The Prognostic Impact of HER2-Low and Menopausal Status in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
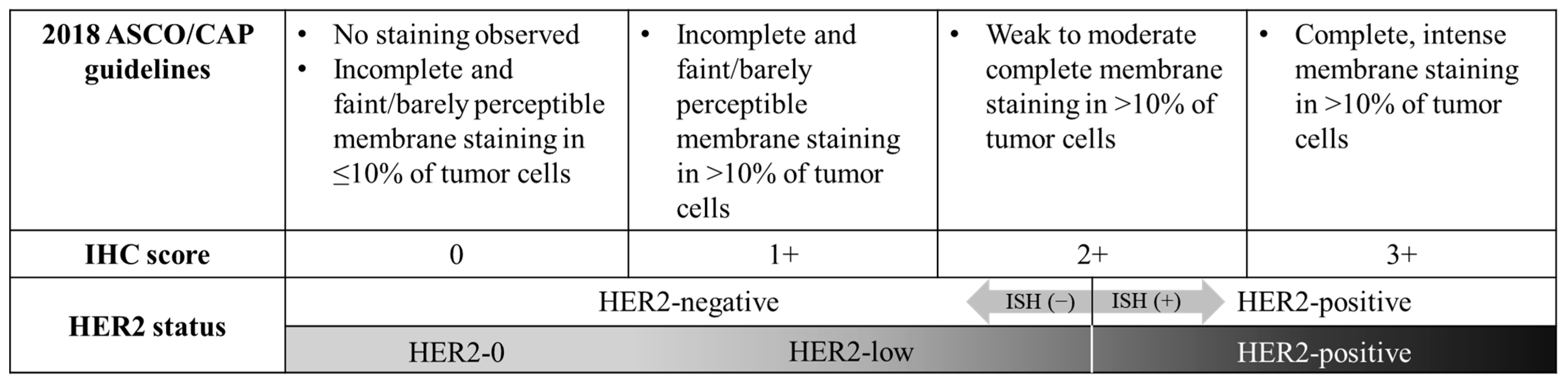
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics According to HER2 Status
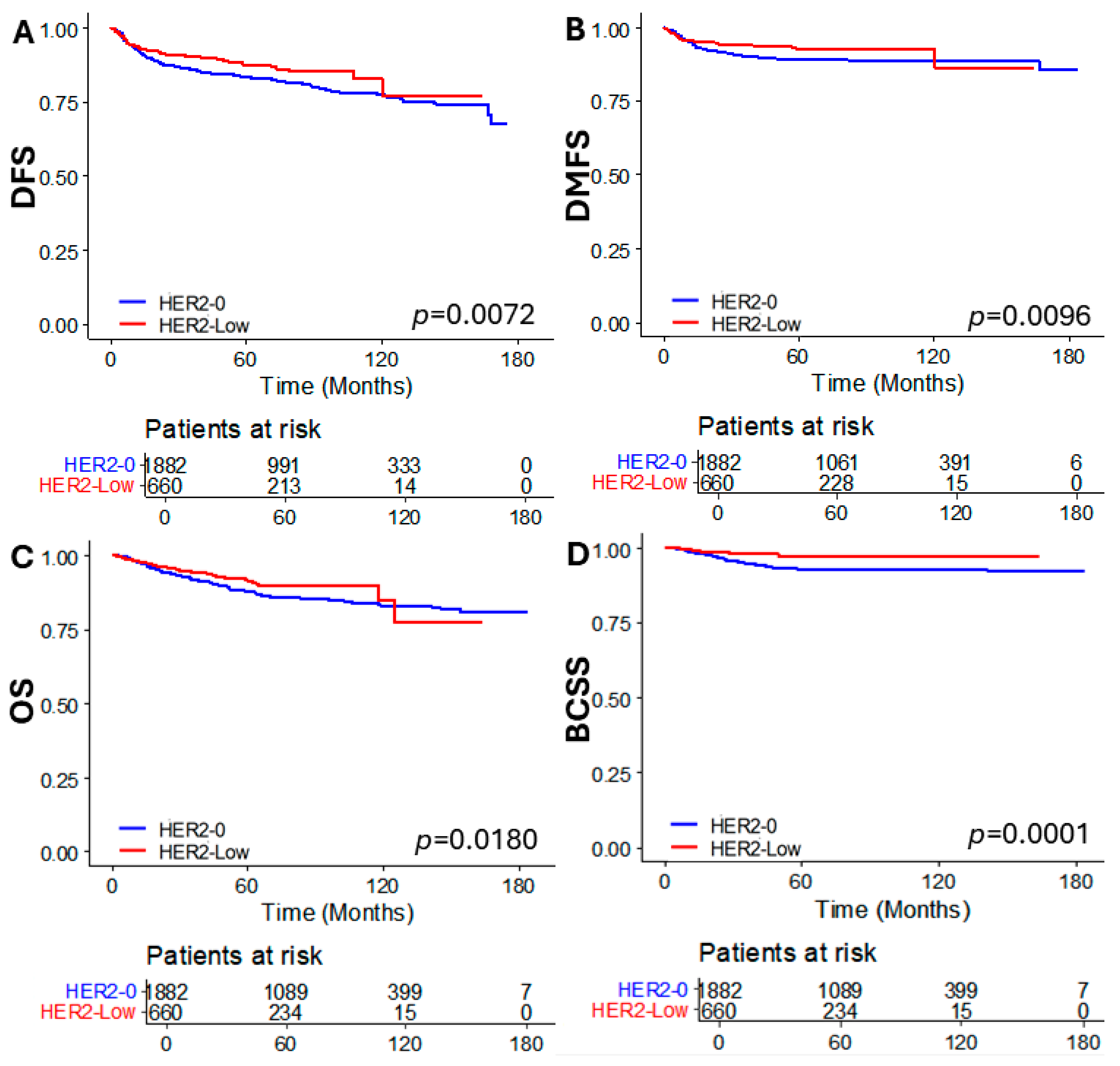
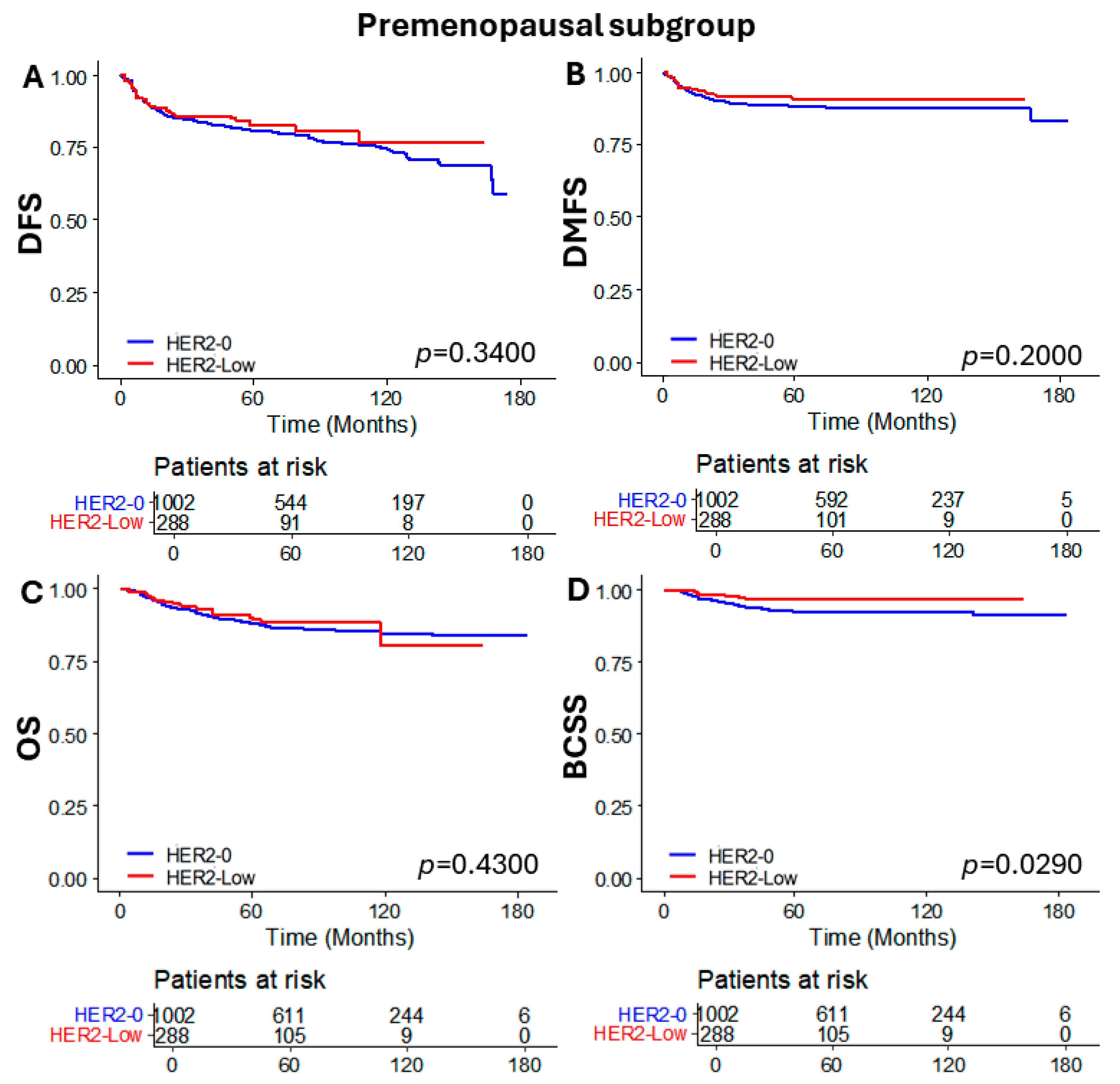
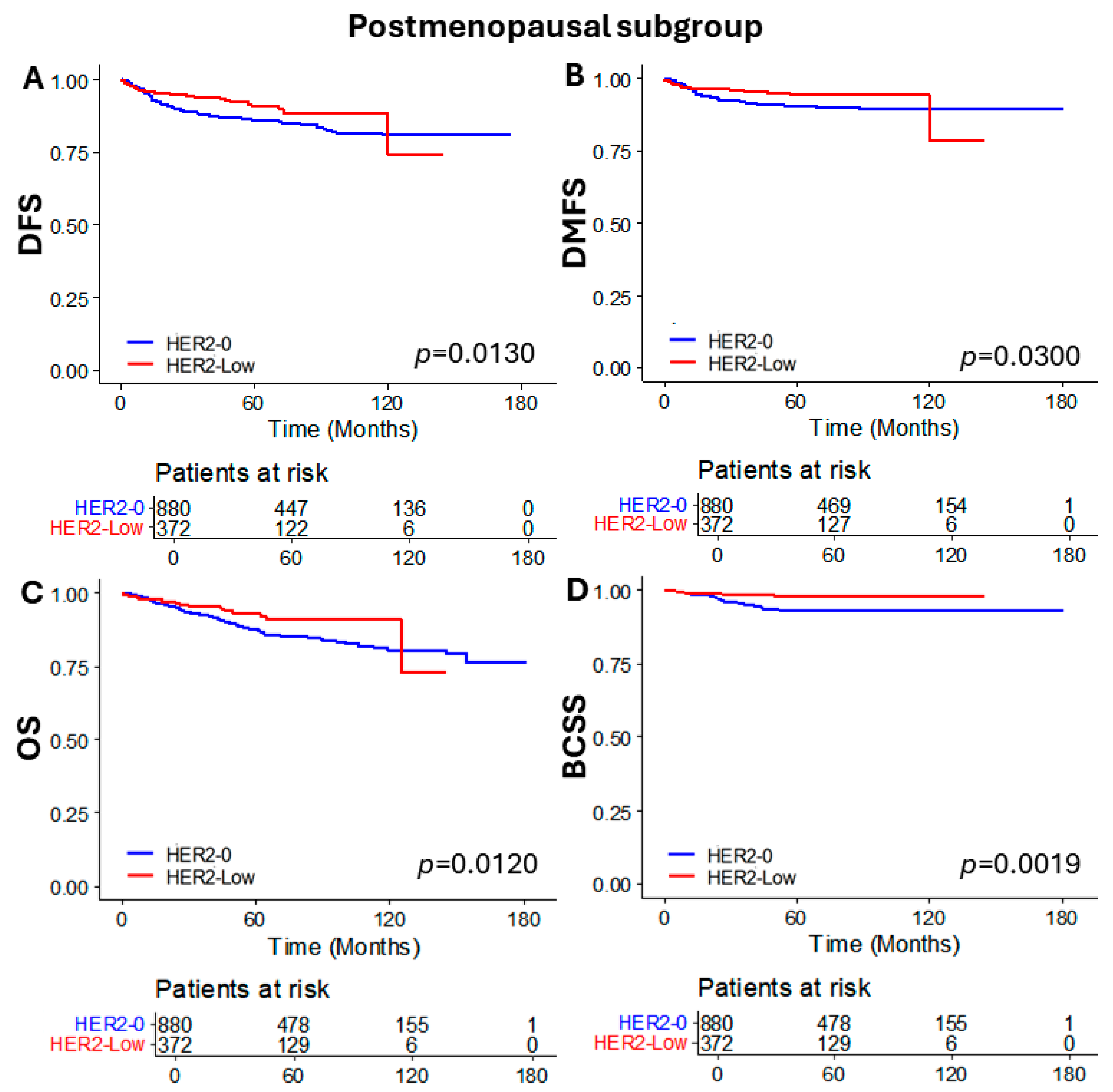
3.2. Oncologic Outcomes According to HER2 Status
3.3. Factors Associated with Oncologic Outcomes
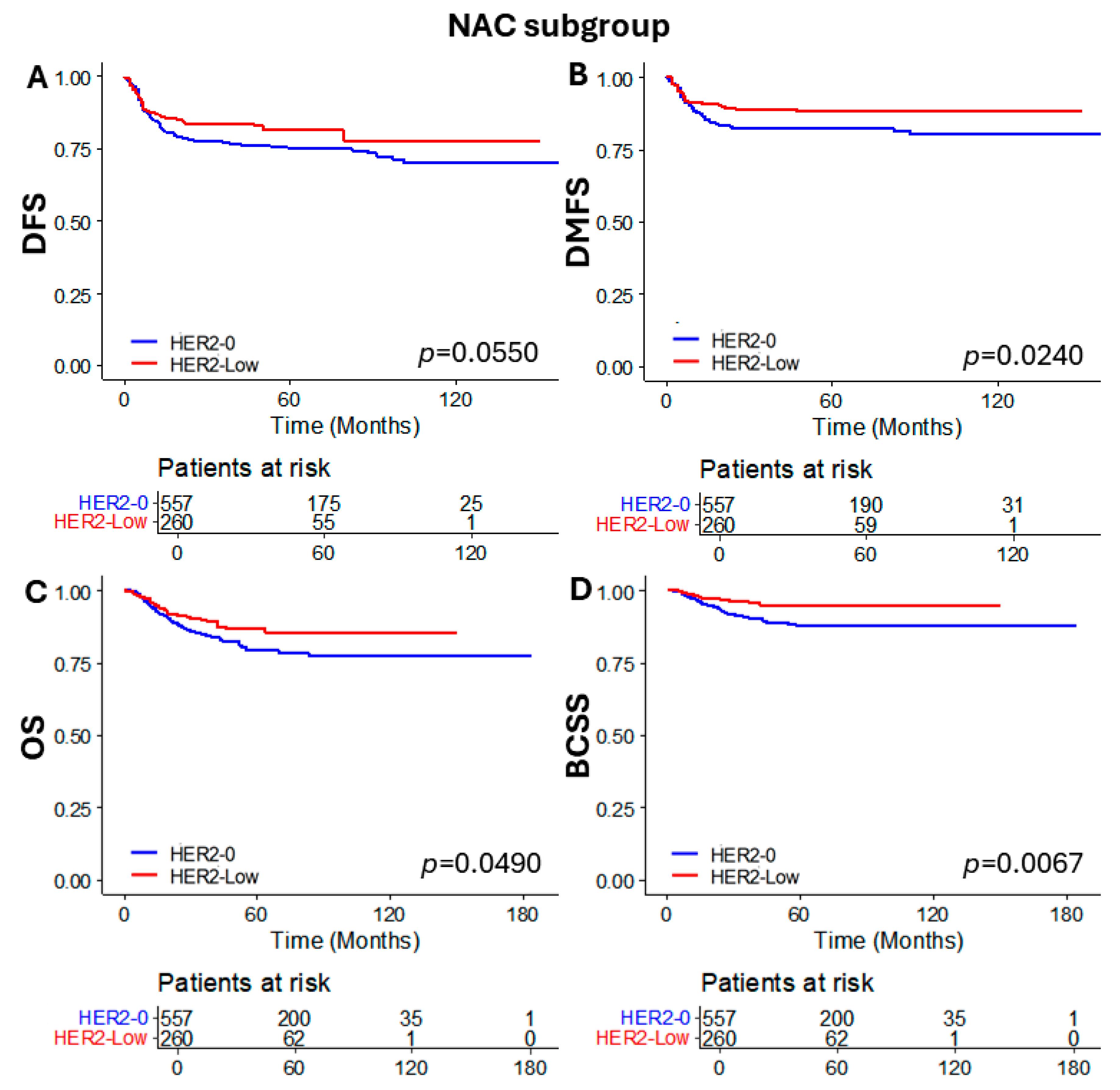
3.4. Subgroup Analysis of Patients Who Received NAC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dai, X.; Li, T.; Bai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhan, J.; Shi, B. Breast cancer intrinsic subtype classification, clinical use and future trends. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2929–2943. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.L.; Ehmsen, S.; Terp, M.G.; Portman, N.; Tuttolomondo, M.; Gammelgaard, O.L.; Hundebol, M.F.; Kaminska, K.; Johansen, L.E.; Bak, M.; et al. Co-targeting CDK4/6 and AKT with endocrine therapy prevents progression in CDK4/6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Vanderplas, A.; Hughes, M.E.; Theriault, R.L.; Edge, S.B.; Wong, Y.N.; Blayney, D.W.; Niland, J.C.; Winer, E.P.; Weeks, J.C. Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer 2012, 118, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.M.; Baselga, J.; Kim, S.B.; Ro, J.; Semiglazov, V.; Campone, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Ferrero, J.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Heeson, S.; et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.M.; Kim, S.B.; Cortes, J.; Ro, J.; Semiglazov, V.; Campone, M.; Ciruelos, E.; Ferrero, J.M.; Schneeweiss, A.; Knott, A.; et al. Pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (CLEOPATRA study): Overall survival results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horisawa, N.; Adachi, Y.; Takatsuka, D.; Nozawa, K.; Endo, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Sugino, K.; Kataoka, A.; Kotani, H.; Yoshimura, A.; et al. The frequency of low HER2 expression in breast cancer and a comparison of prognosis between patients with HER2-low and HER2-negative breast cancer by HR status. Breast Cancer 2022, 29, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.S.; Ahn, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.; Park, H.K.; Kim, Y.S. Clinical significance of HER2-low expression in early breast cancer: A nationwide study from the Korean Breast Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Plichta, J.K.; Li, K.; Jin, Y.; Thomas, S.M.; Ma, F.; Tang, L.; Wei, Q.; He, Y.W.; Chen, Q.; et al. Impact of HER2-low status for patients with early-stage breast