Treatment Strategies for Locoregional Recurrence in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
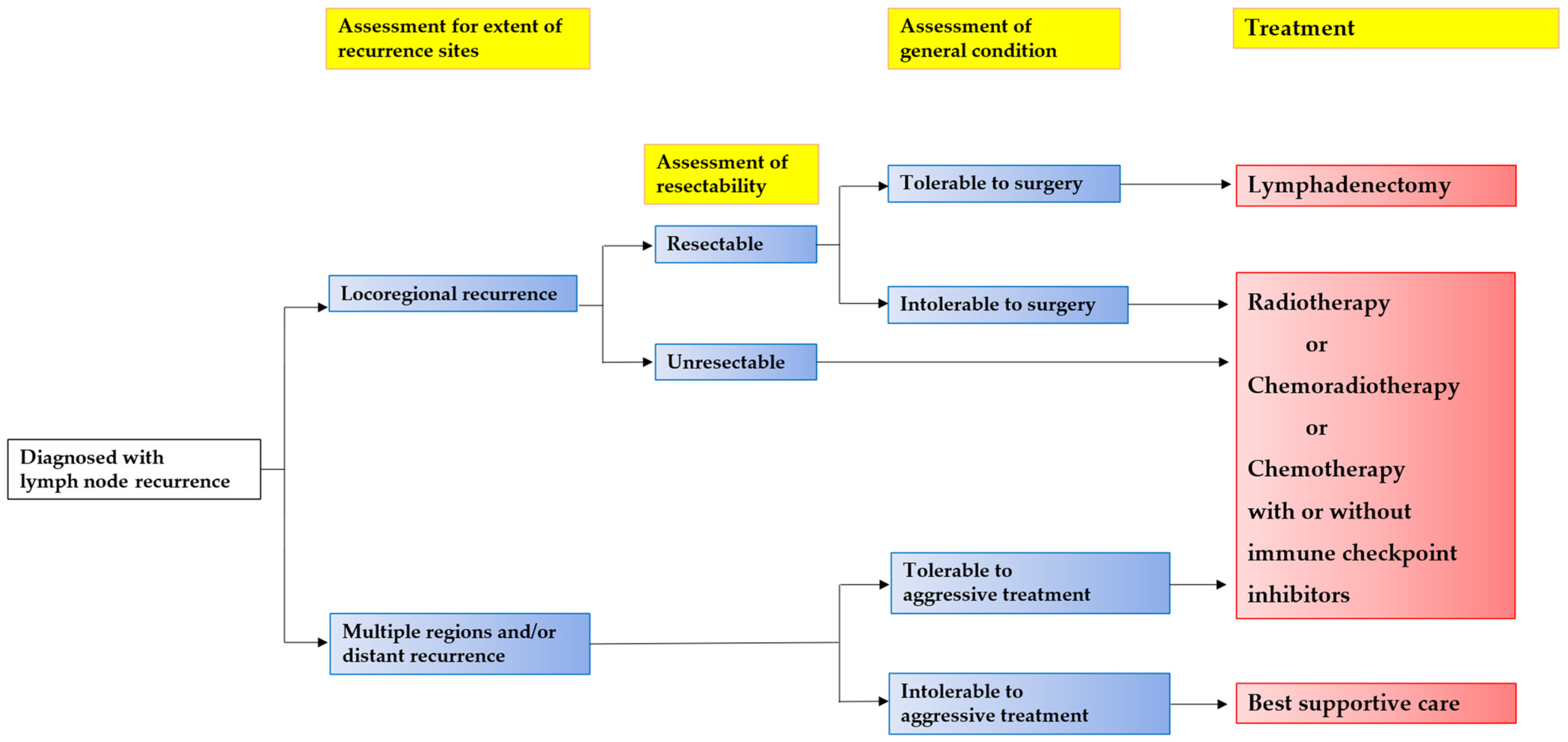
2. Methods
3. Salvage Lymphadenectomy
4. Radiotherapy (RT)/Chemoradiotherapy (CRT)
5. Chemotherapy
- (1)
- KEYNOTE-181 [58]: Pembrolizumab significantly prolonged the OS compared to chemotherapy (paclitaxel, docetaxel, or irinotecan) in patients who had received one prior therapy for advanced/metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
- (2)
- KEYNOTE-590 [59]: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (FP) significantly prolonged the OS and PFS in patients with untreated, advanced, unresectable, or metastatic esophageal cancer or Siewert type 1 gastro-esophageal cancer.
