide plus low-dose post-transplant anti-thymocyte globulin as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with fludarabine-busulfan-cytarabine conditioning in haploidentical peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: A multicentre, randomized controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cadenas, I.; Redondo, S.; Esquirol, A.; Portos, J.M.; Novelli, S.; Saavedra, S.; Moreno, C.; Garrido, A.; Onate, G.; Lopez, J.; et al. Successful Outcome in Patients with Myelofibrosis Undergoing Allogeneic Donor Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Using Reduced Doses of Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide: Challenges and Review of the Literature. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 473.e1–473.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, M.Q.; Pedraza, A.; Charry, P.; Suarez-Lledo, M.; Rodriguez-Lobato, L.G.; Brusosa, M.; Solano, M.T.; Serrahima, A.; Nomdedeu, M.; Cid, J.; et al. Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide and Tacrolimus for Graft-versus-Host Disease Prevention after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation from HLA-Matched Donors Has More Advantages Than Limitations. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2024, 30, 213.e1–213.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringden, O.; Labopin, M.; Gorin, N.C.; Le Blanc, K.; Rocha, V.; Gluckman, E.; Reiffers, J.; Arcese, W.; Vossen, J.M.; Jouet, J.P.; et al. Treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for acute leukemia increases the risk of graft-versus-host disease and death: A study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, A.; Bulley, S.; Beyene, J.; Dupuis, L.L.; Doyle, J.J.; Sung, L. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor after autologous and allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5207–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Meena, J.P.; Haldar, P.; Tanwar, P.; Seth, R. Impact of G-CSF administration post-allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation on outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Blood Res. 2021, 11, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.; Whited, L.; Saliba, R.M.; Rondon, G.; Banchs, J.; Shpall, E.; Champlin, R.; Popat, U. Cardiac toxicity after matched allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant in the posttransplant cyclophosphamide era. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5599–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | Nº (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at transplant | |
| Median (range), years | 53 (38–62) |
| Sex | |
| Male/Female | 16 (73%)/6 (27%) |
| Diagnosis | |
| Acute myeloblastic leukemia | 12 (54%) |
| Myeloproliferative disorders | 5 (23%) |
| Myelodysplastic syndrome | 2 (9%) |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | 2 (9%) |
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | 1 (5%) |
| Disease status | |
| First complete remission | 9 (41%) |
| >Second complete remission | 3 (14%) |
| Partial remission | 6 (27%) |
| Refractory disease/Stable disease | 4 (18%) |
| Disease Risk Index | |
| Very high | 1 (5%) |
| High | 8 (36%) |
| Intermediate | 6 (27%) |
| Low | 3 (14%) |
| Unclassifiable | 4 (18%) |
| Conditioning intensity | |
| RIC | 11 (50%) |
| MAC | 11 (50%) |
| Detailed information on Conditioning Regimens | |
| Reduced-intensity regimens | |
| FLAG/IDA/Bu2 | 2 (9%) |
| FLAG/IDA/Treo | 2 (9%) |
| FLAG/Bu | 1 (5%) |
| Flu + Bu (9.6 mg/kg) | 6 (27%) |
| Myeloablative regimens | |
| Flu + Bu (12.8 mg/kg) | 8 (36%) |
| Flu + TBI (12Gy) | 2 (9%) |
| Flu/Treo | 1 (5%) |
| Hematopoietic cell transplantation-comorbidity index | |
| ≤3 | 8 (36%) |
| >3 | 14 (64%) |
| Karnofsky performance status | |
| ≤80 | 15 (32%) |
| Donor type | |
| Match related donor | 8 (36%) |
| Match unrelated donor | 14 (64%) |
| Donor/recipient gender mismatch | |
| Female/Male | 6 (27%) |
| Dose of CD34+ cells (×106/kg), median (range) | 6.25 (4.96–7.18) |
| Cytomegalovirus risk | |
| High risk | 3 (14%) |
| Intermediate risk | 17 (77%) |
| Prophylaxis with letermovir | 18 (82%) |
| Author | n | Type of Donor | PTCY Dose | Other Immunosuppressant Drugs | II–IV Acute GVHD * | III–IV Acute GVHD * | All-Grade Chronic GVHD ** | Moderate–Severe Chronic GVHD ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juárez et al. | 22 | MRD, MUD | 40 mg/kg/day +3/+4 | Tac | 18.2% | 4.5% | 11.4% | 6.4% |
| Sun et al. [25] | 51 | MRD, MUD | 50 mg/kg/day +3 | ATG + CsA + MMF | 6.2% | 0% | 11.5% | NR |
| Zu et al. [26] | 53 | MRD MUD | 20 mg/kg/day +3/+4 | ATG | 24.5% | NR | 14.1% | NR |
| Solterman et al. [27] | 22 | 1-antigen MMUD | 40 mg/kg/day +3/+4 | CsA + MMF/MTX | 15% | NR | 26% | NR |
| Zhang et al. [28] | 29 | HLA-identical donors | 3 + 3 design trial DL1: 50 mg/kg/day +3/+4 DL2: 50 mg/kg/day +3 and 25 mg/kg/day +4 DL3: 25 mg/kg/day +3/+4 | CsA | 28.6% (for 21 patients with DL3) | 0% (1 patient at day +141) | 37.3% | 16% |
| García-Cadenas et al. [29] | 14 | MRD MUD 1-antigen MMUD | 30 mg/kg/day +3/+4 | Tac | 28.6% | 7% | 36% | 14% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juárez, A.; Salas, M.Q.; Pedraza, A.; Suárez-Lledó, M.; Rodríguez-Lobato, L.G.; Solano, M.T.; Serrahima, A.; Nomdedeu, M.; Cid, J.; Lozano, M.; et al. Reduced Dose of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide with Tacrolimus for the Prevention of Graft-versus-Host Disease in HLA-Matched Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplants: A Prospective Pilot Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142567
Juárez A, Salas MQ, Pedraza A, Suárez-Lledó M, Rodríguez-Lobato LG, Solano MT, Serrahima A, Nomdedeu M, Cid J, Lozano M, et al. Reduced Dose of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide with Tacrolimus for the Prevention of Graft-versus-Host Disease in HLA-Matched Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplants: A Prospective Pilot Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142567
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuárez, Alex, María Queralt Salas, Alexandra Pedraza, María Suárez-Lledó, Luís Gerardo Rodríguez-Lobato, María Teresa Solano, Anna Serrahima, Meritxell Nomdedeu, Joan Cid, Miquel Lozano, and et al. 2024. "Reduced Dose of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide with Tacrolimus for the Prevention of Graft-versus-Host Disease in HLA-Matched Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplants: A Prospective Pilot Study" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142567
APA StyleJuárez, A., Salas, M. Q., Pedraza, A., Suárez-Lledó, M., Rodríguez-Lobato, L. G., Solano, M. T., Serrahima, A., Nomdedeu, M., Cid, J., Lozano, M., Charry, P., Arcarons, J., Llobet, N., Rosiñol, L., Fernández-Avilés, F., Rovira, M., & Martínez, C. (2024). Reduced Dose of Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide with Tacrolimus for the Prevention of Graft-versus-Host Disease in HLA-Matched Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplants: A Prospective Pilot Study. Cancers, 16(14), 2567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142567