cancer and non-pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A National Cancer Database Analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 204, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Ong, W.S.; Lee, K.H.; Lim, A.H.; Park, S.; Park, Y.H.; Lin, C.H.; Lu, Y.S.; Ono, M.; Ueno, T.; et al. HER2 expression, copy number variation and survival outcomes in HER2-low non-metastatic breast cancer: An international multicentre cohort study and TCGA-METABRIC analysis. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosso, C.; Voutsadakis, I.A. Characteristics, Clinical Differences and Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients with Negative or Low HER2 Expression. Clin. Breast Cancer 2022, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergun, Y.; Ucar, G.; Akagunduz, B. Comparison of HER2-zero and HER2-low in terms of clinicopathological factors and survival in early-stage breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 115, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; Seither, F.; Schneeweiss, A.; Link, T.; Blohmer, J.U.; Just, M.; Wimberger, P.; Forberger, A.; Tesch, H.; Jackisch, C.; et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: Pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almstedt, K.; Heimes, A.S.; Kappenberg, F.; Battista, M.J.; Lehr, H.A.; Krajnak, S.; Lebrecht, A.; Gehrmann, M.; Stewen, K.; Brenner, W.; et al. Long-term prognostic significance of HER2-low and HER2-zero in node-negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 173, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinetto, E.; Rediti, M.; Fimereli, D.; Debien, V.; Piccart, M.; Aftimos, P.; Sotiriou, C.; de Azambuja, E. HER2-Low Breast Cancer: Molecular Characteristics and Prognosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douganiotis, G.; Kontovinis, L.; Markopoulou, E.; Ainali, A.; Zarampoukas, T.; Natsiopoulos, I.; Papazisis, K. Prognostic Significance of Low HER2 Expression in Patients With Early Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2022, 2, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shen, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, L. Prognostic impact of HER2-low expression in HER2-negative breast cancer under different hormone receptor status. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 28, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.K.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Yu, J.; Ryu, J.M.; Chae, B.J. The Impact of HER2-Low Expression on Oncologic Outcomes in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.E.; Hayes, D.F.; Dowsett, M.; Allred, D.C.; Hagerty, K.L.; Badve, S.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Francis, G.; Goldstein, N.S.; Hayes, M.