- (3)
- ATTRACTION-3 [52]: Nivolumab significantly improved the OS compared to chemotherapy (paclitaxel or docetaxel) in patients with unresectable, advanced, or recurrent ESCC.
- (4)
- ESCORT-1st [60]: Camrelizumab plus chemotherapy (TP: paclitaxel plus cisplatin) resulted in longer OS and PFS when used as the first-line treatment in patients with untreated, advanced, or metastatic ESCC.
- (5)
- JUPITER-06 [61]: Toripalimab plus chemotherapy (TP) significantly improved the OS and PFS in patients with untreated advanced ESCC.
- (6)
- ORIENT-15 [62]: Sintilimab plus chemotherapy (TP or FP) significantly prolonged the OS and RFS in patients with ESCC who had not received prior systemic therapy.
6. Limitations
7. Future Directions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, T.W.; Patil, D.T.; Blackstone, E.H. 8th edition AJCC/UICC staging of cancers of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: Application to clinical practice. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 6, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mine, S.; Tanaka, K.; Kawachi, H.; Shirakawa, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; Toh, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kamei, T.; Oyama, T.; et al. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer, 12th Edition: Part I. Esophagus 2024, 21, 179–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Ishikawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Oyama, T.; Oyama, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Kawakubo, H.; Kawachi, H.; et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2022 edited by the Japan esophageal society: Part 1. Esophagus 2023, 20, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Ishikawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Oyama, T.; Oyama, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Kawakubo, H.; Kawachi, H.; et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2022 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: Part 2. Esophagus 2023, 20, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, D.; Cao, Y.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Sarkaria, I.S.; Toni, L.; David, R.; et al. Robotic Versus Conventional Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer: A Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, N.; Kato, H.; Igaki, H.; Shinoda, M.; Ozawa, S.; Shimizu, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yabusaki, H.; Aoyama, N.; Kurita, A.; et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kato, K.; Igaki, H.; Ito, Y.; Mizusawa, J.; Ando, N.; Udagawa, H.; Tsubosa, Y.; Daiko, H.; Hironaka, S.; et al. Three-arm phase III trial comparing cisplatin plus 5-FU (CF) versus docetaxel, cisplatin plus 5-FU (DCF) versus radiotherapy with CF (CF-RT) as preoperative therapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer (JCOG1109, NExT study). Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 43, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Ito, Y.; Daiko, H.; Ozawa, S.; Ogata, T.; Hara, H.; Kojima, T.; Abe, T.; Bamba, T.; Watanabe, M.; et al. A randomized controlled phase III trial comparing two chemotherapy regimen and chemoradiotherapy regimen as neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced esophageal cancer, JCOG1109 NExT study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S4), 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Toh, Y.; Ishihara, R.; Kono, K.; Matsubara, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Morita, M.; Murakami, K.; Muro, K.; Numasaki, H.; et al. Comprehensive registry of esophageal cancer in Japan, 2015. Esophagus 2023, 20, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppedijk, V.; van der Gaast, A.; van Lanschot, J.J.; van Hagen, P.; van Os, R.; van Rij, C.M.; van der Sangen, M.J.; Beukema, J.C.; Rütten, H.; Spruit, P.H.; et al. Patterns of recurrence after surgery alone versus preoperative chemoradiotherapy and surgery in the CROSS trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Hulshof, M.; van Hagen, P.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Rieu, M.C.; Filleron, T.; Beluchon, B.; Humeau, M.; Julio, C.H.; Bloom, E.; Ghouti, L.; Kirzin, S.; Portier, G.; Pradère, B.; et al. Recurrence risk after Ivor Lewis oesophagectomy for cancer. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2013, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butter, R.; Lagarde, S.M.; van Oijen, M.G.H.; Anderegg, M.C.J.; Gisbertz, S.S.; Meijer, S.L.; Hulshof, M.; Bergman, J.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M. Treatment strategies in recurrent esophageal or junctional cancer. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagens, E.R.C.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Gisbertz, S.S. Distribution of Lymph Node Metastases in Esophageal Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Upfront Surgery: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kurokawa, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Nakajima, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Konishi, K.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Survival factors in patients with recurrence after curative resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 3353–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.K.; Wang, B.Y.; Huang, C.