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines: Breast Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1419 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Zhang, H.; Katerji, H.; Turner, B.M.; Audeh, W.; Hicks, D.G. HER2-low breast cancers: Incidence, HER2 staining patterns, clinicopathologic features, MammaPrint and BluePrint genomic profiles. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.E.; Yang, P.; Chen, S.; Wei, G.; Yuan, L.; Yang, Z.; Gong, L.; He, L.; Yang, L.; Peng, S.; et al. Clinical and biological heterogeneities in triple-negative breast cancer reveals a non-negligible role of HER2-low. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacot, W.; Maran-Gonzalez, A.; Massol, O.; Sorbs, C.; Mollevi, C.; Guiu, S.; Boissiere-Michot, F.; Ramos, J. Prognostic Value of HER2-Low Expression in Non-Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Correlation with Other Biomarkers. Cancers 2021, 13, 6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampenrieder, S.P.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Tinchon, C.; Petzer, A.; Balic, M.; Heibl, S.; Schmitt, C.; Zabernigg, A.F.; Egle, D.; Sandholzer, M.; et al. Landscape of HER2-low metastatic breast cancer (MBC): Results from the Austrian AGMT_MBC-Registry. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettini, F.; Chic, N.; Braso-Maristany, F.; Pare, L.; Pascual, T.; Conte, B.; Martinez-Saez, O.; Adamo, B.; Vidal, M.; Barnadas, E.; et al. Clinical, pathological, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, P.; Gandini, S.; Nicolo, E.; Trillo, P.; Giugliano, F.; Zagami, P.; Vivanet, G.; Bellerba, F.; Trapani, D.; Marra, A.; et al. Evolution of low HER2 expression between early and advanced-stage breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 163, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambein, K.; Van Bockstal, M.; Vandemaele, L.; Geenen, S.; Rottiers, I.; Nuyts, A.; Matthys, B.; Praet, M.; Denys, H.; Libbrecht, L. Distinguishing score 0 from score 1+ in HER2 immunohistochemistry-negative breast cancer: Clinical and pathobiological relevance. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curigliano, G.; Dent, R.; Earle, H.; Modi, S.; Tarantino, P.; Viale, G.; Tolaney, S.M. Open questions, current challenges, and future perspectives in targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-low breast cancer. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Deluche, E.; Lusque, A.; Le Bescond, L.; Filleron, T.; Pradat, Y.; Ducoulombier, A.; Pistilli, B.; Bachelot, T.; Viret, F.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in metastatic breast cancer with variable HER2 expression: The phase 2 DAISY trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2110–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Study of Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (T-DXd) vs Investigator’s Choice Chemotherapy in HER2-low, Hormone Receptor Positive, Metastatic Breast Cancer (DB-06). 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04494425 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Gentile, D.; Sagona, A.; Spoto, R.; Franceschini, D.; Vaccari, S.; Vinci, V.; Biondi, E.; Scardina, L.; Tinterri, C. Salvage Mastectomy Is not the Treatment of Choice for Aggressive Subtypes of Ipsilateral Breast Cancer Recurrence: A Single-Institution Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Breast Health 2022, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Minckwitz, G.; Untch, M.; Blohmer, J.U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Eiermann, W.; Hilfrich, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moura Leite, L.; Cesca, M.G.; Tavares, M.C.; Santana, D.M.; Saldanha, E.F.; Guimaraes, P.T.; Sa, D.D.S.; Simoes, M.F.E.; Viana, R.L.; Rocha, F.G.; et al. HER2-low status and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2 negative early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 190, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Guan, H.; Zhu, F.; He, Y.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.; Nie, B.; Liu, H. Clinical, Pathological Complete Response, and Prognosis Characteristics of HER2-Low Breast Cancer in the Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Setting: A Retrospective Analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 8026–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Ge, J. HER2-low-positive and response to NACT and prognosis in HER2-negative non-metastatic BC. Breast Cancer 2023, 30, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, T.; Chen, H.; Yao, Y. The impact of HER2-low status on response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically HER2-negative breast cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Xue, D.; Gu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; He, S.; et al. HER2-low status may predict poor neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in HR-negative breast cancer: A real-world multicenter study. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 53, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, R.; Osako, T.; Okumura, Y.; Nakano, M.; Otsuka, H.; Fujisue, M.; Arima, N. Triple Negative Breast Cancer: An Analysis of the Subtypes and the Effects of Menopausal Status on Invasive Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, P.; Jin, Q.; Tayob, N.; Jeselsohn, R.M.; Schnitt, S.J.; Vincuilla, J.; Parker, T.; Tyekucheva, S.; Li, T.; Lin, N.U.; et al. Prognostic and Biologic Significance of ERBB2-Low Expression in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HER2-0 | HER2-Low | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical variables | |||