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Hsu, W.H. Prognostic factors for post-recurrence survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients with recurrence after resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2011, 15, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, Y.; Oki, E.; Minami, K.; Okamura, T. Follow-up and recurrence after a curative esophagectomy for patients with esophageal cancer: The first indicators for recurrence and their prognostic values. Esophagus 2010, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunisaki, C.; Makino, H.; Takagawa, R.; Yamamoto, N.; Nagano, Y.; Fujii, S.; Kosaka, T.; Ono, H.A.; Otsuka, Y.; Akiyama, H.; et al. Surgical outcomes in esophageal cancer patients with tumor recurrence after curative esophagectomy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, M.; Morita, M.; Yoshida, R.; Ando, K.; Egashira, A.; Takefumi, O.; Saeki, H.; Oki, E.; Kakeji, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; et al. Patterns and time of recurrence after complete resection of esophageal cancer. Surg. Today 2012, 42, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Fukuchi, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Nakajima, M.; Kimura, H.; Faried, A.; Sohda, M.; Fukai, Y.; Masuda, N.; Manda, R.; et al. Classification of recurrent esophageal cancer after radical esophagectomy with two- or three-field lymphadenectomy. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abate, E.; DeMeester, S.R.; Zehetner, J.; Oezcelik, A.; Ayazi, S.; Costales, J.; Banki, F.; Lipham, J.C.; Hagen, J.A.; DeMeester, T.R. Recurrence after esophagectomy for adenocarcinoma: Defining optimal follow-up intervals and testing. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 210, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, K.; Guo, W.; Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Salvage lymphadenectomy versus salvage radiotherapy/chemoradiotherapy for recurrence in cervical lymph node after curative resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Ota, M.; Narumiya, K.; Sato, T.; Ohki, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Mitsuhashi, N. Multimodal treatment for lymph node recurrence of esophageal carcinoma after curative resection. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Mine, S.; Yamada, K.; Shigaki, H.; Baba, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Kajiyama, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Sano, T.; Baba, H. Outcomes of lymphadenectomy for lymph node recurrence after esophagectomy or definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 62, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Nishida, K.; Kimura, Y.; Miyazaki, M.; Baba, H. Salvage lymphadenectomy for cervical lymph node recurrence after esophagectomy for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Dis. Esophagus 2012, 25, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeno, T.; Hoshino, A.; Matsunaga, S.; Shimano, R.; Ishibashi, N.; Shinohara, H.; Shiobara, H.; Tomii, C.; Saito, K.; Fujiwara, N.; et al. The impact of lymphadenectomy on lymph node recurrence after performing various treatments for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Surg. 2022, 22, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haefner, M.F.; Lang, K.; Verma, V.; Koerber, S.A.; Uhlmann, L.; Debus, J.; Sterzing, F. Intensity-modulated versus 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy in the definitive treatment of esophageal cancer: Comparison of outcomes and acute toxicity. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Feng, C.; Cai, B.N.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.X.; Ma, L. Comparison of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, and volumetric-modulated arc therapy in the treatment of cervical esophageal carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, J.; Hoffe, S.E.; Almhanna, K.; Dinwoodie, W.; Yue, B.; Fulp, W.; Meredith, K.L.; Shridhar, R. Comparative outcomes for three-dimensional conformal versus intensity-modulated radiation therapy for esophageal cancer. Dis. Esophagus 2015, 28, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, G.; Xu, C.; Chai, G.; Lyu, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Shi, M.; Zhao, L. Re-irradiation for local primary-recurrence esophageal squamous cell carcinoma treated with IMRT/VMAT. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yin, W.; Yao, H.; Gu, W. Salvage treatment for lymph node recurrence after radical resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Jingu, K.; Niibe, Y.; Katsui, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishina, T.; Terahara, A. Definitive salvage radiation therapy and chemoradiation therapy for lymph node oligo-recurrence of esophageal cancer: A Japanese multi-institutional study of 237 patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depypere, L.; Lerut, T.; Moons, J.; Coosemans, W.; Decker, G.; Van Veer, H.; De Leyn, P.; Nafteux, P. Isolated local recurrence or solitary solid organ metastasis after esophagectomy for cancer is not the end of the road. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.; Koom, W.S. Re-irradiation of recurrent esophageal cancer after primary definitive radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2012, 30, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, L.; Harrabi, S.B.; Debus, J. Particle therapy in the future of precision therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroshima, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Sumiya, T.; Murakami, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ishida, T.; Ogawa, K.; Hisakura, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Oda, T.; et al. Clinical Impact of Proton Beam Therapy for Postoperative Lymph Node Oligorecurrence of Esophageal Cancer. In Vivo 2023, 37, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solidum, J.G.N.; Rojo, R.D.; Wo, J.Y.; Dee, E.C. Proton Beam Therapy for Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Lin, S.H. Advances in radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vošmik, M.; Hodek, M.; Buka, D.; Sýkorová, P.; Grepl, J.; Paluska, P.; Paulíková, S.; Sirák, I. Cardiotoxicity of radiation therapy in esophageal cancer. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2020, 25, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.B.; Bentzen, S.M.; Deasy, J.O.; Kong, F.M.; Bradley, J.D.; Vogelius, I.S.; El Naqa, I.; Hubbs, J.L.; Lebesque, J.V.; Timmerman, R.D.; et al. Radiation dose-volume effects in the lung. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, J.; Shigematsu, N.; Takeuchi, H.; Ohashi, T.; Saikawa, Y.; Takaishi, H.; Hanada, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; Fukuda, K. Symptomatic pericardial effusion after chemoradiation therapy in esophageal cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, G.; Constine, L.S.; Moiseenko, V.; Correa, C.; Pierce, L.J.; Allen, A.M.; Marks, L.B. Radiation dose-volume effects in the heart. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S77–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Kawachi, H.; Shirakawa, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; Toh, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kamei, T.; Oyama, T.; et al. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer, 12th Edition: Part II. Esophagus 2024, 21, 216–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleiberg, H.; Conroy, T.; Paillot, B.; Lacave, A.J.; Blijham, G.; Jacob, J.H.; Bedenne, L.; Namer, M.; De Besi, P.; Gay, F.; et al. Randomised phase II study of cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) versus cisplatin alone in advanced squamous cell oesophageal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.H.; Im, Y.H.; Park, S.H. Capecitabine in combination with either cisplatin or weekly paclitaxel as a first-line treatment for metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A randomized phase II study. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzen, S.; Schuster, T.; Porschen, R.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Hofheinz, R.; Thuss-Patience, P.; Moehler, M.; Grabowski, P.; Arnold, D.; Greten, T.; et al. Cetuximab plus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil versus cisplatin-5-fluorouracil alone in first-line metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: A randomized phase II study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moehler, M.; Maderer, A.; Thuss-Patience, P.C.; Brenner, B.; Meiler, J.; Ettrich, T.J.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Vogel, A.; Mueller, L.; et al. Cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil with or without epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition panitumumab for patients with non-resectable, advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell cancer: A prospective, open-label, randomised phase III AIO/EORTC trial (POWER). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.E.; Puccini, A.; Xiu, J.; Raghavan, D.; Lenz, H.J.; Korn, W.M.; Shields, A.F.; Philip, P.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Goldberg, R.M. Comparative Molecular Analyses of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, and Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Cho, B.C.; Takahashi, M.; Okada, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Chin, K.; Kadowaki, S.; Ahn, M.J.; Hamamoto, Y.; Doki, Y.; et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Rutkowski, P.; Grob, J.J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Wagstaff, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ferrucci, P.F.; et al. Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, Y.; Ajani, J.A.; Kato, K.; Xu, J.; Wyrwicz, L.; Motoyama, S.; Ogata, T.; Kawakami, H.; Hsu, C.H.; Adenis, A.; et al. Nivolumab Combination Therapy in Advanced Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Doki, Y.; Ogata, T.; Motoyama, S.; Kawakami, H.; Ueno, M.; Kojima, T.; Shirakawa, Y.; Okada, M.; Ishihara, R.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab or chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A Japanese subgroup analysis of open-label, phase 3 trial (CheckMate 648/ONO-4538-50). Esophagus 2023, 20, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, T.; Shah, M.A.; Muro, K.; Francois, E.; Adenis, A.; Hsu, C.H.; Doi, T.; Moriwaki, T.