| Total no. (%) | 1882 (74.0) | 660 (26.0) | |
| Age | |||
| Median (IQR) | 48 (41–56) | 52 (44–60) | <0.001 |
| Menopausal status, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| Pre | 1002 (53.2) | 288 (43.6) | |
| Post | 880 (46.8) | 372 (56.4) | |
| BRCA 1/2 mutation, no. (%) | 0.510 | ||
| Not detected | 1736 (92.2) | 614 (93.0) | |
| Detected | 146 (7.8) | 46 (7.0) | |
| Laterality | 0.888 | ||
| Unilateral cancer | 1866 (99.1) | 654 (99.1) | |
| Bilateral cancer | 16 (0.9) | 6 (0.9) | |
| Multiplicity | 0.005 | ||
| No | 1567 (83.3) | 514 (77.9) | |
| Yes | 285 (15.1) | 130 (19.7) | |
| Unknown | 30 (1.6) | 16 (2.4) | |
| Breast surgery, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| BCS | 1457 (77.4) | 457 (69.2) | |
| Mastectomy | 425 (22.6) | 203 (30.8) | |
| Axilla surgery, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| SLNB | 1235 (65.6) | 488 (73.9) | |
| ALND | 647 (34.4) | 172 (26.1) | |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 1325 (70.4) | 400 (60.6) | |
| Yes | 557 (29.6) | 260 (39.4) | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 501 (26.6) | 243 (36.8) | |
| Yes | 1381 (73.4) | 417 (63.2) | |
| Radiation therapy, no. (%) | <0.001 | ||
| No | 264 (14.0) | 133 (20.2) | |
| Yes | 1618 (86.0) | 527 (79.8) | |
| Pathologic variables | |||
| Tumor size | 0.109 | ||
| ≤2 cm | 712 (37.8) | 273 (41.4) | |
| >2 cm | 1170 (62.2) | 387 (58.6) | |
| Lymph node metastasis | 0.504 | ||
| Negative | 1069 (56.8) | 365 (55.3) | |
| Positive | 813 (43.2) | 295 (44.7) | |
| Histologic grade | <0.001 | ||
| ≤II | 420 (22.3) | 190 (28.8) | |
| >II | 1295 (68.8) | 405 (61.4) | |
| Unknown | 167 (8.9) | 65 (9.8) | |
| Nuclear grade | 0.001 | ||
| ≤II | 313 (16.6) | 147 (22.3) | |
| >II | 1416 (75.2) | 459 (69.5) | |
| Unknown | 153 (8.2) | 54 (8.2) | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | <0.001 | ||
| No | 881 (46.8) | 444 (67.3) | |
| Yes | 457 (24.3) | 125 (18.9) | |
| Unknown | 544 (28.9) | 91 (13.8) |
| Univariate Model | p-Value | Multivariate Model | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |||
| Disease Free Survival | ||||
| HER-2 status (0 vs. low) | 0.715 (0.559–0.915) | 0.008 | 0.761 (0.581–0.997) | 0.048 |
| Age | 0.977 (0.968–0.985) | <0.001 | 0.980 (0.965–0.995) | 0.009 |
| Menopausal status (pre- vs. post-) | 0.628 (0.518–0.763) | <0.001 | 0.909 (0.649–1.272) | 0.577 |
| BRCA1/2 mutation status (No vs. Yes) | 1.302 (0.950–1.784) | 0.100 | ||
| Laterality (uni- vs. bilateral) | 1.373 (0.568–3.316) | 0.481 | ||
| Multiplicity (single vs. multiple) | 1.290 (1.017–1.636) | 0.036 | 0.830 (0.629–1.094) | 0.186 |
| Breast Surgery (BCS vs. Mastectomy) | 2.040 (1.677–2.481) | <0.001 | 1.573 (1.236–2.002) | <0.001 |
| Axilla Surgery (SLNB vs. ALND) | 2.794 (2.311–3.377) | <0.001 | 2.099 (1.553–2.836) | <0.001 |
| NAC (No vs. Yes) | 2.070 (1.705–2.513) | <0.001 | 1.872 (1.327–2.640) | <0.001 |
| Adjuvant CTx (No vs. Yes) | 0.602 (0.494–0.734) | <0.001 | 0.778 (0.570–1.060) | 0.112 |
| Adjuvant RT (No vs. Yes) | 0.861 (0.670–1.108) | 0.245 | ||
| Tumor size (≤2 cm vs. >2 cm) | 2.017 (1.673–2.573) | <0.001 | 1.393 (1.035–1.875) | 0.029 |
| LN metastasis (No vs. Yes) | 2.115 (1.747–2.559) | <0.001 | 0.777 (0.566–1.066) | 0.118 |
| HG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.073 (0.860–1.339) | 0.532 | ||
| NG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.128 (0.879–1.448) | 0.345 | ||
| LVI (No vs. Yes) | 3.141 (2.529–3.901) | <0.001 | 2.244 (1.746–2.884) | <0.001 |
| Distant Metastasis Free Survival | ||||
| HER-2 status (0 vs. low) | 0.652 (0.470–0.903) | 0.010 | 0.647 (0.451–0.929) | 0.018 |
| Age | 0.984 (0.972–0.995) | 0.005 | 0.989 (0.970–1.009) | 0.281 |
| Menopausal status (pre- vs. post-) | 0.721 (0.559–0.930) | 0.012 | 0.861 (0.559–1.326) | 0.497 |
| BRCA1/2 mutation status (No vs. Yes) | 0.775 (0.460–1.306) | 0.339 | ||
| Laterality (uni- vs. bilateral) | 1.475 (0.472–4.608) | 0.503 | ||
| Multiplicity (single vs. multiple) | 1.069 (0.766–1.491) | 0.696 | ||
| Breast Surgery (BCS vs. Mastectomy) | 3.258 (2.536–4.185) | <0.001 | 2.149 (1.586–2.913) | <0.001 |
| Axilla Surgery (SLNB vs. ALND) | 5.113 (3.901–6.702) | <0.001 | 2.904 (1.912–4.410) | <0.001 |
| NAC (No vs. Yes) | 2.779 (2.159–3.575) | <0.001 | 2.030 (1.334–3.088) | <0.001 |
| Adjuvant CTx (No vs. Yes) | 0.515 (0.399–0.664) | <0.001 | 0.942 (0.647–1.372) | 0.757 |
| Adjuvant RT (No vs. Yes) | 0.849 (0.611–1.180) | 0.331 | ||
| Tumor size (≤2 cm vs. >2 cm) | 3.569 (2.544–5.009) | <0.001 | 2.019 (1.259–3.238) | 0.004 |
| LN metastasis (No vs. Yes) | 3.623 (2.745–4.781) | <0.001 | 0.929 (0.595–1.452) | 0.748 |
| HG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 0.968 (0.725–1.293) | 0.826 | ||
| NG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 0.913 (0.668–1.248) | 0.568 | ||
| LVI (No vs. Yes) | 3.855 (2.891–5.142) | <0.001 | 1.925 (1.382–2.681) | <0.001 |
| Univariate Model | p-Value | Multivariate Model | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |||
| Overall Survival | ||||
| HER-2 status (0 vs. low) | 0.698 (0.517–0.943) | 0.019 | 0.725 (0.526–0.999) | 0.049 |
| Age | 1.006 (0.996–1.016) | 0.271 | ||
| Menopausal status (pre- vs. post-) | 1.052 (0.841–1.316) | 0.656 | ||