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Randomized Phase III KEYNOTE-181 Study of Pembrolizumab Versus Chemotherapy in Advanced Esophageal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.M.; Shen, L.; Shah, M.A.; Enzinger, P.; Adenis, A.; Doi, T.; Kojima, T.; Metges, J.P.; Li, Z.; Kim, S.B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Lu, J.; Bai, Y.; Mao, T.; Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; et al. Effect of Camrelizumab vs. Placebo Added to Chemotherapy on Survival and Progression-Free Survival in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: The ESCORT-1st Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Cui, C.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Feng, J.; Yang, S.; Fan, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Toripalimab plus chemotherapy in treatment-naïve, advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (JUPITER-06): A multi-center phase 3 trial. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 277–288.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Shu, Y.; Liu, L.; Kong, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, G.; Ji, Y.; Cao, G.; et al. Sintilimab versus placebo in combination with chemotherapy as first line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ORIENT-15): Multicentre, randomised, double blind, phase 3 trial. BMJ 2022, 377, e068714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamichi, K.; Kotsuka, M.; Yoshida, T.; Hishikawa, H.; Mukaide, H.; Tokuhara, K.; Inoue, K.; Sekimoto, M. A Case of Unresectable Advanced Lower Esophageal Adenocarcinoma That Achieved Pathological Complete Response after Conversion Surgery following Nivolumab plus SOX Therapy. Gan Kagaku Ryoho 2023, 50, 1765–1767. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.J.; Ajani, J.A.; Kuzdzal, J.; Zander, T.; Van Cutsem, E.; Piessen, G.; Mendez, G.; Feliciano, J.; Motoyama, S.; Lièvre, A.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab in Resected Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Yokoi, R.; Tsuchiya, H.; Sengoku, Y.; Fukada, M.; Yasufuku, I.; Asai, R.; Tajima, J.Y.; Kiyama, S.; et al. Oligometastases of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Trial Name | Enrollment Criteria | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (Line of Treatment) | Treatment Arm | Median OS (Months) | HR | Median PFS (Months) | HR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CheckMate 648 [56,57] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC or adenosquamous-cell carcinoma | Nivolumab (first line) | Nivolumab + ipilimumab (n = 131) vs. chemotherapy alone (n = 137) | 12.7 vs. 10.7 p = 0.01 | 0.78 | 2.9 vs. 5.6 p-value not tested | 1.26 |
| Nivolumab + chemotherapy (n = 126) vs. chemotherapy alone (n = 137) | 13.2 vs. 10.7 p = 0.002 | 0.74 | 5.8 vs. 5.6 p = 0.04 | 0.81 | |||
| KEYNOTE-181 [58] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC or adenocarcinoma | Pembrolizumab (second line) | Pembrolizumab (n = 314) vs. chemotherapy (PD-L1 combined positive score ≥ 10) (n = 314) | 9.3 vs. 6.7 p = 0.074 | 0.69 | 2.1 vs. 3.4 p-value not tested | 1.11 |
| KEYNOTE-590 [59] | Unresectable or metastatic disease: SCC or adenocarcinoma | Pembrolizumab (first line) | Pembrolizumab + chemotherapy (n = 373) vs. chemotherapy alone (n = 376) | 12.4 vs. 9.8 p < 0.0001 | 0.73 | 6.3 vs. 5.8 p < 0.0001 | 0.65 |
| ATTRACTION-3 [52] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC or adenosquamous-cell carcinoma | Nivolumab (second line) | Nivolumab (n = 210) vs. chemotherapy (n = 209) | 10.9 vs. 8.4 p = 0.019 | 0.77 | 1.7 vs. 3.4 p-value not tested | 1.08 |
| ESCORT-1st [60] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC | Camrelizumab (first line) | Camrelizumab + chemotherapy (n = 298) vs. placebo + chemotherapy (n = 298) | 15.3 vs. 12.0 p = 0.001 | 0.70 | 6.9 vs. 5.6 p < 0.001 | 0.56 |
| JUPITER-06 [61] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC | Toripalimab (first line) | Toripalimab + chemotherapy (n = 257) vs. placebo + chemotherapy (n = 257) | 17.0 vs. 11.0 p = 0.0004 | 0.58 | 5.7 vs. 5.5 p < 0.0001 | 0.58 |
| ORIENT-15 [62] | Unresectable, recurrent, or metastatic disease: SCC | Sintilimab (first line) | Sintilimab + chemotherapy (n = 327) vs. placebo + chemotherapy (n = 332) | 16.7 vs. 12.5 p < 0.001 | 0.63 | 7.2 vs. 5.7 p < 0.001 | 0.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitamura, A.; Tsujinaka, S.; Nakano, T.; Sawada, K.; Shibata, C. Treatment Strategies for Locoregional Recurrence in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142539
Mitamura A, Tsujinaka S, Nakano T, Sawada K, Shibata C. Treatment Strategies for Locoregional Recurrence in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142539
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitamura, Atsushi, Shingo Tsujinaka, Toru Nakano, Kentaro Sawada, and Chikashi Shibata. 2024. "Treatment Strategies for Locoregional Recurrence in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142539
APA StyleMitamura, A., Tsujinaka, S., Nakano, T., Sawada, K., & Shibata, C. (2024). Treatment Strategies for Locoregional Recurrence in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: An Updated Review. Cancers, 16(14), 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142539