| BRCA1/2 mutation status (No vs. Yes) | 0.805 (0.512–1.267) | 0.349 | ||
| Laterality (uni- vs. bilateral) | 1.953 (0.807–4.728) | 0.138 | ||
| Multiplicity (single vs. multiple) | 1.116 (0.834–1.494) | 0.461 | ||
| Breast Surgery (BCS vs. Mastectomy) | 2.706 (2.158–3.392) | <0.001 | 1.458 (1.074–1.978) | 0.016 |
| Axilla Surgery (SLNB vs. ALND) | 4.304 (3.391–5.462) | <0.001 | 2.697 (1.858–3.914) | <0.001 |
| NAC (No vs. Yes) | 2.262 (1.799–2.843) | <0.001 | 1.440 (0.953–2.174) | 0.083 |
| Adjuvant CTx (No vs. Yes) | 0.468 (0.372–0.587) | <0.001 | 0.566 (0.395–0.812) | 0.002 |
| Adjuvant RT (No vs. Yes) | 0.706 (0.535–0.933) | 0.014 | 0.726 (0.501–1.054) | 0.092 |
| Tumor size (≤2 cm vs. >2 cm) | 3.075 (2.311–4.093) | <0.001 | 2.070 (1.407–3.045) | <0.001 |
| LN metastasis (No vs. Yes) | 2.942 (2.322–3.729) | <0.001 | 0.880 (0.598–1.294) | 0.516 |
| HG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.052 (0.962–1.152) | 0.266 | ||
| NG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.077 (0.971–1.193) | 0.161 | ||
| LVI (No vs. Yes) | 3.575 (2.768–4.618) | <0.001 | 2.229 (1.657–2.997) | <0.001 |
| Breast cancer Specific Survival | ||||
| HER-2 status (0 vs. low) | 0.368 (0.215–0.630) | <0.001 | 0.476 (0.274–0.827) | 0.008 |
| Age | 0.982 (0.967–0.997) | 0.021 | 0.983 (0.966–1.001) | 0.065 |
| Menopausal status (pre- vs. post-) | 0.757 (0.540–1.060) | 0.105 | ||
| BRCA1/2 mutation status (No vs. Yes) | 0.626 (0.293–1.339) | 0.227 | ||
| Laterality (uni- vs. bilateral) | 1.710 (0.423–6.907) | 0.451 | ||
| Multiplicity (single vs. multiple) | 1.117 (0.724–1.722) | 0.617 | ||
| Breast Surgery (BCS vs. Mastectomy) | 2.640 (1.887–3.694) | <0.001 | 1.494 (0.999–2.234) | 0.05 |
| Axilla Surgery (SLNB vs. ALND) | 5.907 (4.067–8.578) | <0.001 | 3.437 (1.911–6.179) | <0.001 |
| NAC (No vs. Yes) | 2.448 (1.752–3.419) | <0.001 | 1.551 (0.861–2.795) | 0.144 |
| Adjuvant CTx (No vs. Yes) | 0.492 (0.351–0.688) | <0.001 | 0.652 (0.378–1.122) | 0.123 |
| Adjuvant RT (No vs. Yes) | 1.009 (0.634–1.605) | 0.971 | ||
| Tumor size (≤2 cm vs. >2 cm) | 4.981 (2.999–8.274) | <0.001 | 3.107 (1.549–6.230) | 0.001 |
| LN metastasis (No vs. Yes) | 3.299 (2.296–4.739) | <0.001 | 0.797 (0.441–1.440) | 0.452 |
| HG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.117 (0.972–1.283) | 0.118 | ||
| NG (≤GrII vs. >GrII) | 1.109 (0.950–1.295) | 0.191 | ||
| LVI (No vs. Yes) | 4.948 (3.320–7.375) | <0.001 | 2.527 (1.609–3.970) | <0.001 |
| HER2-0 | HER2-Low | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical variables | |||
| Total no. | 557 (68.2) | 260 (31.8) | |
| Age | 0.014 | ||
| Median (IQR) | 46.00 (38–53) | 48.00 (40–55.75) | |
| Menopausal status, no. (%) | 0.066 | ||
| Pre menopause | 342 (61.4) | 142 (54.6) | |
| Post menopause | 215 (38.6) | 118 (45.4) | |
| BRCA 1/2 mutation, no. (%) | 0.906 | ||
| Not detected | 507 (91.0) | 236 (90.8) | |
| Detected | 50 (9.0) | 24 (9.2) | |
| Laterality | 1.000 | ||
| Unilateral cancer | 554 (99.5) | 259 (99.6) | |
| Bilateral cancer | 3 (0.5) | 1 (0.4) | |
| Multiplicity | 0.490 | ||
| No | 442 (83.7) | 209 (85.7) | |
| Yes | 86 (16.3) | 35 (14.3) | |
| Unknown | |||
| Breast surgery, no. (%) | 0.647 | ||
| BCS | 368 (66.1) | 176 (67.7) | |
| Mastectomy | 189 (33.9) | 84 (32.3) | |
| Axilla surgery, no. (%) | 0.245 | ||
| SLNB | 295 (53.0) | 149 (57.3) | |
| ALND | 262 (47.0) | 111 (42.7) | |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy, no. (%) | 0.339 | ||
| No | 385 (69.1) | 171 (65.8) | |
| Yes | 172 (30.9) | 89 (34.2) | |
| Radiation therapy, no. (%) | 0.395 | ||
| No | 53 (9.5) | 20 (7.7) | |
| Yes | 504 (90.5) | 240 (92.3) | |
| Pathologic variables | |||
| Clinical T stage | 0.071 | ||
| 1 | 39 (7.0) | 20 (7.7) | |
| 2 | 377 (67.7) | 190 (73.1) | |
| 3 | 102 (18.3) | 43 916.5) | |
| 4 | 39 (7.0) | 7 (2.7) | |
| Clinical N stage | 0.537 | ||
| 0 | 81 (14.5) | 43 (16.5) | |
| 1 | 212 (38.1) | 108 (41.5) | |
| 2 | 162 (29.1) | 67 (25.8) | |
| 3 | 102 (18.3) | 42 (16.2) | |
| Histologic grade | 0.760 | ||
| ≤II | 126 (31.0) | 65 (32.2) | |
| >II | 281 (69.0) | 137 (67.8) | |
| Unknown | |||
| Nuclear grade | 0.738 | ||
| ≤II | 69 (16.5) | 32 (15.5) | |
| >II | 349 (83.5) | 175 (84.5( | |
| Unknown | |||
| Lymphovascular invasion | 0.007 | ||
| No | 236 (42.4) | 144 (55.4) | |
| Yes | 132 (23.7) | 47 (18.1) | |
| Unknown | 189 (33.9) | 69 (26.5) | |
| Pathologic response | 0.523 | ||
| pCR | 162 (29.1) | 70 (26.9) | |
| non-pCR | 395 (70.9) | 190 (73.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, W.K.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Yu, J.; Lee, S.K.; Ryu, J.M.; Chae, B.J. The Prognostic Impact of HER2-Low and Menopausal Status in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142566
Park WK, Nam SJ, Kim SW, Lee JE, Yu J, Lee SK, Ryu JM, Chae BJ. The Prognostic Impact of HER2-Low and Menopausal Status in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142566
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Woong Ki, Seok Jin Nam, Seok Won Kim, Jeong Eon Lee, Jonghan Yu, Se Kyung Lee, Jai Min Ryu, and Byung Joo Chae. 2024. "The Prognostic Impact of HER2-Low and Menopausal Status in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142566
APA StylePark, W. K., Nam, S. J., Kim, S. W., Lee, J. E., Yu, J., Lee, S. K., Ryu, J. M., & Chae, B. J. (2024). The Prognostic Impact of HER2-Low and Menopausal Status in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers, 16(14), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142566






